1176:. Larger volumes of hematoma at hospital admission as well as greater expansion of the hematoma on subsequent evaluation (usually occurring within 6 hours of symptom onset) are associated with a worse prognosis. Perihematomal edema, or secondary edema surrounding the hematoma, is associated with secondary brain injury, worsening neurological function and is associated with poor outcomes. Intraventricular hemorrhage, or bleeding into the ventricles of the brain, which may occur in 30–50% of patients, is also associated with long-term disability and a poor prognosis. Brain herniation is associated with poor prognoses.
912:, and therefore shows up darker on the CT scan. The oedema surrounding the haemorrhage would rapidly increase in size in the first 48 hours, and reached its maximum extent at day 14. The bigger the size of the haematoma, the larger its surrounding oedema. Brain oedema formation is due to the breakdown of red blood cells, where haemoglobin and other contents of red blood cells are released. The release of these red blood cells contents causes toxic effect on the brain and causes brain oedema. Besides, the breaking down of blood-brain barrier also contributes to the odema formation.
55:
878:
1183:) is 34–50% by 30 days after the injury, and half of the deaths occur in the first 2 days. Even though the majority of deaths occur in the first few days after ICH, survivors have a long-term excess mortality rate of 27% compared to the general population. Of those who survive an intracerebral hemorrhage, 12–39% are independent with regard to self-care; others are disabled to varying degrees and require supportive care.
736:
3332:"Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Group"
1051:
Only 7% of those with ICH are presented with clinical features of seizures while up to 25% of those have subclinical seizures. Seizures are not associated with an increased risk of death or disability. Meanwhile, anticonvulsant administration can increase the risk of death. Therefore, anticonvulsants
442:
The incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage is estimated at 24.6 cases per 100,000 person years with the incidence rate being similar in men and women. The incidence is much higher in the elderly, especially those who are 85 or older, who are 9.6 times more likely to have an intracerebral hemorrhage as
982:
can have higher functional recovery at 90 days post intracerebral haemorrhage, when compared to those who undergone other treatments such as mannitol administration, reversal of anticoagulation (those previously on anticoagulant treatment for other conditions), surgery to evacuate the haematoma, and
826:
peptides in the walls of the small blood vessels of the brain, leading to weakened blood vessel walls and an increased risk of bleeding; is also an important risk factor for the development of intracerebral hemorrhage. Other risk factors include advancing age (usually with a concomitant increase of
433:
Cerebral bleeding affects about 2.5 per 10,000 people each year. It occurs more often in males and older people. About 44% of those affected die within a month. A good outcome occurs in about 20% of those affected. Intracerebral hemorrhage, a type of hemorrhagic stroke, was first distinguished from
915:
Apart from CT scans, haematoma progression of intracerebral haemorrhage can be monitored using transcranial ultrasound. Ultrasound probe can be placed at the temporal lobe to estimate the volume of haematoma within the brain, thus identifying those with active bleeding for further intervention to
557:
30% of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) are primary, confined to the ventricular system and typically caused by intraventricular trauma, aneurysm, vascular malformations, or tumors, particularly of the choroid plexus. However 70% of IVH are secondary in nature, resulting from an expansion of an
1140:
About 8 to 33% of those with intracranial haemorrhage have neurological deterioration within the first 24 hours of hospital admission, where a large proportion of them happens within 6 to 12 hours. Rate of haematoma expansion, perihaematoma odema volume and the presence of fever can affect the
983:
standard rehabilitation care in hospital, while showing similar rate of death at 12%. Early lowering of the blood pressure can reduce the volume of the haematoma, but may not have any effect against the oedema surrounding the haematoma. Reducing the blood pressure rapidly does not cause
3035:
Roberts I, Yates D, Sandercock P, Farrell B, Wasserberg J, Lomas G, et al. (9 October 2016). "Effect of intravenous corticosteroids on death within 14 days in 10008 adults with clinically significant head injury (MRC CRASH trial): randomised placebo-controlled trial".
574:(or weakness localized to one side of the body) and paresthesia (loss of sensation) including hemisensory loss (if localized to one side of the body). These symptoms are usually rapid in onset, sometimes occurring in minutes, but not as rapid as the symptom onset in
1547:
van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der Tweel I, Algra A, Klijn CJ (February 2010). "Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis".
578:. While the duration of onset not be as rapid, it is important that patients go to the emergency department as soon as they notice any symptoms as early detection and management of stroke may lead to better outcomes post-stroke than delayed identification.
868:
Traumautic intracerebral hematomas are divided into acute and delayed. Acute intracerebral hematomas occur at the time of the injury while delayed intracerebral hematomas have been reported from as early as 6 hours post injury to as long as several weeks.
2855:
Boulouis G, Morotti A, Goldstein JN, Charidimou A (April 2017). "Intensive blood pressure lowering in patients with acute intracerebral haemorrhage: clinical outcomes and haemorrhage expansion. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials".
3079:
Edwards P, Arango M, Balica L, Cottingham R, El-Sayed H, Farrell B, et al. (2005). "Final results of MRC CRASH, a randomised placebo-controlled trial of intravenous corticosteroid in adults with head injury-outcomes at 6 months".
2710:"Effects of early intensive blood pressure-lowering treatment on the growth of hematoma and perihematomal edema in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: the Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction in Acute Cerebral Haemorrhage Trial (INTERACT)"
2056:"Clinical audit to assess implications of implementing National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guideline 32: Department of Nutrition and Dietetics at Barts and the London National Health Service (NHS) Trust 2007"
1043:
may be used to stop continued intracerebral hemorrhage in people taking directly oral acting anticoagulants (such as factor Xa inhibitors or direct thrombin inhibitors). However, if these specialized medications are not available,
897:(MRA) have been proved to be effective in diagnosing intracranial vascular malformations after ICH. So frequently, a CT angiogram will be performed in order to exclude a secondary cause of hemorrhage or to detect a "spot sign".
1770:
Xi G, Hua Y, Bhasin RR, Ennis SR, Keep RF, Hoff JT (December 2001). "Mechanisms of edema formation after intracerebral hemorrhage: effects of extravasated red blood cells on blood flow and blood-brain barrier integrity".
1227:
Hemphill JC, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, Becker K, Bendok BR, Cushman M, et al. (Council on
Clinical Cardiology; American Heart Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing) (July 2015).
2899:
Yuan ZH, Jiang JK, Huang WD, Pan J, Zhu JY, Wang JZ (June 2010). "A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of recombinant activated factor VII for patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage without hemophilia".
3460:
3441:
907:
because blood appears brighter than other tissue and is separated from the inner table of the skull by brain tissue. The tissue surrounding a bleed is often less dense than the rest of the brain because of
570:
People with intracerebral bleeding have symptoms that correspond to the functions controlled by the area of the brain that is damaged by the bleed. These localizing signs and symptoms can include
995:
guidelines in 2015 recommended decreasing the blood pressure to a SBP of 140 mmHg. However, later reviews found unclear difference between intensive and less intensive blood pressure control.
818:
Hypertension is the strongest risk factor associated with intracerebral hemorrhage and long term control of elevated blood pressure has been shown to reduce the incidence of hemorrhage.
301:(ischemic stroke being the other). Symptoms can vary dramatically depending on the severity (how much blood), acuity (over what timeframe), and location (anatomically) but can include
2806:
Ma J, Li H, Liu Y, You C, Huang S, Ma L (2015). "Effects of
Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering on Intracerebral Hemorrhage Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials".
1230:"Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association"
620:, nausea, vomiting, a depressed level of consciousness, stupor and death. Continued elevation in the intracranial pressure and the accompanying mass effect may eventually cause
3373:"Long term (13 years) prognosis after primary intracerebral haemorrhage: a prospective population based study of long term mortality, prognostic factors and causes of death"
93:, one-sided numbness, weakness, tingling, or paralysis, speech problems, vision or hearing problems, dizziness or lightheadedness or vertigo, nausea/vomiting, seizures,
1984:
Kidwell CS, Saver JL, Schubert GB, Eckstein M, Starkman S (January 1998). "Design and retrospective analysis of the Los
Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen (LAPSS)".
1720:"Computed tomography angiography or magnetic resonance angiography for detection of intracranial vascular malformations in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage"
1069:
were thought to reduce swelling. However, in large controlled studies, corticosteroids have been found to increase mortality rates and are no longer recommended.
