238:(TRP) family of proteins. The transduction of temperature in cold receptors is mediated in part by the TRPM8 channel. This channel passes a mixed inward cationic (predominantly carried by Na ions although the channel is also permeable to Ca) current of a magnitude that is inversely proportional to temperature. The channel is sensitive over a temperature range spanning about 10-35 °C. TRPM8 can also be activated by the binding of an extracellular ligand. Menthol can activate the TRPM8 channel in this way. Since the TRPM8 is expressed in neurons whose physiological role is to signal cooling, menthol applied to various bodily surfaces evokes a sensation of cooling. The feeling of freshness associated with the activation of cold receptors by menthol, particularly those in facial areas with axons in the
61:(faster conduction velocity). The adequate stimulus for a warm receptor is warming, which results in an increase in their action potential discharge rate. Cooling results in a decrease in warm receptor discharge rate. For cold receptors their firing rate increases during cooling and decreases during warming. Some cold receptors also respond with a brief action potential discharge to high temperatures, i.e. typically above 45 °C, and this is known as a paradoxical response to heat. The mechanism responsible for this behavior has not been determined.
20:
141:
188:, an active chemical commonly found in chili peppers. When coming in contact with your tongue (or any internal surface), the capsaicin de-polarizes the nerve fibers, allowing sodium and calcium into the fibers. In order for fibers to do so, they must have a specific thermoreceptor. The thermoreceptor reacting to capsaicin and other heat producing chemicals is known as
200:
or other cooling agents. Studies performed on mice determined that the presence of both these receptors allows for a gradient of temperature sensing. Mice lacking the TRPV1 receptor were still capable of determining areas significantly colder than on a heated platform. Mice lacking the TRPM8 receptor
183:
cold receptors are thought to respond with an increase in firing rate to cooling produced by evaporation of lacrimal fluid 'tears' and thereby to elicit a blink reflex. Other thermoreceptors will react to opposite triggers and give rise to heat and in some cases even burning sensations. This is often
269:
It has been suggested that it is the constellation of various thermally sensitive proteins together in a neuron that gives rise to a cold receptor. This emergent property of the neuron is thought to comprise, the expression of the aforementioned proteins as well as various voltage-sensitive channels
213:
that may respond to noxious cold, noxious heat or more than one noxious stimulus modality (i.e., they are polymodal). The nerve endings of sensory neurons that respond preferentially to cooling are found in moderate density in the skin but also occur in relatively high spatial density in the
112:. Neurons from the pre-optic and hypothalamic regions of the brain that respond to small changes in temperature have also been described, providing information on core temperature. The hypothalamus is involved in
196:. Unlike TRPV1, TRPM8 produces cooling sensations as mentioned previously. Similar to TRPV1, TRPM8 responds to a certain chemical trigger by opening its ion pathways. In this case, the chemical trigger is often
245:
Another molecular component of cold transduction is the temperature dependence of so-called leak channels which pass an outward current carried by potassium ions. Some leak channels derive from the family of
226:, and facial skin. The speculation is that lingual cold receptors deliver information that modulates the sense of taste; i.e. some foods taste good when cold, while others do not.
192:. In response to heat, the TRPV1 receptor opens up passages that allow ions to pass through, causing the sensation of heat or burning. TRPV1 also has a molecular cousin,
201:
however, were not able to determine the difference between a warm platform and a cold platform, suggesting we rely on TRPM8 to determine cold feelings and sensations.
262:
that extrudes 3Na ions in exchange for 2K ions for each hydrolytic cleavage of ATP. This results in a net movement of positive charge out of the cell, i.e. a
209:
Warm and cold receptors play a part in sensing innocuous environmental temperature. Temperatures likely to damage an organism are sensed by sub-categories of
561:
250:. Amongst the various members of the 2P-domain channels, some close quite promptly at temperatures less than about 28 °C (e.g.
467:
271:
554:
385:
351:
1608:
73:
temperature or pressure sensations enter the spinal cord. The
Lissauer's tract will synapse on first-order neurons in
547:
247:
1026:
242:, accounts for its use in numerous toiletries including toothpaste, shaving lotions, facial creams and the like.
