749:
1281:
divided into two parts. The smaller and doubtlessly less populated area lay north of the Jabbok. Its most important settlement was
Amathus, a strong fortress from the Hellenistic period that had been conquered by Alexander Jannai and had become a Jewish town of some importance, the seat of a local Sanhedrin in the days of Gabinius and the capital of a toparchy. However, the majority of the Jews in Trans-Jordan lived south of the Jabbok, across the river from north-eastern Judea. The capital of this region was Gador (Es-Salt), which was considered the capital of the entire Peraea. South of Gador lay Abila (Abel-shittim) and Beth-haramata, and still farther to the south was the fortress Machaerus. Thus, geographically, the situation of Jewish Trans-Jordan was marked by two characteristics: its nearness to and common border with Judea and its location within the generally hostile neighborhood of the Greek cities to the east and north.
774:
758:
1342:
the second century A.D. but did not record places by Roman provinces—described them as being in (the local geographical unit of) Coele Syria (5.14.18). Furthermore, Philadelphia continued to describe itself on its coins and in inscriptions of the second and third centuries A.D. as being a city of Coele Syria; see above, Philadelphia, n. 9. As for the boundaries of the new province, the northern frontier extended to a little beyond the north of Bostra and east ; the western border ran somewhat east of the Jordan River valley and the Dead Sea but west of the city of Madaba (see M. Sartre,
653:
609:
574:
633:
740:
27:
559:
688:
176:
728:
594:
35:
399:
It is also sufficiently irrigated by mountain streams ; and (should these in the dog-days fail) by ever flowing springs. In length, it extends from
Machaerus to Pella : in breadth, from Philadelphia to the Jordan : its northern districts being bounded, as we have already said, by Pella ; and those on the west, by the river. The land of Moab forms its southern limit ; while Arabia and Silbonitis, with Philadelphia and Gerasa, constitute its eastern boundary.
673:
719:
794:
1662:
1242:"Josephus uses συνέδριον for the first time in connection with the decree of the Roman governor of Syria, Gabinius (57 BCE), who abolished the constitution and the then existing form of government of Palestine and divided the country into five provinces, at the head of each of which a sanhedrin was placed ("Ant." xiv 5, § 4)." via
1575:
however, does not recognize
Idumaea, merging it in Iudaea, and definitely distinguishes Peraea from Judaea. Had Ptolemy derived his divisions from an official source, he would probably have followed this scheme, and in particular would have used the official term Peraea instead of the periphrasis 'across the Jordan'.
1137:
GADARA was the chief city or metropolis of Peraea, lying in the district termed
Gadaritis, some small distance from the southern extremity of the sea of Galilee, sixty stadia from Tiberias, to the south of the river Hieromax, and also of the Scheriat-al-Mandhur (Joseph. Antiq. xiii. 13. 3; Polyb. v.
1574:
Ptolemy's divisions of
Palestine (v. xv) appear to follow popular lines. They are Galilee, Samaria, Judaea (with a subdivision 'across the Jordan'), and Idumaea. These divisions were also for the most part, as Josephus' survey of Palestine (Bell., III. iii. 1-5, §§ 35-57) shows, official. Josephus,
398:
Peraea ...much larger indeed , is generally desert and rugged, and too wild for the growth of delicate fruits. In some parts, however the soil is loamy and prolific, and trees of various kinds cover the plains ; but the olive-tree, the vine, and the palm tree, are those principally cultivated.