754:
raises the risks of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage by two to six times. More common in adults than in children, intraparenchymal bleeds are usually due to
2279:
2841:
4133:
3514:
609:(CPSS). Use of these scales is recommended by professional guidelines. FAST is less reliable in the recognition of posterior circulation stroke.
2249:
602:
3408:
1378:
2609:
2019:
Kothari RU, Pancioli A, Liu T, Brott T, Broderick J (April 1999). "Cincinnati
Prehospital Stroke Scale: reproducibility and validity".
1450:
558:
existing intraparenchymal or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Intraventricular hemorrhage has been found to occur in 35% of moderate to severe
1344:
2637:
48:
Cerebral haemorrhage, cerebral hemorrhage, intra-axial hemorrhage, cerebral hematoma, cerebral bleed, brain bleed, hemorrhagic stroke
2448:
2943:
Eilertsen H, Menon CS, Law ZK, Chen C, Bath PM, Steiner T, Desborough M Jr, Sandset EC, Sprigg N, Al-Shahi Salman R (2023-10-23).
4167:
3507:
3968:
2458:
1601:
586:
1144:
The risk of death from an intraparenchymal bleed in traumatic brain injury is especially high when the injury occurs in the
3766:
1032:. Platelets however appear to worsen outcomes in those with spontaneous intracerebral bleeding on antiplatelet medication.
17:
353:
313:, speech problems, vision or hearing problems, memory loss, attention problems, coordination problems, balance problems,
2315:
1870:
3761:
3562:
2603:
1372:
778:
is not an uncommon cause of intracerebral hemorrhage in patients over the age of 55. A very small proportion is due to
4210:
3552:
3500:
2576:
2520:"Natural history of perihematomal edema after intracerebral hemorrhage measured by serial magnetic resonance imaging"
1444:
948:
and other diagnostic measures are used to determine proper treatment, which may include both medication and surgery.
562:. Thus the hemorrhage usually does not occur without extensive associated damage, and so the outcome is rarely good.
2290:
4068:
3935:
779:
326:
94:
2661:"Implications of INTERACT2 and other clinical trials: blood pressure management in acute intracerebral hemorrhage"
2518:
Venkatasubramanian C, Mlynash M, Finley-Caulfield A, Eyngorn I, Kalimuthu R, Snider RW, Wijman CA (January 2011).
624:(when different parts of the brain are displaced or shifted to new areas in relation to the skull and surrounding
344:
Hemorrhagic stroke may occur on the background of alterations to the blood vessels in the brain, such as cerebral
4103:
3713:
3557:
1045:
890:
894:
3912:
3718:
3155:"Decompressive craniectomy for the treatment of high intracranial pressure in closed traumatic brain injury"
1941:
Harbison J, Massey A, Barnett L, Hodge D, Ford GA (June 1999). "Rapid ambulance protocol for acute stroke".
1132:
holds promise of reduced mortality, but the effects of long‐term neurological outcome remain controversial.
3577:
511:, leading to neurological dysfunction. Substantial displacement of brain parenchyma may cause elevation of
585:(facial droop, arm weakness, speech difficulty, and time to call emergency services), as advocated by the
4006:
4001:
3851:
3645:
1894:"Early Stroke Recognition and Time-based Emergency Care Performance Metrics for Intracerebral Hemorrhage"
1052:
are only reserved for those that have shown obvious clinical features of seizures or seizure activity on
992:
900:
819:
775:
720:
700:
616:
caused by a large mass (due to hematoma expansion) putting pressure on the brain. These symptoms include
598:
594:
527:
468:
349:
290:
286:
127:
3687:
3620:
3123:
988:
767:
415:
153:
4149:
3961:
3756:
3723:
3615:
3605:
1129:
848:
4108:
675:, incoordination of limbs and vomiting. Some cases of cerebellar hemorrhage lead to blockage of the
4220:
4179:
4053:
3794:
3641:
3475:
2757:
Butcher KS, Jeerakathil T, Hill M, Demchuk AM, Dowlatshahi D, Coutts SB, et al. (March 2013).
2145:"Endoscopic management of hypertensive intraventricular haemorrhage with obstructive hydrocephalus"
975:
958:
936:(15%), cerebrum (10–20%), cerebellum (10–13%), pons (7–15%), or elsewhere in the brainstem (1–6%).
559:
2257:
1892:
Colton K, Richards CT, Pruitt PB, Mendelson SJ, Holl JL, Naidech AM, et al. (February 2020).
1674:
Feldmann E, Broderick JP, Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Brass LM, Brott T, et al. (September 2005).
916:
stop the bleeding. Using ultrasound can also reduces radiation risk to the subject from CT scans.
406:
due to strict blood pressure goals and frequent use of both pressors and antihypertensive agents.
4162:
4128:
4085:
4026:
3993:
3885:
3833:
3789:
3703:
3632:
3523:
955:
is indicated in people with decreased level of consciousness or other risk of airway obstruction.
840:
755:
740:
606:
496:
444:
118:
3372:
2196:"Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association"
4184:
4174:
4058:
3985:
2347:"Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage: A prospective study"
1909:
1819:"Time course of early postadmission hematoma expansion in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage"
1053:
979:
836:
472:
221:
161:
145:
3283:"Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality"
2194:
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, et al. (January 2013).
1362:
4118:
4113:
4075:
3907:
3636:
2835:
2708:
Anderson CS, Huang Y, Arima H, Heeley E, Skulina C, Parsons MW, et al. (February 2010).
2593:
2483:
The
Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. Le Journal Canadien des Sciences Neurologiques
712:
613:
512:
423:
365:
3492:
1434:
4215:
4063:
3954:
3667:
3330:
Broderick J, Connolly S, Feldmann E, Hanley D, Kase C, Krieger D, et al. (June 2007).
1817:
Ovesen C, Christensen AF, Krieger DW, Rosenbaum S, Havsteen I, Christensen H (April 2014).
1114:
1025:
852:
2645:
2396:"Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Clinical Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An Update"
430:
is frequently avoided. Sometimes surgery to directly remove the blood can be therapeutic.
8:
4080:
4043:
3930:
3808:
3746:
3657:
3464:
3204:"Time course and predictors of neurological deterioration after intracerebral hemorrhage"
1013:
952:
844:
806:
724:
708:
680:
539:
448:
403:
372:
173:
110:
4095:
4038:
3869:
3708:
3400:
3312:
3228:
3203:
3179:
3154:
3105:
3061:
2925:
2881:
2788:
2739:
2690:
2544:
2519:
2420:
2395:
2371:
2346:
2220:
2195:
2171:
2144:
1966:
1918:
1893:
1848:
1796:
1744:
1719:
1692:
1675:
1651:
1573:
1524:
1318:
1293:
688:
633:
590:
543:
535:
516:
434:
ischemic strokes due to insufficient blood flow, so called "leaks and plugs", in 1823.
345:
85:
66:
3371:
Hansen BM, Nilsson OG, Anderson H, Norrving B, Säveland H, Lindgren A (October 2013).
3093:
3049:
2945:"Haemostatic therapies for stroke due to acute, spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage"
2032:
1954:
1561:
4189:
4021:
4016:
3828:
3823:
3662:
3610:
3392:
3353:
3304:
3233:
3184:
3097:
3053:
3017:
2976:
2964:
2917:
2873:
2823:
2780:
2731:
2682:
2599:
2572:
2549:
2500:
2454:
2425:
2376:
2225:
2176:
2118:
2077:
2036:
2001:
1958:
1923:
1840:
1788:
1749:
1697:
1643:
1638:
1621:
1597:
1565:
1528:
1516:
1440:
1415:
1368:
1323:
1251:
1157:
1149:
862:
832:
795:
500:
452:
240:
209:
73:
3469:
3404:
3109:
3065:
2929:
2885:
2819:
2792:
2694:
1970:
1655:
1577:
843:(LDL) levels (usually below 70). The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as the
54:
4033:
3582:
3572:
3535:
3384:
3343:
3316:
3294:
3223:
3215:
3174:
3170:
3166:
3089:
3045:
3007:
2972:
2960:
2956:
2909:
2865:
2815:
2770:
2743:
2721:
2672:
2539:
2531:
2490:
2444:
2415:
2407:
2366:
2358:
2345:
Ma C, Gurol ME, Huang Z, Lichtenstein AH, Wang X, Wang Y, et al. (July 2019).
