1616:(Moors, or Berbers) situated around and beyond the former Roman frontier. Devolution policies enacted by the Romans in the fifth century would have prepared local rulers for this type of dual rule. The citizens of the Roman cities were subjects of a formal and organized administration headed by appointed officials, such as those appointed by Masuna. The military manpower was derived from the Berber tribes over which control was maintained through the control of key individuals, such as tribal leaders, by issuing honors and estates to them. As Masuna's polity, like others in the region, adopted the military, religious and sociocultural organization of the Roman Empire, it continued to be fully within the Western Latin world. The administrative structure and titulature used by the rulers of the kingdom suggests a certain romanized political identity in the region.
307:
1322:
1903:
57:
430:
1726:(also known as Mastinas) by 535 AD. Pierre Morizot identified Mastinas with Masties, the leader of the Kingdom of the Aurès mentioned above. Procopius states that Mastigas was a fully independent ruler who ruled almost the entire former province of Mauretania Caesariensis, except for the former provincial capital, Caesarea, which had been under control of the Vandals and was in Eastern Roman hands during his time. However, a coin attributed to Mastigas describes him as a
1681:, the final Vandal king, attempted to recruit the Berber kingdoms to fight for him but very few Berber troops took part in fighting for the Vandal side. Though the Vandals had supplied the Berber kings with symbols of their offices similar to those supplied by the Romans, the Berber kings did not consider the Vandals to hold that power securely. During the Vandalic war, most Berber rulers waited out the conflict in order to avoid fighting for the losing side.
293:
1671:. Some writers have conflated Massonas with Masuna, but Gabriel Camps and other historians believe them to be separate people. When Belisarius and the Eastern Roman forces arrived in Northern Africa to invade and restore Roman rule over the region, local Berber rulers willingly submitted to Imperial rule, only demanding in return the symbols of their offices; a silver crown, a staff of silver gilt, a tunic and gilded boots. Essentially
332:
1638:
1250:(in present-day Algeria). Scholars are in disagreement about whether the polity aimed for independence as a kingdom or was part of a loose confederation, an alternative hypothesis drawn from contextual knowledge about Berber tribal alliances. In the fifth century, Roman control over the province weakened and Imperial resources had to be concentrated elsewhere, notably in defending the
1588:("For the health and safety of king Masuna and of the Mauri and Roman peoples, the Castra was built by Masgiven, prefect of Safar, Lidir, procurator of Castra Severiana, whom Masuna installed at Altava and Maximus, procurator of Altava, appointed to command). This was installed in year 369 of the province") The three officials appointed are Masgiven (
1765:(also known as Garmules), a military leader who resisted Eastern Roman rule in Africa, as a later king who continued the maintenance of Masuna's kingdom. In the late 560s, Garmul launched raids into Roman territory, and although he failed to take any significant town, three successive generals, Praetorian prefect Theodore (in 570 AD) and the two
1881:- Gennadius had a large number of troops available for a complete elimination, which might even have been reinforced from the old empire. In addition, as can be seen, he was the focus of the emperor's troop reinforcements, which is all the more remarkable given that the Eastern Roman Empire was again at war with Persia at this time.
1696:, waged several wars against these Berber tribes, leading an army of around 18,000 men into Byzacena. Solomon defeated them and returned to Carthage, though the Berbers later rose again and overran Byzacena. Solomon once again defeated them, this time decisively, scattering the Berber forces. Surviving Berber soldiers retreated into
1675:, many of the Berber rulers proved recalcitrant. Those rulers that were not directly adjacent to Imperial territories were more or less independent, though nominally still Imperial subjects, and were treated with larger amounts of courtesy than the ones directly bordering the Empire, as to keep them in line.
1855:- The preservation of the Roman character, as with the cities further west, does not allow any conclusions to be drawn about the restoration of Roman rule. Close cultural and economic ties are also conceivable, especially as this was not uncommon in antiquity, even between states that were proven to exist.
1821:
So far it has not been clarified whether the Altava area or at least the coastal strip was incorporated into the
Eastern Roman Empire. Only the expansion of Byzantine fortresses by Gennadius is discussed, but not their locations. In any case, the question of the incorporation of parts of the Kingdom
1600:
The historian Alan
Rushworth has proposed that Masuna indeed possessed a kingdom centered at the inscription's location in Altava. In contrast, Jean-Paul Laporte believes that while there were "kings of the Moors and Romans" alive at this time, the inscription is insufficient to conclude that Masuna
1540:
or "king" to describe themselves, the full inscription on which this title is found suggests grander ambitions, the scope of which has been debated by historians. Masuna may have considered himself the chief of a loose confederation, or the founder of a kingdom uniting specific ethnicities. For Greg
1812:
dedicated to various leaders named Iulius and a woman named Iulia
Rogatiana of Altava. The dating of the Jedars and the tombstones is unclear, and other scholars have proposed that the Jedars belonged to a different kingdom or an enemy tribe. Jean-Paul Laporte considers the Jedars to be the actual
1659:
and Moors, and though some
Berbers had assisted the Vandals in their conquests in Africa, Berber expansionism for the most part, was focused against the Vandals and would lead to the expansion of the kingdom of Masuna and other Berber kingdoms of the region, such as the Kingdom of the Aurès.
1586:"Pro sal(ute) et incol(umitate) reg(is) Masunae gent(ium) Maur(orum) et Romanor(um) castrum edific(atum) a Masgivini pref(ecto) de Safar. Lidir proc(uratore) castra Severian(a) quem Masuna Altava posuit, et Maxim(us) pr(ocurator) Alt(ava) prefec(it). P(ositum) p(rovinciae) CCCLXVIIII".
1601:
was actually among them. Andy
Merrills rejects the idea that "any one individual or family enjoyed a monopoly over military power", and suggests that Masuna was part of a larger confederation and that he adopted the title to indicate the prestige accumulated by his construction of a
1795:
with the clear aim of reducing Garmul's kingdom. Preparations were lengthy and careful, but the campaign itself, launched in 577–78 AD, was brief and effective, with
Gennadius utilizing terror tactics against Garmul's subjects. Garmul was defeated and killed in 578 AD.
1799:
Although Garmul was defeated, Gabriel Camps suggests that the kingdom persisted until the Arab invasions of the 7th century. The rulers of the area after Garmul are unattested in historical sources, but they have been variously connected to a group of mausolea called
1463:
communities along the frontier regions of the provinces meant that the Berber chieftains had some experience in governing populations composed of both
Berbers and Romans. Following the final collapse of the Western Roman Empire, the state grew into a fully-fledged
1719:), urged Solomon to pursue the enemy Berbers into Numidia, which he did. Solomon did not engage Iabdas in battle, however, distrusting the loyalty of his allies, and instead constructed a series of fortified posts along the roads linking Byzacena with Numidia.
1844:- No further fighting is known in this part of the Byzantine Maghreb. A connection to the formerly peaceful relations between the Roman-Berber Empire of Altava and the Eastern Roman Empire seems conceivable. Since the Eastern Roman Empire had been at
1487:
in 477 AD, after which they won many victories against the Vandal kingdom and established more or less full control over the former province of
Mauretania. Having feared Gaiseric, the Moors under Vandal control revolted against his successor
1873:- The continued existence of a larger Roman-Berber state would have remained a permanent threat and thus a source of further conflicts. This threat has been proven to be eliminated, for which a weakening was already sufficient.
1421:
As barbarian incursions became more common even in previously secure provinces such as Italy, the
Western Roman military became increasingly occupied to defend territories in the northern parts of the Empire. Even the vital
1418:("Caesarian Mauretania"). The Berber rulers of the inland territories maintained a degree of Roman culture, including the local cities and settlements, and often nominally acknowledged the suzerainty of the Roman Emperors.
1887:- The information on the subsequent battles with the Berbers up to 584 show a temporal connection to the short, rapid campaign against the Altavian king Garmules and could refer to the elimination of pockets of resistance.
