1036:
20:
681:
918:
1124:
640:. Their production has been dated to either the 5th, 6th, or 7th century, with the second of these being considered the most likely today. However, if they were made in the 5th century, while both Aquitaine and Septimani were in Visigothic hands, their existence provides no evidence for a cultural osmosis across the Gothic-Frankish frontier.
409:(508) and Septimania thereafter remained in Visigothic hands, though the Burgundians managed to hold Narbonne for a time and drive Gesalec into exile. Border warfare between Gallo-Roman magnates, including bishops, had existed with the Visigoths during the last phase of the Empire and it continued under the Franks.
559:
The native population of Gallia was referred to by
Visigothic and Iberian writers as the "Gauls" and there is a well-attested hatred between the Goths and the Gauls, which was atypical for the kingdom as a whole. The Gauls commonly insulted the Goths by comparing the strength of their men to that of
1031:
defenders of
Narbonne surrendered to the Frankish forces, proceeding to eliminate the Andalusian garrison after killing the Arab-Berber Muslim troops, and opening the gates of the stronghold to the investing forces of the Carolingian king. Previously, the Frankish king Pepin had promised to uphold
800:
defeated the
Umayyad Muslim army and achieved a decisive and significant victory. The surviving Umayyad forces drove away from Aquitaine with immense losses, in which al-Samh was so seriously wounded that he soon died at Narbonne. Arab and Berber Muslim forces, soundly based in Narbonne and easily
651:
did not circulate in Gaul outside of
Septimania and Frankish coinage did not circulate in the Visigothic Kingdom, including Septimania. If there had been a significant amount of commerce over the frontier, the monies paid had to have been melted down immediately and re-minted as foreign coins have
643:
A unique style of orange pottery was common in the 4th and 5th centuries in southern Gaul, but the later (6th century) examples culled from
Septimania are more orange than their cousins from Aquitaine and Provence and are not found commonly outside of Septimania, a strong indicator that there was
420:
was appointed regent at
Narbonne by Theodoric while Amalaric was still a minor in Iberia. When Theodoric died in 526, Amalaric was elected king in his own right and he immediately made his capital in Narbonne. He ceded Provence, which had at some point passed back into Visigothic control, to the
539:
and
Cabaret (a fort called Ram's Head), both of which lay in Guntram's kingdom. Guntram ignored two pleas for a peace in 586 and Reccared undertook the only Visigothic invasion of Francia in response. However, Guntram was not motivated solely by religious alliance with the fellow Catholic
614:
Different theories exist concerning the nature of the frontier between
Visigothic Septimania and Frankish Gaul. On the one hand, cultural exchange is generally reputed to have been minimal, but the level of trading activity has been disputed. There have been few to no objects of
1238:
rewarded Bernat with a series of counties, which roughly delimit 9th century
Septimania: Narbonne, Béziers, Agde, Magalona, Nîmes and Uzés. Rising against Charles the Bald in 843, Bernat was apprehended at Toulouse and beheaded. Bernat's son, known as
742:, and the ancient province of Septimania. With Narbonne secure, and equally important, its port, for the Arab mariners controlled various areas of the Western Mediterranean, al-Samh invaded the remaining Septimanian cities, still controlled by their
437:, that her husband, Amalaric, had been mistreating her. The Franks however, did not try to hold the province and under Amalaric's successor, the centre of gravity of the kingdom crossed the Pyrenees and Theudis made his capital in Barcelona.
1294:) faded away during the 10th century, as the region fractured into smaller feudal entities, which sometimes retained Carolingian titles, but lost their Carolingian character, as the culture of Septimania evolved into the culture of
457:, the province of Gallia Narbonensis, usually shortened to just Gallia or Narbonensis and never called Septimania, was both an administrative province of the central royal government and an ecclesiastical province whose
1201:
The
Frankish king found Septimania and the borderlands so devastated and depopulated by warfare, with the inhabitants hiding among the mountains, that he made grants of land that were some of the earliest identifiable
177:
down to the 13th century, though it was culturally and politically autonomous from the northern France-based central royal government. The region was under the influence of the people from the count territories of
631:
of a unique regional style, variously labelled Visigothic, Aquitainian, or southwestern Gallic, are prevalent on both sides of the Septimanian border. These sarcophagi are made of locally quarried marble from
1206:
to Visigothic and other refugees. Charlemagne also founded several monasteries in Septimania, around which the people gathered for protection. Beyond Septimania to the south Charlemagne established the
2088:, but clearly did not retain it, and advanced to besiege Narbonne, the centre of Arab control in the March. The Frankish chronicles record his victory over a relieving force sent by the governor
1317:
The name was used because the area was populated by a higher concentration of Goths than in surrounding regions. The rulers of this area, when joined with several counties, were titled the
496:
succeeded to the throne in 568, Septimania was a dangerous frontier province and Iberia was wracked by revolts. Liuva granted Iberia to his son Leovigild and took Septimania to himself.
2413:
2183:
Gleize, Yves; Mendisco, Fanny; Pemonge, Marie-Hélène; Hubert, Christophe; Groppi, Alexis; Houix, Bertrand; Deguilloux, Marie-France; Breuil, Jean-Yves (24 February 2016).
1211:
in the borderlands of his empire. The territory passed to Louis, king in Aquitaine, but it was governed by Frankish margraves and then dukes (from 817) of Septimania.