1041:
90:
234:
This area of research has recently received considerable attention with the identification and cloning of the
1056:
78:
1542:
1408:
1319:
235:
120:
responses to a predicted change in core body temperature in response to changing environmental conditions.
1741:
373:
339:
263:
1280:
1787:
1695:
1031:
303:
1504:
1446:
1257:
613:
47:
297:
1451:
1285:
57:(low conduction velocity), while those responding to cold have both C-fibers and thinly myelinated
179:
Cold-sensitive thermoreceptors give rise to the sensations of cooling, cold and freshness. In the
1431:
807:
132:. The mechanism of activation in response to temperature changes is not completely understood.
1595:
1426:
1036:
822:
641:
495:"Specificity of cold thermotransduction is determined by differential ionic channel expression"
117:
1633:
623:
603:
340:"Chapter 38 - Single-Unit Recordings of Afferent Human Peripheral Nerves by Microneurography"
298:"Warm fibers innervating palmar and digital skin of the monkey: responses to thermal stimuli"
1494:
1461:
1160:
875:
779:
8:
1150:
1135:
1021:
960:
896:
500:
419:
86:
70:
1234:
1186:
1140:
1079:
1064:
618:
525:
444:
431:
407:
101:
35:
1690:
1659:
1436:
1383:
1314:
1155:
1145:
901:
891:
860:
764:
666:
582:
517:
449:
381:
347:
338:
Torebjörk, ERIK; Schmelz, MARTIN (2005-01-01), Dyck, Peter J.; Thomas, P. K. (eds.),
320:
129:
529:
372:
Eliav, Eli; Gracely, Richard H (2008-01-01), Sharav, Yair; Benoliel, Rafael (eds.),
1476:
1421:
1353:
1170:
1113:
1016:
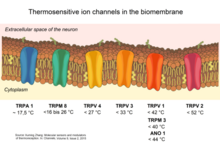
1011:
921:
870:
865:
827:
774:
769:
509:
439:
423:
312:
239:
113:
100:
In mammals, temperature receptors innervate various tissues including the skin (as
427:
295:
Darian-Smith I, Johnson KO, LaMotte C, Shigenaga Y, Kenins P, Champness P (1979).
1393:
1334:
1306:
1122:
1097:
1092:
1087:
1046:
855:
812:
759:
255:
109:
19:
1711:
1562:
1514:
1229:
955:
906:
842:
790:
746:
608:
81:, one or two vertebral levels up. The axons of these second-order neurons then
39:
316:
266:. The magnitude of this current is proportional to the rate of pump activity.
1781:
1731:
1726:
1680:
1618:
1603:
1499:
1221:
1165:
980:
947:
931:
850:
794:
754:
703:
694:
651:
435:
58:
1685:
1664:
1649:
1623:
1441:
1262:
1239:
1211:
1206:
1130:
1069:
832:
817:
539:
521:
453:
274:
and the rapidly activating and inactivating transient potassium channel (IK
1746:
1654:
1628:
1613:
1575:
1398:
1373:
1368:
1358:
1344:
970:
926:
802:
731:
324:
259:
82:
74:
43:
494:
1766:
1721:
1585:
1580:
1552:
1532:
1456:
1416:
1363:
1348:
1272:
736:
726:
633:
574:
210:
1378:
1324:
1191:
721:
711:
656:
646:
185:
140:
1547:
1537:
1527:
1466:
1339:
1196:
994:
294:
94:
54:
513:
1716:
1570:
1522:
1484:
1388:
1329:
661:
468:"Why Does Food Taste Different When It's Cold Vs. When It's Hot?"