2215:
2207:
2166:
2156:
2108:
2067:
2028:
1993:
1950:
1913:
1905:
1852:
1830:
1800:
1780:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1687:
1633:
1557:
1508:
1405:
1394:"Blood Pressure Management for Acute Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: The Evidence"
1313:
1305:
1241:
676:
656:
629:
621:
181:
1010:. It thus overall does not result in better outcomes in those without hemophilia.
3567:
3480:
3348:
3331:
3219:
2775:
2758:
2726:
2709:
2677:
2660:
2535:
2362:
2211:
1835:
1818:
1246:
1229:
1161:
1066:
1007:
692:
637:
575:
547:
492:
427:
407:
384:
330:
226:
193:
98:
2996:"Intracranial haemorrhage: therapeutic interventions and anaesthetic management"
2517:
851:
are thought to have a lower risk of intracerebral hemorrhage as compared to the
3741:
3587:
2913:
1620:
Kalita J, Misra UK, Vajpeyee A, Phadke RV, Handique A, Salwani V (April 2009).
1345:"Brain Bleed/Hemorrhage (Intracranial Hemorrhage): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment"
1180:
1089:
1040:
984:
759:
388:
334:
236:
197:
149:
131:
102:
3751:
3454:
2495:
2478:
2072:
2055:
1997:
1309:
1059:
H2 antagonists or proton pump inhibitors are commonly given to try to prevent
483:
and results from a wide spectrum of disorders. It is more likely to result in
4204:
3388:
3266:
Graham DI, Gennareli TA (2000). "Chapter 5". In Cooper P, Golfinos G (eds.).
2968:
2869:
2323:
2081:
1878:
1676:"Major risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage in the young are modifiable"
1169:
1122:
962:
882:
828:
735:
684:
648:
582:
419:
3450:
3299:
3282:
4157:
3977:
3396:
3357:
3237:
3188:
3101:
3057:
3021:
2980:
2944:
2921:
2877:
2827:
2784:
2735:
2686:
2553:
2504:
2429:
2411:
2380:
2229:
2180:
2122:
2040:
1962:
1927:
1844:
1792:
1753:
1701:
1647:
1569:
1520:
1419:
1410:
1393:
1327:
1255:
1165:
1152:
are almost always fatal, because they cause damage to cranial nerve X, the
1107:
1060:
1036:
1029:
925:
877:
823:
789:
751:
660:
551:
508:
361:
357:
78:
3308:
2161:
2143:
Yadav YR, Mukerji G, Shenoy R, Basoor A, Jain G, Nelson A (January 2007).
2005:
1784:
1512:
1179:
For spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage seen on CT scan, the death rate (
4138:
3012:
2995:
2759:"The Intracerebral Hemorrhage Acutely Decreasing Arterial Pressure Trial"
2479:"Comparison of CTA to DSA in determining the etiology of spontaneous ICH"
1153:
1103:
411:
376:
306:
185:
168:
157:
3433:
2477:
Yeung R, Ahmad T, Aviv RI, de Tilly LN, Fox AJ, Symons SP (March 2009).
29:
Type of intracranial bleeding that occurs within the brain tissue itself
4123:
4048:
3679:
3597:
1718:
Josephson CB, White PM, Krishan A, Al-Shahi Salman R (September 2014).
1173:
1145:
1118:
999:
664:
625:
571:
488:
476:
380:
318:
310:
189:
2113:
2096:
479:. Intraparenchymal hemorrhage accounts for approximately 8-13% of all
105:, memory loss, attention and coordination problems, balance problems,
3861:
3281:
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE, Tomsick T, Huster G (July 1993).
1364:
Imaging of the Brain, Expert
Radiology Series,1: Imaging of the Brain
1021:
1017:
800:
443:
compared to those of middle age. It accounts for 20% of all cases of
314:
247:
3251:
Sanders MJ, McKenna K (2001). "Chapter 22: Head and Facial Trauma".
1717:
3899:
3652:
1099:
1092:
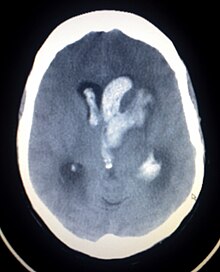
1082:
1078:
1003:
933:
856:
812:
763:
652:
617:
531:
302:
177:
90:
2854:
2642:
eMedicine
Specialties > Neurology > Neurological Emergencies
3784:
1816:
1546:
1499:
1360:
945:
929:
904:
715:, pinpoint (but reactive) pupils, gaze palsies, facial weakness,
672:
396:
392:
322:
214:
201:
62:
3131:
1542:
1540:
1538:
1081:
is greater than 3 cm (1 in), if there is a structural
3527:
3445:
3329:
1226:
1085:
747:
668:
480:
368:, which can cause intraparenchymal or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
298:
3946:
1673:
3544:
3522:
3370:
3078:
3034:
2756:
1891:
1622:"Brain herniations in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage"
1535:
1160:
and breathing. This kind of hemorrhage can also occur in the
909:
771:
504:
484:
338:
294:
135:
106:
3280:
1983:
628:
supporting structures). Brain herniation is associated with
3627:
2272:
716:
704:
696:
641:
123:
2193:
1940:
1361:
Naidich TP, Castillo M, Cha S, Smirniotopoulos JG (2012).
944:
Treatment depends substantially on the type of ICH. Rapid
691:
of the brain leads to a decreased level of consciousness,
1619:
827:
cerebral amyloid angiopathy risk in the elderly), use of
746:
Intracerebral bleeds are the second most common cause of
2707:
2344:
2142:
750:, accounting for 10% of hospital admissions for stroke.
293:, or into both. An ICH is a type of bleeding within the
2053:
2018:
663:
or hemisensory loss. Intracerebral hemorrhage into the
65:
of a spontaneous intracerebral bleed, leaking into the
2638:"Intracranial Haemorrhage: Treatment & Medication"
2476:
2287:
Orlando
Regional Healthcare, Education and Development
1125:
hemorrhages, although successful reports are limited.
1002:
within 4 hours limits the bleeding and formation of a
581:
A mnemonic to remember the warning signs of stroke is
371:
The biggest risk factors for spontaneous bleeding are
2942:
2442:
2250:"CMSD 336 Neuropathologies of Language and Cognition"
1864:
1862:
655:
causes contralateral hemiplegia due to damage to the
612:
Other symptoms include those that indicate a rise in
3423:
3259:
3202:
Lord AS, Gilmore E, Choi HA, Mayer SA (March 2015).
3201:
2256:. Chico: California State University. Archived from
530:(IVH), also known asintraventricular bleeding, is a
4134:
Spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality
3244:
928:, intracerebral hemorrhages typically occur in the
703:. Brainstem hemorrhage most commonly occurs in the
3377:Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry
2858:Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry
1859:
1591:
1398:Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
865:may be a risk factor but the association is weak.
762:. Acceleration-deceleration trauma, rupture of an
414:kept in the normal range. A procedure to place an
2898:
2840:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of September 2024 (
1339:
1337:
987:in those who have intracerebral haemorrhage. The
4202:
3152:
1769:
1291:
402:Treatment should typically be carried out in an
134:(when bleeding is severe or in the brain stem),
3265:
2658:
2387:
2054:Meredith TL, Freed N, Soulsby C, Bay S (2009).
1356:
1354:
1141:chances of getting neurological complications.
542:is produced and circulates through towards the
3250:
2338:
2094:
1898:Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases
1334:
1172:when due to head injury, and sometimes in the
965:, using isotonic rather than hypotonic fluids.
522:
463:
3962:
3508:
1868:
1494:
1492:
1490:
1488:
1486:
1484:
1482:
1480:
603:Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen (LAPSS)
503:. Intracerebral hemorrhages and accompanying
3146:
2993:
2799:
2631:
2629:
2627:
2625:
2623:
2621:
2619:
2511:
2280:"Overview of Adult Traumatic Brain Injuries"
2243:
2241:
2239:
2187:
1478:
1476:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1462:
1460:
1351:
3268:Pathology of Brain Damage After Head Injury
3159:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
2949:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
1724:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
1298:Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America
974:Rapid lowering of the blood pressure using
822:, a disease characterized by deposition of
3969:
3955:
3515:
3501:
2805:
2635:
2138:
2136:
2134:
2132:
1910:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104552
1222:
1220:
1218:
1216:
679:with subsequent impairment of drainage of
53:
3347:
3298:
3227:
3178:
3153:Sahuquillo J, Dennis JA (December 2019).
