356:
97:
1729:
266:. The mechanism of preeclampsia/eclampsia is unknown, but consequences if left untreated can include fetal growth restriction or death, as well as pose medical risks to the mother. Signs and symptoms of preeclampsia can include swelling, protein in the urine, headaches, vomiting, and abnormal labs that assess kidney and liver function, some of which may be considered severe preeclampsia or eclampsia.
247:
in their lungs when they are born, this prevents the pressure in their lungs from falling, which normally facilitates the transition to independent breathing. Since aspiration of meconium can lead to improper oxygenation due to obstruction and carries the potential risk for inflammatory pneumonitis,
227:
If there is too little amniotic fluid around the baby in the uterus, the baby can have trouble moving around in the uterus and its growth and temperature can be impacted. Low amniotic fluid can be caused by placental issues, high gestational blood pressure, some medications, as well as problems with
363:
Instead of referring to "fetal distress", current recommendations hold to look for more specific signs and symptoms, assess them, and take the appropriate steps to remedy the situation through the implementation of intrauterine resuscitation. Traditionally the diagnosis of "fetal distress" led the
346:
Monitoring of the mother and fetus prior to birth is critical to avoid complications after birth. This is often done via electronic fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring, which helps providers monitor the fetus' heart rate to ensure it is receiving enough oxygen, monitor the mother's contractions, and
72:
Treatment primarily consists of intrauterine resuscitation, the goal of which is to restore oxygenation of the fetus. This can involve improving the position, hydration, and oxygenation of the mother, as well as
1037:
968:
953:
69:(CTG), which allows clinicians to measure changes in the fetal cardiac response to declining oxygen. Specifically, heart rate decelerations detected on CTG can represent danger to the fetus and to delivery.
668:
383:. The order of these interventions is set, and each step is done for 30 seconds with heart rate monitoring and assessment of chest movement prior to escalating to the next step in the algorithm.
375:
An algorithm is used to treat/resuscitate babies in need of respiratory support post-birth. The algorithm steps include: clearing the airways and warming, stimulating, and drying the baby,
1030:
910:
1023:
1734:
791:
767:
1288:
180:
rates, even when interpreted by highly experienced medical personnel. Fetal acid-base status is a more reliable predictor, but is not always available.
38:. The term "non-reassuring fetal status" has largely replaced it. It is characterized by changes in fetal movement, growth, heart rate, and presence of
1630:
34:
in which the fetus shows signs of inadequate oxygenation. Due to its imprecision, the term "fetal distress" has fallen out of use in
American
1756:
817:"Intrapartal cardiotocographic patterns and hypoxia-related perinatal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus"
533:"Non-reassuring fetal status: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data"
81:, and correction of fetal acid-base balance. An algorithm is used to treat/resuscitate babies in need of respiratory support post-birth.
176:
Some of these signs are more reliable predictors of fetal compromise than others. For example, cardiotocography can give high
1268:
1235:
328:
154:
Biochemical signs, assessed by collecting a small sample of baby's blood from a scalp prick through the open cervix in labor
177:
1283:
1686:
1541:
1468:
1163:
440:"ACOG Committee Opinion. Number 326, December 2005. Inappropriate use of the terms fetal distress and birth asphyxia"
355:
54:
531:
Gravett C, Eckert LO, Gravett MG, Dudley DJ, Stringer EM, Mujobu TB, Lyabis O, Kochhar S, Swamy GK (December 2016).
437:
347:
monitor the mother's blood pressure and systemic symptoms for gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, or eclampsia.
1713:
413:
1334:
1072:
50:
1215:
1417:
376:
1701:
1484:
1329:
216:
Several conditions and risk factors can lead to fetal distress or non-reassuring fetal status, including:
1497:
1015:
205:
258:
If hypertension in the mother occurs after the 20th week and meets certain criteria, this is considered
1608:
1407:
1381:
1117:
1063:
1645:
1635:
1553:
1453:
287:
164:
1171:
987:
253:
138:
1570:
1492:
1250:
438:
Committee on
Obstetric Practice, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (Dec 2005).
