2930:
2946:
311:
3008:, who was the head of both the Licchavi republic and the Vajjika League; Bimbisāra had chosen Vehalla as his successor following Ajātasattu's falling out of his favour after the latter had been caught conspiring against him, and the Licchavikas had attempted to place Vehalla on the throne of Magadha after Ajātasattu's usurpation and had allowed Vehalla to use their capital Vesālī as base for his revolt. After the failure of this rebellion, Vehalla sought refuge at his grandfather's place in the Licchavika and Vajjika capital of Vesālī, following which Ajātasattu repeatedly attempted to negotiate with the Licchavikas-Vajjikas. After Ajātasattu's repeated negotiation attempts ended in failure, he declared war on the Vajjika League in 484 BCE.
72:
52:
3012:
destroy the
Vajjika League in retaliation, but also because, as an ambitious empire-builder whose mother Vāsavī was Licchavika princess of Vaidehī descent, he was interested in the territory of the former Mahā-Videha kingdom which by then was part of the Vajjika League. Ajātasattu's hostility towards the Vajjika League was also the result of the differing forms of political organisation between Magadha and the Vajjika League, with the former being monarchical and the latter being republican, not unlike the opposition of the
2727:, which the Licchavikas turned into their largest city as well as their capital and stronghold. Meanwhile, the new Videha republic existed in a limited territory centred around Mithilā and located to the north of Licchavi. Many members of the Vaideha aristocracy who had submitted to the Licchavikas joined them in moving to Vesālī, and therefore became members of the Licchavika ruling aristocratic Assembly.
3059:
recourse to diplomacy and intrigues over the span of a decade to finally defeat the
Vajjika League by 468 BCE and annex its territories, including Licchavi, Videha, and Nāya to the kingdom of Magadha, while the Mallakas also became part of Ajātasattu's Māgadhī empire but were allowed a limited degree of autonomy in terms of their internal administration, and stopped existing as a republican tribe when the
2576:
2745:). The Licchavikas themselves henceforth became the leading power within the territory of the former Mahā-Videha kingdom, with the Licchavika Assembly holding the sovereign and supreme rights over this territory. The Licchavikas founded the Vajjika League as a temporary league led by themselves, and named after the
2779:
league, although occasional quarrels did break out between these republics. Unlike the other confederate tribes such as the
Vaidehas and Nāyikas, who had no sovereign rights of their own because they were dependencies of Licchavi, the Mallakas maintained their own sovereign rights within the Vajjika League.
2805:, with this marriage having been contracted because of Siddhārtha's political importance due to the important geographical location close to Vesālī of the Nāya tribe he headed, as well as due to Siddhārtha's membership in the Vajjika Council. The son of Siddhārtha and Trisalā, that is Ceḍaga's nephew, was
2486:, who were organised into two separate republics, were also part of the Vajjika League, although they were not dependencies of the Licchavikas and therefore maintained their independence and sovereign rights within the confederation, hence why Jain sources considered the Licchavikas and the neighbouring
3063:
ruled
Magadha or shortly after. The Licchavikas nevertheless survived their defeat by Ajātasattu, and the structures of the older Licchavi republic subsisted within a degree local autonomy under Māgadhī rule, as attested by how the Licchavika Council instituted a festival in the memory of the decease
2778:
by Jain sources, and both
Mallaka republics joined the Licchavi-led Vajjika League to deal with danger they might have faced in common during periods of instability, and within which they held friendly relations with the Licchavikas, the Vaidehas, and the Nāyikas who were the other members of this
2766:, who were a sub-group of the Vaidehas who formed an independent tribe, were another constituent republic of the Licchavi-led Vajjika League, and hence they held autonomy in matters of internal policy while their war and foreign policies were handled by the Vajjika League. The Licchavikas and the
3058:
s of the
Licchavikas and Mallikas before the fight started. The Vaidehas, Nāyikas, and Mallakas therefore fought on the side of the League against Magadha. The military forces of the Vajjika League were initially too strong for Ajātasattu to be successful against them, and it required him having
3011:
Tensions between
Licchavi and Magadha were exacerbated by the handling of the joint Māgadhī-Licchavika border post of Koṭigāma on the Gaṅgā by the Licchavika-led Vajjika League who would regularly collect all valuables from Koṭigāma and leave none to the Māgadhīs. Therefore Ajātasattu decided to
2761:
residing in and around Mithilā, and governing in the name of the
Licchavika Assembly: the Videha republic was thus under significant influence of the Licchavi republic, and it joined the Vajjika League, within which it had limited autonomy concerning their domestic administration under the
2716:, from where they could best administer the territory of Videha. The consequence of the occupation of Videha by the republican Licchavikas was that the Licchavikas relatively peacefully overthrew the already weakened Vaideha monarchical system and replaced it by a republican system.
2571:
Since the
Licchavikas were the leading tribe of the confederacy, their capital city of Vesālī was the headquarter of the Vajjika League, and their army also functioned as the Vajjika army, although the other confederated tribes were also required to furnish troops to the league.
2915:
claimed shares of his relics while the
Vaidehas and the Nāyikas did not appear among the list of states claiming a share because they were dependencies of the Licchavikas without their own sovereignty, and therefore could not put forth their own claim while Licchavi could.
2567:
The Vajjika League was administered by the Vajjika Council, which consisted of eighteen members, of which nine were from the confederacy's leading Licchavika tribe while the other nine members were from the Videha, Nāya, Vajji, and Malla tribes.
3000:, who was Bimbisāra's son with another Licchavika princess, Vāsavī, after he had killed Bimbisāra and usurped the throne of Magadha. Eventually Licchavi supported a revolt against Ajātasattu by his younger step-brother and the governor of
2446:, meaning "united Vajjis," was given by the peoples of northern South Asia to the Vajjika League. The larger region of the former Mahā-Videha kingdom in which the Vajjika League was located was in turn named after the confederacy.
71:
2723:
to the south of the Ganges, the Licchavikas established their republic in the southern part of the former Videha kingdom and moved their political centre to the until then marginal location of
2661:
in Pāli, located somewhere close to the Licchavika and Vajjika capital of Vesālī to its northeast. Other Nāya settlements included a northeastern suburb of Vesālī named Kollāga, as well as a
2993:, and at some point the relations between Magadha and Licchavi permanently deteriorated as result of a grave offence committed by the Licchavikas towards the Māgadhī king Bimbisāra.
2749:
tribe proper, who had been the most powerful tribe in the region of Vesālī and were one of the constituent tribes of the league, within which they held their own sovereign rights.
