1883:
valley since the 2nd century BCE. (Archaeological evidence shows that as early as the 2nd century BCE, the Pyu had built water-management systems along secondary streams in central and northern parts of the
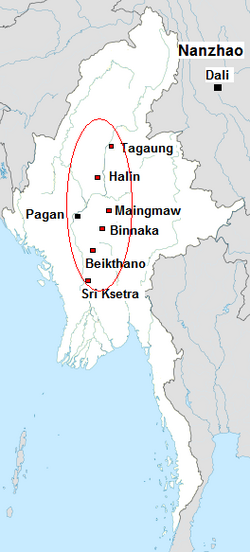
Irrawaddy basin and had founded one of Southeast Asia's earliest urban centres. By the early centuries CE, several walled cities and towns had emerged. The architectural and artistic evidence indicates the Pyu realm's contact with Indian culture by the 4th century CE. The city-states boasted kings and palaces, moats and massive wooden gates, and always 12 gates for each of the signs of the zodiac, one of the many enduring patterns that would continue until the British occupation. Sri Ksetra emerged as the premier Pyu city-state in the 7th century CE. Although the size of the city-states and the scale of political organisation grew during the 7th to early 9th centuries, no sizeable kingdom had yet emerged by the 9th century.)
1853:
1976:, the Pyu city reportedly destroyed by an 832 Nanzhao raid. The region of Pagan received waves of Burman settlements in the mid-to-late 9th century, and perhaps well into the 10th century. By the mid-10th century, Burmans at Pagan had expanded irrigation-based cultivation while borrowing extensively from the Pyus' predominantly Buddhist culture. Pagan's early iconography, architecture and scripts suggest little difference between early Burman and Pyu cultural forms. Moreover, no sharp ethnic distinction between Burmans and linguistically linked Pyus seems to have existed.
365:
324:
2048:
668:
1840:
1960:
847:, and named his kingdom Pugarama. His "kingdom" included 19 villages in the region. The 19 villages were: (1) Nyaung U, (2) Naga Soe, (3) Naga Kyit, (4) Magyi Kyi, (5) Htude, (6) Kyauk Zaga, (7) Ohte Thein, (8) Nyaungwun, (9) Anuradha, (10) Dazaungkun, (11) Ywa Mohn, (12) Kyinlo, (13) Kokko, (14) Taungpa, (15) Myegedwin, (16) Thayet Ya, (17) Singu, (18) Yonlut, and (19) Ywa Zaik.
1950:
summarises the mainstream opinion that "the
Nanzhao Empire had washed up on the banks of the Irrawaddy, and would find a new life, fused with an existing and ancient culture, to produce one of the most impressive little kingdoms of the medieval world. From this fusion would result the Burmese people,
1911:
entered the Pyu realm in the 830s and 840s and settled at the confluence of the
Irrawaddy and Chindwin rivers, perhaps to help Nanzhao pacify the surrounding countryside. Indeed, the naming system of the early Pagan kings—Pyusawhti and his descendants for six generations—was identical to that of the
1923:
The Pagan "kingdom" Pyusawhti led was likely a small settlement among many other small settlements in the area. (The chronicles count 19 settlements.) In the 8th century, Pagan was not yet a city or even a city-state, let alone a "kingdom". The city was merely one of several competing city-states
1920:, who was in the vanguard of the Nanzhao invasions of the upper Irrawaddy valley that began in 754 (and lasted until the 830s). Pyusawhti's victory over the Chinese likely refers to the Nanzhao victory over the Chinese in the same era, in which Pyusawhti and his contingents may have participated.
1882:
The earliest human settlement at Pagan is radiocarbon dated to c. 650 CE. But evidence is inconclusive to prove that it was specifically a Burman settlement, not just another Pyu settlement. The 7th century settlement was part of the Pyu realm, which by then had been in existence in the
Irrawaddy
1367:, son of Htun Chit and rightful heir, and making his son-in-law the heir apparent. Popa Sawrahan died in 640 soon after his new calendar was launched, and Shwe Ohnthi succeeded, restoring the Pyusawhti line. Shwe Ohnthi was followed by another a dozen kings to year 846 CE. In 846 CE, King
2133:(Htin Aung 1967: 367): "Emergence of the Burmese" c. 600 CE. (Htin Aung 1970: 11–15): The chapter titled "The Coming of the Burmese" picks apart Luce's 9th century Nanzhao theory, and seems to indicate an even earlier arrival date than the 600 CE date he proposed in (Htin Aung 1967).
1991:
was already in use by 1035, and perhaps as early as 984 CE. By
Anawrahta's accession in 1044, Pagan had grown into a small principality—about 320 km (200 miles) north to south and about 130 km (80 miles) from east to west, comprising roughly the present districts of
1943:
and Matrii Aung-Thwin write that the 19 villages that first formed the city of Pagan according to the chronicles are "probably" "legendary" but "the origins of the
Burmese speakers in Myanmar may well be earlier than, and had nothing to do with, the Nanzhao raid of AD 832".
45:
1971:
Evidence shows that the actual pace of Burman migration into the Pyu realm was gradual. Indeed, no firm indications have been found at Sri Ksetra or at any other Pyu site to suggest a violent overthrow. Radiocarbon dating shows that human activity existed until c. 870 at
2109:(Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 143): The calendar was reset, leaving two years, in year 640 CE. The starting date of the Burmese calendar was 22 March 638; Year 2 of the Burmese calendar began on 21 March 640 per (Eade 1989: 39).