1783:, presented a clear threat to the province's authorities. Garmul was not the leader of a mere semi-nomadic tribe, but of a fully-fledged barbarian kingdom, with a standing army. Thus, the new Eastern Roman emperor,
1277:. Following the Eastern Roman victory over the Vandals, local leaders maintained their alliance with the Eastern Roman Empire, assisting it in wars against invading Berbers of other tribes and kingdoms, such as the
1654:
Eastern Roman records referring to the Vandal
Kingdom, which had occupied much of the old Roman province of Africa and coastal parts of Mauretania, often refer to it with regards to a trinity of peoples; Vandals,
1867:- Under the Eastern Roman emperors up to and including Maurice there was a claim to bring all former western Roman areas back under imperial control. This was also implemented in the realm of feasibility.
2922:
1254:
itself from invading Germanic tribes. Moors and Romans in Mauretania came to operate independently from the Empire. However, regional leaders may not have necessarily felt abandoned by the Romans.
1165:
1476:, were fully within the borders of the former Roman Empire, the state extended beyond the formal imperial frontier, also encompassing Berber territories never controlled by the Romans.
1596:
of Castra Severiana) and Maximus (procurator of Altava). The "year of the province," was counted from the date when the province was established, so the inscription dates to 508 AD.
1536:, which may be translated as either "king of the people of Mauri and of the Romans" or as "king of the Mauri and Roman peoples". Although many Berber warlords had employed the term
2898:"Rex gentium Maurorum et Romanorum. Recherches sur les royaumes de Maurétanie des VIe et VIIe siècles [Recherches sur les royaumes de Maurétanie des VIe et VIIe siècles]"
3527:
Merrills, Andrew (2018). "The Moorish Kingdoms and the Written Record: Three 'Textual Communities' in Fifth- and Sixth-Century Mauretania". In Elina Screen, Charles West (ed.).
1367:, but the economic importance of the African provinces made them important to retain. To this end, defensive structures were constructed alongside their borders, such as the
1512:, the wars between the Berbers and the Vandals continued. During Thrasamund's reign, the Vandals suffered a disastrous defeat at the hands of a Berber king ruling the city
3736:
374:
360:
346:
1923:
1966:, also saw an economic rise and the construction of several new churches and fortifications. Though the Eastern Roman Praetorian Prefecture of Africa and the later
1931:
3731:
3726:
1545:
was neither a full acceptance of Roman imperial command nor a challenge to it, but an expression of tribal identification within Romanized language and culture.
2931:
1963:
1915:
1373:; a 750 km long linear defensive structure composed of ditches, stone walls and other fortifications. This structure remained in consistent use until the
812:
367:
1684:
Following the Eastern Roman re-conquest of the Vandal Kingdom, the local governors began to experience problems with the local Berber tribes. The province of
1935:
1732:, or Roman military commander. The rulers of Berber polities of this time period continued to regard themselves as subjects of the Eastern Roman Emperor in
1822:
of Altava into the Eastern Roman dominion has not yet been researched, which is why only arguments for or against the thesis can be used at the moment.
877:
1608:
The name Masuna gives to his polity identifies it as being on the territorial interface of two distinct populations, the coastal and settled provincial
3084:
Roman Africa: An Outline of the History of the Roman Occupation of North Africa, Based Chiefly Upon Inscriptions and Monumental Remains in that Country
1504:, which was fully independent by the time of Huneric's death in 484 AD and never came under Vandal rule again. Under the rule of Huneric's successors
1619:
This Roman political identity was maintained by other smaller Berber kingdoms in the region as well, such as in the Kingdom of the Aurès where King
1848:
again since 572, a settlement seems likely in order to withdraw possible reinforcements back to the east, especially since the Persian Great King
1758:, Fisher and Drost suggest that "a political entity with some state-like features" originating with Masuna continued there until roughly 589–599.
1059:
952:
3411:
1568:
1468:
not entirely unlike those that had sprung up in other parts of the former Empire. Though most other Barbarian kingdoms, such as those of the
1093:
1890:− Possibly, Gennadius will have been content with smashing the empire of Altava and having his supremacy recognized by the splinter states.
3586:
1667:
of the Eastern Roman Empire as Massonas allied with the forces of the Eastern Roman Empire in 535 AD against the Vandal Kingdom during the
1200:
1159:
1098:
17:
3199:
3177:
1015:
942:
1459:
and frontier commanders and as Roman control weakened, they established their own kingdoms and polities in the region. The presence of
1845:
1712:
3460:
3220:
1340:, previously a Roman client kingdom, were fully annexed by the Roman Empire in 40 AD and divided into two provinces under Emperor
1083:
523:
1860:- The absence of Byzantine fortress ruins does not mean that Byzantine rule was absent. No ruined forts exist west of Setif and
56:
972:
3555:
3536:
3517:
3470:
3430:
3382:
3329:
3230:
3209:
3187:
3051:
2968:
2248:
1946:
was significantly smaller in size than the Kingdom of Masuna and Garmul had been. In the late fifth and early sixth century,
1541:
Fisher and Alexander Drost, the historical context of Rome's loss of control over North Africa suggests that the Latin term
3746:
1788:
2024:
With the death of Kusaila, the torch of resistance passed to a tribe known as the Jerawa tribe, who had their home in the
3716:
1265:, which had been established following the Vandalic conquest of the Roman province of Africa. The founder of the polity,
947:
870:
3721:
2183:
Possible later rulers can be seen in archaeological evidence. The state may have persisted to 589–599, or even longer.
1736:. Even when they were at war with him or engaged in raids of Imperial territory, Berber rulers employed titles such as
1284:
Eventually, the diplomatic ties between the Eastern Roman Empire and the Altava polity broke down. The military leader
1054:
1004:
3061:
Fisher, Greg; Drost, Alexander (2016). "Structures of Power in Late Antique Borderlands: Arabs, Romans, and Berbers".
3771:
3766:
3449:
3310:
3257:
3144:
3125:
3032:
3006:
2987:
3741:
3579:
1688:
was invaded and the local garrison, including the commanders Gainas and Rufinus, was defeated. The newly appointed
1483:, the Moors only began to truly expand and consolidate their power following the death of the powerful vandal king
1193:
664:
471:
439:
1629:
during his rule around 516 AD, postulating that he had not broken trust with either his Berber or Roman subjects.
1296:
has been proposed as a continuation of Masuna's state. Altava and surrounding kingdoms continued to rule over the
1876:− Nothing is reported about fighting from the other parts of the Byzantine Maghreb until the first Arab advance.
1689:
1672:
1289:
1112:
1078:
609:
1775:
to have been killed by Garmul's forces. His activities, especially when regarded together with the simultaneous
1020:
1982:
1576:(the diocese of Castra Severiana, an ancient bishopric which flourished during Late Antiquity), the control of
1301:
1152:
1073:
3564:
2943:
2149:
Gabriel Camps suggests that a kingdom continued after Mastigas, but does not supply any names before Garmul.
475:
2017:
arrived under Zuhair ibn Kays. Kusaila met them in 690 AD, with the support of Eastern Roman troops, at the
1453:
In Mauretania, local Berber leaders and tribes had long been integrated into the imperial system as allies,
3711:
3407:
1122:
3167:
Laporte, J.-P. 2005. “Les djedars, monuments funéraires berbères de la region de Frenda et de Tiaret.” In
921:
3756:
3572:
1951:
1186:
1146:
409:
1950:
grew to be the fully dominant religion in the Berber Altava kingdom, with syncretic influences from the
1870:- To rule the coastal strip, a strong fleet was needed, which the Byzantine Empire had at its disposal.
3620:
1693:
1359:
Northern Africa was not as well-defended as frontiers that saw frequent attacks, such as those against
865:
911:
3761:
2999:
History of the Later Roman Empire: From the Death of Theodosius I to the Death of Justinian, Volume 2
1593:
2944:"Fossatum Africae. Recherches Aériennes sur l'organisation des confins Sahariens a l'Epoque Romaine"
1864:, although there is evidence of Byzantine rule extending further west on the coast beyond Caesarea.
