614:(GRAS) status to ChromaDex for its preparation of nicotinamide riboside chloride (NRC, Niagen™). It was designated a new dietary ingredient (NDI) for use in dietary supplements by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2015 and 2017. It was listed in Health Canada's Licensed Natural Health Products Database (LNHPD) in 2018. The European Union has granted NRC a "New dietary ingredient" designation as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283, as of 2019. It was authorized for use in food supplements by the EU in 2020. The EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA) considered it as safe as pure nicotinamide for use in food for special medical purposes (FSMP) and total diet replacement for weight control (TDRWC) in adults as of 2021 but noted that further investigation would be required to establish safety for some other types of use. The Australian government has given nicotinamide riboside chloride a positive listing under the compositional guidelines of its Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
579:
246:
24:
33:
538:
which can be found in both cow and human milk. Once internalized into a cell, NR is rapidly phosphorylated by the activity of nicotinamide riboside kinase enzymes (NRK1 and NRK2) to form nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), bypassing the previously known biosynthetic routes to NAD+ production. NMN is
586:
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is utilized through an additional pathway involving phosphorylation by the nicotinamide riboside kinase enzymes (NRK1 and NRK2). In yeasts, NR has also been shown to be degraded by the nucleosidases Pnp1, Urh1 and Meu1, before being converted to NAD⁺ via the Preiss-Handler
559:
synthesis from tryptophan and from NA salvage are ‘deamidated’ pathways, which share a rate-limiting amidation enzyme NADsynthase1 (NADSYN). Disruptions or imbalances in NAD+ metabolism have been observed in many disease conditions, and the possibility of restoring NAD+ levels by administering NAD+
574:
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is now known to be an NAD+ precursor, involved in the biosynthetic pathways that convert B3 vitamins into NAD+. NAD+ is primarily synthesized in mammals de novo from tryptophan, through the Priess-Handler pathway from nicotinic acid (NA) or via a salvage pathway from
554:
Metabolic studies indicate that NAD+, once considered a stable molecule, is continuously turned over and used, requiring tight regulation to maintain metabolic homeostasis. NR utilization in mammals may involve both exogenous dietary sources and endogenous salvage processes that recycle
503:
in 1937. NAD+ (then called coenzyme I) was shown to be extremely low in cases of pellagra, and NA and NAM were identified as molecular precursors in rebuilding NAD+ levels. Pellagra is now understood as a severe, chronic depletion of NAD+, which can be treated through diet.
507:
Subsequent studies of NAD+ metabolism have identified regulatory pathways used by cells and tissues to maintain NAD+ availability. NAD+ and its precursors nicotinic acid (NA) and nicotinamide (NAM) have been shown to be vital cofactors in cellular
550:
gene and appears to be more highly expressed in cases of metabolic stress or cellular damage. Since different types of tissues display differing concentrations of NR and NRKs, it is likely that NR utilization will vary in different tissues.
404:
While the molecular weight of nicotinamide riboside is 255.25 g/mol, that of its chloride salt is 290.70 g/mol. As such, 100 mg of nicotinamide riboside chloride provides 88 mg of nicotinamide riboside.
1506:
555:
intermediates. NR metabolism and the interactions of different NAD+ pathways continue to be studied. The NAM and NR pathways involve an amide group and are referred to as ‘amidated’ pathways. The pathways for
127:
520:
pathway from Trp and two pathways using the NAD+ precursors NA and NAM: a three-step NA-based pathway known as the Preiss-Handler pathway; and an NAM-based pathway involving the enzyme
853:
1657:
1575:
546:
gene. It is found in most tissues but predominantly in the liver and kidney. The NRK2 protein may be related to muscle tissue including cardiac muscle. It is encoded by the
1502:
1543:
1401:"Simultaneous quantitation of nicotinamide riboside, nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in milk by a novel enzyme-coupled assay"
673:
Bogan, KL; Brenner, C (2008). "Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside: a molecular evaluation of NAD+ precursor vitamins in human nutrition".
1316:
932:
World Health
Organization; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2011). "Chapter 9 Identification and Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae".