951:, as heir apparent for the commoner's bravery in defeating enemies of the state. Pyusawhti came to power in 167 CE. He ruled for 45 years, implementing foundation institutions of the state, including its first law treatise (
1915:
Despite the legendary nature of both pre-Buddhist and
Hmannan's Buddhist-inspired stories, a historical Pyusawhti likely existed. Historians conjecture that the historical Pyusawhti was likely a minor chief of the
1932:
historian GE Harvey, the
Burmese chroniclers likely arranged the lists of rulers of early Burmese polities consecutively, "wishing to portray a continuous lineage stretching back to divine antiquity."
820:
visited the future site of Pagan during his lifetime and predicted that a great city would arise at the very site 651 years after his death (107 CE). The 19th century chronicle
2711:
304:
279:
2706:
767:. Burmans at Pagan expanded irrigation-based cultivation while borrowing extensively from the Pyus' predominantly Buddhist culture. It was one of many competing
1967:
at Pagan (Bagan), the only remaining section of the old walls. The main walls are dated to c. 1020 CE and the earliest pieces of the walls to c. 980 CE.
2142:(Aung-Thwin 2005: 167–178, 197–200): The earliest Burmese script (the copper-gilt umbrella inscription of the Mahabodhi Temple) is dated to 1035. If a
1225:
972:
died without leaving an heir, and the throne was contested among three senior ministers at the court. The victor of the power struggle, the minister
771:
until the late 10th century when the principality began absorbing its surrounding states. The expansion accelerated in the 1050s and 1060s when King
521:
1129:
961:
1879:, the earliest inhabitants of Burma of whom records are extant; and that Pagan kings had incorporated the Pyu histories and legends as their own.
1570:
1193:
1145:
977:
2146:
18th century copy of an original stone inscription is permissible as evidence, the
Burmese script had already been in use at least since 984 CE.
1979:
Starting in the late 10th century, the principality grew in authority and grandeur. The earliest mention of Pagan in external sources occurs in
1097:
1427:
1364:
1241:
1113:
1081:
2681:
1544:
1531:
1518:
1505:
1453:
1257:
696:
1899:
of Yunnan between the 750s and 830s CE. Like that of the Pyu, the original home of
Burmans prior to Yunnan is believed to be present-day
1479:
1440:
1348:
1321:
1305:
1289:
1987:
in 1004. The city by now was fortified. Radiocarbon dating of Pagan's walls show that Pagan was fortified most probably c. 1020 CE. The
1557:
1466:
1273:
1924:
until the 10th century. Furthermore, the 38 kings of Pagan Dynasty—from Pyusawhti to Sokkate, prior to the historically verified king
1492:
1355:
on 21 March 640 CE, with the starting date of 22 March 638. (According to scholarship, the Burmese calendar was actually launched at
1161:
969:
759:
that dominated Upper Burma. The city-state of Pagan, according to mainstream scholarship, was founded in the mid 9th century by the
2721:
1371:(r. 846–886) came to power. Three years into his reign, on 23 December 849, he moved the capital to the present-day site of Pagan.
1177:
973:
609:
559:
2641:
2584:
2525:
2487:
2651:
733:
state that the "kingdom" was founded in the second century CE. The seat of power of the small kingdom was first located at
1907:. After the Nanzhao attacks had greatly weakened the Pyu city-states, large numbers of Burman warriors and their families
2622:
603:
341:
337:
2691:
1939:
contends that the arrival of Burmans may have been a few centuries earlier, perhaps the early 7th century. Historians
2506:
2468:
1614:
restored the old royal line in 1001 but 20 years later, he was pushed out by the sons of Nyaung-u Sawrahan. In 1044,
755:
shows the earliest human settlement in the Pagan region dates only from the mid-7th century CE. It existed alongside
2061:
1935:
However, some scholars believe that Burmans had arrived in Myanmar much earlier than the mainstream opinion holds.
855:
689:
597:
591:
565:
1875:
in the mid-to-late 9th century CE; that the earlier parts of the chronicle are the histories and legends of the
788:
Various Burmese chronicles do not agree on the date of foundation of Pagan. One of the earliest chronicles,
615:
571:
529:
1610:(r. 956–1001), the earliest inscriptionally verified king, ruled for 45 years. A descendant of Pyusawhti,
2716:
682:
649:
634:
629:
585:
826:
went further, asserting that the founders of the Pagan dynasty ultimate trace their origins back to the
2577:
Strange Parallels: Southeast Asia in Global Context, c. 800–1830, volume 1, Integration on the Mainland
448:
2696:
1852:
2686:
654:
898:
639:
1625:
The chronicles again do not agree with the dates for this period. The dates in later chronicles
775:
founded the Pagan Empire, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery.
2701:
2605:
1895:
reconstruction, the millennium-old Pyu realm came crashing down under repeated attacks by the
1606:
died in 904 CE, the throne passed on to a series of usurpers for nearly a century to 1001 CE.
1929:
547:
374:
515:
8:
489:
182:
2100:(Yazawin Kyaw 2010: 139–140): Pagan was founded 700 years after the death of the Buddha.
2164:
2120:
2076:
1940:
1776:
1648:
1611:
1385:
1002:
813:
805:
752:
730:
644:
553:
501:
422:
390:
356:
2658:(in Burmese). Vol. 1–3 (2003 ed.). Yangon: Ministry of Information, Myanmar.
2570:(in Burmese). Vol. 1–3 (2006, 4th printing ed.). Yangon: Ya-Pyei Publishing.