223:
197:
975:
965:
671:
254:(TRAAK), TREK). Temperature also modulates the activity of the
219:
215:
180:
105:
51:
1201:
1003:
916:
911:
685:
595:
570:
251:
193:
189:
173:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
32:
1736:
1489:
169:
128:
Thermoreceptors have been classically described as having
23:
Thermoreceptors of the skin sense the temperature of water
716:
46:, primarily within the innocuous range. In the mammalian
491:
408:"Molecular sensors and modulators of thermoreception"
346:, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 1003–1014,
493:
296:
1779:
337:
38:, or more accurately the receptive portion of a
42:, that codes absolute and relative changes in
555:
569:
371:
229:
270:including the hyperpolarization-activated,
562:
548:
492:Viana F, de la Peña E, Belmonte C (2002).
374:"Chapter 3 - Measuring and assessing pain"
443:
184:experienced when coming in contact with
139:
18:
248:two-pore (2P) domain potassium channels
1780:
344:Peripheral Neuropathy (Fourth Edition)
780:Somatosensory system (sense of touch)
543:
405:
272:cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel
50:, warmth receptors are thought to be
16:Receptive portion of a sensory neuron
765:Vestibular system (sense of balance)
380:, Edinburgh: Mosby, pp. 45–56,
13:
760:Auditory system (sense of hearing)
14:
1799:
775:Gustatory system (sense of taste)
770:Olfactory system (sense of smell)
89:as they ascend to neurons in the
1027:Infrared sensing in vampire bats
755:Visual system (sense of vision)
204:
116:, the thermoreceptors allowing
485:
460:
399:
365:
331:
288:
130:free –non-specialized– endings
91:ventral posterolateral nucleus
69:In humans, along the axons of
1:
897:Auditory perception (hearing)
428:10.1080/19336950.2015.1025186
281:
1543:Olfactory reference syndrome
1320:Alice in Wonderland syndrome
236:Transient Receptor Potential
123:
7:
1742:Sensory processing disorder
912:Gustation (taste or flavor)
902:Equilibrioception (balance)
378:Orofacial Pain and Headache
135:
64:
10:
1806:
1696:Supernumerary phantom limb
1032:Infrared sensing in snakes
892:Visual perception (vision)
304:Journal of Neurophysiology
1759:
1704:
1673:
1642:
1594:
1561:
1513:
1475:
1447:Microwave auditory effect
1407:
1305:
1298:
1271:
1248:
1220:
1179:
1121:
1110:
1078:
1055:
1002:
993:
946:
884:
841:
788:
745:
702:
693:
684:
632:
614:Transduction (physiology)
594:
581:
317:10.1152/jn.1979.42.5.1297
230:Mechanism of transduction
48:peripheral nervous system
1452:Music-specific disorders
808:Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
1432:Auditory verbal agnosia
1286:Juxtacapillary receptor
264:hyperpolarizing current
258:. The Na/K-ATPase is a
1427:Auditory hallucination
1037:Surface wave detection
642:Multimodal integration
406:Zhang, Xuming (2015).
176:
24:
1686:Phantom limb syndrome
1634:Tactile hallucination
823:Glossopharyngeal (IX)
624:Active sensory system
143:
31:is a non-specialised
22:
1495:Labyrinthine fistula
1462:Spatial hearing loss
1161:Campaniform sensilla
876:Somatosensory cortex
420:Taylor & Francis
240:trigeminal (V) nerve
1281:Nociceptin receptor
1151:Merkel nerve ending
1136:Mechanotransduction
501:Nature Neuroscience
102:cutaneous receptors
87:spinothalamic tract
1643:Nociception (pain)
1235:Olfactory receptor
1187:Photoreceptor cell
1141:Lamellar corpuscle
1065:Photomorphogenesis
927:nociception (pain)
619:Sensory processing
177:
25:
1788:Sensory receptors
1775:
1774:
1760:Biases and errors
1755:
1754:
1691:Somatoparaphrenia
1660:Pain dissociation
1505:Ménière's disease
1437:Cortical deafness
1315:Visual impairment
1294:
1293:
1156:Bulbous corpuscle
1146:Tactile corpuscle
1114:sensory receptors
1106:
1105:
989:
988:
942:
941:
907:Olfaction (smell)
861:Vestibular cortex
843:Cerebral cortices
680:
679:
667:Motion perception
387:978-0-7234-3412-2
353:978-0-7216-9491-7
1795:
1422:Auditory agnosia
1354:Optic neuropathy
1303:
1302:
1171:Stretch receptor
1119:
1118:
1017:Magnetoreception
1012:Electroreception
1000:
999:
922:mechanoreception
871:Gustatory cortex
866:Olfactory cortex
700:
699:
691:
690:
609:Sensory receptor
592:
591:
564:
557:
550:
541:
540:
534:
533:
497:
489:
483:
482:
480:
479:
464:
458:
457:
447:
403:
397:
396:
395:
394:
369:
363:
362:
361:
360:
335:
329:
328:
311:(5): 1297–1315.
