920:[Note:It can be shown that programs that correctly use mutexes and memory_order_seq_cst operations to prevent all data races and use no other synchronization operations behave as if the operations executed by their constituent threads were simply interleaved, with each value computation of an object being taken from the last side effect on that object in that interleaving. This is normally referred to as “sequential consistency”. However, this applies only to data-race-free programs, and data-race-free programs cannot observe most program transformations that do not change single-threaded program semantics. In fact, most single-threaded program transformations continue to be allowed, since any program that behaves differently as a result must perform an undefined operation.— end note
853:" relation; intuitively, if we can prove that we are in a situation where one memory operation X is guaranteed to be executed to completion before another memory operation Y begins, then we say that "X happens-before Y". If neither "X happens-before Y" nor "Y happens-before X", then we say that X and Y are "not ordered by the hb1 relation". So, the clause "...and they are not ordered by the hb1 relation of the execution" can be intuitively translated as "...and X and Y are potentially concurrent".
1194:
3022:
2253:
1048:, where a user who starts a channel automatically acquires channel-operator privileges. If two users on different servers, on different ends of the same network, try to start the same-named channel at the same time, each user's respective server will grant channel-operator privileges to each user, since neither server will yet have received the other server's signal that it has allocated that channel. (This problem has been largely
38:
1010:. PUFs can be created by designing circuit topologies with identical paths to a node and relying on manufacturing variations to randomly determine which paths will complete first. By measuring each manufactured circuit's specific set of race condition outcomes, a profile can be collected for each circuit and kept secret in order to later verify a circuit's identity.
1036:
error handling, or the success of the entire task can be verified afterwards, before continuing. A more common approach is to simply verify that enough system resources are available before starting a task; however, this may not be adequate because in complex systems the actions of other running programs can be unpredictable.
744:'). Similarly, if one thread reads from a location while another thread is writing to it, it may be possible for the read to return a value that is some arbitrary and meaningless combination of the bits representing the value that the memory location held before the write, and of the bits representing the value being written.
1059:" covers the state of the network (what channels exist, as well as what users started them and therefore have what privileges), which each server can freely change as long as it signals the other servers on the network about the changes so that they can update their conception of the state of the network. However, the
1109:(among other power facilities). A race condition existed in the alarm subsystem; when three sagging power lines were tripped simultaneously, the condition prevented alerts from being raised to the monitoring technicians, delaying their awareness of the problem. This software flaw eventually led to the
876:
A critical difference between the C++ approach and the Java approach is that in C++, a data race is undefined behavior, whereas in Java, a data race merely affects "inter-thread actions". This means that in C++, an attempt to execute a program containing a data race could (while still adhering to the
445:
A race condition can arise in software when a computer program has multiple code paths that are executing at the same time. If the multiple code paths take a different amount of time than expected, they can finish in a different order than expected, which can cause software bugs due to unanticipated
928:
There are various theorems, often provided in the form of memory models, that provide SC for DRF guarantees given various contexts. The premises of these theorems typically place constraints upon both the memory model (and therefore upon the implementation), and also upon the programmer; that is to
739:
This can be dangerous because on many platforms, if two threads write to a memory location at the same time, it may be possible for the memory location to end up holding a value that is some arbitrary and meaningless combination of the bits representing the values that each thread was attempting to
871:
Two accesses to (reads of or writes to) the same variable are said to be conflicting if at least one of the accesses is a write...When a program contains two conflicting accesses (§17.4.1) that are not ordered by a happens-before relationship, it is said to contain a data race...a data race cannot
727:
Not all regard data races as a subset of race conditions. The precise definition of data race is specific to the formal concurrency model being used, but typically it refers to a situation where a memory operation in one thread could potentially attempt to access a memory location at the same time
910:
A program must be correctly synchronized to avoid the kinds of counterintuitive behaviors that can be observed when code is reordered. The use of correct synchronization does not ensure that the overall behavior of a program is correct. However, its use does allow a programmer to reason about the
904:
This is an extremely strong guarantee for programmers. Programmers do not need to reason about reorderings to determine that their code contains data races. Therefore they do not need to reason about reorderings when determining whether their code is correctly synchronized. Once the determination
1035:
not long after landing. A solution is for software to request and reserve all the resources it will need before beginning a task; if this request fails then the task is postponed, avoiding the many points where failure could have occurred. Alternatively, each of those points can be equipped with
889:
manner, greatly easing reasoning about the concurrent behavior of the program. Formal memory models that provide such a guarantee are said to exhibit an "SC for DRF" (Sequential
Consistency for Data Race Freedom) property. This approach has been said to have achieved recent consensus (presumably
174:
combines signals that have traveled along different paths from the same source. The inputs to the gate can change at slightly different times in response to a change in the source signal. The output may, for a brief period, change to an unwanted state before settling back to the designed state.
1030:
A different form of race condition exists in file systems where unrelated programs may affect each other by suddenly using up available resources such as disk space, memory space, or processor cycles. Software not carefully designed to anticipate and handle this race situation may then become
1063:
across the network makes possible the kind of race condition described. In this case, heading off race conditions by imposing a form of control over access to the shared resource—say, appointing one server to control who holds what privileges—would mean turning the distributed network into a
924:
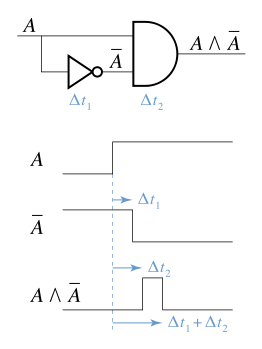
Note that the C++ draft specification admits the possibility of programs that are valid but use synchronization operations with a memory_order other than memory_order_seq_cst, in which case the result may be a program which is correct but for which no guarantee of sequentially consistency is
747:
On many platforms, special memory operations are provided for simultaneous access; in such cases, typically simultaneous access using these special operations is safe, but simultaneous access using other memory operations is dangerous. Sometimes such special operations (which are safe for
1031:
unpredictable. Such a risk may be overlooked for a long time in a system that seems very reliable. But eventually enough data may accumulate or enough other software may be added to critically destabilize many parts of a system. An example of this occurred with the near loss of the
718:
In this case, the final value is 1 instead of the expected result of 2. This occurs because here the increment operations are not mutually exclusive. Mutually exclusive operations are those that cannot be interrupted while accessing some resource such as a memory location.