2637:
2618:
2580:
2521:
2502:
2483:
2464:
1928:—were probably contemporary chiefs of the Pagan area's settlements. According to the
1757:
1607:
884:
459:
168:
2546:
1988:
1900:
1352:
851:
714:
535:
345:
331:
78:
2028:. To the north lay the Nanzhao Kingdom, and to the east still largely uninhibited
1912:
Nanzhao kings where the last name of the father became the first name of the son.
980:, a grandson of Thihtan, was put in power by the court. Tharamon Phya's successor
2159:
2081:
2071:
2013:
1917:
1896:
1872:
1700:
1670:
1603:
1403:
1022:
822:
794:
compiled in 1520, states that the kingdom of Pagan was founded in 156 CE by King
768:
764:
756:
509:
469:
394:
380:
284:
1374:
All four main chronicles are in agreement with the regnal dates in this period.
2053:
1904:
965:
929:
915:
859:
738:
672:
475:
413:
59:
364:
2675:
2169:
2066:
1973:
1964:
1947:
1867:
Modern scholarship, however, holds that the Pagan dynasty was founded by the
1857:
1414:
1344:
833:
Still according to the standard chronicles, Thamoddarit fixed the capital at
726:
481:
463:
453:
434:
297:
144:
854:
tradition, Pagan was known by different classical names even in the ages of
2600:
2595:
1980:
1719:
1664:
1656:
1397:
1391:
1016:
1010:
800:
790:
403:
1363:.) Popa Sawrahan made peace with the royal line by giving his daughter to
991:
The following is the list of Pagan kings as given in the main chronicles.
1892:
1209:
1049:
1033:
981:
809:
495:
120:
976:
ruled until his death in 494. The Pyusawhti line was restored when King
2499:
Southeast Asian Ephemeris: Solar and Planetary Positions, A.D. 638–2000
2033:
2029:
1876:
1839:
1360:
1356:
985:
953:
834:
742:
734:
722:
63:
55:
1983:
records, which report that envoys from Pagan visited the Song capital
1936:
1925:
1861:
1615:
1065:
944:
795:
772:
132:
2650:
1622:, son of Nyaung-u Sawrahan, in single combat and seized the throne.
2009:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1738:
844:
96:
88:
2025:
2017:
2005:
1984:
1814:
1681:
1619:
1368:
156:
92:
2482:(illustrated ed.). Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press.
2463:(illustrated ed.). Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press.
1959:
907:
827:
817:
2021:
1868:
1795:
1583:
760:
746:
67:
2477:
44:
2032:, to the south and the west Pyus, and farther south still,
1347:(r. 613–640). The former monk seized the throne after King
863:
843:), ("the City that Tramples on Enemies"), near present-day
2537:
History of Burma: From the Earliest Times to 10 March 1824
2559:
Burmese History before 1287: A Defence of the Chronicles
721:) was a city-state that existed in the first millennium
1843:
Principality of Pagan at Anawrahta's accession in 1044
2461:
The Mists of Rāmañña: The Legend that was Lower Burma
2604:(in Burmese) (4th printing, 2010 ed.). Yangon:
2124:, the most accurate chronicle for early Pagan dates.
2043:
2478:Aung-Thwin, Michael A.; Maitrii Aung-Thwin (2012).
808:, stating that Pagan was founded in 107 CE by King
2712:States and territories disestablished in the 1040s
2552:. New York and London: Cambridge University Press.
2545:
2673:
2593:
1951:and the foundations of modern Burmese culture."
1860:, as seen in 1868, believed to be built by King
1847:
16:First-millennium CE city-state in Southeast Asia
2520:(3rd ed.). Hutchinson University Library.
2118:(Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 346–349): Dates per
2707:States and territories established in the 650s
2667:(in Burmese). Vol. 1. Yangon: Maha Dagon.
2634:The River of Lost Footsteps—Histories of Burma
2413:
2242:
2240:
2238:
2608:(original publisher), Ya-Pyei (4th printing).
968:, not far from the Pugama site. In 439, King
838:
690:
28:
2388:
2386:
2384:
2363:
2356:
2354:
2297:
2281:
2279:
2267:
2258:
2431:
2422:
2235:
2226:
2217:
2199:
2190:
2181:
862:). The names below are Burmese versions of
2458:
2404:
697:
683:
43:
2574:
2556:
2543:
2440:
2381:
2351:
2276:
2249:
2662:
2480:A History of Myanmar Since Ancient Times
1958:
1886:
1851:
1838:
2631:
2395:
2372:
2333:
2315:
2208:
342:question marks, boxes, or other symbols
2674:
2534:
2342:
2306:
2288:
1618:, son of Kunhsaw Kyaunghpyu, defeated
778:
2612:
2324:
1338:
2652:Royal Historical Commission of Burma
2565:
2515:
2496:
947:, the founder of Pagan according to
2682:Former countries in Burmese history
2539:. London: Frank Cass & Co. Ltd.
1597:
1044:Nephew of Thupyinnya of Sri Ksetra
13:
1602:After Pyinbya's successor and son
1409:Relationship with the predecessor
1028:Relationship with the predecessor
960:The chronicles continue that King
745:until 849 CE when it was moved to
14:
2733:
2273:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 147–154
2264:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 143–146
2246:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 343–347
2232:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 139–141
2223:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 135–138
2205:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 133–134
1676:Relationship with predecessor(s)
1500:Elected by court; of royal blood
984:(r. 516–523) moved the palace to
964:(r. 344–387) moved the palace to
224:• Burmese calendar launched
2046:
1954:
1351:died in 613 CE. He launched the
858:(i.e. before the present era of
804:links the Pagan monarchs to the
666:
363:
322:
302:
277:
2722:1040s disestablishments in Asia
2594:Maha Thilawuntha, Shin (1928).