3751:
1381:. The Mauretanian frontier, not as well defended as that of the African frontier, was known as the
1321:
3660:
2130:
2014:
1784:
1460:
1415:
1378:
1349:
1326:
1288:, whom some historians identify as a successor king to Masuna's state, invaded the Eastern Roman
1243:
1172:
1068:
894:
882:
657:
569:
565:
176:
3655:
2100:
1970:
saw some further Berber rebellions, these were put down and many Berber tribes were accepted as
1919:
1705:
1501:
1278:
593:
3394:
Un nouveau fragment de l'histoire de l'Occident musulman (62–196/682–812): l'épopée d'al Kahina
3155:
2897:
2663:
2210:
2134:
1411:
1088:
962:
889:
3291:
3420:
1716:
819:
510:
3507:
3488:
1402:
control since the fourth century, with direct Roman rule confined to coastal cities such as
3680:
2195:
1985:. He was also leader of the Awraba tribe of the Berbers and possibly Christian head of the
1959:
1911:
1902:
1520:, who almost completely destroyed a Vandal army that had been sent to subjugate the city.
1407:
1391:
1345:
937:
628:
353:
325:
298:
233:
8:
3665:
1967:
1771:
Theoctistus (in 570 AD) and Amabilis (in 571 AD), are recorded by the Visigoth historian
836:
617:
1841:- The source situation regarding the conquest of areas of the Empire of Altava is poor.
3690:
3595:
3401:
3101:
2205:
1560:), dated 508 AD. It states that Masuna possesses Altava and at least two other cities,
1469:
1465:
1141:
1049:
1032:
848:
804:
479:
418:
2025:
1572:, as mentioned is made of officials he appointed there. As the seat of an ecclesiarch
1497:
3675:
3551:
3532:
3513:
3498:
3466:
3445:
3426:
3378:
3363:
3340:
3325:
3306:
3253:
3226:
3205:
3183:
3140:
3121:
3047:
3028:
3019:
3002:
2983:
2964:
2244:
2215:
2032:, the queen of the Kingdom of the Aurès and the last ruler of the romanized Berbers.
1998:
1990:
1943:
1927:
1907:
1383:
1305:
1293:
843:
760:
752:
672:
601:
483:
339:
3281:
3268:
3599:
3494:
3348:
3276:
3245:
2909:
2675:
2200:
2092:
1906:
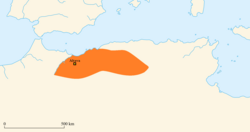
Map depicting later Romano-Berber Kingdoms of northern Africa, from left to right;
1884:- Judging by the extensive preparations, the campaign was surprisingly successful.
1767:
1562:
1369:
1270:
1041:
784:
696:
638:
535:
80:
2021:. Vastly outnumbered, the Awraba and Romans were defeated and Kusaila was killed.
967:
3630:
3071:
2018:
1772:
1364:
1117:
957:
916:
904:
831:
824:
768:
704:
680:
462:
84:
1989:. He is known for having led an effective Berber martial resistance against the
3685:
3650:
3249:
3082:
2096:
1733:
1513:
1473:
1353:
1262:
899:
856:
776:
577:
556:
454:
312:
306:
220:
3594:
2091:. May be the same person as the military leader Massonas, who allied with the
3705:
3353:
3044:
Staying Roman: Conquest and Identity in Africa and the Mediterranean, 439–700
1994:
1027:
736:
2913:
2806:
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 2000, ISBN 0-521-32591-9, p. 561.
2679:
1787:, re-appointed Thomas as praetorian prefect of Africa, and the able general
3018:
Literacy and Private Documentation in Vandal North Africa: The Case of the
2879:
1947:
1668:
1553:
1274:
1239:
1232:
928:
331:
292:
94:
3222:
Vandals, Romans and Berbers: New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa
3025:
Vandals, Romans and Berbers: New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa
429:
1742:
1251:
989:
979:
688:
3105:
1839:- There are no sources about the construction of Byzantine fortresses.
1496:
and the harsh punishments incurred on those who did not convert. In the
1589:
1509:
1505:
1395:
1333:
548:
2171:. Invaded the Eastern Roman provinces in Northern Africa in the 570s.
1942:
Altava remained the capital of a romanized Berber kingdom, though the
1754:
Pointing to the large group of dated Latin inscriptions at Altava and
3615:
3610:
2875:
2010:
1849:
1809:
1776:
1664:
1625:
1480:
1455:
1431:
1430:
had been stripped of troops in order to organize a defense against a
744:
712:
530:
496:
3422:
Framing the Early Middle Ages: Europe and the Mediterranean, 400–800
3094:
The Numismatic Chronicle and Journal of the Royal Numismatic Society
3092:
Grierson, Philip (1959). "Matasuntha or Mastinas: a reattribution".
3670:
2109:
2006:
1723:
1685:
1645:
1641:
1493:
1484:
1435:
1427:
1360:
1352:("Caesarian Mauretania"), with the separating border designated as
1341:
728:
720:
643:
633:
246:
164:
104:
3157:
Mauretania Caesariensis: an archaeological and geographical survey
2241:
A History of Christianity in Africa: From Antiquity to the Present
3625:
2798:
In: Averil Cameron, Bryan Ward-Perkins, Michael Whitby (editor):
2028:: his Christian Berber troops after his death fought later under
1986:
1978:
1808:, as well as to a line of tombstones in the Berber-Roman city of
1755:
1711:
Masuna, allied with the Eastern Empire, and another Berber king,
1697:
1678:
1620:
1573:
1489:
1439:
1399:
1374:
1337:
1297:
1258:
1257:
The rulers of this region repeatedly came into conflict with the
1235:
540:
446:
396:
392:
2742:
2005:
by Kusaila, who forced all Arabs to evacuate their just founded
3635:
2155:
2075:
2029:
2002:
1955:
1805:
1801:
1780:
1762:
1701:
1549:
1529:
1517:
1438:. The undermanned frontier allowed several tribes, such as the
1285:
1266:
1247:
501:
491:
206:
148:
70:
2809:
2633:
2631:
1977:
The last known romanized Berber King to rule from Altava was
1861:
1656:
1447:
1443:
1423:
1403:
1218:
984:
2691:
2689:
2550:
2548:
1958:
in this period. Altava and the other regional kingdoms, the
1450:, to cross the Rhine in 406 AD and invade Roman territory.
3640:
3063:
Globalizing Borderlands Studies in Europe and North America
1637:
1632:
1557:
1523:
111:
2628:
2618:
2616:
2584:
2439:
2437:
1292:
in an attempt at capturing Roman territories. The smaller
3487:
Camps, Gabriel (1995). "Djedar". In Gabriel Camps (ed.).
2878:(545). "Book III-IV: The Vandalic War (pts. 1 & 2)".
2850:
2848:
2833:
2730:
2701:
2686:
2545:
2485:
2449:
2306:
2304:
2302:
2289:
2287:
1728:
1548:
This unique inscription is located on a fortification in
2506:
2262:
2260:
3548:
Trade in the western Mediterranean, AD 400–700, 439–700
2754:
2720:
2718:
2716:
2613:
2572:
2535:
2533:
2461:
2434:
2412:
2410:
2408:
2406:
3506:
Courtot, P. (1987). "Altava". In Gabriel Camps (ed.).
3240:
Merrills, Andy (2022). "The Mauri in Late Antiquity".
3118:: les mondes tribaux dans les provinces maurétaniennes
2845:
2603:
2601:
2599:
2391:
2379:
2299:
2284:
2272:
2129:. Controlled virtually the entire ancient province of
3493:. Vol. 16. Editions Edisud. pp. 2409–2422.
2518:
2473:
2367:
2343:
2331:
2321:
2319:
2257:
2035:
2713:
2560:
2530:
2403:
2099:
and later against a Berber alliance gathered by the
3341:"From Periphery to Core in Late Antique Mauretania"
2821:
2664:"Pour une nouvelle lecture de l'elogium de Masties"
2596:
1852:, who was fond of peace negotiations, died in 579.
1390:The fifth century saw the collapse and fall of the
3512:. Vol. 4. Editions Edisud. pp. 543–552.
2804:Late Antiquity. Empire and Successors. AD 425–600.
2355:
2316:
1993:'s conquest of the Maghreb in the 680s. In 683 AD
1981:. He died in the year 690 AD fighting against the
1273:during their reconquest of Northern Africa in the
3737:States and territories disestablished in the 570s
2643:
2422:
61:The approximate extent of the Mauro-Roman kingdom
3703:
1500:, this led to the foundation of the independent
2920:
2748:
1715:(who ruled a kingdom in the former province of
3732:States and territories established in the 470s
3727:States and territories established in the 420s
3580:
3396:. Cahiers de Tunisie vol. 19. pp. 19–52.