51:
2832:, became a Jain nun, while the diplomatic marriages of his other daughters to various leaders, in turn, contributed to the spreading of Jainism across northern South Asia:
2293:
269:
244:
2509:
The once popular view among scholars that the Vajjika League was constituted of eight clans was based on a misreading of the 5th century CE Buddhist commentator
310:
2829:
2885:
3512:
2857:
2658:
2475:
3788:
2861:
2833:
2203:
2845:
2263:
2897:
2849:
3783:
2327:
2233:
2978:
Sakala's son Siṃha. There were nevertheless occasional tensions between Licchavi and Magadha, such as the competition at the Mallaka capital of
2243:
2929:
2945:
2837:
3793:
2873:
2436:
proper, who had once been the most powerful tribe in the region of the league's capital of Vesālī. According to Chinese pilgrim
3637:
3025:
3584:
3553:
3520:
3140:
3043:
As members of the Vajjika League, the Vaidehas, Nāyikas, and Mallakas were also threatened by Ajātasattu, and the Vajjika
2320:
2053:
3402:
3205:
530:
2788:("head of the republic") of the Licchavikas, that is the head of state of the Licchavikas and of their Council, was
519:
2619:
lived in the southwest region, immediately to the north of the Gaṅgā river and to the east of the Sadānirā river.
3803:
2313:
562:
320:
3386:
Bronkhorst, J. (2007). Greater Magadha, Studies in the culture of Early India, p. 6. Leiden, Boston, MA: Brill
2673:
The Vajjika League was located on the territory of the former Mahā-Videha kingdom founded by the tribe of the
3808:
3763:
2638:
including the lower hill ranges, as well as the northern part of what in present time is the Indian state of
2138:
2665:
named Dūīpalāsa that was nominally part of the Nāyikas' settlement at Kollāga but physically outside of it.
647:
2964:
The relations of the Licchavikas who led the Vajjika League with their southern neighbour, the kingdom of
3768:
3029:
2889:
2248:
2118:
3630:
2681:
cultural region. Around 800 BCE the Mahā-Videha ("greater Videha") kingdom was established between the
2559:
instead referred to the heads of the eight leading ruling families of Vaisali and not to eight tribes.
2298:
3326:
Political History of Ancient India: From the Accession of Parikshit to the Extinction of Gupta Dynasty
3778:
3103:
2596:
The area of the Vajjika League was bounded to the north, east, south, and west, respectively, by the
2268:
2228:
2218:
1693:
1287:
636:
508:
123:
3321:
2802:
2153:
1067:
907:
3004:, Vehalla, who was the son of Bimbisāra by another Licchavika wife of his, Cellanā, a daughter of
3758:
3098:
2951:
Map of the eastern Gangetic plain after Ajātasattu's conquest of the Vajjika League and of Moriya
2825:
2724:
2584:
2459:
2258:
2223:
2058:
1838:
1387:
939:
868:
99:
17:
3798:
3773:
3672:
3329:
2881:
2713:
2173:
2148:
2098:
2038:
1623:
1559:
1357:
573:
448:
3195:
2792:
or Ceḍaga, which also made him the head of the Council of the Vajjika League. Ceḍaga's sister
3623:
3130:
2208:
2178:
2043:
1998:
1828:
1467:
1457:
1427:
1159:
1139:
1000:
369:
331:
3682:
2654:
3033:
2288:
2143:
2128:
2073:
1714:
2893:
2650:
8:
3687:
3545:
3093:
2068:
1796:
1643:
1337:
1317:
729:
677:
2649:
were located in a small area around their capital, which was a minor town called either
2454:
The Vajjika League was a league of republican tribal states under the leadership of the
2731:
2709:
2413:
2273:
2133:
2113:
1758:
1367:
1277:
1047:
1037:
970:
919:
625:
541:
151:
57:
3531:
3580:
3549:
3516:
3398:
3344:
3201:
3136:
2959:
2417:
2283:
2253:
2163:
2158:
2103:
2048:
1878:
1768:
1747:
1703:
1673:
1377:
1307:
1297:
1267:
749:
711:
591:
343:
3384:
2841:
56:
The constituent tribes of the Vajjika League, Licchavi, Videha, and Nāya, among the
3576:
3394:
3390:
3356:
3126:
3088:
3021:
2771:
2705:
2616:
2499:
2467:
2455:
2278:
2213:
2183:
2168:
2123:
2108:
2093:
2063:
1958:
1653:
1437:
1347:
1226:
1216:
1169:
1098:
1077:
667:
657:
496:
431:
262:
2678:
2601:
1736:
1725:
1683:
1663:
1581:
1548:
1129:
1057:
1017:
929:
889:
851:
769:
3677:
2989:
In another case, the Licchavikas once invaded Māgadhī territory from across the
2704:, around the 7th or 6th century BCE, the Mahā-Videha kingdom was invaded by the
76:
Vajji (the Licchavika dependencies within the Vajjika League), Malla, and other
3717:
3037:
3013:
2983:
2869:
2701:
1946:
1898:
1592:
1570:
1538:
1516:
1477:
1407:
1397:
1257:
990:
800:
302:
3752:
3712:
3060:
2979:
2912:
2767:
2746:
2682:
2626:
lived along the foothills of the Himālaya mountains between the Sadānirā and
2609:
2580:
2491:
2487:
2483:
2479:
2433:
1868:
1808:
1633:
1027:
980:
960:
834:
817:
779:
759:
694:
478:
468:
458:
401:
89:
77:
3702:
3646:
3361:
3083:
1988:
1978:
1858:
1848:
1778:
1613:
1603:
1487:
1417:
1199:
1119:
739:
603:
551:
419:
3610:: Research Institute of Prakrit, Jainology & Ahimsa. pp. 388–464.
2762:
supervision of Licchavi, who fully controlled Vaideha foreign policy. The
2730:
Once settled around Vesālī, the Licchavikas formed a state organised as a
2406:
2364:
3599:
3572:
3068:
2997:
2996:
The hostilities between Licchavi and Magadha continued under the rule of
2813:
2739:
2686:
2510:
2008:
1968:
1928:
1327:
1189:
1179:
206:
3345:"Cultural Remnants of the Indigenous Peoples in the Buddhist Scriptures"
2972:
was the Vesālia princess Vāsavī, who was the daughter of the Licchavika
2627:
2421:
1918:
1818:
1528:
2911:
After the death of the Buddha, the Licchavikas, the Mallakas, and the
2432:
The Vajjika League was named after one of its constituent tribes, the
2969:
2901:
2753:
2694:
2597:
2495:
1888:
3727:
3722:
3692:
3071:
2877:
2817:
2806:
2793:
2742:
2437:
2238:
1149:
614:
391:
381:
183:
127:
113:
173:
3707:
3065:
3049:
3005:
2965:
2905:
2821:
2810:
2789:
2720:
1447:
352:
138:
131:
109:
3615:
2896:, who was the son of Trisalā and the elder brother of Mahāvīra;
2763:
2646:
2471:
3697:
3667:
3568:
3017:
2990:
2935:
Map of the eastern Gangetic plain before Ajātasattu's conquests
2775:
2690:
2674:
2662:
2623:
2605:
2503:
2463:
1247:
249:
2575:
3737:
3607:
3603:
3541:
3537:
3508:
2865:
2639:
2635:
2631:
291:
287:
3465:
3463:
2482:
tribe proper, who were dependencies of the Licchavikas. The
3662:
3504:
3501:
History of Jaina Monachism from Inscriptions and Literature
3304:
3302:
3300:
3298:
3285:
3283:
3250:
3248:
3246:
3244:
3242:
3240:
3238:
3236:
3234:
3221:
3219:
3217:
3001:
2853:
2677:, an Indo-Aryan tribe in the eastern Gangetic plain in the
2526:
2513:'s mention that the legal tribunals of Vesālī included the
2401:
2387:
2359:
2345:
1908:
3281:
3279:
3277:
3275:
3273:
3271:
3269:
3267:
3265:
3263:
3460:
3162:
3160:
3158:
3156:
3154:
3152:
3295:
3231:
3214:
2968:, were initially good, and the wife of the Māgadhī king
2816:. Ceṭaka became an adept of the teachings of his nephew
2525:), which was interpreted as meaning "eight tribes." The
3260:
3177:
3175:
3149:
3132:
Between the Empires: Society in India 300 BC to 400 AD
3044:
2973:
2797:
2783:
2754:
2732:
2712:
tribe who temporarily occupied the Vaideha capital of
158:
58:
3411:
2541:) however means "clan" while the word for "tribe" is
3438:
3436:
3434:
3432:
3430:
3428:
3426:
2824:, thus making the Licchavika and Vajjika capital of
2752:
The Videha republic was ruled by an Assembly of the
3513:
Deccan College Post-Graduate and Research Institute
3172:
3475:
3448:
3053:
2554:
2542:
2530:
2514:
2441:
2391:
2349:
3423:
3750:
3565:Republics in Ancient India, C. 1500 B.C.-500 B.C
2770:were considered to be the republican states of
3121:
3119:
2828:a bastion of Jainism, and his sixth daughter,
3631:
2700:Shortly before or during the lifetime of the
2321:
3320:
3116:
2462:. The other members of the league were the
3638:
3624:
3382:
3197:A History of Civilisation in Ancient India
2548:
2536:
2520:
2328:
2314:
70:
50:
3789:5th-century BC disestablishments in India
3360:
3135:. Oxford University Press. pp. 15–.
