1723:. He became known as Levon the Magnificent, due to his numerous contributions to Cilician Armenian statehood in the political, military, and economic spheres. Levon's growing power made him a particularly important ally for the neighbouring crusader state of Antioch, which resulted in intermarriage with noble families there, but his dynastic policies revealed ambition towards the overlordship of Antioch which the Latins ultimately could not countenance. They resulted in the Antiochene Wars of Succession between Levon's grand-nephew Raymond Roupen and Bohemond IV of Antioch-Tripoli. The Rubenids consolidated their power by controlling strategic roads with fortifications that extended from the Taurus Mountains into the plain and along the borders, including the baronial and royal castles at
4568:
130:
2231:
1356:
2213:
2618:
1260:. The Caliphate's occupation of Cilicia and of other areas in Asia Minor led many Armenians to seek refuge and protection further west in the Byzantine Empire, which created demographic imbalances in the region. In order to better protect their eastern territories after their reconquest, the Byzantines resorted largely to a policy of mass transfer and relocation of native populations within the Empire's borders. Nicephorus thus expelled the Muslims living in Cilicia, and encouraged Christians from Syria and Armenia to settle in the region. Emperor
1931:
1425:
112:
4999:
2293:
2093:
2008:, who paid large annual tributes to the Mamluks. Even with the tributes, the Mamluks continued to attack Cilicia every few years. In 1275, an army led by the emirs of the sultan invaded the country without pretext and faced Armenians who had no means of resistance. The city of Tarsus was taken, the royal palace and the church of Saint Sophia was burned, the state treasury was looted, 15,000 civilians were killed, and 10,000 were taken captive to Egypt. Almost the entire population of
1861:
2224:
2495:
2406:
1348:
543:
152:
2556:. The latter, situated on two strategic caravan routes, was the last fully navigable port to the Mediterranean on the Pyramus River and the location of warehouses licensed by the Armenians to the Genoese. Important European merchant communities and colonies came into existence, with their own churches, courts of law, and trading houses. As French became the secondary language of Cilician nobility, the secondary language for Cilician commerce had become
5553:
2194:
1849:
1619:
1574:, T'oros' brother and successor, started his reign in 1129. He integrated the Cilician coastal cities to the Armenian principality, thus consolidating Armenian commercial leadership in the region. During this period, there was continued hostility between Cilician Armenia and the Seljuk Turks, as well as occasional bickering between Armenians and the Principality of Antioch over forts located near southern
1795:
1778:, and the marriage of Bohemond's son Philip to Queen Zabel sealed this; however, Philip was too "Latin" for the Armenians' taste, as he refused to abide by the precepts of the Armenian Church. In 1224, Philip was imprisoned in Sis for stealing the crown jewels of Armenia, and after several months of confinement, he was poisoned and killed. Zabel decided to embrace a monastic life in the city of
1233:
2021:
1582:, who still considered Cilicia to be a Byzantine province, conquered most of the towns and cities located on the Cilician plains. They captured and imprisoned Levon in Constantinople with several other family members, including his sons Ruben and T'oros. Levon died in prison three years later. Ruben was blinded and killed while in prison, but Levon's second son and successor,
2040:, the Armenians had to sign a ten-year truce under harsh terms. The Armenians were obligated to cede many fortresses to the Mamluks and were prohibited to rebuild their defensive fortifications. Cilician Armenia was forced to trade with Egypt, thereby circumventing a trade embargo imposed by the pope. Moreover, the Mamluks were to receive an annual tribute of one million
1313:'s solicitation, the Armenians obtained a partial reprieve, but Malik's succeeding governors continued levying taxes. This led the Armenians to seek refuge in Byzantium and in Cilicia. Some Armenian leaders set themselves up as sovereign lords, while others remained, at least in name, loyal to the Empire. The most successful of these early Armenian warlords was
2464:
notably with their architectural traditions. Europeans incorporated elements of
Armenian castle-building, learned from Armenian masons in the Crusader states, as well as some elements of church architecture. Most Armenian castles made atypical usage of rocky heights, and featured curved walls and round towers, similar to those of the Hospitaller castles
1701:), he elevated the princedom's status to a kingdom. On January 6, 1198, the day Armenians celebrate Christmas, Prince Levon II was crowned with great solemnity in the cathedral of Tarsus, in the presence of the Syrian Jacobite patriarch, the Greek metropolitan of Tarsus, and numerous church dignitaries and military leaders. While he was crowned by the
1568:. The assassins of the latter, three Byzantine brothers who governed the castle, were thus brutally killed. Eventually, there emerged a type of centralized government in the area with the rise of the Rubenid princes. During the twelfth century, they were the closest thing to a ruling dynasty, and wrestled with the Byzantines for power over the region.
1455:, was considered a savior for the Armenians. Constantine saw the Crusaders' arrival as a one-time opportunity to consolidate his rule of Cilicia by eliminating the remaining Byzantine strongholds in the region. With the Crusaders' help, they secured Cilicia from the Byzantines and Turks, both by direct military actions in Cilicia and by establishing
2456:. European tradition was adopted for the knighting of Armenian nobles, while jousts and tournaments similar to those in Europe had become popular in Cilician Armenia. The extent of Western influence over Cilician Armenia is also reflected by the incorporation of two new letters (Ֆ ֆ = "f" and Օ օ = "o") and various Latin-based words into the
4401:
2658:, proclaimed a union between the Armenian Church and the Roman Catholic Church; however, this had no notable effect, as the local clergy and populace was strongly opposed to such a union. The Western Church sent numerous missions to Cilician Armenia to help with rapprochement, but had limited results. The
2463:
In other areas, there was more hostility to the new
Western trends. Above all, most ordinary Armenians frowned on conversion to Roman Catholicism or Greek Orthodoxy. Cultural influence was not merely one-way, however; Cilician Armenians had an important impact on Crusaders returning to the West, most
2425:
Demographically, Cilician
Armenia was heterogeneous with a population of Armenians who constituted the ruling class, and also Greeks, Jews, Muslims, and various Europeans. The multi-ethnic population, as well as commercial and political links with Europeans, particularly France, brought important new
2260:
From 1343 to 1344, a time when the
Armenian population and its feudal rulers refused to adapt to the new Lusignan leadership and its policy of Latinizing the Armenian Church, Cilicia was again invaded by the Mamluks, who were intent on territorial expansion. Frequent appeals for help and support were
2248:, who, by the 12th century, were already established in the eastern Mediterranean island of Cyprus. Had it not been for their presence in Cyprus, the kingdom of Cilician Armenia may have, out of necessity, established itself on the island. In 1342, Levon's cousin Guy de Lusignan, was anointed king as
1926:
from 1259 to 1260. The involvement of Het'um at these two conquests is debated however, with the source for such information - Templar of Tyre - claiming his involvement in a deliberate attempt to integrate
Mongols into a Holy-War conquest narrative. This was to persuade Latin Christendom of the need
1280:
after the fall of
Bagratid Armenia, as it remained under foreign occupation. Following its conquest in 1045, and in the midst of Byzantine efforts to further repopulate the Empire's east, Armenian immigration into Cilicia intensified and turned into a major socio-political movement. Armenians came to
1487:
Among the good deeds which the
Armenian people has done towards the church and the Christian world, it should especially be stressed that, in those times when the Latin Christian princes and the warriors went to retake the Holy Land, no people or nation, with the same enthusiasm, joy and faith came
1379:
upon the
Byzantine emperor's request. Instead of negotiating peace, however, the king was forced to cede his Armenian lands and live in exile. Gagik was later assassinated by Greeks. In 1080, soon after this assassination, Ruben organized a band of Armenian troops and revolted against the Byzantine
2256:
were considered pro-Latin and deeply committed to the supremacy of the Roman
Catholic Church in the Levant. As kings, the Lusignans attempted to impose Catholicism and the European ways. The Armenian nobles largely accepted this, but the peasantry opposed the changes, which eventually led to civil
1904:
in 1247 to negotiate an alliance. He returned in 1250 with an agreement guaranteeing the integrity of
Cilicia, as well as the promise of Mongol aid to recapture forts seized by the Seljuks. Despite his sometimes-burdensome military commitments to the Mongols, Het’um had the financial resources and
2650:
was located in distant Hromkla. He was assisted by fourteen bishops in administering the Armenian Church in the kingdom, a number which grew in later years. The archbishops' seats were located in Tarsus, Sis, Anazarba, Lambron, and Mamistra. There existed up to sixty monastic houses in Cilicia,
1967:
took the field in 1266 with the intention of wiping out the Crusader states from the Middle East. In the same year, he summoned Het'um I to change his allegiance from the Mongols to the Mamluks, and remit to the Mamluks the territories and fortresses the Armenian king had acquired through his
1829:
The apparent unification in marriage of the two main dynasties of Cilicia, Rubenid and Het'umid, ended a century of dynastic and territorial rivalry, while bringing the Het'umids to the forefront of political dominance in Cilician Armenia. Although the accession of Het'um I in 1226 marked the
2779:
is extensive and specific on the alliance (page numbers refer to the French edition): “The Armenians, in the person of their king Hetoum, sided with the Mongols, as well as Prince Bohemond, his son-in-law. The Franks of Acre however adopted a position of neutrality favourable to the muslims”
1946:
masters in Egypt. The Mamluks began as a cavalry corps established from Turkic and other slaves sold to the Egyptian sultan by Genghis Khan. They took control of Egypt and Palestine in 1250 and 1253, respectively, and filled the vacuum caused by the Mongol destruction of the pre-existing
2682:
Whence does the Church of Rome derive the power to pass judgment on the other Apostolic sees while she herself is not subject to their judgments? We ourselves have indeed the authority to bring you to trial, following the example of the Apostles, and you have no right to deny our
2128:), to join his attack on the Mamluks. The Mongols took the city of Aleppo, where they were joined by King Het'um. His forces included Templars and Hospitallers from the kingdom of Armenia, who participated in the rest of the offensive. The combined force defeated the Mamluks in the
2753:, p. 55, describes "the Mongol alliance" entered into by the king of Armenia and the Franks of Antioch ("the King of Armenia decided to engage into the Mongol alliance, an intelligence that the Latin barons lacked, except for Antioch"), and "the Franco-Mongol collaboration."
2289:, his cousin and king of Cyprus. The title of King of Armenia was thus united with the titles of King of Cyprus and King of Jerusalem. The title has also been claimed indirectly by the House of Savoy by claiming the title King of Jerusalem and a number of other thrones.
1281:
serve the Byzantines as military officers or governors, and were given control of important cities on the Byzantine Empire's eastern frontier. The Seljuks also played a significant role in the Armenian population movement into Cilicia. In 1064, the Seljuk Turks led by
2845:Կիլիկյան հայկական պետության ծաղկան ժամանակաշրջանում՝ XIII դարում, նրա տարածությունը կազմում էր 40.000 քառ. կմ, իսկ բնակչության թիվը անցնում էր մեկ միլիոնից։ Կիլիկիայի քաղաքներում ու նավահանգիստներում էր կենտրոնացված Կիլիկիայի մեկ միլիոն բնակչության համարյա կեսը։
1512:. The Armenians and Crusaders were part allies, part rivals for the two centuries to come. Often at the invitation of Armenian barons and kings the Crusaders maintained for varying periods castles in and along the borders of the Kingdom, including
1909:
at Karakorum. He was received with great honors and promised freedom from taxation of the Armenian churches and monasteries located in Mongol territory. Both during his trip to the Mongol court and in his 1256 return to Cilicia, he passed through
2525:, as well as livestock, hides, wool, and cotton. In addition, important products such as timber, grain, wine, raisins, and raw silk were also exported from the country and finished cloth and metal products from the West were made available.
1275:
The formal annexation of Greater Armenia to the Byzantine Empire in 1045 and its conquest by the Seljuk Turks 19 years later caused two new waves of Armenian migration to Cilicia. The Armenians could not re-establish an independent state in
1380:
Empire. He was joined by many other Armenian lords and nobles. Thus, in 1080, the foundations of the independent Armenian princedom of Cilicia, and the future kingdom, were laid under Ruben's leadership. His descendants were called
3956:
The Catalan map does not make much of Ottoman power. The Cilician kingdom of Armenia Minor is more clearly indicated. Founded at the end of the twelfth century, it fell to the Turks in 1375, the very year in which the Atlas was
2673:
was a Franciscan and an advocate of union with the Latin Church. The papal claim of primacy did not contribute positively to the efforts for unity between the Churches. Mkhitar Skewratsi, the Armenian delegate at the council in
2633:
The Catholicosate of the Armenian Apostolic Church followed its people in taking refuge outside the Armenian highlands, which had turned into a battleground of Byzantine and Seljuk contenders. Its seat was first transferred to
1333:
in the east. He invited many Armenian nobles to settle in his territory, and gave them land and castles. But Philaretus's state began to crumble even before his death in 1090, and ultimately disintegrated into local lordships.
1927:
for a war against the Mamluks. According to Arab historians, during Hulagu's conquest of Aleppo, Het'um and his forces were responsible for a massacre and arsons in the main mosque and in the neighboring quarters and souks.
2544:, and granted them certain privileges such as tax exemptions in return for their business. The three primary harbours of the Armenian Kingdom, which were vital to its economy and defense, were the fortified coastal sites at
2687:
After the sacking of Hromkla by the Mamluks in 1293, the Catholicosate was transferred to Sis, the capital of the Cilician Kingdom. Again, in 1441, long after the fall of the kingdom, the Armenian Catholicos of Sis,
3513:"Hethoum I receiving the homage of the Tatars: during his voyage to Mongolia in 1254, Hethoum I was received with honours by the Mongol Khan who 'ordered several of his noble subjects to honour and attend him'" in
1830:
beginning of Cilician Armenia's united dynastic kingdom, the Armenians were confronted by many challenges from abroad. In order to enact revenge for his son's death, Bohemond sought an alliance with Seljuk sultan
1108:
disintegrated, leaving the Armenian Kingdom without any regional allies. After relentless attacks by the Mamluks in Egypt in the fourteenth century, the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, then under the rule of the
2766:
describes the alliance of the Franks of Antioch and Tripoli with the Mongols: (in 1260) "the Frank barons refused an alliance with the Mongols, except for the Armenians and the Prince of Antioch and Tripoli".