3375:Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World
1834:Conquest/subjugation of the entire territory
1194:
3550:. University of Michigan: Tempus Reparatum.
3073:An Economic Survey of Ancient Rome, Volume 4
2980:The New Empire of Diocletian and Constantine
1813:center of power in Mauretania at this time.
27:Early medieval Christian Romano-Berber state
3200:The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire
3178:The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire
3169:Identités et culture dans l’Algérie Antique
3137:The Fall of the Roman Empire: A New History
3060:
2707:
2455:
1974:, as they had been many times in the past.
1222:
3587:
3573:
3531:. Cambridge University. pp. 185–202.
3196:
3174:
2815:
2736:
2695:
2637:
2590:
2554:
2243:. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 42.
1663:A Berber king identified by the historian
1201:
1187:
55:
3462:The Roman Empire and Its Germanic Peoples
3410:) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
3352:
3338:
3280:
2954:(2). Arts et Métiers Graphiques: 557–559.
2783:El África bizantina: reconquista y ocaso.
2760:
2293:
2013:. But in 688 AD Arab reinforcements from
1492:following his attempt to convert them to
1479:According to the Eastern Roman historian
3439:
3361:
3319:
3289:
3242:A Companion to North Africa in Antiquity
3239:
3218:
3171:, ed. C. Briand-Ponsart, 321–406. Rouen.
3112:
3091:
2924:El Africa Bizantina: Reconquista y ocaso
2622:
2578:
2539:
2512:
2467:
2443:
2416:
2310:
2278:
1954:. A new church was built in the capital
1901:
1636:
1633:The Eastern Roman Empire and the Vandals
1580:may have been particularly important.
1528:One of the Berber rulers of Mauretania,
1320:
3458:
3418:
3372:
3266:
3153:
3134:
2941:
2827:
2661:
2397:
2385:
2373:
2349:
2337:
2325:
2266:
2238:
14:
3704:
3368:. The Encyclopedia of Ancient Battles.
3120:. Bordeaux Pessac: Ausonius éditions.
3080:
3041:
3015:
2977:
2958:
2839:
2524:
2491:
2479:
1749:
1308:in the seventh and eighth centuries.
232:• Military independence from the
3568:
3391:
3345:Theoretical Roman Archaeology Journal
3300:
3069:
2895:
2874:
2854:
2724:
2649:
2566:
2428:
2361:
3303:Constantine and the Christian Empire
2996:
2781:bejahend Francisco Aguado Blázquez:
2607:
2065:No one in this region claimed to be
1238:kingdom which dominated much of the
2921:Aguado Blazquez, Francisco (2005).
1831:Incorporation of the coastal areas
1166:List of people on stamps of Algeria
24:
3480:
3465:. University of California Press.
3290:Morcelli, Stefano Antonio (1816).
2036:List of proposed Mauri-Roman kings
25:
3783:
3442:Diocletian and the Roman Recovery
1816:
1534:Rex gentium Maurorum et Romanorum
3499:10.4000/encyclopedieberbere.2177
3339:Rushworth, Alan (6 April 2000).
3197:Martindale, John Robert (1992).
3175:Martindale, John Robert (1980).
2133:, except for the old capital of
1584:In full, the inscription reads:
1269:, allied with the armies of the
428:
372:
358:
344:
330:
305:
291:
3529:Writing the Early Medieval West
3282:10.4000/encyclopedieberbere.508
3087:. Longmans, Green, and Company.
3065:. University of Nebraska Press.
2863:
2788:
2775:
2766:
2655:
2497:
1997:was ambushed and killed in the
1290:Praetorian Prefecture of Africa
36:Kingdom of the Moors and Romans
3377:. Princeton University Press.
3373:Talbert, Richard J.A. (2000).
3301:Odahl, Charles Matson (2004).
3204:. Cambridge University Press.
3182:. Cambridge University Press.
3046:. Cambridge University Press.
3023:within Merrills, Andrew (2004)
2978:Barnes, Timothy David (1982).
2959:Barnes, Timothy David (1981).
2800:The Cambridge Ancient History.
2232:
1983:Muslim conquest of the Maghreb
1700:where they joined forces with
1524:"King of the Moors and Romans"
1153:List of wars involving Algeria
13:
1:
3365:Justinian and Africa, 533–548
3322:A Companion to Late Antiquity
2221:
2161:
2115:
2081:
1410:("Tangerine Mauretania") and
1348:("Tangerine Mauretania") and
1316:
199:
185:
157:
141:
127:
47:
3362:Sarantis, Alexander (2016).
3113:Hamdoune, Christine (2018).
2982:. Harvard University Press.
2963:. Harvard University Press.
2796:Vandal and Byzantine Africa.
2226:
1690:Praetorian prefect of Africa
1394:. The inland territories of
1224:Regnum Maurorum et Romanorum
40:Regnum Maurorum et Romanorum
18:King of the Moors and Romans
7:
3747:Medieval history of Algeria
3425:. Oxford University Press.
3293:Africa christiana, Volume I
2997:Bury, John Bagnell (1958).
2239:Isichei, Elizabeth (1995).
2189:
1952:traditional Berber religion
1147:Military history of Algeria
10:
3788:
3717:Former countries in Africa
3440:Williams, Stephen (1997).
3250:10.1002/9781119071754.ch18
3081:Graham, Alexander (1902).
2868:
1434:army invading Italy under
1311:
3722:Berber Christian kingdoms
3606:
3324:. John Wiley & Sons.
3320:Rousseau, Philip (2012).
3219:Merrills, Andrew (2017).
3042:Conant, Jonathan (2012).
3016:Conant, Jonathan (2004).
2889:
1897:
1761:Gabriel Camps identifies
1246:from the capital city of
1227:), also described as the
1160:Postal history of Algeria
1099:Insurgency in the Maghreb
922:Sétif and Guelma massacre
388:
270:
266:
256:
243:
230:
226:
216:
212:
196:
182:
170:
154:
138:
124:
120:
110:
100:
90:
76:
66:
54:
46:
34:
3772:Morocco in the Roman era
3767:Algeria in the Roman era
3459:Wolfram, Herwig (2005).
3406:: CS1 maint: location (
3392:Talbi, Mohammed (1971).
3354:10.16995/TRAC1999_90_103
3116:Ad fines Africae romanae
2961:Constantine and Eusebius
2662:Morizot, Pierre (1989).
1722:Masuna was succeeded by
1612:(Romans) and the tribal
1329:within the Roman Empire.
3742:Mauretania Caesariensis
3598:established around the
3546:Reynolds, Paul (2010).
3419:Wickham, Chris (2005).
3135:Heather, Peter (2005).
2914:10.3406/antaf.1984.1105
2896:Camps, Gabriel (1984).
2708:Fisher & Drost 2016
2680:10.3406/antaf.1989.1164
2456:Fisher & Drost 2016
2131:Mauretania Caesariensis
2125:. Described himself as
2015:Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan
1785:Tiberius II Constantine
1416:Mauretania Caesariensis
1398:had already been under
1350:Mauretania Caesariensis
1327:Mauretania Caesariensis
1244:Mauretania Caesariensis
1173:History of North Africa
973:Independence referendum
912:Attack on Mers-el-Kébir
3267:Modéran, Yves (2010).
3202:: Volume 3, AD 527–641
3180:: Volume 2, AD 395–527
3070:Frank, Tenney (1959).
3027:. Ashgate Publishing.
3001:. Dover Publications.
2942:Baradez, Jean (1949).
2503:Laporte 2005, p. 394n.