2587:, the capital city of Vajji and Licchavi.
3194:Dutt, Ramesh Chander (5 November 2013).
3125:
3020:to the democratic form of government in
2574:
2937:(Malla shown within the Vajjika League)
27:Republican confederacy in ancient India
14:
3784:6th-century BC establishments in India
3751:
3593:
3562:
3469:
3417:
3342:
3336:
3308:
3289:
3254:
3225:
3181:
3166:
2919:
2634:region and the south-eastern parts of
2416:league which existed during the later
3619:
2449:
3529:
3481:
3454:
3193:
3499:Deo, Shantaram Bhalchandra (1956).
3498:
3442:
24:
3794:Former republics in Indian history
2868:, with their son being the famous
25:
3820:
3645:
3594:Sikdar, Jogendra Chandra (1964).
2982:over acquiring the relics of the
3052:held war consultations with the
2944:
2928:
2888:was married to Ceṭaka's nephew,
2782:During the 6th century BCE, the
309:
267:
242:
3376:
2615:Within the Vajjika League, the
2562:
2498:to be the republican states of
3395:10.1163/ej.9789004157194.i-416
3314:
3187:
563:Ochre Coloured Pottery culture
13:
1:
3596:Studies in the Bhagawatīsūtra
3383:Bronkhorst, Johannes (2007).
3109:
1493:
1232:
1205:
1104:
1083:
1006:
945:
874:
857:
840:
823:
806:
785:
700:
683:
437:
45:c. 6th century BCE–c. 468 BCE
3530:Jain, Kailash Chand (1974).
2693:river in the south, and the
2630:rivers, in what are now the
648:Northern Black Polished Ware
7:
3533:Lord Mahāvīra and His Times
3077:
3054:
3045:
2974:
2798:
2784:
2755:
2733:
2719:Facing the rising power of
2591:
2555:
2543:
2531:
2515:
2458:centred around the city of
2442:
2407:
2392:
2365:
2350:
2244:Influence on Southeast Asia
159:
59:
10:
3825:
3491:
2957:
2796:was married to the Nāyika
2668:
626:Black and Red ware culture
209:of Magadha in 484–468 BCE
3653:
3343:Levman, Bryan G. (2014).
3104:History of Mithila Region
2553:), meaning that the term
2549:
2537:
2521:
637:Painted Grey Ware culture
509:Indus Valley Civilisation
283:
221:
217:
203:
193:
189:
179:
169:
157:
147:
137:
124:Historical Vedic religion
119:
105:
95:
85:
69:
49:
44:
34:
3322:Raychaudhuri, Hemchandra
2900:was married to the king
2860:was married to the king
2836:was married to the king
1288:Gurjara-Pratihara Empire
1268:Eastern Chalukya Kingdom
869:Maha-Megha-Vahana Empire
80:in the Post Vedic period
3656:(c. 600 BCE–c. 300 BCE)
3349:Buddhist Studies Review
3099:List of Indian monarchs
2689:river in the east, the
2685:river in the west, the
2427:
1388:Western Chalukya Empire
531:Mature Harappan culture
3563:Sharma, J. P. (1968).
3362:10.1558/bsrv.v30i2.145
3330:University of Calcutta
2588:
2579:Ananda Stupa, with an
2294:Science and technology
678:Three Crowned Kingdoms
520:Early Harappan culture
335:(2,500,000–250,000 BC)
3804:Former confederations
3654:Great Indian Kingdoms
2578:
2420:period in north-east
2382:, also called simply
2197:Specialised histories
1468:Kalachuris of Kalyani
1458:Kalachuris of Tripuri
1140:Western Ganga Kingdom
1068:Indo-Sassanid Kingdom
1018:Western Satrap Empire
1001:Indo-Parthian Kingdom
991:Indo-Scythian Kingdom
542:Late Harappan culture
303:History of South Asia
152:Aristocratic Republic
106:Common languages
3809:Tribal confederacies
3200:. India: Routledge.
3036:to the Athenian and
2876:was married to king
2848:was married to king
2474:(Skt. *Jñātrika) of
1715:Ahmadnagar Sultanate
1517:Late medieval period
1428:Eastern Ganga Empire
1160:Vishnukundina Empire
205:• Conquered by
3546:Motilal Banarsidass
3332:. pp. 118–126.
3094:History of Hinduism
2920:Conquest by Magadha
1797:Early modern period
1644:Vijayanagara Empire
1624:Chitradurga Kingdom
1318:Bhauma-Kara Kingdom
730:Shaishunaga dynasty
195:• Established
36:Vajjika Confederacy
3769:History of Mithila
3472:, p. 388-464.
3311:, p. 159-168.
3257:, p. 136-158.
3228:, p. 169-181.
3030:ancient Macedonian
2695:Himālaya mountains
2598:Himālaya mountains
2589:
2450:Constituent tribes
2412:), was an ancient
2274:Partition of India
2139:Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
2087:Regional histories
2032:National histories
1919:Travancore Kingdom
1889:Thondaiman Kingdom
1759:Golkonda Sultanate
1368:Somavamshi Kingdom
1338:Rashtrakuta Empire
1278:Rashidun Caliphate
1200:Kabul Shahi Empire
1048:Nagas of Padmavati
971:Indo-Greek Kingdom
911:(230 BC – AD 1206)
604:Vedic Civilisation
552:Vedic Civilisation
449:Ahar-Banas culture
199:c. 6th century BCE
3746:
3745:
3586:978-9-004-02015-3
3555:978-8-120-80805-8
3522:978-9-333-68377-7
3292:, p. 85-135.
