50:
533:
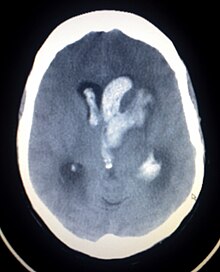
screen may be sent. A CT head is very important to obtain to rule out bleed. In cases where meningitis is suspected, a lumbar puncture must be performed. A serum TSH is an important test to order. In select groups consider vitamin B12 levels. Checking serum ammonia is particularly advised in neonatal coma to discern
267:". A confused person may be bewildered, disoriented, and have difficulty following instructions. The person may have slow thinking and possible memory time loss. This could be caused by sleep deprivation, malnutrition, allergies, environmental pollution, drugs (prescription and nonprescription), and infection.
428:
nresponsive. To determine responsiveness to voice, a caregiver speaks to, or, failing that, yells at the person. Responsiveness to pain is determined with a mild painful stimulus such as a pinch; moaning or withdrawal from the stimulus is considered a response to pain. The ACDU scale, like AVPU,
532:
and gag reflexes, are also means of judging LOC. Once the level of consciousness is determined, clinicians seek clues for the cause of any alteration. Usually the first tests in the ER are pulse oximetry to determine if there is hypoxia, serum glucose levels to rule out hypoglycemia. A urine drug
400:, or an altered level of consciousness. Verbal, motor, and eye-opening responses to stimuli are measured, scored, and added into a final score on a scale of 3–15, with a lower score being a more decreased level of consciousness.
249:
stage from which a person is easily awakened is also considered a normal level of consciousness. "Clouding of consciousness" is a term for a mild alteration of consciousness with alterations in attention and wakefulness.
1301:
1286:
484:
from the reticular formation. Since this system is thought to modulate wakefulness and sleep, interference with it, such as injury, illness, or metabolic disturbances, could alter the level of consciousness.
216:
People who possess the ability to monitor and control their own cognitive processes in addition to meeting all the criteria indicative of a normal level of consciousness. In the field of
524:
Assessing LOC involves determining an individual's response to external stimuli. Speed and accuracy of responses to questions and reactions to stimuli such as touch and pain are noted.
245:: people who are able promptly and spontaneously to state their name, location, and the date or time are said to be oriented to self, place, and time, or "oriented X3". A normal
224:, which receives sensory input signals from divergent cortical regions and implements control through feedback loops which are established utilizing the underlying mechanisms of
545:
A lowered level of consciousness indicate a deficit in brain function. Level of consciousness can be lowered when the brain receives insufficient oxygen (as occurs in
186:
Scales and terms to classify the levels of consciousness differ, but in general, reduction in response to stimuli indicates an altered level of consciousness:
174:(death). Thus it is a valuable measure of a patient's medical and neurological status. In fact, some sources consider level of consciousness to be one of the
1344:
134:
An altered level of consciousness can result from a variety of factors, including alterations in the chemical environment of the brain (e.g. exposure to
449:
119:
have a more depressed level of consciousness and cannot be fully aroused. Those who are not able to be aroused from a sleep-like state are said to be
17:
1500:
685:
Treatment depends on the degree of decrease in consciousness and its underlying cause. Initial treatment often involves the administration of
1495:
1337:
1235:
1202:
1167:
808:
975:
924:
1089:
818:
469:
280:
Some scales have "delirious" below this level, in which a person may be restless or agitated and exhibit a marked deficit in
720:
1330:
263:
People who do not respond quickly with information about their name, location, and the time are considered "obtuse" or "
554:
1245:
1212:
1179:
1118:
1039:
985:
934:
870:
771:
1485:
710:
31:
429:
is easier to use than the GCS and produces similarly accurate results. Using ACDU, a patient is assessed for
500:. Mass lesions in the brain stem normally cause coma due to their effects on the reticular formation. Mass
1490:
1374:
534:
512:
normally do not significantly alter the level of consciousness unless they are very large or affect both
163:
1106:
1027:
1353:
715:
1369:
955:
Dunlosky, J. & Bjork, R. A. (Eds), Handbook of
Metamemory and Memory. Psychology Press: New York.
653:
may also be associated with decreased LOC; for example, an altered LOC is the most common symptom of
1081:
642:
58:
1139:
Mass lesions within monkey coma by virtue of direct effects on the reticular formation of monkey
862:
464:
Although the neural science behind alertness, wakefulness, and arousal are not fully known, the
1505:
650:
630:
217:
1480:
626:
397:
326:, a person has a decreased interest in their surroundings, slowed responses, and sleepiness.
