741:
unstable that they cause ionization. Hence, neutrons are said to be "indirectly ionizing." Even neutrons without significant kinetic energy are indirectly ionizing, and are thus a significant radiation hazard. Not all materials are capable of neutron activation; in water, for example, the most common isotopes of both types atoms present (hydrogen and oxygen) capture neutrons and become heavier but remain stable forms of those atoms. Only the absorption of more than one neutron, a statistically rare occurrence, can activate a hydrogen atom, while oxygen requires two additional absorptions. Thus water is only very weakly capable of activation. The sodium in salt (as in sea water), on the other hand, need only absorb a single neutron to become Na-24, a very intense source of beta decay, with half-life of 15 hours.
526:. ("E" is Energy; "h" is Planck's constant; "c" is the speed of light; "λ" is wavelength.) When an X-ray photon collides with an atom, the atom may absorb the energy of the photon and boost an electron to a higher orbital level or if the photon is extremely energetic, it may knock an electron from the atom altogether, causing the atom to ionize. Generally, larger atoms are more likely to absorb an X-ray photon since they have greater energy differences between orbital electrons. The soft tissue in the human body is composed of smaller atoms than the calcium atoms that make up bone, so there is a contrast in the absorption of X-rays. X-ray machines are specifically designed to take advantage of the absorption difference between bone and soft tissue, allowing physicians to examine structure in the human body.
968:
Artificially generated radio waves are used for fixed and mobile radio communication, broadcasting, radar and other navigation systems, satellite communication, computer networks and innumerable other applications. In addition, almost any wire carrying alternating current will radiate some of the energy away as radio waves; these are mostly termed interference. Different frequencies of radio waves have different propagation characteristics in the Earth's atmosphere; long waves may bend at the rate of the curvature of the Earth and may cover a part of the Earth very consistently, shorter waves travel around the world by multiple reflections off the ionosphere and the Earth. Much shorter wavelengths bend or reflect very little and travel along the line of sight.
1388:
40:
1261:
body. Doctors also find certain diseases by injecting a radioactive substance and monitoring the radiation given off as the substance moves through the body. Radiation used for cancer treatment is called ionizing radiation because it forms ions in the cells of the tissues it passes through as it dislodges electrons from atoms. This can kill cells or change genes so the cells cannot grow. Other forms of radiation such as radio waves, microwaves, and light waves are called non-ionizing. They do not have as much energy so they are not able to ionize cells.
1893:, page 16: "For example, the ingestion coefficient risk for 40K would not be appropriate for an application to ingestion of K in conjunction with an elevated intake of natural potassium. This is because the biokinetic model for potassium used in this document represents the relatively slow removal of potassium (biological half-time 30 days) that is estimated to occur for typical intakes of potassium, whereas an elevated intake of potassium would result in excretion of a nearly equal mass of natural potassium, and hence of K, over a short period."
315:
761:
929:
425:
826:
3014:
269:. The word "ionize" refers to the breaking of one or more electrons away from an atom, an action that requires the relatively high energies that these electromagnetic waves supply. Further down the spectrum, the non-ionizing lower energies of the lower ultraviolet spectrum cannot ionize atoms, but can disrupt the inter-atomic bonds that form molecules, thereby breaking down molecules rather than atoms; a good example of this is sunburn caused by long-
860:) are not energetic enough to detach electrons from atoms or molecules and hence cause their ionization. These include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, and (sometimes) visible light. The lower frequencies of ultraviolet light may cause chemical changes and molecular damage similar to ionization, but is technically not ionizing. The highest frequencies of ultraviolet light, as well as all X-rays and gamma-rays are ionizing.
3040:
53:
611:(two protons and two neutrons). They interact with matter strongly due to their charges and combined mass, and at their usual velocities only penetrate a few centimeters of air, or a few millimeters of low density material (such as the thin mica material which is specially placed in some Geiger counter tubes to allow alpha particles in). This means that alpha particles from ordinary
1062:, which vary from infrared through red (2,500K), to yellow (5,800K), to white and to blue-white (15,000K) as the peak radiance passes through those points in the visible spectrum. When the peak is below the visible spectrum the body is black, while when it is above the body is blue-white, since all the visible colors are represented from blue decreasing to red.
1055:
or below room temperature would thus appear absolutely black, as it would not reflect any incident light nor would it emit enough radiation at visible wavelengths for our eyes to detect. Theoretically, a black-body emits electromagnetic radiation over the entire spectrum from very low frequency radio waves to x-rays, creating a continuum of radiation.
1340:, and many substances that are toxic at very high doses actually have neutral or positive health effects, or are biologically essential, at moderate or low doses. There is some evidence to suggest that this is true for ionizing radiation: normal levels of ionizing radiation may serve to stimulate and regulate the activity of
753:. In addition, very high energy neutrons can cause ionizing radiation by "neutron spallation" or knockout, wherein neutrons cause emission of high-energy protons from atomic nuclei (especially hydrogen nuclei) on impact. The last process imparts most of the neutron's energy to the proton, much like one
1049:
of radiation. For a given temperature of a black-body there is a particular frequency at which the radiation emitted is at its maximum intensity. That maximum radiation frequency moves toward higher frequencies as the temperature of the body increases. The frequency at which the black-body radiation
840:
Even "non-ionizing" radiation is capable of causing thermal-ionization if it deposits enough heat to raise temperatures to ionization energies. These reactions occur at far higher energies than with ionization radiation, which requires only single particles to cause ionization. A familiar example of
836:
The kinetic energy of particles of non-ionizing radiation is too small to produce charged ions when passing through matter. For non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation (see types below), the associated particles (photons) have only sufficient energy to change the rotational, vibrational or electronic
701:
form of electrons. When a positron slows to speeds similar to those of electrons in the material, the positron will annihilate an electron, releasing two gamma photons of 511 keV in the process. Those two gamma photons will be traveling in (approximately) opposite direction. The gamma radiation from
461:
states that "The
Commission is aware of uncertainties and lack of precision of the models and parameter values", "Collective effective dose is not intended as a tool for epidemiological risk assessment, and it is inappropriate to use it in risk projections" and "in particular, the calculation of the
389:, they are quite capable of knocking out electrons and ionizing materials, but since most have an electrical charge, they do not have the penetrating power of ionizing radiation. The exception is neutron particles; see below. There are several different kinds of these particles, but the majority are
1054:
and is a function of the body's absolute temperature. A black-body is one that emits at any temperature the maximum possible amount of radiation at any given wavelength. A black-body will also absorb the maximum possible incident radiation at any given wavelength. A black-body with a temperature at
893:
Light, or visible light, is a very narrow range of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength that is visible to the human eye, or 380–750 nm which equates to a frequency range of 790 to 400 THz respectively. More broadly, physicists use the term "light" to mean electromagnetic radiation of all
567:
Gamma rays can be stopped by a sufficiently thick or dense layer of material, where the stopping power of the material per given area depends mostly (but not entirely) on the total mass along the path of the radiation, regardless of whether the material is of high or low density. However, as is the
491:
starts at about 20 miles (32 km) and extends upward. Some of the ultraviolet spectrum that does reach the ground is non-ionizing, but is still biologically hazardous due to the ability of single photons of this energy to cause electronic excitation in biological molecules, and thus damage them
863:
The occurrence of ionization depends on the energy of the individual particles or waves, and not on their number. An intense flood of particles or waves will not cause ionization if these particles or waves do not carry enough energy to be ionizing, unless they raise the temperature of a body to a
794:
The particles from deep space (inter- and extra-galactic) are much less frequent, but of much higher energies. These particles are also mostly protons, with much of the remainder consisting of helions (alpha particles). A few completely ionized nuclei of heavier elements are present. The origin of
1260:
Radiation and radioactive substances are used for diagnosis, treatment, and research. X-rays, for example, pass through muscles and other soft tissue but are stopped by dense materials. This property of X-rays enables doctors to find broken bones and to locate cancers that might be growing in the
878:
As noted above, the lower part of the spectrum of ultraviolet, called soft UV, from 3 eV to about 10 eV, is non-ionizing. However, the effects of non-ionizing ultraviolet on chemistry and the damage to biological systems exposed to it (including oxidation, mutation, and cancer) are such that even
767:
High-energy neutrons are very penetrating and can travel great distances in air (hundreds or even thousands of meters) and moderate distances (several meters) in common solids. They typically require hydrogen rich shielding, such as concrete or water, to block them within distances of less than a
496:
in DNA, which begins at wavelengths below 365 nm (3.4 eV), which is well below ionization energy. This property gives the ultraviolet spectrum some of the dangers of ionizing radiation in biological systems without actual ionization occurring. In contrast, visible light and longer-wavelength
1015:
in the form of black-body radiation. Infrared or red radiation from a common household radiator or electric heater is an example of thermal radiation, as is the heat emitted by an operating incandescent light bulb. Thermal radiation is generated when energy from the movement of charged particles
740:
cause neutron activation (in fact, they cause it more efficiently). Neutrons do not ionize atoms in the same way that charged particles such as protons and electrons do (by the excitation of an electron), because neutrons have no charge. It is through their absorption by nuclei which then become
572:
add a modest (typically 20% to 30%) amount of stopping power over an equal mass of less dense and lower atomic weight materials (such as water or concrete). The atmosphere absorbs all gamma rays approaching Earth from space. Even air is capable of absorbing gamma rays, halving the energy of such
412:
Most ionizing radiation originates from radioactive materials and space (cosmic rays), and as such is naturally present in the environment, since most rocks and soil have small concentrations of radioactive materials. Since this radiation is invisible and not directly detectable by human senses,
1044:
is an idealized spectrum of radiation emitted by a body that is at a uniform temperature. The shape of the spectrum and the total amount of energy emitted by the body is a function of the absolute temperature of that body. The radiation emitted covers the entire electromagnetic spectrum and the
976:
Very low frequency (VLF) refers to a frequency range of 30 Hz to 3 kHz which corresponds to wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 meters respectively. Since there is not much bandwidth in this range of the radio spectrum, only the very simplest signals can be transmitted, such as for radio
908:
Infrared (IR) light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between 0.7 and 300 micrometers, which corresponds to a frequency range between 430 and 1 THz respectively. IR wavelengths are longer than that of visible light, but shorter than that of microwaves. Infrared may be detected at a
1269:
All modern communication systems use forms of electromagnetic radiation. Variations in the intensity of the radiation represent changes in the sound, pictures, or other information being transmitted. For example, a human voice can be sent as a radio wave or microwave by making the wave vary to
952:
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from as short as one millimeter to as long as one meter, which equates to a frequency range of 300 MHz to 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF (millimeter waves), but various sources use different other
1019:
As noted above, even low-frequency thermal radiation may cause temperature-ionization whenever it deposits sufficient thermal energy to raise temperatures to a high enough level. Common examples of this are the ionization (plasma) seen in common flames, and the molecular changes caused by the
2062:
1166:
through simple experimentation in 1899. Rutherford used a generic pitchblende radioactive source and determined that the rays produced by the source had differing penetrations in materials. One type had short penetration (it was stopped by paper) and a positive charge, which
Rutherford named
967:
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light. Like all other electromagnetic waves, they travel at the speed of light. Naturally occurring radio waves are made by lightning, or by certain astronomical objects.
563:
of excess energy after most nuclear reactions. Both alpha and beta particles have an electric charge and mass, and thus are quite likely to interact with other atoms in their path. Gamma radiation, however, is composed of photons, which have neither mass nor electric charge and, as a result,
995:
Extremely low frequency (ELF) is radiation frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz (10 to 10 meters respectively). In atmosphere science, an alternative definition is usually given, from 3 Hz to 3 kHz. In the related magnetosphere science, the lower frequency electromagnetic oscillations
996:(pulsations occurring below ~3 Hz) are considered to lie in the ULF range, which is thus also defined differently from the ITU Radio Bands. A massive military ELF antenna in Michigan radiates very slow messages to otherwise unreachable receivers, such as submerged submarines.
913:
can detect and focus infrared by use of a pinhole lens in their heads, called "pits". Bright sunlight provides an irradiance of just over 1 kilowatt per square meter at sea level. Of this energy, 53% is infrared radiation, 44% is visible light, and 3% is ultraviolet radiation.
626:
are ingested or inhaled (breathed or swallowed). This brings the radioisotope close enough to sensitive live tissue for the alpha radiation to damage cells. Per unit of energy, alpha particles are at least 20 times more effective at cell-damage as gamma rays and X-rays. See
744:
In addition, high-energy (high-speed) neutrons have the ability to directly ionize atoms. One mechanism by which high energy neutrons ionize atoms is to strike the nucleus of an atom and knock the atom out of a molecule, leaving one or more electrons behind as the
1298:. In this process, scientists bombard a sample of a substance with particles called neutrons. Some of the atoms in the sample absorb neutrons and become radioactive. The scientists can identify the elements in the sample by studying the emitted radiation.
728:
fission or fusion reactions are active; this happens for about 10 microseconds in a thermonuclear explosion, or continuously inside an operating nuclear reactor; production of the neutrons stops almost immediately in the reactor when it goes non-critical.
1010:
Thermal radiation is a common synonym for infrared radiation emitted by objects at temperatures often encountered on Earth. Thermal radiation refers not only to the radiation itself, but also the process by which the surface of an object radiates its
953:
limits. In all cases, microwaves include the entire super high frequency band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum, with RF engineering often putting the lower boundary at 1 GHz (30 cm), and the upper around 100 GHz (3mm).
47:
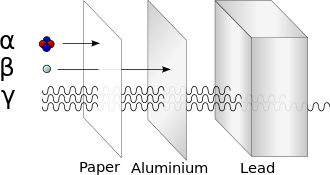
to penetrate solid matter. Typical alpha particles (α) are stopped by a sheet of paper, while beta particles (β) are stopped by 3mm aluminum foil. Gamma radiation (γ) is dampened when it penetrates lead. Note caveats in the text about this simplified
852:
is the range of all possible electromagnetic radiation frequencies. The electromagnetic spectrum (usually just spectrum) of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted by, or absorbed by, that particular object.
786:
There are two sources of high energy particles entering the Earth's atmosphere from outer space: the sun and deep space. The sun continuously emits particles, primarily free protons, in the solar wind, and occasionally augments the flow hugely with
837:
valence configurations of molecules and atoms. The effect of non-ionizing forms of radiation on living tissue has only recently been studied. Nevertheless, different biological effects are observed for different types of non-ionizing radiation.
1140:. While experimenting with high voltages applied to an evacuated tube on 8 November 1895, he noticed a fluorescence on a nearby plate of coated glass. Within a month, he discovered the main properties of X-rays that we understand to this day.
1278:
Researchers use radioactive atoms to determine the age of materials that were once part of a living organism. The age of such materials can be estimated by measuring the amount of radioactive carbon they contain in a process called
529:
X-rays are also totally absorbed by the thickness of the earth's atmosphere, resulting in the prevention of the X-ray output of the sun, smaller in quantity than that of UV but nonetheless powerful, from reaching the surface.
497:
electromagnetic radiation, such as infrared, microwaves, and radio waves, consists of photons with too little energy to cause damaging molecular excitation, and thus this radiation is far less hazardous per unit of energy.
545:
588:
449:. However, calculating the exact risk and chance of cancer forming in cells caused by ionizing radiation is still not well understood, and currently estimates are loosely determined by population-based data from the
1179:
discovered a third neutrally charged and especially penetrating type of radiation from radium, and after he described it, Rutherford realized it must be yet a third type of radiation, which in 1903 Rutherford named
619:, and these are capable of penetrating the body and even thin metal plates. However, they are of danger only to astronauts, since they are deflected by the Earth's magnetic field and then stopped by its atmosphere.