3142:978-0-19-977507-1
3127:Olivelle, Patrick
2986:after his death.
2960:Magadha-Vajji war
2338:
2337:
2023:
2022:
2017:
2016:
1937:
1936:
1839:Thanjavur Kingdom
1787:
1786:
1748:Bijapur Sultanate
1704:Deccan sultanates
1582:Tughlaq Sultanate
1529:Ghaznavid Dynasty
1507:
1506:
1378:Chaulukya Kingdom
1308:Mallabhum kingdom
1298:Umayyad Caliphate
1038:Bharshiva Dynasty
934:(200 BC – AD 300)
924:(230 BC – AD 220)
920:Satavahana Empire
898:
897:
894:(247 BC – AD 224)
750:Macedonian Empire
724:(450 BC – AD 489)
712:Achaemenid Empire
582:
581:
487:
486:
410:
409:
360:
359:
344:Madrasian culture
297:
296:
279:
278:
275:
274:
255:
254:
16:(Redirected from
3816:
3779:History of Bihar
3640:
3633:
3626:
3617:
3616:
3611:
3590:
3559:
3526:
3485:
3479:
3473:
3467:
3458:
3452:
3446:
3440:
3421:
3415:
3409:
3408:
3380:
3374:
3373:
3371:
3369:
3364:
3340:
3334:
3333:
3318:
3312:
3306:
3293:
3287:
3258:
3252:
3229:
3223:
3212:
3211:
3191:
3185:
3179:
3170:
3169:, p. 81-84.
3164:
3147:
3146:
3129:(13 July 2006).
3123:
3089:History of India
3057:
3048:
2977:
2948:
2932:
2801:
2787:
2758:
2736:
2657:in Sanskrit) or
2558:
2552:
2551:
2546:
2540:
2539:
2534:
2524:
2523:
2518:
2445:
2410:
2395:
2368:
2353:
2330:
2323:
2316:
2279:Pakistan studies
2119:Himachal Pradesh
1959:Portuguese India
1955:
1954:
1951:
1909:Sikh Confederacy
1805:
1804:
1801:
1654:Bengal Sultanate
1593:Sayyid Sultanate
1571:Khalji Sultanate
1560:Mamluk Sultanate
1525:
1524:
1521:
1502:
1498:
1495:
1438:Kakatiya Kingdom
1348:Paramara Kingdom
1241:
1237:
1234:
1210:
1207:
1150:Kamarupa Kingdom
1113:
1109:
1106:
1099:Kalabhras Empire
1092:
1088:
1085:
1011:
1008:
995:(50 BC – AD 400)
975:(180 BC – AD 10)
954:
950:
947:
916:
915:
912:
883:
879:
876:
862:
859:
845:
842:
828:
825:
811:
808:
794:
790:
787:
705:
702:
688:
685:
668:Haryanka dynasty
658:Pradyota dynasty
600:
599:
596:
505:
504:
501:
442:
439:
432:Anarta tradition
428:
427:
424:
392:Mehrgarh culture
382:Bhirrana culture
378:
377:
374:
373:(10,800–3300 BC)
340:
339:
336:
326:
325:
313:
299:
298:
271:
270:
263:Haryanka dynasty
259:
258:
246:
245:
239:
238:
223:
222:
162:
74:
62:
54:
32:
31:
21:
3824:
3823:
3819:
3818:
3817:
3815:
3814:
3813:
3749:
3748:
3747:
3742:
3718:Maccha (Matsya)
3668:Asmaka (Assaka)
3655:
3649:
3644:
3614:
3587:
3556:
3523:
3494:
3489:
3488:
3480:
3476:
3468:
3461:
3453:
3449:
3441:
3424:
3416:
3412:
3405:
3381:
3377:
3367:
3365:
3341:
3337:
3319:
3315:
3307:
3296:
3288:
3261:
3253:
3232:
3224:
3215:
3208:
3192:
3188:
3180:
3173:
3165:
3150:
3143:
3124:
3117:
3112:
3080:
2962:
2956:
2955:
2954:
2953:
2952:
2949:
2940:
2939:
2938:
2936:
2933:
2922:
2679:Greater Magadha
2671:
2594:
2565:
2452:
2430:
2334:
2305:
2304:
2303:
2198:
2190:
2189:
2188:
2088:
2080:
2079:
2078:
2033:
2025:
2024:
2019:
2018:
1952:
1949:
1947:Colonial states
1939:
1938:
1829:Madurai Kingdom
1802:
1799:
1789:
1788:
1737:Bidar Sultanate
1726:Berar sultanate
1694:Ladakh Kingdom
1684:Gajapati Empire
1664:Garhwal Kingdom
1549:Delhi Sultanate
1522:
1519:
1509:
1508:
1500:
1496:
1478:Chutiya Kingdom
1448:Zamorin Kingdom
1239:
1235:
1227:Maukhari Empire
1217:Chalukya Empire
1208:
1170:Maitraka Empire
1111:
1107:
1090:
1086:
1078:Vakataka Empire
1058:Sasanian Empire
1009:
952:
948:
930:Kuninda Kingdom
913:
910:
908:Middle Kingdoms
900:
899:
890:Parthian Empire
881:
877:
860:
843:
826:
809:
792:
788:
703:
686:
597:
594:
584:
583:
502:
499:
489:
488:
440:
425:
422:
412:
411:
402:Edakkal culture
375:
372:
362:
361:
353:Soanian culture
337:
334:
323:
290:
268:
243:
210:
196:
130:
126:
112:
81:
65:
40:
37:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3822:
3812:
3811:
3806:
3801:
3796:
3791:
3786:
3781:
3776:
3771:
3766:
3761:
3759:Vajjika League
3744:
3743:
3741:
3740:
3735:
3730:
3725:
3720:
3715:
3710:
3705:
3700:
3695:
3690:
3685:
3680:
3675:
3670:
3665:
3659:
3657:
3651:
3650:
3643:
3642:
3635:
3628:
3620:
3613:
3612:
3591:
3585:
3560:
3554:
3548:. p. 66.
3527:
3521:
3495:
3493:
3490:
3487:
3486:
3474:
3459:
3447:
3422:
3420:, p. 149.
3410:
3403:
3375:
3355:(2): 145–180.
3335:
3313:
3294:
3259:
3230:
3213:
3206:
3186:
3171:
3148:
3141:
3114:
3113:
3111:
3108:
3107:
3106:
3101:
3096:
3091:
3086:
3079:
3076:
3061:Maurya dynasty
2950:
2943:
2942:
2941:
2934:
2927:
2926:
2925:
2924:
2923:
2921:
2918:
2842:Sindhu-Sauvīra
2697:in the north.