487:
and depends on the relative timing between interfering threads. Problems of this nature can therefore disappear when running in debug mode, adding extra logging, or attaching a debugger. A bug that disappears like this during debugging attempts is often referred to as a
360:
A practical example of a race condition can occur when logic circuitry is used to detect certain outputs of a counter. If all the bits of the counter do not change exactly simultaneously, there will be intermediate patterns that can trigger false matches.
810:
if it contains two potentially concurrent conflicting actions, at least one of which is not atomic, and neither happens before the other, except for the special case for signal handlers described below . Any such data race results in undefined behavior.
877:
spec) crash or could exhibit insecure or bizarre behavior, whereas in Java, an attempt to execute a program containing a data race may produce undesired concurrency behavior but is otherwise (assuming that the implementation adheres to the spec) safe.
925:
provided. In other words, in C++, some correct programs are not sequentially consistent. This approach is thought to give C++ programmers the freedom to choose faster program execution at the cost of giving up ease of reasoning about their program.
911:
possible behaviors of a program in a simple way; the behavior of a correctly synchronized program is much less dependent on possible reorderings. Without correct synchronization, very strange, confusing and counterintuitive behaviors are possible.
1239:
in 1934, an accident occurred because the signalman accepted another train before the fireman arrived. Modern signalling practice removes the race condition by making it possible for the driver to instantaneously contact the signal box by radio.
1026:
or the like) has exclusive access to the file, and all other processes that need to access the data in that file do so only via interprocess communication with that one process. This requires synchronization at the process level.
1566:
1235:. According to this rule, if a train was stopped on a running line by a signal, the locomotive fireman would walk to the signal box in order to remind the signalman that the train was present. In at least one case, at
728:
that a memory operation in another thread is writing to that memory location, in a context where this is dangerous. This implies that a data race is different from a race condition as it is possible to have
229:
780:
The precise definition of data race differs across formal concurrency models. This matters because concurrent behavior is often non-intuitive and so formal reasoning is sometimes applied.
315:
936:
with sequentially consistent special operations), VAX memory model, and data-race-free-0 memory models. The PLpc memory model provides SC for DRF and allows the optimizations of the TSO (
856:
The paper considers dangerous only those situations in which at least one of the memory operations is a "data operation"; in other parts of this paper, the paper also defines a class of "
1574:
929:
say, typically it is the case that there are programs which do not meet the premises of the theorem and which could not be guaranteed to execute in a sequentially consistent manner.
403:
occurs when it results in multiple transitions when only one is intended. They are due to interaction between gates. It can be eliminated by using no more than two levels of gating.
2027:
960:
implications. A race condition allows an attacker with access to a shared resource to cause other actors that utilize that resource to malfunction, resulting in effects including
183:
for further systems that contain memory, for example, the system can rapidly depart from its designed behaviour (in effect, the temporary glitch becomes a permanent glitch).
834:
if they access the same location and at least one of them is a write operation... "Two memory operations, x and y, in a sequentially consistent execution form a race 〈x,y〉,
1825:
1132:
Thread Safety
Analysis is a static analysis tool for annotation-based intra-procedural static analysis, originally implemented as a branch of gcc, and now reimplemented in
857:
1176:
DataRaceBench is a benchmark suite designed to systematically and quantitatively evaluate data race detection tools which analyze multi-threaded applications written in
272:
355:
335:
249:
2348:
1150:, a sampling based, SIMD vectorization optimization and shared memory threading assistance tool for C, C++, C#, and Fortran software developers and architects;
2017:
937:
916:
By contrast, a draft C++ specification does not directly require an SC for DRF property, but merely observes that there exists a theorem providing it:
500:
Assume that two threads each increment the value of a global integer variable by 1. Ideally, the following sequence of operations would take place:
1018:
Two or more programs may collide in their attempts to modify or access a file system, which can result in data corruption or privilege escalation.
607:
In the case shown above, the final value is 2, as expected. However, if the two threads run simultaneously without locking or synchronization (via
740:
write; this could result in memory corruption if the resulting value is one that neither thread attempted to write (sometimes this is called a '
2074:
1992:
2438:
948:
with processor consistency special operations) models. DRFrlx provides a sketch of an SC for DRF theorem in the presence of relaxed atomics.
453:. Critical race conditions often happen when the processes or threads depend on some shared state. Operations upon shared states are done in
193:
1022:
provides a commonly used solution. A more cumbersome remedy involves organizing the system in such a way that one unique process (running a
2290:
741:
384:
occurs when the order in which internal variables are changed does not determine the eventual state that the state machine will end up in.
1691:
2162:
1146:, a memory and thread checking and debugging tool to increase the reliability, security, and accuracy of C/C++ and Fortran applications;
357:
changes from false to true then a brief period will ensue during which both inputs are true, and so the gate's output will also be true.
1911:
905:
that the code is correctly synchronized is made, the programmer does not need to worry that reorderings will affect his or her code.
410:
occurs when an input has two transitions in less than the total feedback propagation time. Sometimes they are cured using inductive
1835:
1507:
3057:
3052:
2124:
1440:
1932:
Fuhrer, R.M.; Lin, B.; Nowick, S.M. (March 1995). "Algorithms for the optimal state assignment of asynchronous state machines".
900:
If a program is correctly synchronized, then all executions of the program will appear to be sequentially consistent (§17.4.3).
3077:
2419:
885:
An important facet of data races is that in some contexts, a program that is free of data races is guaranteed to execute in a
1949:
1666:
890:
compared to approaches which guarantee sequential consistency in all cases, or approaches which do not guarantee it at all).
2459:
2686:
1967:
1165:
tool for detecting synchronisation errors in C, C++ and
Fortran programs that use the POSIX pthreads threading primitives.
3047:
2709:
1314:
611:), the outcome of the operation could be wrong. The alternative sequence of operations below demonstrates this scenario:
1649:
Colesa, Adrian; Tudoran, Radu; Banescu, Sebastian (2008). "Software Random Number
Generation Based on Race Conditions".
1379:
1358:
815:
The parts of this definition relating to signal handlers are idiosyncratic to C++ and are not typical of definitions of
3067:
2598:
2157:
2147:
2067:
1284:
1121:
Many software tools exist to help detect race conditions in software. They can be largely categorized into two groups:
2454:
1032:
128:
on the sequence or timing of other uncontrollable events, leading to unexpected or inconsistent results. It becomes a
2704:
2681:
2152:
732:
due to timing even in a program without data races, for example, in a program in which all memory accesses use only
2283:
1003:
281:
1068:
897:
A program is correctly synchronized if and only if all sequentially consistent executions are free of data races.
