362:, owing to their exposition to the perturbations coming from the North Atlantic Ocean. These regions are relatively humid with irregular precipitations but occasionally torrential. The annual rainfall is between 600 and 1,000 mm (24 and 39 in). The drought in the summer months, interrupted by thunderstorms, is usually intense. Snow falls between November and April, but can persist from September to June in the peaks. Important rivers flow through the valleys (including Asif Melloul, Oued n'Fis, and Oued Tessaout) supply the fertile basins like Aït Bou Guemez and Imilchil. These conditions allow the existence of pine, oak and cedar forests. However, these forests are declining because of the reducing of annual precipitation, over-exploitation of the trees (used for construction and heating), and sheep-goat
91:
25:
1287:
170:
804:
400:
332:
377:, and is present in the southern part of the Central High Atlas, from Toubkal to Imilchil, and the whole Oriental High-Atlas down of Imilchil. These regions are marked by variations in temperatures. It extends southward from the steppe lands into rocky desert. In addition, some localized valleys supplied by irrigation make agriculture possible. Forests are almost rare. This portion of High-Atlas is very similar to the
493:
323:
lands into fertile valleys called locally by Agdal (garden in Berber). This technique has intrigued many
Western agriculturalists, in which they were impressed by the high efficiency of this agricultural system. Many scientists, particularly French scientists, make yearly expeditions to observe the community and their living system.
639:
Following the
Triassic red bed deposition, marine conditions prevailed during the Early and Middle Jurassic resulting in the development of carbonate and mixed depositional systems. The Jurassic Atlas basin was open to the east (western Tethys realm) with Paleozoic provenance areas located toward the
322:
The High-Atlas
Mountains are inhabited by Berbers, who live from agriculture and pastoralism in the valleys. In the steppe zone of the High-Atlas, where precipitations are low, the locals created a smart technique in managing the low precipitations and the weak soil. They turn the rather semi-arid
655:
times, resulting in north to south compartmentalization of the basin. Pliensbachian carbonate platforms preferentially developed in the margins basin and in synsedimentary structural highs, promoting abrupt transitions in the marine sedimentary record from shallow water to basinal facies.
720:
red beds record the sedimentation of continental to shallow marine transitional deposits that characterize the central High Atlas domain. Fully marine environmental conditions and platform carbonate deposits, which locally crop out in the margins of the Atlas System, dominated between
685:
developed in the margins of the central High Atlas basin, whereas the basin axis was occupied by a mixed carbonate-siliciclastic platform system prograding eastward to basinal deposits. This mixed system progressively graded to an extensive shallow water carbonate platform of the
587:, an area of pre-Mesozoic basement exposures located south of Marrakesh. The central and eastern High Atlas basin developed as a multiphase rift system opened toward the east by two major rift episodes occurring during Middle-Late Triassic and Early Jurassic (late
602:
Subordinate NW-SE trending structural highs bounding equal-trend synclines are also present. Cretaceous and later syntectonic
Tertiary units are also locally present (e.g., Miocene-Pliocene La Cathédrale conglomerates and sandstones).
1202:
1264:
853:. The formation is composed of rounded columns patterned with horizontal ridges that occurred as a result of erosion, which caused travellers to nickname it "the Cathedral", for its resemblance to a
464:
A solid chalk mass morphologically dominated by tabular zones reaching an altitude of 2,500 m (8,200 ft) extends from Azilal to
Ouarzazate. Here, the contrasting landscapes are similar to
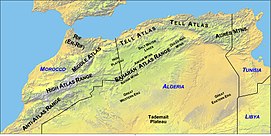
576:. The Moroccan Atlas is formed by the ENE-WSW-striking High Atlas and the NE-SW-trending Middle Atlas. The former is divided into three segments named western, central, and eastern High Atlas.