2367:
in the 17th century. Cilicia was one of the most important regions for the Ottoman Armenians, because it managed to preserve Armenian character well throughout the years. In 1909, Cilician Armenians were
2780:(p. 261), “Bohemond of Antioch and Hethoum of Armenia, principal allies of the Mongols” (p. 265), “Hulagu (…) still had enough strength to prevent the punishment of his allies ” (p. 267).
1996:
was sacked and burnt, thousands of Armenians were massacred and 40,000 taken captive. Het'um ransomed Levon for a high price, giving the Mamluks control of many fortresses and a large sum of money. The
2139:, south of Damascus, on April 21, 1303. It is considered to be the last major Mongol invasion of Syria. When Ghazan died on May 10, 1304, all hope of reconquest of the Holy Land died in conjunction.
2135:
In 1303, the Mongols tried to conquer Syria once again in larger numbers (approximately 80,000) along with the Armenians, but they were defeated at Homs on March 30, 1303, and during the decisive
1488:
to their aid as the Armenians did, who supplied the Crusaders with horses, provision and guidance. The Armenians assisted these warriors with their utter courage and loyalty during the Holy wars.
1116:
Commercial and military interactions with Europeans brought new Western influences to the Cilician Armenian society. Many aspects of Western European life were adopted by the nobility including
1560:, and expanded the Rubenid domain. He transferred the Cilician capital from Tarsus to Sis after having eliminated the small Byzantine garrison stationed there. In 1112, he took the castle of
1120:, fashions in clothing, and the use of French titles, names, and language. Moreover, the organization of the Cilician society shifted from its traditional system to become closer to Western
1586:, escaped in 1141 and returned to Cilicia to lead the struggle with the Byzantines. Initially, he was successful in repelling Byzantine invasions; but, in 1158, he paid homage to Emperor
3504:
Natasha Hodgson, Conflict and Cohabitation Marriage and Diplomacy between Latins and Cilician Armenians c. 1150-1254’ in The Crusades and the Near East, ed. C Kostick (Routledge, 2010)
6528:
2513:
Cilician Armenia had become a prosperous state due to its strategic position on the eastern shores of the Mediterranean. It was located at the juncture of many trade routes linking
1124:. The European Crusaders themselves borrowed know-how, such as elements of Armenian castle-building and church architecture. Cilician Armenia thrived economically, with the port of
1963:, which further made the Armenian Kingdom a potential Mamluk target. Armenia also engaged in an economic battle with the Mamluks for control of the spice trade. The Mamluk leader
1896:
against the Seljuk Turks. The Mongol conquest was disastrous for Greater Armenia, but not Cilicia, as Het'um preemptively chose to cooperate with the Mongols. He sent his brother
1681:. Prince Levon II profited from the situation by improving relations with the Europeans. Cilician Armenia's prominence in the region is attested by letters sent in 1189 by Pope
3571:"The king of Armenia and the Prince of Antioch went to the military camp of the Tatars, and they all went off to take Damascus". Le Templier de Tyr. Quoted in Rene Grousset,
2891:
2506:
2261:
made by the Armenians to their co-religionists in Europe, and the kingdom was also involved in planning new crusades. Amidst failed Armenian pleas for help from Europe, the
468:
454:
440:
415:
401:
387:
2285:
at the death of John I and died in exile in Paris in 1393, after having called in vain for another crusade. In 1396, Levon's title and privileges were transferred to
2826:
1914:. On his return voyage, he remained much longer, receiving visits from local princes, bishops, and abbots. Het'um and his forces fought under the Mongol banner of
1686:
2528:
During the reign of King Levon, the economy of Cilician Armenia progressed greatly and became heavily integrated with Western Europe. He secured agreements with
1955:
governments. Cilician Armenia also expanded and recovered lands crossed by important trade routes on the Cappadocian, Mesopotamian, and Syrian borders, including
4478:
2642:, where had existed a significant Armenian population. Later, it moved to various locations in Cilicia; Tavbloor in 1062; Dzamendav in 1066; Dzovk in 1116; and
1404:. The Het'umids contended with the Rubenids for power and influence over Cilicia. Various Armenian lords and former generals of Philaretos were also present in
2132:, on December 23, 1299. The bulk of the Mongol army was then obligated to retreat. In their absence, the Mamluks regrouped, and regained the area in May 1300.
6202:
4810:
2697:
2269:, his daughter Marie, and her husband Shahan had taken refuge, put an end to the kingdom. The final king, Levon V, was granted safe passage and arrived in
129:
6513:
2718:
1770:
was proclaimed the new ruler of Cilician Armenia and placed under the regency of Adam of Baghras. Baghras was assassinated and the regency passed to
1317:, a former Byzantine general who was alongside Romanus Diogenes at Manzikert. Between 1078 and 1085, Philaretus built a principality stretching from
4567:
1892:
and reached the Middle East, conquering Mesopotamia and Syria in their advance towards Egypt. On June 26, 1243, they secured a decisive victory at
1905:
political autonomy to build new and impressive fortifications, such as the castle at Tamrut. In 1253, Het'um himself visited the new Mongol ruler
4820:
4815:
2166:, brother of Het'um, immediately marched against Bularghu to retaliate and vanquished him, forcing him to leave Cilicia. Bulargu was executed by
5748:
3562:
Christianian, Jirair, “The Inscription at Tamrut Castle: The Case for a Revision of Armenian History,” Le Muséon 132 (1-2), 2019, pp.107-122.
1834:, who captured regions west of Seleucia. Het'um also struck coins with his figure on one side, and with the name of the sultan on the other.
3919:
2840:
2836:
1774:
from the Het'umid dynasty, a very influential Armenian family. In order to fend off the Seljuk threat, Constantine sought an alliance with
905:
1256:. However, the Caliphate failed to gain a permanent foothold in Anatolia, as Cilicia was reconquered in the year 965 by Byzantine Emperor
5057:
4471:
3192:(2008). "The Founding and the Coalescence of the Rubenian Principality, 1073–1129". In Hovannisian, Richard G.; Payaslian, Simon (eds.).
3127:
2044:
from the Armenians. The Mamluks, despite the above, continued to raid Cilician Armenia on numerous occasions. In 1292, it was invaded by
3906:
The Cilician kingdom of Armenia Minor is more clearly indicated. Founded at the end of the twelfth century, it fell to the Turks in 1375
6195:
4915:
406:
5224:
46:
6538:
6523:
2567:
In the thirteenth century, under the rule of Toros, Cilician Armenia already struck its own coins. Gold and silver coins, called
2328:. As a result, 30,000 wealthy Armenians left Cilicia and settled in Cyprus, still ruled by the Lusignan dynasty until 1489. Many
294:
4003:(in Armenian). Athens: Հրատարակութիւն ազգային ուսումնակաան խորհուրդի (Council of National Education Publishing). pp. 53–56.
3431:(in Armenian). Athens: Հրատարակութիւն ազգային ուսումնակաան խորհուրդի (Council of National Education Publishing). pp. 42–44.
3373:(in Armenian). Athens: Հրատարակութիւն ազգային ուսումնակաան խորհուրդի (Council of National Education Publishing). pp. 33–36.
2150:
friar; however, he emerged from his monastic cell to help Levon defend Cilicia from a Mamluk army, which was thus defeated near
6493:
4464:
3444:
The letter of love and concord : a revised diplomatic edition with historical and textual comments and English translation
4354:. UCLA Armenian History and Culture Series: Historic Armenian Cities and Provinces, 7. Costa Mesa, CA: Mazda Publishers, 2008.
3822:
3594:
3344:
3309:
1268:
in the east and Arab-held Syria towards the south. As a result of the Byzantine military campaigns, the Armenians spread into
4391:
4367:
4244:
4160:
4132:
4094:
3949:
3899:
3671:
3452:
3256:
3231:
3201:
3090:
2857:
2830:
2324:
had taken over Cilicia, they were unable to hold it. Turkic tribes settled there, leading to the conquest of Cilicia led by
1689:, in which he asks Armenian military and financial assistance to the crusaders. Thanks to the support given to Levon by the
6533:
6518:
6498:
6483:
6188:
5733:
3547:
3067:
The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times, Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiquity to the Fourteenth Century
5723:
5666:
5583:
4954:
2170:
for his crime at the request of the Armenians. Oshin was crowned new king of Cilician Armenia upon his return to Tarsus.
31:
5505:
5087:
2430:, fashion, and the use of French Christian names. The structure of Cilician society became more synonymous with Western
1157:
Syria, weakened by a bloody civil war, offered their allegiance to the ambitious Armenian king. Tigranes then conquered
6503:
5500:
5179:
4664:
3247:
Bozoyan, Azat A. (2008). "Armenian Political Revival in Cilicia". In Hovannisian, Richard G.; Payaslian, Simon (eds.).
2388:. The lion, emblem of the Cilician Armenian state, remains a symbol of Armenian statehood to this day, featured on the
1500:. The friendly relationship between the Armenians and Crusaders was cemented by frequent intermarriages. For instance,
847:
4019:
The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393)
3971:
The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393)
3401:
The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393)
3163:
The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393)
3022:
The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins (1080–1393)
135:
6160:
5237:
4336:
4317:
4273:
4195:
4051:
4026:
3978:
3872:
3799:
3765:
3732:
3696:
3621:
3408:
3289:
3170:
3074:
3029:
2913:
2806:
2799:
The Armenian Kingdom in Cilicia During the Crusades: The Integration of Cilician Armenians with the Latins, 1080-1393
1229:
territories. Many served in the Byzantine army as soldiers or as generals, and rose to prominent imperial positions.
2472:. The Cilician period also produced some important examples of Armenian art, notably the illuminated manuscripts of
1388:). After Ruben's death in 1095, the Rubenid principality, centered around their fortresses, was led by Ruben's son,
1289:
in Byzantine-held Armenia. Seven years later, they earned a decisive victory against Byzantium by defeating Emperor
6211:
6027:
1436:
1389:
898:
17:
3851:
5442:
5437:
4658:
2410:
2249:
852:
792:
782:
6266:
2873:"1080 A.D. Rhupen, cousin of the Bagratonian kings, sets up on Mount Taurus (overlooking the Mediterranean Sea)
1392:; however, there were several other Armenian principalities both inside and beyond Cilicia, such as that of the
6066:
5754:
5593:
5356:
5128:
4504:
3646:
2952:
2426:
influences on Armenian culture. The Cilician nobility adopted many aspects of Western European life, including
2084:
to the Turks. In 1293, he abdicated in favor of his brother T'oros III, and entered the monastery of Mamistra.
1976:
to obtain military support, but in his absence, the Mamluks invaded Cilician Armenia. Het'um's sons T'oros and
1015:
652:
4442:
5833:
5803:
5639:
5062:
4908:
4488:
817:
587:
577:
30:
This article is about the Kingdom of Cilicia under Armenian rule. For a list of other Armenian Kingdoms, see
5149:
3839:
Angus, Stewart, "The assassination of King Het'um II". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, 2005 pp. 45–61.
6077:
5994:
5761:
5686:
5252:
5217:
4430:
4300:
1716:
1698:
873:
775:
38:
2976:] (in Armenian). Vol. II. Athens: Հրատարակութիւն ազգային ուսումնակաան խորհուրդի . pp. 43–44.
2489:
1492:
To show their appreciation to their Armenian allies, the Crusaders honored Constantine with the titles of
6061:
6056:
5960:
5843:
5818:
5718:
5537:
5279:
5110:
4737:
2270:
2129:
1992:
overran the heavily outnumbered Armenians, killing T'oros and capturing Levon. Afterwards the capital of
1306:
891:
667:
562:
522:
3939:
1443:
took place. An army of Western European Christians marched through Anatolia and Cilicia on their way to
6488:
6401:
5531:
4732:
4616:
4516:
4187:
3476:
2356:
remained in Cilicia. They nevertheless maintained their foothold in the region throughout Turkic rule.
1364:
1085:
822:
732:
692:
503:
111:
6508:
6046:
5743:
5618:
5613:
5598:
5526:
5495:
4594:
4550:
2612:
2205:
2197:
2105:
1783:
1782:, but she was later forced to marry Constantine's son Het'um in 1226. Het'um became co-ruler as King
1767:
1571:
1066:
842:
717:
243:
3282:
A History of the Crusades, Vol. I: The First Crusade and the Foundations of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
2908:(Second ed.). Madison, Milwaukee, and London: University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 630–659.
2204:. "Les chevaliers de Saint-Jean-de-Jerusalem rétablissant la religion en Arménie", 1844 painting by
835:
6051:
6016:
5623:
5047:
4901:
2143:
1654:
1101:
247:
4383:
4265:
3540:
The Armenian Kingdom and the Mamluks: War and Diplomacy During the Reigns of Het'um II (1289–1307)
3224:
The Armenian Kingdom and the Mamluks: War and Diplomacy During the Reigns of Het'um II (1289–1307)
542:
6104:
5971:
5798:
5793:
5713:
5696:
5671:
5628:
5304:
5284:
5269:
5210:
5027:
4961:
4933:
4652:
3386:
A History of the Crusades – Volume II.: The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East: 1100–1187
2887:
2389:
2005:
1998:
1977:
1893:
1843:
1603:
1460:
1217:
After the 395 AD partition of the Roman Empire into halves, Cilicia became incorporated into the
877:
752:
567:
6180:
1756:
6099:
5861:
5788:
5701:
5052:
5032:
5020:
4842:
4347:
3938:(1991). "Observations and Beliefs: The World of the Catalan Atlas". In Levenson, Jay A. (ed.).
3691:. UCLA Armenian History and Culture Series (in French). France: CNRS Editions. pp. 74–75.
3196:. UCLA Armenian History and Culture Series 8. United States: Mazda Publishers. pp. 79–83.
2947:. Washington D. C.: Dumbarton Oaks, Trustees for Harvard University. pp. vii–xxxi, 3–288.