2211:Byzantine North Africa
1939:
1651:
1330:
1302:conquest of the region
1223:
455:Iberomaurusian Culture
2948:L'Antiquité Classique
2902:Antiquités africaines
2668:Antiquités africaines
2087:Described himself as
1987:Sanhaja confederation
1905:
1828:No further expansion
1717:Mauretania Sitifensis
1640:
1623:claimed the title of
1324:
1079:High Council of State
859:(19th–20th centuries)
820:Emirate of Beni Abbas
807:(16th–19th centuries)
511:Archeology of Algeria
77:Common languages
3656:Kingdom of the Aurès
3616:Anglo-Saxon kingdoms
3509:Encyclopedie Berbere
3490:Encyclopedie Berbere
3273:Encyclopédie berbère
3244:. pp. 317–331.
3154:Lawless, R. (1969).
2749:Aguado Blazquez 2005
2201:Eastern Roman Empire
2196:Western Roman Empire
2101:Kingdom of the Aurès
2093:Eastern Roman Empire
1964:Kingdom of the Hodna
1960:Kingdom of Ouarsenis
1532:, titled himself as
1502:Kingdom of the Aurès
1408:Mauretania Tingitana
1392:Western Roman Empire
1346:Mauretania Tingitana
1279:Kingdom of the Aurès
1271:Eastern Roman Empire
629:Early African Church
610:Prefecture of Africa
594:Kingdom of the Aurès
368:Kingdom of the Hodna
354:Kingdom of Ouarsenis
326:Eastern Roman Empire
299:Western Roman Empire
234:Western Roman Empire
3712:Mauro-Roman Kingdom
3666:Ostrogothic kingdom
2881:History of the Wars
2842:, pp. 280–281.
2818:, pp. 509–510.
2772:Laporte 2005, p.396
2494:, pp. 199–224.
1968:Exarchate of Africa
1750:Possible continuity
1556:, in the region of
1261:of the neighboring
1215:Mauro-Roman Kingdom
837:Barbary Slave Trade
618:Exarchate of Africa
586:Mauro-Roman Kingdom
3757:Barbarian kingdoms
3691:Visigothic kingdom
3651:Kingdom of Odoacer
3621:Burgundian kingdom
3611:Alamannian kingdom
3596:Barbarian kingdoms
2206:Barbarian Kingdoms
1940:
1652:
1592:of Safar), Lidir (
1494:Arian Christianity
1379:province of Africa
1331:
1142:Outline of Algeria
1050:Algerian Civil War
849:Second Barbary War
805:Regency of Algiers
3699:
3698:
3676:Sub-Roman Britain
3646:Kingdom of Altava
3557:978-0-86054-782-2
3538:978-1-107-19839-5
3519:978-2-85744-282-0
3472:978-0-520-24490-0
3432:978-0-19-921296-5
3384:978-0-691-04945-8
3331:978-1-405-11980-1
3275:(30): 4678–4682.
3232:978-1-138-25268-4
3211:978-0-521-20159-9
3189:978-0-521-20159-9
3053:978-1-107-53072-0
3020:Albertini Tablets
2970:978-0-674-16531-1
2857:, pp. 19–52.
2751:, pp. 45–46.
2250:978-1-4674-2081-5
2216:Kingdom of Capsus
2187:
2186:
1999:Battle of Vescera
1991:Umayyad Caliphate
1944:Kingdom of Altava
1895:
1894:
1804:located south of
1706:King of the Aurès
1466:Barbarian kingdom
1426:frontier against
1384:Limes Mauretaniae
1306:Umayyad Caliphate
1294:Kingdom of Altava
1229:Kingdom of Masuna
1211:
1210:
1123:COVID-19 pandemic
844:First Barbary War
813:Ottoman governors
673:Umayyad Caliphate
602:Kingdom of Altava
402:
401:
384:
383:
380:
379:
340:Kingdom of Altava
318:
317:
16:(Redirected from
3779:
3762:Christian states
3626:Frankish kingdom
3600:Migration Period
3589:
3582:
3575:
3566:
3565:
3561:
3542:
3523:
3502:
3476:
3455:
3436:
3415:
3405:
3397:
3388:
3369:
3358:
3356:
3335:
3316:
3297:
3286:
3284:
3263:
3236:
3215:
3193:
3164:
3162:
3150:
3131:
3109:
3088:
3077:
3076:. Pageant Books.
3066:
3057:
3038:
3012:
2993:
2974:
2955:
2938:
2936:
2930:. Archived from
2929:
2917:
2885:
2858:
2852:
2843:
2837:
2831:
2825:
2819:
2813:
2807:
2794:Averil Cameron:
2792:
2786:
2779:
2773:
2770:
2764:
2758:
2752:
2746:
2740:
2734:
2728:
2722:
2711:
2705:
2699:
2693:
2684:
2683:
2659:
2653:
2647:
2641:
2635:
2626:
2620:
2611:
2605:
2594:
2588:
2582:
2576:
2570:
2564:
2558:
2552:
2543:
2537:
2528:
2522:
2516:
2515:, pp. 87–8.
2510:
2504:
2501:
2495:
2489:
2483:
2477:
2471:
2465:
2459:
2453:
2447:
2441:
2432:
2426:
2420:
2414:
2401:
2395:
2389:
2383:
2377:
2371:
2365:
2359:
2353:
2347:
2341:
2335:
2329:
2323:
2314:
2308:
2297:
2291:
2282:
2276:
2270:
2264:
2255:
2254:
2236:
2177:Unknown ruler(s)
2163:
2143:Unknown ruler(s)
2117:
2083:
2059:Unknown ruler(s)
2040:
2039:
2009:and withdraw to
1825:
1824:
1793:magister militum
1768:magistri militum
1578:Castra Severiana
1563:Castra Severiana
1377:conquest of the
1370:Fossatum Africae
1325:The province of
1263:Vandalic Kingdom
1226:
1203:
1196:
1189:
1168:
1155:
1106:2010s to present
1021:1965 coup d'état
1005:Contemporary era
871:French governors
789:
781:
773:
765:
757:
749:
741:
733:
725:
717:
709:
701:
693:
685:
677:
669:
639:Fossatum Africae
622:
614:
606:
598:
590:
582:
574:
561:
553:
545:
536:Ancient Carthage
467:
459:
451:
432:
422:
404:
403:
376:
375:
362:
361:
348:
347:
334:
322:
321:
309:
295:
288:
287:
272:
271:
245:• Death of
201:
187:
159:
143:
129:
59:
49:
32:
31:
21:
3787:
3786:
3782:
3781:
3780:
3778:
3777:
3776:
3752:Former kingdoms
3702:
3701:
3700:
3695:
3681:Suebian kingdom
3661:Lombard kingdom
3631:Frisian kingdom
3602:
3593:
3558:
3545:
3539:
3526:
3520:
3505:
3486:
3483:
3481:Further reading
3473:
3452:
3433:
3399:
3398:
3385:
3332:
3313:
3260:
3233:
3212:
3190:
3160:
3147:
3128:
3054:
3035:
3009:
2990:
2971:
2934:
2927:
2892:
2871:
2866:
2861:
2853:
2846:
2838:
2834:
2826:
2822:
2816:Martindale 1980
2814:
2810:
2793:
2789:
2780:
2776:
2771:
2767:
2759:
2755:
2747:
2743:
2737:Martindale 1992
2735:
2731:
2727:, pp. 217.
2723:
2714:
2706:
2702:
2696:Martindale 1992
2694:
2687:
2660:
2656:
2648:
2644:
2640:, p. 1172.
2638:Martindale 1992
2636:
2629:
2621:
2614:
2606:
2597:
2593:, p. 1171.
2591:Martindale 1992
2589:
2585:
2577:
2573:
2569:, pp. 198.
2565:
2561:
2555:Martindale 1980
2553:
2546:
2538:
2531:
2523:
2519:
2511:
2507:
2502:
2498:
2490:
2486:
2478:
2474:
2466:
2462:
2454:
2450:
2442:
2435:
2427:
2423:
2415:
2404:
2396:
2392:
2384:
2380:
2372:
2368:
2360:
2356:
2348:
2344:
2336:
2332:
2324:
2317:
2309:
2300:
2292:
2285:
2277:
2273:
2265:
2258:
2251:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2224:
2192:
2069:before Masuna.