370:, the Frankish king, invaded the Visigothic kingdom, whose capital lay in Toulouse, with the consent of the leading men of the tribe. Clovis defeated the Goths in the
863:, now threatened by Umayyad occupation of several cities lying in the lower Rhône, or maybe it provided the excuse he needed to intervene in this territory ruled by
300:. The Visigoths were then holding the area around Toulouse against the legal claims of the Empire, though they had more than once offered to exchange it for the
527:
and was seeking to join up with his Frankish allies. Alternatively, the invasion may have occurred in response to Hermenegild's death. Reccared meanwhile took
544:. It is clear that the Franks, throughout the sixth century, had coveted Septimania, but were unable to take it and the invasion of 589 was the last attempt.
2418:
644:
little commerce over the frontier or at its ports. In fact, Septimania helped to isolate both Aquitaine and Iberia from the rest of the Mediterranean world.
1218:
was the ruler of these lands from 826 to 832. His career (he was beheaded in 844) characterized the turbulent 9th century in Septimania. His appointment as
1095:
began in the early 8th century, when Andalusian Muslim forces managed to temporarily push into Aquitaine. In the wake of Narbonne's submission, Pepin took
158:, the Muslim Arabs and Berbers were defeated by the Christian Franks and retreated to their Andalusian heartland after forty years of occupation, and the
1078:, the Muslim Arabs and Berbers were defeated by the Christian Franks and expelled to their Andalusian heartland after 40 years of occupation, and the
488:
by the Franks before Theudis moved the capital there permanently. Under Theodoric Septimania had been safe from Frankish assault, but was raided by
473:. There is archaeological evidence that some enclaves of Visigothic population remained in Frankish Gaul, near the Septimanian border, after 507.
108:. There is archaeological evidence that some enclaves of Visigothic population remained in Frankish Gaul, near the Septimanian border, after 507.
595:
was still prevalent. The council set down penance to be done for not working on Thursday save for church festivals and commanded the practice of
1100:
2147:
551:(dukes), who were typically Visigoths. Most public offices were also held by Goths, far out of proportion to their part of the population.
1023:, who defeated him. Northeastern Iberia and the remainder of Septimania was left without any relevant commander in charge. Finally, the
315:, granted the Visigoths the western half of the province of Gallia Narbonensis in which to settle. The Visigoths additionally occupied
859:. While his reasons for leading a military expedition south remain unclear, it seems that he wanted to seal his newly secured grip on
715:
476:
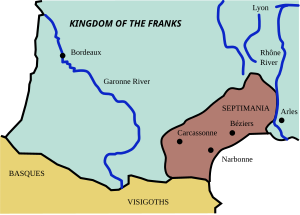
The province of Gallia held a unique place in the Visigothic Kingdom, as it was the only province outside of Iberia, north of the
124:
1032:
and respect the Gothic laws and probably their own government, so garnering the allegiance of the Gothic nobility of Septimania.
1007:
replaced Umar ibn Umar. In 759, Narbonne was not receiving reinforcements from al-Andalus, rife as it was with internal fights.
2128:
834:
560:
Gaulish women, though the Iberians regarded themselves as the defenders and protectors of the Gauls. It is only in the time of
2359:
2070:
would or those whose primary interests lay in the south would welcome the extension into their region of the authority of the
1062:, and the county was granted to Miló, the Gothic count in Muslim times, thus earning the loyalty of Septimanian Goths against
718:. Following the Islamic invasion, al-Andalus was divided into five administrative areas, roughly corresponding to present-day
198:, after which it was assigned governors. From the end of the thirteenth century Septimania evolved into the royal province of
2346:
2056:
1560:
1008:
946:
2423:
194:. This area was finally brought under effective control of the French kings in the early 13th century as a result of the
895:
but his forces were unable to take the city. However, when the Arabs sent reinforcements from Muslim-ruled Iberia, the
675:
587:, which found "the sacrilege of idolatry firmly implanted throughout almost the whole of Iberia and Septimania." The
92:, Septimania was both an administrative province of the central royal government and an ecclesiastical province whose
1944:
1820:
1475:
484:. The kings after Alaric II favoured Narbonne as a capital, but twice (611 and 531) were defeated and forced back to
77:
1194:. When Charlemagne invaded the Upper March in 778, Husayn refused allegiance and he had to retire. In the Pyrénées,
2080:. For that matter it was not with any sense of obligation to free formerly Christian lands from Islamic rule that
1085:
came up reinforced. The siege remained as a key battlefield in the context of the Carolingian expedition south to
628:
1112:
1075:
1055:
1044:
922:
899:
884:
789:
155:
136:
132:
999:
In 754, an anti-Frankish reaction, led by Ermeniard, killed Ansemund, but the uprising was without success and
2403:
1889:
693:
569:
1298:. This fragmentation in small feudal entities and the resulting fading and the gradual shifting of the name
512:
190:. It was part of the wider cultural and linguistic region comprising the southern third of France known as
2185:"Early Medieval Muslim Graves in France: First Archaeological, Anthropological and Palaeogenomic Evidence"
2105:
984:, having some authority over the remaining counts. The Gothic counts and the Franks then began to besiege
2438:
2428:
2408:
2398:
1544:
1219:
1035:
698:
541:
72:. The territory of Septimania roughly corresponds with the modern French former administrative region of
2433:
1147:
was taken by the Franks in 760. Pepin then diverted northwest to Aquitaine, triggering the war against
608:
166:
1984:
903:
2003:
caused him to make an expedition to hold onto that land. Charles Martel had subjected the whole of
2285:
1195:
872:
782:
707:
665:
637:
588:
112:
2182:
2044:
892:
710:
the region of Septimania and deposed the local Visigothic Kingdom in 720. The region was renamed
584:
540:
Hermenegild, for he invaded Septimania again in 589 and was roundly defeated near Carcassonne by
458:
93:
2092:, but their uniform silence makes it clear that despite this he failed to take the city itself.