380:
302:
65:. The condition is detected most often with electronic fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring through
1691:
1665:
1443:
1263:
1258:
1230:
1207:
1107:
1655:
1650:
1102:
1660:
1529:
1424:
1245:
1220:
335:
189:
8:
1696:
1640:
1534:
1463:
1448:
1429:
1278:
1092:
972:
312:
1761:
1670:
1625:
1600:
1565:
1412:
1402:
1097:
856:
843:
816:
720:
693:
606:
581:
557:
532:
271:
62:
981:
977:
248:
this is an important diagnosis to make in the setting of newborn respiratory distress.
1575:
1547:
1507:
1502:
1437:
1311:
1112:
1087:
1055:
998:
892:
860:
848:
725:
650:
611:
562:
504:
500:
469:
461:
456:
439:
369:
318:
297:
743:
1458:
1397:
1129:
884:
838:
828:
715:
705:
642:
601:
593:
552:
544:
496:
451:
119:
66:
694:"Maternal and fetal Acid-base chemistry: a major determinant of perinatal outcome"
548:
1613:
1580:
1369:
1354:
1134:
992:
888:
630:
323:
221:
168:
58:
815:
Tarvonen M, Hovi P, Sainio S, Vuorela P, Andersson S, Teramo K (November 2021).
646:
1708:
1618:
1374:
1363:
1303:
1181:
875:
Garite TJ, Simpson KR (March 2011). "Intrauterine resuscitation during labor".
833:
292:
229:
201:
193:
112:
77:
to restore sufficient amniotic fluid, delaying preterm labor contractions with
1003:
1750:
1590:
1560:
1293:
1176:
710:
654:
597:
465:
259:
74:
962:
1585:
1519:
896:
852:
729:
615:
566:
473:
365:
192:, most notably increased mortality risk. Other complications include fetal
96:
89:
Generally it is preferable to describe specific signs in lieu of declaring
1045:
508:
1524:
1273:
1225:
1158:
1139:
1124:
307:
134:
130:
945:
1144:
1051:
144:
126:
35:
31:
1188:
1047:
263:
78:
27:
582:"Fetal heart rate monitoring: from Doppler to computerized analysis"
45:
Risk factors for fetal distress/non-reassuring fetal status include
1082:
244:
237:
158:
108:
39:
1387:
379:(PPV), supplementary oxygen, intubation, chest compressions, and
197:
487:
Parer JT, Livingston EG (June 1990). "What is fetal distress?".
1391:
957:
282:
276:
46:
1350:
1321:
1154:
1289:
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP)
368:
to recommend rapid delivery by instrumental delivery or by
911:"Respiratory Support in Neonates and Infants - Pediatrics"
669:"Respiratory Support in Neonates and Infants - Pediatrics"
530:
814:
792:"Preeclampsia and Eclampsia - Gynecology and Obstetrics"
100:
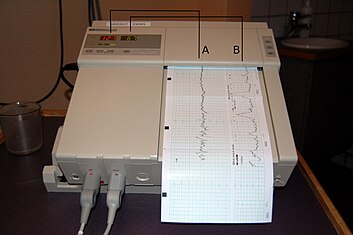
Cardiotocography is used to monitor fetal heart rate.
935:
188:Complications are primarily those associated with
1631:Childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder
1748:
359:Newborn receiving positive pressure ventilation
486:
288:Abnormal position and presentation of the fetus
628:
1031:
874:
868:
808:
768:"Meconium Aspiration Syndrome - Pediatrics"
685:
573:
1038:
1024:
691:
480:
163:elevated fetal blood lactate levels (from
842:
832:
719:
709:
635:Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine
605:
556:
455:
744:"Low Amniotic Fluid | Michigan Medicine"
579:
354:
95:
61:or meconium in the amniotic fluid, or a
1749:
1269:Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
1236:Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
1019:
329:Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
105:Decreased movement felt by the mother
84:
1757:Complications of labour and delivery
1335:Pregnancy-induced hypercoagulability
526:
524:
522:
520:
518:
408:
406:
404:
402:
400:
398:
396:
372:if vaginal delivery is not advised.