3011:
2774:
2725:
2676:
2616:
2566:
2543:
2494:
2453:. Cambridge University Press. p. 6.
2419:
2393:
2370:
2247:
2236:
2219:
2170:
2160:
2112:
2071:
1917:
1834:
1743:
1691:
1637:
1457:
1432:
1409:
1367:. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 387.
1317:
1287:
1285:
1245:
1214:
1212:
1210:
1208:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1198:
1196:
1110:, avoiding invasive surgical procedures.
1006:. However, it also increases the risk of
499:, and therefore constitutes an immediate
162:hemorrhagic conversion of ischemic stroke
2659:Anderson CS, Qureshi AI (January 2015).
2598:. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 49.
2313:
2307:
2097:"Posterior circulation ischaemic stroke"
1292:Caceres JA, Goldstein JN (August 2012).
1283:
1281:
1279:
1277:
1275:
1273:
1271:
1269:
1267:
1265:
876:
835:, the presence of cerebral microbleeds,
739:Axial CT scan showing hemorrhage in the
734:
475:in which there is bleeding within brain
2591:
2394:An SJ, Kim TJ, Yoon BW (January 2017).
2129:
1426:
14:
4203:
3274:
3270:(4th ed.). New York: Morgan Hill.
1391:
1193:
3950:
3496:
2472:
2470:
1812:
1810:
1765:
1763:
1713:
1711:
1669:
1667:
1665:
1615:
1613:
1498:
1262:
1164:or subcortical areas, usually in the
1148:. Intraparenchymal bleeds within the
587:Department of Health (United Kingdom)
565:
3767:Partial anterior circulation infarct
2060:Proceedings of the Nutrition Society
1501:The New England Journal of Medicine
1156:, which plays an important role in
758:, but can also be due to depressed
607:Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale
410:should be reversed if possible and
354:cerebral arteriovenous malformation
24:
3762:Total anterior circulation infarct
3563:Posterior cerebral artery syndrome
2467:
2254:The Neuroscience on the Web Series
1807:
1760:
1708:
1693:10.1161/01.str.0000177480.62341.6b
1662:
1610:
1592:Schutta HS, Lechtenberg R (1998).
659:. Other possible symptoms include
113:(when bleed is in the brain stem)
25:
4232:
3553:Anterior cerebral artery syndrome
3419:
2095:Merwick Á, Werring D (May 2014).
507:may disrupt or compress adjacent
4069:Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
3936:Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
3411:from the original on 2014-02-22.
2994:Fogarty Mack P (December 2014).
2902:Journal of Clinical Neuroscience
2612:from the original on 2017-03-12.
1639:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2008.01095.x
1453:from the original on 2016-10-02.
1392:Ko SB, Yoon BW (December 2017).
1381:from the original on 2016-10-02.
780:cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
327:decreased level of consciousness
289:(i.e. the parenchyma), into its
4104:Anterior spinal artery syndrome
3976:
3714:Anterior spinal artery syndrome
3558:Middle cerebral artery syndrome
3364:
3323:
3195:
3116:
3072:
3028:
2987:
2936:
2892:
2848:
2820:10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9270-13.0
2750:
2701:
2652:
2636:Liebeskind DS (7 August 2006).
2585:
2560:
2436:
2088:
2047:
2012:
1977:
1934:
1885:
1063:, a condition linked with ICH.
1046:prothrombin complex concentrate
891:computed tomography angiography
437:
395:use. Diagnosis is typically by
3255:(2nd revised ed.). Mosby.
3171:10.1002/14651858.CD003983.pub3
3000:British Journal of Anaesthesia
2961:10.1002/14651858.CD005951.pub5
1736:10.1002/14651858.CD009372.pub2
1584:
1385:
969:
895:magnetic resonance angiography
785:Risk factors for ICH include:
13:
1:
3719:Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
3094:10.1016/s0140-6736(05)66552-x
3050:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17188-2
2033:10.1016/S0196-0644(99)70299-4
1955:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)00966-6
1869:Vinas FC, Pilitsis J (2006).
1626:Acta Neurologica Scandinavica
1594:Neurology practice guidelines
1562:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70340-0
1186:
1102:may be passed into the brain
1035:The specific reversal agents
770:(AVM), and bleeding within a
447:in the United States, behind
379:. Other risk factors include
325:, nausea/vomiting, seizures,
3349:10.1161/strokeaha.107.183689
3220:10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007704
2776:10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000188
2727:10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.561795
2678:10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006321
2536:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.590646
2363:10.1212/WNL.0000000000007853
2212:10.1161/CIR.0b013e31828124ad
2021:Annals of Emergency Medicine
1836:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003608
1247:10.1161/str.0000000000000069
1135:
939:
872:
683:from the brain. The ensuing
515:(ICP) and potentially fatal
285:, is a sudden bleeding into
260:2.5 per 10,000 people a year
7:
4007:Intraventricular hemorrhage
4002:Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
1077:Surgery is required if the
993:American Stroke Association
919:
901:Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
820:Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
725:reticular activating system
723:(if there is damage to the
721:persistent vegetative state
701:persistent vegetative state
693:total loss of consciousness
599:National Stroke Association
595:American Stroke Association
528:Intraventricular hemorrhage
523:Intraventricular hemorrhage
469:Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
464:Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
350:cerebral amyloid angiopathy
331:total loss of consciousness
154:arteriovenous malformations
128:persistent vegetative state
99:total loss of consciousness
10:
4237:
3688:Cerebellar stroke syndrome
3621:Lateral medullary syndrome
3253:Mosby's Paramedic Textbook
3128:Cedars-Sinai Health System
2914:10.1016/j.jocn.2009.11.020
1986:Prehospital Emergency Care
1072:
1028:may be given in case of a
989:American Heart Association
849:direct thrombin inhibitors
768:arteriovenous malformation
687:, or fluid buildup in the
416:external ventricular drain
4180:Injury of accessory nerve
4148:
4094:
3984:
3923:
3913:Charcot–Bouchard aneurysm
3898:
3878:
3860:
3842:
3816:
3807:
3777:
3757:Transient ischemic attack
3734:
3724:Subclavian steal syndrome
3696:
3678:
3616:Medial medullary syndrome
3606:Brainstem stroke syndrome
3596:
3543:
3534:
3427:
2496:10.1017/s0317167100006533
2073:10.1017/s0029665109002080
1998:10.1080/10903129808958878
1871:"Penetrating Head Trauma"
1310:10.1016/j.emc.2012.06.003
1294:"Intracranial hemorrhage"
730:
309:, numbness, tingling, or
264:
256:
246:
232:
220:
208:
167:
141:
117:
84:
72:
61:
52:
44:
39:
4211:Cerebrovascular diseases
4054:Post-concussion syndrome
3795:Transient global amnesia
3642:Lateral pontine syndrome
3578:Dejerine–Roussy syndrome
3524:Cerebrovascular diseases
3389:10.1136/jnnp-2013-305200
2870:10.1136/jnnp-2016-315346
2569:Handbook of Neurosurgery
2450:Intracerebral Hemorrhage
1121:drainage may be used in
976:antihypertensive therapy
833:antiplatelet medications
560:traumatic brain injuries
458:
287:the tissues of the brain
275:Intracerebral hemorrhage
268:44% die within one month
40:Intracerebral hemorrhage
4163:Peripheral nerve injury
4129:Posterior cord syndrome
4086:Penetrating head injury
4027:Subarachnoid hemorrhage
3994:Intracranial hemorrhage
3886:Intracranial hemorrhage
3704:Carotid artery stenosis
3633:Medial pontine syndrome
3300:10.1161/01.STR.24.7.987
2822:(inactive 2024-09-12).
1596:. New York: M. Dekker.
1439:. Remedica. p. 1.
1106:to close off or dilate
841:low density lipoprotein
774:are additional causes.
756:penetrating head trauma
707:and is associated with
636:, pupillary asymmetry,
497:subarachnoid hemorrhage
445:cerebrovascular disease
4185:Brachial plexus injury
4175:Wallerian degeneration
4109:Brown-Séquard syndrome
4059:Second-impact syndrome
3986:Traumatic brain injury
3124:"Cerebral Hemorrhages"
3006:(Suppl 2): ii17–ii25.