2459:Aung-Thwin, Michael A. (2005).
2452:
2136:
2127:
2112:
2020:, and the riverine portions of
116:• 107–152 CE (chronicles)
2579:. Cambridge University Press.
2501:. Ithaca: Cornell University.
2103:
2094:
1834:
1:
2636:. Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
2575:Lieberman, Victor B. (2003).
2214:Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 136
2175:
2153:
1848:A settlement in the Pyu realm
798:. The 18th century chronicle
729:in the mid 11th century. The
204:• ThiriPyissaya founded
2613:Moore, Elizabeth H. (2007).
2561:. Oxford: The Asoka Society.
2410:Aung-Thwin et al 2012: 77–78
1639:
1376:
1343:The next important king was
993:
868:
783:
769:city-states in the Pyu realm
140:• 613–640 (chronicles)
128:• 167–242 (chronicles)
7:
2615:Early Landscapes of Myanmar
2039:
1637:dates from 846 CE forward.
943:Thamoddarit then appointed
10:
2738:
2665:Studies in Burmese History
2187:Maha Yazawin 2006: 132–133
1076:Son-in-law of Thamoddarit
214:• Tampawaddy founded
2692:Former monarchies of Asia
2557:Htin Aung, Maung (1970).
2544:Htin Aung, Maung (1967).
1809:Son of Nyaung-u Sawrahan
1675:
1661:
1653:
1645:
1642:
1408:
1382:
1379:
1027:
1007:
999:
996:
920:Tambadvipa( तांबाद्वीप )
877:
874:
871:
839:
718:
256:
252:
242:
232:
228:21 March 640 (chronicles)
222:
212:
202:
192:
188:
178:
174:
162:
150:
138:
126:
114:
110:
102:
84:
74:
51:
42:
37:
29:
23:
2617:. Bangkok: River Books.
2087:
889:Pandupalāsh(पाण्डुपलाश)
725:before the emergence of
2632:Myint-U, Thant (2006).
2062:Pagan kings family tree
988:, near Thiri Pyissaya.
903:Dharmakuṭī( धर्मकुटी )
548:British colonial period
2606:Burma Research Society
2535:Harvey, G. E. (1925).
2419:Aung-Thwin 2005: 36–37
1968:
1864:
1844:
934:Arimardan( अरिमर्दन )
330:This article contains
244:• Disestablished
25:Early Kingdom of Bagan
2516:Hall, D.G.E. (1960).
2392:Lieberman 2003: 90–91
1962:
1887:Arrival of the Mranma
1855:
1842:
892:The withered foliage
522:Nyaungyan Restoration
449:Warring states period
375:Prehistory of Myanmar
234:• Pagan founded
75:Common languages
2369:Aung-Thwin 1985: 205
2303:Aung-Thwin 2005: 185
1930:British colonial era
1359:(Pyay/Prome) by the
1204:Grandson of Thihtan
566:Nationalist movement
530:Restored Hanthawaddy
516:First Toungoo Empire
492:1287–1539, 1550–1552
218:516–523 (chronicles)
208:344–387 (chronicles)
2497:Eade, J.C. (1989).
2437:Aung-Thwin 2005: 38
2428:Aung-Thwin 1985: 21
2360:Myint-U 2006: 56–57
2285:Myint-U 2006: 44–45
2196:Than Tun 1964: ix–x
923:land of the Bronze
779:Chronicle tradition
711:Early Pagan Kingdom
598:Ne Win dictatorship
572:Japanese occupation
560:Resistance movement
490:Hanthawaddy Kingdom
441:Early Pagan Kingdom
183:Classical Antiquity
2717:650 establishments
2548:A History of Burma
2446:Harvey 1925: 24–25
2348:Lieberman 2003: 90
2312:Lieberman 2003: 89
2165:Sri Ksetra Kingdom
2121:Zatadawbon Yazawin
2077:Sri Ksetra Kingdom
1969:
1941:Michael Aung-Thwin
1865:
1845:
1777:Kunhsaw Kyaunghpyu
1649:Zatadawbon Yazawin
1612:Kunhsaw Kyaunghpyu
1386:Zatadawbon Yazawin
1339:Middle Early Pagan
1003:Zatadawbon Yazawin
828:clan of the Buddha
814:Sri Ksetra Kingdom
806:Sri Ksetra Kingdom
753:Radiocarbon dating
731:Burmese chronicles
673:Myanmar portal
604:SLORC / SPDC junta
554:Anglo-Burmese Wars
502:Kingdom of Mrauk U
423:Arakanese kingdoms
391:Sri Ksetra Kingdom
357:History of Myanmar
194:• Foundation
2663:Than Tun (1964).
2643:978-0-374-16342-6
2586:978-0-521-80496-7
2527:978-1-4067-3503-1
2489:978-1-86189-901-9
1871:(Burmans) of the
1832:
1831:
1758:Nyaung-u Sawrahan
1608:Nyaung-u Sawrahan
1595:
1594:
1336:
1335:
941:
940:
899:Koṇāgamana Buddha
885:Kakusandha Buddha
707:
706:
610:Political reforms
383:200 BCE – 1050 CE
338:rendering support
318:
317:
314:
313:
310:
309:
290:
289:
169:Nyaung-u Sawrahan
2729:
2697:Burmese monarchy
2668:
2659:
2647:
2628:
2609:
2590:
2571:
2568:Maha Yazawin Gyi
2566:Kala, U (1724).