708:
598:
licensed patents in July 2012, and began to develop a process to bring NR to market as TruNiagen. ChromaDex has been in a patent dispute with
282:
935:
Laboratory
Methods for the Diagnosis of Meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae
820:
942:
842:
527:
In 2004, a previously unknown pathway was reported when nicotinamide riboside (NR) was identified as an additional NAD+ precursor in
1649:
1564:
569:
1176:
521:
788:
1529:
1428:
1378:
1219:
1399:
Ummarino, S; Mozzon, M; Zamporlini, F; Amici, A; Mazzola, F; Orsomando, G; Ruggieri, S; Raffaelli, N (15 April 2017).
643:
436:
389:
260:
484:. Pellagra was the first disease to be associated with NAD+ deficiency. It was linked to nutritional deficiency by
350:
578:
1685:
1534:
1270:
971:"Codehydrogenase I and Other Pyridinium Compounds as V-Factor for Hemophilus influenzae and H. parainfluenzae"
413:
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) has been identified as an NAD precursor, involved in salvage NAD synthesis in both
59:
653:
611:
203:
1602:"Extension of use of nicotinamide riboside chloride as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283"
812:
623:
440:
224:
241:
931:
435:) and V factor (NAD) to grow. V factor, purified from blood, was shown to exist in three forms:
1503:"ChromaDex Licenses Exclusive Patent Rights for Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) Vitamin Technologies"
1695:
1073:"Balancing NAD+ deficits with nicotinamide riboside: therapeutic possibilities and limitations"
941:(Second ed.). Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press, World Health Organization. pp. 87–104.
516:
synthesis. Classic NAD+ synthesis pathways characterized in eukaryotes include an eight-step
513:
421:. In bacteria, it was first described in 1944 as a necessary growth factor for the culture of
702:
423:
45:
933:
167:
212:
686:
103:
8:
1215:"The emergence of the nicotinamide riboside kinases in the regulation of NAD+ metabolism"
245:
93:
147:
1690:
1626:
1601:
1479:
1454:
1370:
1308:
1271:"Preclinical and clinical evidence of NAD(+) precursors in health, disease, and ageing"
1241:
1214:
1168:
1105:
1072:
909:
884:
757:
730:
628:
489:
995:
970:
1631:
1484:
1420:
1374:
1362:
1312:
1300:
1246:
1172:
1160:
1152:
1110:
1092:
1038:
1000:
914:
762:
690:
485:
1132:
1621:
1613:
1474:
1466:
1416:
1412:
1354:
1290:
1282:
1236:
1228:
1144:
1100:
1084:
1030:
990:
982:
904:
896:
780:
752:
742:
682:
473:
depends entirely on salvage of NAD precursors from other cells in its environment.
305:
192:
1358:
986:
500:
1470:
1295:
1088:
1034:
599:
542:
Research in mammals indicates that NRK1 is a cytosolic protein, encoded by the
454:
344:
1286:
1148:
1679:
1617:
1156:
1096:
466:
23:
1400:
1338:
1635:
1488:
1424:
1366:
1304:
1250:
1164:
1114:
1042:
1004:
918:
766:
694:
633:
458:
1021:
Belenky, P.; et al. (2007). "NAD+ Metabolism in Health and
Disease".
900:
731:"Nicotinamide Riboside-The Current State of Research and Therapeutic Uses"
1232:
476:
The identification of
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) as an NAD precursor in
1269:
Reiten, OK; Wilvang, MA; Mitchell, SJ; Hu, Z; Fang, EF (October 2021).
747:
638:
532:
528:
493:
477:
462:
418:
382:
378:
332:
158:
32:
443:
and NR. NR was the compound that led to the most rapid growth of the
595:
343:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
481:
414:
374:
269:
InChI=1S/C11H14N2O5/c12-10(17)6-2-1-3-13(4-6)11-9(16)8(15)7(5-14)18
126:
1339:"Nicotinamide riboside, a trace nutrient in foods, is a vitamin B
648:
610:
602:
over the rights to nicotinamide riboside supplements since 2016.
179:
524:(NAMPT) and the formation of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
1654:
Department of Health and Aged Care, Commonwealth of
Australia
1398:
885:"Microbial NAD metabolism: lessons from comparative genomics"
509:
432:
393:
138:
116:
1131:
Katsyuba, E; Romani, M; Hofer, D; Auwerx, J (January 2020).
229:
1453:
McReynolds, MR; Chellappa, K; Baur, JA (22 February 2020).