2412:10.5853/jos.2016.00864
2289:. 2004. Archived from
1411:10.1055/s-0037-1608777
1054:electroencephalography
980:hypertensive emergency
961:are given to maintain
886:
837:chronic kidney disease
743:
473:intracerebral bleeding
426:, however, the use of
222:Differential diagnosis
4119:Central cord syndrome
4114:Cauda equina syndrome
4076:Diffuse axonal injury
3908:Intracranial aneurysm
3697:Extracranial arteries
2567:Greenberg MS (2016).
2162:10.1186/1471-2377-7-1
1785:10.1161/hs1201.099820
1550:The Lancet. Neurology
1513:10.1056/NEJMra2201449
1026:platelet transfusions
903:can be recognized on
881:Spontaneous ICH with
880:
853:vitamin K antagonists
792:(high blood pressure)
738:
713:cranial nerve palsies
614:intracranial pressure
546:. It can result from
513:intracranial pressure
471:(IPH) is one form of
424:intracranial pressure
418:may be used to treat
366:intracranial aneurysm
4064:Dementia pugilistica
3844:Cerebral/Intra-axial
3790:Binswanger's disease
2808:Turkish Neurosurgery
2447:, Hanley DF (2009).
2248:McCaffrey P (2001).
1433:Hennerici M (2003).
1115:stereotactic surgery
1095:in a young patient.
845:factor Xa inhibitors
647:Hemorrhage into the
517:herniation syndromes
18:Cerebral haemorrhage
4081:Abusive head trauma
4044:Cerebral laceration
3931:Cerebral vasculitis
3809:Haemorrhagic stroke
3747:Cerebral infarction
3088:(9475): 1957–1959.
3044:(9442): 1321–1328.
2592:Prayson RA (2012).
2314:Shepherd S (2004).
2107:(may19 33): g3175.
953:Tracheal intubation
926:high blood pressure
807:alcohol consumption
752:High blood pressure
709:shortness of breath
681:cerebrospinal fluid
540:cerebrospinal fluid
449:cerebral thrombosis
404:intensive care unit
373:high blood pressure
174:High blood pressure
111:shortness of breath
4096:Spinal cord injury
4039:Cerebral contusion
3870:Duret haemorrhages
3013:10.1093/bja/aeu397
1048:may also be used.
887:
776:Amyloid angiopathy
744:
591:Stroke Association
566:Signs and symptoms
552:hemorrhagic stroke
544:subarachnoid space
536:ventricular system
346:arteriolosclerosis
307:one-sided weakness
283:hemorrhagic stroke
239:control, surgery,
67:lateral ventricles
4198:
4197:
4190:Traumatic neuroma
4150:Peripheral nerves
4022:Epidural hematoma
4017:Subdural hematoma
3944:
3943:
3894:
3893:
3803:
3802:
3668:Claude's syndrome
3663:Benedikt syndrome
3490:
3489:
3383:(10): 1150–1155.
2460:978-0-521-87331-4
2400:Journal of Stroke
2114:10.1136/bmj.g3175
1779:(12): 2932–2938.
1603:978-0-8247-0104-8
1507:(17): 1589–1596.
1436:Imaging in Stroke
1158:blood circulation
1150:medulla oblongata
863:Cigarette smoking
796:Diabetes mellitus
634:extensor rigidity
534:into the brain's
501:medical emergency
453:cerebral embolism
281:), also known as
272:
271:
241:ventricular drain
210:Diagnostic method
34:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
4228:
4034:Brain herniation
3971:
3964:
3957:
3948:
3947:
3852:Intraventricular
3814:
3813:
3658:Weber's syndrome
3583:Watershed stroke
3573:Moyamoya disease
3541:
3540:
3536:Ischaemic stroke
3517:
3510:
3503:
3494:
3493:
3425:
3424:
3413:
3412:
3368:
3362:
3361:
3351:
3342:(6): 2001–2023.
3327:
3321:
3320:
3302:
3278:
3272:
3271:
3263:
3257:
3256:
3248:
3242:
3241:
3231:
3199:
3193:
3192:
3182:
3165:(12): CD003983.
3150:
3144:
3143:
3141:
3139:
3130:. Archived from
3120:
3114:
3113:
3076:
3070:
3069:
3032:
3026:
3025:
3015:
2991:
2985:
2984:
2975: 10591281.
2955:(10): CD005951.
2940:
2934:
2933:
2896:
2890:
2889:
2852:
2846:
2845:
2839:
2831:
2803:
2797:
2796:
2778:
2754:
2748:
2747:
2729:
2705:
2699:
2698:
2680:
2656:
2650:
2649:
2644:. Archived from
2633:
2614:
2613:
2589:
2583:
2582:
2564:
2558:
2557:
2547:
2515:
2509:
2508:
2498:
2474:
2465:
2464:
2440:
2434:
2433:
2423:
2391:
2385:
2384:
2374:
2357:(5): e445–e457.
2342:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2331:
2322:. Archived from
2311:
2305:
2304:
2302:
2301:
2295:
2284:
2276:
2270:
2269:
2267:
2265:
2245:
2234:
2233:
2223:
2191:
2185:
2184:
2174:
2164:
2140:
2127:
2126:
2116:
2092:
2086:
2085:
2075:
2051:
2045:
2044:
2016:
2010:
2009:
1981:
1975:
1974:
1938:
1932:
1931:
1921:
1889:
1883:
1882:
1877:. Archived from
1866:
1857:
1856:
1838:
1814:
1805:
1804:
1767:
1758:
1757:
1747:
1715:
1706:
1705:
1695:
1686:(9): 1881–1885.
1671:
1660:
1659:
1641:
1617:
1608:
1607:
1588:
1582:
1581:
1544:
1533:
1532:
1496:
1455:
1454:
1430:
1424:
1423:
1413:
1389:
1383:
1382:
1358:
1349:
1348:
1341:
1332:
1331:
1321:
1289:
1260:
1259:
1249:
1240:(7): 2032–2060.
1224:
677:fourth ventricle
657:internal capsule
630:hyperventilation
622:brain herniation
297:and one kind of
252:20% good outcome
182:high cholesterol
57:
37:
36:
21:
4236:
4235:
4231:
4230:
4229:
4227:
4226:
4225:
4221:Types of stroke
4201:
4200:
4199:
4194:
4144:
4090:
3980:
3975:
3945:
3940:
3919:
3890:
3874:
3856:
3838:
3799:
3773:
3730:
3692:
3674:
3592:
3568:Amaurosis fugax
3530:
3521:
3491:
3486:
3485:
3436:
3422:
3417:
3416:
3369:
3365:
3328:
3324:
3279:
3275:
3264:
3260:
3249:
3245:
3200:
3196:
3151:
3147:
3137:
3135:
3122:
3121:
3117:
3077:
3073:
3033:
3029:
2992:
2988:
2941:
2937:
2897:
2893:
2853:
2849:
2833:
2832:
2804:
2800:
2755:
2751:
2706:
2702:
2657:
2653:
2634:
2617:
2606:
2590:
2586:
2579:
2565:
2561:
2516:
2512:
2475:
2468:
2461:
2443:Carhuapoma JR,
2441:
2437:
2392:
2388:
2343:
2339:
2329:
2327:
2312:
2308:
2299:
2297:
2293:
2282:
2278:
2277:
2273:
2263:
2261:
2246:
2237:
2192:
2188:
2141:
2130:
2093:
2089:
2052:
2048:
2017:
2013:
1982:
1978:
1939:
1935:
1890:
1886:
1867:
1860:
1815:
1808:
1768:
1761:
1730:(9): CD009372.