2676:
2491:
1985:
17:
2014:
2783:
2697:
2646:
2097:
1007:
3007:
2841:
2692:
2379:
2257:
2223:
2060:
1567:"CVE-2015-8461: A race condition when handling socket errors can lead to an assertion failure in resolver.c"
1458:
1289:
992:
729:
1049:
3026:
2972:
2432:
2276:
2233:
2218:
2213:
2008:
1570:
1259:
1110:
434:
932:
The DRF1 memory model provides SC for DRF and allows the optimizations of the WO (weak ordering), RCsc (
2951:
2746:
2631:
2593:
2443:
2333:
484:
465:
1480:
838:
x and y conflict, and they are not ordered by the hb1 relation of the execution. The race 〈x,y〉, is a
2967:
2946:
2891:
2778:
2768:
2741:
2603:
2208:
2107:
1328:
1205:
469:
373:
occurs when the order in which internal variables are changed determines the eventual state that the
2000:
1423:
2921:
2547:
2486:
2399:
1126:
1094:
1071:, in which case the performance of the program can be dependent on the speed of the network link.
756:
operations, whereas the ordinary operations (which are unsafe for simultaneous access) are called
2982:
2977:
2836:
2427:
2238:
1172:
There are several benchmarks designed to evaluate the effectiveness of data race detection tools
1122:
886:
608:
426:
encourage designers to recognize and eliminate race conditions before they cause problems. Often
446:
behavior. A race can also occur between two programs, resulting in security issues (see below.)
3072:
2721:
2653:
2557:
2449:
2404:
1695:
1530:
Kourosh
Gharachorloo and Sarita V. Adve and Anoop Gupta and John L. Hennessy and Mark D. Hill,
988:
2813:
2773:
2726:
2716:
2511:
2374:
2313:
2112:
1651:
2008 10th
International Symposium on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing
1228:
941:
155:
1856:
Schmidt, Robert; Leventhal, Daniel K; Mallet, Nicolas; Chen, Fujun; Berke, Joshua D (2013).
1531:
254:
3062:
2753:
2641:
2636:
2626:
2613:
2409:
2083:
1909:
Karam, G.M.; Buhr, R.J.A. (August 1990). "Starvation and
Critical Race Analyzers for Ada".
1113:. GE Energy later developed a software patch to correct the previously undiscovered error.
1080:
965:
31:
1625:"security: stat cache *very large* race condition if caching when follow_symlink disabled"
464:
A data race is a type of race condition. Data races are important parts of various formal
8:
2916:
2871:
2671:
2537:
2102:
1978:
A Novel
Framework for Solving the State Assignment Problem for Event-Based Specifications
1254:
1090:
machine, which led to the death of at least three patients and injuries to several more.
945:
933:
846:
Here we have two memory operations accessing the same location, one of which is a write.
787:, in draft N4296 (2014-11-19), defines data race as follows in section 1.10.23 (page 14)
1993:"Secure programmer: Prevent race conditions—Resource contention can be used against you"
1599:
1545:
2941:
2790:
2763:
2588:
2552:
2542:
2501:
2343:
2323:
2318:
2299:
1955:
1882:
1857:
1739:
1672:
1498:
1439:
Adve, Sarita & Hill, Mark & Miller, Barton & H. B. Netzer, Robert. (1991).
1236:
1224:
Neuroscience is demonstrating that race conditions can occur in mammal brains as well.
1023:
477:
340:
320:
234:
151:
2987:
2663:
2621:
2516:
1981:
1945:
1887:
1793:
1662:
1274:
1087:
961:
957:
860:" which are safe for potentially simultaneous use, in contrast to "data operations".
775:
411:
62:
849:
The hb1 relation is defined elsewhere in the paper, and is an example of a typical "
2997:
2796:
2731:
2578:
2394:
2389:
2384:
2353:
2172:
2139:
1959:
1937:
1920:
1877:
1869:
1676:
1654:
1340:
1106:
733:
483:
A race condition can be difficult to reproduce and debug because the end result is
458:
454:
427:
159:
140:
125:
2035:
1757:
2861:
2801:
2736:
2583:
2573:
2506:
2496:
2338:
2328:
2129:
2119:
2021:
1971:
1964:
1775:
1443:. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News. 19. 234–243. 10.1109/ISCA.1991.1021616.
1269:
1168:
Data Race
Detector is designed to find data races in the Go Programming language.
1143:
1060:
1056:
1534:, Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 1992, volume 15, pages 399–407.
2808:
2465:
2358:
1941:
1264:
1249:
972:
850:
492:". It is therefore better to avoid race conditions by careful software design.
971:
A specific kind of race condition involves checking for a predicate (e.g. for
3041:
2881:
2758:
2187:
1718:
1709:
1147:
374:
147:
2167:
1481:"Semantics of Shared Variables & Synchronization (a.k.a. Memory Models)"
2481:
2177:
1891:
1830:
1658:
1624:
1294:
1279:
1019:
984:
450:
423:
180:
129:
2036:"Interview with Dmitriy Vyukov - the author of Relacy Race Detector (RRD)"
768:
operations, such a race may be nondeterministic but otherwise safe; but a
3002:
2203:
2042:
1977:
1713:
1401:
872:
cause incorrect behavior such as returning the wrong length for an array.
113:
1811:
1359:"ISO/IEC 9899:2011 - Information technology - Programming languages - C"
1193:
975:), then acting on the predicate, while the state can change between the
802:
they are unsequenced, and at least one is performed by a signal handler.
764:
race; on many platforms, where there is a race condition involving only
69:
changes from low to high, the circuit outputs a short spike of duration
2052:
2047:
1405:
1067:
Race conditions can also exist when a computer program is written with
1064:
centralized one (at least for that one part of the network operation).
414:
elements to effectively increase the time duration of an input signal.
171:
2030:, with sample source code and comparison to C code, by Chiral Software
1553:
Efficient
Coherence and Consistency for Specialized Memory Hierarchies
1344:
2876:
2851:
2268:
1924:
1500:
Designing Memory Consistency Models For Shared-Memory Multiprocessors
1098:
1084:
489:
476:
standards specify that a C or C++ program containing a data race has
143:'s doctoral thesis "The synthesis of sequential switching circuits".