2038:
2026:Aurès Mountains
2019:Battle of Mamma
1900:
1846:war with Persia
1819:
1773:John of Biclaro
1752:
1635:
1526:
1498:Aurès Mountains
1319:
1314:
1207:
1178:
1177:
1164:
1162:
1151:
1149:
1137:
1129:
1128:
1127:
1103:
1037:
1007:
997:
996:
995:
994:
917:Operation Torch
905:Cheikh Bouamama
890:Emir Abdelkader
866:French conquest
853:
832:Barbary pirates
825:Emirate of Kuku
801:
793:
792:
787:
779:
771:
763:
755:
747:
739:
731:
723:
715:
707:
699:
691:
683:
675:
667:
660:
650:
649:
648:
620:
612:
604:
596:
588:
580:
573:(146 BC–590 AD)
572:
559:
551:
543:
526:
516:
515:
506:
465:
463:Capsian culture
457:
449:
447:Aterian Culture
442:
420:
413:
395:
373:
359:
345:
259:
258:• Decline
249:
236:
203:
189:
173:
172:• 545–546
161:
145:
131:
85:African Romance
62:
42:
37:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3785:
3775:
3774:
3769:
3764:
3759:
3754:
3749:
3744:
3739:
3734:
3729:
3724:
3719:
3714:
3697:
3696:
3694:
3693:
3688:
3686:Vandal kingdom
3683:
3678:
3673:
3671:Rugian kingdom
3668:
3663:
3658:
3653:
3648:
3643:
3638:
3633:
3628:
3623:
3618:
3613:
3607:
3604:
3603:
3592:
3591:
3584:
3577:
3569:
3563:
3562:
3556:
3543:
3537:
3524:
3518:
3503:
3482:
3479:
3478:
3477:
3471:
3456:
3450:
3437:
3431:
3416:
3389:
3383:
3370:
3359:
3336:
3330:
3317:
3311:
3298:
3287:
3264:
3258:
3237:
3231:
3216:
3210:
3194:
3188:
3172:
3165:
3151:
3145:
3132:
3126:
3110:
3089:
3078:
3067:
3058:
3052:
3039:
3033:
3013:
3007:
2994:
2988:
2975:
2969:
2956:
2939:
2937:on 2011-07-07.
2918:
2908:(1): 183–218.
2891:
2888:
2887:
2886:
2870:
2867:
2865:
2862:
2860:
2859:
2844:
2832:
2820:
2808:
2787:
2774:
2765:
2761:Rushworth 2000
2753:
2741:
2739:, p. 504.
2729:
2712:
2700:
2698:, p. 851.
2685:
2674:(1): 263–284.
2654:
2642:
2627:
2625:, p. 126.
2612:
2610:, p. 143.
2595:
2583:
2581:, p. 127.
2571:
2559:
2557:, p. 734.
2544:
2529:
2527:, p. 280.
2517:
2505:
2496:
2484:
2482:, p. 281.
2472:
2470:, p. 130.
2460:
2448:
2446:, p. 326.
2433:
2421:
2402:
2400:, p. 195.
2390:
2388:, p. 335.
2378:
2366:
2354:
2352:, p. 162.
2342:
2340:, p. 457.
2330:
2315:
2313:, p. 327.
2298:
2294:Rushworth 2000
2283:
2281:, p. 361.
2271:
2269:, p. 170.
2256:
2249:
2230:
2228:
2225:
2223:
2220:
2219:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2198:
2191:
2188:
2185:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2173:
2172:
2167:Also known as
2165:
2159:
2151:
2150:
2147:
2145:
2139:
2138:
2121:Also known as
2119:
2113:
2105:
2104:
2097:Vandal Kingdom
2085:
2079:
2071:
2070:
2063:
2061:
2055:
2054:
2049:
2044:
2037:
2034:
1899:
1896:
1893:
1892:
1878:
1857:
1836:
1835:
1832:
1829:
1818:
1817:Incorporation?
1815:
1791:was posted as
1751:
1748:
1734:Constantinople
1634:
1631:
1598:
1597:
1525:
1522:
1354:Moulouya River
1318:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1209:
1208:
1206:
1205:
1198:
1191:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1170:
1157:
1144:
1138:
1136:Related topics
1135:
1134:
1131:
1130:
1126:
1125:
1120:
1118:Hirak Movement
1115:
1109:
1102:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1065:
1064:
1063:
1062:
1057:
1046:
1036:
1035:
1030:
1024:
1023:
1018:
1012:
1008:
1003:
1002:
999:
998:
993:
992:
987:
982:
976:
975:
970:
965:
960:
955:
950:
945:
940:
934:
925:
924:
919:
914:
908:
907:
902:
900:Mokrani Revolt
897:
895:Fatma N'Soumer
892:
886:
885:
880:
874:
873:
868:
862:
857:French Algeria
852:
851:
846:
840:
839:
834:
828:
827:
822:
816:
815:
809:
802:
799:
798:
795:
794:
791:
790:
788:(1235–1556 AD)
782:
780:(1229–1574 AD)
774:
772:(1215–1465 AD)
766:
764:(1121–1269 AD)
758:
756:(1040–1147 AD)
750:
748:(1014–1152 AD)
742:
734:
726:
718:
710:
702:
694:
686:
678:
670:
661:
656:
655:
652:
651:
647:
646:
641:
636:
631:
625:
624:
623:
615:
607:
599:
591:
583:
578:Vandal Kingdom
575:
562:
557:Jugurthine War
554:
546:
538:
533:
527:
522:
521:
518:
517:
514:
513:
505:
504:
499:
494:
488:
487:
486:
468:
460:
452:
443:
438:
437:
434:
433:
425:
424:
415:
414:
407:
400:
399:
390:
386:
385:
382:
381:
378:
377:
370:
364:
363:
356:
350:
349:
342:
336:
335:
328:
319:
316:
315:
313:Vandal Kingdom
310:
302:
301:
296:
284:
283:
278:
268:
267:
264:
263:
260:
257:
254:
253:
250:
244:
241:
240:
237:
231:
228:
227:
224:
223:
221:Late antiquity
218:
217:Historical era
214:
213:
210:
209:
204:
197:
194:
193:
190:
183:
180:
179:
174:
171:
168:
167:
162:
155:
152:
151:
146:
139:
136:
135:
132:
125:
122:
121:
118:
117:
114:
108:
107:
102:
98:
97:
92:
88:
87:
78:
74:
73:
68:
64:
63:
60:
52:
51:
44:
43:
38:
35:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3784:
3773:
3770:
3768:
3765:
3763:
3760:
3758:
3755:
3753:
3750:
3748:
3745:
3743:
3740:
3738:
3735:
3733:
3730:
3728:
3725:
3723:
3720:
3718:
3715:
3713:
3710:
3709:
3707:
3692:
3689:
3687:
3684:
3682:
3679:
3677:
3674:
3672:
3669:
3667:
3664:
3662:
3659:
3657:
3654:
3652:
3649:
3647:
3644:
3642:
3641:Hunnic empire
3639:
3637:
3636:Gepid kingdom
3634:
3632:
3629:
3627:
3624:
3622:
3619:
3617:
3614:
3612:
3609:
3608:
3605:
3601:
3597:
3590:
3585:
3583:
3578:
3576:
3571:
3570:
3567:
3559:
3553:
3549:
3544:
3540:
3534:
3530:
3525:
3521:
3515:
3511:
3510:
3504:
3500:
3496:
3492:
3491:
3485:
3484:
3474:
3468:
3464:
3463:
3457:
3453:
3451:0-415-91827-8
3447:
3444:. Routledge.
3443:
3438:
3434:
3428:
3424:
3423:
3417:
3413:
3409:
3403:
3395:
3390:
3386:
3380:
3376:
3371:
3367:
3366:
3360:
3355:
3350:
3346:
3342:
3337:
3333:
3327:
3323:
3318:
3314:
3312:0-415-17485-6
3308:
3305:. Routledge.
3304:
3299:
3295:
3294:
3288:
3283:
3278:
3274:
3270:
3265:
3261:
3259:9781444350012
3255:
3251:
3247:
3243:
3238:
3234:
3228:
3225:. Routledge.
3224:
3223:
3217:
3213:
3207:
3203:
3201:
3195:
3191:
3185:
3181:
3179:
3173:
3170:
3166:
3159:
3158:
3152:
3148:
3146:0-333-98914-7
3142:
3139:. Macmillan.
