819:
947:
Thracia". The establishment of Roman colonies and mostly several Greek cities, as was
Nicopolis, Topeiros, Traianoupolis, Plotinoupolis, and Hadrianoupolis resulted from the Roman Empire's urbanization. The Roman provincial policy in Thrace favored mainly not the Romanization but the Hellenization of the country, which had started as early as the Archaic period through the Greek colonisation and was completed by the end of Roman antiquity. As regards the competition between the Greek and Latin language, the very high rate of Greek inscriptions in Thrace extending south of
1027:
38:
92:
58:
100:
128:
78:
112:
834:
1086:
962:), the Roman citizenship to all the free inhabitants of the Roman Empire. During the same period (in the 1st-2nd century AD), a remarkable presence of Thracians is testified by the inscriptions outside the borders (extra fines) both in the Greek territory and in all the Roman provinces, especially in the provinces of Eastern Roman Empire.
913:, the locally ruled Thracian tribes of the mountainous regions maintained a warrior tradition, while the tribes based in the plains were purportedly more peaceable. Recently discovered funeral mounds in Bulgaria suggest that Thracian kings did rule regions of Thrace with distinct Thracian national identity.
942:
and the subjugation of
Macedonia to the Romans, Thrace also lost its independence and became tributary to Rome. Towards the end of the 1st century BC Thrace lost its status as a client kingdom as the Romans began to directly appoint their kings. This situation lasted until 46 AD, when the Romans
946:
During the Roman domination, within the geographical borders of ancient Thrace, there were two separate Roman provinces, namely Thrace ("provincia
Thracia") and Lower Moesia ("Moesia inferior"). Later, in the times of Diocletian, the two provinces were joined and formed the so-called "Dioecesis
1005:
the lost regions in the late 10th century until the
Bulgarians regained control of the northern half at the end of the 12th century. Throughout the 13th century and the first half of the 14th century, the region was changing in the hands of the Bulgarian and the Byzantine Empire (excluding
984:
began to crumble, Thracia fell from the authority of Rome and into the hands of
Germanic tribal rulers. With the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Thracia turned into a battleground territory for the better part of the next 1,000 years. The surviving eastern portion of the
754:: Tereus, the King of Thrace, lusts after his sister-in-law, Philomela. He kidnaps her, holds her captive, rapes her, and cuts out her tongue. Philomela manages to get free, however. She and her sister, Procne, plot to get revenge, by killing her son
1763:,1992, page 597: "We have no way of knowing what the Thracians called themselves and if indeed they had a common name...Thus the name of Thracians and that of their country were given by the Greeks to a group of tribes occupying the territory..."
1858:
D. C. Samsaris, Les
Thraces dans l' Empire romain d' Orient (Asie Mineure, Syrie, Palestine et Arabie). Etude ethno-démographique et sociale, VIe Symposium Internazionale di Tracologia (Firenze 11-13 maggio 1989), Roma 1992, p. 184-204
958:(civitas Romana) with all its privileges. Epigraphic evidence show a large increase in such naturalizations in the times of Trajan and Hadrian, while in 212 AD the emperor Caracalla granted, with his well-known decree (
423:. This usage lasted until the Roman conquest. Henceforth, (classical) Thrace referred only to the tract of land largely covering the same extent of space as the modern geographical region. In its early period, the
403:) were added. In one ancient Greek source, the very Earth is divided into "Asia, Libya, Europa and Thracia". As the Greeks gained knowledge of world geography, "Thrace" came to designate the area bordered by the
1755:, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond,
1848:
D. C. Samsaris, Les
Thraces dans l' Empire romain d' Orient (Le territoire de la Grèce actuelle). Etude ethno-démographique, sociale, prosopographique et anthroponymique, Jannina (Université) 1993, pp.
1787:
D. C. Samsaris, Le royaume client thrace aux temps de Tibere et la tutelle romaine de
Trebellenus Rufus (Le stade transitif de la clientele a la provincialisation de la Thrace), Dodona 17 (1), 1988, p.
951:
proves the complete language
Hellenization of this region. The boundaries between the Greek and Latin speaking Thrace are placed just above the northern foothills of Haemus Mountains.