1873:
1546:"Chapter 3: Efficient Support for and Evaluation of Relaxed Atomics"
2926:
2906:
2831:
1628:
1162:
1154:
275:
187:
117:
27:
When a system's behavior depends on timing of uncontrollable events
1858:"Canceling actions involves a race between basal ganglia pathways"
776:
Example definitions of data races in particular concurrency models
2931:
2911:
2886:
2521:
1934:
Advanced Research in VLSI, 1995. Proceedings., 16th Conference on
1232:
473:
337:
take longer to propagate to the second input than the first when
37:
2901:
2896:
1177:
1161:-based instrumentation, and supports PThreads; and Helgrind, a
1083:
can be disastrous. Race conditions were among the flaws in the
880:
176:
121:
30:"Critical race" redirects here. For the academic movement, see
1133:
162:
can prevent race conditions in distributed software systems.
1600:"Vulnerability in rmtree() and remove_tree(): CVE-2017-6512"
893:
For example, in Java, this guarantee is directly specified:
772:
race could lead to memory corruption or undefined behavior.
2936:
2866:
2856:
2182:
1603:
1158:
1102:
132:
when one or more of the possible behaviors is undesirable.
1855:
461:. Failure to obey this rule can corrupt the shared state.
2846:
2823:
1045:
835:
433:
As well as these problems, some logic elements can enter
278:), on another input in theory never output a true value:
1044:
In networking, consider a distributed chat network like
437:, which create further problems for circuit designers.
387:
224:{\displaystyle {\text{output}}=A\wedge {\overline {A}}}
170:
A typical example of a race condition may occur when a
1424:"Working Draft, Standard for Programming Language C++"
1231:, a race condition would arise in the carrying out of
1055:
In this case of a race condition, the concept of the "
1002:
Race conditions are also intentionally used to create
396:
occurs when a signal and its complement are combined.
449:
Critical race conditions cause invalid execution and
343:
323:
284:
257:
237:
196:
1648:
2028:
Race conditions, security, and immutability in Java
1617:
1532:
Programming for Different Memory Consistency Models
1555:(PhD). University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign.
364:
349:
329:
309:
266:
243:
223:
1740:"Thread Safety Analysis – Clang 10 documentation"
3039:
1594:
1592:
2024:" (Secure Programming for Linux and Unix HOWTO)
1931:
1834:. Discover Magazine. 2013-08-03. Archived from
1315:The synthesis of sequential switching circuits.
842:iff at least one of x or y is a data operation.
430:can be added to eliminate some kinds of races.
956:Many software race conditions have associated
2284:
2068:
1692:"An Investigation of Therac-25 Accidents – I"
1589:
1559:
760:operations. This is probably why the term is
310:{\displaystyle A\wedge {\overline {A}}\neq 1}
1826:"How Brains Race to Cancel Errant Movements"
1329:"Hazards, Critical Races, and Metastability"
881:Sequential Consistency for Data Race Freedom
65:of the logic elements. When the input value
1441:Detecting Data Races on Weak Memory Systems
824:Detecting Data Races on Weak Memory Systems
799:they are performed by different threads, or
139:was already in use by 1954, for example in
124:where the system's substantive behavior is
2291:
2277:
2075:
2061:
1758:"ThreadSanitizer – Clang 10 documentation"
1912:IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering
1908:
1881:
1689:
1478:
41:Race condition in a logic circuit. Here,
2082:
1543:
1479:Adve, Sarita V.; Boehm, Hans-J. (2010).
1074:
1052:by various IRC server implementations.)
146:Race conditions can occur especially in
36:
1990:
1708:
1474:
1472:
317:. If, however, changes in the value of
14:
3040:
2298:
2033:
1453:
1451:
1449:
1400:
806:The execution of a program contains a
2272:
2056:
1326:
987:exists in security-sensitive code, a
1991:Wheeler, David A. (7 October 2004).
1496:
1469:
1188:
1153:ThreadSanitizer, which uses binary (
951:
388:Static, dynamic, and essential forms
1980:" by Luciano Lavagno, Cho W. Moon,
1814:. July 25, 2019 – via GitHub.
1776:"Helgrind: a thread error detector"
1694:. Courses.cs.vt.edu. Archived from
1446:
186:Consider, for example, a two-input
24:
1285:Synchronization (computer science)
468:. The memory model defined in the
258:
179:but if this output functions as a
175:Certain systems can tolerate such
25:
3089:
1902:
1690:Leveson, Nancy; Turner, Clark S.
1184:
1139:Dynamic analysis tools include:
1004:hardware random number generators
867:provides a different definition:
826:provides a different definition:
165:
3021:
3020:
2252:
2251:
1544:Sinclair, Matthew David (2017).
1192:
748:simultaneous access) are called
2492:Analysis of parallel algorithms
2034:Karpov, Andrey (6 April 2009).
1986:Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli
1849:
1818:
1804:
1786:
1768:
1750:
1732:
1702:
1683:
1642:
1537:
1524:
1513:from the original on 2021-12-09
1490:
1459:"Chapter 17. Threads and Locks"
1111:North American Blackout of 2003
1013:
1008:physically unclonable functions
365:Critical and non-critical forms
251:on one input and its negation,
3058:Distributed computing problems
3053:Concurrency (computer science)
2258:Category: Concurrent computing
1497:Adve, Sarita (December 1993).
1433:
1416:
1406:"Race Condition vs. Data Race"
1394:
1372:
1351:
1333:IEEE Transactions on Computers
1320:
1307:
440:
417:
190:fed with the following logic:
13:
1:
3078:Timing in electronic circuits
2439:Simultaneous and heterogenous
2043:Microsoft Support description
1300:
1039:
3027:Category: Parallel computing
2048:Race Condition vs. Data Race
1290:Time of check to time of use
993:time-of-check-to-time-of-use
722:
296:
216:
7:
2219:Dining philosophers problem
1812:"Data race benchmark suite"
1714:"Tracking the blackout bug"
1571:Internet Systems Consortium
1243:
865:Java Language Specification
382:non-critical race condition
10:
3094:
3048:Computer security exploits
2334:High-performance computing
2108:Concurrent data structures
1942:10.1109/ARVLSI.1995.515611
858:synchronization operations
495:
422:Design techniques such as
29:
3068:Logic in computer science
3016:
2968:Automatic parallelization
2960:
2822:
2662:
2612:
2604:Application checkpointing
2566:
2530:
2474:
2418:
2367:
2306:
2247:
2224:Producer–consumer problem
2209:Cigarette smokers problem
2196:
2138:
2090:
1327:Unger, S.H. (June 1995).
158:software programs. Using
1116:
1095:energy management system
408:essential race condition
2983:Embarrassingly parallel
2978:Deterministic algorithm
2239:Sleeping barber problem
2234:Readers–writers problem
1382:. ISO. 2 September 2011
1136:, supporting PThreads.