1716:
1709:
1672:
1663:
1618:
1611:
1604:
1589:
1585:
1545:
1536:
1497:
1458:
1447:
1431:
1427:
1390:
1386:
1375:
1359:
1352:
1343:
1342:
1335:
1290:
1263:
1225:
1194:
1189:
1138:
1075:
1067:Corticosteroids
1008:thromboembolism
978:for those with
972:
942:
922:
875:
760:skull fractures
741:posterior fossa
733:
638:pyramidal signs
576:ischemic stroke
568:
548:physical trauma
525:
493:ischemic stroke
466:
461:
440:
428:corticosteroids
408:Anticoagulation
385:low cholesterol
319:lightheadedness
227:Ischemic stroke
194:low cholesterol
95:decreased level
35:
30:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4234:
4224:
4223:
4218:
4213:
4196:
4195:
4193:
4192:
4187:
4182:
4177:
4172:
4171:
4170:
4168:classification
4165:
4154:
4152:
4146:
4145:
4143:
4142:
4141:(Quadriplegia)
4136:
4131:
4126:
4121:
4116:
4111:
4106:
4100:
4098:
4092:
4091:
4089:
4088:
4083:
4078:
4073:
4072:
4071:
4066:
4061:
4056:
4046:
4041:
4036:
4031:
4030:
4029:
4024:
4019:
4011:
4010:
4009:
4004:
3996:
3990:
3988:
3982:
3981:
3974:
3973:
3966:
3959:
3951:
3942:
3941:
3939:
3938:
3933:
3927:
3925:
3921:
3920:
3918:
3917:
3916:
3915:
3904:
3902:
3896:
3895:
3892:
3891:
3889:
3888:
3882:
3880:
3876:
3875:
3873:
3872:
3866:
3864:
3858:
3857:
3855:
3854:
3848:
3846:
3840:
3839:
3837:
3836:
3831:
3826:
3820:
3818:
3811:
3805:
3804:
3801:
3800:
3798:
3797:
3792:
3787:
3781:
3779:
3775:
3774:
3772:
3771:
3770:
3769:
3764:
3759:
3752:Classification
3749:
3744:
3742:Brain ischemia
3738:
3736:
3735:Classification
3732:
3731:
3729:
3728:
3727:
3726:
3716:
3711:
3706:
3700:
3698:
3694:
3693:
3691:
3690:
3684:
3682:
3676:
3675:
3673:
3672:
3671:
3670:
3665:
3660:
3650:
3649:
3648:
3646:Millard-Gubler
3639:
3625:
3624:
3623:
3618:
3608:
3602:
3600:
3594:
3593:
3591:
3590:
3588:Lacunar stroke
3585:
3580:
3575:
3570:
3565:
3560:
3555:
3549:
3547:
3538:
3532:
3531:
3520:
3519:
3512:
3505:
3497:
3488:
3487:
3484:
3483:
3472:
3457:
3437:
3432:
3431:
3429:
3428:Classification
3421:
3420:External links
3418:
3415:
3414:
3363:
3322:
3293:(7): 987–993.
3273:
3258:
3243:
3214:(3): 647–652.
3194:
3145:
3115:
3071:
3027:
2986:
2935:
2908:(6): 685–693.
2891:
2864:(4): 339–345.
2847:
2814:(4): 544–551.
2798:
2769:(3): 620–626.
2749:
2720:(2): 307–312.
2700:
2671:(1): 291–295.
2651:
2648:on 2009-03-12.
2615:
2605:978-1437709490
2604:
2595:Neuropathology
2584:
2577:
2559:
2510:
2489:(2): 176–180.
2466:
2459:
2435:
2386:
2337:
2306:
2271:
2235:
2206:(1): e6–e245.
2186:
2128:
2087:
2046:
2027:(4): 373–378.
2011:
1992:(4): 267–273.
1976:
1949:(9168): 1935.
1933:
1884:
1881:on 2005-09-13.
1858:
1829:(4): 994–999.
1806:
1759:
1707:
1661:
1632:(4): 254–260.
1609:
1602:
1583:
1556:(2): 167–176.
1534:
1456:
1445:
1425:
1404:(6): 718–725.
1384:
1374:978-1416050094
1373:
1350:
1333:
1304:(3): 771–794.
1261:
1191:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1170:temporal lobes
1137:
1134:
1113:Aspiration by
1074:
1071:
1041:andexanet alfa
985:brain ischemia
971:
968:
967:
966:
956:
941:
938:
921:
918:
874:
871:
829:anticoagulants
816:
815:
809:
803:
798:
793:
732:
729:
567:
564:
524:
521:
465:
462:
460:
457:
439:
436:
389:blood thinners
335:neck stiffness
270:
269:
266:
262:
261:
258:
254:
253:
250:
244:
243:
237:Blood pressure
234:
230:
229:
224:
218:
217:
212:
206:
205:
198:blood thinners
171:
165:
164:
143:
139:
138:
132:cardiac arrest
121:
115:
114:
103:neck stiffness
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
59:
58:
50:
49:
46:
42:
41:
33:
28:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4233:
4222:
4219:
4217:
4214:
4212:
4209:
4208:
4206:
4191:
4188:
4186:
4183:
4181:
4178:
4176:
4173:
4169:
4166:
4164:
4161:
4160:
4159:
4156:
4155:
4153:
4151:
4147:
4140:
4137:
4135:
4132:
4130:
4127:
4125:
4122:
4120:
4117:
4115:
4112:
4110:
4107:
4105:
4102:
4101:
4099:
4097:
4093:
4087:
4084:
4082:
4079:
4077:
4074:
4070:
4067:
4065:
4062:
4060:
4057:
4055:
4052:
4051:
4050:
4047:
4045:
4042:
4040:
4037:
4035:
4032:
4028:
4025:
4023:
4020:
4018:
4015:
4014:
4012:
4008:
4005:
4003:
4000:
3999:
3997:
3995:
3992:
3991:
3989:
3987:
3983:
3979:
3972:
3967:
3965:
3960:
3958:
3953:
3952:
3949:
3937:
3934:
3932:
3929:
3928:
3926:
3922:
3914:
3911:
3910:
3909:
3906:
3905:
3903:
3901:
3897:
3887:
3884:
3883:
3881:
3877:
3871:
3868:
3867:
3865:
3863:
3859:
3853:
3850:
3849:
3847:
3845:
3841:
3835:
3832:
3830:
3827:
3825:
3822:
3821:
3819:
3815:
3812:
3810:
3806:
3796:
3793:
3791:
3788:
3786:
3783:
3782:
3780:
3776:
3768:
3765:
3763:
3760:
3758:
3755:
3754:
3753:
3750:
3748:
3745:
3743:
3740:
3739:
3737:
3733:
3725:
3722:
3721:
3720:
3717:
3715:
3712:
3710:
3707:
3705:
3702:
3701:
3699:
3695:
3689:
3686:
3685:
3683:
3681:
3677:
3669:
3666:
3664:
3661:
3659:
3656:
3655:
3654:
3651:
3647:
3643:
3640:
3638:
3634:
3631:
3630:
3629:
3626:
3622:
3619:
3617:
3614:
3613:
3612:
3609:
3607:
3604:
3603:
3601:
3599:
3595:
3589:
3586:
3584:
3581:
3579:
3576:
3574:
3571:
3569:
3566:
3564:
3561:
3559:
3556:
3554:
3551:
3550:
3548:
3546:
3542:
3539:
3537:
3533:
3529:
3525:
3518:
3513:
3511:
3506:
3504:
3499:
3498:
3495:
3482:
3478:
3477:
3473:
3471:
3467:
3466:
3462:
3458:
3456:
3452:
3448:
3447:
3443:
3439:
3438:
3435:
3430:
3426:
3410:
3406:
3402:
3398:
3394:
3390:
3386:
3382:
3378:
3374:
3367:
3359:
3355:
3350:
3345:
3341:
3337:
3333:
3326:
3318:
3314:
3310:
3306:
3301:
3296:
3292:
3288:
3284:
3277:
3269:
3262:
3254:
3247:
3239:
3235:
3230:
3225:
3221:
3217:
3213:
3209:
3205:
3198:
3190:
3186:
3181:
3176:
3172:
3168:
3164:
3160:
3156:
3149:
3134:on 2009-03-12
3133:
3129:
3125:
3119:
3111:
3107:
3103:
3099:
3095:
3091:
3087:
3083:
3075:
3067:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3047:
3043:
3039:
3031:
3023:
3019:
3014:
3009:
3005:
3001:
2997:
2990:
2982:
2978:
2974:
2970:
2966:
2962:
2958:
2954:
2950:
2946:
2939:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2919:
2915:
2911:
2907:
2903:
2895:
2887:
2883:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2867:
2863:
2859:
2851:
2843:
2837:
2829:
2825:
2821:
2817:
2813:
2809:
2802:
2794:
2790:
2786:
2782:
2777:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2760:
2753:
2745:
2741:
2737:
2733:
2728:
2723:
2719:
2715:
2711:
2704:
2696:
2692:
2688:
2684:
2679:
2674:
2670:
2666:
2662:
2655:
2647:
2643:
2639:
2632:
2630:
2628:
2626:
2624:
2622:
2620:
2611:
2607:
2601:
2597:
2596:
2588:
2580:
2578:9781626232419
2574:
2570:
2563:
2555:
2551:
2546:
2541:
2537:
2533:
2529:
2525:
2521:
2514:
2506:
2502:
2497:
2492:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2473:
2471:
2462:
2456:
2452:
2451:
2446:
2439:
2431:
2427:
2422:
2417:
2413:
2409:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2390:
2382:
2378:
2373:
2368:
2364:
2360:
2356:
2352:
2348:
2341:
2326:on 2005-10-26
2325:
2321:
2320:Emedicine.com
2317:
2316:"Head Trauma"
2310:
2296:on 2008-02-27
2292:
2288:
2281:
2275:
2260:on 2005-11-25
2259:
2255:
2251:
2244:
2242:
2240:
2231:
2227:
2222:
2217:
2213:
2209:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2190:
2182:
2178:
2173:
2168:
2163:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2149:BMC Neurology
2146:
2139:
2137:
2135:
2133:
2124:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2106:
2102:
2098:
2091:
2083:
2079:
2074:
2069:
2065:
2061:
2057:
2050:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2026:
2022:
2015:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1980:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1937:
1929:
1925:
1920:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1904:(2): 104552.