334:Maternal diabetes (Type 1 or 2) or
331:, a liver disorder during pregnancy
143:decreased variability in the fetal
13:
1284:Pruritic folliculitis of pregnancy
631:"Intrauterine fetal resuscitation"
16:Paediatric and children's diseases
14:
1773:
1542:Pain management during childbirth
1469:Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
931:
629:Kither H, Monaghan S (Jul 2019).
515:
393:
137:), especially during and after a
1728:
1727:
1714:Sexual activity during pregnancy
495:(6): 1421–5, discussion 1425–7.
457:10.1097/00006250-200512000-00056
183:
118:Non-reassuring patterns seen on
915:MSD Manual Professional Edition
903:
796:MSD Manual Professional Edition
784:
772:MSD Manual Professional Edition
760:
673:MSD Manual Professional Edition
580:Kwon JY, Park IY (March 2016).
317:Premature closure of the fetal
1216:Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
736:
661:
622:
431:
418:American Pregnancy Association
190:insufficient fetal oxygenation
1:
1418:Prelabor rupture of membranes
692:Omo-Aghoja L (January 2014).
549:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.03.043
386:
377:positive-pressure ventilation
341:
125:increased or decreased fetal
1697:Systemic lupus erythematosus
1348:Maternal care related to the
1330:Gestational thrombocytopenia
889:10.1097/GRF.0b013e31820a062b
501:10.1016/0002-9378(90)90901-i
350:
167:) indicating the baby has a
7:
1498:Cephalopelvic disproportion
647:10.1016/j.mpaic.2019.04.006
57:or cardiovascular disease,
51:restriction of fetal growth
24:non-reassuring fetal status
10:
1778:
1609:Breastfeeding difficulties
1408:Constriction ring syndrome
1382:Braxton Hicks contractions
834:10.1007/s00592-021-01756-0
336:gestational diabetes (GDM)
115:("meconium stained fluid")
1722:
1679:
1646:Peripartum cardiomyopathy
1636:Pubic symphysis diastasis
1599:
1483:
1347:
1320:
1302:
1244:
1206:
1197:
1153:
1071:
1062:
939:
444:Obstetrics and Gynecology
211:
165:fetal scalp blood testing
1172:Gestational hypertension
711:10.4103/2141-9248.126602
598:10.5468/ogs.2016.59.2.79
254:Gestational Hypertension
206:neurodevelopmental delay
26:, is a condition during
1571:Umbilical cord prolapse
1493:Amniotic fluid embolism
1251:dermatoses of pregnancy
381:pharmacological therapy
303:Umbilical cord prolapse
1687:Concomitant conditions
1666:Postpartum thyroiditis
1444:Circumvallate placenta
1264:Impetigo herpetiformis
1259:Gestational pemphigoid
1231:Hyperemesis gravidarum
1164:hypertensive disorders
698:Ann Med Health Sci Res
360:
240:in the amniotic fluid
101:
1656:Postpartum infections
1651:Postpartum depression
358:
99:
55:maternal hypertension
1661:Postpartum psychosis
1530:Obstetrical bleeding
1425:Obstetrical bleeding
1246:Integumentary system
1221:Gestational diabetes
1200:related to pregnancy
1198:Other, predominantly
228:the fetal kidney or
220:Low amniotic fluid (
1641:Postpartum bleeding
1464:Placental abruption
1449:Monochorionic twins
1279:Prurigo gestationis
877:Clin Obstet Gynecol
489:Am J Obstet Gynecol
313:Placental abruption
272:Post-term pregnancy
63:post-term pregnancy
1671:Puerperal mastitis
1626:Breast engorgement
1413:Monoamniotic twins
1403:Chorionic hematoma
748:www.uofmhealth.org
586:Obstet Gynecol Sci
361:
149:late decelerations
102:
85:Signs and symptoms
59:low amniotic fluid
1744:
1743:
1702:Thyroid disorders
1692:Diabetes mellitus
1576:Uterine inversion
1508:Shoulder dystocia
1503:Obstructed labour
1479:
1478:
1343:
1342:
1312:Chorea gravidarum
1088:Ectopic pregnancy
1013:
1012:
827:(11): 1563–1573.