1093:Another example is the
887:sequentially consistent
830:"two memory operations
371:critical race condition
112:is the condition of an
2698:Associative processing
2654:Non-blocking algorithm
2460:Clustered multi-thread
2113:Concurrent hash tables
1659:10.1109/synasc.2008.36
989:security vulnerability
922:
914:
874:
844:
813:
793:potentially concurrent
401:dynamic race condition
351:
331:
311:
268:
267:{\displaystyle \neg A}
245:
225:
101:
2814:Hardware acceleration
2727:Superscalar processor
2717:Dataflow architecture
2314:Distributed computing
2015:Avoid Race Conditions
1229:UK railway signalling
1081:life-critical systems
1075:Life-critical systems
942:Processor Consistency
918:
895:
869:
828:
789:
394:static race condition
352:
332:
312:
269:
246:
226:
40:
2693:Pipelined processing
2642:Explicit parallelism
2637:Implicit parallelism
2627:Dataflow programming
2084:Concurrent computing
2006:on February 1, 2009.
1794:"Data Race Detector"
1653:. pp. 439–444.
1410:Embedded in Academia
1380:"ISO/IEC 14882:2011"
1069:non-blocking sockets
983:. When this kind of
966:privilege escalation
341:
321:
282:
255:
235:
194:
32:Critical race theory
2917:Parallel Extensions
2722:Pipelined processor
2103:Concurrency control
1862:Nature Neuroscience
1313:Huffman, David A. "
1255:Concurrency control
1157:-based) or source,
1033:Mars Rover "Spirit"
946:Release Consistency
934:Release Consistency
2791:Massively parallel
2769:distributed shared
2589:Cache invalidation
2553:Instruction window
2344:Manycore processor
2324:Massively parallel
2319:Parallel computing
2300:Parallel computing
2020:2014-03-09 at the
1997:IBM developerWorks
1970:2021-06-10 at the
1936:. pp. 59–75.
1204:. You can help by
1079:Software flaws in
999:) bug is created.
478:undefined behavior
459:mutually exclusive
347:
327:
307:
264:
241:
221:
102:
63:propagation delays
3035:
3034:
2988:Parallel slowdown
2622:Stream processing
2512:Karp–Flatt metric
2266:
2265:
1982:Robert K. Brayton
1951:978-0-8186-7047-3
1668:978-0-7695-3523-4
1345:10.1109/12.391185
1275:Racetrack problem
1222:
1221:
1088:radiation therapy
962:denial of service
958:computer security
952:Computer security
938:Total Store Order
734:atomic operations
716:
715:
605:
604:
455:critical sections
435:metastable states
350:{\displaystyle A}
330:{\displaystyle A}
299:
244:{\displaystyle A}
219:
200:
16:(Redirected from
3085:
3024:
3023:
2998:Software lockout
2797:Computer cluster
2732:Vector processor
2687:Array processing
2672:Flynn's taxonomy
2579:Memory coherence
2354:Computer network
2293:
2286:
2279:
2270:
2269:
2255:
2254:
2197:Classic problems
2173:Ambient calculus
2120:Concurrent users
2077:
2070:
2063:
2054:
2053:
2039:
2007:
2005:
1999:. Archived from
1963:
1928:
1925:10.1109/32.57622
1896:
1895:
1885:
1853:
1847:
1846:
1844:
1843:
1822:
1816:
1815:
1808:
1802:
1801:
1790:
1784:
1783:
1772:
1766:
1765:
1754:
1748:
1747:
1736:
1730:
1729:
1727:
1726:
1706:
1700:
1699:
1687:
1681:
1680:
1646:
1640:
1639:
1637:
1635:
1621:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1610:
1596:
1587:
1586:
1584:
1582:
1573:. Archived from
1563:
1557:
1556:
1550:
1541:
1535:
1528:
1522:
1521:
1519:
1518:
1512:
1505:
1494:
1488:
1487:
1485:
1476:
1467:
1466:
1455:
1444:
1437:
1431:
1430:
1428:
1420:
1414:
1413:
1398:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1387:
1376:
1370:
1369:
1367:
1366:
1355:
1349:
1348:
1324:
1318:
1311:
1217:
1214:
1196:
1189:
1127:dynamic analysis
1107:FirstEnergy Corp
791:Two actions are
614:
613:
503:
502:
485:nondeterministic
428:logic redundancy
377:will end up in.
356:
354:
353:
348:
336:
334:
333:
328:
316:
314:
313:
308:
300:
292:
276:Boolean negation
273:
271:
270:
265:
250:
248:
247:
242:
230:
228:
227:
222:
220:
212:
201:
198:
160:mutual exclusion
141:David A. Huffman
99:
68:
60:
50:
21:
3093:
3092:
3088:
3087:
3086:
3084:
3083:
3082:
3038:
3037:
3036:
3031:
3012:
2956:
2862:Coarray Fortran
2818:
2802:Beowulf cluster
2658:
2608:
2599:Synchronization
2584:Cache coherence
2574:Multiprocessing
2562:
2526:
2507:Cost efficiency
2502:Gustafson's law
2470:
2414:
2363:
2339:Multiprocessing
2329:Cloud computing
2302:
2297:
2267:
2262:
2243:
2192:
2140:Process calculi
2134:
2130:Linearizability
2086:
2081:
2022:Wayback Machine
2003:
1972:Wayback Machine
1952:
1905:
1900:
1899:
1874:10.1038/nn.3456
1854:
1850:
1841:
1839:
1824:
1823:
1819:
1810:
1809:
1805:
1792:
1791:
1787:
1774:
1773:
1769:
1756:
1755:
1751:
1738:
1737:
1733:
1724:
1722:
1707:
1703:
1688:
1684:
1669:
1647:
1643:
1633:
1631:
1623:
1622:
1618:
1608:
1606:
1598:
1597:
1590:
1580:
1578:
1565:
1564:
1560:
1548:
1542:
1538:
1529:
1525:
1516:
1514:
1510:
1503:
1495:
1491:
1483:
1477:
1470:
1463:docs.oracle.com
1457:
1456:
1447:
1438:
1434:
1426:
1422:
1421:
1417:
1399:
1395:
1385:
1383:
1378:
1377:
1373:
1364:
1362:
1357:
1356:
1352:
1325:
1321:
1312:
1308:
1303:
1270:Linearizability
1246:
1218:
1212:
1209:
1202:needs expansion
1187:
1144:Intel Inspector
1123:static analysis
1119:
1077:
1057:shared resource
1042:
1016:
954:
883:
778:
766:synchronization
754:synchronization
725:
498:
443:
420:
390:
367:
342:
339:
338:
322:
319:
318:
291:
283:
280:
279:
256:
253:
252:
236:
233:
232:
231:A logic signal
211:
197:
195:
192:
191:
168:
98:
91:
84:
77:
70:
66:
59:
52:
49:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
18:Race conditions
15:
12:
11:
5:
3091:
3081:
3080:
3075:
3070:
3065:
3060:
3055:
3050:
3033:
3032:
3030:
3029:
3017:
3014:
3013:
3011:
3010:
3005:
3000:
2995:
2993:Race condition