1877:
It is important to recognize that the potassium content of the body is under strict homeostatic control and is not influenced by variations in environmental levels. For this reason, the dose from K in the body is
658:
346:. Thus "ionizing radiation" is somewhat artificially separated from particle radiation and electromagnetic radiation, simply due to its great potential for biological damage. While an individual cell is made of
432:
Ionizing radiation has many practical uses in medicine, research, and construction, but presents a health hazard if used improperly. Exposure to radiation causes damage to living tissue; high doses result in
948:
part of the electromagnetic field around a transmitter. A part of the "near-field" close to the transmitter, is part of the changing electromagnetic field, but does not count as electromagnetic radiation.
1119:
preparations more quickly than violet light. Ritter's experiments were an early precursor to what would become photography. Ritter noted that the UV rays were capable of causing chemical reactions.
409:(eV) are ionizing (some authorities use 33 eV, the ionization energy for water). Particle radiation from radioactive material or cosmic rays almost invariably carries enough energy to be ionizing.
300:
in relation to the distance from its source. Like any ideal law, the inverse-square law approximates a measured radiation intensity to the extent that the source approximates a geometric point.
338:
off atoms, creating ions. Ionization occurs when an electron is stripped (or "knocked out") from an electron shell of the atom, which leaves the atom with a net positive charge. Because living
559:
Gamma (γ) radiation consists of photons with a wavelength less than 3x10 meters (greater than 10 Hz and 41.4 keV). Gamma radiation emission is a nuclear process that occurs to rid an unstable
277:. Radio wavelengths and below generally are not regarded as harmful to biological systems. These are not sharp delineations of the energies; there is some overlap in the effects of specific
273:
solar ultraviolet. The waves of longer wavelength than UV in visible light, infrared, and microwave frequencies cannot break bonds but can cause vibrations in the bonds which are sensed as
292:
that apply to all types of radiation. Because such radiation expands as it passes through space, and as its energy is conserved (in vacuum), the intensity of all types of radiation from a
511:
X-rays are electromagnetic waves with a wavelength less than about 10 m (greater than 3x10 Hz and 1,240 eV). A smaller wavelength corresponds to a higher energy according to the equation
1366:(WHO) released a statement adding radio frequency electromagnetic fields (including microwave and millimeter waves) to their list of things which are possibly carcinogenic to humans.
940:
of power so that the total radiation energy that crosses through an imaginary spherical surface is the same, no matter how far away from the antenna the spherical surface is drawn.
678:
can be stopped with a few centimeters of plastic or a few millimeters of metal. It occurs when a neutron decays into a proton in a nucleus, releasing the beta particle and an
864:
point high enough to ionize small fractions of atoms or molecules by the process of thermal-ionization (this, however, requires relatively extreme radiation intensities).
724:. These neutrons may be emitted during either spontaneous or induced nuclear fission. Neutrons are rare radiation particles; they are produced in large numbers only where
350:
of atoms, only a small fraction of those will be ionized at low to moderate radiation powers. The probability of ionizing radiation causing cancer is dependent upon the
1417:
417:
are usually required to detect its presence. In some cases, it may lead to secondary emission of visible light upon its interaction with matter, as in the case of
1805:
807:, which are galaxy-wide jet phenomena similar to GRBs but known for their much larger size, and which seem to be a violent part of the universe's early history.
1076:
Electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths other than visible light were discovered in the early 19th century. The discovery of infrared radiation is ascribed to
615:
do not penetrate the outer layers of dead skin cells and cause no damage to the live tissues below. Some very high energy alpha particles compose about 10% of
1270:
corresponding variations in the voice. Musicians have also experimented with gamma rays sonification, or using nuclear radiation, to produce sound and music.
1233:
were discovered by cloud chamber examination of cosmic ray reactions shortly thereafter, and others types of particle radiation were produced artificially in
1283:. Similarly, using other radioactive elements, the age of rocks and other geological features (even some man-made objects) can be determined; this is called
445:, often occurs when nuclear weapons and reactors are the radiation source because of the biological proclivities of the radioactive iodine fission product,
1929:
1726:
1312:
Radiation is not always dangerous, and not all types of radiation are equally dangerous, contrary to several common medical myths. For example, although
458:
1126:
in 1887, using electrical circuits calculated to produce oscillations in the radio frequency range, following formulas suggested by the equations of
736:, is the primary method used to produce radioactive sources for use in medical, academic, and industrial applications. Even comparatively low speed
1147:
found that rays emanating from certain minerals penetrated black paper and caused fogging of an unexposed photographic plate. His doctoral student
1336:. Radiation is ubiquitous on Earth, and humans are adapted to survive at the normal low-to-moderate levels of radiation found on Earth's surface.
674:
Beta-minus (β) radiation consists of an energetic electron. It is more penetrating than alpha radiation but less than gamma. Beta radiation from
484:. Although present in space, this part of the UVA spectrum is not of biological importance, because it does not reach living organisms on Earth.
1403:
On Earth there are different sources of radiation, natural as well as artificial. Natural radiation can come from the Sun, Earth itself or from
1373:. As of 12 July 2019 it has 28,547 publications and 6,369 summaries of individual scientific studies on the effects of electromagnetic fields.
2532:
1198:
Cosmic ray radiations striking the Earth from outer space were finally definitively recognized and proven to exist in 1912, as the scientist
476:
Ultraviolet, of wavelengths from 10 nm to 125 nm, ionizes air molecules, causing it to be strongly absorbed by air and by ozone (O
210:. This is an important distinction due to the large difference in harmfulness to living organisms. A common source of ionizing radiation is
1684:
1171:
The other was more penetrating (able to expose film through paper but not metal) and had a negative charge, and this type
Rutherford named
2517:
1359:
1122:
The first radio waves detected were not from a natural source, but were produced deliberately and artificially by the German scientist
480:) in particular. Ionizing UV therefore does not penetrate Earth's atmosphere to a significant degree, and is sometimes referred to as
342:
and, more importantly, the DNA in those cells can be damaged by this ionization, exposure to ionizing radiation increases the risk of
856:
The non-ionizing portion of electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves that (as individual quanta or particles, see
450:
437:(ARS), with skin burns, hair loss, internal organ failure, and death, while any dose may result in an increased chance of cancer and
932:
In electromagnetic radiation (such as microwaves from an antenna, shown here) the term "radiation" applies only to the parts of the
803:(GRB), which feature magnetic fields capable of the huge accelerations measured from these particles. They may also be generated by
2085:
On
Radiation: the "Rede" Lecture delivered in the Senate-House before the University of Cambridge on Tuesday, May 16, 1865
2486:
1645:
Proceedings of the
International Conference on Non-Ionizing Radiation at UNITEN ICNIR2003 Electromagnetic Fields and Our Health
1395:
flux map combining geoneutrinos from natural 238U and 232Th decay in the Earth’s crust and mantle as well as manmade reactor-v̄
981:
band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one myriameter (an obsolete metric unit equal to 10 kilometers).
1957:
1870:
1739:
1509:
1433:
1324:(K), which emit ionizing radiation when undergoing radioactive decay, the levels of such radiation are far too low to induce
1658:
1206:
to various altitudes in a free balloon flight. The nature of these radiations was only gradually understood in later years.