1341:
The problem of indicating precise ancient boundaries in
Transjordan is difficult and complex and varies according to the time period under discussion. After the creation of the Roman province of Arabia in 106 A.D. Gerasa and Philadelphia were included in it. Nonetheless, Ptolemy—who was writing in
1280:
Jewish Trans-Jordan reached from the hellenized city Pella (Fahal) in the north to
Machaerus, east of the Dead Sea, in the south. Its western border was the Jordan River, and in the east it extended until the territory of the Greek cities Gerasa and Philadelphia. The settled area of the Peraea was
377:
The part of Judaea adjoining Syria is called
Galilee, and that next to Arabia and Egypt Peraea. Peraea is covered with rugged mountains, and is separated from the other parts of Judaea by the river Jordan (in the original Latin: "Supra Idumaeam et Samariam Iudaea longe lateque funditur. Pars eius
1179:
What may be concluded from these observations is that it was probably Gadara of the Peraea, not the more famous city of the
Decapolis, that Yannai conquered early in his reign, as indicated in War 1.86 // Ant 13.356. This allows us to maintain an early dating of 102/101 BCE for the conquest of
1633:
provided a great compendium of knowledge in terms of the placements of cities and lands in the ancient world, information that would form the basis of medieval cartography, resulting in a standard
Ptolemaic map of Asia, including Palestine. The information about Judaea appears in Book 5, where
1138:
71. 3; Joseph. De Bell. Jud. iv. 8. 3; Plin. Hist. Nat. v. 15). It was fortified, and stood on a hill of limestone. Its inhabitants were mostly heathens. Josephus says of it in conjunction with Gaza and Hippos 'they were Grecian cities' (Antiq. xvii. 11. 4).
1358:, 90-109). Gadara in Peraea is identified today with es-Salt near Tell Jadur, a place that is near the western boundary of the province of Arabia. And this region could have been described by Stephanos as being located "between Coele Syria and Arabia."
147:
in size, as Galilee spanned approximately 2,200 square kilometers. Josephus depicted Perea mainly as "desert" and "rugged," with pockets of well-cultivated areas, a feature now undergoing transformation due to extensive irrigation initiatives.
1200:
1029:
1003:
982:
961:
940:
773:
1311:...Jewish TransJordan was represented by two councils: one in Gadara (Gedor), identified as E-tell in Peraea, near modern es-Salt in Jordan, and the other in Amathus (Hamthan), southeast of the Sea of Galilee.
1638:
are mentioned as well as the main cities. In the region east of the Jordan, there are sites that are not all easy to determine: Cosmas, Libias, Callirhoe, Gazorus, Epicaeros (Ptolemy, Geogr. 5: 15: 6).
1221:.: "And when he had ordained five councils (συνέδρια), he distributed the nation into the same number of parts. So these councils governed the people; the first was at Jerusalem, the second at
209:), to a point about one third down the eastern shore of the Dead Sea; it did not extend very far to the east. Herod the Great's kingdom was bequeathed to four heirs, of which
608:
748:
652:
1052:. Texts and Studies in Ancient Judaism / Texte Und Studien Zum Antiken Judentum, Volume 122 (reprint of 2008 Mohr Siebeck ed.). Wipf and Stock. p. 188.
632:
573:
417:, but rather the periphrasis "across the Jordan". And he enumerates the "Perean" cities; Cosmas, Libias, Callirhoe, Gazorus, Epicaeros in this district.
378:
Syriae iuncta Galilaea vocatur, Arabiae vero et Aegypto proxima Peraea, asperis dispersa montibus et a ceteris Iudaeis Iordane amne discreta.")
558:
1707:
687:
1373:
Sepphoris on the Eve of the Great Revolt. Papers of the 2nd International Conference on Galilee in Antiquity, 1997, Duke University
672:
593:
1622:
1567:
1334:
1304:
1273:
1099:
915:
873:
727:
241:
and for the first time, Perea. From that time Perea was part of the shifting Roman provinces to its west: Judaea, and later
1599:
describes the Peraea by a periphrasis as the eastern side of Jordan which may imply that the name was no longer in vogue.
478:, which usually refers only to the northern part of the Transjordan, to refer to all the region east of the Jordan River.
1424:
1675:
1094:. Routledge Revivals. Variorum Collected Studies, CS 735 (reprint of 2002 Ashgate ed.). Routledge. p. VI/16.