2689:
2499:
1775:
1771:
1720:
1650:
1633:
1505:
1428:
1097:
1073:
281:
4236:
3757:
3189:
3119:
1053:, and saw itself as a bastion of Christendom in the East. It also served as a focal point for
6457:
5892:
5691:
5676:
5472:
5139:
5134:
4648:
4600:
4153:
Muslim military architecture in greater Syria: from the coming of Islam to the Ottoman Period
4124:
4118:
3889:
3724:
2728:
2663:
2655:
2033:
1712:
1708:
1314:
787:
727:
4228:
1657:'s grandsons and brother of Ruben III, acceded the throne in 1187. He fought the Seljuks of
1636:. Levon II is considered the first king of Cilicia due to the Byzantine refusal of previous
1355:
6462:
5989:
5853:
5738:
5708:
5681:
5608:
5561:
4949:
4800:
4456:
3829:. United States of America: Armenian General Benevolent Union of America. pp. 253–254.
3601:. United States of America: Armenian General Benevolent Union of America. pp. 246–248.
3351:. United States of America: Armenian General Benevolent Union of America. pp. 213–226.
2903:
2097:
1897:
1748:
1694:
1674:
1521:
1501:
1218:
1057:, since Armenia proper was under foreign occupation at the time. Cilicia's significance in
1027:
6341:
2036:, a truce was forced on Armenia. Further, in 1285, following a powerful offensive push by
1272:, and eastward from Cilicia into the mountainous areas of northern Syria and Mesopotamia.
8:
6447:
6442:
6306:
6038:
5939:
5828:
5823:
5654:
5144:
5075:
4670:
4642:
3935:
3251:. UCLA Armenian History and Culture Series. United States: Mazda Publishers. p. 68.
2693:
2622:
2608:
2465:
2377:
2329:
2212:
2201:
2121:
1703:
1690:
1452:
1413:
1330:
1302:
1294:
1290:
1041:, which at various times had held the throne of Armenia. Their capital was originally at
1019:
862:
555:
6276:
5159:
2617:
6321:
6291:
6261:
6153:
5954:
5875:
5838:
5776:
5588:
5578:
5349:
5245:
5184:
5080:
5067:
5042:
4971:
4834:
4632:
4584:
3470:
2537:
2266:
2112:, for his support. In response, Ghâzân marched towards Syria and invited the Franks of
2069:
1993:
1968:
submission to the Mongols. After these threats, Het'um went to the Mongol court of the
1930:
1815:
1724:
1310:
1253:
1237:
1142:
1058:
1054:
1046:
1011:
742:
672:
657:
642:
531:
307:
191:
3316:. United States of America: Armenian General Benevolent Union of America. p. 202.
3156:
3154:
3152:
3150:
3148:
3146:
3144:
3098:
2575:, were struck at the royal mints of Sis and Tarsus. Foreign coins such as the Italian
6396:
6366:
6009:
5999:
5979:
5922:
5902:
5887:
5813:
5728:
5521:
5402:
5371:
5344:
4988:
4978:
4867:
4622:
4610:
4526:
4387:
4363:
4332:
4313:
4269:
4240:
4229:
4191:
4156:
4128:
4090:
4047:
4022:
3974:
3945:
3895:
3868:
3795:
3791:
3785:
3761:
3750:
3728:
3717:
3692:
3667:
3642:
3617:
3543:
3458:
3448:
3404:
3285:
3252:
3227:
3197:
3166:
3070:
3025:
2948:
2909:
2802:
2560:
due to the three Italian city-states' extensive involvement in the Cilician economy.
2533:
2457:
2373:
2308:
2286:
2274:
2178:
2174:
2136:
1869:
1587:
1472:
1468:
1424:
1368:
1110:
1038:
945:
812:
807:
737:
682:
461:
447:
209:
4035:
2024:
Little Armenia, a Christian exclave in Anatolia, and its surrounding states in 1300.
6437:
6427:
6376:
6356:
6256:
6169:
6071:
6021:
5984:
5949:
5944:
5932:
5927:
5907:
5467:
5412:
5376:
5097:
4966:
4862:
4544:
4522:
4512:
4409:
4406:
Seventeen lectures on the study of medieval and modern history and kindred subjects
4080:
4078:
3141:
3061:
2899:
2557:
2529:
2414:
2321:
2253:
2182:
2163:
2125:
2061:
2045:
1939:
1911:
1807:
1579:
1509:
1464:
1397:
1277:
1226:
1222:
999:
722:
705:
687:
582:
502:
Although the kingdom was established in 1198, its foundations were laid in 1080 by
433:
420:
314:
221:
4222:
4220:
3752:
The Last Templar: The Tragedy of Jacques de Molay, Last Grand Master of the Temple
3719:
The Last Templar: The Tragedy of Jacques de Molay, Last Grand Master of the Temple
3059:
3057:
3055:
3053:
3051:
3049:
3047:
3045:
3043:
3041:
2108:, again facing threats of attack by the Mamluks, asked the Mongol khan of Persia,
1665:, and added new lands to Cilicia, doubling its Mediterranean coast. At the time,
1405:
1169:). Many of the inhabitants of conquered cities were sent to the new metropolis of
6331:
6286:
6109:
5479:
5366:
5339:
5274:
5037:
4924:
4638:
4588:
4508:
4446:
4434:
4148:
3514:
3277:
2746:
2723:
2670:
2669:
Het'um II became a Franciscan friar after his abdication. The Armenian historian
2117:
1943:
1591:
1456:
1448:
1194:
1162:
1154:
1104:. In the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, the Crusader states and the Mongol
1077:
923:
881:
802:
797:
747:
635:
258:
229:
5154:
5070:
4075:
2832:Հայ Ժողովրդի Պատմություն, Հ. 3. [History of the Armenian People. Vol. 3]
1868:, "receiving the homage of the Mongols". Miniature from "Histoire des Tartars",
1590:
through a short-lived treaty. Around 1151, during T'oros' rule, the head of the
1080:, Cilician Armenia became a kingdom. In 1226, the crown was passed to the rival
6406:
6351:
6251:
6094:
5917:
5462:
5121:
5116:
4788:
4778:
4626:
4397:
4217:
4179:
3818:
3590:
3340:
3305:
3069:. Ed. Richard G. Hovannisian. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1997, pp. 283–290.
3038:
2895:
2541:
2440:
system of Armenia. In fact, during the Cilician period, Western titles such as
2369:
2360:
2332:
also fled westward and founded or joined with existing diaspora communities in
2292:
2277:
to recover his kingdom. While in Castille, he was granted the title of Lord of
2220:(1375) appears heavily fortified within green walls, with its ports and flags (
2065:
1981:
1823:
1819:
1763:
1529:
1401:
1376:
1174:
1150:
1096:
and the Middle East, Hethum and succeeding Hethumid rulers sought to create an
1042:
757:
647:
225:
183:
179:
4998:
2173:
The Het'umids continued ruling an unstable Cilicia until the assassination of
1906:
1885:
1719:. By securing his crown, he became the first King of Armenian Cilicia as King
1396:. This important Armenian dynasty was founded by the former Byzantine general
6477:
6271:
5911:
5808:
5457:
5452:
5397:
5361:
5102:
4793:
4783:
4692:
4141:
3781:
3462:
2372:. Descendants of the remaining Cilician Armenians have been dispersed in the
2364:
2304:
2217:
2109:
2092:
1985:
1877:
1678:
1440:
1257:
1241:
1003:
662:
392:
61:
48:
4413:
2545:
2177:
in 1341, at the hands of an angry mob. Levon IV formed an alliance with the
1141:
Armenian presence in Cilicia dates back to the first century BC, when under
6452:
6381:
6361:
6119:
6114:
5897:
5633:
5573:
5447:
5432:
5015:
5007:
4722:
2675:
2518:
2514:
2473:
2418:
2297:
2167:
2162:. Bularghu, a recent convert to Islam, murdered the entire Armenian party.
2057:
1889:
1881:
1860:
1508:, brother of Godfrey, married Constantine's niece, daughter of his brother
1298:
1206:
1170:
1166:
1093:
239:
195:
163:
3921:
Historic Maps of Armenia - The Cartographic Heritage. Abridged and updated
3442:
2494:
1736:
1305:
and levied repressive taxes on the Armenian inhabitants. After Catholicos
6391:
6371:
6301:
6281:
6134:
5294:
3533:
3531:
3529:
3527:
2659:
2522:
2405:
2341:
2262:
2081:
2029:
2009:
1740:
1682:
1537:
1525:
1347:
1249:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1125:
592:
310:
268:
37:"Kingdom of Cilicia" redirects here. For the ancient Luwian kingdom, see
4304:. vol. V. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1979, pp. 406–428.
1252:
invasions in the seventh century and was entirely incorporated into the
1209:
conquered Cilicia and transformed it into one of its eastern provinces.
1165:. The southern border of his domain reached as far as Ptolemais (modern
6326:
6231:
5603:
5427:
4872:
4847:
4742:
4727:
3217:
3215:
3213:
2701:
2647:
2639:
2561:
2553:
2147:
1831:
1282:
1269:
1265:
1062:
1033:
The kingdom had its origins in the principality founded c. 1080 by the
217:
3524:
1711:, Levon received a banner with the insignia of a lion from Archbishop
151:
6386:
6296:
6004:
5422:
5417:
4707:
4540:
2651:
although the exact locations of the majority of them remain unclear.
2431:
2353:
2245:
2193:
2159:
2028:
In 1281, following the defeat of the Mongols and the Armenians under
1901:
1865:
1848:
1803:
1752:
1728:
1607:
1583:
1553:
1543:
1517:
1444:
1212:
1158:
1145:, the Kingdom of Armenia expanded and conquered a vast region in the
1121:
1105:
1081:
995:
677:
140:
4402:
The Medieval Kingdoms of Cyprus and Armenia: (Oct. 26 and 29, 1878.)
3210:
2945:
The Fortifications of Armenian Cilicia, Dumbarton Oaks Studies No.23
2244:
There had always been close relations between the Armenians and the
1806:
had settled into western Cilicia, primarily in the highlands of the
6346:
6336:
6311:
6246:
6241:
5392:
5314:
5202:
5189:
4941:
4852:
4717:
4702:
4604:
4536:
4439:
4427:
2905:
A History of the Crusades, Volume II: The Later Crusades, 1189–1311
2626:
2436:
2427:
2381:
2315:
2155:
1923:
1662:
1628:
1599:
1565:
1561:
1552:, who succeeded him in around 1100. During his rule, he faced both
1549:
1393:
1372:
1261:
1198:
1117:
1113:
and mired in an internal religious conflict, finally fell in 1375.
1089:
1050:
1034:
712:
607:
507:
168:
118:
4893:
3852:
Recueil des Historiens des Croisades, Documents Armeniens I, p.664
2564:, for example, set out on his journey to China from Ayas in 1271.
1744:
1061:
and statehood is also attested by the transfer of the seat of the
6411:
6316:
6210:
6124:
5552:
5319:
5299:
5233:
4882:
4857:
4805:
4762:
4712:
4697:
4556:
4360:
Arméniens et autres Chrétiens d'Orient sous la domination Mongole
4120:
The Armenians: from kings and priests to merchants and commissars
3664:
Arméniens et autres Chrétiens d'Orient sous la domination mongole
2713:
2692:, proclaimed the union of the Armenian and Latin churches at the
2643:
2549:
2477:
2385:
2265:
to the Mamluks, followed by the fortress of Gaban in 1375, where
2158:, the Mongol representative in Cilicia, at his camp just outside
2073:
2041:
2037:
1989:
1969:
1964:
1960:
1952:
1948:
1853:
1811:
1779:
1666:
1642:
1595:
1564:
in order to avenge the death of the last Bagratid Armenian king,
1557:
1409:
1381:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1023:
1007:
857:
597:
3823:"Chapter XXX: The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia — Mongol Invasion"
3595:"Chapter XXX: The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia — Mongol Invasion"
2056:, who had conquered the remnants of the Kingdom of Jerusalem in
6236:
5329:
5324:
5309:
4752:
4268:(in French). Vol. 464. France: Gallimard. pp. 71–72.
3447:. Pogossian, Zaroui. Leiden: Brill. 2010. p. 17, note 46.
2997:
Der Nersessian. "The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia", pp. 645–653.
2835:(in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences. pp.
2469:
2345:
2333:
2300:
2282:
2278:
2151:
2113:
2077:
2049:
2020:
1973:
1956:
1919:
1915:
1618:
1575:
1533:
1513:
1375:. Ruben was alongside the Armenian ruler Gagik when he went to
1193:
to the Mediterranean. Tigranes invaded as far southeast as the
1146:
622:
617:
602:
494:
486:
3614:
The New Cambridge Medieval History, Volume IV: c. 1024-c. 1198
3585:
3583:
3581:
3335:
3333:
3331:
3329:
3327:
3325:
3323:
1794:
1181:). At its height, Tigranes' Armenian Empire extended from the
6129:
5334:
4877:
4451:
3994:
3992:
3990:
3422:
3420:
3364:
3362:
3360:
3358:
2993:
2991:
2989:
2987:
2985:
2983:
2635:
2349:
2337:
2325:
2239:
2142:
Het'um II abdicated in favour of his sixteen-year-old nephew
2053:
1670:
1658:
1497:
1493:
1363:
One of the princes who came after Philaretos' invitation was
934:
612:
490:
213:
4486:
2521:
to the Mediterranean. The kingdom was thus important in the
1447:. The Armenians in Cilicia gained powerful allies among the
1232:
6226:
5289:
5166:
4757:
4747:
3578:
3320:
3310:"Chapter XXV: Magnificence to be soon followed by Calamity"
3284:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 195–201.
2505:
1837:
1732:
1471:. The Armenians also helped the Crusaders; as described by
1202:
1069:, spiritual leader of the Armenian people, to the region.
572:
3987:
3542:. Netherlands: Brill Academic Publishers. pp. 43–46.
3417:
3355:
3226:. Netherlands: Brill Academic Publishers. pp. 33–34.
2980:
2621:
The St. Gregory the Illuminator Armenian Cathedral at the
1610:, succeeded T'oros in 1169, 1170, and 1175, respectively.
1225:. In the sixth century AD, Armenian families relocated to
6529:
States and territories disestablished in the 14th century
2961:
2678:
in 1261, summed the Armenian frustration in these words:
1578:. In this context, in 1137, the Byzantines under Emperor
1286:
3867:(in French). France: Découvertes Gallimard. p. 77.