938:
colonists followed them after the war. The special interest of Athens to Thrace is underlined by the numerous finds of
Athenian silverware in Thracian tombs. In 168 BC, after the
1773:
427:
was of this extent, but after the administrative reforms of the late 3rd century, Thracia's much reduced territory became the six small provinces which constituted the
1839:
D. C. Samsaris, Surveys in the history, topography and cults of the Roman provinces of Macedonia and Thrace (in Greek), Thessaloniki 1984, p. 131-302
1361:
1965:
954:
During the imperial period many Thracians – particularly members of the local aristocracy of the cities – had been granted the right of the
883:, who divided the vast realm between his generals. Notably, Thracian troops are known to have accompanied Alexander when he crossed the
1731:
1535:
1049:
completely within a matter of two decades and ruled it for five centuries in general peace. In 1821, several parts of Thrace, such as
140:
136:
2066:
415:, whose borders varied over time. After the Macedonian conquest, this region's former border with Macedonia was shifted from the
1799:
D. C. Samsaris, The Hellenization of Thrace during the Greek and Roman Antiquity (Diss. in Greek), Thessaloniki 1980, p. 26-36
758:(by Tereus) and serving him to his father for dinner. At the end of the myth, all three turn into birds – Procne into a
2071:
2046:
1341:
1883:
1579:
1420:
993:, retained control over Thrace until the 7th century when the northern half of the entire region was incorporated into the
1977:
1453:
1346:
1808:
D. C. Samsaris, Historical Geography of Western Thrace during the Roman Antiquity (in Greek), Thessaloniki 2005, p. 7-14
1614:
1563:
1553:
905:
Divided into separate tribes, the Thracians did not form any lasting political organizations until the founding of the
1968:
including images of the comprehensive art collection of Thracian gold found on the territory of contemporary Bulgaria.
1760:
1529:
174:
1210:. He is known primarily for three claims: (1) that man is the measure of all things, often interpreted as a sort of
2041:
1997:
1046:
1985:
1962:
Bulgaria's most famous Thracian Treasure - The Panagyurishte Gold Treasure to return home after two years lapse
1955:
1739:
1002:
743:
1910:
1126:
864:
2061:
1775:
Theseus in Thrace. The Silver Lining on the Clouds of the Athenian-Thracian Relations in the 5th Century BC
1312:
848:
were divided into numerous tribes. The first to take greater control of Thrace, in part or whole, were the
384:
818:
1470:
1437:
396:
302:(ancient Greek Εὐρώπη), also at first referred to this region, before that term expanded to include its
2051:
1906:
1465:
1432:
1401:
1129:. In Summer 1934, up to 10,000 Jews were maltreated, bereaved, and then forced to quit the region (see
1752:
1250:, the belief that all matter is made up of various imperishable indivisible elements which he called
1074:
1031:
837:
794:
189:
1303:, etc.). These emperors were elevated via a military career (hence the resultant nickname for them,
1260:
was a Thracian who led a large slave uprising in what is now Italy in 73–71 BC. His army of escaped
407:
on the north, by the Euxine Sea (Black Sea) on the east, by northern Macedonia in the south, and by
880:
521:
451:
424:
1701:
1680:
1637:
1185:
959:
875:. Persians' presence in Thracia lasted for more than a century, ending with the conquests in the
539:
347:
31:
17:
1516:. Washington, DC; Cambridge; New York: Woodrow Wilson Center Press; Cambridge University Press.
663:, on the Thracian (northern) side of the Hellespont, which formed part of the contingent led by
1214:, (2) that he could make the "worse (or weaker) argument appear the better (or stronger)" (see
994:
798:
529:
525:
326:
358:
In terms of ancient Greek mythology the name appears to derive from the heroine and sorceress
1506:
209:
981:
939:
37:
1894:
1828:
1817:
1797:
643:
mentions three separate contingents from Thrace: Thracians led by Acamas and Peiros, from
342:, "Land of the Romans", which was the name traditionally given by Turkic societies to the
8:
1356:
1130:
782:
535:
367:
1695:
1674:
1631:
934:
as Athenian and Ionian colonies were set up in Thrace before the war. Spartan and other
2056:
1300:
1101:
in 1878, Northern Thrace was incorporated into the semi-autonomous Ottoman province of
1098:
849:
698:
640:
359:
268:
180:
1983:
Possible Orphic Lyre rock engraving discovered in Bulgaria's Eastern Rhodope Mountains
1756:
1735:
1610:
1559:
1525:
1396:
1269:
1026:
971:
931:
930:
Sections of Thrace particularly in the south started to become hellenized before the
888:
690:
664:
579:
428:
319:
318:, meaning "black river"), According to an alternative theory, Hebros means "goat" in
260:
66:
867:. Thracian soldiers were used in Persian armies and are depicted in carvings of the
1517:
1304:
1211:
990:
948:
613:
553:
545:
432:
412:
343:
232:
228:
220:
153:
132:
116:
104:
62:
2036:
1989:
1959:
1657:
1487:
1475:
1442:
1386:
1366:
1325:
1284:
1229:
1206:
and subjects connected to virtue and political life, often regarded as the first
1102:
1015:
774:
686:
575:
435:
244:
1243:
1228:
was a Greek physician of the fifth century BC who is considered the founder of
1199:
1039:
998:
975:
876:
872:
856:
557:
501:
395:, a region which "had no definite boundaries" and to which other regions (like
387:
employed the term "Thrace" to refer to all of the territory which lay north of
248:
200:
2030:
2012:
1999:
1672:
1521:
1461:
1428:
1276:
1247:
1042:
955:
738:
284:
91:
509:
1308:
1280:
1265:
1105:, which united with Bulgaria in 1885. The rest of Thrace was divided among
1007:
986:
927:
lived in Thrace, where they served as philosophers, priests, and prophets.