539:
then converted to NAD+ by NMN-adenylyltransferase (NMNAT).
469:(Asp), which were the previously known precursors of NAD+.
1130:
1347:
Current
Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care
1452:
1268:
1343:
with effects on energy metabolism and neuroprotection"
1070:
672:
570:
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide § Biosynthesis
728:
587:pathway and the action of the nicotinamidase Pnc1.
560:precursors is an area of interest for researchers.
1495:
1071:Cercillieux, A; Ciarlo, E; Canto, C (2022-08-02).
1530:"Firms feud over purported age-fighting molecule"
729:Mehmel, M; Jovanović, N; Spitz, U (31 May 2020).
1677:
191:
1448:
1446:
1264:
1262:
1260:
1208:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1198:
1196:
1194:
1126:
1124:
1066:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1056:
1054:
1052:
968:
396:, through a two-step and a three-step pathway.
102:
1212:
1016:
1014:
964:
962:
878:
876:
874:
724:
722:
720:
718:
1521:
1593:
1443:
1392:
1330:
1257:
1191:
1121:
1049:
883:Gazzaniga, F; et al. (September 2009).
707:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1020:
1011:
959:
871:
715:
666:
431:was identified as requiring both X factor (
1527:
1133:"NAD(+) homeostasis in health and disease"
889:Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews
244:
166:
1625:
1478:
1294:
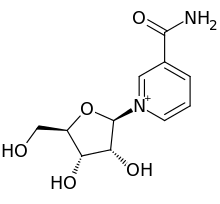
1240:
1104:
994:
908:
882:
756:
746:
211:
1336:
835:
807:
805:
773:
577:
1600:Turck, D; et al. (November 2021).
582:NRK1/2 mediated pathway from NR to NAD+
240:
1678:
925:
605:
522:Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase
1660:from the original on 16 February 2023
1599:
1431:from the original on 16 February 2023
1179:from the original on 11 November 2022
969:Gingrich, W; Schlenk, F (June 1944).
823:from the original on 11 February 2017
802:
687:10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155443
531:. NR is now recognized as a form of
146:
1275:Mechanisms of Ageing and Development
1077:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
590:
1581:from the original on 2 January 2023
1337:Chi, Y; Sauve, AA (November 2013).
843:"Spherix/ChromaDex GRAS submission"
182:
13:
1220:Journal of Molecular Endocrinology
14:
1707:
859:from the original on 4 March 2017
644:Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
437:Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
390:nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
388:. It functions as a precursor to
1650:"Nicotinamide riboside chloride"
31:
22:
1642:
1557:
1546:from the original on 2022-11-16
1535:Chemical & Engineering News
1509:from the original on 2019-02-15
1381:from the original on 2023-02-13
1319:from the original on 2023-02-13
1213:Fletcher RS, Lavery GG (2018).
948:from the original on 2023-02-12
791:from the original on 2017-02-20
563:
347:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
1528:Bomgardner, Melody M. (2018).
1417:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.032
1023:Trends in Biochemical Sciences
488:in 1914, and to deficiency of
480:developed out of the study of
461:(NAM), or amino acids such as
290:c1cc(c(c1)2(((O2)CO)O)O)C(=O)N
1:
659:
510:oxidation/reduction reactions
77:-Ribofuranosyl)nicotinamide;
1455:"Age-related NAD(+) decline"
1359:10.1097/MCO.0b013e32836510c0
987:10.1128/JB.47.6.535-550.1944
654:Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
612:Generally recognized as safe
399:
53:-ribofuranosyl)pyridin-1-ium
7:
1565:"GRAS Notice (GRN) No. 635"
1471:10.1016/j.exger.2020.110888
813:"GRAS Notices, GRN No. 635"
624:Nicotinamide mononucleotide
617:
64:3-Carbamoyl-1-pyridin-1-ium
10:
1712:
1089:10.1007/s00018-022-04499-5
1035:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.11.006
567:
408:
337:255.25 g/mol
1287:10.1016/j.mad.2021.111567
1149:10.1038/s42255-019-0161-5
341:
298:
278:
256:
86:
70:
58:
44:
39:
30:
21:
1618:10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6843
1459:Experimental Gerontology
785:pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
975:Journal of Bacteriology
781:"Nicotinamide riboside"
817:www.accessdata.fda.gov
583:
17:Nicotinamide riboside
1686:Anti-aging substances
901:10.1128/MMBR.00042-08
581:
424:Haemophilus influenza
363:Nicotinamide riboside
60:Systematic IUPAC name
575:nicotinamide (NAM).