300:
292:
144:Channels shown:
114:thermoregulation
71:Lissauer's tract
1805:
1804:
1798:
1797:
1796:
1794:
1793:
1792:
1778:
1777:
1776:
1771:
1751:
1700:
1669:
1638:
1590:
1557:
1509:
1471:
1403:
1394:Stereoblindness
1335:Color blindness
1290:
1267:
1244:
1216:
1175:
1123:Mechanoreceptor
1112:
1102:
1098:Machine hearing
1093:Computer vision
1088:Robotic sensing
1074:
1051:
985:
938:
880:
856:Auditory cortex
837:
784:
747:Sensory systems
741:
676:
628:
586:
584:
577:
568:
538:
537:
490:
486:
477:
475:
466:
465:
461:
404:
400:
392:
390:
388:
370:
366:
358:
356:
354:
336:
332:
293:
289:
284:
277:
232:
207:
138:
126:
110:urinary bladder
67:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1803:
1802:
1791:
1790:
1773:
1772:
1770:
1769:
1763:
1761:
1757:
1756:
1753:
1752:
1750:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1734:
1729:
1724:
1719:
1714:
1708:
1706:
1702:
1701:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1677:
1675:
1674:Proprioception
1671:
1670:
1668:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1646:
1644:
1640:
1639:
1637:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1621:
1616:
1611:
1606:
1600:
1598:
1592:
1591:
1589:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1573:
1567:
1565:
1559:
1558:
1556:
1555:
1550:
1545:
1540:
1535:
1530:
1525:
1519:
1517:
1511:
1510:
1508:
1507:
1502:
1497:
1492:
1487:
1481:
1479:
1473:
1472:
1470:
1469:
1464:
1459:
1454:
1449:
1444:
1439:
1434:
1429:
1424:
1419:
1413:
1411:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1401:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1342:
1337:
1332:
1327:
1322:
1317:
1311:
1309:
1300:
1296:
1295:
1292:
1291:
1289:
1288:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1265:
1260:
1254:
1252:
1250:Thermoreceptor
1246:
1245:
1243:
1242:
1237:
1232:
1230:Taste receptor
1226:
1224:
1218:
1217:
1215:
1214:
1209:
1204:
1199:
1194:
1189:
1183:
1181:
1177:
1176:
1174:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1158:
1153:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1127:
1125:
1116:
1108:
1107:
1104:
1103:
1101:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1084:
1082:
1076:
1075:
1073:
1072:
1067:
1061:
1059:
1053:
1052:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1008:
1006:
997:
991:
990:
987:
986:
984:
983:
978:
973:
968:
963:
958:
956:Proprioception
952:
950:
944:
943:
940:
939:
937:
936:
935:
934:
929:
924:
914:
909:
904:
899:
894:
888:
886:
882:
881:
879:
878:
873:
868:
863:
858:
853:
847:
845:
839:
838:
836:
835:
830:
828:Trigeminal (V)
825:
820:
815:
810:
805:
799:
797:
786:
785:
783:
782:
777:
772:
767:
762:
757:
751:
749:
743:
742:
740:
739:
734:
729:
724:
719:
714:
708:
706:
704:Sensory organs
697:
688:
682:
681:
678:
677:
675:
674:
669:
664:
659:
654:
649:
644:
638:
636:
630:
629:
627:
626:
621:
616:
611:
606:
600:
598:
589:
579:
578:
567:
566:
559:
552:
544:
536:
535:
508:(3): 254–260.