2880:
4155:. Netherlands: Brill Academic Publishers. p. 293.
2307:, retained a substantial Armenian population until the
1131:
3813:
3811:
3616:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 634.
2154:. In 1307, both the current and former kings met with
2100:
to accompany Kutlushah on the 1303 attack on Damascus.
968:
954:
4044:
The later Crusades, 1 274-1580: from Lyons to Alcazar
2509:
Coin of the Cilician Armenian kingdom, ca. 1080–1375.
2087:
927:
4235:. United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing ltd. p.
1856:
in Cilician Armenia built c. the thirteenth century.
4329:
The Armenian kingdom in Cilicia during the Crusades
4294:Poghosyan, S.; Katvalyan, M.; Grigoryan, G. et al.
4112:
4110:
4108:
4106:
3808:
3184:
3182:
2719:
List of monarchs of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
1918:in the conquest of Muslim Syria and the capture of
1136:
3749:
3716:
3240:
1622:Little Armenia and its surrounding states in 1200.
1544:Armenian-Byzantine and Armenian-Seljuk contentions
1213:Mass Armenian migration under the Byzantine Empire
4046:. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 21.
3611:
2824:
2696:; this was countered by an Armenian schism under
2185:, but could not resist attacks from the Mamluks.
2015:
2004:In 1269, Het'um I abdicated in favour of his son
1613:
1285:made their advance towards Anatolia by capturing
6475:
4103:
4087:The Treatment of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire
4001:Պատմութիւն Հայոց (History of Armenia), Volume II
3689:Le Royaume Arménien de Cilicie, XIIe-XIVe siècle
3429:Պատմութիւն Հայոց (History of Armenia), Volume II
3371:Պատմութիւն Հայոց (History of Armenia), Volume II
3179:
3065:Bournoutian, Ani Atamian. "Cilician Armenia" in
2316:Dispersion of the Armenian population of Cilicia
1431:receiving the homage of the Armenians in Edessa.
1416:, the latter two being located outside Cilicia.
1342:
4231:The Blackwell Companion to Eastern Christianity
4012:
4010:
3489:
3345:"Chapter XXVII: The Barony of Cilician Armenia"
3085:
3083:
4396:
4123:. London: Columbia University Press. pp.
4071:. New York: Kalaydjian Foundation. p. 12.
2886:
2769:
2756:
2740:
961:
6196:
5218:
4909:
4472:
3537:
3221:
2666:himself arrived in Cilician Armenia in 1288.
2188:
1297:, north of Lake Van. Alp Arslan's successor,
1100:against common Muslim foes, most notably the
899:
4089:. Germany: Textor Verlag. pp. 465–467.
4007:
3377:
3080:
2395:
2363:dominion and officially became known as the
2104:In the summer of 1299, Het'um I's grandson,
1980:were left to defend the country. During the
1049:. Cilicia was a strong ally of the European
5058:County Palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos
4174:
4172:
3998:
3710:
3708:
3426:
3368:
3272:
3270:
3268:
3015:
3013:
3011:
3009:
3007:
3005:
3003:
2967:
2490:Armenian merchantry § Cilician Armenia
1477:
1092:. As the Mongols conquered vast regions of
6514:States and territories established in 1080
6203:
6189:
5225:
5211:
4916:
4902:
4479:
4465:
3612:Luscombe, David; W. Hazard, Harry (2004).
2770:
2757:
2741:
2252:. Guy de Lusignan and his younger brother
2240:Decline and fall with the Lusignan dynasty
906:
892:
150:
4326:
4116:
4066:
4016:
3968:
3941:Circa 1492: Art in the Age of Exploration
3917:
3891:Circa 1492: Art in the Age of Exploration
3817:
3666:(in French). Geuthner. pp. 128–129.
3589:
3483:
3398:
3339:
3304:
3160:
3019:
2938:
2936:
2934:
2932:
2930:
2928:
2926:
2796:
2700:, who moved the See of the Catholicos to
2646:in 1149. During King Levon I's rule, the
1876:During the rule of Zabel and Het'um, the
1864:Hethum I (seated) in the Mongol court of
1818:, which commanded strategic roads to the
1504:married the daughter of Constantine, and
1359:The Barony of Cilician Armenia, 1080–1199
1264:(976–1025) tried to expand into Armenian
1128:serving as a center for East–West trade.
407:Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynasty
4357:
4259:
4178:
4169:
3862:
3747:
3714:
3705:
3686:
3661:
3276:
3265:
3000:
2616:
2504:
2493:
2404:
2359:In the 16th century, Cilicia fell under
2291:
2211:
2192:
2091:
2019:
1929:
1859:
1847:
1838:Armeno-Mongol alliance and Mamluk threat
1810:. Their two great dynastic castles were
1793:
1617:
1423:
1354:
1346:
1231:
448:Kingdom of Cyprus, Jerusalem and Armenia
4655:, Shanazarians and Avanians, 1603–1822)
4260:Mahé, Annie; Mahé, Jean-Pierre (2005).
4147:
4041:
3934:
3888:Massing, Jean Michel (1 January 1991).
3887:
3863:Mahé, Annie; Mahé, Jean-Pierre (2005).
3780:
3246:
3188:
2942:
2281:and other cities. He left Castille for
1789:
337:40,000 km (15,000 sq mi)
14:
6476:
4312:. Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press.
3636:
2923:
2820:
2818:
1766:to claim the throne, Levon's daughter
1337:
27:State in southern Anatolia (1080–1375)
6184:
5206:
4897:
4460:
4307:
4226:
4084:
4067:Hadjilyra, Alexander-Michael (2009).
3944:. Yale University Press. p. 27.
3894:. Yale University Press. p. 27.
3790:. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. p.
3130:from the original on 21 February 2007
2662:were put in charge of this activity.
280:• Prince Leo II crowned as King
5232:
3856:
3383:
2734:
2448:replaced their Armenian equivalents
1400:, and was centered southwest of the
1161:and Cilicia, effectively ending the
1132:Early Armenian migrations to Cilicia
1037:, an alleged offshoot of the larger
510:principality of Cilicia was founded.
4923:
2815:
2012:, Armenian, and Frankish perished.
1798:Flag of Hetumid Dynasty (1226–1341)
1762:In 1219, after a failed attempt by
1367:, who had close ties with the last
24:
5749:President of the National Assembly
4386:(n° 464), Paris: Gallimard, 2005,
4285:
4184:The New Cambridge Medieval History
3924:. BENNETT & BLOOM. p. 59.
3521:, p.58, quoting Hayton of Corycus.
2088:Campaigns with Mongols (1299–1303)
1626:The Principality of Cilicia was a
541:
25:
6550:
4421:
4380:L'Arménie à l'épreuve des siècles
4262:L'Arménie à l'épreuve des Siècles
3865:L'Arménie à l'épreuve des Siècles
3756:. London: Profile Books. p.
3723:. London: Profile Books. p.
3641:. Richmond: Curzon. p. 253.
3639:The Kingdom of Armenia: A History
2892:"The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia"
2599:were also accepted by merchants.
2273:seeking assistance from the King
1934:A young Cilician Armenian knight.
1309:'s assistant and representative,
1002:by Armenian refugees fleeing the
80:Armenian Principality of Cilicia
6212:States in late medieval Anatolia
5551:
4997:
4566:
4523:Kingdom of Armenia (Middle Ages)
2654:In 1198, the Catholicos of Sis,
2540:, as well as the French and the
2229:
2222:
2001:further devastated the country.
1942:had been replacing their former
1632:kingdom before the ascension of
1419:
1201:, located in modern-day western
1137:Cilicia under Tigranes the Great
988:Armenian Principality of Cilicia
466:
452:
438:
413:
399:
385:
128:
110:
4659:Republic of Mountainous Armenia
4639:Zakarid Principality of Armenia
4310:The Cilician Kingdom of Armenia
4253:
4204:
4060:
4021:. Routledge. pp. 159–161.
3962:
3928:
3911:
3881:
3842:
3833:
3774:
3741:
3680:
3655:
3630:
3605:
3565:
3556:
3507:
3498:
3435:
3403:. Routledge. pp. 118–120.
3392:
3298:
3112:
2858:"Landmarks in Armenian history"
2250:Constantine II, King of Armenia
2072:. Het'um was forced to abandon
1351:Coat of arms of Rubenid dynasty
853:Republic of Mountainous Armenia
6539:Former monarchies of West Asia
6524:1375 disestablishments in Asia
5129:Livonian Brothers of the Sword
5016:Latin Empire of Constantinople
4505:Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity)
4452:Cilician Armenian Architecture
3519:Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie
3492:The Crusader States, 1192–1243
2850:
2790:
2777:The Crusades through Arab eyes
2751:Le Royaume Arménien de Cilicie
2016:Truce with Mamluks (1281–1295)
1614:Principality becomes a kingdom
1072:In 1198, with the crowning of
992:Կիլիկիայի հայկական իշխանութիւն
13:
1:
6494:Former countries in West Asia
5063:Lordship of Argos and Nauplia
4212:Arméniens et autres Chrétiens
3538:Donal Stewart, Angus (2001).
3222:Donal Stewart, Angus (2001).
3165:. Routledge. pp. 39–42.
3024:. Routledge. pp. 54–55.
2968:Kurdoghlian, Mihran (1996).
2181:, then ruled by the Frankish
2064:was also sacked, forcing the
1343:Emergence of Cilician Armenia
936:Kiligio Hayoc’ T’akavorut’iun
4327:Ghazarian, Jacob G. (2000).
4301:Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia
4017:Ghazarian, Jacob G. (2000).
3999:Kurdoghlian, Mihran (1996).
3969:Ghazarian, Jacob G. (2000).
3427:Kurdoghlian, Mihran (1996).
3399:Ghazarian, Jacob G. (2000).
3369:Kurdoghlian, Mihran (1996).
3161:Ghazarian, Jacob G. (2000).
3120:"King Tigran II – The Great"
3020:Ghazarian, Jacob G. (2000).
2784:
2552:, and the river emporium of
1717:Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor
1055:Armenian cultural production
986:, and formerly known as the
935:
929:Կիլիկիոյ Հայոց Թագաւորութիւն
96:Կիլիկիոյ Հայոց Թագաւորութիւն
88:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
39:Kingdom of Cilicia (ancient)
7:
6534:1198 establishments in Asia
6519:1080 establishments in Asia
6499:States in medieval Anatolia
6484:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
6433:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
6062:Armenian Brotherhood Church
6057:Armenian Evangelical Church
5408:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
5111:State of the Teutonic Order
4984:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
4533:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
4358:Luisetto, Frédéric (2007).
4350:and Simon Payaslian (eds.)
3662:Luisetto, Frédéric (2007).
3490:Nickerson Hardwicke, Mary.
2943:Edwards, Robert W. (1987).
2902:; Hazard, Harry W. (eds.).
2707:
2602:
2480:in the thirteenth century.
2130:Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar
1984:, the Mamluks under Sultan
1685:to Levon and to Catholicos
1548:The son of Constantine was
1307:Gregory II the Martyrophile
969:
955:
920:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
668:Christianization of Armenia
10:
6555:
5532:Armenian national movement
4617:Kingdom of Tashir-Dzoraget
4440:"Kilikia" song with lyrics
4331:. Routledge. p. 256.
4188:Cambridge University Press
4117:Panossian, Razmik (2006).
3973:. Routledge. p. 150.
3918:Galichian, Rouben (2014).
2875:the kingdom of New Armenia
2606:
2487:
2483:
2400:
2189:Demise of Cilician Armenia
1841:
1646:kings, rather than dukes.
928:
733:Kingdom of Tashir-Dzoraget
693:Muslim conquest of Armenia
36:
29:
6504:History of Adana Province
6420:
6219:
6147:
6087:
6047:Armenian Apostolic Church
6037:
5970:
5883:
5874:
5852:
5784:
5775:
5724:National Security Service
5662:
5653:
5569:
5560:
5549:
5527:Nagorno-Karabakh conflict
5514:
5496:First Republic of Armenia
5488:
5443:1508–1828 Iranian Armenia
5385:
5262:
5244:
5175:
5096:
5006:
4995:
4940:
4931:
4831:
4771:
4680:
4673:(1991–2023, unrecognized)
4651:(Beglarians, Israelians,
4595:Principality of Hamamshen
4575:
4564:
4495:
4362:. Geuthner. p. 262.
3687:Mutafian, Claude (2002).
2797:Ghazarian, Jacob (2018).
2613:Roman Catholicism in Asia
2396:Cilician Armenian society
2198:Constantin III of Armenia
2116:(the King of Cyprus, the
1067:Armenian Apostolic Church
1022:, it was centered in the
991:
962:
949:
843:First Republic of Armenia
718:Principality of Hamamshen
588:Lchashen–Metsamor culture
578:Trialeti–Vanadzor culture
500:
482:
364:
360:
350:
346:
341:
333:
328:
324:
304:
291:
278:
274:
264:
254:
235:
205:
175:
158:
149:
106:
101:
78:
6052:Armenian Catholic Church
5667:Administrative divisions
5048:Duchy of the Archipelago
4308:Boase, T. S. R. (1978).
4085:Bryce, Viscount (2008).
4042:Housley, Norman (1992).
3748:Demurger, Alain (2005).
3715:Demurger, Alain (2005).
2969:
2888:Der Nersessian, Sirarpie
2704:, and marginalized Sis.
2434:than to the traditional
2216:Armenian Cilicia on the
1938:Meanwhile, the Egyptian
1802:By the 11th century the
1390:Constantine I of Armenia
1026:region northwest of the
998:state formed during the
293:• Tributary to the
5629:Shikahogh State Reserve
5280:Shulaveri–Shomu culture
5028:Kingdom of Thessalonica
4962:Principality of Antioch
4934:List of Crusader states
4428:Cilician Armenian Coins
4348:Hovannisian, Richard G.
4069:The Armenians of Cyprus
2877:which lasts 300 years."