2512:
2481:
2426:
1307:
1071:
2145:
686:
accelerators is far more energetic and penetrating than natural beta radiation. It is sometimes used therapeutically in
2461:
1058:
The color of a radiating black-body tells the temperature of its radiating surface. It is responsible for the color of
1974:
Low-dose radiation from A-bombs elongated lifespan and reduced cancer mortality relative to un-irradiated individuals
1513:
628:
359:
487:
There is a zone of the atmosphere in which ozone absorbs some 98% of non-ionizing but dangerous UV-C and UV-B. This
2625:
2527:
1175:
This was the radiation that had been first detected by
Becquerel from uranium salts. In 1900, the French scientist
347:
1973:
2084:
462:
number of cancer deaths based on collective effective doses from trivial individual doses should be avoided."
2593:
1890:
1778:
544:
587:
3060:
2716:
2710:
2349:
1382:
1295:
1255:
1021:
265:
Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy range of ultraviolet light constitute the ionizing part of the
1351:
Ionizing radiation in certain conditions can damage living organisms, causing cancer or genetic damage.
56:
The international symbol for types and levels of ionizing radiation (radioactivity) that are unsafe for
3030:
2581:
2436:
2409:
2046:
1369:
RWTH Aachen
University's EMF-Portal web site presents one of the biggest database about the effects of
1051:
910:
31:
1151:
discovered that only certain chemical elements gave off these rays of energy. She named this behavior
3044:
2466:
2319:
1518:
1370:
1363:
1345:
1089:
1024:" during food-cooking, which is a chemical process that begins with a large component of ionization.
941:
820:
89:
17:
757:
striking another. The charged protons and other products from such reactions are directly ionizing.
657:
2404:
2314:
2178:
1449:
849:
830:
434:
266:
2902:
2344:
2138:
1637:
1085:
990:
842:
175:
1806:"Are bananas really 'radioactive'? An expert clears up common misunderstandings about radiation"
1688:
1597:
1354:
Non-ionizing radiation in certain conditions also can cause damage to living organisms, such as
2585:
2496:
2170:
1469:
1329:
816:
365:
If the source of the ionizing radiation is a radioactive material or a nuclear process such as
194:
2001:
1941:
1907:
1862:
2589:
2324:
1988:
1659:"ICRP Publication 103 The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Protection"
1332:. It would not be physically possible to eat enough bananas to cause radiation poisoning, as
1234:
1112:
933:
788:
259:
1933:
1387:
1301:
845:
reactions in common food items induced by infrared radiation, during broiling-type cooking.
288:(i.e., traveling outward in all directions) from a source. This aspect leads to a system of
2618:
2446:
2334:
2291:
2241:
1945:
1504:
1422:
1033:
198:
depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10
2002:"IARC Classifies Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields As Possibly Carcinogenic To Humans"
631:
for a discussion of this. Examples of highly poisonous alpha-emitters are all isotopes of
8:
2829:
2764:
2563:
2441:
2354:
2007:(Press release). The WHO/International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). 31 May 2011.
1903:
1545:
1498:
1486:
1440:
1428:
1325:
1317:
1251:
1127:
715:
418:
169:
2522:
1949:
720:
Neutrons are categorized according to their speed/energy. Neutron radiation consists of
39:
3065:
2558:
2379:
2359:
2339:
2223:
2131:
1492:
1464:
1288:
1284:
1280:
1187:
Henri
Becquerel himself proved that beta rays are fast electrons, while Rutherford and
945:
937:
795:
these galactic cosmic rays is not yet well understood, but they seem to be remnants of
733:
481:
454:
382:
378:
374:
309:
297:
188:
128:
44:
1919:. Attributes the title statement to Geoff Meggitt, former UK Atomic Energy Authority.
1133:
354:
of the radiation and is a function of the damaging tendency of the type of radiation (
2451:
2329:
2266:
2231:
2105:
2097:
1953:
1934:
1866:
1735:
1523:
1459:
1214:
1163:
1005:
711:
675:
211:
145:
60:
humans. Radiation, in general, exists throughout nature, such as in light and sound.
2817:
2706:
2676:
2456:
2113:
1756:
1712:
1480:
1404:
1077:
569:
493:
428:
Graphic showing relationships between radioactivity and detected ionizing radiation
57:
1908:"Bananas are radioactive—But they aren't a good way to explain radiation exposure"
1045:
intensity of the radiation (power/unit-area) at a given frequency is described by
3017:
2892:
2847:
2741:
2736:
2726:
2611:
2568:
2553:
2369:
2281:
2271:
2123:
1856:
1489:– making electronics resistant to failure in high ionizing radiation environments
1333:
1144:
1116:
1046:
800:
769:
737:
516:
366:
355:
314:
215:
137:
1638:"Non-Ionizing Radiations – Sources, Biological Effects, Emissions and Exposures"
1294:
Radiation is used to determine the composition of materials in a process called
1115:
made the discovery of ultraviolet by noting that the rays from a prism darkened
760:
732:
Neutrons can make other objects, or material, radioactive. This process, called
2416:
2374:
2364:
2286:
2276:
2246:
1474:
1218:
1192:
1123:
1012:
725:
608:
591:
560:
519:
442:
438:
414:
390:
370:
339:
141:
1840:
1831:
1195:
proved in 1914 that gamma rays are like X-rays, but with shorter wavelengths.
928:
424:
3054:
2701:
2491:
2251:
2236:
1571:
1159:
1152:
754:
746:
702:
positron annihilation consists of high energy photons, and is also ionizing.
668:
598:
552:
406:
394:
351:
323:
219:
207:
199:
110:
2042:
1977:
1104:
part of the spectrum), through an increase in the temperature recorded by a
643:, due to the amount of decay that occur in these short half-life materials.
564:
penetrates much further through matter than either alpha or beta radiation.
2925:
2911:
2471:
2431:
2296:
2109:
2089:
2079:
2068:
1858:
Environmental radioactivity: from natural, industrial, and military sources
1731:
1321:
1203:
1188:
1176:
825:
750:
721:
687:
679:
623:
293:
165:
2117:
2884:
2759:
2213:
1701:
1302:
Possible damage to health and environment from certain types of radiation
1199:
1148:
1105:
962:
873:
781:
665:
612:
595:
582:
549:
488:
471:
239:
133:
114:
1291:, to identify the pathways taken by pollutants through the environment.
2976:
2857:
2261:
2208:
1341:
1191:
proved in 1909 that alpha particles are ionized helium. Rutherford and
1081:
1039:
978:
698:
652:
616:
523:
446:
405:. Roughly speaking, photons and particles with energies above about 10
289:
270:
255:
157:
102:
98:
1221:
in 1932. A number of other high energy particulate radiations such as
568:
case with X-rays, materials with a high atomic number such as lead or
2935:
2897:
2842:
2782:
2603:
2548:
2421:
2256:
2203:
2193:
1181:
923:
841:
thermal ionization is the flame-ionization of a common fire, and the
796:
661:
539:
278:
180:
151:
122:
879:
this part of ultraviolet is often compared with ionizing radiation.
573:
waves by passing through, on the average, 500 ft (150 m).
2986:
2930:
2862:
2797:
2683:
2671:
2643:
2198:
2183:
1444:
1418:
Australian
Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA)
1337:
1222:
903:
772:, where a meters-thick water layer is used as effective shielding.
694:
640:
605:
386:
335:
319:
227:
223:
106:
81:
43:
Illustration of the relative abilities of three different types of
2057:
2981:
2969:
2907:
2837:
2812:
2772:
2751:
2721:
2476:
2093:
1454:
1348:
of any kind of radiation will eventually become lethal, however.