2085:
2008:
1004:
561:
462:
97:
1451:
945:. Umayyad rule collapsed by 750, and Umayyad territories in Europe were ruled autonomously by
2036:
1920:
1520:
1231:
845:
826:
583:
in Visigothic Septimania. The Council may have been responding in part to the orders of the
128:
2196:
1215:
289:
285:
73:
2288:(1980). "Septimania and its frontier: an archaeological approach". In Edward James (ed.).
1123:
371:
8:
1936:
1932:
1334:
1148:
1079:
1063:
993:
950:
849:
624:
576:
572:
becomes evident in Septimania: Julian referred to it as a "brothel of blaspheming Jews."
511:, possibly in support of Hermenegild's revolt, since the latter was married to his niece
434:
413:
301:
195:
187:
159:
131:, which had been expanding from the south during the same century, before its subsequent
2200:
2165:
989:
731:
2219:
2184:
2089:
2067:
1950:
1867:
1540:
1275:
1248:
1187:
1179:
1128:
1000:
786:
671:
648:
636:
and are of varied design, but with generally flat relief which distinguishes them from
446:
336:
179:
170:
81:
44:
1279:
781:
to him on the same terms as Septimania. But his plans were thwarted in the disastrous
2342:
2224:
2052:
1940:
1881:
1859:
1816:
1556:
1528:
1471:
1447:
1263:
1172:
1089:
and Septimania starting in 752. The Iberian Christian counter-offensive known as the
830:
814:
805:
on the north-western fringes of Septimania (725) and penetrating eastwards as far as
797:
416:
reconquered Narbonne from the Burgundians and retained it as the provincial capital.
350:
214:
57:
31:
1988:
1954:
977:
911:
599:, rest from rural work on Sundays, to be adopted. Also punished by the council were
296:(455–456), but Sidonius is probably considering Visigothic settlement in and around
2255:
2214:
2204:
2071:
1972:
1924:
1548:
1374:
1366:
1240:
896:
661:
565:
508:
2209:
2048:
1361:
1353:
1244:
1235:
1208:
1082:
1059:
1020:
953:
864:
723:
600:
596:
580:
528:
162:
35:
2074:, or that a sense of Christian solidarity should mean more than the dictates of
1552:
1048:
883:
stock had concluded different military and political arrangements to oppose the
245:. Septimania extended to a line halfway between the Mediterranean and the river
2081:
1960:
888:
852:
312:
39:
2311:
Paganism and Pagan Survivals in Spain up to the Fall of the Visigothic Kingdom
532:
19:
2392:
2374:
2361:
2032:
1877:
1863:
1516:
1463:
942:
934:
822:
793:
685:
477:
450:
258:
85:
633:
2228:
980:
and declared their loyalty to the Frankish king—the Gothic count of Nîmes,
680:
604:
489:
426:
324:
174:
53:
2309:
2076:
1267:
1259:
1183:
1091:
1028:
930:
880:
802:
500:
470:
402:
394:
390:
105:
1871:
1302:
are the most probable origins of the ancient geographical area known as
1160:
2298:
2000:
1968:
1271:
1144:
1096:
938:
763:
703:
406:
405:, a fortified site guarding the Septimanian coast, was defeated by the
238:
116:
1996:
973:
751:
206:
2148:"Medieval Muslim Graves in France Reveal a Previously Unseen History"
1893:
1467:
1311:
1295:
1223:
1168:
1108:
1071:
917:
868:
778:
739:
727:
719:
620:
520:
485:
466:
454:
430:
422:
342:
280:
275:
199:
191:
101:
89:
49:
759:
234:
205:
The name "Septimania" may derive from the Roman name of the city of
2064:
1980:
1976:
1964:
1191:
1164:
1156:
1104:
1086:
1040:
1016:
985:
981:
965:
860:
856:
841:
810:
774:
616:
536:
524:
516:
515:. The Frankish attack of 585 was repulsed by Hermenegild's brother
398:
397:
allies proceeded to conquer most of Visigothic Gaul, including the
383:
375:
367:
362:, whose land was under constant threat from the Goths south of the
358:
346:
316:
297:
254:
230:
217:
in the city. The name can also be an allusion to the seven cities (
183:
1058:
only after Pepin promised the defenders of the city to uphold the
961:
767:
503:(583–585) against his father Leovigild, Septimania was invaded by
250:
242:
1536:
1458:. Routledge Library Editions: The Medieval World (1st ed.).
1318:
871:, far off from the Frankish centre in the north of Gaul. In 737,
504:
493:
417:
379:
308:
246:
2300:
The Development of Southern French and Catalan Society, 718–1050
2129:"Earliest Known Medieval Muslim Graves are Discovered in France"
523:
that year and it is possible that he had escaped confinement in
519:, who was ruling Narbonensis as a sub-king. Hermenegild died at
2004:
1532:
1459:
1176:
910:) and achieved a decisive and significant victory, after which
735:
481:
353:
319:(eastern Narbonensis) and only in 475 did the Visigothic king,
293:
139:
465:. Originally, the Goths may have maintained their hold on the
100:. Originally, the Goths may have maintained their hold on the
1885:
1024:
957:
929:
Around 747, the government of the Septimania region (and the
876:
806:
743:
714:
and turned into a military base for future operations by the
363:
320:
213:, which in turn alludes to the settlement of veterans of the
123:
and turned into a military base for future operations by the
1270:, but other names became regionally more prominent such as,
1992:
1983:
came to relieve Narbonne. Charles marched against them and
1850:
Baker, Patrick S. (2013). "The Battle of the River Berre".
1811:
Holt, P. M., Lambton, Ann K. S. and Lewis, Bernard (1977).