151:
100:
1073:
472:
is a postulated group of neural connections that receives sensory input and projects to the
412:
scale is another means of measuring LOC: people are assessed to determine whether they are
242:
763:
8:
1305:
1074:
662:
550:
513:
509:
465:
159:
1459:
1426:
855:
570:
453:
393:
387:
365:
128:
1310:
1439:
1241:
1208:
1175:
1124:
1114:
1085:
1045:
1035:
981:
930:
866:
814:
767:
725:
574:
546:
452:
classes people on a scale of I to V along a scale of confusion, stupor, deep stupor,
340:
228:(see chapters by Schwartz & Bacon and Shimamura, in Dunlosky & Bjork, 2008).
221:
155:
66:
49:
614:
497:
1389:
1361:
756:
670:
558:
473:
225:
629:(the pressure within the skull) can also cause altered LOC. It can result from
307:
and responds to stimuli only with incoherent mumbles or disorganized movements.
753:
638:
606:
505:
357:
171:
166:
have been injured. A decreased level of consciousness correlates to increased
115:; someone in this state can be aroused with little difficulty. People who are
30:
This article is about the medical concept. For the psychological concept, see
1474:
1399:
1322:
677:, which is a mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) may result in decreased LOC.
601:
outside of the range the brain can tolerate will also alter LOC. Exposure to
586:
562:
208:
104:
1295:
220:, metacognitive monitoring and control have been viewed as functions of the
1434:
1128:
1049:
654:
618:
582:
566:
167:
339:
People with an even lower level of consciousness, stupor, only respond by
1379:
622:
594:
322:
312:
116:
1278:
396:(GCS). It has come into almost universal use for assessing people with
1409:
674:
634:
489:
361:
304:
299:
289:
175:
147:
139:
127:
is the inability to make any purposeful response. Scales such as the
71:
1416:
646:
375:
331:
281:
264:
233:
158:. A deficit in the level of consciousness suggests that both of the
108:
75:
1111:
Clinical
Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations
1032:
Clinical
Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations
99:) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to
698:
694:
686:
673:. A decreased LOC can also result from a combination of factors. A
666:
658:
529:
481:
477:
356:
Comatose people do not even make this response to stimuli, have no
336:
Sleep-like state (not unconscious); little/no spontaneous activity
272:
255:
112:
1240:. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 219.
813:. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 835.
392:
The most commonly used tool for measuring LOC objectively is the
374:
Altered level of consciousness is sometimes described as altered
88:
810:
488:
Normally, stupor and coma are produced by interference with the
1394:
1290:
1168:"Diagnosis and management of depressed states of consciousness"
690:
590:
578:
525:
501:
493:
277:
Disoriented; restlessness, hallucinations, sometimes delusions
143:
135:
120:
1404:
610:
246:
154:. Prolonged unconsciousness is understood to be a sign of a
754:
Kandel E.R.; Jessell, Thomas M.; Schwartz, James H. (2000).
1384:
689:
if the blood sugar is low as well as the administration of
602:
409:
348:
124:
929:(5th ed.). Guilford, Conn: Globe Pequot. p. 13.
131:
have been designed to measure the level of consciousness.
1204:
Medical Speech-language
Pathology: A Practitioner's Guide
857:
980:. Totowa, N.J: Rowman & Allanheld. pp. 57–58.
598:
1071:
1268:
103:from the environment. A mildly depressed level of
1233:
854:
755:
317:Decreased alertness; slowed psychomotor responses
1472:
977:Nursing the Neurological and Neurotrauma Patient
1200:
1072:Posner JB, Saper CB, Schiff ND, Plum F (2007).
1352:
1076:Plum and Posner's Diagnosis of Stupor and Coma
1338:
260:Disoriented; impaired thinking and responses
61:, one cause of altered level of consciousness
1165:
1021:
1019:
1017:
852:
1161:
1159:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1151:
1149:
1147:
1067:
1065:
1015:
1013:
1011:
1009:
1007:
1005:
1003:
1001:
999:
997:
645:are other causes of altered consciousness.
1345:
1331:
1109:. In Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW (eds.).
1104:
1098:
1030:. In Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW (eds.).
1025:
918:
916:
893:
891:
848:
846:
844:
842:
840:
838:
836:
749:
747:
745:
743:
741:
353:Cannot be aroused; no response to stimuli
48:
1194:
969:
967:
965:
963:
961:
922:
802:
800:
798:
796:
794:
792:
540:
1237:Infections of the Central Nervous System
1234:Scheld WM, Whitley RJ, Marra CM (2004).