484:
459:
398:
386:
364:
352:
330:
286:
285:
283:
280:
275:
231:
228:
206:
203:
137:
134:
125:
122:
85:, joining the
66:
63:
59:A delta fibers
40:sensory neuron
29:thermoreceptor
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1801:
1800:
1789:
1786:
1785:
1783:
1768:
1765:
1764:
1762:
1758:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1732:Hallucination
1730:
1728:
1727:Derealization
1725:
1723:
1720:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1697:
1694:
1692:
1689:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1681:Asomatognosia
1679:
1678:
1676:
1672:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1645:
1641:
1635:
1632:
1630:
1627:
1625:
1622:
1620:
1619:Hyperesthesia
1617:
1615:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1604:Astereognosis
1602:
1601:
1599:
1597:
1593:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1568:
1566:
1564:
1560:
1554:
1551:
1549:
1546:
1544:
1541:
1539:
1536:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1520:
1518:
1516:
1512:
1506:
1503:
1501:
1500:Labyrinthitis
1498:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1488:
1486:
1483:
1482:
1480:
1478:
1474:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1458:
1455:
1453:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1430:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1418:
1415:
1414:
1412:
1410:
1406:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1365:
1362:
1360:
1357:
1355:
1352:
1350:
1346:
1343:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1331:
1328:
1326:
1323:
1321:
1318:
1316:
1313:
1312:
1310:
1308:
1304:
1301:
1297:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1274:
1270:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1256:
1255:
1253:
1251:
1247:
1241:
1238:
1236:
1233:
1231:
1228:
1227:
1225:
1223:
1222:Chemoreceptor
1219:
1213:
1210:
1208:
1205:
1203:
1200:
1198:
1195:
1193:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1184:
1182:
1180:Photoreceptor
1178:
1172:
1169:
1167:
1166:Slit sensilla
1164:
1162:
1159:
1157:
1154:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1129:
1128:
1126:
1124:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1109:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1085:
1083:
1081:
1077:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1013:
1010:
1009:
1007:
1005:
1001:
998:
996:
992:
982:
981:Visceral pain
979:
977:
974:
972:
969:
967:
964:
962:
959:
957:
954:
953:
951:
949:
945:
933:
932:thermoception
930:
928:
925:
923:
920:
919:
918:
915:
913:
910:
908:
905:
903:
900:
898:
895:
893:
890:
889:
887:
883:
877:
874:
872:
869:
867:
864:
862:
859:
857:
854:
852:
851:Visual cortex
849:
848:
846:
844:
840:
834:
831:
829:
826:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
813:Olfactory (I)
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
800:
798:
796:
795:spinal nerves
792:
787:
781:
778:
776:
773:
771:
768:
766:
763:
761:
758:
756:
753:
752:
750:
748:
744:
738:
735:
733:
730:
728:
725:
723:
720:
718:
715:
713:
710:
709:
707:
705:
701:
698:
696:
692:
689:
687:
683:
673:
670:
668:
665:
663:
660:
658:
655:
653:
652:Consciousness
650:
648:
645:
643:
640:
639:
637:
635:
631:
625:
622:
620:
617:
615:
612:
610:
607:
605:
602:
601:
599:
597:
593:
590:
588:
580:
576:
572:
565:
560:
558:
553:
551:
546:
545:
542:
531:
527:
523:
519:
515:
514:10.1038/nn809
511:
507:
503:
502:
496:
488:
473:
469:
463:
455:
451:
446:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
402:
389:
383:
379:
375:
368:
355:
349:
345:
341:
334:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
306:
305:
299:
291:
287:
279:
273:
267:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
243:
241:
237:
227:
225:
221:
217:
212:
202:
199:
195:
191:
187:
182:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
142:
133:
131:
121:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
98:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
62:
60:
56:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
34:
30:
21:
1665:Phantom pain
1650:Hyperalgesia
1624:Hypoesthesia
1442:Hearing loss
1263:TRP channels
1249:
1240:Osmoreceptor
1207:Photopigment
1131:Baroreceptor
1070:Gravitropism
1042:Frog hearing
1022:Echolocation
818:Facial (VII)
505:
499:
487:
476:. Retrieved
474:. 2017-04-22
471:
462:
415:
411:
401:
391:, retrieved
377:
367:
357:, retrieved
343:
333:
308:
302:
290:
268:
244:
233:
208:
205:Distribution
178:
127:
118:feed-forward
99:
68:
52:unmyelinated
28:
26:
1747:Synesthesia
1655:Hypoalgesia
1629:Paresthesia
1614:Formication
1609:CMT disease
1576:Hypergeusia
1399:Visual snow
1374:Photophobia
1369:Papilledema
1359:Oscillopsia
1345:Hemeralopia
1212:Aureochrome
1047:Toad vision
971:Suffocation
885:Perceptions
472:Science ABC
307:(Article).