315:
The High Atlas forms the basins for a multiplicity of river systems. The majority of the year-round rivers flow to the north, providing the basis for the settlements there. A number of
681:
occurred in close association with regional drowning of the lower
Liassic platforms and localized deposition of basinal marls. From Toarcian times, carbonate platforms of the
982:
Allain, Ronan; Najat
Aquesbi; Jean Dejax; Christian Meyer; Michel Monbaron; Christian Montenat; Philippe Richir; Mohammed Rochdy; Dale Russell; Philippe Taquet (2004).
595:. At present, the central High Atlas is characterized by a folded domain that is dominated by NE-SW striking structural highs or ridges separating elongated and wide
565:
1178:
1148:
584:
130:
1323:
674:
199:
304:
from the
Mediterranean and continental zones to the north and west. In the higher elevations of the massif, snow falls regularly, allowing
648:) that progressively backstepped toward the basin margins, to more localized platform development flanking the depocenters (Sinemurian).
983:
531:
308:. Snow lasts well into late spring in the High Atlas, mostly on the northern faces of the range. On the Western High Atlas, there is
1235:
895:
890:
616:
1044:"The oldest Gondwanan record of the extinct durophagous hybodontiform chondrichthyan, Strophodus from the Bajocian of Morocco"
281:
border. At the
Atlantic and to the southwest the range drops abruptly and makes an impressive transition to the coast and the
511:. This portion of the range includes the solid mass of the Tamlelt whose northern edge is occupied by its higher peaks, such
1328:
885:
413:
In the west lies the oldest portion of the range. Its high point is the Jbel
Toubkal, which is visible from the city of
1123:
515:
at 3,747 m (12,293 ft). The altitude falls towards the east where the mountains join the pre-Saharan zone.
68:
46:
1304:
39:
476:, and peaks sometimes splintered by erosion. Several peaks in this area exceed 4,000 m (13,000 ft), with
1263:. Nouveaux guides geologiques et miniers du Maroc - New Geological and Mining Guidebooks of Morocco. Vol. 7.
625:, the central High Atlas extensional basin was characterized by the synrift deposition of red beds and localized
640:
west and south. Liassic sedimentary systems evolved from extensive peritidal shallow water carbonate platforms (
534:, where it was discovered. The creature, about 15 metres (49 feet) long, is postulated to be an ancestor of the
1140:
503:
The eastern part of the High Atlas forms vast plateaux at high altitude which provide the headwaters for the
90:
849:
At approximately mid-range, the Amesfrane Rock Wall rises some 1,650 feet (500 m) from a dry riverbed
192:
123:
1237:
Rift opening and inversion in the Marrakech High Atlas - integrated structural and thermochronologic study
1203:"Diapiric growth within an Early Jurassic rift basin: The Tazoult salt wall (central High Atlas, Morocco)"
518:
This massif became an internationally famous paleontological site after the discovery of the bones of a
456:. The Ourika Valley is also a location where a diverse flora was recorded as early as the 19th century.
1042:
Stumpf, Sebastian; Kettler, Christoph; Kindlimann, René; Cuny, Gilles; Kriwet, Jürgen (December 2023).
319:
and seasonal rivers terminate in the deserts to the south and plateaux to the east of the mountains.
417:. Jbel Toubkal lies in the Toubkal national park, which was created in 1942. The massif consists of
538:
found in America. Until 140 million years ago, the African and American continents were connected.
33:
1244:
1093:
1273:
296:, which at 4,167 m (2.589 mi; 13,671 ft) is the highest in the range and lies in
836:
707:
300:. The range serves as a weather system barrier in Morocco running east–west and separating the
50:
407:
382:
347:
297:
238:
998:
1022:
480:
at 4068 m being the highest peak in this part of the High Atlas. The area is populated by
8:
1207:
854:
546:
The Atlas Mountains define an ENE-WSW trending intracontinental belt, resulting from the
1002:
860:
Among the summits at a height of 1,600 m (5,200 ft) height lies the Kasbah of
1290:
1083:
938:
Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences à Paris, Sciences de la Terre et des Planètes
547:
425:
formations notched by deep erosion-carved valleys. This part of the range includes the
1269:
1119:
1065:
1014:
669:
1224:
1055:
1006:
717:
687:
682:
816:
1308:
936:
n.g., n.sp., a brachiosaurid-like sauropod from the Middle Jurassic of Morocco".