3138:
3133:
3129:
3127:9782356132147
3123:
3119:
3115:
3111:
3107:
3103:
3099:
3095:
3090:
3086:
3085:
3079:
3075:
3074:
3068:
3064:
3059:
3055:
3049:
3045:
3040:
3036:
3034:0-7546-4145-7
3030:
3026:
3022:
3021:
3014:
3010:
3008:0-486-20399-9
3004:
3000:
2995:
2991:
2989:0-7837-2221-4
2985:
2981:
2976:
2972:
2966:
2962:
2957:
2953:
2949:
2945:
2940:
2933:
2926:
2925:
2919:
2915:
2911:
2907:
2903:
2899:
2894:
2893:
2883:
2882:
2877:
2873:
2872:
2856:
2851:
2849:
2841:
2836:
2829:
2824:
2817:
2812:
2805:
2801:
2797:
2791:
2784:
2778:
2769:
2763:, p. 96.
2762:
2757:
2750:
2745:
2738:
2733:
2726:
2721:
2719:
2717:
2710:, p. 52.
2709:
2704:
2697:
2692:
2690:
2681:
2677:
2673:
2669:
2665:
2658:
2651:
2646:
2639:
2634:
2632:
2624:
2623:Grierson 1959
2619:
2617:
2609:
2604:
2602:
2600:
2592:
2587:
2580:
2579:Grierson 1959
2575:
2568:
2563:
2556:
2551:
2549:
2541:
2540:Rousseau 2012
2536:
2534:
2526:
2521:
2514:
2513:Merrills 2017
2509:
2500:
2493:
2488:
2481:
2476:
2469:
2468:Morcelli 1816
2464:
2458:, p. 49.
2457:
2452:
2445:
2444:Merrills 2022
2440:
2438:
2430:
2425:
2418:
2417:Merrills 2017
2413:
2411:
2409:
2407:
2399:
2394:
2387:
2382:
2376:, p. 18.
2375:
2370:
2364:, p. 68.
2363:
2358:
2351:
2346:
2339:
2334:
2327:
2322:
2320:
2312:
2311:Merrills 2022
2307:
2305:
2303:
2296:, p. 95.
2295:
2290:
2288:
2280:
2279:Hamdoune 2018
2275:
2268:
2263:
2261:
2252:
2246:
2242:
2235:
2231:
2217:
2214:
2212:
2209:
2207:
2204:
2202:
2199:
2197:
2194:
2193:
2182:
2180:
2178:
2175:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2160:
2158:
2157:
2153:
2152:
2148:
2146:
2144:
2141:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2120:
2114:
2112:
2111:
2107:
2106:
2102:
2098:
2094:
2090:
2086:
2080:
2078:
2077:
2073:
2072:
2068:
2064:
2062:
2060:
2057:
2056:
2053:
2050:
2048:
2045:
2042:
2041:
2033:
2031:
2027:
2022:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2004:
2000:
1996:
1995:Uqba ibn Nafi
1992:
1988:
1984:
1980:
1975:
1973:
1969:
1965:
1961:
1957:
1953:
1949:
1945:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1925:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1904:
1891:
1888:
1885:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1871:
1868:
1865:
1863:
1858:
1856:
1853:
1851:
1847:
1842:
1838:
1837:
1833:
1830:
1827:
1826:
1823:
1814:
1811:
1807:
1803:
1797:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1769:
1764:
1759:
1757:
1747:
1745:
1744:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1730:
1725:
1720:
1718:
1714:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1682:
1680:
1676:
1674:
1670:
1666:
1661:
1658:
1650:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1630:
1628:
1627:
1622:
1617:
1615:
1611:
1606:
1604:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1582:
1581:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1570:
1565:
1564:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1546:
1544:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1521:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1486:
1482:
1477:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1462:
1458:
1457:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1419:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1405:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1388:
1386:
1385:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1371:
1366:
1362:
1357:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1328:
1323:
1309:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1282:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1255:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1240:ancient Roman
1237:
1234:
1230:
1225:
1220:
1216:
1204:
1199:
1197:
1192:
1190:
1185:
1184:
1182:
1181:
1174:
1171:
1167:
1161:
1158:
1154:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1140:
1139:
1133:
1132:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1114:
1111:
1110:
1108:
1107:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1094:Peace Charter
1092:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1084:Civil Concord
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1066:
1061:
1058:
1056:
1053:
1052:
1051:
1048:
1047:
1045:
1044:
1043:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1028:Berber Spring
1026:
1025:
1022:
1019:
1017:
1016:FFS rebellion
1014:
1013:
1011:
1006:
1001:
1000:
991:
988:
986:
983:
981:
978:
977:
974:
971:
969:
968:Évian Accords
966:
964:
961:
959:
956:
954:
951:
949:
946:
944:
941:
939:
936:
935:
933:
932:
930:
923:
920:
918:
915:
913:
910:
909:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
887:
884:
881:
879:
876:
875:
872:
869:
867:
864:
863:
861:
860:
858:
850:
847:
845:
842:
841:
838:
835:
833:
830:
829:
826:
823:
821:
818:
817:
814:
811:
810:
808:
806:
797:
796:
786:
783:
778:
775:
770:
767:
762:
759:
754:
751:
746:
743:
740:(973–1152 AD)
738:
735:
732:(970–1068 AD)
730:
727:
724:(909–1171 AD)
722:
719:
714:
711:
706:
703:
698:
695:
690:
687:
684:(742–1066 AD)
682:
679:
674:
671:
666:
665:Arab conquest
663:
662:
659:
654:
653:
645:
642:
640:
637:
635:
632:
630:
627:
626:
619:
616:
611:
608:
603:
600:
595:
592:
587:
584:
579:
576:
571:
567:
563:
558:
555:
550:
547:
542:
539:
537:
534:
532:
529:
528:
525:
520:
519:
512:
508:
507:
503:
500:
498:
495:
493:
490:
489:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
464:
461:
456:
453:
448:
445:
444:
441:
436:
435:
431:
427:
426:
423:
417:
416:
411:
406:
405:
398:
394:
391:
389:Today part of
387:
371:
369:
366:
365:
357:
355:
352:
351:
343:
341:
338:
337:
333:
329:
327:
324:
323:
320:
314:
311:
308:
304:
303:
300:
297:
294:
290:
289:
286:
285:
282:
279:
277:
274:
273:
269:
265:
261:
255:
251:
248:
242:
238:
235:
229:
225:
222:
219:
215:
211:
208:
205:
195:
191:
184:• 546 –
181:
178:
175:
169:
166:
163:
153:
150:
147:
137:
133:
123:
119:
115:
113:
109:
106:
103:
99:
96:
93:
89:
86:
82:
79:
75:
72:
69:
65:
58:
53:
45:
41:
33:
30:
19:
3645:
3547:
3528:
3508:
3489:
3461:
3441:
3421:
3393:
3374:
3364:
3347:(1999): 90.