1313:
1210:
1093:
936:
that radiate into infinite space and decrease in intensity by an
398:
251:
65:
2101:
2018:
1483:– adverse effects of ionizing radiation on materials and devices
2964:
2957:
2666:
2661:
2635:
1437:
1137:
857:
804:
632:
512:
492:
by means of unwanted reactions. An example is the formation of
402:
343:
331:
231:
203:
94:
73:
1338:
The relationship between dose and toxicity is often non-linear
52:
2994:
2952:
2945:
2940:
2777:
2731:
2693:
2651:
2301:
2188:
1600:. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 December 2015
1059:
888:
683:
636:
506:
247:
235:
161:
118:
1991:, Bioscience 2005, American Institute of Biological Sciences
768:
meter. A common source of neutron radiation occurs inside a
358:) and the sensitivity of the irradiated organism or tissue (
2872:
2807:
2802:
2792:
2787:
2656:
1355:
1287:. Environmental scientists use radioactive atoms, known as
1230:
1226:
274:
243:
77:
258:
that are produced after primary cosmic rays interact with
2052:
1936:
Radiation
Hormesis and the Linear-No-Threshold Assumption
1477:, radiation by a source into the surrounding environment.
1101:
1097:
284:
The word "radiation" arises from the phenomenon of waves
1425:, which actually refers to background ionizing radiation
1016:
within atoms is converted to electromagnetic radiation.
1989:
Nancy Trautmann: The Dose Makes the Poison--Or Does It?
1685:"Static Electric and Magnetic Fields and Human Health"
3028:
1501:– adverse effects of ionizing radiation on life forms
1072:
Electromagnetic radiation § History of discovery
453:
and from follow-up of reactor accidents, such as the
1084:. Herschel published his results in 1800 before the
1902:
1779:"The Most Common Medical Radiation Myths Dispelled"
1495:– ionizing radiation dosage threshold damage theory
459:
International Commission on Radiological Protection
84:through space or a material medium. This includes:
2153:
1237:, through the last half of the twentieth century.
254:and other particles that constitute the secondary
1334:the radiation dose from bananas is non-cumulative
622:Alpha radiation is dangerous when alpha-emitting
179:, in the form of gravitational waves, ripples in
3052:
749:is broken. This leads to production of chemical
2058:Health Physics Society Public Education Website
909:distance from the radiating objects by "feel."
1889:U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (1999),
1854:
1376:
2619:
2139:
2069:Q&A: Health effects of radiation exposure
1748:
1635:
2078:
1855:Eisenbud, Merril; Gesell, Thomas F. (1997).
1682:
1158:Alpha rays (alpha particles) and beta rays (
759:
330:Radiation with sufficiently high energy can
1631:
1629:
1627:
1625:
1623:
1621:
1619:
1617:
1615:
1360:International Agency for Research on Cancer
999:
693:Beta-plus (β) radiation is the emission of
2626:
2612:
2146:
2132:
984:
1982:
1978:https://doi.org/10.1186/s41021-018-0114-3
810:
451:atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
186:Radiation is often categorized as either
1994:
1803:
1723:
1612:
1386:
927:
824:
656:
586:
543:
465:
423:
313:
51:
38:
1928:
1530:
1027:
385:by nuclear reactions. Because of their
27:Waves or particles moving through space
14:
3053:
2633:
2487:Wireless electronic devices and health
1883:
1676:
1100:and detected the infrared (beyond the
234:, respectively. Other sources include
2607:
2127:
1543:
1510:Radiation Protection Convention, 1960
1434:Cosmic microwave background radiation
971:
894:wavelengths, whether visible or not.
303:
2513:List of civilian radiation accidents
2482:Wireless device radiation and health
2477:Biological dose units and quantities
2427:Electromagnetic radiation and health
1976:. Genes and Environment, 40(1), 26.
1754:
1636:Kwan-Hoong Ng (20–22 October 2003).
1399:emitted by power reactors worldwide.
1308:Electromagnetic radiation and health
867:
705:
1804:Loughran, Sarah (3 November 2022).
775:
377:to consider. Particle radiation is
334:atoms; that is to say it can knock
72:is the emission or transmission of
24:
2462:Radioactivity in the life sciences
1330:bananas are not a radiation hazard
576:
533:
132:consists of particles of non-zero
25:
3077:
2036:
1550:Eric Weisstein's World of Physics
1514:International Labour Organization
646:
629:relative biological effectiveness
3038:
3013:
3012:
1264:
1088:. Herschel, like Ritter, used a
882:
664:(beta radiation) detected in an
2011:
1966:
1922:
1896:
1848:
1842:The Dose Makes the Poison (2/2)
1833:The Dose Makes the Poison (1/2)
1823:
1797:
1771:
1240:
548:Gamma radiation detected in an
441:; a particular form of cancer,
322:radiation can be detected in a
290:measurements and physical units
2065:from World Health Organization
1717:
1706:
1695:
1651:
1598:"The Electromagnetic Spectrum"
1590:
1564:
1537:
1111:In 1801, the German physicist
977:navigation. Also known as the
956:
206:atoms and molecules and break
13:
1:
1576:The free dictionary by Farlex
690:to treat superficial tumors.
2063:Ionizing Radiation and Radon
1316:contain naturally occurring
1065:
917:
7:
2350:Cosmic background radiation
1861:. Academic Press. pp.
1410:
1383:Environmental radioactivity
1377:Environmental radioactivity
1296:neutron activation analysis
1256:Medical radiation scientist
1245:
897:
10:
3082:
2579:
2437:Lasers and aviation safety
1891:Federal Guidance Report 13
1380:
1305:
1273:
1249:
1069:
1050:is at maximum is given by
1031:
1003:
988:
960:
921:
901:
886:
871:
814:
779:
709:
650:
580:
537:
504:
469:
307:
168:, dependent on a physical
144:(β), proton radiation and
32:Radiation (disambiguation)
29:
3008:
2921:
2880:
2871:
2828:
2750:
2692:
2642:
2577:
2541:
2505:
2467:Radioactive contamination
2392:
2320:Electromagnetic radiation
2310:
2222:
2169:
2162:
1519:Radioactive contamination
1371:Electromagnetic radiation
1364:World Health Organization
1162:) were differentiated by
942:Electromagnetic radiation
821:Electromagnetic radiation
500:
90:electromagnetic radiation
2580:See also the categories
2518:1996 Costa Rica accident
2179:Acoustic radiation force
2092:(1st ed.), London:
1724:Bellenir, Karen (2007).
1450:Electromagnetic spectrum
1000:Thermal radiation (heat)
850:electromagnetic spectrum
831:electromagnetic spectrum
435:Acute radiation syndrome
421:and radio-luminescence.
267:electromagnetic spectrum
2492:Radiation heat-transfer
2345:Gravitational radiation
1783:AdventHealth University
1391:AGM2015: A wordlwide v̄
1086:Royal Society of London
1052:Wien's displacement law
991:Extremely low frequency
985:Extremely low frequency
911:Infrared sensing snakes
176:gravitational radiation
2533:1990 Zaragoza accident
2528:1984 Moroccan accident
2497:Linear energy transfer
2171:Non-ionizing radiation
1757:"Making Nuclear Music"
1470:Non-ionizing radiation
1400:
949:
833:
817:Non-ionizing radiation
811:Non-ionizing radiation
789:coronal mass ejections
764:
682:. Beta radiation from
671:
601:
556:
429:
327:
61:
49:
2523:1987 Goiânia accident
2325:Synchrotron radiation
2315:Earth's energy budget
2297:Radioactive materials
2292:Particle accelerators
1390:
1342:DNA repair mechanisms
1235:particle accelerators
1136:discovered and named
1113:Johann Wilhelm Ritter
1070:Further information:
934:electromagnetic field
931:
828:
763:
660:
590:
547:
466:Ultraviolet radiation
427:
317:
212:radioactive materials
202:, which is enough to
55:
42:
2893:Evolutionary history
2594:Radiation protection
2447:Radiation protection
2335:Black-body radiation
2242:Background radiation
2157:(physics and health)
1755:Dunn, Peter (2014).
1734:. pp. 112–113.