846:, fortified village) still in use. The ksar is widely used in the film industry.
827:
824:
771:
713:
555:
437:
378:
267:
869:
1060:
1043:
1010:
580:
573:
504:
374:
340:
274:
255:
231:
526:', which populated Morocco 180 million years ago. This dinosaur is also named
1317:
1089:
1069:
1018:
752:
652:
592:
569:
551:
527:
481:
469:
426:
214:
201:
145:
132:
981:
309:
169:
787:
specimen of this genus at the time of discovery. The new species was named
665:
612:
445:
403:
355:
351:
305:
293:
263:
175:
106:
1286:
1118:. United States of America: Reader's Digest Association, Inc. p. 42.
1301:
1228:
873:
512:
363:
1296:
803:
775:
758:
726:
645:
641:
588:
558:
523:
430:
422:
282:
865:
767:
748:
695:
633:
626:
535:
477:
414:
399:
370:
286:
331:
792:
784:
780:
763:
745:
741:
691:
678:
622:
596:
562:
519:
508:
465:
418:
359:
861:
496:
492:
453:
433:
350:, dominates the north and south of the Western High Atlas until (
278:
259:
583:
and is separated from the central and eastern High Atlas by the
444:, is found; however, this primate is also found in parts of the
808:
737:
722:
630:
473:
301:
113:
984:"A basal sauropod dinosaur from the Early Jurassic of Morocco"
770:
deposits of this range, respectively. In 2023, a fossil of a
698:
in age that is recognized throughout the central High Atlas.
1041:
850:
820:
651:
Normal faulting and block tilting increased notably during
354:), as well as the northern part of Central High Atlas from
316:
579:
The western High Atlas was part of the Atlantic Jurassic
449:
429:, which is the only location in the High Atlas where the
1186:
Joseph Dalton Hooker, John Ball and George Maw (1878)
277:
and stretches in an eastern direction to the Moroccan-
1114:
Scheffel, Richard L.; Wernet, Susan J., eds. (1980).
932:
M. Monbaron, D. A. Russell, and P. Taquet. (1999). "
923:
Joseph Dalton Hooker, John Ball and George Maw, 1878
841:
1233:
1265:Ministry of Energy, Mining, Water and Environment
677:during the latest Pliensbachian and the earliest
1315:
1188:Journal of a Tour in Morocco and the Great Atlas
968:
966:
964:
962:
952:
950:
948:
946:
1037:
1035:
599:filled by Early and Middle Jurassic sediments.
1113:
744:animals are known from High Atlas. Remains of
1200:
1107:
959:
943:
312:, one of three main ski stations in Morocco.
1032:
1297:Photo Gallery of Morocco and the High Atlas
1182:, Globaltwitcher.com, ed. Nicklas Stromberg
1085:Desert Film Set - Sahara with Michael Palin
1141:"Natural wonders of the Maghreb (Morocco)"
1059:
285:range. To the north, in the direction of
69:Learn how and when to remove this message
1201:Martín Martín, J.D; et al. (2016).
815:At the foot of the High Atlas one finds
802:
783:deposits of High Atlas. It's the oldest
491:
398:
330:
273:The High Atlas rises in the west at the
32:This article includes a list of general
1194:
1171:
926:
896:Mediterranean High Atlas juniper steppe
891:Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests
174:Location of the Atlas Mountains across
1324:Mountain ranges of the Atlas Mountains
1316:
1258:
791:, after the mountain range where its
487:
472:, with high plateaux, gorges and box
459:
394:
1138:
798:
606:
289:, the range descends less abruptly.
18:
1234:Domènech Verdaguer, Mireia (2015).
886:Mediterranean woodlands and forests
831:
530:, after the name of the village of
13:
1259:Medina, Fida; et al. (2011).