1227:
1172:Current Surgical Diagnosis and Treatment
1144:
1080:. Oxford University Press, US. pp.
1062:
994:
973:
900:
949:
913:
888:
861:. Boston: Jones and Bartlett. pp.
833:
806:
738:
468:is known to play a role in these. The
14:
1501:Symptoms and signs of mental disorders
1473:
958:
789:
665:can also affect consciousness, as can
343:or drawing away from painful stimuli.
1326:
926:Wilderness Medicine, Beyond First Aid
470:ascending reticular activating system
381:
1174:. McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 863.
721:Level of consciousness (esotericism)
549:); insufficient blood (as occurs in
241:Assessment of LOC involves checking
27:Measure of arousal other than normal
597:can also produce an altered LOC. A
24:
1207:. Stuttgart: Thieme. p. 142.
762:. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp.
589:(decreased and elevated levels of
459:
25:
1517:
1264:
553:, in children for example due to
1496:Central nervous system disorders
1201:Johnson AF, Jacobson BH (1998).
18:Decreased level of consciousness
557:); or has an alteration in the
711:Altered state of consciousness
85:altered level of consciousness
43:Altered level of consciousness
32:Altered state of consciousness
13:
1:
1166:von Koch CS, Hoff JT (2005).
853:Pollak AN, Gupton CL (2002).
731:
617:that is too high or too low (
613:may also lower LOC, as may a
496:or indirect effects, such as
492:, such as can be caused by a
420:erbal stimuli, responsive to
181:
758:Principles of neural science
680:
519:
150:in the brain, and excessive
7:
1375:Persistent vegetative state
704:
593:, respectively) as well as
535:inborn errors of metabolism
164:reticular activating system
10:
1522:
1354:Disorders of consciousness
1113:. Butterworth Publishers.
1034:. Butterworth Publishers.
716:Disorders of consciousness
385:
29:
1448:
1425:
1370:Minimally conscious state
1360:
1272:
581:can alter consciousness.
569:can alter consciousness.
403:
152:pressure within the skull
65:
56:
47:
42:
1107:"Level of consciousness"
1028:"Level of consciousness"
1486:Intensive care medicine
1170:. In Doherty GM (ed.).
883:level of consciousness.
784:level of consciousness.
567:conditions of the lungs
563:Conditions of the heart
364:, and they may have no
303:person shows excessive
191:Levels of consciousness
59:intracranial hemorrhage
651:central nervous system
631:traumatic brain injury
541:Differential diagnosis
218:cognitive neuroscience
93:Level of consciousness
627:intracranial pressure
514:cerebral hemispheres
416:lert, responsive to
160:cerebral hemispheres
91:other than normal.
1105:Tindall SC (1990).
1026:Tindall SC (1990).
671:post-seizure states
663:intracranial cavity
571:Metabolic disorders
510:tentorium cerebelli
466:reticular formation
424:ainful stimuli, or
193:
1491:Emergency medicine
1460:Locked-in syndrome
923:Forgey WW (1999).
454:abnormal posturing
394:Glasgow Coma Scale
388:Glasgow Coma Scale
382:Glasgow Coma Scale
366:pupillary response
189:
129:Glasgow coma scale
111:may be classed as
87:is any measure of
1468:
1467:
1440:Vasovagal episode
1320:
1319:
1091:978-0-19-532131-9
974:Kruse MJ (1986).
820:978-0-7817-7087-3
726:Cognitive deficit
575:diabetes mellitus
559:brain's chemistry
445:nresponsiveness.
372:
371:
222:prefrontal cortex
156:medical emergency
81:
80:
37:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1513:
1347:
1340:
1333:
1324:
1323:
1270:
1269:
1258:
1257:
1255:
1254:
1231:
1225:
1224:
1222:
1221:
1198:
1192:
1191:
1189:
1188:
1163:
1142:
1141:
1136:
1135:
1102:
1096:
1095:
1079:
1069:
1060:
1059:
1057:
1056:
1023:
992:
991:
971:
956:
953:
947:
946:
944:
943:
920:
911:
904:
898:
895:
886:
885:
880:
879:
860:
850:
831:
830:
828:
827:
807:Porth C (2007).