2390:Coat of arms of Armenia
2200:on his throne with the
1999:1269 Cilicia earthquake
1900:to the Mongol court of
1844:Armeno-Mongol relations
1594:transferred his see to
1325:in the south, and from
1301:, further expanded the
1084:through Leo's daughter
753:Principality of Khachen
618:Urartu (Kingdom of Van)
563:Shulaveri–Shomu culture
546:Coat of Arms of Armenia
6100:Armenian eternity sign
5862:South Caucasus Railway
5150:Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek
5053:Triarchy of Negroponte
5033:Principality of Achaea
5021:Duchy of Philippopolis
4832:Other provinces under
4772:Other Armenian regions
4619:(Kiurikians, 979–1118)
4487:Historical states and
3475:: CS1 maint: others (
2690:Grigor IX Musabekiants
2685:
2630:
2510:
2502:
2422:
2411:illuminated manuscript
2312:
2296:Cilicia, particularly
2236:
2209:
2101:
2032:by the Mamluks at the
2025:
1935:
1888:rapidly expanded from
1873:
1857:
1799:
1776:Bohemond IV of Antioch
1772:Constantine of Baberon
1623:
1490:
1478:
1432:
1360:
1352:
1245:
1178:
1098:Armeno-Mongol alliance
1074:Leo I, King of Armenia
1014:and distinct from the
1010:. Located outside the
547:
6458:Philaretos Brachamios
5473:Treaty of Turkmenchay
5140:Bishopric of Courland
5135:Archbishopric of Riga
4649:Melikdoms of Karabakh
4601:Kingdom of Vaspurakan
4384:Découvertes Gallimard
4298:("Cilician Armenia")
4266:Découvertes Gallimard
3637:Chahin, Mack (2001).
3573:Histoire des Croisade
2729:Order of Saint Blaise
2680:
2664:John of Monte Corvino
2620:
2508:
2497:
2476:, who was at work in
2408:
2295:
2215:
2196:
2096:Ghazan ordering King
2095:
2034:Second Battle of Homs
2023:
1933:
1863:
1851:
1797:
1621:
1485:
1427:
1358:
1350:
1315:Philaretos Brachamios
1278:their native highland
1235:
1045:, and later moved to
728:Kingdom of Vaspurakan
545:
206:Common languages
5794:AMX (stock exchange)
4950:Kingdom of Jerusalem
4801:Armenian Mesopotamia
4661:(1921, unrecognized)
4635:(Khachen, 1000–1261)
4496:Independent Armenian
4296:«Կիլիկյան Հայաստան»
3936:Massing, Jean Michel
1790:The Het'umid dynasty
1755:, and Gaban (modern
1695:Frederick Barbarossa
1675:Kingdom of Jerusalem
1502:Joscelin I of Edessa
1435:During the reign of
1258:Nicephorus II Phocas
1219:Eastern Roman Empire
1028:Gulf of Alexandretta
858:Contemporary Armenia
352:• 13th century
6448:Knights Hospitaller
6443:Empire of Trebizond
5804:Central Depository
5506:Independent Armenia
5285:Kura–Araxes culture
5145:Bishopric of Dorpat
5076:Knights Hospitaller
4557:Republic of Armenia
4551:Republic of Armenia
4378:Mahé, Jean-Pierre.
4227:Parry, Ken (2010).
2698:Kirakos I Virapetsi
2694:Council of Florence
2623:Holy See of Cilicia
2609:Holy See of Cilicia
2466:Krak des Chevaliers
2378:Holy See of Cilicia
2352:. Only the humbler
1691:Holy Roman Emperors
1677:, which led to the
1453:Godfrey of Bouillon
1429:Baldwin of Boulogne
1338:The Rubenid dynasty
1291:Romanus IV Diogenes
863:Republic of Artsakh
613:Nairi Confederation
568:Kura–Araxes culture
212:(native language),
58: /
6322:Kadi Burhan al-Din
5834:Telecommunications
5755:more on government
5579:Armenian highlands
5357:Kingdom of Armenia
5350:Satrapy of Armenia
5185:Crusading movement
5081:Hospitaller Rhodes
5043:Duchy of Neopatras
4835:Tigranes the Great
4633:Kingdom of Artsakh
4585:Satrapy of Armenia
4576:Minor or dependent
4489:regions of Armenia
4445:2011-06-28 at the
4433:2021-01-25 at the
3827:History of Armenia
3599:History of Armenia
3384:Runciman, Steven.
3349:History of Armenia
3314:History of Armenia
3091:"Cilician Kingdom"
2974:History of Armenia
2896:Setton, Kenneth M.
2825:Bornozyan, S. V.;
2762:Claude Lebedel in
2631:
2511:
2503:
2423:
2421:completed in 1268.
2370:massacred in Adana
2313:
2237:
2235:) clearly visible.
2210:
2102:
2026:
1988:and the commander
1936:
1884:and his successor
1874:
1858:
1800:
1624:
1449:Frankish Crusaders
1433:
1361:
1353:
1311:Parsegh of Cilicia
1254:Rashidun Caliphate
1246:
1238:Armenian highlands
1221:, also called the
1143:Tigranes the Great
1016:Kingdom of Armenia
1012:Armenian Highlands
763:Kingdom of Cilicia
743:Kingdom of Artsakh
723:Kingdom of Armenia
713:Emirate of Armenia
673:Kingdom of Sophene
653:Kingdom of Armenia
643:Satrapy of Armenia
548:
287:January 6, 1198/99
244:Armenian Apostolic
32:Kingdom of Armenia
6489:Armenian kingdoms
6471:
6470:
6178:
6177:
6143:
6142:
5995:Ethnic minorities
5870:
5869:
5771:
5770:
5734:Political parties
5719:National Assembly
5687:Foreign relations
5649:
5648:
5547:
5546:
5522:Armenian genocide
5403:Bagratuni Armenia
5372:Byzantine Armenia
5345:Achaemenid Empire
5330:Kingdom of Urartu
5200:
5199:
5167:Free City of Riga
4989:Kingdom of Cyprus
4979:County of Tripoli
4891:
4890:
4623:Kingdom of Syunik
4611:Kingdom of Vanand
4392:978-2-07-031409-6
4369:978-2-7053-3791-9
4246:978-0-631-23423-4
4162:978-90-04-14713-3
4134:978-0-231-13926-7
4096:978-3-938402-15-3
3951:978-0-300-05167-4
3901:978-0-300-05167-4
3673:978-2-7053-3791-9
3454:978-90-04-19189-1
3258:978-1-56859-154-4
3233:978-90-04-12292-5
3203:978-1-56859-154-4
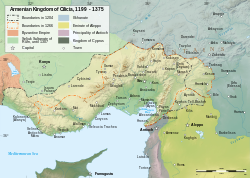
3095:Globe Weekly News
2900:Wolff, Robert Lee
2735:Explanatory notes
2595:, and the French
2458:Armenian language
2374:Armenian diaspora
2330:merchant families
2309:Armenian genocide
2275:John I of Castile
2179:Kingdom of Cyprus
2137:Battle of Shaqhab
2060:the year before.
1870:Hayton of Corycus
1709:Gregory VI Abirad
1640:kings as genuine
1473:Pope Gregory XIII
1236:Situation in the
1039:Bagratuni dynasty
956:Kilikyan Hayastan
950:Կիլիկեան Հայաստան
940:), also known as
916:
915:
823:National movement
813:Armenian genocide
808:Armenian question
738:Kingdom of Syunik
683:Byzantine Armenia
515:
514:
478:
477:
474:
473:
462:Ramadanid Emirate
426:
425:
248:Armenian Catholic
92:
84:
16:(Redirected from
6546:
6509:Christian states
6438:Empire of Nicaea
6428:Byzantine Empire
6421:Christian states
6377:Sultanate of Rum
6205:
6198:
6191:
6182:
6181:
6163:
6156:
5881:
5880:
5844:Waste management
5782:
5781:
5660:
5659:
5567:
5566:
5555:
5468:Karabakh Khanate
5377:Sasanian Armenia
5260:
5259:
5256:
5227:
5220:
5213:
5204:
5203:
5160:Order of Dobrzyń
5088:Genoese colonies
5001:
4967:County of Edessa
4918:
4911:
4904:
4895:
4894:
4686:of Armenia Major
4570:
4519:, 553 BC–428 AD)
4481:
4474:
4467:
4458:
4457:
4417:
4373:
4352:Armenian Cilicia
4342:
4323:
4293:
4280:
4279:
4257:
4251:
4250:
4234:
4224:
4215:
4208:
4202:
4201:
4176:
4167:
4166:
4149:Kennedy, Hugh N.
4145:
4139:
4138:
4114:
4101:
4100:
4082:
4073:
4072:
4064:
4058:
4057:
4039:
4033:
4032:
4014:
4005:
4004:
3996:
3985:
3984:
3966:
3960:
3959:
3932:
3926:
3925:
3915:
3909:
3908:
3885:
3879:
3878:
3860:
3854:
3850:
3846:
3840:
3837:
3831:
3830:
3819:Kurkdjian, Vahan
3815:
3806:
3805:
3778:
3772:
3771:
3755:
3745:
3739:
3738:
3722:
3712:
3703:
3702:
3684:
3678:
3677:
3659:
3653:
3652:
3634:
3628:
3627:
3609:
3603:
3602:
3591:Kurkdjian, Vahan
3587:
3576:
3569:
3563:
3560:
3554:
3553:
3549:978-90-0412292-5
3535:
3522:
3511:
3505:
3502:
3496:
3495:
3487:
3481:
3480:
3474:
3466:
3439:
3433:
3432:
3424:
3415:
3414:
3396:
3390:
3389:
3381:
3375:
3374:
3366:
3353:
3352:
3341:Kurkdjian, Vahan
3337:
3318:
3317:
3306:Kurkdjian, Vahan
3302:
3296:
3295:
3278:Runciman, Steven
3274:
3263:
3262:
3249:Armenian Cilicia
3244:
3238:
3237:
3219:
3208:
3207:
3194:Armenian Cilicia
3186:
3177:
3176:
3158:
3139:
3138:
3136:
3135:
3116:
3110:
3109:
3107:
3106:
3097:. Archived from
3087:
3078:
3063:
3036:
3035:
3017:
2998:
2995:
2978:
2977:
2970:Պատմութիւն Հայոց
2965:
2959:
2958:
2940:
2921:
2919:
2884:
2878:
2872:
2870:
2868:
2862:Internet Archive
2854:
2848:
2847:
2827:Zulalyan, Manvel
2822:
2813:
2812:
2794:
2775:Amin Maalouf in
2774:
2761:
2745:
2656:Grigor VI Apirat
2415:John the Apostle
2234:
2233:
2232:
2227:
2226:
2225:
2183:Lusignan dynasty
2126:Teutonic Knights
2046:Al-Ashraf Khalil
1982:Disaster of Mari
1808:Taurus Mountains
1481:
1451:, whose leader,
1412:(Melitene), and
1321:in the north to
1248:Cilicia fell to
1223:Byzantine Empire
1205:. In 27 BC, the
1149:. In 83 BC, the
1111:Lusignan dynasty
1088:second husband,
1082:Hethumid dynasty
1059:Armenian history
1000:High Middle Ages
993:
972:
970:Haykakan Kilikia
965:
964:
963:Հայկական Կիլիկիա
958:
951:
942:Cilician Armenia
938:
931:
930:
908:
901:
894:
776:Early modern age
688:Sasanian Armenia
535:
517:
516:
470:
469:
456:
455:
442:
441:
434:Mamluk Sultanate
430:
429:
421:Bagratid Armenia
417:
416:
403:
402:
389:
388:
382:
381:
366:
365:
315:Egyptian Mamluks
201:
189:
154:
141:Hethumid dynasty
132:
123:
114:
93:
90:
85:
82:
76:
75:
73:
72:
70:
69:
68:
63:
59:
56:
55:
54:
51:
21:
18:Armenian Cilicia
6554:
6553:
6549:
6548:
6547:
6545:
6544:
6543:
6474:
6473:
6472:
6467:
6463:Zaccaria family
6416:
6215:
6209:
6179:
6174:
6166:
6159:
6152:
6139:
6120:National anthem
6083:
6033:
5966:
5866:
5848:
5809:Dram (currency)
5767:
5645:
5556:
5543:
5510:
5484:
5480:Russian Armenia
5438:Ottoman Armenia
5381:
5367:Parthian Empire
5340:Orontid dynasty
5250:
5249:
5240:
5231:
5201:
5196:
5180:Military orders
5171:
5100:
5092:
5038:Duchy of Athens
5002:
4993:
4936:
4927:
4925:Crusader states
4922:
4892:
4887:
4833:
4827:
4767:
4685:
4676:
4653:Hasan-Jalalians
4578:Armenian states
4577:
4571:
4562:
4497:
4491:
4485:
4447:Wayback Machine
4435:Wayback Machine
4424:
4370:
4339:
4320:
4291:
4288:
4286:Further reading
4283:
4276:
4258:
4254:
4247:
4225:
4218:
4209:
4205:
4198:
4190:. p. 440.
4180:Abulafia, David
4177:
4170:
4163:
4146:
4142:
4135:
4115:
4104:
4097:
4083:
4076:
4065:
4061:
4054:
4040:
4036:
4029:
4015:
4008:
3997:
3988:
3981:
3967:
3963:
3952:
3933:
3929:
3916:
3912:
3902:
3886:
3882:
3875:
3861:
3857:
3848:
3847:
3843:
3838:
3834:
3816:
3809:
3802:
3779:
3775:
3768:
3746:
3742:
3735:
3713:
3706:
3699:
3685:
3681:
3674:
3660:
3656:
3649:
3635:
3631:
3624:
3610:
3606:
3588:
3579:
3570:
3566:
3561:
3557:
3550:
3536:
3525:
3515:Claude Mutafian
3512:
3508:
3503:
3499:
3488:
3484:
3468:
3467:
3455:
3441:
3440:
3436:
3425:
3418:
3411:
3397:
3393:
3382:
3378:
3367:
3356:
3338:
3321:
3303:
3299:
3292:
3275:
3266:
3259:
3245:
3241:
3234:
3220:
3211:
3204:
3190:Dédéyan, Gérard
3187:
3180:
3173:
3159:
3142:
3133:
3131:
3118:
3117:
3113:
3104:
3102:
3089:
3088:
3081:
3064:
3039:
3032:
3018:
3001:
2996:
2981:
2971:
2966:
2962:
2955:
2941:
2924:
2916:
2885:
2881:
2866:
2864:
2856:
2855:
2851:
2823:
2816:
2809:
2795:
2791:
2787:
2747:Claude Mutafian
2737:
2724:Rubenid dynasty
2710:
2671:Nerses Balients
2615:
2605:
2492:
2486:
2403:
2398:
2318:
2242:
2230:
2228:
2223:
2221:
2206:Henri Delaborde
2191:
2090:
2018:
1912:Greater Armenia
1846:
1840:
1816:Papeŕōn/Baberon
1792:
1715:in the name of
1713:Conrad of Mainz
1697:, and his son,
1616:
1592:Armenian Church
1546:
1479:Ecclesia Romana
1457:Crusader states
1422:
1371:Armenian king,
1345:
1340:
1329:in the west to
1215:
1189:, and from the
1163:Seleucid Empire
1153:aristocracy of
1139:
1134:
1078:Rubenid dynasty
1035:Rubenid dynasty
924:Middle Armenian
912:
868:
867:
848:Armenian S.S.R.