1190:, Macmillan and company, 499 pages
617:Triassic–Jurassic extinction event
38:it lacks sufficient corresponding
14:
1340:
1279:
868:. The canyons and ravines of the
16:Mountain range in central Morocco
1285:
1180:Barbary Macaque: Macaca sylvanus
168:
89:
23:
1166:
1151:from the original on 2018-06-23
1132:
1096:from the original on 2021-12-12
972:Martín Martín et al., 2016, p.5
956:Martín Martín et al., 2016, p.4
811:in the Dades valley, High Atlas
732:
389:
1076:
1048:Swiss Journal of Palaeontology
975:
917:
908:
507:. It extends from the town of
1:
901:
876:are also points of interest.
701:
118:4,167 m (13,671 ft)
1293:travel guide from Wikivoyage
1116:Natural Wonders of the World
7:
879:
842:
659:
10:
1345:
1329:Mountain ranges of Morocco
1061:10.1186/s13358-023-00270-w
1011:10.1016/j.crpv.2004.03.001
705:
663:
610:
541:
326:
266:, the highest part of the
499:in the eastern High Atlas
230:
191:
183:
166:
161:
122:
112:
102:
97:
88:
83:
1245:Universitat de Barcelona
1177:C. Michael Hogan (2008)
779:was collected from the
339:There are two types of
53:more precise citations.
1302:Accommodation in Imlil
991:Comptes Rendus Palevol
914:C. Michael Hogan, 2008
812:
708:Ksar Metlili Formation
500:
452:, as well as parts of
410:
336:
1261:Haut Atlas Occidental
806:
789:Strophodus atlasensis
495:
408:Toubkal National Park
402:
383:western United States
348:Mediterranean climate
334:
298:Toubkal National Park
239:Atlas Mountain System
1229:10.1002/2016TC004300
1195:Geology publications
1172:Ecology publications
712:Finally, the middle
629:capped by extensive
146:31.06194°N 7.91611°W
1139:UKGE (2016-06-07).
1028:on October 7, 2022.
1003:2004CRPal...3..199A
934:Atlasaurus imelakei
343:in the High Atlas:
292:The range includes
211: /
142: /
1307:2011-06-04 at the
813:
762:were found in the
548:tectonic inversion
501:
488:Eastern High Atlas
460:Central High Atlas
411:
395:Western High Atlas
337:
250:, also called the
151:31.06194; -7.91611
98:Highest point
1267:. pp. 1–106.
1145:Deposits Magazine
840:
799:Areas of interest
670:Toarcian turnover
607:Triassic-Jurassic
244:
243:
193:Range coordinates
79:
78:
71:
1336:
1289:
1268:
1255:
1253:
1252:
1247:. pp. 1–157
1242:
1223:
1221:
1220:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1156:
1136:
1130:
1129:
1111:
1105:
1104:
1102:
1101:
1080:
1074:
1073:
1063:
1039:
1030:
1029:
1027:
1021:. Archived from
988:
979:
973:
970:
957:
954:
941:
930:
924:
921:
915:
912:
855:gothic cathedral
845:
835:
833:
718:Lower Cretaceous
688:Anoual Formation
683:Azilal Formation
585:Paleozoic Massif
234:
226:
225:
223:
222:
221:
216:
215:31.433°N 6.933°W
212:
209:
208:
207:
204:
172:
157:
156:
154:
153:
152:
147:
143:
140:
139:
138:
135:
93:
81:
80:
74:
67:
63:
60:
54:
49:this article by
40:inline citations
27:
26:
19:
1344:
1343:
1339:
1338:
1337:
1335:
1334:
1333:
1314:
1313:
1309:Wayback Machine
1282:
1250:
1248:
1240:
1218:
1216:
1197:
1174:
1169:
1164:
1163:
1154:
1152:
1137:
1133:
1126:
1112:
1108:
1099:
1097:
1082:
1081:
1077:
1040:
1033:
1025:
986:
980:
976:
971:
960:
955:
944:
931:
927:
922:
918:
913:
909:
904:
882:
864:on the road to
801:
735:
710:
704:
672:
662:
619:
609:
574:Eurasian Plates
556:Middle Jurassic
544:
490:
462:
442:Macaca sylvanus
438:Barbary macaque
397:
392:
379:Rocky Mountains
341:Alpine Climates
329:
268:Atlas Mountains
232:
219:
217:
213:
210:
205:
202:
200:
198:
197:
179:
178:
150:
148:
144:
141:
136:
133:
131:
129:
128:
75:
64:
58:
55:
45:Please help to
44:
28:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1342:
1332:
1331:
1326:
1312:
1311:
1299:
1294:
1281:
1280:External links
1278:
1277:
1276:
1256:
1243:(PhD thesis).
