167:
141:
154:
180:
129:
117:
20:
166:
140:
275:
220:. Those who claimed the right to bear arms had to provide proof either of a grant of arms to them by the College, or of descent from an ancestor entitled to arms. It was for this reason that pedigrees were recorded by the visitations. Pedigrees continue to be registered at the College of Arms and kept up to date on a voluntary basis but they are not accessible to the general public without payment of a fee.
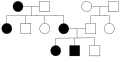
82:". Pedigrees use a standardized set of symbols, squares represent males and circles represent females. Pedigree construction is a family history, and details about an earlier generation may be uncertain as memories fade. If the sex of the person is unknown a diamond is used. Someone with the phenotype in question is represented by a filled-in (darker) symbol.
153:
179:
172:
In a X-linked recessive disorder, males are more likely to be affected than females. Affected sons typically have unaffected mothers. The father also must be affected for daughter to be affected and the mother must be affected or a carrier for the daughter to be affected. The disorder is also never
146:
In an autosomal recessive disorder, both parents can not express the trait, however, if both are carriers, their offspring can express the trait. Autosomal recessive disorders typically skip a generation, so affected offspring typically have unaffected parents. With an autosomal recessive disorder,
242:
A pedigree may be used to establish the probability of a child having a particular disorder or condition. It may be used to discover where the genes in question are located (x, y, or autosome chromosome), and to determine whether a trait is dominant or recessive. When a pedigree shows a condition
89:
Relationships in a pedigree are shown as a series of lines. Parents are connected by a horizontal line and a vertical line leads to their offspring. The offspring are connected by a horizontal sibship line and listed in birth order from left to right. If the offspring are twins then they will be
128:
159:
Autosomal dominant disorders do not skip a generation, so affected offspring have affected parents. One parent must have the disorder for its offspring to be affected. Both males and females are equally likely to be affected, so it is an autosomal
116:
185:
In a X-linked dominant disorder, if the father is affected all daughters will be affected and no sons will be affected. It does not skip a generation and if the mother is affected she has a 50% chance of passing it onto her
105:
can determine whether a trait has a dominant or recessive pattern of inheritance. Pedigrees are often constructed after a family member afflicted with a genetic disorder has been identified. This individual, known as the
134:
In mitochondrial disorders it is only passed on if the mother is affected. If the mother is affected, all offspring will be affected. If the father is affected, he does not pass it on to his offspring.
502:
306:
are formed and are dedicated to the accurate tracking of pedigrees and maintaining accurate records of birth, death and identifying characteristics of each registered animal.
484:
71:
or "crane's foot", either because the typical lines and split lines (each split leading to different offspring of the one parent line) resemble the thin leg and foot of a
90:
connected by a triangle. If an offspring dies then its symbol will be crossed by a line. If the offspring is still born or aborted it is represented by a small triangle.
122:
In a Y-linked disorder, only males can be affected. If the father is affected all sons will be affected. It also does not skip a generation.
506:
173:
passed from father to son. Only females can be carriers for the disorders. X-linked recessive disorders also typically skip a generation.
78:
A pedigree results in the presentation of family information in the form of an easily readable chart. It can be simply called as a "
438:
488:
598:
345:
538:
1121:
208:, which has records going back to the Middle Ages, including pedigrees collected during roving inquiries by its
1043:
330:
248:
1182:
842:
1276:
955:
377:
364:
1192:
1158:
298:, pedigree charts are used to track the ancestry of animals and assist in the planning of suitable
1235:
1133:
471:
320:
1286:
1199:
558:
340:
266:. Some examples of recessive traits include: small eyes, little body hair, and tall stature.
102:
97:(I, II, III, and so on), and each individual within the same generation is identified by an
1255:
1240:
1187:
1143:
1053:
985:
531:
86:, when identifiable, are indicated by a shade dot inside a symbol or a half-filled symbol.
8:
1225:
1177:
1170:
872:
829:
213:
442:
283:
224:
110:, is indicated on the pedigree by an arrow. These changes may occur yearly or monthly.