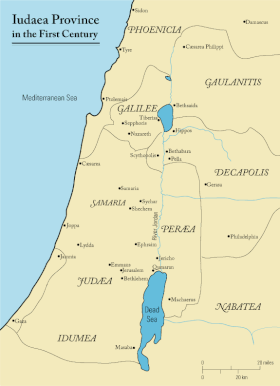
1381:
1057:
1243:
1180:
Gadara of the Peraea, alongside Amathus, while it also allows us to accept the inscription of 84 BCE as providing a
1717:
302:
112:(Nahal Arnon) in the south. The region extended from the Jordan River westwards to the foothills eastward towards
1697:
1296:
Josephus, the Jewish War: Newly Translated with Extensive Commentary and Archaeological Background Illustrations
1702:
349:
in Judea, mentioned by Josephus under a Hellenised form of its Semitic name, Gadara, edited to "Gazara" in the
1732:
895:
853:
485:
1727:
1671:
1680:
1712:
757:
183:
536:
named a major village "Perea" in honor of the important significance of Perea as the resting place of
1722:
1410:
143:
Encompassing roughly 2,625 square kilometers, Josephus was accurate in stating that Perea surpassed
426:
285:) was the chief city or metropolis of Perea (a Jewish city, not to be confused with Gadara of the
368:
93:
156:
The territory of what would at one point in history become known as Peraea or Perea was part of
1742:
1737:
1528:
457:
350:
259:
1612:
1555:
1462:
1371:
1324:
1265:
1132:
1126:
1089:
1047:
1508:
1500:
1214:
812:
237:. With his death in 44 CE, Agrippa's merged territory was made a province again, including
157:
62:
8:
1530:
A History of the Jewish People in the Time of Jesus Christ: Two Divisions in Five Volumes
807:
469:
413:
269:
165:
1398:
1019:
Two cities of Perea, Abela and Iulias (Livias), make an exception, having been kept by
822:
659:
334:
194:
1594:
1618:
1563:
1377:
1330:
1300:
1269:
1258:
1095:
1063:
1053:
911:
869:
549:
444:
306:
116:(then known as Philadelphia). Josephus notes that Perea's northern boundary was near
1496:
1163:
903:
861:
708:
679:
537:
246:
242:
180:
1454:
1294:
1211:
739:
580:
565:
448:
363:
190:
85:
20:
1478:
26:
1167:
389:
298:
226:
202:
89:
54:
39:
1432:
907:
865:
474:'beyond the Jordan'). In some cases, the Tanakh uses the related term
175:
61:") was the term used mainly during the early Roman period for part of ancient
1691:
1666:
1588:
1458:
1067:
639:
615:
481:
447:. The original text does not use the word "Perea", but rather a Hebrew term (
210:
117:
1653:
600:
440:
432:
290:
253:' books, the term was in rarer use in the late Roman period. It appears in
229:. In 39 CE, Perea and Galilee were transferred from disfavoured Antipas to
198:
105:
74:
34:
1326:
The Hellenistic Settlements in Syria, the Red Sea Basin, and North Africa
694:
161:
718:
1293:Ḳornfeld, Geʾalyahu; Mazar, Benjamin; Maier, Paul L. (1 January 1982).
1122:
1020:
501:
489:
169:
109:
1091:
Geography, Urbanisation and Settlement Patterns in the Roman Near East
793:
1230:
832:
525:
517:
505:
326:
318:
314:
310:
286:
230:
137:
125:
78:
1665: This article incorporates text from a publication now in the
1501:"BOOK III. CHAPTER 3. A Description of Galilee, Samaria, and Judea"
1222:
1196:
1151:
1025:
999:
978:
957:
936:
780:
384:
342:
254:
250:
234:
222:
206:
1661:
1522:
1226:
643:
619:
529:
521:
497:
493:
408:
338:
330:
322:
282:
214:
144:
129:
70:
1526:
827:
817:
784:
663:
475:
436:
294:
264:
238:
218:
121:
58:
346:
309:
into five districts of legal and religious councils known as
113:
66:
1453:
1376:. Duke Judaic studies, volume 1. Eisenbrauns. p. 113.