2990:
2985:
2980:
2975:
2970:
2964:
2962:
2958:
2957:
2955:
2954:
2949:
2944:
2939:
2934:
2929:
2924:
2919:
2914:
2909:
2904:
2899:
2894:
2889:
2884:
2879:
2874:
2869:
2864:
2859:
2854:
2849:
2844:
2839:
2834:
2828:
2826:
2820:
2819:
2817:
2816:
2811:
2806:
2805:
2804:
2794:
2788:
2787:
2786:
2781:
2776:
2771:
2766:
2761:
2751:
2750:
2749:
2744:
2737:Multiprocessor
2734:
2729:
2724:
2719:
2714:
2713:
2712:
2707:
2702:
2701:
2700:
2695:
2690:
2679:
2668:
2666:
2660:
2659:
2657:
2656:
2651:
2650:
2649:
2644:
2639:
2629:
2624:
2618:
2616:
2610:
2609:
2607:
2606:
2601:
2596:
2591:
2586:
2581:
2576:
2570:
2568:
2564:
2563:
2561:
2560:
2555:
2550:
2545:
2540:
2534:
2532:
2528:
2527:
2525:
2524:
2519:
2514:
2509:
2504:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2484:
2478:
2476:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2468:
2466:Hardware scout
2463:
2457:
2452:
2447:
2441:
2436:
2430:
2424:
2422:
2420:Multithreading
2416:
2415:
2413:
2412:
2407:
2402:
2397:
2392:
2387:
2382:
2377:
2371:
2369:
2365:
2364:
2362:
2361:
2359:Systolic array
2356:
2351:
2346:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2321:
2316:
2310:
2308:
2304:
2303:
2296:
2295:
2288:
2281:
2273:
2264:
2263:
2261:
2260:
2248:
2245:
2244:
2242:
2241:
2236:
2231:
2229:Race condition
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2200:
2198:
2194:
2193:
2191:
2190:
2185:
2180:
2175:
2170:
2165:
2160:
2155:
2150:
2144:
2142:
2136:
2135:
2133:
2132:
2127:
2122:
2117:
2116:
2115:
2105:
2100:
2094:
2092:
2088:
2087:
2080:
2079:
2072:
2065:
2057:
2051:
2050:
2045:
2040:
2031:
2025:
2011:
1988:
1974:
1950:
1929:
1919:(8): 829–843.
1904:
1903:External links
1901:
1898:
1897:
1868:(8): 1118–24.
1848:
1817:
1803:
1785:
1767:
1762:clang.llvm.org
1749:
1744:clang.llvm.org
1731:
1712:(2004-04-07).
1710:Poulsen, Kevin
1701:
1698:on 2017-12-15.
1682:
1667:
1641:
1616:
1588:
1577:on 9 June 2016
1558:
1536:
1523:
1506:(PhD thesis).
1489:
1468:
1445:
1432:
1415:
1404:(2011-03-13).
1393:
1371:
1350:
1339:(6): 754–768.
1319:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1299:
1298:
1297:
1292:
1287:
1282:
1277:
1272:
1267:
1265:Hazard (logic)
1262:
1257:
1252:
1250:Call collision
1245:
1242:
1220:
1219:
1199:
1197:
1186:
1185:In other areas
1183:
1182:
1181:
1170:
1169:
1166:
1151:
1118:
1115:
1076:
1073:
1041:
1038:
1015:
1012:
973:authentication
953:
950:
882:
879:
851:happens-before
804:
803:
800:
777:
774:
730:nondeterminism
724:
721:
714:
713:
710:
707:
704:
701:
700:
697:
694:
692:
688:
687:
684:
682:
681:increase value
679:
676:
675:
672:
670:
668:
667:increase value
664:
663:
660:
657:
654:
651:
650:
647:
644:
642:
638:
637:
634:
632:
630:
627:
626:
625:Integer value
623:
621:
618:
603:
602:
599:
596:
593:
590:
589:
586:
584:
583:increase value
581:
578:
577:
574:
571:
568:
565:
564:
561:
558:
556:
552:
551:
548:
546:
544:
543:increase value
540:
539:
536:
533:
531:
527:
526:
523:
521:
519:
516:
515:
514:Integer value
512:
510:
507:
497:
494:
442:
439:
419:
416:
389:
386:
366:
363:
346:
326:
306:
303:
298:
295:
290:
287:
263:
260:
240:
218:
215:
210:
207:
204:
167:
166:In electronics
164:
148:logic circuits
137:race condition
106:race condition
96:
89:
82:
75:
61:represent the
57:
47:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3090:
3079:
3076:
3074:
3073:Software bugs
3071:
3069:
3066:
3064:
3061:
3059:
3056:
3054:
3051:
3049:
3046:
3045:
3043:
3028:
3019:
3018:
3015:
3009:
3006:
3004:
3001:
2999:
2996:
2994:
2991:
2989:
2986:
2984:
2981:
2979:
2976:
2974:
2971:
2969:
2966:
2965:
2963:
2959:
2953:
2950:
2948:
2945:
2943:
2940:
2938:
2935:
2933:
2930:
2928:
2925:
2923:
2920:
2918:
2915:
2913:
2910:
2908:
2905:
2903:
2900:
2898:
2895:
2893:
2890:
2888:
2885:
2883:
2882:Global Arrays
2880:
2878:
2875:
2873:
2870:
2868:
2865:
2863:
2860:
2858:
2855:
2853:
2850:
2848:
2845:
2843:
2840:
2838:
2835:
2833:
2830:
2829:
2827:
2825:
2821:
2815:
2812:
2810:
2809:Grid computer
2807:
2803:
2800:
2799:
2798:
2795:
2792:
2789:
2785:
2782:
2780:
2777:
2775:
2772:
2770:
2767:
2765:
2762:
2760:
2757:
2756:
2755:
2752:
2748:
2745:
2743:
2740:
2739:
2738:
2735:
2733:
2730:
2728:
2725:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2711:
2708:
2706:
2703:
2699:
2696:
2694:
2691:
2688:
2685:
2684:
2683:
2680:
2678:
2675:
2674:
2673:
2670:
2669:
2667:
2665:
2661:
2655:
2652:
2648:
2645:
2643:
2640:
2638:
2635:
2634:
2633:
2630:
2628:
2625:
2623:
2620:
2619:
2617:
2615:
2611:
2605:
2602:
2600:
2597:
2595:
2592:
2590:
2587:
2585:
2582:
2580:
2577:
2575:
2572:
2571:
2569:
2565:
2559:
2556:
2554:
2551:
2549:
2546:
2544:
2541:
2539:
2536:
2535:
2533:
2529:
2523:
2520:
2518:
2515:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2503:
2500:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2490:
2488:
2485:
2483:
2480:
2479:
2477:
2473:
2467:
2464:
2461:
2458:
2456:
2453:
2451:
2448:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2434:
2431:
2429:
2426:
2425:
2423:
2421:
2417:
2411:
2408:
2406:
2403:
2401:
2398:
2396:
2393:
2391:
2388:
2386:
2383:
2381:
2378:
2376:
2373:
2372:
2370:
2366:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2350:
2347:
2345:
2342:
2340:
2337:
2335:
2332:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2322:
2320:
2317:
2315:
2312:
2311:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2294:
2289:
2287:
2282:
2280:
2275:
2274:
2271:
2259:
2250:
2249:
2246:
2240:
2237:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2201:
2199:
2195:
2189:
2188:Join-calculus