804:
787:
786:
781:
780:
761:
751:
625:). Increases in
615:core temperature
498:brain herniation
450:Grady Coma Scale
194:
188:
142:), insufficient
52:
40:
39:
21:
1521:
1520:
1516:
1515:
1514:
1512:
1511:
1510:
1471:
1470:
1469:
1464:
1451:
1444:
1421:
1390:Brainstem death
1362:Unconsciousness
1356:
1351:
1321:
1316:
1315:
1281:
1267:
1262:
1261:
1252:
1250:
1248:
1232:
1228:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1199:
1195:
1186:
1184:
1182:
1164:
1145:
1133:
1131:
1121:
1103:
1099:
1092:
1070:
1063:
1054:
1052:
1042:
1024:
995:
988:
972:
959:
954:
950:
941:
939:
937:
921:
914:
905:
901:
896:
889:
877:
875:
873:
851:
834:
825:
823:
821:
805:
790:
778:
776:
774:
752:
739:
734:
707:
683:
639:Ischemic stroke
555:intussusception
543:
522:
474:cerebral cortex
462:
460:Pathophysiology
441:rowsiness, and
406:
390:
384:
226:neuroplasticity
200:Summary (Kruse)
184:
170:(sickness) and
38:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1519:
1509:
1508:
1503:
1498:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1466:
1465:
1463:
1462:
1456:
1454:
1446:
1445:
1443:
1442:
1437:
1431:
1429:
1423:
1422:
1420:
1419:
1414:
1413:
1412:
1407:
1402:
1392:
1387:
1382:
1377:
1372:
1366:
1364:
1358:
1357:
1350:
1349:
1342:
1335:
1327:
1318:
1317:
1314:
1313:
1298:
1282:
1277:
1276:
1274:
1273:Classification
1266:
1265:External links
1263:
1260:
1259:
1246:
1226:
1213:
1193:
1180:
1143:
1119:
1097:
1090:
1061:
1040:
993:
986:
957:
948:
935:
912:
899:
887:
871:
832:
819:
788:
772:
736:
735:
733:
730:
729:
728:
723:
718:
713:
706:
703:
682:
679:
643:brain bleeding
542:
539:
528:, such as the
521:
518:
461:
458:
405:
402:
386:Main article:
383:
380:
370:
369:
354:
351:
345:
344:
337:
334:
328:
327:
318:
315:
309:
308:
295:
292:
286:
285:
278:
275:
269:
268:
261:
258:
252:
251:
239:
236:
230:
229:
214:
213:Preternatural
211:
205:
204:
201:
198:
183:
180:
79:
78:
69:
63:
62:
54:
53:
45:
44:
36:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1518:
1507:
1506:Consciousness
1504:
1502:
1499:
1497:
1494:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1476:
1461:
1458:
1457:
1455:
1453:
1452:consciousness
1450:Alteration of
1447:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1432:
1430:
1428:
1424:
1418:
1415:
1411:
1408:
1406:
1403:
1401:
1398:
1397:
1396:
1393:
1391:
1388:
1386:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1367:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1348:
1343:
1341:
1336:
1334:
1329:
1328:
1325:
1312:
1308:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1297:
1293:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1283:
1280:
1275:
1271:
1249:
1247:0-7817-4327-3
1243:
1239:
1238:
1230:
1216:
1214:0-86577-688-1
1210:
1206:
1205:
1197:
1183:
1181:0-07-142315-X
1177:
1173:
1169:
1162:
1160:
1158:
1156:
1154:
1152:
1150:
1148:
1140:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1120:9780409900774
1116:
1112:
1108:
1101:
1093:
1087:
1083:
1078:
1077:
1068:
1066:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1041:9780409900774
1037:
1033:
1029:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1016:
1014:
1012:
1010:
1008:
1006:
1004:
1002:
1000:
998:
989:
987:0-8476-7451-7
983:
979:
978:
970:
968:
966:
964:
962:
952:
938:
936:0-7627-0490-X
932:
928:
927:
919:
917:
909:
903:
897:Porth, p. 838
894:
892:
884:
874:
872:0-7637-1666-9
868:
864:
859:
858:
849:
847:
845:
843:
841:
839:
837:
822:
816:
812:
811:
803:
801:
799:
797:
795:
793:
785:
775:
773:0-8385-7701-6
769:
765:
760:
759:
750:
748:
746:
744:
742:
737:
727:
724:
722:
719:
717:
714:
712:
709:
708:
702:
700:
696:
692:
688:
678:
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
587:hypernatremia
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
538:
536:
531:
527:
517:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
486:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
457:
455:
451:
446:
444:
440:
436:
432:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
401:
399:
395:
389:
379:
377:
367:
363:
359:
355:
352:
350:
347:
346:
342:
338:
335:
333:
330:
329:
325:
324:
319:
316:
314:
311:
310:
306:
302:
301:
296:
293:
291:
288:
287:
283:
279:
276:
274:
271:
270:
266:
262:
259:
257:
254:
253:
248:
244:
240:
237:
235:
232:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
212:
210:
209:Metaconscious
207:
206:
202:
199:
196:
195:
192:
187:
179:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
132:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
105:consciousness
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
77:
73:
70:
68:
64:
60:
55:
51:
46:
41:
33:
19:
1481:Neuroscience
1449:
1435:Heat syncope
1300:
1285:
1251:. Retrieved
1236:
1229:
1218:. Retrieved
1203:
1196:
1185:. Retrieved
1171:
1138:
1132:. Retrieved
1110:
1100:
1075:
1053:. Retrieved
1031:
976:
951:
940:. Retrieved
925:
907:
902:
882:
876:. Retrieved
856:
824:. Retrieved
809:
783:
777:. Retrieved
757:
684:
655:encephalitis
619:hyperthermia
544:
523:
487:
476:through the
463:
456:, and coma.