1903:
1899:
1895:
1888:
1880:
1876:
1875:Emedicine.com
1872:
1865:
1863:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1837:
1832:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1813:
1811:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1766:
1764:
1755:
1751:
1746:
1741:
1737:
1733:
1729:
1725:
1721:
1714:
1712:
1703:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1685:
1681:
1677:
1670:
1668:
1666:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1645:
1640:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1616:
1614:
1605:
1599:
1595:
1590:Page 117 in:
1587:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1543:
1541:
1539:
1530:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1495:
1493:
1491:
1489:
1487:
1485:
1483:
1481:
1479:
1477:
1475:
1473:
1471:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1463:
1461:
1452:
1448:
1446:9781901346251
1442:
1438:
1437:
1429:
1421:
1417:
1412:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1388:
1380:
1376:
1370:
1366:
1365:
1357:
1355:
1346:
1340:
1338:
1329:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1288:
1286:
1284:
1282:
1280:
1278:
1276:
1274:
1272:
1270:
1268:
1266:
1257:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1192:
1184:
1182:
1177:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1142:
1133:
1131:
1126:
1124:
1123:basal ganglia
1120:
1116:
1111:
1109:
1108:blood vessels
1105:
1101:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1087:
1084:
1080:
1070:
1068:
1064:
1062:
1061:stress ulcers
1057:
1055:
1049:
1047:
1042:
1038:
1033:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1014:Frozen plasma
1011:
1009:
1005:
1001:
996:
994:
990:
986:
981:
977:
964:
963:fluid balance
960:
957:
954:
951:
950:
949:
947:
937:
935:
931:
927:
917:
913:
911:
906:
902:
898:
896:
892:
884:
883:hydrocephalus
879:
870:
866:
864:
860:
858:
854:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
825:
821:
814:
810:
808:
804:
802:
799:
797:
794:
791:
788:
787:
786:
783:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
742:
737:
728:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
686:
685:hydrocephalus
682:
678:
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
650:
649:basal ganglia
645:
643:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
610:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
579:
577:
573:
563:
561:
555:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
520:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
470:
456:
454:
450:
446:
435:
431:
429:
425:
422:or increased
421:
420:hydrocephalus
417:
413:
409:
405:
400:
398:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
369:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
342:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
249:
245:
242:
238:
235:
231:
228:
225:
223:
219:
216:
213:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
179:
175:
172:
170:
166:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
144:
140:
137:
133:
129:
125:
122:
120:
119:Complications
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
68:
64:
60:
56:
51:
47:
43:
38:
32:
27:
19:
4158:Nerve injury
4013:Extra-axial
3998:Intra-axial
3843:
3834:Subarachnoid
3474:
3459:
3440:
3380:
3376:
3366:
3339:
3335:
3325:
3290:
3286:
3276:
3267:
3261:
3252:
3246:
3211:
3207:
3197:
3162:
3158:
3148:
3136:. Retrieved
3132:the original
3127:
3118:
3085:
3081:
3074:
3041:
3037:
3030:
3003:
2999:
2989:
2952:
2948:
2938:
2905:
2901:
2894:
2861:
2857:
2850:
2836:cite journal
2811:
2807:
2801:
2766:
2762:
2752:
2717:
2713:
2703:
2668:
2664:
2654:
2646:the original
2641:
2594:
2587:
2568:
2562:
2530:(1): 73–80.
2527:
2523:
2513:
2486:
2482:
2449:
2438:
2403:
2399:
2389:
2354:
2350:
2340:
2328:. Retrieved
2324:the original
2319:
2309:
2298:. Retrieved
2291:the original
2286:
2274:
2262:. Retrieved
2258:the original
2253:
2203:
2199:
2189:
2152:
2148:
2104:
2100:
2090:
2063:
2059:
2049:
2024:
2020:
2014:
1989:
1985:
1979:
1946:
1942:
1936:
1901:
1897:
1887:
1879:the original
1874:
1826:
1822:
1776:
1772:
1727:
1723:
1683:
1679:
1629:
1625:
1593:
1586:
1553:
1549:
1504:
1500:
1435:
1428:
1401:
1397:
1387:
1363:
1301:
1297:
1237:
1233:
1178:
1143:
1139:
1127:
1112:
1097:
1076:
1065:
1058:
1050:
1037:idarucizumab
1034:
1030:coagulopathy
1012:
997:
973:
943:
924:When due to
923:
914:
899:
888:
867:
861:
824:amyloid beta
817:
790:Hypertension
784:
745:
661:gaze palsies
646:
611:
580:
569:
556:
538:, where the
526:
509:brain tissue
467:
441:
438:Epidemiology
432:
401:
370:
362:brain tumors
358:brain trauma
343:
282:
278:
274:
273:
169:Risk factors
158:brain tumors
146:Brain trauma
79:Neurosurgery
31:
26:
4216:Neurotrauma
4139:Tetraplegia
3978:Neurotrauma
3817:Extra-axial
3709:precerebral
3138:25 February
2406:(1): 3–10.
2200:Circulation
1154:vagus nerve
1130:craniectomy
1104:vasculature
1000:Factor VIIa
970:Medications
644:and death.
412:blood sugar
377:amyloidosis
186:amyloidosis
45:Other names
4205:Categories
4124:Paraplegia
4049:Concussion
3680:Cerebellum
3598:Brain stem
3526:including
2571:. Thieme.
2300:2008-01-16
1187:References
1174:cerebellum
1146:brain stem
1119:endoscopic
1093:hemorrhage
893:(CTA) and
885:on CT scan
839:, and low
805:Excessive
689:ventricles
667:may cause
665:cerebellum
626:dura mater
601:(US), the
572:hemiplegia
489:disability
477:parenchyma
451:(40%) and
381:alcoholism
291:ventricles
190:alcoholism
3862:Brainstem
3637:Foville's
2969:1469-493X
2351:Neurology
2082:0029-6651
1529:253159180
1181:mortality
1136:Prognosis
1022:protamine
1018:vitamin K
959:IV fluids
940:Treatment
932:(50%) or
873:Diagnosis
801:Menopause
618:headaches
487:or major
315:dizziness
311:paralysis
257:Frequency
248:Prognosis
233:Treatment
150:aneurysms
74:Specialty
3900:Aneurysm
3829:Subdural
3824:Epidural
3653:Midbrain
3409:Archived
3405:40379279
3397:23715913
3358:17478736
3238:25657190
3189:31887790
3110:27713031
3102:15936423
3066:30210176
3058:15474134
3022:25498578
2981:37870112
2930:30590573
2922:20399668
2886:25397701
2878:28214798
2828:26242330
2793:54488358
2785:23391776
2736:20044534
2695:45730236
2687:25395408
2610:Archived
2554:21164136
2505:19378710
2445:Mayer SA
2430:28178408
2381:31266905
2230:23239837
2181:17204141
2123:24842277
2066:(OCE1).
2041:10092713
1971:36692451
1963:10371574
1928:31839545
1845:24627116
1793:11739998
1754:25177839
1702:16081867
1656:21870062
1648:19053952
1578:25364307
1570:20056489
1521:36300975
1451:Archived
1420:29262429
1379:Archived
1328:22974648
1256:26022637
1100:catheter
1083:vascular
1079:hematoma
1004:hematoma
934:thalamus
920:Location
905:CT scans
857:warfarin
855:such as
813:migraine
764:aneurysm
653:thalamus
605:and the
589:and the
550:or from
532:bleeding
303:headache
178:diabetes
91:Headache
86:Symptoms
3879:General
3785:CADASIL
3611:Medulla
3481:D002543
3317:3107793
3309:8322400
3229:4739782
3180:6953357
2744:5871420
2545:3074599
2421:5307940
2372:6693427
2330:19 June
2264:19 June
2221:5408511
2172:1780056
2006:9799012
1919:6954314
1853:7716659
1801:7089563
1745:6544803
1319:3443867
1166:frontal
1073:Surgery
1056:(EEG).