2186:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2176:
2174:
2171:
2169:
2166:
2164:
2161:
2159:
2156:
2154:
2151:
2149:
2146:
2145:
2143:
2141:
2137:
2131:
2128:
2126:
2125:Indeterminacy
2123:
2121:
2118:
2114:
2111:
2110:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2099:
2096:
2095:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2078:
2073:
2071:
2066:
2064:
2059:
2058:
2055:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2037:
2032:
2029:
2026:
2023:
2019:
2016:
2012:
2010:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1989:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1973:
1969:
1966:
1961:
1957:
1953:
1947:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1918:
1914:
1913:
1907:
1906:
1893:
1889:
1884:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1852:
1838:on 2013-08-06
1837:
1833:
1832:
1827:
1821:
1813:
1807:
1799:
1795:
1789:
1781:
1777:
1771:
1763:
1759:
1753:
1745:
1741:
1735:
1721:
1720:
1719:SecurityFocus
1715:
1711:
1705:
1697:
1693:
1686:
1678:
1674:
1670:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1645:
1630:
1626:
1620:
1605:
1601:
1595:
1593:
1576:
1572:
1568:
1562:
1554:
1547:
1540:
1533:
1527:
1509:
1502:
1501:
1493:
1482:
1475:
1473:
1464:
1460:
1454:
1452:
1450:
1442:
1436:
1429:. 2014-11-19.
1425:
1419:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1397:
1381:
1375:
1360:
1354:
1346:
1342:
1338:
1334:
1330:
1323:
1316:
1310:
1306:
1296:
1293:
1291:
1288:
1286:
1283:
1281:
1278:
1276:
1273:
1271:
1268:
1266:
1263:
1261:
1258:
1256:
1253:
1251:
1248:
1247:
1241:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1225:
1216:
1207:
1203:
1200:This section
1198:
1195:
1191:
1190:
1179:
1175:
1174:
1173:
1167:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1149:
1148:Intel Advisor
1145:
1142:
1141:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1130:
1128:
1124:
1114:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1082:
1072:
1070:
1065:
1062:
1058:
1053:
1051:
1047:
1037:
1034:
1028:
1025:
1021:
1011:
1009:
1005:
1000:
998:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
977:time of check
974:
969:
967:
963:
959:
949:
947:
944:), and RCpc (
943:
939:
935:
930:
926:
921:
917:
913:
912:
907:
906:
901:
898:
894:
891:
888:
878:
873:
868:
866:
861:
859:
854:
852:
847:
843:
841:
837:
833:
827:
825:
820:
818:
812:
809:
801:
798:
797:
796:
794:
788:
786:
781:
773:
771:
767:
763:
759:
755:
751:
745:
743:
737:
735:
731:
720:
711:
708:
705:
703:
702:
698:
695:
693:
690:
689:
685:
683:
680:
678:
677:
673:
671:
669:
666:
665:
661:
658:
655:
653:
652:
648:
645:
643:
640:
639:
635:
633:
631:
629:
628:
624:
622:
619:
616:
615:
612:
610:
600:
597:
594:
592:
591:
587:
585:
582:
580:
579:
575:
572:
569:
567:
566:
562:
559:
557:
554:
553:
549:
547:
545:
542:
541:
537:
534:
532:
529:
528:
524:
522:
520:
518:
517:
513:
511:
508:
505:
504:
501:
493:
491:
486:
481:
479:
475:
471:
467:
466:memory models
462:
460:
457:that must be
456:
452:
451:software bugs
447:
438:
436:
431:
429:
425:
424:Karnaugh maps
415:
413:
409:
404:
402:
397:
395:
385:
383:
378:
376:
375:state machine
372:
362:
358:
344:
324:
304:
301:
293:
288:
285:
277:
261:
238:
213:
208:
205:
202:
189:
184:
182:
178:
173:
163:
161:
157:
153:
152:multithreaded
149:
144:
142:
138:
133:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
95:
88:
81:
74:
64:
56:
46:
39:
33:
19:
2992:
2567:Coordination
2497:Amdahl's law
2433:Simultaneous
2228:
2178:API-Calculus
2001:the original
1996:
1933:
1916:
1910:
1865:
1861:
1851:
1840:. Retrieved
1836:the original
1831:Neuroskeptic
1829:
1820:
1806:
1797:
1788:
1779:
1770:
1761:
1752:
1743:
1734:
1723:. Retrieved
1717:
1704:
1696:the original
1685:
1650:
1644:
1632:. Retrieved
1619:
1607:. Retrieved
1579:. Retrieved
1575:the original
1561:
1552:
1539:
1526:
1515:. Retrieved
1499:
1492:
1462:
1435:
1418:
1409:
1402:Regehr, John
1396:
1384:. Retrieved
1374:
1363:. Retrieved
1353:
1336:
1332:
1322:
1309:
1295:Test-and-set
1280:Symlink race
1226:
1223:
1213:October 2016
1210:
1206:adding to it
1201:
1171:
1138:
1131:
1120:
1101:and used by
1097:provided by
1092:
1078:
1066:
1054:
1043:
1029:
1020:File locking
1017:
1014:File systems
1001:
996:
980:
976:
970:
955:
940:), PSO, PC (
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
909:
908:
903:
902:
899:
896:
892:
884:
875:
870:
864:
862:
855:
848:
845:
839:
831:
829:
823:
821:
816:
814:
807:
805:
792:
790:
785:C++ standard
784:
782:
779:
769:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
746:
738:
726:
717:
606:
499:
482:
463:
448:
444:
432:
421:
407:
405:
400:
398:
393:
391:
381:
379:
370:
368:
359:
274:(the ¬ is a
185:
181:clock signal
169:
145:
136:
134:
109:
105:
103:
93:
86:
79:
72:
54:
44:
3063:Logic gates
3003:Scalability
2764:distributed
2647:Concurrency
2614:Programming
2455:Cooperative
2444:Speculative
2380:Instruction
2204:ABA problem
2098:Concurrency
1386:3 September
981:time of use
441:In software
418:Workarounds
156:distributed
120:, or other
114:electronics
110:race hazard
3042:Categories
3008:Starvation
2747:asymmetric
2482:PRAM model
2450:Preemptive
2168:π-calculus
1842:2013-08-07
1725:2011-09-19
1517:2021-12-09
1365:2018-01-30
1301:References
1125:tools and
1040:Networking
822:The paper
742:torn write
706:write back
691:write back
656:read value
641:read value
609:semaphores
595:write back
570:read value
555:write back
530:read value
412:delay line
172:logic gate
2742:symmetric
2487:PEM model
2013:Chapter "
1361:. Iso.org
1317:" (1954).