838:
828:
827:
818:Western Armenia
803:Armenian Oblast
798:Russian Armenia
793:Ottoman Armenia
783:Iranian Armenia
778:
768:
767:
748:Zakarid Armenia
708:
698:
697:
658:Armenian Empire
638:
628:
627:
558:
533:
526:
511:
493:
489:
467:
453:
439:
414:
400:
386:
353:
317:
297:
284:
259:Feudal monarchy
199:
190:
187:
167:
145:
144:
143:
138:
133:
125:
124:
121:
119:Rubenid dynasty
115:
97:
94:
89:
87:
86:
81:
66:
64:
60:
57:
52:
49:
47:
45:
44:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
6552:
6542:
6541:
6536:
6531:
6526:
6521:
6516:
6511:
6506:
6501:
6496:
6491:
6486:
6469:
6468:
6466:
6465:
6460:
6455:
6450:
6445:
6440:
6435:
6430:
6424:
6422:
6418:
6417:
6415:
6414:
6409:
6404:
6399:
6394:
6389:
6384:
6379:
6374:
6369:
6364:
6359:
6354:
6352:Ottoman Empire
6349:
6344:
6339:
6334:
6329:
6324:
6319:
6314:
6309:
6304:
6299:
6294:
6289:
6284:
6279:
6274:
6269:
6264:
6259:
6254:
6252:Candaroğulları
6249:
6244:
6239:
6234:
6229:
6223:
6221:
6217:
6216:
6208:
6207:
6200:
6193:
6185:
6176:
6175:
6173:
6172:
6165:
6164:
6157:
6149:
6148:
6145:
6144:
6141:
6140:
6138:
6137:
6132:
6127:
6122:
6117:
6112:
6107:
6102:
6097:
6095:Armenian Cross
6091:
6089:
6085:
6084:
6082:
6081:
6074:
6069:
6064:
6059:
6054:
6049:
6043:
6041:
6035:
6034:
6032:
6031:
6024:
6019:
6014:
6013:
6012:
6002:
5997:
5992:
5987:
5982:
5976:
5974:
5968:
5967:
5965:
5964:
5957:
5952:
5947:
5942:
5937:
5936:
5935:
5930:
5920:
5915:
5905:
5900:
5895:
5890:
5884:
5878:
5872:
5871:
5868:
5867:
5865:
5864:
5858:
5856:
5850:
5849:
5847:
5846:
5841:
5836:
5831:
5826:
5824:Pension reform
5821:
5816:
5811:
5806:
5801:
5796:
5791:
5785:
5779:
5773:
5772:
5769:
5768:
5766:
5765:
5758:
5751:
5746:
5744:Prime Minister
5741:
5736:
5731:
5726:
5721:
5716:
5711:
5706:
5705:
5704:
5694:
5689:
5684:
5679:
5674:
5669:
5663:
5657:
5651:
5650:
5647:
5646:
5644:
5643:
5636:
5631:
5626:
5621:
5616:
5614:Municipalities
5611:
5606:
5601:
5599:Extreme points
5596:
5591:
5586:
5581:
5576:
5570:
5564:
5558:
5557:
5550:
5548:
5545:
5544:
5542:
5541:
5534:
5529:
5524:
5518:
5516:
5512:
5511:
5509:
5508:
5503:
5501:Soviet Armenia
5498:
5492:
5490:
5486:
5485:
5483:
5482:
5477:
5476:
5475:
5470:
5465:
5463:Erivan Khanate
5455:
5450:
5445:
5440:
5435:
5430:
5425:
5420:
5415:
5410:
5405:
5400:
5395:
5389:
5387:
5383:
5382:
5380:
5379:
5374:
5369:
5364:
5359:
5354:
5353:
5352:
5342:
5337:
5335:Median kingdom
5332:
5327:
5322:
5317:
5312:
5307:
5302:
5297:
5292:
5287:
5282:
5277:
5272:
5266:
5264:
5257:
5242:
5241:
5230:
5229:
5222:
5215:
5207:
5198:
5197:
5195:
5194:
5193:
5192:
5182:
5176:
5173:
5172:
5170:
5169:
5164:
5163:
5162:
5152:
5147:
5142:
5137:
5132:
5126:
5125:
5124:
5122:Livonian Order
5119:
5117:Teutonic Order
5107:
5105:
5094:
5093:
5091:
5090:
5085:
5084:
5083:
5073:
5065:
5060:
5055:
5050:
5045:
5040:
5035:
5030:
5025:
5024:
5023:
5012:
5010:
5004:
5003:
4996:
4994:
4992:
4991:
4986:
4981:
4976:
4975:
4974:
4964:
4959:
4958:
4957:
4946:
4944:
4938:
4937:
4932:
4929:
4928:
4921:
4920:
4913:
4906:
4898:
4889:
4888:
4886:
4885:
4880:
4875:
4870:
4865:
4860:
4855:
4850:
4845:
4839:
4837:
4829:
4828:
4826:
4825:
4824:
4823:
4818:
4813:
4803:
4798:
4797:
4796:
4791:
4786:
4779:Lesser Armenia
4775:
4773:
4769:
4768:
4766:
4765:
4760:
4755:
4750:
4745:
4740:
4735:
4730:
4725:
4720:
4715:
4710:
4705:
4700:
4695:
4689:
4687:
4678:
4677:
4675:
4674:
4668:
4665:Soviet Armenia
4662:
4656:
4646:
4636:
4630:
4620:
4614:
4608:
4598:
4592:
4581:
4579:
4573:
4572:
4565:
4563:
4561:
4560:
4559:(1991–present)
4554:
4548:
4530:
4520:
4501:
4499:
4493:
4492:
4484:
4483:
4476:
4469:
4461:
4455:
4454:
4449:
4437:
4423:
4422:External links
4420:
4419:
4418:
4398:William Stubbs
4394:
4375:
4374:
4368:
4355:
4344:
4343:
4337:
4324:
4318:
4305:
4287:
4284:
4282:
4281:
4274:
4252:
4245:
4216:
4203:
4196:
4168:
4161:
4140:
4133:
4102:
4095:
4074:
4059:
4052:
4034:
4027:
4006:
3986:
3979:
3961:
3950:
3927:
3910:
3900:
3880:
3873:
3855:
3841:
3832:
3807:
3800:
3782:Nicolle, David
3773:
3766:
3740:
3733:
3704:
3697:
3679:
3672:
3654:
3647:
3629:
3622:
3604:
3577:
3575:, III, p. 586.
3564:
3555:
3548:
3523:
3506:
3497:
3482:
3453:
3434:
3416:
3409:
3391:
3376:
3354:
3319:
3297:
3290:
3264:
3257:
3239:
3232:
3209:
3202:
3178:
3171:
3140:
3111:
3079:
3037:
3030:
2999:
2979:
2960:
2953:
2922:
2920:, pp. 630–631.
2914:
2879:
2849:
2814:
2807:
2788:
2786:
2783:
2782:
2781:
2767:
2754:
2736:
2733:
2732:
2731:
2726:
2721:
2716:
2709:
2706:
2604:
2601:
2485:
2482:
2402:
2399:
2397:
2394:
2317:
2314:
2241:
2238:
2190:
2187:
2106:King Het'um II
2089:
2086:
2066:Catholicossate
2017:
2014:
1839:
1836:
1820:Cilician Gates
1791:
1788:
1764:Raymond-Roupen
1661:, Aleppo, and
1615:
1612:
1572:Prince Levon I
1545:
1542:
1421:
1418:
1402:Cilician Gates
1377:Constantinople
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1214:
1211:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
980:Little Armenia
976:Lesser Armenia
914:
913:
911:
910:
903:
896:
888:
885:
884:
870:
869:
866:
865:
860:
855:
850:
845:
839:
834:
833:
830:
829:
826:
825:
820:
815:
810:
805:
800:
795:
790:
788:Five Melikdoms
785:
779:
774:
773:
770:
769:
766:
765:
760:
758:Mongol Armenia
755:
750:
745:
740:
735:
730:
725:
720:
715:
709:
704:
703:
700:
699:
696:
695:
690:
685:
680:
675:
670:
665:
660:
655:
650:
645:
639:
634:
633:
630:
629:
626:
625:
620:
615:
610:
605:
600:
595:
590:
585:
580:
575:
573:Legend of Hayk
570:
565:
559:
554:
553:
550:
549:
538:
537:
528:
527:
520:
513:
512:
501:
498:
497:
484:
480:
479:
476:
475:
472:
471:
464:
458:
457:
450:
444:
443:
436:
427:
424:
423:
418:
410:
409:
404:
396:
395:
390:
378:
377:
372:
362:
361:
358:
357:
354:
351:
348:
347:
344:
343:
339:
338:
335:
331:
330:
326:
325:
322:
321:
318:
305:
302:
301:
298:
292:
289:
288:
285:
279:
276:
275:
272:
271:
266:
265:Historical era
262:
261:
256:
252:
251:
237:
233:
232:
207:
203:
202:
184:Tarsus, Mersin
177:
173:
172:
160:
156:
155:
147:
146:
134:
127:
126:
116:
109:
108:
107:
104:
103:
99:
98:
95:
79:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
6551:
6540:
6537:
6535:
6532:
6530:
6527:
6525:
6522:
6520:
6517:
6515:
6512:
6510:
6507:
6505:
6502:
6500:
6497:
6495:
6492:
6490:
6487:
6485:
6482:
6481:
6479:
6464:
6461:
6459:
6456:
6454:
6451:
6449:
6446:
6444:
6441:
6439:
6436:
6434:
6431:
6429:
6426:
6425:
6423:
6419:
6413:
6410:
6408:
6405:
6403:
6400:
6398:
6395:
6393:
6390:
6388:
6385:
6383:
6380:
6378:
6375:
6373:
6370:
6368:
6365:
6363:
6360:
6358:
6355:
6353:
6350:
6348:
6345:
6343:
6340:
6338:
6335:
6333:
6330:
6328:
6325:
6323:
6320:
6318:
6315:
6313:
6310:
6308:
6305:
6303:
6300:
6298:
6295:
6293:
6290:
6288:
6285:
6283:
6280:
6278:
6275:
6273:
6272:Danishmendids
6270:
6268:
6267:Çubukoğulları
6265:
6263:
6260:
6258:
6255:
6253:
6250:
6248:
6245:
6243:
6240:
6238:
6235:
6233:
6230:
6228:
6225:
6224:
6222:
6220:Muslim states
6218:
6213:
6206:
6201:
6199:
6194:
6192:
6187:
6186:
6183:
6171:
6168:
6167:
6162:
6158:
6155:
6151:
6150:
6146:
6136:
6133:
6131:
6128:
6126:
6123:
6121:
6118:
6116:
6113:
6111:
6108:
6106:
6103:
6101:
6098:
6096:
6093:
6092:
6090:
6086:
6080:
6079:
6075:
6073:
6070:
6068:
6065:
6063:
6060:
6058:
6055:
6053:
6050:
6048:
6045:
6044:
6042:
6040:
6036:
6030:
6029:
6025:
6023:
6020:
6018:
6017:Social issues
6015:
6011:
6008:
6007:
6006:
6003:
6001:
5998:
5996:
5993:
5991:
5988:
5986:
5983:
5981:
5978:
5977:
5975:
5973:
5969:
5963:
5962:
5958:
5956:
5953:
5951:
5948:
5946:
5943:
5941:
5938:
5934:
5931:
5929:
5926:
5925:
5924:
5921:
5919:
5916:
5913:
5909:
5906:
5904:
5901:
5899:
5896:
5894:
5891:
5889:
5886:
5885:
5882:
5879:
5877:
5873:
5863:
5860:
5859:
5857:
5855:
5851:
5845:
5842:
5840:
5837:
5835:
5832:
5830:
5827:
5825:
5822:
5820:
5817:
5815:
5812:
5810:
5807:
5805:
5802:
5800:
5797:
5795:
5792:
5790:
5787:
5786:
5783:
5780:
5778:
5774:
5764:
5763:
5759:
5757:
5756:
5752:
5750:
5747:
5745:
5742:
5740:
5737:
5735:
5732:
5730:
5727:
5725:
5722:
5720:
5717:
5715:
5712:
5710:
5707:
5703:
5700:
5699:
5698:
5695:
5693:
5690:
5688:
5685:
5683:
5680:
5678:
5675:
5673:
5670:
5668:
5665:
5664:
5661:
5658:
5656:
5652:
5642:
5641:
5637:
5635:
5632:
5630:
5627:
5625:
5622:
5620:
5617:
5615:
5612:
5610:
5607:
5605:
5602:
5600:
5597:
5595:
5592:
5590:
5587:
5585:
5582:
5580:
5577:
5575:
5572:
5571:
5568:
5565:
5563:
5559:
5554:
5540:
5539:
5535:
5533:
5530:
5528:
5525:
5523:
5520:
5519:
5517:
5513:
5507:
5504:
5502:
5499:
5497:
5494:
5493:
5491:
5487:
5481:
5478:
5474:
5471:
5469:
5466:
5464:
5461:
5460:
5459:
5456:
5454:
5453:Afsharid Iran
5451:
5449:
5446:
5444:
5441:
5439:
5436:
5434:
5431:
5429:
5426:
5424:
5421:
5419:
5416:
5414:
5411:
5409:
5406:
5404:
5401:
5399:
5396:
5394:
5391:
5390:
5388:
5384:
5378:
5375:
5373:
5370:
5368:
5365:
5363:
5362:Roman Armenia
5360:
5358:
5355:
5351:
5348:
5347:
5346:
5343:
5341:
5338:
5336:
5333:
5331:
5328:
5326:
5323:
5321:
5318:
5316:
5313:
5311:
5308:
5306:
5303:
5301:
5298:
5296:
5293:
5291:
5288:
5286:
5283:
5281:
5278:
5276:
5273:
5271:
5268:
5267:
5265:
5261:
5258:
5254:
5247:
5243:
5239:
5235:
5228:
5223:
5221:
5216:
5214:
5209:
5208:
5205:
5191:
5188:
5187:
5186:
5183:
5181:
5178:
5177:
5174:
5168:
5165:
5161:
5158:
5157:
5156:
5153:
5151:
5148:
5146:
5143:
5141:
5138:
5136:
5133:
5130:
5127:
5123:
5120:
5118:
5115:
5114:
5112:
5109:
5108:
5106:
5104:
5099:
5095:
5089:
5086:
5082:
5079:
5078:
5077:
5074:
5072:
5069:
5066:
5064:
5061:
5059:
5056:
5054:
5051:
5049:
5046:
5044:
5041:
5039:
5036:
5034:
5031:
5029:
5026:
5022:
5019:
5018:
5017:
5014:
5013:
5011:
5009:
5005:
5000:
4990:
4987:
4985:
4982:
4980:
4977:
4973:
4970:
4969:
4968:
4965:
4963:
4960:
4956:
4953:
4952:
4951:
4948:
4947:
4945:
4943:
4939:
4935:
4930:
4926:
4919:
4914:
4912:
4907:
4905:
4900:
4899:
4896:
4884:
4881:
4879:
4876:
4874:
4871:
4869:
4866:
4864:
4861:
4859:
4856:
4854:
4851:
4849:
4846:
4844:
4841:
4840:
4838:
4836:
4830:
4822:
4819:
4817:
4814:
4812:
4809:
4808:
4807:
4804:
4802:
4799:
4795:
4792:
4790:
4787:
4785:
4782:
4781:
4780:
4777:
4776:
4774:
4770:
4764:
4761:
4759:
4756:
4754:
4751:
4749:
4746:
4744:
4741:
4739:
4736:
4734:
4731:
4729:
4726:
4724:
4721:
4719:
4716:
4714:
4711:
4709:
4706:
4704:
4701:
4699:
4696:
4694:
4693:Upper Armenia
4691:
4690:
4688:
4684:
4681:Provinces or
4679:
4672:
4669:
4666:
4663:
4660:
4657:
4654:
4650:
4647:
4644:
4640:
4637:
4634:
4631:
4628:
4624:
4621:
4618:
4615:
4612:
4609:
4606:
4602:
4599:
4596:
4593:
4591:, 522–331 BC)
4590:
4586:
4583:
4582:
4580:
4574:
4569:
4558:
4555:
4552:
4549:
4546:
4542:
4538:
4534:
4531:
4528:
4524:
4521:
4518:
4514:
4510:
4506:
4503:
4502:
4500:
4494:
4490:
4482:
4477:
4475:
4470:
4468:
4463:
4462:
4459:
4453:
4450:
4448:
4444:
4441:
4438:
4436:
4432:
4429:
4426:
4425:
4415:
4411:
4407:
4403:
4399:
4395:
4393:
4389:
4385:
4381:
4377:
4376:
4371:
4365:
4361:
4356:
4353:
4349:
4346:
4345:
4340:
4338:0-7007-1418-9
4334:
4330:
4325:
4321:
4319:0-7073-0145-9
4315:
4311:
4306:
4303:
4302:
4297:
4292:(In Armenian)
4290:
4289:
4277:
4275:2-07-031409-X
4271:
4267:
4263:
4256:
4248:
4242:
4238:
4233:
4232:
4223:
4221:
4213:
4207:
4199:
4197:0-521-36289-X
4193:
4189:
4185:
4181:
4175:
4173:
4164:
4158:
4154:
4150:
4144:
4136:
4130:
4126:
4122:
4121:
4113:
4111:
4109:
4107:
4098:
4092:
4088:
4081:
4079:
4070:
4063:
4055:
4053:0-19-822136-3
4049:
4045:
4038:
4030:
4028:0-7007-1418-9
4024:
4020:
4013:
4011:
4002:
3995:
3993:
3991:
3982:
3980:0-7007-1418-9
3976:
3972:
3965:
3958:
3953:
3947:
3943:
3942:
3937:
3931:
3923:
3922:
3914:
3907:
3903:
3897:
3893:
3892:
3884:
3876:
3874:2-07-031409-X
3870:
3866:
3859:
3853:
3845:
3836:
3828:
3824:
3820:
3814:
3812:
3803:
3801:1-84176-179-6
3797:
3793:
3789:
3788:
3783:
3777:
3769:
3767:1-86197-529-5
3763:
3759:
3754:
3753:
3744:
3736:
3734:1-86197-529-5
3730:
3726:
3721:
3720:
3711:
3709:
3700:
3698:2-271-05105-3
3694:
3690:
3683:
3675:
3669:
3665:
3658:
3650:
3644:
3640:
3633:
3625:
3623:0-521-41411-3
3619:
3615:
3608:
3600:
3596:
3592:
3586:
3584:
3582:
3574:
3568:
3559:
3551:
3545:
3541:
3534:
3532:
3530:
3528:
3520:
3516:
3510:
3501:
3493:
3486:
3478:
3472:
3464:
3460:
3456:
3450:
3446:
3445:
3438:
3430:
3423:
3421:
3412:
3410:0-7007-1418-9
3406:
3402:
3395:
3387:
3380:
3372:
3365:
3363:
3361:
3359:
3350:
3346:
3342:
3336:
3334:
3332:
3330:
3328:
3326:
3324:
3315:
3311:
3307:
3301:
3293:
3291:0-521-35997-X
3287:
3283:
3279:
3273:
3271:
3269:
3260:
3254:
3250:
3243:
3235:
3229:
3225:
3218:
3216:
3214:
3205:
3199:
3195:
3191:
3185:
3183:
3174:
3172:0-7007-1418-9
3168:
3164:
3157:
3155:
3153:
3151:
3149:
3147:
3145:
3129:
3125:
3121:
3115:
3101:on 2010-11-23
3100:
3096:
3092:
3086:
3084:
3076:
3075:1-4039-6421-1
3072:
3068:
3062:
3060:
3058:
3056:
3054:
3052:
3050:
3048:
3046:
3044:
3042:
3033:
3031:0-7007-1418-9
3027:
3023:
3016:
3014:
3012:
3010:
3008:
3006:
3004:
2994:
2992:
2990:
2988:
2986:
2984:
2975:
2964:
2956:
2950:
2946:
2939:
2937:
2935:
2933:
2931:
2929:
2927:
2917:
2915:0-299-04844-6
2911:
2907:
2906:
2901:
2897:
2893:
2889:
2883:
2876:
2863:
2859:
2853:
2846:
2842:
2838:
2834:
2833:
2828:
2821:
2819:
2810:
2808:9781136124181
2804:
2801:. Routledge.
2800:
2793:
2789:
2778:
2773:
2772:
2768:
2765:
2764:Les Croisades
2760:
2759:
2755:
2752:
2748:
2744:
2743:
2739:
2738:
2730:
2727:
2725:
2722:
2720:
2717:
2715:
2712:
2711:
2705:
2703:
2699:
2695:
2691:
2684:
2679:
2677:
2672:
2667:
2665:
2661:
2657:
2652:
2649:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2628:
2624:
2619:
2614:
2610:
2600:
2598:
2594:
2590:
2586:
2582:
2578:
2574:
2570:
2565:
2563:
2559:
2555:
2551:
2547:
2543:
2539:
2535:
2531:
2526:
2524:
2520:
2516:
2507:
2501:
2498:Coin of King
2496:
2491:
2481:
2479:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2461:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2447:
2443:
2439:
2438:
2433:
2429:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2407:
2393:
2391:
2387:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2371:
2366:
2365:Adana Vilayet
2362:
2357:
2355:
2351:
2347:
2343:
2339:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2320:Although the
2310:
2306:
2305:Adana Vilayet
2302:
2299:
2294:
2290:
2288:
2284:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2258:
2255:
2251:
2247:
2219:
2218:Catalan Atlas
2214:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2186:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2171:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2153:
2149:
2146:and became a
2145:
2140:
2138:
2133:
2131:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2099:
2094:
2085:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2022:
2013:
2011:
2007:
2002:
2000:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1986:Al-Mansur Ali
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1945:
1941:
1932:
1928:
1925:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1908:
1903:
1899:
1895:
1891:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1871:
1867:
1862:
1855:
1850:
1845:
1835:
1833:
1827:
1825:
1821:
1817:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1796:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1760:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1730:
1726:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1705:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1680:
1679:Third Crusade
1676:
1673:defeated the
1672:
1668:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1647:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1630:
1620:
1611:
1609:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1541:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1489:
1484:
1482:
1480:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1441:First Crusade
1438:
1437:Constantine I
1430:
1426:
1420:First Crusade
1417:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1357:
1349:
1335:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1303:Seljuk Empire
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1279:
1273:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1243:
1242:Seljuk Empire
1239:
1234:
1230:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1210:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1129:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1114:
1112:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1070:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
989:
985:
981:
977:
973:
971:
959:
957:
947:
943:
939:
937:
925:
921:
909:
904:
902:
897:
895:
890:
889:
887:
886:
883:
879:
875:
872:
871:
864:
861:
859:
856:
854:
851:
849:
846:
844:
841:
840:
837:
832:
831:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
789:
786:
784:
781:
780:
777:
772:
771:
764:
761:
759:
756:
754:
751:
749:
746:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
731:
729:
726:
724:
721:
719:
716:
714:
711:
710:
707:
702:
701:
694:
691:
689:
686:
684:
681:
679:
676:
674:
671:
669:
666:
664:
663:Roman Armenia
661:
659:
656:
654:
651:
649:
648:Armenia Minor
646:
644:
641:
640:
637:
632:
631:
624:
621:
619:
616:
614:
611:
609:
606:
604:
601:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
574:
571:
569:
566:
564:
561:
560:
557:
552:
551:
544:
540:
539:
536:
530:
529:
524:
519:
518:
509:
505:
499:
496:
492:
488:
485:
483:Today part of
481:
465:
463:
460:
459:
451:
449:
446:
445:
437:
435:
432:
431:
428:
422:
419:
412:
411:
408:
405:
398:
397:
394:
393:Seljuk Empire
391:
384:
383:
380:
379:
376:
373:
371:
368:
367:
363:
359:
355:
349:
345:
340:
336:
332:
327:
323:
319:
316:
312:
309:
303:
299:
296:
290:
286:
283:
277:
273:
270:
267:
263:
260:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
238:
234:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
208:
204:
197:
193:
185:
181:
178:
174:
170:
165:
161:
157:
153:
148:
142:
137:
131:
120:
113:
105:
100:
77:
74:
71:
62:37.0°N 35.5°E
40:
33:
19:
6453:Latin Empire
6432:
6382:Sahib Ataids
6362:Qara Qoyunlu
6214:(after 1071)
6115:Mount Ararat
6105:Coat of arms
6076:
6026:
5972:Demographics
5959:
5893:Architecture
5799:Central Bank
5760:
5753:
5697:Human rights
5672:Constitution
5638:
5634:Shirak Plain
5574:Ararat Plain
5536:
5448:Safavid Iran
5433:Kara Koyunlu
5407:
5155:Dobrzyń Land
5071:Stato da Màr
4983:
4723:Nor Shirakan
4682:
4645:, 1201–1335)
4547:, 1080–1375)
4532:
4405:
4379:
4359:
4351:
4328:
4309:
4299:
4295:
4261:
4255:
4230:
4211:
4206:
4183:
4152:
4143:
4119:
4086:
4068:
4062:
4043:
4037:
4018:
4000:
3970:
3964:
3955:
3940:
3930:
3920:
3913:
3905:
3890:
3883:
3864:
3858:
3844:
3835:
3826:
3787:The Crusades
3786:
3776:
3751:
3743:
3718:
3688:
3682:
3663:
3657:
3638:
3632:
3613:
3607:
3598:
3572:
3567:
3558:
3539:
3518:
3509:
3500:
3491:
3485:
3443:
3437:
3428:
3400:
3394:
3385:
3379:
3370:
3348:
3313:
3300:
3281:
3248:
3242:
3223:
3193:
3162:
3132:. Retrieved
3123:
3114:
3103:. Retrieved
3099:the original
3094:
3066:
3021:
2973:
2963:
2944:
2904:
2882:
2874:
2865:. Retrieved
2861:
2852:
2844:
2831:
2798:
2792:
2776:
2771:
2763:
2758:
2750:
2742:
2686:
2681:
2668:
2653:
2632:
2596:
2592:
2588:
2587:, the Greek
2584:
2580:
2576:
2572:
2568:
2566:
2527:
2519:Persian Gulf
2515:Central Asia
2512:
2474:Toros Roslin
2462:
2453:
2449:
2445:
2441:
2435:
2424:
2419:Toros Roslin
2380:is based in
2358:
2319:
2267:King Levon V
2259:
2243:
2202:Hospitallers
2172:
2141:
2134:
2122:Hospitallers
2103:
2030:Möngke Temur
2027:
2003:
1937:
1890:Central Asia
1882:Genghis Khan
1875:
1852:Fortress of
1828:
1801:
1761:
1737:Vaner/Kovara
1702:
1648:
1641:
1637:
1627:
1625:
1570:
1547:
1491:
1486:
1476:
1434:
1385:
1362:
1299:Malik-Shah I
1274:
1247:
1216:
1207:Roman Empire
1179:Tigranocerta
1140:
1115:
1094:Central Asia
1071:
1032:
1006:invasion of
987:
983:
979:
975:
967:
953:
941:
933:
919:
917:
762:
598:Arme–Shupria
375:Succeeded by
374:
369:
334:13th century
311:conquered by
240:Christianity
196:Kozan, Adana
164:principality
162:Independent
136:Coat of arms
117:Flag of the
102:1198/99–1375
43:
6402:Tanrıbermiş
6397:Tacettinids
6392:Sarukhanids
6372:Shah-Armens
6357:Pervâneoğlu
6342:Mengüjekids
6302:Germiyanids
6282:Dulkadirids
6135:Pomegranate
5789:Agriculture
5762:on politics
5702:LGBT rights
5594:Earthquakes
5295:Hayasa-Azzi
4811:Mountainous
4667:(1920–1991)
4629:, 987–1170)
4607:, 908–1021)
4553:(1918–1920)
4529:, 884–1045)
4408:: 156–207.