447:
442:
438:
434:
430:
425:
421:
417:
413:
407:
398:brain injury
391:
373:
321:
298:
203:Description
190:
185:
133:
96:
92:
84:
82:
1380:Obtundation
661:within the
623:hypothermia
595:dehydration
504:that occur
323:obtundation
243:orientation
176:vital signs
140:intoxicants
1475:Categories
1410:Somnolence
1253:2008-07-04
1220:2008-07-04
1187:2008-07-04
1134:2008-07-04
1055:2008-07-04
942:2008-07-04
878:2008-07-04
826:2008-07-03
779:2008-07-03
732:References
675:concussion
647:Infections
635:concussion
490:brain stem
437:onfusion,
433:lertness,
368:to light.
362:gag reflex
305:drowsiness
182:Definition
148:blood flow
72:Psychiatry
1417:Cataplexy
681:Treatment
659:Neoplasms
520:Diagnosis
376:sensorium
341:grimacing
332:Stuporous
300:somnolent
290:Somnolent
282:attention
273:Delirious
234:Conscious
172:mortality
168:morbidity
121:stuporous
109:alertness
76:Neurology
67:Specialty
1129:21250221
1050:21250221
910:. p. 530
705:See also
699:thiamine
695:naloxone
687:dextrose
667:epilepsy
633:such as
573:such as
526:Reflexes
482:thalamus
478:midbrain
349:Comatose
313:Obtunded
265:confused
256:Confused
117:obtunded
113:lethargy
1427:Syncope
906:Scheld
649:of the
607:alcohol
547:hypoxia
502:lesions
358:corneal
294:Sleepy
238:Normal
162:or the
136:poisons
101:stimuli
89:arousal
1395:Stupor
1244:
1211:
1178:
1127:
1117:
1088:
1048:
1038:
984:
933:
908:et al.
869:
817:
770:
691:oxygen
611:toxins
605:(e.g.
591:sodium
579:uremia
494:lesion
404:Others
144:oxygen
1405:Sleep
1400:Sopor
1311:780.0
609:) or
603:drugs
583:Hypo-
551:shock
530:cough
506:above
247:sleep
197:Level
1385:Coma
1306:9-CM
1242:ISBN
1209:ISBN
1176:ISBN
1125:PMID
1115:ISBN
1086:ISBN
1046:PMID
1036:ISBN
982:ISBN
931:ISBN
867:ISBN
815:ISBN
768:ISBN
697:and
669:and
641:and
637:.
577:and
565:and
508:the
480:and
448:The
410:AVPU
408:The
125:Coma
1302:ICD
1296:R40
1287:ICD
863:140
764:901
621:or
585:or
360:or
320:In
146:or
138:or
107:or
97:LOC
83:An
57:An
1477::
1309::
1294::
1291:10
1146:^
1137:.
1123:.
1084:.
1082:41
1064:^
1044:.
996:^
960:^
915:^
890:^
881:.
865:.
835:^
791:^
782:.
766:.
740:^
701:.
693:,
657:.
599:pH
561:.
537:.
516:.
378:.
297:A
284:.
178:.
123:.
74:,
1346:e
1339:t
1332:v
1304:-
1289:-
1279:D
1256:.
1223:.
1190:.
1094:.
1058:.
990:.
945:.
829:.
443:u
439:d
435:c
431:a
426:u
422:p
418:v
414:a
95:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.