1322:
1283:
1222:
in 826 occasioned a general uprising of the Catalan lords (
1203:
1152:
1003:
was designated new count by the Frankish court. About 755,
969:
907:
755:
747:
592:
226:
222:
777:, a possession that would open up the bordering region of
627:
provenance discovered in Septimania. However, a series of
547:
In the 7th century, Gallia often had its own governors or
480:, and bordering a strong foreign nation, in this case the
773:
By 721, al-Samh was reinforced and ready to lay siege to
684:
Military campaigns and geopolitical situation around the
323:, cede it to the Empire via a treaty whereby the emperor
2011:
and Narbonne there. He did not have the time to conquer
1262:. It retained these two names while it was ruled by the
1226:) at this intrusion of Frankish power over the lands of
891:
attempted to conquer the whole region of Septimania and
142:
in 759, who by the end of the 9th century renamed it as
2414:
Geographical, historical and cultural regions of France
655:
292:
refers to Septimania as "theirs" during the reign of
1929:
The Journal of Medieval Military History: Volume III
1310:
which has reached our days as the present region of
821:
by the Franks, was an ally of the Duke of Aquitaine
429:, invaded Septimania in 531 and chased Amalaric to
1914:
1912:
1910:
1908:
1906:
1904:
801:resupplied by sea, struck in the 720s, conquering
257:; and to the south its boundary was formed by the
76:that merged into the new administrative region of
579:of 590, a good deal can be known about surviving
330:
52:in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king,
2390:
1456:A History of Early Medieval Europe: From 476–911
1442:
904:intercepted them at the mouth of the River Berre
809:(725). In 731, the Berber lord of the region of
706:, sweeping up the Iberian peninsula, by 719 had
2318:
2027:
2025:
2023:
1901:
1832:
1642:
1640:
1638:
1511:
1509:
1507:
1440:
1438:
1436:
1434:
1432:
1430:
1428:
1426:
1424:
1422:
1196:the Basques defeated his forces in Roncesvalles
554:
2084:launched a raid into western Provence in 737.
1884:, lifted the siege. Eudo's army decimated the
1708:
1706:
1669:
1667:
1505:
1503:
1501:
1499:
1497:
1495:
1493:
1491:
1489:
1487:
1118:
1039:Arab and Berber Muslim troops retreating from
401:(507) and Toulouse (508). The attempt to take
2262:. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
1921:"The Role of the Cavalry in Medieval Warfare"
1845:
1843:
1841:
327:recognised the Visigoths' full independence.
274:Under Theodoric II, the Visigoths settled in
2419:History of Occitania (administrative region)
2020:
1652:
1635:
1625:
1623:
1610:
1608:
1419:
1390:
1388:
1386:
1384:
1019:in 756, and immediately head south to fight
914:. Islamic burials have been found in Nîmes.
873:the Frankish king went on to attack Narbonne
829:, but the rebel lord was killed by the Arab
469:, but if so it was conquered by the time of
104:, but if so it was conquered by the time of
2339:A Jewish Princedom in Feudal France 768–900
1987:. Charles still devastated the area around
1747:
1745:
1703:
1679:
1664:
1484:
1015:of al-Andalus, had to quash a rebellion in
906:(located in the present-day Département of
2260:Merovingian Military Organization, 481–751
2166:"France's Earliest 'Muslim Burials' Found"
1985:defeated them along the banks of the Berre
1918:
1838:
1409:
1407:
1405:
1403:
1127:Marches of the eastern Pyrénées under the
440:
2336:
2218:
2208:
2063:It would be quite anachronistic that the
1815:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
1620:
1605:
1381:
1056:Narbonne capitulated to the Franks in 759
855:directed his attention to Septimania and
382:was elected to replace him and rule from
378:was carried for safety into Iberia while
264:
38:. It referred to the western part of the
2327:
2303:. Austin, TX: University of Texas Press.
2254:
1742:
1724:
1697:
1685:
1673:
1658:
1646:
1614:
1599:
1587:
1575:
1446:
1243:, also served as Count of Barcelona and
1122:
1034:
992:was probably the count (as successor to
916:
692:The Arab and Berber Muslim forces under
679:
652:not been preserved across the frontier.
165:came up reinforced. Septimania became a
18:
16:Historical region in southeastern France
2341:. New York: Columbia University Press.
2314:. Catholic University of America Press.
2307:
2275:
2266:
2126:
2103:
2031:
2007:, again by battles, and had to besiege
1712:
1629:
1515:
1400:
1099:, and then directed his effort against
2391:
2145:
1045:Frankish conquest of Septimania in 759
835:Abd al-Rahman ibn Abd Allah al-Ghafiqi
591:of not working Thursdays in honour of
575:Thanks to the preserved canons of the
433:in response to pleas from his sister,
2296:
2284:
2127:Netburn, Deborah (24 February 2016).
2072:eastern Frankish Mayors of the Palace
1849:
1799:
1787:
1775:
1763:
1751:
1736:
1413:
1394:
1373:
1360:
269:
2146:Newitz, Annalee (24 February 2016).
1167:were conquered. In 777, the wali of
1076:Frankish conquest of Narbonne in 759
656:Muslim-ruled and Frankish Septimania
356:in Gaul. The Franks allied with the
211:Colonia Julia Septimanorum Baeterrae
156:Frankish conquest of Narbonne in 759
60:, the region was variously known as
2041:The Arab Conquest of Spain: 710–797
13:
2269:The Arab Conquest of Spain, 710–97
976:refused allegiance to the emir at
912:the Frankish army marched on Nîmes
676:Muslim presence in medieval France
581:Gothic Pagan beliefs and practices
307:In 462, the Empire, controlled by
249:in the northwest; in the east the
48:that passed to the control of the
14:
2450:
2104:Meadows, Ian (March–April 1993).