1099:GE Energy
1085:Therac-25
991:called a
840:data race
817:data race
808:data race
723:Data race
490:Heisenbug
302:≠
297:¯
289:∧
259:¬
217:¯
209:∧
135:The term
126:dependent
2973:Deadlock
2961:Problems
2927:pthreads
2907:OpenHMPP
2832:Ateji PX
2793:computer
2664:Hardware
2531:Elements
2517:Slowdown
2428:Temporal
2410:Pipeline
2214:Deadlock
2018:Archived
1968:Archived
1892:23852117
1780:Valgrind
1629:lighttpd
1508:Archived
1260:Deadlock
1244:See also
1163:Valgrind
1155:Valgrind
979:and the
832:conflict
620:Thread 2
617:Thread 1
509:Thread 2
506:Thread 1
188:AND gate
177:glitches
118:software
2932:RaftLib
2912:OpenACC
2887:GPUOpen
2877:C++ AMP
2852:Charm++
2594:Barrier
2538:Process
2522:Speedup
2307:General
2091:General
2009:Alt URL
1976:Paper "
1960:4435912
1883:3733500
1677:1586029
1237:Winwick
1233:Rule 55
1129:tools.
1105:-based
1061:latency
997:TOCTTOU
496:Example
3025:
2902:OpenCL
2897:OpenMP
2842:Chapel
2759:shared
2754:Memory
2689:(SIMT)
2632:Models
2543:Thread
2475:Theory
2446:(SpMT)
2400:Memory
2385:Thread
2368:Levels
2256:
1984:, and
1965:as PDF
1958:
1948:
1890:
1880:
1798:Golang
1675:
1665:
1634:5 June
1609:5 June
1581:5 June
1178:OpenMP
1050:solved
1024:daemon
750:atomic
199:output
122:system
2872:Dryad
2837:Boost
2558:Array
2548:Fiber
2462:(CMT)
2435:(SMT)
2349:GPGPU
2163:LOTOS
2004:(PDF)
1956:S2CID
1673:S2CID
1549:(PDF)
1511:(PDF)
1504:(PDF)
1484:(PDF)
1427:(PDF)
1134:Clang
1117:Tools
474:C++11
85:) − ∆
2937:ROCm
2867:CUDA
2857:Cilk
2824:APIs
2784:COMA
2779:NUMA
2710:MIMD
2705:MISD
2682:SIMD
2677:SISD
2405:Loop
2395:Data
2390:Task
2183:PEPA
1946:ISBN
1888:PMID
1663:ISBN
1636:2017
1611:2017
1604:CPAN
1583:2017
1388:2011
1159:LLVM
1103:Ohio
1006:and
964:and
863:The
783:The
770:data
762:data
758:data
472:and
51:and
2952:ZPL
2947:TBB
2942:UPC
2922:PVM
2892:MPI
2847:HPX
2774:UMA
2375:Bit
2158:ACP
2153:CCS
2148:CSP
1938:doi
1921:doi
1878:PMC
1870:doi
1655:doi
1341:doi
1227:In
1208:.
1046:IRC
985:bug
836:iff
795:if
752:or
470:C11
406:An
154:or
150:or
130:bug
108:or
92:= ∆
78:+ ∆
3044::
1995:.
1954:.
1944:.
1917:16
1915:.
1886:.
1876:.
1866:16
1864:.
1860:.
1828:.
1796:.
1778:.
1760:.
1742:.
1716:.
1671:.
1661:.
1627:.
1602:.
1591:^
1569:.
1551:.
1471:^
1461:.
1448:^
1408:.
1337:44
1335:.
1331:.
968:.
819:.
736:.
712:1
699:1
686:0
674:0
662:0
649:0
636:0
601:2
588:1
576:1
563:1
550:0
538:0
525:0
480:.
399:A
392:A
380:A
369:A
116:,
104:A
71:(∆
2292:e
2285:t
2278:v
2076:e
2069:t
2062:v
2038:.
1962:.
1940::
1927:.
1923::
1894:.
1872::
1845:.
1800:.
1782:.
1764:.
1746:.
1728:.
1679:.
1657::
1638:.
1613:.
1585:.
1520:.
1486:.
1465:.
1412:.
1390:.
1368:.
1347:.
1343::
1215:)
1211:(
1180:.
995:(
709:→
696:→
659:←
646:←
598:→
573:←
560:→
535:←
488:"
345:A
325:A
305:1
294:A
286:A
262:A
239:A
214:A
206:A
203:=
100:.
97:1
94:t
90:2
87:t
83:2
80:t
76:1
73:t
67:A
58:2
55:t
53:∆
48:1
45:t
43:∆
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.