623:
533:
133:
1049:
Herod's Judaea: A Mediterranean State in the Classic World
435:, the Transjordan region was home to the Israelite tribes
281:
Gadara or Gadora of Perea (identified as Tell Jadur near
164:
period changed hands between the states of the heirs of
1560:
The Cities of the Eastern Roman Provinces, 2nd Edition
197:, from a point about one third the way down the lower
1505:
The Jewish War of Flavius Josephus: A New Translation
1329:. University of California Press. p. 284, n. 1.
462:
120:, while to the east, it bordered the territories of
564:Hasmonean Kingdom established in 167-160 BCE under
1521:Silbonitis is a textual error for Sebonitis, i.e.
1292:
1257:
1256:Malamat, Abraham; Ben-Sasson, Haim Hillel (1976).
787:(map as reconstructed by George Adam Smith, 1915).
1656:entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
1255:
1152:"When Did Alexander Yannai Capture Which Gadara?"
73:, which were situated on the western side of the
1689:
1495:
1184:for the conquest of the Gadara of the Decapolis.
30:Perea and its surroundings in the 1st century CE
1370:Meyers, Eric M. (1999). Meyers, Eric M. (ed.).
356:
108:. It stretched from Wadi Yabis in the north to
1507:. Vol. 2. Houlston and Stoneman. p.
693:Hasmonean Kingdom collapse in 67-66 BCE under
104:Perea was a slender piece of land east of the
496::1) and ending with the anointing by Mary in
488:, beginning with his departure from Galilee (
88:and his descendants, and later of subsequent
1562:. Wipf & Stock Publishers. p. 500.
733:Herod's kingdom was divided between his sons
221:in the north of the Dead Sea to the wife of
1149:
1614:The Essenes, the Scrolls, and the Dead Sea
1479:"Pliny the Elder: Natural History, Book V"
1299:. Zondervan Publishing House. p. 42.
900:Viewing Ancient Jewish Art and Archaeology
858:Viewing Ancient Jewish Art and Archaeology
543:
511:
276:
1590:A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography
701:
1617:. Oxford University Press. p. 238.
893:
851:
189:Perea was the portion of the kingdom of
174:
33:
25:
1684:. London and New York: Frederick Warne.
1527:Emil Schürer D.D. M.A.; Aeterna Press.
1087:
638:Hasmonean Kingdom in 104-103 BCE under
614:Hasmonean Kingdom in 134-104 BCE under
599:Hasmonean Kingdom in 142-135 BCE under
579:Hasmonean Kingdom in 161-143 BCE under
337:(Perea) and Gadara (either in Perea at
132:. To the south, it was adjacent to the
1690:
1610:
1369:
1225:, the third at Amathus, the fourth at
1081:
765:
658:Hasmonean Kingdom in 103-76 BCE under
1586:
1553:
1323:Cohen, Getzel M. (3 September 2006).
1322:
1128:The Cyclopædia of Biblical Literature
1121:
1045:
678:Hasmonean Kingdom in 76-67 BCE under
1708:Jews and Judaism in the Roman Empire
1670:
1264:. Harvard University Press. p.
1195:
1039:
1024:
998:
977:
956:
935:
289:−a Hellenistic city). Following the
257:' Greek language geographical work,
1611:Taylor, Joan E. (30 January 2015).
896:"11 An Approach to Herodian Peraea"
854:"11 An Approach to Herodian Peraea"
452:
411:does not use the term Perea in his
313:(in Jewish context better known as
140:marking its southernmost fortress.
124:and Philadelphia (both part of the
13:
1544:Ptolemy, Geographia Book 5 Ch.15:6
1425:"PLINY'S NATURAL HISTORY - Book V"
263:, but in the Latin translation by
193:occupying the eastern side of the
14:
1754:
1647:
201:(i.e. the segment connecting the
84:Perea was part of the kingdom of
1660:
1554:Jones, A. H. M. (30 June 2004).
1354:61 236–42; and especially id..