481:
416:
1555:
Thracians and Mycenaeans: Proceedings of the Fourth International Congress
57:
1715:
1233:
1219:
1150:
1122:
1118:
1090:
763:
714:
628:
439:
420:
255:), roughly the Roman Province of Thrace. Lands also inhabited by ancient
252:
99:
943:
finally turned Thrace into a Roman province (Romana provincia Thracia).
894:
The Thracians recorded no collective name for themselves; terms such as
683:
in addition to the tribe that Homer specifically calls the "Thracians".
469:
1381:
1329:
1239:
1195:
1070:
1011:
884:
868:
680:
632:
236:
123:
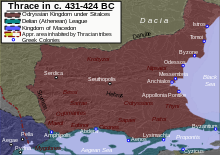
c. 431–424 BC, showing the territories of several Thracian tribes.
1261:
1257:
1225:
1066:
910:
845:
809:
636:
392:
291:
256:
240:
329:, long before the ancient Greeks started referring to the region as
306:. The region could have been named after the principal river there,
1982:
1953:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1218:), and (3) that one could not tell if the gods existed or not (see
1203:
1161:
1134:
1106:
1054:
920:
917:
906:
852:
826:
822:
778:
710:
706:
672:
652:
497:
457:
388:
120:
70:
42:
1006:
Constantinople). In 1265 the area suffered a Mongol raid from the
465:
127:
1592:
1391:
1371:
1215:
1207:
1181:
1142:
1138:
1058:
935:
924:
813:
759:
726:
722:
702:
676:
648:
627:
Homeric Thrace was vaguely defined, and stretched from the River
621:
617:
493:
461:
408:
400:
363:
307:
298:Θρᾷκες), an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name
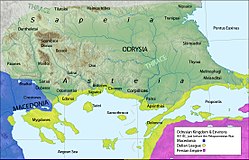
264:
667:. Ancient Thrace was home to numerous other tribes, such as the
77:
1376:
1169:
1165:
1114:
1110:
1050:
860:
767:
751:
747:
718:
694:
660:
656:
605:
601:
564:
549:
505:
489:
485:
477:
473:
404:
338:
315:
303:
50:
46:
1607:
Stephanus von Byzanz: Stephani Byzantii Ethnica / Delta - Iota
1188:, the chief representative of the art of song and playing the
1454:
1421:
1351:
833:
668:
592:
587:
561:
243:
to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria (
586:, who was said to reside in Thrace. The Thracians appear in
156:
1971:
1697:
A summary of geography and history, both ancient and modern
1251:
1189:
1062:
755:
733:
644:
597:
583:
162:
111:
1947:
1085:
825:(Thracian) soldier of the Achaemenid army, circa 480 BC.
1950:, comprehensive website on Thracian history and culture.
1514:
The idea of Europe: from antiquity to the European Union
1976:
The People of the God-Sun Ar and Areia (modern Thrace)
1895:
https://www.historystudies.net/trakyanin-yeni-sakinleri
1830:
D. C. Samsaris, The Hellenization of Thrace, p. 320-330
1307:), from the condition of common soldiers in one of the
859:. The region was incorporated into their empire as the
194:
1978:
The People of the God-Sun Ar and Areia (Modern Thrace)
1673:
Johann Joachim Eschenburg, Nathan Welby Fiske (1855).