2670:
2667:
2593:
2590:
2564:
2561:
2451:
2448:
2429:
2426:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2332:
2325:
2318:
2310:
2307:
2306:
2302:
2301:
2296:
2291:
2286:
2281:
2276:
2271:
2266:
2261:
2256:
2251:
2246:
2241:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2200:
2199:
2196:
2195:
2192:
2191:
2187:
2186:
2181:
2176:
2171:
2166:
2161:
2156:
2151:
2146:
2141:
2136:
2131:
2126:
2121:
2116:
2111:
2106:
2101:
2096:
2090:
2089:
2086:
2085:
2082:
2081:
2077:
2076:
2071:
2066:
2061:
2056:
2051:
2046:
2041:
2035:
2034:
2031:
2030:
2027:
2026:
2021:
2020:
2015:
2014:
2011:
2005:
2004:
2001:
1995:
1994:
1991:
1985:
1984:
1981:
1975:
1974:
1971:
1965:
1964:
1961:
1953:
1945:
1944:
1941:
1940:
1935:
1934:
1931:
1925:
1924:
1921:
1915:
1914:
1911:
1905:
1904:
1901:
1899:Maratha Empire
1895:
1894:
1891:
1885:
1884:
1881:
1879:Sikkim Kingdom
1875:
1874:
1871:
1869:Marava Kingdom
1865:
1864:
1861:
1855:
1854:
1851:
1845:
1844:
1841:
1835:
1834:
1831:
1825:
1824:
1821:
1815:
1814:
1811:
1803:
1795:
1794:
1791:
1790:
1785:
1784:
1781:
1775:
1774:
1771:
1769:Keladi Kingdom
1765:
1764:
1761:
1754:
1753:
1750:
1743:
1742:
1739:
1732:
1731:
1728:
1721:
1720:
1717:
1710:
1709:
1706:
1700:
1699:
1696:
1690:
1689:
1686:
1680:
1679:
1676:
1674:Mysore Kingdom
1670:
1669:
1666:
1660:
1659:
1656:
1650:
1649:
1646:
1640:
1639:
1636:
1630:
1629:
1626:
1620:
1619:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1606:
1604:Lodi Sultanate
1599:
1598:
1595:
1588:
1587:
1584:
1577:
1576:
1573:
1566:
1565:
1562:
1555:
1554:
1551:
1545:
1544:
1541:
1539:Ghurid Dynasty
1535:
1534:
1531:
1523:
1515:
1514:
1511:
1510:
1505:
1504:
1490:
1484:
1483:
1480:
1474:
1473:
1470:
1464:
1463:
1460:
1454:
1453:
1450:
1444:
1443:
1440:
1434:
1433:
1430:
1424:
1423:
1420:
1414:
1413:
1410:
1408:Hoysala Empire
1404:
1403:
1400:
1398:Lohara Kingdom
1394:
1393:
1390:
1384:
1383:
1380:
1374:
1373:
1370:
1364:
1363:
1360:
1354:
1353:
1350:
1344:
1343:
1340:
1334:
1333:
1330:
1324:
1323:
1320:
1314:
1313:
1310:
1304:
1303:
1300:
1294:
1293:
1290:
1284:
1283:
1280:
1274:
1273:
1270:
1264:
1263:
1260:
1258:Tibetan Empire
1254:
1253:
1250:
1244:
1243:
1229:
1223:
1222:
1219:
1213:
1212:
1202:
1196:
1195:
1192:
1186:
1185:
1182:
1176:
1175:
1172:
1166:
1165:
1162:
1156:
1155:
1152:
1146:
1145:
1142:
1136:
1135:
1132:
1130:Kadamba Empire
1126:
1125:
1122:
1116:
1115:
1101:
1095:
1094:
1080:
1074:
1073:
1070:
1064:
1063:
1060:
1054:
1053:
1050:
1044:
1043:
1040:
1034:
1033:
1030:
1024:
1023:
1020:
1014:
1013:
1003:
997:
996:
993:
987:
986:
983:
977:
976:
973:
967:
966:
963:
957:
956:
942:
936:
935:
932:
926:
925:
922:
914:
906:
905:
902:
901:
896:
895:
892:
886:
885:
871:
865:
864:
854:
852:Pallava Empire
848:
847:
837:
831:
830:
820:
814:
813:
803:
797:
796:
782:
776:
775:
772:
770:Seleucid India
766:
765:
762:
756:
755:
752:
746:
745:
742:
736:
735:
732:
726:
725:
722:
718:
717:
714:
708:
707:
697:
695:Maha Janapadas
691:
690:
680:
674:
673:
670:
664:
663:
660:
654:
653:
650:
643:
642:
639:
632:
631:
630:(1300–1000 BC)
628:
621:
620:
617:
610:
609:
606:
598:
590:
589:
586:
585:
580:
579:
576:
569:
568:
567:(2000–1600 BC)
565:
558:
557:
554:
548:
547:
546:(1900–1300 BC)
544:
537:
536:
535:(2600–1900 BC)
533:
526:
525:
524:(3300–2600 BC)
522:
515:
514:
513:(3300–1300 BC)
511:
503:
500:(3300–1300 BC)
495:
494:
491:
490:
485:
484:
481:
475:
474:
473:(1600–1300 BC)
471:
465:
464:
461:
455:
454:
453:(3000–1500 BC)
451:
445:
444:
434:
426:
423:(3500–1500 BC)
418:
417:
414:
413:
408:
407:
406:(5000–3000 BC)
404:
398:
397:
396:(7000–3300 BC)
394:
388:
387:
386:(7570–6200 BC)
384:
376:
368:
367:
364:
363:
358:
357:
355:
349:
348:
346:
338:
330:
329:
324:
319:
318:
315:
314:
306:
305:
295:
294:
285:
281:
280:
277:
276:
273:
272:
265:
256:
253:
252:
247:
235:
234:
229:
219:
218:
215:
214:
211:
204:
201:
200:
197:
194:
191:
190:
187:
186:
181:
180:Historical era
177:
176:
171:
167:
166:
163:
155:
154:
149:
145:
144:
141:
135:
134:
121:
117:
116:
107:
103:
102:
97:
93:
92:
87:
83:
82:
75:
67:
66:
55:
47:
46:
42:
41:
38:
35:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3821:
3810:
3807:
3805:
3802:
3800:
3799:Ancient Nepal
3797:
3795:
3792:
3790:
3787:
3785:
3782:
3780:
3777:
3775:
3774:Mahajanapadas
3772:
3770:
3767:
3765:
3762:
3760:
3757:
3756:
3754:
3739:
3738:Vatsa (Vamsa)
3736:
3734:
3731:
3729:
3726:
3724:
3721:
3719:
3716:
3714:
3711:
3709:
3706:
3704:
3701:
3699:
3696:
3694:
3691:
3689:
3686:
3684:
3681:
3679:
3676:
3674:
3671:
3669:
3666:
3664:
3661:
3660:
3658:
3652:
3648:
3647:Mahajanapadas
3641:
3636:
3634:
3629:
3627:
3622:
3621:
3618:
3609:
3605:
3601:
3597:
3592:
3588:
3582:
3578:
3574:
3570:
3566:
3561:
3557:
3551:
3547:
3543:
3539:
3535:
3534:
3528:
3524:
3518:
3514:
3510:
3506:
3502:
3497:
3496:
3484:, p. 66.