2562:
2553:
2551:
2540:
2531:
2512:
2493:
2474:
2447:
2444:
2438:
2435:
2429:
2426:
2420:
2417:
2411:
2408:
2402:
2401:Harvey 1925: 364
2399:
2393:
2390:
2379:
2378:Harvey 1925: 308
2376:
2370:
2367:
2361:
2358:
2349:
2346:
2340:
2337:
2331:
2328:
2322:
2319:
2313:
2310:
2304:
2301:
2295:
2292:
2286:
2283:
2274:
2271:
2265:
2262:
2256:
2253:
2247:
2244:
2233:
2230:
2224:
2221:
2215:
2212:
2206:
2203:
2197:
2194:
2188:
2185:
2147:
2140:
2134:
2131:
2125:
2116:
2110:
2107:
2101:
2098:
2056:
2051:
2050:
2049:
1640:
1633:now depart from
1598:Late Early Pagan
1377:
1353:Burmese calendar
1226:Thinli Kyaung II
994:
869:
856:previous Buddhas
852:Burmese Buddhist
842:
841:
727:the Pagan Empire
720:
719:ခေတ်ဦး ပုဂံ ပြည်
699:
692:
685:
671:
670:
669:
650:Military history
645:Royal chronicles
635:List of capitals
592:AFPFL government
536:Konbaung dynasty
417:
398:
367:
353:
352:
344: instead of
326:
325:
306:
305:
294:
293:
281:
280:
274:
273:
258:
257:
248:16 December 1044
164:• 956–1001
47:
32:
31:
30:ခေတ်ဦး ပုဂံ ပြည်
21:
20:
2737:
2736:
2732:
2731:
2730:
2728:
2727:
2726:
2687:Former kingdoms
2672:
2671:
2656:Hmannan Yazawin
2644:
2625:
2624:978-974-9863312
2587:
2528:
2509:
2490:
2471:
2455:
2450:
2445:
2441:
2436:
2432:
2427:
2423:
2418:
2414:
2409:
2405:
2400:
2396:
2391:
2382:
2377:
2373:
2368:
2364:
2359:
2352:
2347:
2343:
2338:
2334:
2329:
2325:
2321:Moore 2007: 236
2320:
2316:
2311:
2307:
2302:
2298:
2293:
2289:
2284:
2277:
2272:
2268:
2263:
2259:
2255:Hall 1960: 8–10
2254:
2250:
2245:
2236:
2231:
2227:
2222:
2218:
2213:
2209:
2204:
2200:
2195:
2191:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2160:Tagaung Kingdom
2156:
2151:
2150:
2141:
2137:
2132:
2128:
2117:
2113:
2108:
2104:
2099:
2095:
2090:
2082:Tagaung Kingdom
2072:Pyu city-states
2052:
2047:
2045:
2042:
1957:
1918:Nanzhao Kingdom
1905:Gansu provinces
1897:Nanzhao Kingdom
1889:
1873:Nanzhao Kingdom
1850:
1837:
1671:Hmannan Yazawin
1631:Hmannan Yazawin
1600:
1404:Hmannan Yazawin
1341:
1023:Hmannan Yazawin
835:Arimaddana-pura
823:Hmannan Yazawin
786:
781:
765:Nanzhao Kingdom
757:Pyu city-states
703:
667:
665:
510:Toungoo dynasty
470:Sagaing Kingdom
411:
395:Tagaung Kingdom
388:
381:Pyu city-states
351:
350:
349:
336:Without proper
327:
323:
303:
285:Pyu city-states
278:
245:
238:23 December 849
235:
225:
215:
205:
195:
165:
153:
152:• 846–886
141:
129:
117:
33:
26:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2735:
2725:
2724:
2719:
2714:
2709:
2704:
2699:
2694:
2689:
2684:
2670:
2669:
2660:
2648:
2642:
2629:
2623:
2610:
2591:
2585:
2572:
2563:
2554:
2541:
2532:
2526:
2513:
2507:
2494:
2488:
2475:
2469:
2454:
2451:
2449:
2448:
2439:
2430:
2421:
2412:
2403:
2394:
2380:
2371:
2362:
2350:
2341:
2332:
2330:Harvey 1925: 3
2323:
2314:
2305:
2296:
2287:
2275:
2266:
2257:
2248:
2234:
2225:
2216:
2207:
2198:
2189:
2179:
2177:
2174:
2173:
2172:
2167:
2162:
2155:
2152:
2149:
2148:
2135:
2126:
2111:
2102:
2092:
2091:
2089:
2086:
2085:
2084:
2079:
2074:
2069:
2064:
2058:
2057:
2054:Myanmar portal
2041:
2038:
1989:Burmese script
1956:
1953:
1888:
1885:
1849:
1846:
1836:
1833:
1830:
1829:
1826:
1823:
1820:
1817:
1811:
1810:
1807:
1804:
1801:
1798:
1792:
1791:
1790:Son of Tannet
1788:
1785:
1782:
1779:
1773:
1772:
1769:
1766:
1763:
1760:
1754:
1753:
1750:
1747:
1744:
1741:
1735:
1734:
1731:
1728:
1725:
1722:
1716:
1715:
1712:
1709:
1706:
1703:
1697:
1696:
1693:
1690:
1687:
1684:
1678:
1677:
1674:
1660:
1652:
1644:
1599:
1596:
1593:
1592:
1589:
1586:
1580:
1579:
1576:
1573:
1567:
1566:
1563:
1560:
1554:
1553:
1550:
1547:
1541:
1540:
1537:
1534:
1528:
1527:
1524:
1521:
1515:
1514:
1511:
1508:
1502:
1501:
1498:
1495:
1489:
1488:
1485:
1482:
1476:
1475:
1472:
1469:
1463:
1462:
1459:
1456:
1450:
1449:
1446:
1443:
1437:
1436:
1433:
1430:
1424:
1423:
1420:
1417:
1411:
1410:
1407:
1381:
1340:
1337:
1334:
1333:
1330:
1327:
1324:
1318:
1317:
1314:
1311:
1308:
1302:
1301:
1298:
1295:
1292:
1286:
1285:
1282:
1279:
1276:
1270:
1269:
1266:
1263:
1260:
1254:
1253:
1250:
1247:
1244:
1238:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1228:
1222:
1221:
1218:
1215:
1212:
1206:
1205:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1190:
1189:
1186:
1183:
1180:
1174:
1173:
1170:
1167:
1164:
1158:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1142:
1141:
1138:
1135:
1132:
1130:Thili Kyaung I
1126:
1125:
1122:
1119:
1116:
1110:
1109:
1106:
1103:
1100:
1094:
1093:
1090:
1087:
1084:
1078:
1077:
1074:
1071:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1058:
1055:
1052:
1046:
1045:
1042:
1039:
1036:
1030:
1029:
1026:
1006:
998:
966:Thiri Pyissaya
962:Thili Kyaung I
939:
938:
935:
932:
930:Gautama Buddha
925:
924:
921:
918:
916:Kassapa Buddha
911:
910:
904:
901:
894:
893:
890:
887:
880:
879:
876:
873:
860:Gautama Buddha
785:
782:
780:
777:
739:Thiri Pyissaya
705:
704:
702:
701:
694:
687:
679:
676:
675:
662:
661:
660:
659:
658:
657:
647:
642:
637:
632:
624:
623:
622:
621:
620:
619:
613:
607:
601:
595:
580:
579:
578:
577:
576:
575:
569:
563:
557:
542:
541:
540:
539:
533:
527:
526:
525:
519:
507:
506:
505:
499:
493:
487:
486:
485:
479:
476:Kingdom of Ava
473:
467:
464:Pinya Kingdoms
446:
445:
444:
429:
428:
427:
426:
419:
418:
414:Thaton Kingdom
408:
407:
400:
399:
385:
384:
378:
377:11,000–200 BCE
369:
368:
360:
359:
346:Burmese script
340:, you may see
332:Burmese script
328:
321:
320:
319:
316:
315:
312:
311:
308:
307:
300:
291:
288:
287:
282:
270:
269:
264:
254:
253:
250:
249:
246:
243:
240:
239:
236:
233:
230:
229:
226:
223:
220:
219:
216:
213:
210:
209:
206:
203:
200:
199:
196:
193:
190:
189:
186:
185:
180:
179:Historical era
176:
175:
172:
171:
166:
163:
160:
159:
154:
151:
148:
147:
142:
139:
136:
135:
130:
127:
124:
123:
118:
115:
112:
111:
108:
107:
104:
100:
99:
86:
82:
81:
76:
72:
71:
60:Thiri Pyissaya
53:
49:
48:
40:
39:
38:c. 650 CE–1044
35:
34:
27:
24:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2734:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2713:
2710:
2708:
2705:
2703:
2702:Pagan Kingdom
2700:
2698:
2695:
2693:
2690:
2688:
2685:
2683:
2680:
2679:
2677:
2666:
2661:
2657:
2653:
2649:
2645:
2639:
2635:
2630:
2626:
2620:
2616:
2611:
2607:
2603:
2602:
2597:
2592:
2588:
2582:
2578:
2573:
2569:
2564:
2560:
2555:
2550:
2549:
2542:
2538:
2533:
2529:
2523:
2519:
2514:
2510:
2508:0-87727-704-4
2504:
2500:
2495:
2491:
2485:
2481:
2476:
2472:
2470:9780824828868
2466:
2462:
2457:
2456:
2443:
2434:
2425:
2416:
2407:
2398:
2389:
2387:
2385:
2375:
2366:
2357:
2355:
2345:
2339:Hall 1960: 11
2336:
2327:
2318:
2309:
2300:
2291:
2282:
2280:
2270:
2261:
2252:
2243:
2241:
2239:
2229:
2220:
2211:
2202:
2193:
2184:
2180:
2171:
2170:Pagan Kingdom
2168:
2166:
2163:
2161:
2158:
2157:
2145:
2139:
2130:
2123:
2122:
2115:
2106:
2097:
2093:
2083:
2080:
2078:
2075:
2073:
2070:
2068:
2067:Pagan Kingdom
2065:
2063:
2060:
2059:
2055:
2044:
2037:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1977:
1975:
1966:
1965:Tharabha Gate
1961:
1955:Rise of Pagan
1952:
1949:
1948:Thant Myint-U
1945:
1942:
1938:
1933:
1931:
1927:
1921:
1919:
1913:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1891:According to
1884:
1880:
1878:
1874:
1870:
1863:
1859:
1858:Bupaya Pagoda
1854:
1841:
1827:
1824:
1821:
1818:
1816:
1813:
1812:
1808:
1805:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1793:
1789:
1786:
1783:
1780:
1778:
1775:
1774:
1770:
1767:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1756:
1755:
1751:
1748:
1745:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1736:
1732:
1729:
1726:
1723:
1721:
1718:
1717:
1713:
1710:
1707:
1704:
1702:
1699:
1698:
1694:
1691:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1679:
1673:
1672:
1667:
1666:
1659:
1658:
1651:
1650:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1623:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1582:
1581:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1571:Saw Khin Hnit
1569:
1568:
1564:
1561:
1559:
1556:
1555:
1551:
1548:
1546:
1543:
1542:
1538:
1535:
1533:
1530:
1529:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1517:
1516:
1512:
1509:
1507:
1504:
1503:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1486:
1483:
1481:
1478:
1477:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1465:
1464:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1451:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1438:
1434:
1431:
1429:
1426:
1425:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1415:Popa Sawrahan
1413:
1412:
1406:
1405:
1400:
1399:
1394:
1393:
1388:
1387:
1378:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1345:Popa Sawrahan
1331:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1319:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1299:
1296:
1293:
1291:
1288:
1287:
1283:
1280:
1277:
1275:
1272:
1271:
1267:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1256:
1255:
1251:
1248:
1245:
1243:
1240:
1239:
1235:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1219:
1216:
1213:
1211:
1208:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1194:Tharamon Phya
1192:
1191:
1187:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1171:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1155:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1146:Kyaung Tu Yit
1144:
1143:
1139:
1136:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1123:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1107:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1095:
1091:
1088:
1085:
1083:
1080:
1079:
1075:
1072:
1069:
1067:
1064:
1063:
1059:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1047:
1043:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1031:
1025:
1024:
1019:
1018:
1013:
1012:
1005:
1004:
995:
992:
989:
987:
983:
979:
978:Tharamon Phya
975:
971:
967:
963:
958:
956:
955:
950:
946:
936:
933:
931:
927:
926:
922:
919:
917:
913:
912:
909:
908:Righteousness
905:
902:
900:
896:
895:
891:
888:
886:
882:
881:
870:
867:
865:
861:
857:
853:
850:According to
848:
846:
836:
831:
829:
825:
824:
819:
815:
812:, a scion of
811:
807:
803:
802:
797:
793:
792:
776:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
750:
748:
744:
740:
736:
732:
728:
724:
716:
712:
700:
695:
693:
688:
686:
681:
680:
678:
677:
674:
664:
663:
656:
655:Military rule
653:
652:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
636:
633:
631:
628:
627:
626:
625:
617:
614:
611:
608:
605:
602:
599:
596:
593:
590:
589:
588:1948–present
587:
584:
583:
582:
581:
573:
570:
567:
564:
561:
558:
555:
552:
551:
549:
546:
545:
544:
543:
537:
534:
531:
528:
523:
520:
517:
514:
513:
511:
508:
503:
500:
497:
494:
491:
488:
483:
482:Prome Kingdom
480:
477:
474:
471:
468:
465:
461:
458:
457:
455:
454:Upper Myanmar
452:
451:
450:
447:
442:
439:
438:
436:
435:Pagan Kingdom
433:
432:
431:
430:
424:
421:
420:
415:
410:
409:
406:825?–1057? CE
405:
402:
401:
396:
392:
387:
386:
382:
379:
376:
373:
372:
371:
370:
366:
362:
361:
358:
355:
354:
347:
343:
339:
335:
333:
301:
299:
298:Pagan Kingdom
296:
295:
292:
286:
283:
276:
275:
272:
271:
268:
265:
263:
260:
259:
255:
251:
247:
241:
237:
231:
227:
221:
217:
211:
207:
201:
197:
191:
187:
184:
181:
177:
173:
170:
167:
161:
158:
155:
149:
146:
145:Popa Sawrahan
143:
137:
134:
131:
125:
122:
119:
113:
109:
105:
101:
98:
94:
90:
87:
83:
80:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
54:
50:
46:
41:
36:
22:
19:
2664:
2655:
2633:
2614:
2601:Yazawin Kyaw
2599:
2596:Pe Maung Tin
2576:
2567:
2558:
2547:
2536:
2517:
2498:
2479:
2460:
2453:Bibliography
2442:
2433:
2424:
2415:
2406:
2397:
2374:
2365:
2344:
2335:
2326:
2317:
2308:
2299:
2294:Hall 1960: 7
2290:
2269:
2260:
2251:
2228:
2219:
2210:
2201:
2192:
2183:
2143:
2138:
2129:
2119:
2114:
2105:
2096:
1981:Song Chinese
1978:
1970:
1946:
1934:
1922:
1914:
1908:
1890:
1881:
1866:
1720:Sale Ngahkwe
1669:
1665:Yazawin Thit
1663:
1657:Maha Yazawin
1655:
1647:
1635:Maha Yazawin
1634:
1630:
1627:Yazawin Thit
1626:
1624:
1601:
1402:
1398:Yazawin Thit
1396:
1392:Maha Yazawin
1390:
1384:
1373:
1342:
1098:Yin Min Paik
1021:
1017:Yazawin Thit
1015:
1011:Maha Yazawin
1009:
1001:
990:
959:
952:
949:Yazawin Kyaw
948:
942:
937:Foe-crusher
849:
840:အရိမဒ္ဒနာပူရ
832:
821:
801:Maha Yazawin
799:
791:Yazawin Kyaw
789:
787:
751:
710:
708:
618:2021–present
440:
404:Mon kingdoms
329:
267:Succeeded by
266:
261:
18:
1893:G.H. Luce's
1835:Scholarship
1435:Son-in-law
1428:Shwe Ohnthi
1365:Shwe Ohnthi
1242:Thinli Paik
1210:Thaik Taing
1114:Paik Thinli
1082:Hti Min Yin
1050:Yathekyaung
1034:Thamoddarit
982:Thaik Taing
810:Thamoddarit
496:Shan States
262:Preceded by
121:Thamoddarit
2676:Categories
2176:References
2030:Shan Hills
1877:Pyu people
1819:1038–1044
1800:1021–1038
1781:1001–1021
1662:Reign per
1654:Reign per
1646:Reign per
1545:Shwe Hmauk
1532:Htun Htwin
1519:Shwe Laung
1506:Thein Khun
1454:Peit Taung
1383:Reign per
1357:Sri Ksetra
1258:Khan Laung
1060:Caretaker
1008:Reign per
1000:Reign per
986:Tampawaddy
954:dhammathat
743:Tampawaddy
735:Arimaddana
586:Modern era
550:1824–1948
512:1510–1752
456:1297–1555
103:Government
64:Tampawaddy
56:Arimaddana
1937:Htin Aung
1926:Anawrahta
1862:Pyusawhti
1856:Original
1825:992–1017
1822:977–1002
1762:956–1001
1616:Anawrahta
1480:Myingyway
1441:Peit Thon
1349:Htun Chit
1322:Htun Chit
1306:Htun Pyit
1290:Htun Taik
1066:Pyusawhti
945:Pyusawhti
906:House of
796:Pyusawhti
784:Formation
773:Anawrahta
749:(Bagan).