3849:(in French)
2683:competency.
2660:Franciscans
2638:in 1058 in
2591:, the Arab
2523:spice trade
2342:Netherlands
2263:fall of Sis
2082:Tel Hamdoun
2068:to move to
1907:Möngke Khan
1886:Ögedei Khan
1749:T‛il Hamtun
1741:Sarvandikar
1683:Clement III
1538:Sarvandikar
1522:T‛il Hamtun
1240:during the
1197:capital of
1187:Mesopotamia
1183:Pontic Alps
1171:Tigranakert
990:(Armenian:
984:New Armenia
706:Middle Ages
593:Hayasa-Azzi
532:History of
370:Preceded by
269:Middle Ages
200:(1198–1375)
188:(1080–1198)
171:(1198–1375)
166:(1080–1198)
122:(1198–1219)
91:(1198–1375)
83:(1080–1198)
65: /
6478:Categories
6367:Ramadanids
6327:Karamanids
6277:Dilmachids
6232:Aq Qoyunlu
5940:Literature
5692:Government
5677:Corruption
5604:Lake Sevan
5458:Qajar Iran
5428:Aq Qoyunlu
4873:Cappadocia
4848:Atropatene
4743:Paytakaran
4728:Vaspurakan
4613:(963–1064)
4597:(790–1486)
4527:Bagratunis
4414:Q107247875
4210:Luisetto.
3648:0700714529
3134:2007-01-17
3105:2009-12-28
2954:0884021637
2702:Echmiadzin
2648:Catholicos
2640:Cappadocia
2629:, Lebanon.
2607:See also:
2562:Marco Polo
2554:Mopsuestia
2488:See also:
2376:, and the
2148:Franciscan
2124:, and the
2052:sultan of
1842:See also:
1832:Kayqubad I
1704:catholicos
1687:Gregory IV
1554:Byzantines
1293:' army at
1283:Alp Arslan
1270:Cappadocia
1266:Vaspurakan
1086:Isabella's
1063:Catholicos
994:), was an
836:Modern age
556:Prehistory
356:1,000,000+
342:Population
255:Government
218:Old French
67:37.0; 35.5
6387:Saltukids
6297:Eshrefids
6262:Chobanids
5990:Education
5854:Transport
5739:President
5709:Judiciary
5682:Elections
5609:Mountains
5562:Geography
5423:Chobanids
5418:Ilkhanate
5413:Sallarids
4708:Turuberan
4643:Zakarians
4605:Artsrunis
4545:Lusignans
4541:Hethumids
4513:Artaxiads
4400:(1886). "
3471:cite book
3463:729872723
2890:(1969) .
2785:Citations
2636:Sebasteia
2446:constable
2432:feudalism
2354:Armenians
2246:Lusignans
2144:Levon III
1902:Karakorum
1866:Karakorum
1804:Het‘umids
1653:, one of
1608:Ruben III
1584:Thoros II
1518:Trapessac
1445:Jerusalem
1394:Het'umids
1386:Rubenians
1295:Manzikert
1227:Byzantine
1159:Phoenicia
1122:feudalism
1106:Ilkhanate
1051:Crusaders
1020:antiquity
882:Etymology
678:Commagene
636:Antiquity
506:when the
236:Religion
6347:Menteshe
6332:Karasids
6312:Hamidids
6307:Hacıemir
6292:Erzincan
6287:Eretnids
6247:Aydinids
6242:Artuqids
6170:Category
6039:Religion
6010:diaspora
5923:Language
5888:Alphabet
5829:Taxation
5714:Military
5655:Politics
5515:By topic
5393:Arminiya
5315:Urumeans
5253:timeline
5238:articles
5190:Crusades
5068:Venetian
4853:Adiabene
4718:Corduene
4703:Arzanene
4683:Ashkhars
4589:Orontids
4537:Rubenids
4517:Arsacids
4509:Orontids
4443:Archived
4431:Archived
4410:Wikidata
4382:, coll.
4214:, p. 98.
4182:(1999).
4151:(2006).
3821:(1958).
3784:(2001).
3593:(1958).
3343:(1958).
3308:(1958).
3280:(1951).
3128:Archived
3124:Hye Etch
2867:June 22,
2829:(1976).
2708:See also
2627:Antelias
2603:Religion
2585:zecchino
2573:tagvorin
2542:Catalans
2517:and the
2454:sparapet
2450:nakharar
2437:nakharar
2428:chivalry
2382:Antelias
2271:Castille
2257:strife.
2175:Levon IV
2160:Anazarba
2156:Bularghu
2118:Templars
2098:Hetum II
2006:Levon II
1924:Damascus
1894:Köse Dağ
1784:Het'um I
1780:Seleucia
1729:Anavarza
1699:Henry VI
1663:Damascus
1651:Levon II
1638:de facto
1634:Levon II
1629:de facto
1600:Ruben II
1588:Manuel I
1566:Gagik II
1562:Cyzistra
1550:Thoros I
1530:Selefkia
1382:Rubenids
1373:Gagik II
1369:Bagratid
1262:Basil II
1199:Ecbatana
1195:Parthian
1155:Seleucid
1118:chivalry
1090:Hethum I
996:Armenian
946:Armenian
874:Timeline
523:a series
521:Part of
210:Armenian
6412:Tzachas
6317:Inalids
6154:Outline
6125:Apricot
6088:Symbols
6078:more...
6067:Judaism
6028:more...
5961:more...
5955:Theatre
5933:Western
5928:Eastern
5908:Cuisine
5876:Culture
5839:Tourism
5777:Economy
5640:more...
5589:Climate
5538:more...
5320:Diauehi
5300:Mitanni
5270:Origins
5246:History
5234:Armenia
5103:Livonia
5098:Prussia
4955:vassals
4883:Osroene
4868:Albania
4858:Assyria
4806:Cilicia
4763:Ayrarat
4738:Artsakh
4713:Moxoene
4698:Sophene
4671:Artsakh
2714:Cilicia
2644:Hromkla
2558:Italian
2550:Korikos
2484:Economy
2478:Hromkla
2401:Culture
2386:Lebanon
2361:Ottoman
2322:Mamluks
2287:James I
2168:Oljeitu
2152:Baghras
2074:Behesni
2062:Hromkla
2042:dirhams
2038:Qalawun
1990:Qalawun
1970:Il-Khan
1965:Baibars
1961:Behesni
1953:Abbasid
1949:Ayyubid
1944:Ayyubid
1940:Mamluks
1878:Mongols
1872:, 1307.
1854:Korikos
1822:and to
1812:Lampron
1721:Levon I
1667:Saladin
1659:Iconium
1655:Levon I
1649:Prince
1643:de jure
1596:Hromkla
1580:John II
1558:Seljuks
1526:Harunia
1506:Baldwin
1475:in his
1469:Tripoli
1461:Antioch
1410:Malatia
1327:Cilicia
1323:Antioch
1319:Malatia
1191:Caspian
1102:Mamluks
1076:of the
1065:of the
1024:Cilicia
1008:Armenia
878:Origins
534:Armenia
508:Rubenid
504:Ruben I
306:•
295:Mongols
222:Italian
176:Capital
169:Kingdom
139:of the
53:35°30′E
50:37°00′N
6237:Alaiye
6005:People
6000:Health
5980:Census
5903:Cinema
5819:Mining
5814:Energy
5729:Police
5619:Rivers
5584:Cities
5489:Modern
5398:Sajids
5386:Middle
5325:Etiuni
5310:Mushki
5248:
5236:
5008:Greece
4972:Marash
4942:Levant
4863:Iberia
4789:Second
4753:Gugark
4733:Syunik
4627:Siunis
4498:states
4412:
4390:
4366:
4335:
4316:
4272:
4243:
4194:
4159:
4131:
4093:
4050:
4025:
3977:
3957:made.8
3948:
3898:
3871:
3798:
3764:
3731:
3695:
3670:
3645:
3620:
3546:
3461:
3451:
3407:
3288:
3255:
3230:
3200:
3169:
3073:
3028:
2951:
2912:
2805:
2593:dirham
2589:besant
2583:, and
2581:florin
2538:Venice
2536:, and
2500:Leo II
2470:Marqab
2348:, and
2346:Poland
2340:, the
2334:France
2301:sanjak
2283:France
2279:Madrid
2120:, the
2114:Cyprus
2110:Ghâzân
2080:, and
2078:Marash
2050:Mamluk
2048:, the
1974:Persia
1957:Marash
1920:Aleppo
1916:Hulagu
1880:under
1824:Tarsus
1753:Hadjin
1745:Kuklak
1606:, and
1576:Amanus
1536:, and
1534:Amouda
1514:Bagras
1510:T'oros
1467:, and
1465:Edessa
1439:, the
1414:Edessa
1406:Marash
1331:Edessa
1147:Levant
1043:Tarsus
1004:Seljuk
623:Etiuni
603:Mushki
583:Armani
525:on the
495:Cyprus
487:Turkey
230:Syriac
180:Tarson
159:Status
6337:Ladik
6257:Canik
6161:Index
6130:Grape
6072:Islam
6022:Women
5985:Crime
5950:Sport
5945:Music
5918:Dance
5624:Lakes
5305:Nairi
5263:Early
4878:Judea
4843:Syria
4821:Rocky
4816:Plain
4794:Third
4784:First
4125:63–66
2972:[
2894:. In
2597:livre
2577:ducat
2534:Genoa
2442:baron
2350:Spain
2338:Italy
2326:Timur
2298:Kozan
2164:Oshin
2054:Egypt
1978:Levon
1898:Smbat
1768:Zabel
1757:Geben
1733:Vahka
1671:Egypt
1498:Baron
1494:Comes
1398:Oshin
1365:Ruben
1175:Latin
1151:Greek
960:, or
608:Urumu
491:Syria
282:Leo I
226:Greek
214:Latin
6407:Teke
6227:Ahis
6110:Flag
5912:wine
5290:Hayk
5275:Name
5101:and
4758:Tayk
4748:Utik
4543:and
4515:and
4388:ISBN
4364:ISBN
4333:ISBN
4314:ISBN
4270:ISBN
4241:ISBN
4192:ISBN
4157:ISBN
4129:ISBN
4091:ISBN
4048:ISBN
4023:ISBN
3975:ISBN
3946:ISBN
3896:ISBN
3869:ISBN
3796:ISBN
3762:ISBN
3729:ISBN
3693:ISBN
3668:ISBN
3643:ISBN
3618:ISBN
3544:ISBN
3477:link
3459:OCLC
3449:ISBN
3405:ISBN
3286:ISBN
3253:ISBN
3228:ISBN
3198:ISBN
3167:ISBN
3071:ISBN
3026:ISBN
2949:ISBN
2910:ISBN
2869:2010
2803:ISBN
2676:Acre
2611:and
2571:and
2569:dram
2548:and
2546:Ayas
2530:Pisa
2468:and
2452:and
2444:and
2254:John
2058:Acre
2010:Ayas
1959:and
1951:and
1922:and
1814:and
1604:Mleh
1556:and
1496:and
1384:(or
1250:Arab
1203:Iran
1167:Acre
1126:Ayas
918:The
329:Area
320:1375
313:the
300:1236
5898:Art
4404:".
3758:109
2841:724
2837:672
2749:in
2625:in
2417:by
2413:of
2409:An
2303:of
2070:Sis
1994:Sis
1972:in
1759:).
1725:Sis
1669:of
1459:in
1287:Ani
1185:to
1047:Sis
1018:of
982:or
974:),
308:Sis
192:Sis
6480::
5113:*
4539:,
4511:,
4264:.
4239:.
4237:43
4219:^
4186:.
4171:^
4127:.
4105:^
4077:^
4009:^
3989:^
3954:.
3904:.
3825:.
3810:^
3794:.
3792:80
3760:.
3727:.
3725:93
3707:^
3597:.
3580:^
3526:^
3517:,
3473:}}
3469:{{
3457:.
3419:^
3357:^
3347:.
3322:^
3312:.
3267:^
3212:^
3181:^
3143:^
3126:.
3122:.
3093:.
3082:^
3040:^
3002:^
2982:^
2925:^
2898:;
2860:.
2843:.
2839:,
2817:^
2579:,
2532:,
2460:.
2392:.
2384:,
2344:,
2336:,
2076:,
1826:.
1786:.
1751:,
1747:,
1743:,
1739:,
1735:,
1731:,
1727:,
1707:,
1602:,
1598:.
1540:.
1532:,
1528:,
1524:,
1520:,
1516:,
1483::
1463:,
1408:,
1177::
1030:.
978:,
966:,
952:,
948::
932:,
926::
880:•
876:•
246:,
228:,
220:,
216:,
198:)
186:)
6204:e
6197:t
6190:v
5914:)
5910:(
5255:)
5251:(
5226:e
5219:t
5212:v
5131:*
4917:e
4910:t
4903:v
4641:(
4625:(
4603:(
4587:(
4535:(
4525:(
4507:(
4480:e
4473:t
4466:v
4416:.
4372:.
4341:.
4322:.
4278:.
4249:.
4200:.
4165:.
4137:.
4099:.
4056:.
4031:.
3983:.
3877:.
3804:.
3770:.
3737:.
3701:.
3676:.
3651:.
3626:.
3552:.
3494:.
3479:)
3465:.
3413:.
3388:.
3294:.
3261:.
3236:.
3206:.
3175:.
3137:.
3108:.
3077:.
3034:.
2957:.
2918:.
2871:.
2811:.
2311:.
2208:.
1693:(
1244:.
1173:(
944:(
922:(
907:e
900:t
893:v
250:)
242:(
224:,
194:(
182:(
41:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.