3483:
3478:
3471:
3466:
3464:
3457:, p. 67.
3456:
3451:
3445:, p. 71.
3444:
3439:
3437:
3435:
3433:
3431:
3429:
3427:
3419:
3414:
3406:
3404:9789047419655
3400:
3396:
3392:
3388:
3387:
3379:
3363:
3358:
3354:
3350:
3346:
3339:
3331:
3327:
3323:
3317:
3310:
3305:
3303:
3301:
3299:
3291:
3286:
3284:
3282:
3280:
3278:
3276:
3274:
3272:
3270:
3268:
3266:
3264:
3256:
3251:
3249:
3247:
3245:
3243:
3241:
3239:
3237:
3235:
3227:
3222:
3220:
3218:
3209:
3207:9781136381898
3203:
3199:
3198:
3190:
3184:, p. 83.
3183:
3178:
3176:
3168:
3163:
3161:
3159:
3157:
3155:
3153:
3144:
3138:
3134:
3133:
3128:
3122:
3120:
3115:
3105:
3102:
3100:
3097:
3095:
3092:
3090:
3087:
3085:
3082:
3081:
3075:
3073:
3070:
3067:
3062:
3056:
3051:
3047:
3041:
3039:
3035:
3031:
3027:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3014:ancient Greek
3009:
3007:
3003:
2999:
2994:
2992:
2987:
2985:
2981:
2976:
2971:
2967:
2961:
2947:
2931:
2917:
2914:
2909:
2907:
2903:
2899:
2895:
2891:
2890:Nandivardhana
2887:
2883:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2867:
2863:
2859:
2855:
2851:
2847:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2823:
2819:
2815:
2812:
2808:
2804:
2800:
2795:
2791:
2786:
2780:
2777:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2760:
2757:
2750:
2748:
2744:
2741:
2737:
2735:
2728:
2726:
2722:
2717:
2715:
2711:
2707:
2703:
2698:
2696:
2692:
2688:
2684:
2680:
2676:
2666:
2664:
2660:
2656:
2652:
2648:
2643:
2641:
2637:
2633:
2629:
2625:
2620:
2618:
2613:
2611:
2607:
2603:
2599:
2586:
2582:
2581:Asokan pillar
2577:
2573:
2569:
2560:
2557:
2545:
2533:
2528:
2517:
2512:
2507:
2505:
2501:
2497:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2481:
2477:
2473:
2469:
2465:
2461:
2457:
2447:
2444:
2439:
2435:
2425:
2423:
2419:
2415:
2411:
2409:
2403:
2399:
2394:
2389:
2385:
2381:
2377:
2373:
2369:
2367:
2361:
2357:
2352:
2347:
2343:
2331:
2326:
2324:
2319:
2317:
2312:
2311:
2309:
2308:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2290:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2277:
2275:
2272:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2201:
2194:
2193:
2185:
2182:
2180:
2177:
2175:
2172:
2170:
2167:
2165:
2162:
2160:
2157:
2155:
2154:Uttar Pradesh
2152:
2150:
2147:
2145:
2142:
2140:
2137:
2135:
2132:
2130:
2127:
2125:
2122:
2120:
2117:
2115:
2112:
2110:
2107:
2105:
2102:
2100:
2097:
2095:
2092:
2091:
2084:
2083:
2075:
2072:
2070:
2067:
2065:
2062:
2060:
2057:
2055:
2052:
2050:
2047:
2045:
2042:
2040:
2037:
2036:
2029:
2028:
2012:
2010:
2007:
2006:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1996:
1992:
1990:
1987:
1986:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1976:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1966:
1962:
1960:
1957:
1956:
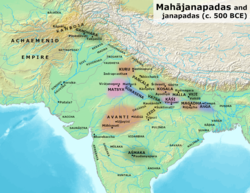
1948:
1943:
1942:
1932:
1930:
1927:
1926:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1916:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1906:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1896:
1892:
1890:
1887:
1886:
1882:
1880:
1877:
1876:
1872:
1870:
1867:
1866:
1862:
1860:
1857:
1856:
1852:
1850:
1847:
1846:
1842:
1840:
1837:
1836:
1832:
1830:
1827:
1826:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1812:
1810:
1809:Mughal Empire
1807:
1806:
1798:
1793:
1792:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1776:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1766:
1762:
1760:
1756:
1755:
1751:
1749:
1745:
1744:
1740:
1738:
1734:
1733:
1729:
1727:
1723:
1722:
1718:
1716:
1712:
1711:
1707:
1705:
1702:
1701:
1697:
1695:
1692:
1691:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1681:
1677:
1675:
1672:
1671:
1667:
1665:
1662:
1661:
1657:
1655:
1652:
1651:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1641:
1637:
1635:
1634:Reddy Kingdom
1632:
1631:
1627:
1625:
1622:
1621:
1617:
1615:
1612:
1611:
1607:
1605:
1601:
1600:
1596:
1594:
1590:
1589:
1585:
1583:
1579:
1578:
1574:
1572:
1568:
1567:
1563:
1561:
1557:
1556:
1552:
1550:
1547:
1546:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1536:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1526:
1518:
1513:
1512:
1491:
1489:
1486:
1485:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1475:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1465:
1461:
1459:
1456:
1455:
1451:
1449:
1446:
1445:
1441:
1439:
1436:
1435:
1431:
1429:
1426:
1425:
1421:
1419:
1416:
1415:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1405:
1401:
1399:
1396:
1395:
1391:
1389:
1386:
1385:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1371:
1369:
1366:
1365:
1361:
1359:
1358:Yadava Empire
1356:
1355:
1351:
1349:
1346:
1345:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1335:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1325:
1321:
1319:
1316:
1315:
1311:
1309:
1306:
1305:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1295:
1291:
1289:
1286:
1285:
1281:
1279:
1276:
1275:
1271:
1269:
1266:
1265:
1261:
1259:
1256:
1255:
1251:
1249:
1248:Harsha Empire
1246:
1245:
1230:
1228:
1225:
1224:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1214:
1203:
1201:
1198:
1197:
1193:
1191:
1188:
1187:
1183:
1181:
1178:
1177:
1173:
1171:
1168:
1167:
1163:
1161:
1158:
1157:
1153:
1151:
1148:
1147:
1143:
1141:
1138:
1137:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1117:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1096:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1075:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1055:
1051:
1049:
1046:
1045:
1041:
1039:
1036:
1035:
1031:
1029:
1028:Kushan Empire
1026:
1025:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1015:
1004:
1002:
999:
998:
994:
992:
989:
988:
984:
982:
979:
978:
974:
972:
969:
968:
964:
962:
961:Shunga Empire
959:
958:
943:
941:
940:Mitra Dynasty
938:
937:
933:
931:
928:
927:
923:
921:
918:
917:
909:
904:
903:
893:
891:
888:
887:
882: AD 500
878: 250 BC
872:
870:
867:
866:
861: 250 AD
855:
853:
850:
849:
844: 300 BC
838:
836:
833:
832:
827: 300 BC
821:
819:
818:Chera Kingdom
816:
815:
810: 300 BC
804:
802:
801:Pandya Empire
799:
798:
793: 300 AD
789: 300 BC
783:
781:
780:Sangam period
778:
777:
773:
771:
768:
767:
763:
761:
760:Maurya Empire
758:
757:
753:
751:
748:
747:
743:
741:
738:
737:
733:
731:
728:
727:
723:
720:
719:
715:
713:
710:
709:
698:
696:
693:
692:
687: 600 BC
681:
679:
676:
675:
671:
669:
666:
665:
661:
659:
656:
655:
651:
649:
645:
644:
641:(1200–600 BC)
640:
638:
634:
633:
629:
627:
623:
622:
619:(1500–600 BC)
618:
616:
612:
611:
608:(1500–500 BC)
607:
605:
602:
601:
595:(1500–200 BC)
593:
588:
587:
578:(1600–500 BC)
577:
575:
571:
570:
566:
564:
560:
559:
556:(2000–500 BC)
555:
553:
550:
549:
545:
543:
539:
538:
534:
532:
528:
527:
523:
521:
517:
516:
512:
510:
507:
506:
498:
493:
492:
483:(1400–700 BC)
482:
480:
479:Jorwe culture
477:
476:
472:
470:
469:Malwa culture
467:
466:
463:(1600–750 BC)
462:
460:
459:Pandu culture
457:
456:
452:
450:
447:
446:
435:
433:
430:
429:
421:
416:
415:
405:
403:
400:
399:
395:
393:
390:
389:
385:
383:
380:
379:
371:
366:
365:
356:
354:
351:
350:
347:
345:
342:
341:
333:
328:
327:
322:
317:
316:
312:
308:
307:
304:
301:
300:
293:
289:
286:
284:Today part of
282:
266:
264:
261:
260:
257:
251:
248:
241:
240:
237:
236:
233:
230:
228:
225:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
202:
198:
192:
188:
185:
182:
178:
175:
172:
168:
164:
161:
156:
153:
150:
146:
142:
140:
136:
133:
129:
125:
122:
118:
115:
111:
108:
104:
101:
98:
94:
91:
90:Confederation
88:
84:
79:
78:Mahajanapadas
73:
68:
64:
61:
53:
48:
43:
33:
30:
19:
3764:Gaṇa saṅghas
3732:
3595:
3564:
3532:
3500:
3477:
3450:
3413:
3385:
3378:
3366:. Retrieved
3352:
3348:
3338:
3325:
3316:
3196:
3189:
3131:
3084:Mahajanapada
3042:
3028:between the
3010:
2995:
2988:
2963:
2910:
2820:and adopted
2781:
2751:
2740:aristocratic
2729:
2718:
2699:
2672:
2644:
2621:
2614:
2595:
2570:
2566:
2563:Organisation
2508:
2470:region, the
2453:
2431:
2405:
2397:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2371:
2363:
2355:
2341:
2339:
2219:Demographics
2209:Architecture
1989:French India
1979:Danish India
1859:Bengal Subah
1849:Bhoi dynasty
1779:Koch Kingdom
1614:Ahom Kingdom
1488:Deva Kingdom
1180:Huna Kingdom
1120:Gupta Empire
1022:(AD 35–405 )
981:Kanva Empire
953: 50 BC
835:Chola Empire
774:(312–303 BC)
764:(321–184 BC)
754:(330–323 BC)
744:(380–321 BC)
740:Nanda Empire
734:(424–345 BC)
716:(550–330 BC)
672:(684–424 BC)
662:(799–684 BC)
652:(700–200 BC)
574:Swat culture
420:Chalcolithic
332:Palaeolithic
232:Succeeded by
231:
226:
29:
3600:Muzaffarpur
3577:E. J. Brill
3573:Netherlands
3470:Sikdar 1964
3418:Sharma 1968
3309:Sharma 1968
3290:Sharma 1968
3255:Sharma 1968
3226:Sharma 1968
3182:Sharma 1968
3167:Sharma 1968
3069:Tīrthaṅkara
3046:Gaṇa Mukhya
3040:republics.
3026:hostilities
3016:kingdom of
2850:Dadhivāhana
2814:Tīrthaṅkara
2809:, the 24th
2799:Gaṇa Mukhya
2785:Gaṇa Mukhya
2706:Licchavikas
2617:Licchavikas
2556:aṭṭhakulika
2516:aṭṭhakulika
2511:Buddhaghosa
2456:Licchavikas
2440:, the name
2376:Confederacy
2204:Agriculture
2174:South India
2149:Maharashtra
2099:Balochistan
2039:Afghanistan
2013:(1858–1947)
2009:British Raj
2003:(1757–1858)
1999:Company Raj
1993:(1759–1954)
1983:(1620–1869)
1973:(1605–1825)
1969:Dutch India
1963:(1510–1961)
1950:(1510–1961)
1933:(1799–1849)
1929:Sikh Empire
1923:(1729–1947)
1913:(1707–1799)
1903:(1674–1818)
1893:(1650–1948)
1883:(1642–1975)
1873:(1600–1750)
1863:(1576–1757)
1853:(1541–1804)
1843:(1532–1673)
1833:(1529–1736)
1823:(1540–1556)
1813:(1526–1858)
1800:(1526–1858)
1783:(1515–1947)
1773:(1499–1763)
1763:(1518–1687)
1752:(1492–1686)
1741:(1492–1619)
1730:(1490–1574)
1719:(1490–1636)
1708:(1490–1596)
1698:(1470–1842)
1688:(1434–1541)
1678:(1399–1947)
1668:(1358–1803)
1658:(1352–1576)
1648:(1336–1646)
1638:(1325–1448)
1628:(1300–1779)
1618:(1228–1826)
1608:(1451–1526)
1597:(1414–1451)
1586:(1320–1414)
1575:(1290–1320)
1564:(1206–1290)
1553:(1206–1526)
1543:(1170–1206)
1520:(1206–1526)
1501: 1300
1497: 1200
1482:(1187–1673)
1472:(1156–1184)
1452:(1102–1766)
1442:(1083–1323)
1432:(1078–1434)
1422:(1070–1230)
1418:Sena Empire
1412:(1040–1347)
1402:(1003–1320)
1328:Pala Empire
1190:Rai Kingdom
1032:(AD 60–240)
965:(185–73 BC)
721:Ror Dynasty
441: 3950
227:Preceded by
170:Legislature
160:Gaṇa Mukhya
3753:Categories
3110:References
3024:, and the
2998:Ajātasattu
2958:See also:
2834:Prabhāvatī
2803:Siddhārtha
2734:gaṇasaṅgha
2710:Indo-Aryan
2655:Kuṇḍagrāma
2600:, and the
2478:, and the
2422:South Asia
2414:Indo-Aryan
2284:Philosophy
2264:Metallurgy
2254:Literature
2179:Tamil Nadu
2044:Bangladesh
1819:Sur Empire
1533:(977–1186)
1499: – c.
1462:(675–1210)
1392:(973–1189)
1382:(942–1244)
1372:(882–1110)
1362:(850–1334)
1352:(800–1327)
1332:(750–1174)
1312:(694–1947)
1292:(650–1036)
1272:(624–1075)
1240: 700
1238: – c.