792:
772:
756:
747:
738:
726:
717:
686:
671:
651:
631:
607:
592:
572:
557:
403:
1604:
1580:
1547:
1538:
1515:
1489:
1471:
1447:
1417:
1363:
1316:
1286:
1249:
1236:
1189:
1143:
1131:. Newman & Ivison. p.
1115:
779:Perea in c.350 CE according to
420:
16:Portion of the Herodian kingdom
1533:. Aeterna Press. p. 1513.
1260:A History of the Jewish People
1244:Jewish Encyclopedia: Sanhedrin
1150:Piotrkowski, Meron M. (2011).
1013:
992:
971:
950:
929:
894:Kokkinos, Nikos (2016-01-01),
887:
852:Kokkinos, Nikos (2016-01-01),
845:
1:
1088:MacAdam, Henry Innes (2018).
838:
484:commentators speak of Jesus'
172:, and the Jewish Hasmoneans.
524:and forcibly settled in the
508:commencing from Mark 10:32.
357:Pliny the Elder and Josephus
99:
7:
902:, Brill, pp. 271–272,
860:, Brill, pp. 271–272,
801:
504::6) or his journey towards
463:
217:. He dedicated the city of
10:
1759:
1168:10.1628/094457011797248453
1036:.) to his death c. 100 CE.
424:
151:
18:
908:10.1163/9789004306592_012
866:10.1163/9789004306592_012
293:conquest of Judea led by
65:. It lay broadly east of
1681:The Nuttall Encyclopædia
1156:Jewish Studies Quarterly
427:Transjordan in the Bible
213:received both Perea and
1718:Jordan in the Roman era
1587:Smith, William (1873).
1483:www.thelatinlibrary.com
1467:. Teubner. p. 339.
1346:, 17-75; Bowersock, ZPE
544:Hasmonean incorporation
520:who were deported from
512:Other sites named Perea
277:Gadara/Gadora in Peraea
77:, and southwest of the
1698:Judea (Roman province)
1455:Gaius Plinius Secundus
1046:Rocca, Samuel (2015).
1010:. and notes 1370, 1376
702:Herodian incorporation
401:
380:
341:, in the Decapolis at
225:, Julia Augusta, born
186:
43:
31:
1703:New Testament regions
1636:pars Asphatitem lacum
1593:. J. Murray. p.
1556:"Appendix 2. Ptolemy"
425:Further information:
396:
375:
249:. Attested mostly in
178:
37:
29:
19:For the surname, see
1733:Transjordan (region)
813:Transjordan (region)
1229:, and the fifth at
808:Transjordan (Bible)
766:Later incorporation
662:(after conquest of
642:(after conquest of
618:(after conquest of
583:(after conquest of
372:, Book 5(15) wrote;
305:, split the former
195:Jordan River valley
179:Incorporation into
166:Alexander the Great
38:Incorporation into
1728:Herodian tetrarchy
1464:Naturalis historia
1182:terminus post quem
660:Alexander Jannaeus
393:, Book 3(3) wrote;
369:Naturalis Historia
187:
59:the country beyond
44:
32:
1713:Regions of Jordan
1624:978-0-19-870974-9
1569:978-1-59244-748-0
1435:on 1 January 2017
1336:978-0-520-93102-2
1306:978-0-310-39210-1