19:
414:
1281:
1153:
980:
950:
703:
588:
236:
1245:
917:
907:
902:
877:
708:
687:
583:
299:
247:. When the condition predominantly affects males in the pedigree it is considered
1148:
1128:
1116:
1048:
897:
892:
882:
772:
578:
573:
524:
205:
98:
223:
More visible, therefore, are the pedigrees recorded in published works, such as
1080:
995:
990:
912:
852:
762:
732:
568:
303:
94:
1270:
1215:
1010:
927:
857:
757:
255:
228:
217:
83:
1138:
1100:
1095:
922:
767:
287:
72:
1020:
975:
819:
713:
668:
325:
259:
79:
75:
or because such a mark was used to denote succession in pedigree charts.
1220:
1165:
1038:
1000:
862:
807:
802:
797:
789:
777:
717:
673:
401:
315:
101:(1, 2, 3, and so on). Analysis of the pedigree using the principles of
24:
1230:
937:
814:
563:
367:
Genealogy
Glossary - About.com, a part of The New York Times Company.
291:
212:
during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. The purpose of these
36:
439:"pedigree - definition of pedigree in English | Oxford Dictionaries"
1033:
970:
965:
942:
887:
847:
633:
462:
Michael R. Cummings "Human
Heredity Principles and issues" pg 59-60
335:
274:
263:
244:
44:
40:
243:
appearing in a 50:50 ratio between men and women it is considered
960:
867:
837:
750:
645:
640:
197:
107:
1250:
1090:
1085:
740:
722:
650:
616:
611:
606:
547:
232:
209:
48:
1075:
678:
623:
485:"Dominant and Recessive Genes In Humans | Science Brainwaves"
295:
201:
67:
The word pedigree is a corruption of the Anglo-Norman French
56:
1005:
745:
682:
628:
516:
147:
both males and females are equally likely to be affected.
52:
35:
is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance of
1268:
47:from one generation to the next, most commonly
532:
1019:
539:
525:
254:Some examples of dominant traits include:
231:in the United Kingdom and, in continental
204:pedigrees are officially recorded in the
378:"HELP - Ancestral File - Pedigree Chart"
273:
216:was to register and regulate the use of
18:
1269:
269:
520:
346:Certificate of Degree of Indian Blood
404:By Melody Daisson - GeneaSearch.com
278:Pedigree of horse Shagya IX b. 1895
93:Each generation is identified by a
13:
23:Example of a pedigree chart using
14:
1298:
178:
165:
152:
139:
127:
115:
402:Documenting Your Pedigree Chart
191:
1044:Genealogical numbering systems
495:
477:
465:
456:
431:
407:
395:
370:
358:
331:Genealogical numbering systems
1:
1183:International Day of Families
843:Australian Aboriginal kinship
351:
302:to enhance desirable traits.
62:
441:. 2016-09-25. Archived from
286:of animals, particularly in
7:
309:
10:
1303:
546:
1208:
1144:National Grandparents Day
1109:
1068:
936:
828:
788:
731:
696:
661:
597:
554:
415:"Definition of PEDIGREE"
39:of a particular gene or
1236:Sociology of the family
1086:Philia (brotherly love)
662:Second-degree relatives
419:www.merriam-webster.com
16:Diagram used in biology
1091:Storge (familial love)
697:Third-degree relatives
599:First-degree relatives
279:
28:
1200:National Adoption Day
1076:Agape (parental love)
341:Foundation bloodstock
277:
103:Mendelian inheritance
22:
1256:Dysfunctional family
1241:Museum of Motherhood
1188:National Family Week
1054:Quarters of nobility
503:"Selective Breeding"
214:heraldic visitations
1226:Wedding anniversary
1178:American Family Day
1134:Father–Daughter Day
1081:Eros (marital love)
830:Kinship terminology
282:In the practice of
270:In animal husbandry
1277:Classical genetics
986:collateral descent
284:selective breeding
280:
29:
1264:
1263:
1064:
1063:
981:Lineal descendant
951:Bilateral descent