411:
to the west. This largely coincided with the Thracian
27:
Geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe
383:
The historical boundaries of Thrace have varied. The
175:
165:
1117:
at the beginning of the 20th century, following the
159:
61:
The physical–geographical boundaries of Thrace: the
1819:
D. C. Samsaris, The Hellenization of Thrace, passim
1246:(c. 460–370 BC.) His main contribution is the
214:
1662:. London: Little, Brown and Company. p. 1176.
107:in 1585, stating both the names Thrace and Europe.
333:, it was known as Aria (Αρια) and Perki (Περκη).
2028:
1488:"Greek goddess Europa adorns new five-euro note"
1045:conducted their first incursion into the region
578:provides the Thracians with a mythical ancestor
1242:was a Greek philosopher and mathematician from
887:which abuts Thrace, during the invasion of the
1629:
1093:. This photocopy came from a larger color map.
1089:Proposal to cede East Thrace to Greece during
1014:, and between 1305 and 1307 was raided by the
616:, another Thracian king, makes an appearance.
227:) is a geographical and historical region in
1414:
803:
515:
1636:. Simpkin, Marshall & Company. p.
1604:
1362:Destruction of Thracian Bulgarians in 1913
689:is replete with Thracian kings, including
570:
1332:"are named after the historical region."
997:and the remainder was reorganized in the
336:In Turkey, it is commonly referred to as
1651:
1649:
1647:
1084:
1025:
832:
817:
126:
110:
98:
90:
76:
56:
36:
1659:Dictionary of Greek and Roman geography
14:
2029:
1717:Stephanus of Byzantium, Ethnica, §D230
1551:
1504:
1141:between 1934 and 1938 a large wave of
1655:
1644:
1507:"Europe: Conceptualizing a Continent"
1342:1989 expulsion of Turks from Bulgaria
1232:. He is believed to have been one of
865:Scythian campaign of Darius the Great
777:in Thrace was named after the son of
1693:
1175:
1030:Flag of rebels of Thrace during the
916:During this period, a subculture of
624:, is also given as a Thracian king.
620:, father-in-law to the Trojan elder
290:(Θρᾴκη), referred originally to the
259:extended in the north to modern-day
251:), and the European part of Turkey (
1633:The history and geography of Greece
1347:Celtic settlement of Eastern Europe
1202:(c. 490–420 BC.) An expert in
989:in the Balkans, later known as the
965:
41:The modern boundaries of Thrace in
24:
1732:"A companion to Ancient Macedonia"
456:The largest cities of Thrace are:
310:, possibly from the Indo-European
25:
2083:
1941:
1730:Joseph Roisman, Ian Worthington.
1080:
1021:
135:showing several Thracian tribes.
1593:Stephanus Of Byzantium - Ethnica
1541:from the original on 2022-10-09.
152:
1900:
1888:
1876:
1862:
1852:
1842:
1833:
1822:
1811:
1802:
1791:
1781:
1778:(Sofia 2015), pp. 13-14, 79-82.
1766:
1745:
1724:
1708:
1687:
1666:
1630:Swinburne Carr, Thomas (1838).
1605:Billerbeck, Margarethe (2010).
1279:of the 3rd–5th century were of
1160:is a geographical term used in
980:By the mid-5th century, as the
314:"white river" (the opposite of
2067:Historical regions in Bulgaria
1676:Manual of classical literature
1623:
1598:
1586:
1572:
1545:
1498:
1480:
1447:
881:Alexander the Great of Macedon
366:and Parthenope, and sister of
103:Map of Ancient Thrace made by
95:The Byzantine thema of Thrace.
13:
1:
1972:Information on Ancient Thrace
1966:Bulgaria's Thracian Heritage.
1948:Ethnological Museum of Thrace
1920:
1911:Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
1872:. Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana.
1734:John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
1609:(in German). pp. Theta.
1311:to the foremost positions of
1198:was a Greek philosopher from
902:were assigned by the Greeks.
655:, from southern Thrace, near
438:contained only what today is
82:
81:The Roman province of Thrace
2072:Historical regions in Turkey
2047:Historical regions in Greece
1512:. In Pagden, Anthony (ed.).
1264:and slaves defeated several
909:in the 4th century BC. Like
373:
353:
274:
7:
1656:Smith, Sir William (1857).
