20:
368:
Le Proche-Orient de
Justinien aux Abbasides. Peuplement et dynamiques spatiales. Actes du colloque "Continuites de l'occupation entre les periodes byzantine et abbasside au Proche-Orient, VIe-IXe siecles" Paris, 18-20 octobre
356:
Die
Renaissance der Städte in Nordsyrien und Nordmesopotamien. Städtische Entwicklung und wirtschaftliche Bedingungen in ar-Raqqa und Harrān von der Zeit der beduinischen Vorherrschaft bis zu den Seldschuken
172:
199:
as governor of Edessa and the Diyar Mudar, but Thoros retreated after some time to
Melitene (though he was reappointed again as governor by the Seljuks in 1094).
326:
The
Armenians in the Medieval Islamic World: Armenian Realpolitik in the Islamic World and Diverging Paradigmscase of Cilicia Eleventh to Fourteenth C
144:
Geographically and politically, in early
Islamic times the Diyar Mudar was usually part of al-Jazira. In the mid-10th century, the region came under
283:
401:
334:
241:
406:
301:
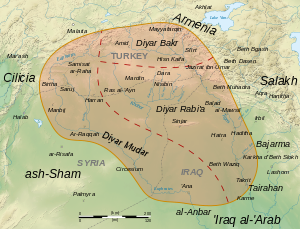
259:
366:(2011). "The Agricultural Hinterland of Baghdad, al-Raqqa and Samarra': Settlement Patterns in the Diyar Muḍar.".
226:
66:
411:
183:
in 1032. Thereafter the region became divided into a mostly
Christian-ruled northern portion, subject to
191:
raids began in the 1060s and 1070s but they could not take the region. After the battle of
Manzikert,
167:
After the loss of control of the
Hamdanids, the Diyar Mudar and its cities came under the sway of the
187:
colonization, while the area from Harran to the
Euphrates was dominated by Arab nomadic tribes.
90:
44:
192:
358:. Islamic History and Civilization Studies and Texts 40 (in German). Leiden et al.: Brill.
8:
56:
117:
85:, all three provinces were named after the main Arab tribes that were settled there by
330:
311:
269:
157:
70:
24:
363:
351:
214:
196:
176:
168:
161:
145:
100:
Diyar Mudar encompasses the region on both banks of the middle course of the river
175:
becoming autonomous governor of Harran by 1002, while Edessa was conquered by the
324:
218:
180:
78:
35:
296:
292:
254:
250:
395:
315:
288:
273:
246:
188:
149:
86:
371:. Bibliothèque de l’antiquitè tardive 19. Turnhout: Brepols. pp. 43–58.
206:
113:
82:
16:
Medieval Arabic name of the westernmost of the three provinces of al-Jazira
74:
184:
101:
160:. In the same period, the region came under attack by the resurgent
217:) and a Muslim south, which lasted until the mid-12th century. The
210:
105:
133:
128:(al-Ruha in Arabic) in the north, and other major cities included
222:
203:
129:
125:
62:
209:
had unified the province under his control. The advent of the
153:
121:
94:
19:
213:
re-established the division between a
Christian north (the
109:
93:
of the 7th century. The Diyar Mudar was settled by the
152:
it was detached from the Jazira and the Hamdanids of
377:
49:
282:
240:
65:name of the westernmost of the three provinces of
393:
156:and subordinated to the northern Syria-based
281:Canard, Marius & Cahen, Claude (1965).
280:
239:Canard, Marius & Cahen, Claude (1965).
238:
302:The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition
260:The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition
61:'abode of Mudar') is the medieval
362:
350:
310:. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 347–348.
268:. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 343–345.
18:
383:
322:
81:. According to the medieval geographer
394:
27:) with its provinces in medieval times
323:Dadoyan, Seta B. (1 November 2012).
221:gained control of the region under
116:and the lower reaches of the river
39:
13:
14:
423:
112:, and includes the area of the
173:Waththab ibn Ja'bar al-Numayri
1:
227:Mongol invasion of the Levant
402:Medieval history of Anatolia
7:
50:
10:
428:
407:Medieval Upper Mesopotamia
329:. Transaction Publishers.
232:
139:
225:, and kept it until the
120:. Its main cities were
73:), the other two being
91:early Muslim conquests
28:
193:Philaretos Brachamios
89:in the course of the
22:
202:By 1086 the Seljuk
148:control, and under
104:, from the area of
412:Historical regions
29:
23:Map of al-Jazira (
364:Heidemann, Stefan
352:Heidemann, Stefan
336:978-1-4128-4782-7
158:Emirate of Aleppo
132:, and Saruj (now
124:in the south and
71:Upper Mesopotamia
60:
48:
25:Upper Mesopotamia
419:
387:
381:
372:
359:
347:
345:
343:
319:
286:
277:
244:
215:County of Edessa
177:Byzantine Empire
162:Byzantine Empire
55:
53:
43:
41:
427:
426:
422:
421:
420:
418:
417:
416:
392:
391:
390:
382:
378:
341:
339:
337:
235:
181:George Maniakes
142:
108:to the town of
17:
12:
11:
5:
425:
415:
414:
409:
404:
389:
388:
375:
374:
373:
360:
348:
335:
320:
278:
234:
231:
141:
138:
40:دِيَارُ مُضَرَ
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
424:
413:
410:
408:
405:
403:
400:
399:
397:
386:, p. 38.
385:
380:
376:
370:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
338:
332:
328:
327:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
303:
298:
294:
290:
285:
284:"Diyār Mudar"
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
261:
256:
252:
248:
243:
237:
236:
230:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
205:
200:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
170:
165:
163:
159:
155:
151:
150:Sayf al-Dawla
147:
137:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
98:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
58:
52:
46:
37:
33:
26:
21:
384:Dadoyan 2012
379:
367:
355:
340:. Retrieved
325:
307:
300:
265:
258:
242:"Diyār Bakr"
207:Malik-Shah I
201:
166:
143:
114:Balikh River
99:
83:al-Baladhuri
79:Diyar Rabi'a
31:
30:
342:25 February
297:Schacht, J.
293:Pellat, Ch.
255:Schacht, J.
251:Pellat, Ch.
169:Banu Numayr
51:Diyār Muḍar
32:Diyar Mudar
396:Categories
306:Volume II:
264:Volume II:
195:appointed
87:Mu'awiya I
75:Diyar Bakr
316:495469475
289:Lewis, B.
274:495469475
247:Lewis, B.
229:in 1260.
102:Euphrates
67:al-Jazira
45:romanized
354:(2002).
299:(eds.).
257:(eds.).
219:Ayyubids
211:Crusades
185:Armenian
146:Hamdanid
106:Samosata
233:Sources
223:Saladin
171:, with
140:History
97:tribe.
59:
47::
333:
314:
295:&
272:
253:&
204:sultan
197:Thoros
189:Seljuk
179:under
130:Harran
126:Edessa
118:Khabur
63:Arabic
36:Arabic
287:. In
245:. In
154:Mosul
134:Suruç
122:Raqqa
95:Mudar
369:2007
344:2024
331:ISBN
312:OCLC
270:OCLC
110:Anah
77:and
57:lit.
308:C–G
266:C–G
136:).
398::
304:.
291:;
262:.
249:;
164:.
54:,
42:,
38::
346:.
318:.
276:.
69:(
34:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.