998:Giving
946:CT scan
930:putamen
811:Severe
673:vertigo
481:strokes
455:(30%).
397:CT scan
393:cocaine
364:and an
323:vertigo
215:CT scan
202:cocaine
63:CT scan
3528:stroke
3403:
3395:
3356:
3336:Stroke
3315:
3307:
3287:Stroke
3236:
3226:
3208:Stroke
3187:
3177:
3108:
3100:
3082:Lancet
3064:
3056:
3038:Lancet
3020:
2979:
2967:
2928:
2920:
2884:
2876:
2826:
2791:
2783:
2763:Stroke
2742:
2734:
2714:Stroke
2693:
2685:
2665:Stroke
2602:
2575:
2552:
2542:
2524:Stroke
2503:
2457:
2428:
2418:
2379:
2369:
2228:
2218:
2179:
2169:
2121:
2080:
2039:
2004:
1969:
1961:
1943:Lancet
1926:
1916:
1851:
1843:
1823:Stroke
1799:
1791:
1773:Stroke
1752:
1742:
1700:
1680:Stroke
1654:
1646:
1600:
1576:
1568:
1527:
1519:
1443:
1418:
1371:
1326:
1316:
1254:
1234:Stroke
1162:cortex
1086:lesion
748:stroke
731:Causes
719:, and
699:, and
669:ataxia
597:, the
593:, the
391:, and
337:, and
299:stroke
265:Deaths
142:Causes
3924:Other
3778:Other
3545:Brain
3455:P10.1
3401:S2CID
3313:S2CID
3106:S2CID
3062:S2CID
2926:S2CID
2882:S2CID
2789:S2CID
2740:S2CID
2691:S2CID
2294:(PDF)
2283:(PDF)
2155:: 1.
1967:S2CID
1849:S2CID
1797:S2CID
1652:S2CID
1574:S2CID
1525:S2CID
1090:lobar
1024:, or
910:edema
889:Both
772:tumor
505:edema
491:than
485:death
459:Types
339:fever
295:skull
136:death
107:fever
3628:Pons
3476:MeSH
3465:9-CM
3393:PMID
3354:PMID
3305:PMID
3234:PMID
3185:PMID
3163:2019
3140:2009
3098:PMID
3054:PMID
3018:PMID
2977:PMID
2965:ISSN
2953:2023
2918:PMID
2874:PMID
2842:link
2824:PMID
2781:PMID
2732:PMID
2683:PMID
2600:ISBN
2573:ISBN
2550:PMID
2501:PMID
2455:ISBN
2426:PMID
2377:PMID
2332:2007
2266:2007
2226:PMID
2177:PMID
2119:PMID
2078:ISSN
2037:PMID
2002:PMID
1959:PMID
1924:PMID
1841:PMID
1789:PMID
1750:PMID
1728:2014
1698:PMID
1644:PMID
1598:ISBN
1566:PMID
1517:PMID
1441:ISBN
1416:PMID
1369:ISBN
1324:PMID
1252:PMID
1039:and
991:and
717:coma
705:pons
697:coma
642:coma
583:FAST
375:and
124:Coma
3470:431
3461:ICD
3451:I61
3442:ICD
3385:doi
3344:doi
3295:doi
3224:PMC
3216:doi
3175:PMC
3167:doi
3090:doi
3086:365
3046:doi
3042:364
3008:doi
3004:113
2973:PMC
2957:doi
2910:doi
2866:doi
2816:doi
2771:doi
2722:doi
2673:doi
2540:PMC
2532:doi
2491:doi
2416:PMC
2408:doi
2367:PMC
2359:doi
2216:PMC
2208:doi
2204:127
2167:PMC
2157:doi
2109:doi
2105:348
2101:BMJ
2068:doi
2029:doi
1994:doi
1951:doi
1947:353
1914:PMC
1906:doi
1831:doi
1781:doi
1740:PMC
1732:doi
1688:doi
1634:doi
1630:119
1558:doi
1509:doi
1505:387
1406:doi
1314:PMC
1306:doi
1242:doi
1168:or
1117:or
1088:or
847:or
831:or
766:or
727:).
651:or
495:or
329:or
321:or
317:or
279:ICH
204:use
97:or
4207::
3644:/
3635:/
3479::
3468::
3453:,
3449::
3446:10
3407:.
3399:.
3391:.
3381:84
3379:.
3375:.
3352:.
3340:38
3338:.
3334:.
3311:.
3303:.
3291:24
3289:.
3285:.
3232:.
3222:.
3212:46
3210:.
3206:.
3183:.
3173:.
3161:.
3157:.
3126:.
3104:.
3096:.
3084:.
3060:.
3052:.
3040:.
3016:.
3002:.
2998:.
2971:.
2963:.
2951:.
2947:.
2924:.
2916:.
2906:17
2904:.
2880:.
2872:.
2862:88
2860:.
2838:}}
2834:{{
2812:25
2810:.
2787:.
2779:.
2767:44
2765:.
2761:.
2738:.
2730:.
2718:41
2716:.
2712:.
2689:.
2681:.
2669:46
2667:.
2663:.
2640:.
2618:^
2608:.
2548:.
2538:.
2528:42
2526:.
2522:.
2499:.
2487:36
2485:.
2481:.
2469:^
2424:.
2414:.
2404:19
2402:.
2398:.
2375:.
2365:.
2355:93
2353:.
2349:.
2318:.
2285:.
2252:.
2238:^
2224:.
2214:.
2202:.
2198:.
2175:.
2165:.
2151:.
2147:.
2131:^
2117:.
2103:.
2099:.
2076:.
2064:68
2062:.
2058:.
2035:.
2025:33
2023:.
2000:.
1988:.
1965:.
1957:.
1945:.
1922:.
1912:.
1902:29
1900:.
1896:.
1873:.
1861:^
1847:.
1839:.
1827:45
1825:.
1821:.
1809:^
1795:.
1787:.
1777:32
1775:.
1762:^
1748:.
1738:.
1726:.
1722:.
1710:^
1696:.
1684:36
1682:.
1678:.
1664:^
1650:.
1642:.
1628:.
1624:.
1612:^
1572:.
1564:.
1552:.
1537:^
1523:.
1515:.
1503:.
1459:^
1449:.
1414:.
1402:38
1400:.
1396:.
1377:.
1353:^
1336:^
1322:.
1312:.
1302:30
1300:.
1296:.
1264:^
1250:.
1238:46
1236:.
1232:.
1195:^
1128:A
1098:A
1020:,
1016:,
859:.
782:.
711:,
695:,
671:,
640:,
632:,
554:.
519:.
399:.
387:,
383:,
360:,
356:,
352:,
348:,
341:.
333:,
305:,
200:,
196:,
192:,
188:,
184:,
180:,
176:,
160:,
156:,
152:,
148:,
130:,
126:,
109:,
101:,
3970:e
3963:t
3956:v
3516:e
3509:t
3502:v
3463:-
3444:-
3434:D
3387::
3360:.
3346::
3319:.
3297::
3240:.
3218::
3191:.
3169::
3142:.
3112:.
3092::
3068:.
3048::
3024:.
3010::
2983:.
2959::
2932:.
2912::
2888:.
2868::
2844:)
2830:.
2818::
2795:.
2773::
2746:.
2724::
2697:.
2675::
2581:.
2556:.
2534::
2507:.
2493::
2463:.
2432:.
2410::
2383:.
2361::
2334:.
2303:.
2268:.
2232:.
2210::
2183:.
2159::
2153:7
2125:.
2111::
2084:.
2070::
2043:.
2031::
2008:.
1996::
1990:2
1973:.
1953::
1930:.
1908::
1855:.
1833::
1803:.
1783::
1756:.
1734::
1704:.
1690::
1658:.
1636::
1606:.
1580:.
1560::
1554:9
1531:.
1511::
1422:.
1408::
1347:.
1330:.
1308::
1258:.
1244::
277:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.