1275:978-0-674-39731-6
1101:978-1-138-74056-3
917:978-90-04-30659-2
875:978-90-04-30659-2
550:Hasmonean dynasty
473:
461:
445:tribe of Manasseh
431:According to the
345:, or at biblical
307:Hasmonean kingdom
245:, Palaestina and
1750:
1723:Herodian kingdom
1685:
1664:
1641:
1640:
1608:
1602:
1601:
1584:
1578:
1577:
1551:
1545:
1542:
1536:
1534:
1519:
1513:
1512:
1497:Flavius Josephus
1493:
1487:
1486:
1475:
1469:
1468:
1451:
1445:
1444:
1442:
1440:
1431:. Archived from
1421:
1415:
1414:
1408:
1404:
1402:
1394:
1392:
1390:
1367:
1361:
1360:
1320:
1314:
1313:
1290:
1284:
1283:
1263:
1253:
1247:
1240:
1234:
1220:
1210:
1206:
1193:
1187:
1186:
1176:
1174:
1147:
1141:
1140:
1119:
1113:
1112:
1110:
1108:
1085:
1079:
1078:
1076:
1074:
1043:
1037:
1035:
1017:
1011:
1009:
996:
990:
988:
975:
969:
967:
954:
948:
946:
933:
927:
926:
925:
924:
891:
885:
884:
883:
882:
849:
796:
776:
760:
751:
742:
730:
721:
709:Herodian kingdom
690:
680:Salome Alexandra
675:
655:
635:
611:
596:
576:
561:
538:John the Baptist
468:
466:
456:
454:
247:Palaestina Prima
243:Syria Palaestina
181:Seleucid Kingdom
1758:
1757:
1753:
1752:
1751:
1749:
1748:
1747:
1688:
1687:
1674:, ed. (1907). "
1650:
1645:
1644:
1625:
1609:
1605:
1585:
1581:
1570:
1552:
1548:
1543:
1539:
1520:
1516:
1494:
1490:
1477:
1476:
1472:
1452:
1448:
1438:
1436:
1423:
1422:
1418:
1406:
1405:
1396:
1395:
1388:
1386:
1384:
1368:
1364:
1350:, 37-39; id.,
1349:
1337:
1321:
1317:
1307:
1291:
1287:
1276:
1254:
1250:
1241:
1237:
1218:
1212:Perseus Project
1208:
1194:
1190:
1172:
1170:
1148:
1144:
1120:
1116:
1106:
1104:
1102:
1086:
1082:
1072:
1070:
1060:
1044:
1040:
1018:
1014:
997:
993:
989:. and note 1164
976:
972:
955:
951:
934:
930:
922:
920:
918:
892:
888:
880:
878:
876:
850:
846:
841:
804:
797:
788:
777:
768:
761:
752:
743:
734:
731:
722:
704:
697:
691:
682:
676:
667:
656:
647:
636:
627:
612:
603:
597:
588:
581:Jonathan Apphus
577:
568:
566:Judas Maccabeus
562:
546:
514:
486:Perean Ministry
464:ʿeven hayyarden
443:, and the half
429:
423:
406:
364:Pliny the Elder
359:
317:) and based at
301:, proconsul of
279:
191:Herod the Great
170:Nabataean Arabs
160:, which in the
154:
102:
90:Roman provinces
86:Herod the Great
24:
21:Perea (surname)
17:
12:
11:
5:
1756:
1746:
1745:
1740:
1735:
1730:
1725:
1720:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1700:
1658:
1657:
1649:
1648:External links
1646:
1643:
1642:
1623:
1603:
1579:
1568:
1546:
1537:
1514:
1488:
1470:
1459:Sillig, Julius
1446:
1416:
1382:
1362:
1347:
1335:
1315:
1305:
1285:
1274:
1248:
1235:
1188:
1162:(3): 266–276.