1236: 550
1209: 500
1154:(350–1100)
1144:(350–1000)
1112: 600
1110: – c.
1108: 250
1091: 500
1089: – c.
1087: 250
1010: 130
985:(75–26 BC)
951: – c.
949: 150
880: – c.
846:– AD 1279)
829:– AD 1102)
812:– AD 1345)
791: – c.
704: 600
689:– AD 1600)
497:Bronze Age
213:c. 468 BCE
207:Ajātasattu
148:Government
139:Demonym(s)
60:Gaṇasaṅgha
3482:Jain 1974
3455:Jain 1974
3034:Philip II
2970:Bimbisāra
2902:Bimbisāra
2894:Kuṇḍagāma
2846:Padmāvatī
2830:Sujyeṣṭhā
2659:Kuṇḍapura
2651:Kuṇḍagāma
2522:अट्ठकुलिक
2476:Kuṇḍapura
2234:Education
2224:Dynasties
2144:Rajasthan
2129:Karnataka
2074:Sri Lanka
1342:(753–982)
1322:(736–916)
1302:(661–750)
1282:(632–661)
1262:(618–841)
1252:(606–647)
1221:(543–753)
1194:(489–632)
1184:(475–576)
1174:(475–767)
1164:(420–624)
1134:(345–525)
1124:(280–550)
1072:(230–360)
1062:(224–651)
1052:(210–340)
1042:(170–350)
1005:(AD 21 –
863:– AD 800)
615:Janapadas
443:–1900 BC)
370:Neolithic
120:Religion
3728:Surasena
3723:Panchala
3683:Gandhara
3443:Deo 1956
3324:(1953).
3078:See also
3072:Mahāvīra
2980:Kusinārā
2878:Pradyota
2862:Śatānīka
2858:Mṛgāvatī
2818:Mahāvīra
2807:Mahāvīra
2768:Mallakas
2756:kṣatriya
2743:republic
2683:Sadānirā
2675:Vaidehas
2624:Vaidehas
2612:rivers.
2610:Sadānirā
2602:Mahānadī
2592:Location
2492:Kusinārā
2488:Mallakas
2484:Mallakas
2464:Vaidehas
2443:Saṃvajji
2438:Xuanzang
2434:Vajjikas
2418:Iron Age
2299:Timeline
2289:Religion
2269:Military
2259:Maritime
2249:Language
2239:Indology
2069:Pakistan
2059:Maldives
1757: –
1746: –
1735: –
1724: –
1713: –
1602: –
1591: –
1580: –
1569: –
1558: –
706:–300 BC)
646: –
635: –
624: –
613: –
592:Iron Age
572: –
561: –
540: –
529: –
518: –
184:Iron Age
128:Buddhism
114:Sanskrit
3708:Magadha
3693:Kamboja
3492:Sources
3064:of the
2966:Magadha
2906:Magadha
2898:Cellaṇā
2886:Jyeṣṭhā
2870:Udayana
2838:Udāyana
2822:Jainism
2794:Trisalā
2764:Nāyikas
2721:Magadha
2714:Mithilā
2687:Kauśikī
2669:History
2647:Nāyikas
2628:Kauśikī
2472:Nāyikas
2468:Mithila
2466:in the
2356:Vrijika
2351:Vajjika
2342:Vajjika
2229:Economy
2214:Coinage
2134:Kashmir
2114:Gujarat
1211:– 1026)
321:Outline
143:Vajjika
132:Jainism
110:Prakrit
96:Capital
18:Vajjika
3698:Kosala
3673:Avanti
3583:
3569:Leiden
3552:
3519:
3401:
3368:4 June
3204:
3139:
3050:Ceḍaga
3038:Theban
3022:Athens
3018:Sparta
3006:Ceḍaga
2984:Buddha
2975:Nāyaka
2913:Sakyas
2882:Avanti
2826:Vesālī
2790:Ceṭaka
2776:Kosala
2725:Vesālī
2702:Buddha
2691:Ganges
2663:cetiya
2608:, and
2585:Vesālī
2504:Kosala
2460:Vesālī
2380:Sangha
2372:League
2366:Vṛjika
2164:Odisha
2159:Punjab
2104:Bengal
2049:Bhutan
250:Videha
165:
100:Vesālī
86:Status
3733:Vajji
3713:Malla
3688:Kashi
3678:Chedi
3608:India
3604:Bihar
3542:India
3538:Delhi
3509:India
3032:king
2991:Gaṅgā
2866:Vatsa
2747:Vajji
2708:, an
2640:Bihār
2636:Nepal
2632:Tarāī
2606:Gaṅgā
2583:, at
2529:term
2480:Vajji
2398:Vriji
2396:) or
2393:Vajji
2384:Vajji
2378:, or
2354:) or
2184:Tibet
2169:Sindh
2124:Kabul
2109:Bihar
2094:Assam
2064:Nepal
2054:India
292:Nepal
288:India
174:Sabhā
3703:Kuru
3663:Anga
3581:ISBN
3550:ISBN
3517:ISBN
3505:Pune
3399:ISBN
3370:2022
3202:ISBN
3137:ISBN
3066:Jain
3055:rājā
3002:Aṅga
2874:Śivā
2854:Aṅga
2811:Jain
2772:Kāsī
2738:(an
2645:The
2622:The
2544:jana
2532:kula
2527:Pāli
2500:Kāsī
2496:Pāvā
2494:and
2428:Name
2408:Vṛji
2402:IAST
2388:Pāli
2360:IAST
2346:Pāli
2340:The
39:Vṛji
3391:doi
3357:doi
2904:of
2892:of
2884:;
2880:of
2864:of
2852:of
2840:of
2538:कुल
2490:of
3755::
3606:,
3602:,
3598:.
3579:.
3575::
3571:,
3567:.
3544::
3540:,
3536:.
3515:.
3511::
3507:,
3503:.
3462:^
3425:^
3397:.
3389:.
3353:30
3351:.
3347:.
3328:.
3297:^
3262:^
3233:^
3216:^
3174:^
3151:^
3118:^
3074:.
2908:.
2872:;
2856:;
2844:;
2642:.
2604:,
2550:जन
2506:.
2424:.
2404::
2390::
2374:,
2370:)
2362::
2348::
1494:c.
1233:c.
1206:c.
1105:c.
1084:c.
1007:c.
946:c.
875:c.
858:c.
841:c.
824:c.
807:c.
786:c.
701:c.
684:c.
438:c.
3639:e
3632:t
3625:v
3589:.
3558:.
3525:.
3407:.
3393::
3372:.
3359::
3210:.
3145:.
2774:-
2759:s
2653:(
2547:(
2535:(
2519:(
2502:-
2400:(
2386:(
2358:(
2344:(
2329:e
2322:t
2315:v
1503:)
1492:(
1242:)
1231:(
1204:(
1114:)
1103:(
1093:)
1082:(
1012:)
955:)
944:(
884:)
873:(
856:(
839:(
822:(
805:(
795:)
784:(
699:(
682:(
436:(
63:s
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.