1231:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1184:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1131:
1124:
1106:
1092:. 2007-09-17.
1075:
1031:
997:(3): 199–208.
974:
958:
942:
925:
916:
906:
905:
903:
900:
899:
898:
893:
888:
881:
878:
800:
797:
734:
731:
703:
700:
661:
658:
608:
605:
581:passive margin
543:
540:
505:Moulouya River
489:
486:
461:
458:
396:
393:
391:
388:
387:
386:
375:steppe climate
367:
328:
325:
275:Atlantic Ocean
256:mountain range
242:
241:
236:
228:
227:
220:31.433; -6.933
195:
189:
188:
185:
181:
180:
173:
167:
164:
163:
159:
158:
126:
120:
119:
116:
110:
109:
104:
100:
99:
95:
94:
86:
85:
77:
76:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1341:
1330:
1327:
1325:
1322:
1321:
1319:
1310:
1306:
1303:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1283:
1275:
1271:
1266:
1262:
1257:
1246:
1239:
1238:
1232:
1230:
1226:
1214:
1210:
1209:
1204:
1199:
1198:
1189:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1176:
1175:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1135:
1127:
1125:0-89577-087-3
1121:
1117:
1110:
1095:
1091:
1090:BBC Worldwide
1087:
1086:
1079:
1071:
1067:
1062:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1038:
1036:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
985:
978:
969:
967:
965:
963:
953:
951:
949:
947:
939:
935:
929:
920:
911:
907:
897:
894:
892:
889:
887:
884:
883:
877:
875:
871:
867:
863:
858:
856:
852:
847:
844:
838:
829:
826:
822:
818:
817:Aït Benhaddou
810:
805:
796:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
777:
773:
772:hybodontiform
769:
765:
761:
760:
755:
754:
753:Tazoudasaurus
750:
747:
743:
739:
730:
728:
724:
719:
715:
709:
699:
697:
693:
689:
684:
680:
676:
675:Global anoxia
671:
667:
657:
654:
653:Pliensbachian
649:
647:
643:
637:
635:
632:
628:
624:
618:
614:
604:
600:
598:
594:
593:Pliensbachian
590:
586:
582:
577:
575:
571:
567:
564:
560:
557:
553:
552:Late Triassic
549:
539:
537:
533:
529:
528:Tazoudasaurus
525:
521:
516:
514:
510:
506:
498:
494:
485:
483:
479:
475:
471:
470:United States
467:
457:
455:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
432:
428:
427:Ourika Valley
424:
420:
416:
409:
405:
401:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
346:
345:
344:
342:
333:
324:
320:
318:
313:
311:
307:
306:winter sports
303:
299:
295:
290:
288:
284:
280:
276:
271:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
240:
237:
235:
229:
224:
196:
194:
190:
186:
182:
177:
171:
165:
160:
155:
127:
125:
121:
117:
115:
111:
108:
105:
101:
96:
92:
87:
82:
73:
70:
62:
52:
48:
42:
41:
35:
30:
21:
20:
1260:
1249:. Retrieved
1236:
1217:. Retrieved
1212:
1206:
1187:
1179:
1167:Bibliography
1153:. Retrieved
1144:
1134:
1115:
1109:
1098:. Retrieved
1084:
1078:
1051:
1047:
1023:the original
994:
990:
977:
940:329:519-526.