1979:and besieged it. Then an army of
1975:. Charles marched afterwards to
1009:Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri
947:Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri
349:, met with the opposition of the
2290:Visigothic Spain: New Approaches
1251:and Septimania from 865 to 878.
956:headed south to Septimania. The
949:and his supporters. In 752, the
2319:O'Callaghan, Joseph F. (1983).
2235:
2176:
2158:
2139:
2120:
2097:
1963:advanced against the nobles in
1826:
1805:
1793:
1781:
1769:
1757:
1730:
1718:
1691:
923:Pepin's expedition and conquest
2337:Zuckerman, Arthur J. (1972) .
2297:Lewis, Archibald Ross (1965).
1813:The Cambridge History of Islam
1593:
1581:
1569:
1346:
1182:, offered their submission to
825:after he revolted against the
716:Andalusian military commanders
649:Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania
425:. The Frankish king of Paris,
331:Visigothic Kingdom of Narbonne
125:Andalusian military commanders
1:
2328:Thompson, E. A. (1969).
1892:and drove the survivors from
1111:in Aquitaine, leading to the
694:al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani
221:) of the territory: Béziers,
111:The region of Septimania was
2210:10.1371/journal.pone.0148583
1858:(2). Karwansaray BV: 44–48.
875:, but the local nobility of
555:Culture of Gothic Septimania
345:, perhaps because they were
7:
2323:. Cornell University Press.
2321:A History of Medieval Spain
1553:10.1007/978-1-349-26924-2_4
1545:University of Toronto Press
1328:
1290:(along with the older name
1254:Septimania became known as
1186:and also the submission of
1119:Gothia in Carolingian times
848:'s detachment attempt, the
542:Claudius, Duke of Lusitania
453:by the end of the reign of
127:. It passed briefly to the
88:by the end of the reign of
10:
2455:
2424:Medieval history of France
2332:. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
2292:. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
2271:. Oxford University Press.
2247:
1923:. In Rogers, Clifford J.;
1919:Verbruggen, J. F. (2005).
1521:"Italy and Spain, 773–801"
1321:of Gothia (and, also, the
669:
659:
589:traditional Roman practice
492:twice (531 and 541). When
449:, which became centred on
334:
84:, which became centred on
2308:McKenna, Stephen (1938).
2278:Visigothic Spain, 409–711
1967:and placed the region of
1266:during early part of the
1066:, the independent ruler (
783:battle of Toulouse in 721
2241:Lewis, Archibald R. 1965
2106:"The Arabs in Occitania"
1452:"The Later Merovingians"
1340:
893:besieged Narbonne in 737
885:expanding Frankish realm
666:Islamic invasion of Gaul
638:ancient Roman sarcophagi
23:Map of Septimania in 537
2280:. Blackwell Publishing.
2276:Collins, Roger (2004).
2267:Collins, Roger (1989).
2045:Chichester, West Sussex
1971:under the authority of
585:Third Council of Toledo
570:large Jewish population
441:Gothic province of Gaul
1370:
1357:
1140:
1052:
1005:Abd ar-Rahman ibn Uqba
926:
702:(governor-general) of
689:
564:(reigned 672–680) and
463:Archbishop of Narbonne
265:Visigothic Narbonensis
98:Archbishop of Narbonne
24:
1999:, but an uprising in
1375:[septiˈmanjɔ]
1232:Berenguer of Toulouse
1126:
1038:
920:
688:and Septimania in 740
683:
670:Further information:
499:During the revolt of
412:The Ostrogothic king
22:
2256:Bachrach, Bernard S.
2037:"Conquerors Divided"
1955:10.7722/j.ctt81qwd.6
1925:Bachrach, Bernard S.
1876:After three months,
1470:. pp. 244–245.
1216:Bernat of Septimania
1113:battle for Aquitaine
290:Sidonius Apollinaris
286:Western Roman Empire
215:Roman Seventh Legion
74:Languedoc-Roussillon
2371: /
2201:2016PLoSO..1148583G
2172:. 25 February 2016.
1933:Woodbridge, Suffolk
1362:[sɛptimani]
1335:Septimania timeline
1258:after the reign of
1214:The Frankish noble
1149:Waifer of Aquitaine
629:Germanic sarcophagi
577:Council of Narbonne
414:Theodoric the Great
374:and the child-king
196:Albigensian Crusade
188:County of Barcelona
119:in 719, renamed as
2439:Visigothic Kingdom
2429:Merovingian period
2409:Gallia Narbonensis
2404:Emirate of Córdoba
2399:Carolingian Empire
2330:The Goths in Spain
2110:Saudi Aramco World
1939:. pp. 55–56.
1833:O'Callaghan (1983)
1790:, pp. 240–241
1739:, pp. 228–229
1715:, pp. 117–118
1547:. pp. 65–66.
1541:Palgrave Macmillan
1448:Deanesly, Margaret
1264:counts of Toulouse
1249:Margrave of Gothia
1234:and the Catalans,
1230:. For suppressing
1220:Count of Barcelona
1198:(August 15, 778).