1142:
1114:
1100:
1080:
1058:
1038:
1012:
991:
970:
949:
928:
916:
886:
874:
843:
842:
840:
837:
836:
835:
830:
825:
820:
815:
810:
803:
800:
799:
798:
791:
789:
778:
771:
767:
764:
763:
762:
755:
753:
746:
744:
737:
735:
732:
725:
723:
716:
713:
712:
703:
700:
699:
698:
692:
685:
683:
677:
670:
668:
657:
650:
648:
637:
630:
628:
613:
606:
604:
598:
591:
589:
578:
571:
569:
563:
556:
553:
552:
545:
542:
516:The Christian
513:
510:
422:
419:
405:
402:
395:
394:
390:The Jewish War
374:
373:
358:
355:
299:Aulus Gabinius
278:
275:
227:Livia Drusilla
203:Sea of Galilee
153:
150:
101:
98:
92:that included
40:Arabia Petraea
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1755:
1744:
1743:Herod Antipas
1741:
1739:
1738:Herod Agrippa
1736:
1734:
1731:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1699:
1696:
1695:
1693:
1686:
1683:
1682:
1677:
1673:
1668:
1667:public domain
1663:
1655:
1652:
1651:
1639:
1637:
1632:
1626:
1620:
1616:
1615:
1607:
1600:
1596:
1592:
1591:
1583:
1576:
1571:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1550:
1541:
1532:
1531:
1524:
1518:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1492:
1484:
1480:
1474:
1466:
1465:
1460:
1456:
1450:
1434:
1430:
1429:masseiana.org
1426:
1420:
1412:
1400:
1385:
1383:9781575060408
1379:
1375:
1374:
1366:
1359:
1357:
1353:
1345:
1338:
1332:
1328:
1327:
1319:
1312:
1308:
1302:
1298:
1297:
1289:
1282:
1277:
1271:
1267:
1262:
1261:
1252:
1245:
1239:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1216:
1213:
1204:
1203:
1198:
1192:
1185:
1183:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1146:
1139:
1134:
1130:
1129:
1124:
1118:
1103:
1097:
1093:
1092:
1084:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1059:9781498224543
1055:
1051:
1050:
1042:
1033:
1032:
1027:
1022:
1016:
1007:
1006:
1001:
995:
986:
985:
980:
974:
965:
964:
959:
953:
944:
943:
938:
932:
919:
913:
909:
905:
901:
897:
890:
877:
871:
867:
863:
859:
855:
848:
844:
834:
831:
829:
826:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
809:
806:
805:
795:
790:
786:
782:
775:
770:
769:
759:
754:
750:
745:
741:
736:
729:
724:
720:
715:
714:
710:
706:
705:
696:
689:
684:
681:
674:
669:
665:
661:
654:
649:
645:
641:
640:Aristobulus I
634:
629:
625:
621:
617:
616:John Hyrcanus
610:
605:
602:
595:
590:
586:
582:
575:
570:
567:
560:
555:
554:
551:
548:
547:
541:
539:
535:
531:
527:
523:
519:
509:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
482:New Testament
479:
477:
471:
465:
459:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
428:
418:
416:
415:
410:
404:Other authors
400:
392:
391:
387:in his work,
386:
382:
381:
379:
371:
370:
366:in his work,
365:
361:
360:
354:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
274:
272:
271:
266:
262:
261:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
211:Herod Antipas
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
185:
182:
177:
173:
171:
167:
163:
159:
149:
146:
141:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
97:
95:
91:
87:
82:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
41:
36:
28:
22:
1679:
1659:
1635:
1630:
1628:
1613:
1606:
1598:
1589:
1582:
1573:
1559:
1549:
1540:
1529:
1517:
1504:
1491:
1482:
1473:
1463:
1449:
1437:. Retrieved
1433:the original
1428:
1419:
1387:. Retrieved
1372:
1365:
1355:
1351:
1343:
1340:
1325:
1318:
1310:
1295:
1288:
1279:
1259:
1251:
1238:
1233:in Galilee."
1201:
1191:
1181:
1178:
1171:. Retrieved
1159:
1155:
1145:
1136:
1127:
1117:
1105:. Retrieved
1090:
1083:
1071:. Retrieved
1048:
1041:
1030:
1015:
1004:
994:
983:
973:
962:
952:
941:
931:
921:, retrieved
899:
889:
879:, retrieved
857:
847:
601:Simon Thassi
584:
515:
480:
433:Hebrew Bible
430:
421:In the Bible
412:
407:
397:
388:
376:
367:
351:Loeb edition
280:
268:
258:
199:Jordan River
188:
158:Trans-Jordan
155:
142:
134:Land of Moab
106:Jordan River
103:
83:
75:Jordan River
50:
46:
45:
1672:Wood, James
1631:Geographica
1407:|work=
1123:Kitto, John
1023:(Mason, S.