81:-Ribosylnicotinamide
1296:20.500.11850/506217
1233:10.1530/JME-18-0085
606:Safety designations
18:
748:10.3390/nu12061616
584:
351:Infobox references
16:
1137:Nature Metabolism
591:Commercialization
486:Joseph Goldberger
359:Chemical compound
357:
356:
225:CompTox Dashboard
128:Interactive image
76:
52:
49:3-Carbamoyl-1-(β-
1703:
1670:
1669:
1667:
1665:
1646:
1640:
1639:
1629:
1597:
1591:
1590:
1588:
1586:
1580:
1569:
1561:
1555:
1554:
1552:
1551:
1525:
1519:
1518:
1516:
1514:
1499:
1493:
1492:
1482:
1450:
1441:
1440:
1438:
1436:
1396:
1390:
1389:
1387:
1386:
1334:
1328:
1327:
1325:
1324:
1298:
1266:
1255:
1254:
1244:
1227:(1): R107–R121.
1210:
1189:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1128:
1119:
1118:
1108:
1068:
1047:
1046:
1018:
1009:
1008:
998:
966:
957:
956:
954:
953:
947:
940:
929:
923:
922:
912:
880:
869:
868:
866:
864:
858:
847:
839:
833:
832:
830:
828:
809:
800:
799:
797:
796:
777:
771:
770:
760:
750:
726:
713:
712:
706:
698:
670:
306:Chemical formula
249:
248:
233:
231:
215:
195:
184:
170:
150:
130:
106:
74:
50:
35:
26:
19:
15:
1711:
1710:
1706:
1705:
1704:
1702:
1701:
1700:
1676:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1663:
1661:
1648:
1647:
1643:
1598:
1594:
1584:
1582:
1578:
1567:
1563:
1562:
1558:
1549:
1547:
1526:
1522:
1512:
1510:
1501:
1500:
1496:
1451:
1444:
1434:
1432:
1397:
1393:
1384:
1382:
1342:
1335:
1331:
1322:
1320:
1267:
1258:
1211:
1192:
1182:
1180:
1129:
1122:
1069:
1050:
1019:
1012:
967:
960:
951:
949:
945:
938:
930:
926:
881:
872:
862:
860:
856:
845:
841:
840:
836:
826:
824:
811:
810:
803:
794:
792:
779:
778:
774:
727:
716:
700:
699:
675:Annu. Rev. Nutr
671:
667:
662:
620:
608:
593:
572:
566:
536:
501:Conrad Elvehjem
497:
453:cannot grow on
411:
402:
386:
360:
353:
348:
326:
322:
318:
314:
308:
294:
291:
286:
285:
274:
271:
270:
264:
263:
252:
242:DTXSID501010039
234:
227:
218:
198:
185:
173:
153:
133:
120:
109:
96:
82:
66:
65:
54:
12:
11:
5:
1709:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1672:
1671:
1641:
1612:(11): e06843.
1592:
1556:
1520:
1505:. 2012-07-16.
1494:
1442:
1405:Food Chemistry
1391:
1340:
1329:
1256:
1190:
1120:
1048:
1010:
958:
924:
870:
834:
801:
772:
714:
664:
663:
661:
658:
657:
656:
651:
646:
641:
636:
631:
626:
619:
616:
607:
604:
600:Elysium Health
592:
589:
568:Main article:
565:
562:
534:
495:
455:nicotinic acid
410:
407:
401:
398:
384:
381:and a form of
358:
355:
354:
349:
345:standard state
342:
339:
338:
335:
329:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
309:
304:
301:
300:
296:
295:
293:
292:
289:
281:
280:
279:
276:
275:
273:
272:
268:
267:
259:
258:
257:
254:
253:
251:
250:
237:
235:
223:
220:
219:
217:
216:
208:
206:
200:
199:
197:
196:
188:
186:
178:
175:
174:
172:
171:
163:
161:
155:
154:
152:
151:
143:
141:
135:
134:
132:
131:
123:
121:
114:
111:
110:
108:
107:
99:
97:
92:
89:
88:
84:
83:
72:
68:
67:
63:
62:
56:
55:
48:
42:
41:
37:
36:
28:
27:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1708:
1697:
1696:Nicotinamides
1694:
1692:
1689:
1687:
1684:
1683:
1681:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1645:
1637:
1633:
1628:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1603:
1596:
1577:
1573:
1566:
1560:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1536:
1531:
1524:
1508:
1504:
1498:
1490:
1486:
1481:
1476:
1472:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1449:
1447:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1395:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1353:(6): 657–61.