1335:
215:
195:
10:
2088:
1455:
1422:
1402:Turkish Republic of Thrace
969:
807:
792:
788:
560:inhabitants of Thrace are
533:
519:
449:
378:
362:, who was the daughter of
29:
1897:-gocmenler-1934-1938_1634
1753:Cambridge Ancient History
1319:
1075:Greek War of Independence
1032:Greek War of Independence
838:Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak
804:Ancient and Roman history
795:History of Western Thrace
582:, the son of the war-god
516:Demographics and religion
445:
204:
184:
1694:Adam, Alexander (1802).
1522:10.1017/CBO9780511496813
1505:Pagden, Anthony (2002).
1407:
1268:in what is known as the
522:Demographics of Bulgaria
452:List of cities of Thrace
425:Roman province of Thrace
247:), northeastern Greece (
139:was Northern Thrace and
115:Thrace and the Thracian
2042:Ancient Greek geography
1679:. E.C. Biddle. p.
1471:A Greek–English Lexicon
1438:A Greek–English Lexicon
1186:Ancient Greek mythology
960:constitutio Antoniniana
732:Thrace is mentioned in
659:; and from the city of
576:Ancient Greek mythology
571:Ancient Greek mythology
540:Turks of Western Thrace
32:Thrace (disambiguation)
1700:. A. Strahan. p.
1094:
1035:
995:First Bulgarian Empire
841:
830:
799:History of East Thrace
530:Demographics of Turkey
526:Demographics of Greece
327:Stephanus of Byzantium
239:to the south, and the
224:
144:
124:
108:
96:
88:
74:
69:(highlighted) and the
54:
1580:"The Plovdiv Project"
1462:Liddell, Henry George
1429:Liddell, Henry George
1088:
1029:
836:
821:
267:and to the west into
130:
114:
102:
94:
80:
60:
40:
1870:La Venjança catalana
1552:Pieter, Jan (1989).
1073:rebelled during the
982:Western Roman Empire
940:Third Macedonian war
766:, and Tereus into a
742:, in the episode of
556:, while most of the
143:was Southern Thrace.
30:For other uses, see
2062:Geography of Turkey
2009: /
1494:. January 10, 2013.
1131:1934 Thrace pogroms
1003:The Empire regained
762:, Philomela into a
631:in the west to the
554:Orthodox Christians
536:Thracian Bulgarians
348:Orthodox Christians
1988:2021-05-10 at the
1958:2021-05-10 at the
1926:Hoddinott, R. F.,
1145:immigrants called
1099:Congress of Berlin
1095:
1036:
842:
831:
641:Catalogue of Ships
235:to the north, the
145:
125:
109:
97:
89:
75:
65:to the north, the
55:
2052:History of Thrace
1558:. Brill Archive.
1397:Thracian treasure
1270:Third Servile War
1176:Notable Thracians
1127:Greco-Turkish War
972:Macedonia (theme)
956:Roman citizenship
932:Peloponnesian War
861:Satrapy of Skudra
639:in the east. The
429:Diocese of Thrace
391:inhabited by the
261:Northern Bulgaria
231:. Bounded by the
213:
193:
67:Rhodope Mountains
16:(Redirected from
2079:
2024:
2023:
2021:
2020:
2019:
2014:
2010:
2007:
2006:
2005:
2002:
1914:
1907:Trakiya Heights.