543:(49): 6084–6092.
370:caesarean section
319:ductus arteriosus
298:Shoulder dystocia
1769:
1731:
1730:
1566:Postmature birth
1554:Placenta accreta
1459:Placenta praevia
1454:Placenta accreta
1398:Chorioamnionitis
1208:Digestive system
1204:
1203:
1130:Fetal resorption
1118:Rudimentary horn
1075:abortive outcome
1069:
1068:
1040:
1033:
1026:
1017:
1016:
937:
936:
925:
924:
922:
921:
907:
901:
900:
872:
866:
864:
846:
836:
812:
806:
805:
803:
802:
788:
782:
781:
779:
778:
764:
758:
757:
755:
754:
740:
734:
733:
723:
713:
689:
683:
682:
680:
679:
665:
659:
658:
626:
620:
619:
609:
577:
571:
570:
560:
528:
513:
512:
484:
478:
477:
459:
450:(6): 1469–1470.
435:
429:
428:
426:
425:
414:"Fetal Distress"
410:
157:fetal metabolic
120:cardiotocography
67:cardiotocography
22:, also known as
1777:
1776:
1772:
1771:
1770:
1768:
1767:
1766:
1747:
1746:
1745:
1740:
1718:
1675:
1619:Cracked nipples
1614:Low milk supply
1595:
1581:Uterine rupture
1475:
1370:Oligohydramnios
1355:amniotic cavity
1349:
1339:
1316:
1298:
1249:
1240:
1199:
1193:
1162:
1149:
1135:Molar pregnancy
1074:
1058:
1044:
1014:
1009:
1008:
948:
934:
929:
928:
919:
917:
909:
908:
904:
873:
869:
813:
809:
800:
798:
790:
789:
785:
776:
774:
766:
765:
761:
752:
750:
742:
741:
737:
690:
686:
677:
675:
667:
666:
662:
627:
623:
578:
574:
529:
516:
485:
481:
436:
432:
423:
421:
412:
411:
394:
389:
353:
344:
324:Uterine rupture
293:Multiple births
243:If a fetus has
222:oligohydramnios
214:
186:
169:lactic acidosis
87:
42:stained fluid.
17:
12:
11:
5:
1775:
1765:
1764:
1759:
1742:
1741:
1739:
1738:
1723:
1720:
1719:
1717:
1716:
1711:
1709:Maternal death
1706:
1705:
1704:
1699:
1694:
1683:
1681:
1677:
1676:
1674:
1673:
1668:
1663:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1633:
1628:
1623:
1622:
1621:
1616:
1605:
1603:
1597:
1596:
1594:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1558:
1557:
1556:
1544:
1539:
1538:
1537:
1527:
1522:
1517:
1515:Fetal distress
1512:
1511:
1510:
1500:
1495:
1489:
1487:
1481:
1480:
1477:
1476:
1474:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1446:
1434:
1433:
1432:
1422:
1421:
1420:
1415:
1410:
1405:
1400:
1384:
1379:
1378:
1377:
1375:Polyhydramnios
1372:
1364:amniotic fluid
1359:
1357:
1345:
1344:
1341:
1340:
1338:
1337:
1332:
1326:
1324:
1318:
1317:
1315:
1314:
1308:
1306:
1304:Nervous system
1300:
1299:
1297:
1296:
1291:
1286:
1281:
1276:
1271:
1266:
1261:
1255:
1253:
1242:
1241:
1239:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1212:
1210:
1201:
1195:
1194:
1192:
1191:
1186:
1185:
1184:
1182:HELLP syndrome
1174:
1168:
1166:
1151:
1150:
1148:
1147:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1127:
1122:
1121:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1105:
1100:
1095:
1085:
1079:
1077:
1073:Pregnancy with
1066:
1060:
1059:
1043:
1042:
1035:
1028:
1020:
1011:
1010:
1007:
1006:
995:
984:
965:
949:
944:
943:
941:
940:Classification
933:
932:External links
930:
927:
926:
902:
867:
807:
783:
759:
735:
684:
660:
641:(7): 385–388.