937:
933:
928:
919:
910:
859:
848:
814:
788:
774:
757:
751:
736:
733:Paleontology
711:
673:
666:Azilal Group
650:
638:
620:
613:Argana Group
601:
578:
568:between the
545:
517:
502:
463:
446:Middle Atlas
441:
412:
404:Jbel Toubkal
390:Subdivisions
369:Continental
356:Jbel Toubkal
352:Jbel Toubkal
338:
321:
314:
294:Jbel Toubkal
291:
272:
264:North Africa
251:
247:
245:
233:Parent range
176:North Africa
107:Jbel Toubkal
65:
56:
37:
795:was found.
621:During the
566:convergence
561:during the
513:Jbel Ayachi
364:overgrazing
258:in central
252:Grand Atlas
218: /
149: /
124:Coordinates
51:introducing
1318:Categories
1291:High Atlas
1251:2020-03-28
1219:2020-03-28
1155:2017-02-11
1100:2017-02-11
902:References
776:Strophodus
759:Atlasaurus
727:Cenomanian
706:See also:
702:Cretaceous
664:See also:
646:Sinemurian
642:Hettangian
634:lava flows
627:evaporites
611:See also:
589:Sinemurian
559:rift basin
524:Atlasaurus
478:Jbel Mgoun
431:endangered
423:Cretaceous
335:High Atlas
310:Oukaïmeden
283:Anti-Atlas
248:High Atlas
134:31°03′43″N
84:High Atlas
34:references
1274:0374-9789
1208:Tectonics
1070:1664-2376
1019:1631-0683
866:Marrakech
837:romanized
785:Gondwanan
768:Bathonian
749:dinosaurs
696:Bathonian
694:to early
597:synclines
536:Sauropoda
415:Marrakech
371:semi-arid
287:Marrakech
162:Geography
137:7°54′58″W
114:Elevation
59:June 2008
1305:Archived
1149:Archived
1094:Archived
880:See also
872:and the
825:Maghribi
793:holotype
781:Bajocian
764:Toarcian
746:sauropod
742:Mesozoic
692:Bajocian
679:Toarcian
660:Toarcian
631:basaltic
623:Triassic
563:Cenozoic
522:called '
520:dinosaur
509:Khenifra
466:Colorado
448:and the
419:Jurassic
360:Imilchil
279:Algerian
999:Bibcode
862:Telouet
839::
738:Fossils
729:times.
644:-lower
570:African
550:of the
542:Geology
532:Tazouda
497:Village
482:Berbers
474:canyons
468:in the
454:Algeria
434:primate
381:in the
327:Climate
260:Morocco
254:, is a
203:31°26′N
187:Morocco
184:Country
47:improve
1272:
1215:: 1–31
1122:
1068:
1017:
828:Arabic
809:Kasbah
723:Aptian
714:Dogger
436:, the
358:until
302:Sahara
206:6°56′W
36:, but
1241:(PDF)
1054:(1).
1026:(PDF)
987:(PDF)
874:Todra
870:Dadès
832:قـصـر
317:wadis
1270:ISSN
1120:ISBN
1066:ISSN
1015:ISSN
851:wadi
843:qṣer
821:ksar
819:, a
766:and
756:and
725:and
668:and
615:and
591:and
572:and
421:and
246:The
103:Peak
1225:doi
1056:doi
1052:142
1007:doi
740:of
716:to
554:to
450:Rif
406:in
373:or
1320::
1213:35
1211:.
1205:.
1147:.
1143:.
1088:.
1064:.
1050:.
1046:.
1034:^
1013:.
1005:.
993:.
989:.
961:^
945:^
857:.
834:,
830::
807:A
690:,
636:.
484:.
440:,
270:.
262:,
1254:.
1227::
1222:.
1158:.
1128:.
1103:.
1072:.
1058::
1009::
1001::
995:3
823:(
385:.
366:.
72:)
66:(
61:)
57:(
43:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.