704:Great-grandparent
589:Matrifocal family
300:breeding programs
237:Almanach de Gotha
1294:
1246:Astronaut family
1017:
1016:
918:Iroquois kinship
908:Sudanese kinship
903:Hawaiian kinship
878:Family of choice
709:Great-grandchild
584:Immediate family
541:
534:
527:
518:
517:
511:
510:
505:. Archived from
499:
493:
492:
487:. Archived from
481:
475:
469:
463:
460:
454:
453:
451:
450:
435:
429:
428:
426:
425:
411:
405:
399:
393:
392:
390:
388:
382:familysearch.org
374:
368:
362:
304:Breed registries
182:
169:
156:
143:
131:
119:
1302:
1301:
1297:
1296:
1295:
1293:
1292:
1291:
1267:
1266:
1265:
1260:
1204:
1105:
1060:
1049:Seize quartiers
1015:
956:Common ancestor
940:
932:
898:Chinese kinship
893:Nurture kinship
883:Fictive kinship
824:
784:
773:daughter-in-law
727:
692:
657:
593:
579:Conjugal family
574:Extended family
550:
545:
515:
514:
501:
500:
496:
483:
482:
478:
472:Pedigree Charts
470:
466:
461:
457:
448:
446:
437:
436:
432:
423:
421:
413:
412:
408:
400:
396:
386:
384:
376:
375:
371:
363:
359:
354:
312:
272:
225:Burke's Peerage
206:College of Arms
194:
187:
183:
174:
170:
161:
157:
148:
144:
135:
132:
123:
120:
65:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1300:
1290:
1289:
1284:
1279:
1262:
1261:
1259:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1212:
1210:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1202:
1197:
1196:
1195:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1174:
1173:
1163:
1162:
1161:
1154:Children's Day
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1131:
1126:
1125:
1124:
1113:
1111:
1107:
1106:
1104:
1103:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1083:
1078:
1072:
1070:
1066:
1065:
1062:
1061:
1059:
1058:
1057:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1036:
1031:
1029:Pedigree chart
1025:
1023:
1014:
1013:
1008:
1003:
998:
996:Patrilineality
993:
991:Matrilineality
988:
983:
978:
973:
968:
963:
958:
953:
947:
945:
934:
933:
931:
930:
925:
920:
915:
913:Eskimo kinship
910:
905:
900:
895:
890:
885:
880:
875:
870:
865:
860:
855:
850:
845:
840:
834:
832:
826:
825:
823:
822:
817:
812:
811:
810:
805:
794:
792:
786:
785:
783:
782:
781:
780:
775:
765:
763:Sibling-in-law
760:
755:
754:
753:
748:
737:
735:
729:
728:
726:
725:
720:
711:
706:
700:
698:
694:
693:
691:
690:
685:
676:
671:
665:
663:
659:
658:
656:
655:
654:
653:
648:
638:
637:
636:
631:
621:
620:
619:
614:
603:
601:
595:
594:
592:
591:
586:
581:
576:
571:
569:Nuclear family
566:
561:
555:
552:
551:
544:
543:
536:
529:
521:
513:
512:
509:on 2009-08-02.
494:
491:on 2012-01-29.
476:
474:isite.lps.org
464:
455:
430:
406:
394:
369:
365:pedigree chart
356:
355:
353:
350:
349:
348:
343:
338:
333:
328:
323:
318:
311:
308:
271:
268:
193:
190:
189:
188:
184:
177:
175:
171:
164:
162:
158:
151:
149:
145:
138:
136:
133:
126:
124:
121:
114:
99:Arabic numeral
64:
61:
33:pedigree chart
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1299:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1274:
1272:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1216:Single parent
1214:
1213:
1211:
1207:
1201:
1198:
1194:
1191:
1190:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1172:
1169:
1168:
1167:
1164:
1160:
1157:
1156:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1123:
1120:
1119:
1118:
1115:
1114:
1112:
1108:
1102:
1099:
1097:
1094:
1092:
1089:
1087:
1084:
1082:
1079:
1077:
1074:
1073:
1071:
1069:Relationships
1067:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1018:
1012:
1011:Royal descent
1009:
1007:
1004:
1002:
999:
997:
994:
992:
989:
987:
984:
982:
979:
977:
974:
972:
969:
967:
964:
962:
959:
957:
954:
952:
949:
948:
946:
944:
939:
935:
929:
928:Omaha kinship
926:
924:
921:
919:
916:
914:
911:
909:
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
874:
871:
869:
866:
864:
861:
859:
858:Consanguinity
856:
854:
851:
849:
846:
844:
841:
839:
836:
835:
833:
831:
827:
821:
818:
816:
813:
809:
806:
804:
801:
800:
799:
796:
795:
793:
791:
787:
779:
776:
774:
771:
770:
769:
766:
764:
761:
759:
758:Parent-in-law
756:
752:
749:
747:
744:
743:
742:
739:
738:
736:
734:
733:Family-in-law
730:
724:
721:
719:
715:
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
701:
699:
695:
689:
686:
684:
680:
677:
675:
672:
670:
667:
666:
664:
660:
652:
649:
647:
644:
643:
642:
639:
635:
632:
630:
627:
626:
625:
622:
618:
615:
613:
610:
609:
608:
605:
604:
602:
600:
596:
590:
587:
585:
582:
580:
577:
575:
572:
570:
567:
565:
562:
560:
557:
556:
553:
549:
542:
537:
535:
530:
528:
523:
522:
519:
508:
504:
498:
490:
486:
480:
473:
468:
459:
445:on 2016-09-25
444:
440:
434:
420:
416:
410:
403:
398:
383:
379:
373:
366:
361:
357:
347:
344:
342:
339:
337:
334:
332:
329:
327:
324:
322:
319:
317:
314:
313:
307:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
276:
267:
265:
261:
257:
256:male baldness
252:
250:
246:
240:
238:
234:
230:
229:Landed Gentry
226:
221:
219:
218:coats of arms
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
181:
176:
168:
163:
155:
150:
142:
137:
130:
125:
118:
113:
112:
111:
109:
104:
100:
96:
95:Roman numeral
91:
87:
85:
84:Heterozygotes
81:
76:
74:
70:
60:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
26:
21:
1287:Family trees
1149:Parents' Day
1139:Siblings Day
1129:Father's Day
1117:Mother's Day
1101:Polyfidelity
1096:Filial piety
1028:
1021:Family trees
923:Crow kinship
873:Estrangement
768:Child-in-law
688:Niece/Nephew
507:the original
497:
489:the original
479:
467:
458:
447:. Retrieved
443:the original
433:
422:. Retrieved
418:
409:
397:
385:. Retrieved
381:
372:
360:
321:Cousin chart
294:, including
288:animal fancy
281:
253:
241:
227:and Burke's
222:
195:
192:In human use
92:
88:
77:
68:
66:
32:
30:
976:Inheritance
961:Family name
820:Stepsibling
714:Great-uncle
669:Grandparent
326:Family tree
260:astigmatism
80:family tree
55:, and race
1271:Categories
1221:Only child
1166:Family Day
1039:Ahnentafel
1001:Progenitor
863:Disownment
808:stepmother
803:stepfather
798:Stepparent
790:Stepfamily
778:son-in-law
718:Great-aunt
674:Grandchild
449:2023-01-10
424:2023-01-10
352:References
316:Ahnentafel
186:offspring.
69:pé de grue
63:Definition
37:phenotypes
25:Ahnentafel
1231:Godparent
938:Genealogy
815:Stepchild
564:Household
292:livestock
245:autosomal
160:disorder.
45:ancestors
27:numbering
1282:Diagrams
1110:Holidays
1034:Genogram
971:Heredity
966:Heirloom
888:Marriage
853:Affinity
848:Adoption
634:daughter
336:Genogram
310:See also
264:dwarfism
249:x-linked
43:and its
41:organism
1209:Related
943:lineage
868:Divorce
838:Kinship
751:husband
646:brother
641:Sibling
559:History
387:6 April
235:by the
210:heralds
198:England
108:proband
51:, show
1251:Incest
1171:Canada
741:Spouse
723:Cousin
651:sister
617:father
612:mother
607:Parent
548:Family
296:horses
262:, and
233:Europe
57:horses
49:humans
1159:Japan
679:Uncle
624:Child
202:Wales
73:crane
1122:U.S.
1006:Clan
941:and
746:wife
683:Aunt
389:2018
290:and
200:and
53:dogs
629:son
196:In
1273::
1193:UK
417:.
380:.
258:,
251:.
239:.
59:.
31:A
716:/
681:/
540:e
533:t
526:v
452:.
427:.
391:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.