621:
572:
514:
479:
430:
391:
390:
388:
385:
352:
349:
343:
340:
339:
338:
332:
326:
321:
315:
310:
305:
300:
295:
290:
285:
280:
274:
269:
268:
267:
251:
250:
249:
235:
234:
233:
213:
210:
202:cerebral palsy
194:encephalopathy
185:
182:
178:false positive
174:
173:
172:
171:
161:
152:
151:
150:
147:
141:
116:
113:amniotic fluid
106:
93:that include:
91:fetal distress
86:
83:
20:Fetal distress
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1774:
1763:
1760:
1758:
1755:
1754:
1752:
1737:
1736:
1732:
1725:
1724:
1721:
1715:
1712:
1710:
1707:
1703:
1700:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1689:
1688:
1685:
1684:
1682:
1678:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1664:
1662:
1659:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1632:
1629:
1627:
1624:
1620:
1617:
1615:
1612:
1611:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1604:
1602:
1598:
1592:
1591:Uterine atony
1589:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1561:Preterm birth
1559:
1555:
1552:
1551:
1550:
1549:
1545:
1543:
1540:
1536:
1533:
1532:
1531:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1509:
1506:
1505:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1488:
1486:
1482:
1470:
1467:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1441:
1440:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1428:
1427:
1426:
1423:
1419:
1416:
1414:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1404:
1401:
1399:
1396:
1395:
1394:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1383:
1380:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1367:
1366:
1365:
1361:
1360:
1358:
1356:
1352:
1346:
1336:
1333:
1331:
1328:
1327:
1325:
1323:
1319:
1313:
1310:
1309:
1307:
1305:
1301:
1295:
1294:Stretch marks
1292:
1290:
1287:
1285:
1282:
1280:
1277:
1275:
1272:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1257:
1256:
1254:
1252:
1247:
1243:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1205:
1202:
1196:
1190:
1187:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1178:
1177:Pre-eclampsia
1175:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1165:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1146:
1143:
1141:
1138:
1136:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1119:
1116:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1090:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1078:
1076:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1046:Pathology of
1041:
1036:
1034:
1029:
1027:
1022:
1021:
1018:
1005:
1001:
1000:
996:
994:
990:
989:
985:
983:
979:
975:
974:
970:
966:
964:
960:
959:
955:
951:
950:
947:
942:
938:
916:
912:
906:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
871:
862:
858:
854:
850:
845:
840:
835:
830:
826:
822:
821:Acta Diabetol
818:
811:
797:
793:
787:
773:
769:
763:
749:
745:
739:
731:
727:
722:
717:
712:
707:
703:
699:
695:
688:
674:
670:
664:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
632:
625:
617:
613:
608:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
583:
576:
568:
564:
559:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
534:
527:
525:
523:
521:
519:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
483:
475:
471:
467:
463:
458:
453:
449:
445:
441:
434:
419:
415:
409:
407:
405:
403:
401:
399:
397:
392:
384:
382:
378:
373:
371:
367:
357:
348:
337:
333:
330:
327:
325:
322:
320:
316:
314:
311:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
294:
291:
289:
286:
284:
281:
278:
275:
273:
270:
265:
261:
257:
256:
255:
252:
246:
242:
241:
239:
236:
231:
230:urinary tract
226:
225:
223:
219:
218:
217:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
184:Complications
181:
179:
170:
166:
162:
160:
156:
155:
153:
148:
146:
142:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
123:
121:
117:
114:
110:
107:
104:
103:
98:
94:
92:
82:
80:
76:
75:amnioinfusion
70:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
43:
41:
37:
33:
29:
25:
21:
1733:
1726:
1586:Vasa praevia
1546:
1520:Locked twins
1514:
1436:
1386:
1362:
1108:Interstitial
997:
986:
967:
952:
918:. Retrieved
914:
905:
883:(1): 28–39.