1531:Notes and references
1505:Radiation properties
1423:Background radiation
1318:radioactive isotopes
1034:Black-body radiation
1028:Black-body radiation
604:Alpha particles are
413:instruments such as
30:For other uses, see
2830:Natural environment
2564:Radiation hardening
2506:Radiation incidents
2442:Medical radiography
2401:Radiation syndrome
2355:Cherenkov radiation
1950:2010rhln.book.....S
1904:Maggie Koerth-Baker
1544:Weisstein, Eric W.
1499:Radiation poisoning
1487:Radiation hardening
1441:blackbody radiation
1429:Cherenkov radiation
1326:radiation poisoning
1252:Medical radiography
1217:were discovered by
1128:James Clerk Maxwell
716:Neutron temperature
419:Cherenkov radiation
383:relativistic speeds
379:subatomic particles
214:that emit α, β, or
200:electron volts (eV)
170:transmission medium
123:gamma radiation (γ)
3061:Physical phenomena
3045:Nuclear technology
2559:Radioactive source
2380:Radiation exposure
2360:Askaryan radiation
2340:Particle radiation
2224:Ionizing radiation
1972:Sutou, S. (2018).
1906:(27 August 2010).
1552:. Wolfram Research
1493:Radiation hormesis
1465:Ionizing radiation
1401:
1346:High enough levels
1285:Radiometric dating
1281:radiocarbon dating
972:Very low frequency
950:
938:inverse-square law
834:
765:
734:neutron activation
672:
602:
557:
482:vacuum ultraviolet
455:Chernobyl disaster
430:
375:particle radiation
328:
310:Ionizing radiation
304:Ionizing radiation
298:inverse-square law
260:Earth's atmosphere
129:particle radiation
62:
50:
45:ionizing radiation
3026:
3025:
3004:
3003:
2677:chemical elements
2601:
2600:
2582:Radiation effects
2452:Radiation therapy
2388:
2387:
2330:Thermal radiation
2267:Neutron radiation
2232:Radioactive decay
1959:978-3-642-03719-1
1872:978-0-12-235154-9
1741:978-0-7808-0947-5
1727:Cancer Sourcebook
1683:Moulder, John E.
1524:Radioactive decay
1460:Hawking radiation
1215:neutron radiation
1164:Ernest Rutherford
1006:Thermal radiation
868:Ultraviolet light
712:Neutron radiation
706:Neutron radiation
676:radioactive decay
494:pyrimidine dimers
242:examinations and
146:neutron radiation
16:(Redirected from
3073:
3043:
3042:
3041:
3034:
3016:
3015:
2888:
2878:
2877:
2818:tropical cyclone
2768:
2628:
2621:
2614:
2605:
2604:
2542:Related articles
2457:Radiation damage
2282:Nuclear reactors
2167:
2166:
2148:
2141:
2134:
2125:
2124:
2120:
2030:
2029:
2027:
2025:
2015:
2009:
2008:
2006:
1998:
1992:
1986:
1980:
1970:
1964:
1963:
1939:
1930:Sanders, Charles
1926:
1920:
1918:
1916:
1914:
1900:
1894:
1887:
1881:
1880:
1852:
1846:
1845:
1836:
1827:
1821:
1820:
1818:
1816:
1810:The Conversation
1801:
1795:
1794:
1792:
1790:
1775:
1769:
1768:
1766:
1764:
1752:
1746:
1745:
1721:
1715:
1713:Nuclear medicine
1710:
1704:
1699:
1693:
1692:
1691:on 14 July 2007.
1687:. Archived from
1680:
1674:
1673:
1671:
1669:
1663:
1655:
1649:
1648:
1642:
1633:
1610:
1609:
1607:
1605:
1594:
1588:
1587:
1585:
1583:
1568:
1562:
1561:
1559:
1557:
1541:
1481:Radiation damage
1405:cosmic radiation
1078:William Herschel
801:gamma-ray bursts
776:Cosmic radiation
738:thermal neutrons
697:, which are the
570:depleted uranium
218:, consisting of
21:
3081:
3080:
3076:
3075:
3074:
3072:
3071:
3070:
3051:
3050:
3049:
3039:
3037:
3029:
3027:
3022:
3000:
2917:
2886:
2867:
2824:
2766:
2746:
2737:Gaia hypothesis
2727:Plate tectonics
2688:
2638:
2632:
2602:
2597:
2596:
2573:
2569:Havana syndrome
2554:Nuclear physics
2537:
2501:
2394:
2384:
2370:Unruh radiation
2306:
2287:Nuclear weapons
2272:Nuclear fission
2218:
2158:
2152:
2075:, 21 July 2011.
2039:
2034:
2033:
2023:
2021:
2017:
2016:
2012:
2004:
2000:
1999:
1995:
1987:
1983:
1971:
1967:
1960:
1927:
1923:
1912:
1910:
1901:
1897:
1888:
1884:
1873:
1853:
1849:
1839:
1837:
1830:
1828:
1824:
1814:
1812:
1802:
1798:
1788:
1786:
1777:
1776:
1772:
1762:
1760:
1753:
1749:
1742:
1730:. Detroit, MI:
1722:
1718:
1711:
1707:
1700:
1696:
1681:
1677:
1667:
1665:
1661:
1657:
1656:
1652:
1640:
1634:
1613:
1603:
1601:
1596:
1595:
1591:
1581:
1579:
1570:
1569:
1565:
1555:
1553:
1542:
1538:
1533:
1528:
1443:that fills the
1413:
1398:
1394:
1385:
1379:
1358:. In 2011, the
1320:, particularly
1310:
1304:
1276:
1267:
1258:
1250:Main articles:
1248:
1243:
1145:Henri Becquerel
1134:Wilhelm Röntgen
1117:silver chloride
1096:light from the
1074:
1068:
1036:
1030:
1008:
1002:
993:
987:
974:
965:
959:
926:
920:
906:
900:
891:
885:
876:
870:
823:
815:Main articles:
813:
799:and especially
784:
778:
770:nuclear reactor
718:
710:Main articles:
708:
655:
649:
594:detected in an
585:
579:
577:Alpha radiation
542:
536:
534:Gamma radiation
509:
503:
479:
474:
468:
415:Geiger counters
391:alpha particles
381:accelerated to
356:equivalent dose
312:
306:
138:alpha radiation
76:in the form of
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3079:
3069:
3068:
3063:
3048:
3047:
3024:
3023:
3021:
3020:
3009:
3006:
3005:
3002:
3001:
2999:
2998:
2991:
2990:
2989:
2984:
2974:
2973:
2972:
2967:
2962:
2961:
2960:
2950:
2949:
2948:
2933:
2928:
2922:
2919:
2918:
2916:
2915:
2905:
2900:
2895:
2890:
2881:
2875:
2869:
2868:
2866:
2865:
2860:
2855:
2850:
2845:
2840:
2834:
2832:
2826:
2825:
2823:
2822:
2821:
2820:
2815:
2805:
2800:
2795:
2790:
2785:
2780:
2775:
2770:
2762:
2756:
2754:
2748:
2747:
2745:
2744:
2739:
2734:
2729:
2724:
2719:
2714:
2704:
2698:
2696:
2690:
2689:
2687:
2686:
2681:
2680:
2679:
2674:
2664:
2659:
2654:
2648:
2646:
2640:
2639:
2631:
2630:
2623:
2616:
2608:
2599:
2598:
2578:
2575:
2574:
2572:
2571:
2566:
2561:
2556:
2551:
2545:
2543:
2539:
2538:
2536:
2535:
2530:
2525:
2520:
2515:
2509:
2507:
2503:
2502:
2500:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2484:
2479:
2474:
2469:
2464:
2459:
2454:
2449:
2444:
2439:
2434:
2429:
2424:
2419:
2417:Health physics
2414:
2413:
2412:
2407:
2398:
2396:
2390:
2389:
2386:
2385:
2383:
2382:
2377:
2375:Dark radiation
2372:
2367:
2365:Bremsstrahlung
2362:
2357:
2352:
2347:
2342:
2337:
2332:
2327:
2322:
2317:
2311:
2308:
2307:
2305:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2289:
2284:
2279:
2277:Nuclear fusion
2274:
2269:
2264:
2259:
2254:
2249:
2247:Alpha particle
2244:
2239:
2234:
2228:
2226:
2220:
2219:
2217:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2201:
2196:
2191:
2186:
2181:
2175:
2173:
2164:
2160:
2159:
2151:
2150:
2143:
2136:
2128:
2122:
2121:
2076:
2066:
2060:
2055:
2038:
2037:External links
2035:
2032:
2031:
2010:
1993:
1981:
1965:
1958:
1921:
1895:
1882:
1871:
1847:
1822:
1796:
1770:
1759:. Slice of MIT
1747:
1740:
1716:
1705:
1694:
1675:
1650:
1611:
1589:
1563:
1535:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1527:
1526:
1521:
1516:
1507:
1502:
1496:
1490:
1484:
1478:
1475:Radiant energy
1472:
1467:
1462:
1457:
1452:
1447:
1431:
1426:
1420:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1396:
1392:
1381:Main article:
1378:
1375:
1362:(IARC) of the
1303:
1300:
1275:
1272:
1266:
1263:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1219:James Chadwick
1193:Edward Andrade
1160:beta particles
1124:Heinrich Hertz
1067:
1064:
1032:Main article:
1029:
1026:
1013:thermal energy
1004:Main article:
1001:
998:
989:Main article:
986:
983:
973:
970:
961:Main article:
958:
955:
922:Main article:
919:
916:
902:Main article:
899:
896:
887:Main article:
884:
881:
872:Main article:
869:
866:
812:
809:
780:Main article:
777:
774:
726:chain reaction
707:
704:
651:Main article:
648:
647:Beta radiation
645:
592:Alpha particle
581:Main article:
578:
575:
538:Main article:
535:
532:
505:Main article:
502:
499:
477:
470:Main article:
467:
464:
443:thyroid cancer
439:genetic damage
407:electron volts
395:beta particles
360:effective dose
318:Some kinds of
308:Main article:
305:
302:
208:chemical bonds
184:
183:
172:
148:
142:beta radiation
125:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3078:
3067:
3064:
3062:
3059:
3058:
3056:
3046:
3036:
3035:
3032:
3019:
3011:
3010:
3007:
2997:
2996:
2992:
2988:
2985:
2983:
2980:
2979:
2978:
2975:
2971:
2968:
2966:
2963:
2959:
2956:
2955:
2954:
2951:
2947:
2944:
2943:
2942:
2939:
2938:
2937:
2934:
2932:
2929:
2927:
2924:
2923:
2920:
2913:
2909:
2906:
2904:
2901:
2899:
2896:
2894:
2891:
2889:
2887:(abiogenesis)
2883:
2882:
2879:
2876:
2874:
2870:
2864:
2861:
2859:
2856:
2854:
2851:
2849:
2846:
2844:
2841:
2839:
2836:
2835:
2833:
2831:
2827:
2819:
2816:
2814:
2811:
2810:
2809:
2806:
2804:
2801:
2799:
2796:
2794:
2791:
2789:
2786:
2784:
2781:
2779:
2776:
2774:
2771:
2769:
2763:
2761:
2758:
2757:
2755:
2753:
2749:
2743:
2740:
2738:
2735:
2733:
2730:
2728:
2725:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2712:
2708:
2705:
2703:
2702:Earth science
2700:
2699:
2697:
2695:
2691:
2685:
2682:
2678:
2675:
2673:
2670:
2669:
2668:
2665:
2663:
2660:
2658:
2655:
2653:
2650:
2649:
2647:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2629:
2624:
2622:
2617:
2615:
2610:
2609:
2606:
2595:
2591:
2587:
2586:Radioactivity
2583:
2576:
2570:
2567:
2565:
2562:
2560:
2557:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2546:
2544:
2540:
2534:
2531:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2514:
2511:
2510:
2508:
2504:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2490:
2488:
2485:
2483:
2480:
2478:
2475:
2473:
2470:
2468:
2465:
2463:
2460:
2458:
2455:
2453:
2450:
2448:
2445:
2443:
2440:
2438:
2435:
2433:
2430:
2428:
2425:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2411:
2408:
2406:
2403:
2402:
2400:
2399:
2397:
2391:
2381:
2378:
2376:
2373:
2371:
2368:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2346:
2343:
2341:
2338:
2336:
2333:
2331:
2328:
2326:
2323:
2321:
2318:
2316:
2313:
2312:
2309:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2288:
2285:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2265:
2263:
2260:
2258:
2255:
2253:
2252:Beta particle
2250:
2248:
2245:
2243:
2240:
2238:
2237:Cluster decay
2235:
2233:
2230:
2229:
2227:
2225:
2221:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2200:
2197:
2195:
2192:
2190:
2187:
2185:
2182:
2180:
2177:
2176:
2174:
2172:
2168:
2165:
2163:Main articles
2161:
2156:
2149:
2144:
2142:
2137:
2135:
2130:
2129:
2126:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2103:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2086:
2081:
2077:
2074:
2070:
2067:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2050:
2049:
2044:
2041:
2040:
2020:
2014:
2003:
1997:
1990:
1985:
1979:
1975:
1969:
1961:
1955:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1938:
1937:
1931:
1925:
1909:
1905:
1899:
1892:
1886:
1879:
1874:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1859:
1851:
1844:
1843:
1835:
1834:
1826:
1811:
1807:
1800:
1785:. 21 May 2018
1784:
1780:
1774:
1758:
1751:
1743:
1737:
1733:
1729:
1728:
1720:
1714:
1709:
1703:
1698:
1690:
1686:
1679:
1660:
1654:
1646:
1639:
1632:
1630:
1628:
1626:
1624:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1616:
1599:
1593:
1578:. Farlex, Inc
1577:
1573:
1567:
1551:
1547:
1540:
1536:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1517:
1515:
1511:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1500:
1497:
1494:
1491:
1488:
1485:
1482:
1479:
1476:
1473:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1451:
1448:
1446:
1442:
1439:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1424:
1421:
1419:
1416:
1415:
1408:
1406:
1389:
1384:
1374:
1372:
1367:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1352:
1349:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1309:
1299:
1297:
1292:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1271:
1265:Communication
1262:
1257:
1253:
1238:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1207:
1205:
1201:
1196:
1194:
1190:
1185:
1183:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1165:
1161:
1156:
1154:
1153:radioactivity
1150:
1146:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1129:
1125:
1120:
1118:
1114:
1109:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1073:
1063:
1061:
1056:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1041:
1035:
1025:
1023:
1017:
1014:
1007:
997:
992:
982:
980:
969:
964:
954:
947:
944:includes the
943:
939:
935:
930:
925:
915:
912:
905:
895:
890:
883:Visible light
880:
875:
865:
861:
859:
854:
851:
846:
844:
838:
832:
827:
822:
818:
808:
806:
802:
798:
792:
790:
783:
773:
771:
762:
758:
756:
755:billiard ball
752:
751:free radicals
748:
747:chemical bond
742:
739:
735:
730:
727:
723:
722:free neutrons
717:
713:
703:
700:
696:
691:
689:
685:
681:
677:
670:
669:cloud chamber
667:
663:
659:
654:
644:
642:
638:
634:
630:
625:
624:radioisotopes
620:
618:
614:
610:
607:
600:
599:cloud chamber
597:
593:
589:
584:
574:
571:
565:
562:
554:
553:cloud chamber
551:
546:
541:
531:
527:
525:
521:
518:
514:
508:
498:
495:
490:
485:
483:
473:
463:
460:
456:
452:
448:
444:
440:
436:
426:
422:
420:
416:
410:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
363:
361:
357:
353:
352:absorbed dose
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
325:
324:cloud chamber
321:
316:
311:
301:
299:
295:
291:
287:
282:
280:
276:
272:
268:
263:
261:
257:
253:
250:, positrons,
249:
245:
241:
238:from medical
237:
233:
229:
225:
221:
220:helium nuclei
217:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
196:
191:
190:
182:
178:
177:
173:
171:
167:
166:seismic waves
163:
159:
155:
153:
149:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
130:
126:
124:
120:
116:
112:
111:visible light
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
91:
87:
86:
85:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
59:
54:
46:
41:
37:
33:
19:
2993:
2926:Biodiversity
2912:astrobiology
2852:
2634:Elements of
2590:Radiobiology
2472:Radiobiology
2432:Laser safety
2154:
2090:Rede Lecture
2083:
2080:John Tyndall
2072:
2047:
2022:. Retrieved
2019:"EMF-Portal"
2013:
1996:
1984:
1968:
1935:
1924:
1911:. Retrieved
1898:
1885:
1876:
1857:
1850:
1841:
1832:
1825:
1813:. Retrieved
1809:
1799:
1787:. Retrieved
1782:
1773:
1761:. Retrieved
1750:
1732:Omnigraphics
1725:
1719:
1708:
1697:
1689:the original
1678:
1666:. Retrieved
1653:
1644:
1602:. Retrieved
1592:
1580:. Retrieved
1575:
1566:
1554:. Retrieved
1549:
1539:
1402:
1368:
1353:
1350:
1322:potassium-40
1311:
1293:
1289:tracer atoms
1277:
1268:
1259:
1241:Applications
1208:
1204:electrometer
1197:
1189:Thomas Royds
1186:
1177:Paul Villard
1172:
1168:
1157:
1142:
1132:
1121:
1110:
1075:
1057:
1047:Planck's law
1038:
1037:
1018:
1009:
994:
975:
966:
951:
907:
892:
877:
862:
855:
847:
839:
835:
793:
785:
766:
743:
731:
719:
692:
688:radiotherapy
680:antineutrino
673:
621:
603:
566:
558:
528:
510:
486:
475:
431:
411:
364:
329:
294:point source
285:
283:
264:
195:non-ionizing
193:
187:
185:
174:
150:
127:
93:consists of
88:
69:
63:
36:
2977:Prokaryotes
2765:Atmosphere
2760:Meteorology
2214:Ultraviolet
2209:Radio waves
2048:In Our Time
1702:Radiography
1668:12 December
1572:"Radiation"
1546:"Radiation"
1202:carried an
1200:Victor Hess
1169:alpha rays.
1149:Marie Curie
1106:thermometer
963:Radio waves
957:Radio waves
874:Ultraviolet
782:Cosmic rays
666:isopropanol
617:cosmic rays
613:alpha decay
596:isopropanol
583:Alpha decay
550:isopropanol
489:ozone layer
472:Ultraviolet
373:, there is
296:follows an
279:frequencies
256:cosmic rays
240:radiography
216:γ radiation
134:rest energy
115:ultraviolet
99:radio waves
3055:Categories
2858:Wilderness
2711:geological
2395:and health
2393:Radiation
2262:Cosmic ray
1940:. p.
1815:6 November
1789:5 November
1582:11 January
1556:11 January
1306:See also:
1182:gamma rays
1082:astronomer
1040:Black-body
979:myriameter
797:supernovae
699:antimatter
653:Beta decay
447:iodine-131
271:wavelength
158:ultrasound
156:, such as
136:, such as
103:microwaves
97:, such as
58:unshielded
3066:Radiation
2936:Eukaryota
2903:Hierarchy
2898:Biosphere
2863:Wildfires
2853:Radiation
2843:Ecosystem
2783:Moonlight
2717:Structure
2672:particles
2549:Half-life
2422:Dosimetry
2257:Gamma ray
2204:Microwave
2194:Starlight
2155:Radiation
2118:Q19086230
2043:Radiation
1878:constant.
1763:29 August
1604:29 August
1223:positrons
1143:In 1896,
1066:Discovery
1042:radiation
946:far field
924:Microwave
918:Microwave
695:positrons
662:Electrons
540:Gamma ray
348:trillions
336:electrons
286:radiating
228:positrons
224:electrons
181:spacetime
154:radiation
82:particles
70:radiation
18:Radiating
3018:Category
2987:bacteria
2970:protista
2931:Organism
2798:Sunlight
2644:Universe
2199:Sunlight
2184:Infrared
2114:Wikidata
2102:05005356
2082:(1865),
2073:BBC News
1932:(2010).
1445:Universe
1411:See also
1246:Medicine
1022:browning
904:Infrared
898:Infrared
843:browning
641:polonium
606:helium-4
399:neutrons
320:ionizing
252:neutrons
189:ionizing
152:acoustic
107:infrared
48:diagram.
2995:Viruses
2982:archaea
2958:animals
2910: (
2908:Biology
2885:Origin
2838:Ecology
2813:tornado
2773:Climate
2767:(Earth)
2752:Weather
2722:Geology
2709: (
2707:History
2410:chronic
2110:4920745
2094:Longman
2051:at the
2024:12 July
1946:Bibcode
1863:171–172
1455:FASTRAD
1314:bananas
1274:Science
1211:Neutron
1094:refract
805:quasars
791:(CME).
561:nucleus
403:protons
387:momenta
367:fission
232:photons
95:photons
66:physics
3031:Portal
2946:plants
2778:Clouds
2742:Future
2732:Oceans
2684:Change
2667:Matter
2662:Energy
2636:nature
2592:, and
2116:
2108:
2100:
1956:
1913:25 May
1869:
1738:
1664:. ICRP
1328:, and
1229:, and
1138:X-rays
1080:, the
858:photon
639:, and
633:radium
609:nuclei
501:X-rays
457:. The
401:, and
371:fusion
344:cancer
332:ionize
248:mesons
236:X-rays
230:, and
204:ionize
164:, and
121:, and
119:x-rays
74:energy
2965:fungi
2953:fauna
2941:flora
2848:Field
2803:Tides
2694:Earth
2652:Space
2405:acute
2302:X-ray
2189:Light
2005:(PDF)
1662:(PDF)
1641:(PDF)
1512:– by
1356:burns
1231:pions
1227:muons
1173:beta.
1090:prism
1060:stars
889:Light
684:linac
637:radon
507:X-ray
340:cells
244:muons
162:sound
140:(α),
78:waves
2873:Life
2808:Wind
2793:Snow
2788:Rain
2657:Time
2106:OCLC
2098:LCCN
2026:2019
1954:ISBN
1915:2011
1867:ISBN
1817:2022
1791:2022
1765:2018
1736:ISBN
1670:2013
1606:2018
1584:2014
1558:2014
1436:, 3
1254:and
1213:and
1209:The
848:The
829:The
819:and
714:and
275:heat
2053:BBC
2045:on
1838:b.
1829:a.
1102:red
1098:Sun
1092:to
369:or
362:).
226:or
192:or
80:or
64:In
3057::
2588:,
2584:,
2112:,
2104:,
2096:,
2088:,
2071:,
1952:.
1944:.
1942:47
1875:.
1865:.
1808:.
1781:.
1643:.
1614:^
1574:.
1548:.
1407:.
1344:.
1225:,
1184:.
1155:.
1130:.
1108:.
635:,
397:,
393:,
281:.
262:.
246:,
222:,
160:,
117:,
113:,
109:,
105:,
101:,
68:,
3033::
2914:)
2713:)
2627:e
2620:t
2613:v
2147:e
2140:t
2133:v
2028:.
1962:.
1948::
1917:.
1819:.
1793:.
1767:.
1744:.
1672:.
1647:.
1608:.
1586:.
1560:.
1438:K
1397:e
1393:e
1020:"
555:.
524:λ
522:/
520:c
517:h
515:=
513:E
478:3
326:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.