1175:, and the wali of
1163:, and the city of
1141:
1129:Carolingian Empire
1053:
1047:. Illustration by
927:
921:Septimania during
827:Emirate of Córdoba
690:
672:Carolingian Empire
568:, however, that a
447:Visigothic Kingdom
337:Visigothic Kingdom
270:Gothic acquisition
253:separated it from
171:Carolingian Empire
129:Emirate of Córdoba
117:Andalusian Muslims
82:Visigothic Kingdom
62:Gallia Narbonensis
45:Gallia Narbonensis
25:
2434:Umayyad Caliphate
2348:978-0-231-03298-8
2133:Los Angeles Times
2058:978-0-631-19405-7
1882:Duke of Aquitaine
1562:978-1-349-26924-2
1173:Sulayman al-Arabi
815:Uthman ibn Naissa
798:Duke of Aquitaine
609:sold into slavery
531:(Ugernum) on the
421:Ostrogothic king
372:Battle of Vouillé
58:Early Middle Ages
32:historical region
2446:
2386:
2385:
2383:
2382:
2381:
2376:
2372:
2369:
2368:
2367:
2364:
2352:
2333:
2324:
2315:
2304:
2293:
2281:
2272:
2263:
2242:
2239:
2233:
2232:
2222:
2212:
2180:
2174:
2173:
2162:
2156:
2155:
2143:
2137:
2136:
2124:
2118:
2117:
2101:
2095:
2094:
2029:
2018:
2017:
1916:
1899:
1898:
1852:Medieval Warfare
1847:
1836:
1830:
1824:
1809:
1803:
1797:
1791:
1785:
1779:
1773:
1767:
1761:
1755:
1749:
1740:
1734:
1728:
1722:
1716:
1710:
1701:
1695:
1689:
1683:
1677:
1671:
1662:
1656:
1650:
1644:
1633:
1627:
1618:
1612:
1603:
1597:
1591:
1590:, pp. 10–11
1585:
1579:
1573:
1567:
1566:
1513:
1482:
1481:
1444:
1417:
1411:
1398:
1392:
1379:
1377:
1364:
1350:
1325:of Septimania).
1241:Bernat of Gothia
1209:Hispanic Marches
1080:Carolingian king
951:Carolingian king
850:Carolingian king
840:After capturing
732:Castile and Léon
662:Frankish kingdom
566:Julian of Toledo
509:King of Burgundy
389:Clovis, his son
347:Arian Christians
160:Carolingian king
2454:
2453:
2449:
2448:
2447:
2445:
2444:
2443:
2389:
2388:
2379:
2377:
2373:
2370:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2358:
2357:
2355:
2349:
2250:
2245:
2240:
2236:
2195:(2): e0148583.
2181:
2177:
2164:
2163:
2159:
2144:
2140:
2125:
2121:
2102:
2098:
2086:He took Avignon
2059:
2049:Wiley-Blackwell
2030:
2021:
1947:
1917:
1902:
1848:
1839:
1831:
1827:
1810:
1806:
1798:
1794:
1786:
1782:
1774:
1770:
1762:
1758:
1750:
1743:
1735:
1731:
1725:Thompson (1969)
1723:
1719:
1711:
1704:
1698:Thompson (1969)
1696:
1692:
1686:Thompson (1969)
1684:
1680:
1674:Thompson (1969)
1672:
1665:
1659:Thompson (1969)
1657:
1653:
1647:Thompson (1969)
1645:
1636:
1628:
1621:
1615:Thompson (1969)
1613:
1606:
1600:Bachrach (1971)
1598:
1594:
1588:Bachrach (1971)
1586:
1582:
1576:Bachrach (1971)
1574:
1570:
1563:
1514:
1485:
1478:
1445:
1420:
1412:
1401:
1393:
1382:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1331:
1286:, and the name
1236:Louis the Pious
1137:Marca Hispanica
1121:
1083:Pepin the Short
1021:Abd ar-Rahman I
954:Pepin the Short
941:) was given to
844:on the wake of
678:
668:
660:Main articles:
658:
647:Coinage of the
605:publicly lashed
597:Martin of Braga
557:
443:
339:
333:
311:in the name of
272:
267:
163:Pepin the Short
36:southern France
17:
12:
11:
5:
2452:
2442:
2441:
2436:
2431:
2426:
2421:
2416:
2411:
2406:
2401:
2354:
2353:
2347:
2334:
2325:
2316:
2305:
2294:
2282:
2273:
2264:
2251:
2249:
2246:
2244:
2243:
2234:
2175:
2157:
2138:
2119:
2096:
2082:Charles Martel
2057:
2051:. p. 92.