880:
876:
870:
824:
820:
810:
799:. Retrieved
795:
786:
775:. Retrieved
771:
762:
751:. Retrieved
747:
738:
701:
697:
687:
676:. Retrieved
672:
663:
638:
634:
624:
592:(2): 79–84.
589:
585:
575:
540:
536:
492:
488:
482:
447:
443:
433:
422:. Retrieved
420:. 2014-08-28
417:
374:
366:obstetrician
362:
345:
260:preeclampsia
215:
187:
175:
90:
88:
71:
44:
23:
19:
18:
1525:Nuchal cord
1274:Linea nigra
1226:Hepatitis E
1159:proteinuria
1140:Miscarriage
1125:Embryo loss
1103:Heterotopic
704:(1): 8–17.
308:Nuchal cord
139:contraction
135:bradycardia
131:tachycardia
1751:Categories
1535:Postpartum
1430:Antepartum
1145:Stillbirth
1056:puerperium
1054:, and the
1052:childbirth
999:DiseasesDB
920:2021-09-10
801:2021-09-13
777:2021-09-10
753:2021-09-13
678:2021-09-13
424:2021-09-09
387:References
342:Prevention
145:heart rate
127:heart rate
36:obstetrics
1762:Midwifery
1601:Puerperal
1189:Eclampsia
1093:Abdominal
1064:Pregnancy
1048:pregnancy
861:235487220
655:1472-0299
466:0029-7844
351:Treatment
277:Breathing
264:eclampsia
79:tocolysis
28:pregnancy
1735:Category
1548:placenta
1438:placenta
1098:Cervical
1083:Abortion
897:21278499
853:34151398
730:24669324
616:27004196
567:27461459
474:16319282
279:problems
245:meconium
238:Meconium
198:seizures
159:acidosis
109:Meconium
40:meconium
1388:chorion
1113:Ovarian
993:D005316
844:8505288
721:3952302
607:4796090
558:5139811
537:Vaccine
509:2193513
111:in the
1392:amnion
895:
859:
851:
841:
728:
718:
653:
614:
604:
565:
555:
507:
472:
464:
283:Anemia
212:Causes
204:, and
47:anemia
1680:Other
1485:Labor
1351:fetus
1322:Blood
1161:, and
1155:Edema
982:768.4
978:768.2
857:S2CID
32:labor
1353:and
1004:4882
988:MeSH
973:9-CM
893:PMID
849:PMID
726:PMID
651:ISSN
612:PMID
563:PMID
505:PMID
470:PMID
462:ISSN
133:and
969:ICD
963:O68
954:ICD
885:doi
839:PMC
829:doi
716:PMC
706:doi
643:doi
602:PMC
594:doi
553:PMC
545:doi
497:doi
493:162
452:doi
448:106
30:or
1753::
1390:/
1157:,
1050:,
1002::
991::
976::
961::
958:10
913:.
891:.
881:54
879:.
855:.
847:.
837:.
825:58
823:.
819:.
794:.
770:.
746:.
724:.
714:.
700:.
696:.
671:.
649:.
639:20
637:.
633:.
610:.
600:.
590:59
588:.
584:.
561:.
551:.
541:34
539:.
535:.
517:^
503:.
491:.
468:.
460:.
446:.
442:.
416:.
395:^
224:)
208:.
200:,
196:,
122::
53:,
49:,
1248:/
1039:e
1032:t
1025:v
980:-
971:-
956:-
946:D
923:.
899:.
887::
865:}
863:.
831::
804:.
780:.
756:.
732:.
708::
702:4
681:.
657:.
645::
618:.
596::
569:.
547::
511:.
499::
476:.
454::
427:.
262:/
232:.
129:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.