1904:
1898:
1892:
1886:
1880:
1874:
1873:
1866:
1860:
1856:
1850:
1846:
1840:
1837:
1831:
1826:
1820:
1815:
1809:
1806:
1800:
1795:
1789:
1785:
1779:
1770:
1764:
1749:
1743:
1728:
1722:
1721:
1712:
1706:
1705:
1691:
1685:
1684:
1670:
1664:
1663:
1653:
1642:
1641:
1627:
1621:
1620:
1602:
1596:
1590:
1584:
1583:
1576:
1570:
1569:
1549:
1543:
1542:
1540:
1511:
1502:
1496:
1495:
1484:
1478:
1458:
1457:
1451:
1445:
1425:
1424:
1418:
1305:Barracks Emperor
1301:Leo the Thracian
1212:moral relativism
991:Byzantine Empire
966:Medieval history
949:Haemus Mountains
413:Odrysian kingdom
344:Byzantine Empire
233:Balkan Mountains
229:Southeast Europe
218:
208:
206:
198:
188:
186:
172:
171:
168:
167:
164:
161:
158:
133:Odrysian Kingdom
117:Odrysian Kingdom
105:Abraham Ortelius
87:
84:
63:Balkan Mountains
21:
2087:
2086:
2082:
2081:
2080:
2078:
2077:
2076:
2027:
2026:
2017:
2015:
2011:
2008:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1996:
1995:
1990:Wayback Machine
1960:Wayback Machine
1944:
1933:Ilieva, Sonya,
1923:
1918:
1917:
1905:
1901:
1893:
1889:
1881:
1877:
1868:
1867:
1863:
1857:
1853:
1847:
1843:
1838:
1834:
1827:
1823:
1816:
1812:
1807:
1803:
1796:
1792:
1786:
1782:
1771:
1767:
1750:
1746:
1729:
1725:
1714:
1713:
1709:
1692:
1688:
1671:
1667:
1654:
1645:
1628:
1624:
1617:
1603:
1599:
1591:
1587:
1578:
1577:
1573:
1566:
1550:
1546:
1538:
1532:
1509:
1503:
1499:
1486:
1485:
1481:
1476:Perseus Project
1452:
1448:
1443:Perseus Project
1419:
1415:
1410:
1387:Music of Thrace
1367:Hawks of Thrace
1338:
1326:Trakiya Heights
1322:
1313:political power
1285:Maximinus Thrax
1230:sports medicine
1178:
1103:Eastern Rumelia
1083:
1024:
1016:Catalan company
978:
970:Main articles:
968:
816:
808:Main articles:
806:
801:
791:
687:Greek mythology
608:. Later in the
600:allies, led by
573:
552:population are
542:
532:
520:Main articles:
518:
454:
448:
436:theme of Thrace
431:. The medieval
381:
376:
356:
294:(ancient Greek
277:
245:Northern Thrace
155:
151:
85:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2085:
2075:
2074:
2069:
2064:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2044:
2039:
1993:
1992:
1980:
1974:
1969:
1963:
1951:
1943:
1942:External links
1940:
1939:
1938:
1931:
1922:
1919:
1916:
1915:
1899:
1887:
1875:
1861:
1851:
1841:
1832:
1821:
1810:
1801:
1790:
1780:
1765:
1744:
1723:
1707:
1686:
1665:
1643:
1622:
1616:978-3111738505
1615:
1597:
1585:
1571:
1565:978-9004088641
1564:
1544:
1530:
1497:
1479:
1446:
1412:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1405:
1404:
1399:
1394:
1389:
1384:
1379:
1374:
1369:
1364:
1359:
1354:
1349:
1344:
1337:
1334:
1321:
1318:
1317:
1316:
1277:Roman emperors
1273:
1255:
1244:Abdera, Thrace
1237:
1223:
1200:Abdera, Thrace
1193:
1177:
1174:
1082:
1081:Modern history
1079:
1023:
1022:Ottoman period
1020:
999:Thracian theme
976:Thrace (theme)
967:
964:
907:Odrysian state
889:Persian Empire
877:4th century BC
873:Naqsh-e Rostam
857:6th century BC
805:
802:
790:
787:
572:
569:
517:
514:
502:Alexandroupoli
450:Main article:
447:
444:
385:ancient Greeks
380:
377:
375:
372:
355:
352:
276:
273:
249:Western Thrace
131:Thrace in the
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2084:
2073:
2070:
2068:
2065:
2063:
2060:
2058:
2055:
2053:
2050:
2048:
2045:
2043:
2040:
2038:
2035:
2034:
2032:
2025:
2022:
1991:
1987:
1984:
1981:
1979:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1967:
1964:
1961:
1957:
1954:
1952:
1949:
1946:
1945:
1936:
1932:
1929:
1928:The Thracians
1925:
1924:
1912:
1908:
1903:
1896:
1891:
1885:
1879:
1871:
1865:
1855:
1845:
1836:
1829:
1825:
1818:
1814:
1805:
1798:
1794:
1784:
1777:
1776:
1769:
1762:
1761:0-521-22717-8
1758:
1754:
1748:
1741:
1737:
1733:
1727:
1719:
1718:
1711:
1703:
1699:
1698:
1690:
1682:
1678:
1677:
1669:
1661:
1660:
1652:
1650:
1648:
1639:
1635:
1634:
1626:
1618:
1612:
1608:
1601:
1595:, Theta 316.9
1594:
1589:
1581:
1575:
1567:
1561:
1557:
1556:
1548:
1537:
1533:
1531:9780511496813
1527:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1508:
1501:
1493:
1489:
1483:
1477:
1473:
1472:
1467:
1466:Scott, Robert
1463:
1459:
1450:
1444:
1440:
1439:
1434:
1433:Scott, Robert
1430:
1426:
1417:
1413:
1403:
1400:
1398:
1395:
1393:
1390:
1388:
1385:
1383:
1380:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1365:
1363:
1360:
1358:
1355:
1353:
1350:
1348:
1345:
1343:
1340:
1339:
1333:
1331:
1327:
1314:
1310:
1309:Roman legions
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1283:backgrounds (
1282:
1278:
1274:
1271:
1267:
1266:Roman legions
1263:
1259:
1256:
1253:
1249:
1248:atomic theory
1245:
1241:
1238:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1224:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1194:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1173:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1154:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1092:
1087:
1078:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1041:
1038:In 1352, the
1033:
1028:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
983:
977:
973:
963:
961:
957:
952:
950:
944:
941:
937:
933:
928:
926:
922:
919:
914:
912:
908:
903:
901:
897:
892:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
851:
847:
839:
835:
828:
824:
820:
815:
811:
800:
796:
786:
784:
780:
776:
771:
769:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
740:
739:Metamorphoses
735:
730:
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
682:
678:
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
625:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
594:
589:
585:
581:
577:
568:
566:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
541:
537:
531:
527:
523:
513:
511:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
453:
443:
441:
437:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
390:
386:
371:
369:
365:
361:
351:
349:
345:
341:
340:
334:
332:
328:
325:According to
323:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
286:
285:ancient Greek
282:
272:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
217:
211:
202:
197:
191:
182:
178:
177:
170:
149:
142:
138:
134:
129:
122:
118:
113:
106:
101:
93:
86: 200 AD
79:
72:
68:
64:
59:
52:
48:
44:
39:
33:
19:
1994:
1934:
1927:
1902:
1890:
1878:
1869:
1864:
1854:
1844:
1835:
1824:
1813:
1804:
1793:
1783:
1774:
1772:A. Sideris,
1768:
1747:
1726:
1716:
1710:
1696:
1689:
1675:
1668:
1658:
1632:
1625:
1606:
1600:
1588:
1574:
1554:
1547:
1513:
1500:
1491:
1482:
1469:
1449:
1436:
1416:
1323:
1281:Thraco-Roman
1275:A number of
1157:
1155:
1146:
1096:
1037:
1008:Golden Horde
987:Roman Empire
979:
953:
945:
929:
915:
904:
899:
895:
893:
863:, after the
855:in the late
843:
829:tomb relief.
773:The city of
772:
737:
731:
685:
626:
609:
591:
574:
544:Most of the
543:
482:Stara Zagora
455:
417:Struma River
382:
357:
337:
335:
330:
324:
311:
304:modern sense
299:
295:
287:
280:
278:
147:
146:
2016: /
1234:Hippocrates
1220:Agnosticism
1151:East Thrace
1123:World War I
1119:Balkan Wars
1091:World War I
1047:subduing it
923:called the
850:Achaemenian
844:Indigenous
764:nightingale
725:(father of
715:Polymnestor
440:East Thrace
421:Mesta River
253:East Thrace
2031:Categories
1935:Thracology
1921:References
1884:footnote 4
1740:144435163X
1382:Moesogoths
1330:Antarctica
1262:gladiators
1240:Democritus
1196:Protagoras
1071:Samothraki
1067:Callipolis
1012:Nogai Khan
885:Hellespont
869:Persepolis
793:See also:
633:Hellespont
534:See also:
510:Kırklareli
237:Aegean Sea
2057:Thracians
2013:42°N 26°E
1258:Spartacus
1236:' tutors.
1226:Herodicus
1204:rhetorics
1147:Göçmenler
1097:With the
1059:Sozopolis
1010:, led by
911:Illyrians
900:Thracians
846:Thracians
810:Thracians
744:Philomela
637:Black Sea
546:Bulgarian
433:Byzantine
399:and even
397:Macedonia
393:Thracians
374:Geography
354:Mythology
292:Thracians
279:The word
275:Etymology
269:Macedonia
257:Thracians
241:Black Sea
210:romanized
190:romanized
181:Bulgarian
1986:Archived
1956:Archived
1536:Archived
1492:BBC News
1357:Dardania
1336:See also
1297:Aureolus
1293:Galerius
1289:Licinius
1184:was, in
1162:Bulgaria
1158:Thracian
1149:went to
1135:Bulgaria
1133:). From
1125:and the
1107:Bulgaria
1055:Maroneia
921:ascetics
918:celibate
891:itself.