3344:
3321:
3302:
3292:
3272:
3241:
3221:
3198:
3176:
3168:
3156:
3136:
3117:
3114:
3097:
3093:
3083:
3072:
3062:
3043:
3024:
3017:
2998:
2979:
2960:
2951:
2947:
2932:the original
2923:
2905:
2901:
2880:
2864:Bibliography
2835:
2828:Lawless 1969
2823:
2811:
2803:
2799:
2795:
2790:
2782:
2777:
2768:
2756:
2744:
2732:
2703:
2671:
2667:
2657:
2645:
2586:
2574:
2562:
2520:
2508:
2499:
2487:
2475:
2463:
2451:
2424:
2398:Heather 2005
2393:
2386:Wickham 2005
2381:
2374:Wickham 2005
2369:
2357:
2350:Baradez 1949
2345:
2338:Talbert 2000
2333:
2326:Modéran 2010
2274:
2267:Wolfram 2005
2240:
2234:
2176:
2168:
2154:
2142:
2126:
2122:
2108:
2095:against the
2088:
2074:
2066:
2058:
2051:
2046:
2023:
1976:
1971:
1948:Christianity
1941:
1889:
1886:
1883:
1880:
1875:
1872:
1869:
1866:
1859:
1854:
1843:
1840:
1820:
1798:
1792:
1766:
1760:
1753:
1741:
1737:
1727:
1721:
1710:
1683:
1677:
1673:client kings
1669:Vandalic War
1662:
1653:
1648:
1624:
1618:
1613:
1609:
1607:
1602:
1599:
1585:
1577:
1567:
1561:
1554:Ouled Mimoun
1547:
1542:
1537:
1533:
1527:
1478:
1454:
1452:
1420:
1389:
1382:
1368:
1358:
1336:and western
1332:
1283:
1275:Vandalic War
1256:
1242:province of
1228:
1214:
1212:
1105:
1104:
1089:Black Spring
1039:
1038:
1009:
929:Algerian War
927:
926:
883:Pacification
855:
854:
803:
800:Modern times
716:(800–909 AD)
708:(789–828 AD)
700:(776–909 AD)
692:(771–793 AD)
676:(703–744 AD)
668:(647–709 AD)
621:(585–698 AD)
613:(534–585 AD)
605:(578–708 AD)
597:(484–703 AD)
589:(477–578 AD)
585:
581:(435–534 AD)
560:(111–106 BC)
552:(264–146 BC)
470:Rock art in
281:Succeeded by
280:
275:
95:Christianity
39:
29:
3100:: 119–130.
2840:Conant 2012
2785:p. 47.
2525:Conant 2012
2492:Conant 2004
2480:Graham 1902
1779:attacks in
1252:Roman Italy
1113:Arab Spring
990:Oujda Group
980:Pieds-noirs
963:1961 putsch
958:1958 crisis
938:Nationalism
931:(1954–1962)
689:Muhallabids
658:Middle Ages
544:(202–46 BC)
466:(10,000 BC)
458:(20,000 BC)
450:(80,000 BC)
419:History of
276:Preceded by
3706:Categories
3296:. Brescia.
2855:Talbi 1971
2725:Camps 1984
2650:Camps 1984
2567:Camps 1984
2362:Frank 1959
2222:References
2164:570 – 578
1594:procurator
1510:Thrasamund
1506:Gunthamund
1432:Visigothic
1396:Mauretania
1334:Mauretania
1317:Background
1300:until the
1033:1988 riots
878:Resistance
753:Almoravids
566:Mauretania
549:Punic Wars
440:Prehistory
202:570 – 578
101:Government
3402:cite book
2876:Procopius
2802:Band 14:
2608:Bury 1958
2429:Procopius
2227:Citations
2011:Cyrenaica
1972:foederati
1912:Ouarsenis
1850:Khosrow I
1810:Volubilis
1789:Gennadius
1665:Procopius
1626:Imperator
1481:Procopius
1470:Visigoths
1461:romanized
1456:foederati
1233:Christian
1060:Massacres
1010:1960s–80s
785:Ziyyanids
745:Hammadids
729:Maghrawas
713:Aghlabids
697:Rustamids
531:Phoenicia
524:Antiquity
509:Related:
497:Madghacen
192:(unknown)
134:(unknown)
91:Religion
3269:"Masuna"
3106:42662366
2190:See also
2169:Garmules
2135:Caesarea
2123:Mastinas
2110:Mastigas
2043:Monarch
2007:Kairouan
1962:and the
1936:Tripolis
1924:Nemencha
1777:Visigoth
1724:Mastigas
1686:Byzacena
1646:Mastigas
1642:Monogram
1552:(modern
1516:, named
1514:Tripolis
1485:Gaiseric
1428:Germania
1412:Caesarea
1361:Germania
1342:Claudius
1231:, was a
1055:Timeline
769:Marinids
761:Almohads
721:Fatimids
705:Idrisids
681:Ifranids
644:Gemellae
634:Partenia
410:a series
408:Part of
247:Gaiseric
165:Mastigas
105:Monarchy
2869:Ancient
1979:Kusaila
1932:Dorsale
1756:Tlemcen
1713:Ortaias
1698:Numidia
1694:Solomon
1679:Gelimer
1621:Masties
1603:castrum
1590:prefect
1574:diocese
1490:Huneric
1474:Vandals
1440:Vandals
1338:Numidia
1312:History
1304:by the
1298:Maghreb
1259:Vandals
777:Hafsids
541:Numidia
484:Ahaggar
480:Tassili
421:Algeria
397:Morocco
393:Algeria
262:578-599
198:•
156:•
140:•
126:•
67:Capital
3554:
3535:
3516:
3469:
3448:
3429:
3381:
3328:
3309:
3256:
3229:
3208:
3186:
3143:
3124:
3104:
3050:
3031:
3005:
2986:
2967:
2890:Modern
2247:
2156:Garmul
2076:Masuna
2030:Kahina
2003:Biskra
1956:Altava
1928:Capsus
1908:Altava
1898:Legacy
1806:Tiaret
1802:Jedars
1781:Spania
1763:Garmul
1702:Iabdas
1610:Romani
1550:Altava
1530:Masuna
1518:Cabaon
1436:Alaric
1404:Septem
1400:Berber
1375:Vandal
1365:Persia
1286:Garmul
1267:Masuna
1248:Altava
1236:Berber
1040:1990s–
985:Harkis
737:Zirids
570:Africa
564:Roman
502:Jedars
492:Roknia
476:Djelfa
412:on the
207:Garmul
149:Masuna
116:
81:Berber
71:Altava
3161:(PDF)
3102:JSTOR
2935:(PDF)
2928:(PDF)
2052:Notes
2047:Reign
2001:near
1920:Aurès
1916:Hodna
1862:Tobna
1657:Alans
1614:Mauri
1569:Safar
1448:Suebi
1444:Alans
1424:Rhine
1219:Latin
1042:2000s
3552:ISBN
3533:ISBN
3514:ISBN
3467:ISBN
3446:ISBN
3427:ISBN
3412:link
3408:link
3379:ISBN
3326:ISBN
3307:ISBN
3254:ISBN
3227:ISBN
3206:ISBN
3184:ISBN
3141:ISBN
3122:ISBN
3048:ISBN
3029:ISBN
3003:ISBN
2984:ISBN
2965:ISBN
2245:ISBN
2118:541
2084:508
1934:and
1649:Dux.
1566:and
1558:Oran
1508:and
1472:and
1446:and
1363:and
1213:The
953:GPRA
943:RCUA
568:and
482:and
472:Oran
188:570
177:John
160:541
144:508
130:477
112:King
3495:doi
3349:doi
3277:doi
3246:doi
2910:doi
2676:doi
2127:dux
2089:rex
2067:rex
1743:rex
1740:or
1738:dux
1729:dux
1644:of
1543:rex
1538:rex
1414:in
1406:in
1387:.
1356:.
1074:GIA
1069:FIS
948:FLN
252:477
239:429
50:477
3708::
3404:}}
3400:{{
3343:.
3271:.
3252:.
3098:19
3096:.
2952:19
2950:.
2946:.
2906:20
2904:.
2900:.
2847:^
2715:^
2688:^
2672:25
2670:.
2666:.
2630:^
2615:^
2598:^
2547:^
2532:^
2436:^
2405:^
2318:^
2301:^
2286:^
2259:^
2162:c.
2137:.
2116:c.
2103:.
2082:c.
1930:,
1926:,
1922:,
1918:,
1914:,
1910:,
1746:.
1708:.
1704:,
1692:,
1605:.
1442:,
1344:;
1281:.
1221::
478:,
474:,
200:c.
186:c.
158:c.
142:c.
128:c.
83:,
48:c.
3588:e
3581:t
3574:v
3560:.
3541:.
3522:.
3501:.
3497::
3475:.
3454:.
3435:.
3414:)
3387:.
3357:.
3351::
3334:.
3315:.
3285:.
3279::
3262:.
3248::
3235:.
3214:.
3192:.
3163:.
3149:.
3130:.
3108:.
3056:.
3037:.
3011:.
2992:.
2973:.
2916:.
2912::
2884:.
2830:.
2682:.
2678::
2652:.
2542:.
2431:.
2419:.
2328:.
2253:.
1938:.
1217:(
1202:e
1195:t
1188:v
1169:)
1163:(
1156:)
1150:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.