1352:
1348:
1344:
1333:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1297:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1265:
1263:
1261:
1252:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1221:
1216:
1209:
1207:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1195:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1127:
1125:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1067:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1059:
1057:
1055:
1053:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1017:
1015:
1006:
1002:
997:
992:
988:
984:
981:(6): 535–50.
980:
976:
972:
965:
963:
944:
937:
936:
928:
920:
916:
911:
906:
902:
898:
895:(3): 529–41.
894:
890:
886:
879:
877:
875:
855:
851:
844:
838:
822:
818:
814:
808:
806:
790:
786:
782:
776:
768:
764:
759:
754:
749:
744:
740:
736:
732:
725:
723:
721:
719:
710:
704:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
669:
665:
655:
652:
650:
647:
645:
642:
640:
637:
635:
632:
630:
627:
625:
622:
621:
615:
613:
603:
601:
597:
588:
580:
576:
571:
561:
558:
552:
549:
545:
540:
537:
530:
525:
523:
519:
515:
511:
505:
502:
498:
491:
487:
483:
479:
474:
472:
468:
467:aspartic acid
464:
460:
456:
452:
448:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
425:
420:
416:
406:
397:
395:
391:
387:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
352:
346:
340:
336:
334:
331:
330:
310:
307:
303:
302:
297:
288:
287:
284:
277:
266:
265:
262:
255:
247:
243:
239:
238:
236:
226:
222:
221:
214:
210:
209:
207:
205:
202:
201:
194:
190:
189:
187:
181:
177:
176:
169:
165:
164:
162:
160:
157:
156:
149:
145:
144:
142:
140:
137:
136:
129:
125:
124:
122:
118:
113:
112:
105:
101:
100:
98:
95:
91:
90:
85:
80:
69:
61:
57:
47:
43:
38:
34:
29:
25:
20:
1662:. Retrieved
1653:
1644:
1609:
1606:EFSA Journal
1605:
1595:
1583:. Retrieved
1571:
1559:
1548:. Retrieved
1539:
1533:
1523:
1511:. Retrieved
1497:
1462:
1458:
1433:. Retrieved
1408:
1404:
1394:
1383:. Retrieved
1350:
1346:
1332:
1321:. Retrieved
1278:
1274:
1224:
1218:
1181:. Retrieved
1140:
1136:
1080:
1076:
1029:(1): 12–19.
1026:
1022:
978:
974:
950:. Retrieved
934:
927:
892:
888:
861:. Retrieved
849:
837:
825:. Retrieved
816:
793:. Retrieved
784:
775:
738:
734:
703:cite journal
678:
674:
668:
634:Nicotinamide
609:
594:
585:
573:
564:Biosynthesis
556:
553:
547:
543:
541:
526:
517:
506:
475:
471:H. influenza
470:
459:nicotinamide
451:H. influenza
450:
449:
445:H. influenza
444:
429:H. influenza
428:
422:
412:
403:
370:
366:
362:
361:
87:Identifiers
78:
71:Other names
1664:16 February
1585:15 February
1513:15 February
1435:16 February
1411:: 161–168.
1143:(1): 9–31.
863:18 February
827:18 February
741:(6): 1616.
681:: 115–130.
447:bacterium.
299:Properties
148:CHEBI:15927
1680:Categories
1550:2022-11-16
1465:: 110888.
1385:2023-02-13
1323:2023-02-13
1281:: 111567.
1183:6 February
1083:(8): 463.