260:P-type pump
256:Na/K-ATPase
211:nociceptors
79:dorsal horn
75:grey matter
44:temperature
1767:Pareidolia
1722:Allochiria
1705:Multimodal
1586:Parageusia
1581:Hypogeusia
1553:Phantosmia
1533:Hyperosmia
1477:Vestibular
1457:Palinopsia
1417:Amblyaudia
1364:Palinopsia
1349:Nyctalopia
1273:Nociceptor
1080:Artificial
803:Optic (II)
634:Perception
583:Processes
575:perception
478:2023-09-06
414:(Review).
393:2023-09-13
359:2023-06-21
282:References
1563:Gustatory
1515:Olfactory
1379:Photopsia
1325:Amaurosis
1299:Disorders
1192:Cone cell
1111:Types of
722:Inner ear
657:Cognition
647:Awareness
596:Sensation
571:Sensation
436:1933-6969
422:: 73–81.
186:capsaicin
124:Structure
83:decussate
1782:Category
1548:Parosmia
1538:Hyposmia
1528:Dysosmia
1467:Tinnitus
1409:Auditory
1384:Polyopia
1340:Diplopia
1197:Rod cell
995:Nonhuman
948:Internal
789:Sensory
695:External
604:Stimulus
587:concepts
530:21291629
522:11836533
454:25868381
412:Channels
136:Function
95:thalamus
65:Location
55:C-fibres
36:receptor
1717:Agnosia
1596:Tactile
1571:Ageusia
1523:Anosmia
1485:Vertigo
1389:Scotoma
1330:Anopsia
791:cranial
662:Feeling
445:4594430
224:bladder
198:menthol
93:of the
77:of the
1307:Visual
1258:Cilium
1004:Animal
976:Nausea
966:Thirst
961:Hunger
833:Spinal
672:Qualia
528:
520:
452:
442:
434:
384:
350:
325:114608
323:
220:tongue
216:cornea
181:cornea
106:cornea
1202:ipRGC
1057:Plant
917:Touch
732:Mouth
686:Human
526:S2CID
432:eISSN
418:(2).
252:KCNK4
194:TRPM8
190:TRPV1
174:TRPV2
166:TRPM3
162:TRPV1
158:TRPV3
154:TRPV4
150:TRPM8
146:TRPA1
33:sense
1737:HSAN
1712:Aura
1490:BPPV
1347:and
793:and
737:Skin
727:Nose
717:Ears
712:Eyes
585:and
573:and
518:PMID
450:PMID
382:ISBN
348:ISBN
321:PMID
170:ANO1
108:and
510:doi
440:PMC
424:doi
313:doi
278:).
104:),
1784::
524:.
516:.
504:.
498:.
470:.
448:.
438:.
430:.
410:.
376:,
342:,
319:.
309:42
301:.
222:,
218:,
172:,
168:,
164:,
160:,
156:,
152:,
148:,
97:.
27:A
563:e
556:t
549:v
532:.
512::
506:5
481:.
456:.
426::
416:9
327:.
315::
276:A
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.