853:Persians
827:Xerxes I
823:Skudrian
779:Poseidon
711:Eumolpus
707:Tegyrius
699:Lycurgus
691:Diomedes
681:Bistones
673:Bisaltae
653:Euphemus
498:Komotini
470:Tekirdağ
458:Istanbul
389:Thessaly
320:Thracian
121:Sitalces
71:Bosporus
43:Bulgaria
1930:, 1981.
1788:159-168
1474:at the
1441:at the
1392:Paionia
1372:Macedon
1216:Sophism
1208:sophist
1182:Orpheus
1156:Today,
1143:Muslims
1139:Romania
1040:Ottoman
925:Ctistae
814:Thracia
789:History
783:Dicaeus
760:swallow
727:Orpheus
723:Oeagrus
703:Phineus
677:Cicones
657:Ismaros
651:led by
649:Cicones
622:Antenor
618:Cisseus
565:Muslims
558:Turkish
494:Haskovo
462:Plovdiv
419:to the
409:Illyria
401:Scythia
379:Borders
364:Oceanus
296:Thrakes
283:, from
265:Romania
221:Turkish
212::
196:Trakiya
192::
176:thrayss
18:Trakiya
2037:Thrace
2018:42; 26
1937:, 2001
1759:
1738:
1613:
1562:
1528:
1377:Moesia
1320:Legacy
1170:Greece
1168:, and
1166:Turkey
1115:Greece
1111:Turkey
1069:, and
1051:Lavara
896:Thrace
775:Dicaea
768:hoopoe
752:Tereus
750:, and
748:Procne
721:, and
719:Poltys
695:Tereus
679:, and
669:Edones
661:Sestus
614:Rhesus
606:Peiros
602:Acamas
598:Trojan
528:, and
508:, and
506:Xanthi
490:Yambol
486:Sliven
478:Edirne
474:Burgas
446:Cities
405:Danube
368:Europa
360:Thrace
339:Rumeli
331:Thrace
316:Vardar
308:Hebros
300:Europe
288:Thrake
281:Thrace
225:Trakya
216:Thráki
185:Тракия
148:Thrace
141:Asteia
137:Sapeia
119:under
51:Turkey
49:, and
47:Greece
1909:SCAR
1742:p 343
1539:(PDF)
1510:(PDF)
1423:Θρᾴκη
1408:Notes
1352:Dacia
1252:atoms
1063:Aenos
1043:Turks
936:Doric
665:Asius
645:Aenus
629:Axios
610:Iliad
593:Iliad
588:Homer
580:Thrax
562:Sunni
550:Greek
466:Çorlu
205:Θράκη
201:Greek
2004:26°E
2001:42°N
1882:see
1757:ISBN
1751:The
1736:ISBN
1611:ISBN
1560:ISBN
1526:ISBN
1456:Θρᾷξ
1324:The
1190:lyre
1137:and
1113:and
974:and
898:and
871:and
812:and
797:and
756:Itys
734:Ovid
635:and
604:and
584:Ares
548:and
538:and
346:and
263:and
1849:372
1702:344
1518:doi
1328:in
879:by
736:'s
729:).
596:as
590:'s
312:arg
2033::
1683:n.
1681:20
1646:^
1638:56
1534:.
1524:.
1490:.
1468:;
1464:;
1460:.
1435:;
1431:;
1427:.
1299:,
1295:,
1291:,
1287:,
1222:).
1172:.
1164:,
1153:.
1121:,
1109:,
1077:.
1065:,
1061:,
1057:,
1053:,
1018:.
1001:.
785:.
781:,
770:.
746:,
717:,
713:,
709:,
705:,
701:,
697:,
693:,
675:,
671:,
647:;
612:,
567:.
524:,
512:.
504:,
500:,
496:,
492:,
488:,
484:,
480:,
476:,
472:,
468:,
464:,
460:,
442:.
370:.
350:.
322:.
271:.
223::
219:;
207:,
203::
199:;
187:,
183::
179:;
173:,
163:eɪ
83:c.
45:,
1913:.
1720:.
1704:.
1640:.
1619:.
1582:.
1568:.
1520::
1315:.
1272:.
1254:.
1192:.
1034:.
840:.
169:/
166:s
160:r
157:θ
154:/
150:(
73:.
53:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.