2033:Collins, Roger
2019:
1961:Charles Martel
1945:
1900:
1878:Eudo the Great
1837:
1825:
1804:
1792:
1780:
1768:
1756:
1741:
1729:
1717:
1713:McKenna (1938)
1702:
1690:
1678:
1663:
1651:
1634:
1630:Collins (2004)
1619:
1604:
1592:
1580:
1568:
1561:
1517:Collins, Roger
1483:
1476:
1418:
1399:
1380:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1338:
1337:
1330:
1327:
1143:The region of
1120:
1117:
1060:Visigothic law
889:Charles Martel
853:Charles Martel
657:
654:
601:fortunetellers
556:
553:
442:
439:
335:Main article:
332:
329:
313:Libius Severus
271:
268:
266:
263:
186:, and ancient
40:Roman province
34:in modern-day
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2451:
2440:
2437:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2427:
2425:
2422:
2420:
2417:
2415:
2412:
2410:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2400:
2397:
2396:
2394:
2387:
2384:
2350:
2344:
2340:
2335:
2331:
2326:
2322:
2317:
2313:
2312:
2306:
2302:
2301:
2295:
2291:
2287:
2286:James, Edward
2283:
2279:
2274:
2270:
2265:
2261:
2257:
2253:
2252:
2238:
2230:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2202:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2179:
2171:
2167:
2161:
2153:
2149:
2142:
2134:
2130:
2123:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2100:
2093:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2078:
2073:
2069:
2066:
2060:
2054:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2028:
2026:
2024:
2016:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1956:
1952:
1948:
1946:9781846154058
1942:
1938:
1937:Boydell Press
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1915:
1913:
1911:
1909:
1907:
1905:
1897:
1895:
1891:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1873:
1869:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1853:
1846:
1844:
1842:
1835:, p. 142
1834:
1829:
1822:
1821:0-521-29135-6
1818:
1814:
1808:
1802:, p. 239
1801:
1796:
1789:
1784:
1778:, p. 238
1777:
1772:
1766:, p. 230
1765:
1760:
1754:, p. 229
1753:
1748:
1746:
1738:
1733:
1726:
1721:
1714:
1709:
1707:
1699:
1694:
1688:, p. 228
1687:
1682:
1676:, p. 227
1675:
1670:
1668:
1660:
1655:
1648:
1643:
1641:
1639:
1631:
1626:
1624:
1616:
1611:
1609:
1601:
1596:
1589:
1584:
1577:
1572:
1564:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1512:
1510:
1508:
1506:
1504:
1502:
1500:
1498:
1496:
1494:
1492:
1490:
1488:
1479:
1477:9780367184582
1473:
1469:
1465:
1464:New York City
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1443:
1441:
1439:
1437:
1435:
1433:
1431:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1423:
1416:, p. 236
1415:
1410:
1408:
1406:
1404:
1397:, p. 223
1396:
1391:
1389:
1387:
1385:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1349:
1345:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1326:
1324:
1320:
1315:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1252:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1212:
1210:
1205:
1199:
1197:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1138:
1134:
1133:Marca Gothica
1130:
1125:
1116:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1093:
1088:
1084:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1037:
1033:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
997:
995:
994:Count Gilbert
991:
987:
983:
979:
975:
971:
967:
963:
959:
958:Gothic counts
955:
952:
948:
944:
943:Umar ibn Umar
940:
936:
932:
924:
919:
915:
913:
909:
905:
901:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
851:
847:
843:
838:
836:
832:
828:
824:
823:Odo the Great
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
799:
795:
794:Odo the Great
791:
788:
784:
780:
776:
771:
769:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
744:Gothic counts
741:
737:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
700:
695:
687:
682:
677:
673:
667:
663:
653:
650:
645:
641:
639:
635:
630:
626:
622:
618:
612:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
578:
573:
571:
567:
563:
552:
550:
545:
543:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
497:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
474:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
452:
448:
438:
436:
432:
428:
424:
419:
415:
410:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
387:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
366:, and in 507
365:
361:
360:
355:
352:
348:
344:
338:
328:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
305:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
283:
282:
277:
262:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
203:
201:
197:
193:
189:
185:
181:
176:
172:
168:
164:
161:
157:
154:). After the
153:
152:Marca Gothica
149:
145:
141:
138:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
109:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
56:. During the
55:
51:
47:
46:
41:
37:
33:
29:
21:
2375:43.6°N 3.2°E
2356:
2338:
2329:
2320:
2310:
2299:
2289:
2277:
2268:
2259:
2237:
2192:
2188:
2178:
2169:
2160:
2152:Ars Technica
2151:
2141:
2132:
2122:
2113:
2109:
2099:
2075:
2062:
2040:
2012:
1958:
1928:
1875:
1855:
1851:
1828:
1812:
1807:
1800:James (1980)
1795:
1788:James (1980)
1783:
1776:James (1980)
1771:
1764:James (1980)
1759:
1752:James (1980)
1737:James (1980)
1732:
1727:, p. 23
1720:
1700:, p. 54
1693:
1681:
1661:, p. 95
1654:
1649:, p. 75
1632:, p. 60
1617:, p. 19
1602:, p. 16
1595:
1583:
1571:
1524:
1455:
1414:James (1980)
1395:James (1980)
1348:
1316:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1291:
1287:
1255:
1253:
1227:
1213:
1200:
1142:
1136:
1132:
1090:
1074:. After the
1067:
1054:
1049:Émile Bayard
1012:
998:
928:
839:
818:
792:army led by
772:
711:
697:
691:
646:
642:
613:
574:
558:
548:
546:
498:
490:Childebert I
475:
459:metropolitan
444:
427:Childebert I
411:
388:
357:
340:
325:Julius Nepos
306:
279:
273:
218:
210:
204:
175:West Francia
151:
148:Gothic March
147:
143:
120:
110:
94:metropolitan
69:
65:
61:
54:Theodoric II
43:
27:
26:
2378: /
2077:realpolitik
2068:aristocracy
1578:, p. 7
1525:Charlemagne
1268:Middle Ages
1260:Charlemagne
1184:Charlemagne
1092:Reconquista
1064:Duke Waifer
1029:Gallo-Roman
933:, from the
931:Upper March
881:Gallo-Roman
846:Duke Hunald
803:Carcassonne
603:, who were
501:Hermenegild
471:Chilperic I
403:Carcassonne
391:Theuderic I
106:Chilperic I
70:Narbonensis
2393:Categories
2013:Septimania
1973:his counts
1969:Marseilles
1959:After 734
1371:Septimània
1358:Septimanie
1319:Marquesses
1308:Cathalania
1304:Gathalania
1292:Septimania
1272:Roussillon
1190:, wali of
1145:Roussillon
1097:Roussillon
1043:after the
990:Count Miló
939:Ebro River
865:Visigothic
833:commander
787:Aquitanian
764:Maguelonne
704:al-Andalus
634:Saint-Béat
625:Burgundian
621:Austrasian
407:Ostrogoths
395:Burgundian
393:, and his
239:Maguelonne
28:Septimania
2380:43.6; 3.2
2065:Provençal
1894:Aquitaine
1888:, killed
1864:2211-5129
1468:Routledge
1312:Catalonia
1296:Languedoc
1247:, and as
1224:Bellonids
1169:Barcelona
1109:Albigeois
1072:Aquitaine
925:(752–759)
900:Christian
869:Roman law
817:, called
790:Christian
779:Aquitaine
746:, taking
740:Catalonia
728:Lusitania
720:Andalusia
617:Neustrian
529:Beaucaire
521:Tarragona
486:Barcelona
467:Albigeois
455:Leovigild
435:Chrotilda
431:Barcelona
423:Athalaric
343:Visigoths
281:foederati
276:Aquitaine
219:civitates
200:Languedoc
192:Occitania
173:and then
137:Christian
102:Albigeois
90:Leovigild
80:. In the
78:Occitanie
50:Visigoths
2258:(1971).