616:SAC junta
612:2011–2015
606:1988–2010
600:1962–1988
594:1948–1962
574:1942–1945
568:1900–1948
562:1885–1895
556:1824–1885
538:1752–1885
532:1740–1757
524:1599–1752
518:1510–1599
504:1429–1785
498:1215–1563
484:1482–1542
478:1365–1555
472:1315–1365
466:1297–1365
460:Myinsaing
437:849–1297
425:788?–1406
198:c. 650 CE
133:Pyusawhti
85:Religion
2654:(1832).
2154:See also
2040:See also
2010:Yamethin
2002:Myingyan
1998:Meiktila
1994:Mandalay
1985:Bianjing
1828:Brother
1806:986–992
1803:971–977
1787:964–986
1784:950–971
1771:Usurper
1768:931–964
1765:917–950
1749:915–931
1746:901–917
1743:934–956
1739:Theinhko
1733:Usurper
1730:906–915
1727:876–901
1724:904–934
1711:878–906
1708:858–876
1705:886–904
1695:Brother
1692:846–878
1689:846–858
1686:846–886
1588:829–846
1575:802–829
1565:Brother
1562:785–802
1558:Htun Lut
1549:762–785
1536:753–762
1523:744–753
1510:734–744
1497:726–734
1487:Usurper
1484:716–726
1474:Brother
1471:710–716
1467:Min Khwe
1458:660–710
1448:Brother
1445:652–660
1432:640–652
1422:Usurper
1419:613–640
1329:598–613
1326:586–613
1313:582–598
1310:570–586
1297:569–582
1294:557–570
1284:Brother
1281:557–569
1278:545–557
1274:Khan Lat
1268:Brother
1265:547–557
1262:535–545
1252:Brother
1249:532–547
1246:530–535
1233:523–532
1230:521–530
1217:516–523
1214:514–521
1201:494–516
1198:492–514
1188:Usurper
1185:439–494
1182:477–492
1169:412–439
1166:440–477
1153:387–412
1150:415–440
1137:344–387
1134:371–415
1121:324–344
1118:334–371
1105:299–324
1102:249–334
1089:242–299
1086:222–249
1073:167–242
1070:140–222
1057:152–167
1054:125–140
1041:107–152
878:Meaning
845:Nyaung U
630:Timeline
443:849–1044
106:Monarchy
97:Hinduism
89:Buddhism
2598:(ed.).
2026:Pakkoku
2018:Sagaing
2006:Kyaukse
1901:Qinghai
1815:Sokkate
1682:Pyinbya
1620:Sokkate
1493:Theinga
1369:Pyinbya
1162:Thihtan
1038:80–125
970:Thihtan
928:Era of
914:Era of
897:Era of
883:Era of
866:names.
715:Burmese
640:Leaders
157:Pyinbya
93:animism
79:Burmese
70:(Bagan)
52:Capital
2640:
2621:
2583:
2524:
2505:
2486:
2467:
2144:recast
1869:Mranma
1701:Tannet
1604:Tannet
1401:, and
1020:, and
818:Buddha
816:. The
761:Mranma
741:, and
2518:Burma
2088:Notes
2022:Minbu
2014:Magwe
1974:Halin
1909:first
1796:Kyiso
1643:Name
1584:Khelu
1380:Name
1178:Thuye
997:Name
974:Thuye
875:Name
747:Pagan
68:Pagan
2638:ISBN
2619:ISBN
2581:ISBN
2522:ISBN
2503:ISBN
2484:ISBN
2465:ISBN
2034:Mons
2024:and
1963:The
1903:and
1752:Son
1714:Son
1668:and
1629:and
1591:Son
1578:Son
1552:Son
1539:Son
1526:Son
1513:Son
1461:Son
1332:Son
1316:Son
1300:Son
1236:Son
1220:Son
1172:Son
1156:Son
1140:Son
1124:Son
1108:Son
1092:Son
872:Era
864:Pali
709:The
462:and
1361:Pyu
957:).
763:of
2678::
2383:^
2353:^
2278:^
2237:^
2036:.
2016:,
2012:,
2008:,
2004:,
2000:,
1996:,
1395:,
1389:,
1014:,
830:.
737:,
723:CE
717::
393:,
95:,
91:,
66:,
62:,
58:,
2646:.
2627:.
2589:.
2530:.
2511:.
2492:.
2473:.
837:(
713:(
698:e
691:t
684:v
416:)
412:(
397:)
389:(
348:.
334:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.