952:2023-02-12
795:2017-02-20
660:References
639:Vitamin B3
529:eukaryotes
478:eukaryotes
463:tryptophan
419:eukaryotes
379:nucleoside
333:Molar mass
213:0I8H2M0L7N
159:ChemSpider
115:3D model (
94:CAS Number
46:IUPAC name
1691:Ribosides
1375:205782942
1313:237459655
1173:214277961
1157:2522-5812
1097:1420-9071
735:Nutrients
596:ChromaDex
533:vitamin B
494:vitamin B
465:(Trp) or
400:Chemistry
383:vitamin B
104:1341-23-7
1658:Archived
1636:34804232
1576:Archived
1544:Archived
1507:Archived
1489:32097708
1429:Archived
1425:27979136
1379:Archived
1367:24071780
1317:Archived
1305:34517020
1251:30307159
1177:Archived
1165:32694684
1115:35918544
1043:17161604
1005:16560803
943:Archived
919:19721089
854:Archived
821:Archived
789:Archived
767:32486488
695:18429699
618:See also
482:pellagra
439:(NAD+),
415:bacteria
375:pyridine
1627:8586847
1480:7442590
1242:6145238
1106:9345839
910:2738131
850:FDA.gov
758:7352172
649:Sirtuin
557:de novo
518:de novo
409:History
373:) is a
327:
180:PubChem
1634:
1624:
1542:(33).
1487:
1477:
1423:
1373:
1365:
1311:
1303:
1249:
1239:
1171:
1163:
1155:
1113:
1103:
1095:
1041:
1003:
996:373952
993:
917:
907:
765:
755:
693:
629:Niacin
490:niacin
457:(NA),
283:SMILES
193:439924
168:388956
40:Names
1579:(PDF)
1568:(PDF)
1371:S2CID
1309:S2CID
1169:S2CID
946:(PDF)
939:(PDF)
857:(PDF)
846:(PDF)
548:Nmrk2
544:Nmrk1
499:) by
433:hemin
392:, or
371:SR647
261:InChI
139:ChEBI
117:JSmol
73:1-(β-
1666:2023
1632:PMID
1587:2023
1515:2019
1485:PMID
1437:2023
1421:PMID
1363:PMID
1301:PMID
1247:PMID
1185:2023
1161:PMID
1153:ISSN
1111:PMID
1093:ISSN
1039:PMID
1001:PMID
915:PMID
865:2019
829:2019
763:PMID
709:link
691:PMID
512:and
417:and
394:NAD+
204:UNII
1622:PMC
1614:doi
1572:FDA
1475:PMC
1467:doi
1463:134
1413:doi
1409:221
1355:doi
1291:hdl
1283:doi
1279:199
1237:PMC
1229:doi
1145:doi
1101:PMC
1085:doi
1031:doi
991:PMC
983:doi
905:PMC
897:doi
753:PMC
743:doi
683:doi
514:ATP
441:NMN
427:,
230:EPA
183:CID
1682::
1656:.
1652:.
1630:.
1620:.
1610:19
1608:.
1604:.
1574:.
1570:.
1540:96
1538:.
1532:.
1483:.
1473:.
1461:.
1457:.
1445:^
1427:.
1419:.
1407:.
1403:.
1377:.
1369:.
1361:.
1351:16
1349:.
1345:.
1315:.
1307:.
1299:.
1289:.
1277:.
1273:.
1259:^
1245:.
1235:.
1225:61
1223:.
1217:.
1193:^
1175:.
1167:.
1159:.
1151:.
1139:.
1135:.
1123:^
1109:.
1099:.
1091:.
1081:79
1079:.
1075:.
1051:^
1037:.
1027:32
1025:.
1013:^
999:.
989:.
979:47
977:.
973:.
961:^
913:.
903:.
893:73
891:.
887:.
873:^
852:.
848:.
819:.
815:.
804:^
787:.
783:.
761:.
751:.
739:12
737:.
733:.
717:^
705:}}
701:{{
689:.
679:28
677:.
369:,
367:NR
317:15
313:11
1668:.
1638:.
1616::
1589:.
1553:.
1517:.
1491:.
1469::
1439:.
1415::
1388:.
1357::
1341:3
1326:.
1293::
1285::
1253:.
1231::
1187:.
1147::
1141:2
1117:.
1087::
1045:.
1033::
1007:.
985::
955:.
921:.
899::
867:.
831:.
798:.
769:.
745::
711:)
697:.
685::
535:3
496:3
492:(
385:3
377:-
365:(
325:5
323:O
321:2
319:N
315:H
311:C
232:)
228:(
119:)
79:N
75:D
51:D
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.