2229:26910855
2189:PLOS ONE
2170:BBC News
2116:: 24–29.
2035:(1995).
1981:Saracens
1977:Narbonne
1965:Burgundy
1927:(eds.).
1872:48578218
1823:, p. 95.
1519:(1998).
1450:(2019).
1329:See also
1276:Conflent
1192:Zaragoza
1180:Abu Taur
1165:Toulouse
1161:Gévaudan
1157:Rouergue
1105:Rouergue
1101:Toulouse
1087:Provence
1068:princeps
1041:Narbonne
1017:Zaragoza
988:, where
986:Narbonne
982:Ansemund
966:Melguelh
935:Pyrénées
897:Frankish
861:Burgundy
857:Provence
842:Bordeaux
811:Cerdagne
775:Toulouse
686:Pyrénées
537:Tarascon
525:Valencia
517:Reccared
513:Ingundis
478:Pyrénées
461:was the
399:Rouergue
384:Narbonne
376:Amalaric
368:Clovis I
359:Armorici
351:Catholic
317:Provence
302:Auvergne
298:Toulouse
288:(450s).
259:Pyrénées
255:Provence
231:Narbonne
184:Provence
180:Toulouse
133:conquest
96:was the
2363:43°36′N
2248:Sources
2220:4765927
2197:Bibcode
2009:Avignon
1997:Béziers
1890:As-Sahm
1537:Toronto
1529:Buffalo
1367:Occitan
1051:, 1880.
978:Córdoba
974:Béziers
937:to the
831:Umayyad
752:Béziers
724:Galicia
712:Arbūnah
708:invaded
593:Jupiter
505:Guntram
494:Liuva I
445:In the
418:Theudis
380:Gesalec
309:Ricimer
284:of the
247:Garonne
207:Béziers
169:of the
146:or the
135:by the
121:Arbūnah
115:by the
113:invaded
2366:3°12′E
2345:
2227:
2217:
2055:
2005:Gallia
2001:Saxony
1995:, and
1953:
1943:
1870:
1862:
1819:
1559:
1535:, and
1533:London
1474:
1460:London
1354:French
1300:Gothia
1288:Gothia
1256:Gothia
1245:Girona
1228:Gothia
1188:Husayn
1177:Huesca
1107:, and
1025:Gothic
1001:Radulf
972:, and
877:Gothic
819:Munuza
785:; the
766:, and
760:Lodève
738:, and
736:Aragon
482:Franks
451:Toledo
354:Franks
294:Avitus
241:, and
235:Lodève
144:Gothia
140:Franks
86:Toledo
66:Gallia
2090:ʿUqba
1989:Nîmes
1951:JSTOR
1886:Moors
1868:JSTOR
1341:Notes
1323:Dukes
1280:Razès
1204:fiefs
1070:) of
962:Nîmes
902:army
807:Autun
768:Nîmes
623:, or
562:Wamba
549:duces
535:near
533:Rhône
364:Loire
321:Euric
251:Rhône
243:Nîmes
167:march
68:, or
30:is a
2343:ISBN
2225:PMID
2053:ISBN
1993:Agde
1941:ISBN
1860:ISSN
1817:ISBN
1557:ISBN
1472:ISBN
1462:and
1284:Foix
1153:Albi
1135:and
1027:and
1013:wali
970:Agde
908:Aude
879:and
867:and
756:Agde
748:Alet
699:wāli
674:and
664:and
607:and
341:The
227:Agde
223:Elne
2215:PMC
2205:doi
1549:doi
1306:or
1282:or
996:).
960:of
278:as
42:of
2395::
2223:.
2213:.
2203:.
2193:11
2191:.
2187:.
2168:.
2150:.
2131:.
2114:44
2112:.
2108:.
2061:.
2047::
2043:.
2039:.
2022:^
1991:,
1957:.
1949:.
1935::
1931:.
1903:^
1880:,
1874:.
1866:.
1854:.
1840:^
1744:^
1705:^
1666:^
1637:^
1622:^
1607:^
1555:.
1539::
1531:,
1527:.
1523:.
1486:^
1466::
1454:.
1421:^
1402:^
1383:^
1369::
1365:;
1356::
1314:.
1278:,
1274:,
1171:,
1159:,
1155:,
1151:.
1131::
1115:.
1103:,
1011:,
968:,
964:,
887:.
837:.
813:,
796:,
770:.
762:,
758:,
754:,
750:,
734:,
730:,
726:,
722:,
696:,
619:,
611:.
507:,
386:.
304:.
261:.
237:,
233:,
229:,
225:,
209:,
202:.
182:,
64:,
2351:.
2231:.
2207::
2199::
2154:.
2135:.
2015:.
1896:.
1856:3
1565:.
1551::
1543:/
1480:.
1378:)
1352:(
1139:.
150:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.