695:Hyrcanus II
297:in 63 BCE,
270:Transjordan
260:Onomasticon
162:Hellenistic
63:Transjordan
57:: Περαία, "
1692:Categories
1629:Ptolemy's
1021:Agrippa II
923:2024-01-30
881:2024-01-30
839:References
532:region of
502:Matthew 26
490:Matthew 19
453:עבר הירדן
315:sanhedrins
110:Wadi Mujib
42:106–630 CE
1409:ignored (
1399:cite book
1344:Trois ét.
1231:Sepphoris
1205:. 14.5.4.
1068:0721-8753
1034:. 2.13.2.
1008:. 2.11.6.
833:Machaerus
711:of Judaea
526:New Julfa
518:Armenians
506:Jerusalem
458:romanized
414:Geography
383:c. 75 CE
362:c. 78 CE
327:Sepphoris
319:Jerusalem
287:Decapolis
273:is used.
231:Agrippa I
205:with the
138:Machaerus
126:Decapolis
100:Geography
79:Decapolis
1499:(1851).
1461:(1831).
1439:1 August
1215:AJ14.5.4
1197:Josephus
1125:(1851).
1026:Josephus
1000:Josephus
987:. 2.9.6.
979:Josephus
966:. 2.9.1.
958:Josephus
945:. 2.6.3.
937:Josephus
802:See also
781:Eusebius
385:Josephus
343:Umm Qais
311:synedria
255:Eusebius
251:Josephus
235:Caligula
223:Augustus
207:Dead Sea
1669::
1523:Heshbon
1227:Jericho
823:Amathus
644:Galilee
620:Samaria
530:Isfahan
522:Armenia
498:Bethany
494:Mark 10
472:
460::
409:Ptolemy
339:Al-Salt
335:Amathus
331:Galilee
323:Jericho
283:Al-Salt
215:Galilee
184:200 BCE
152:History
145:Galilee
136:, with
130:Heshbon
71:Samaria
1621:
1566:
1389:30 May
1380:
1356:Arabia
1333:
1303:
1272:
1223:Gadara
1219:
1209:
1173:4 July
1107:5 June
1098:
1073:5 June
1066:
1056:
914:
872:
828:Livias
818:Gilead
785:Jerome
664:Iturea
624:Idumea
476:Gilead
449:Hebrew
437:Reuben
295:Pompey
265:Jerome
239:Judaea
219:Livias
168:, the
128:) and
122:Gerasa
94:Iudaea
51:Peraea
1676:Perea
1654:Perea
585:Perea
347:Gezer
303:Syria
291:Roman
118:Pella
114:Amman
67:Judea
55:Greek
47:Perea
1619:ISBN
1564:ISBN
1441:2015
1411:help
1391:2020
1378:ISBN
1331:ISBN
1301:ISBN
1270:ISBN
1175:2016
1109:2020
1096:ISBN
1075:2020
1064:ISSN
1054:ISBN
912:ISBN
870:ISBN
783:and
707:The
622:and
534:Iran
492::1;
470:lit.
69:and
1678:".
1595:533
1525:. (
1352:JRS
1266:262
1164:doi
1133:723
904:doi
862:doi
441:Gad
353:).
333:),
233:by
49:or
1694::
1627:.
1597:.
1572:.
1558:.
1503:.
1481:.
1457:;
1427:.
1403::
1401:}}
1397:{{
1339:.
1309:.
1278:.
1268:.
1202:AJ
1199:.
1177:.
1160:18
1158:.
1154:.
1135:.
1062:.
1031:BJ
1028:.
1005:BJ
1002:.
984:BJ
981:.
963:BJ
960:.
942:BJ
939:.
910:,
898:,
868:,
856:,
540:.
467:,
455:,
451::
439:,
325:,
321:,
267:,
96:.
81:.
1535:)
1511:.
1509:9
1485:.
1443:.
1413:)
1393:.
1348:5
1246::
1217:,
1207:,
1166::
1111:.
1077:.
968:.
947:.
906::
864::
666:)
646:)
626:)
587:)
528:/
500:(
329:(
53:(
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.