20:
2764:
269:
951:) can trigger this repair pathway. Short stretches of single stranded DNA containing such damaged nucleotide are removed from duplex DNA by separate endonucleases effecting nicks upstream and downstream of the damage. Deletions or mutations which affect these nucleases instigate increased sensitivity to ultraviolet damage and carcinogenesis. Such abnormalities can even impinge neural development.
491:
other, and to the recognition sequence itself, are determined by the identity of the restriction endonuclease. Different endonucleases yield different sets of cuts, but one endonuclease will always cut a particular base sequence the same way, no matter what DNA molecule it is acting on. Once the cuts have been made, the DNA molecule will break into fragments.
1096:
less frequent digestion. For example, a given four-base sequence (corresponding to the recognition site for a hypothetical nuclease) would be predicted to occur every 256 base pairs on average (where 4^4=256), but any given six-base sequence would be expected to occur once every 4,096 base pairs on average (4^6=4096).
684:
enzyme is then used to join the phosphate backbones of the two molecules. The cellular origin, or even the species origin, of the sticky ends does not affect their stickiness. Any pair of complementary sequences will tend to bond, even if one of the sequences comes from a length of human DNA, and the
490:
A restriction endonuclease functions by "scanning" the length of a DNA molecule. Once it encounters its particular specific recognition sequence, it will bind to the DNA molecule and makes one cut in each of the two sugar-phosphate backbones. The positions of these two cuts, both in relation to each
1095:
The frequency at which a particular nuclease will cut a given DNA molecule depends on the complexity of the DNA and the length of the nuclease's recognition sequence; due to the statistical likelihood of finding the bases in a particular order by chance, a longer recognition sequence will result in
667:
When the enzyme encounters this sequence, it cleaves each backbone between the G and the closest A base residues. Once the cuts have been made, the resulting fragments are held together only by the relatively weak hydrogen bonds that hold the complementary bases to each other. The weakness of these
281:
A nuclease must associate with a nucleic acid before it can cleave the molecule. That entails a degree of recognition. Nucleases variously employ both nonspecific and specific associations in their modes of recognition and binding. Both modes play important roles in living organisms, especially in
668:
bonds allows the DNA fragments to separate from each other. Each resulting fragment has a protruding 5' end composed of unpaired bases. Other enzymes create cuts in the DNA backbone which result in protruding 3' ends. Protruding ends—both 3' and 5'—are sometimes called "
452:
II. These restriction enzymes generally have names that reflect their origin—The first letter of the name comes from the genus and the second two letters come from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated. For example,
759:. The polymerase elongates the new strand in the 5' → 3' direction. The exonuclease removes erroneous nucleotides from the same strand in the 3’ → 5’ direction. This exonuclease activity is essential for a DNA polymerase's ability to proofread.
685:
other comes from a length of bacterial DNA. In fact, it is this quality of stickiness that allows production of recombinant DNA molecules, molecules which are composed of DNA from different sources, and which has given birth to the
1107:
applications in complex organisms such as plants and mammals, where typically larger genomes (numbering in the billions of base pairs) would result in frequent and deleterious site-specific digestion using traditional nucleases.
859:. MutS recognizes and binds to mismatches, where it recruits MutL and MutH. MutL mediates the interaction between MutS and MutH, and enhances the endonucleasic activity of the latter. MutH recognizes hemimethylated
309:, and PvuII, this nonspecific binding involves electrostatic interactions between minimal surface area of the protein and the DNA. This weak association leaves the overall shape of the DNA undeformed, remaining in
264:
is by and large poorly conserved and minimally conserved at active sites, the surfaces of which primarily comprise acidic and basic amino acid residues. Nucleases can be classified into folding families.
1103:, which are characterized by having larger, and therefore less common, recognition sequences consisting of 12 to 40 base pairs. These nucleases are particularly useful for genetic engineering and
174:" DNA molecules. What was then needed was a tool that would cut DNA at specific sites, rather than at random sites along the length of the molecule, so that scientists could cut
337:
Some nucleases involved in DNA repair exhibit partial sequence-specificity. However most are nonspecific, instead recognizing structural abnormalities produced in the DNA
2245:
2191:
722:. Most nucleases involved in DNA repair are not sequence-specific. They recognize damage sites through deformation of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) secondary structure.
503:
II described above. Many endonucleases cleave the DNA backbones in positions that are not directly opposite each other, creating overhangs. For example, the nuclease
448:
There are more than 900 restriction enzymes, some sequence specific and some not, have been isolated from over 230 strains of bacteria since the initial discovery of
229:
706:
is an error prone process, and DNA molecules themselves are vulnerable to modification by many metabolic and environmental stressors. Ubiquitous examples include
718:. Many nucleases participate in DNA repair by recognizing damage sites and cleaving them from the surrounding DNA. These enzymes function independently or in
1618:
783:, causing the DNA polymerases and associated machinery to abandon the fork. It must then be processed by fork-specific proteins. The most notable is
252:(EC-number 3.1), a subgroup of the hydrolases. The esterases to which nucleases belong are classified with the EC-numbers 3.1.11 - EC-number 3.1.31.
162:, while the other cleaved unmethylated DNA at a wide variety of locations along the length of the molecule. The first type of enzyme was called a "
1853:
893:, where it nicks the DNA strand on the 5' side of the mismatched thymine (underlined in the previous sequence). One of the exonucleases RecJ,
2014:
840:
in any given organism is effected by a suite of mismatch-specific endonucleases. In prokaryotes, this role is primarily filled by MutSLH and
139:
1671:
2110:
702:
With all cells depending on DNA as the medium of genetic information, genetic quality control is an essential function of all organisms.
1057:
Holliday junctions into two separate dsDNAs by cleaving the junctions at two symmetrical sites near the junction centre. In eukaryotes,
985:, various exogenous and endogenous chemical agents, and halted replication forks. Intentional breaks are generated as intermediaries in
468:
strain Rd. Numbers following the nuclease names indicate the order in which the enzymes were isolated from single strains of bacteria:
1821:
1074:
1001:. Both cases require the ends in double strand breaks be processed by nucleases before repair can take place. One such nuclease is
382:
206:
1838:
2085:
1028:
participates in this reaction. Although
Artemis exhibits 5' → 3' ssDNA exonuclease activity when alone, its complexing with
1999:
958:
complex. In budding yeast, Rad2 and the Rad1-Rad10 complex make the 5' and 3' cuts, respectively. In mammals, the homologs
935:, not to be confused with base excision repair, involves the removal and replacement of damaged nucleotides. Instances of
2100:
2094:
1895:
1645:
212:, that always cut DNA molecules at a particular point within a specific sequence of six base pairs. They found that the
1943:
2483:
2054:
1843:
776:
290:
1035:
allows for endonucleasic processing of the stem-loops. Defects of either protein confers severe immunodeficiency.
672:" because they tend to bond with complementary sequences of bases. In other words, if an unpaired length of bases
2161:
2049:
327:
83:
stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of
1970:
1880:
1833:
981:, both intentional and unintentional, regularly occur in cells. Unintentional breaks are commonly generated by
2639:
2392:
2333:
1417:"The crystal structure of EcoRV endonuclease and of its complexes with cognate and non-cognate DNA fragments"
1271:"Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli, X. In vitro restriction of phage fd replicative form"
2437:
2004:
1994:
1152:
912:
formation is a common occurrence in dsDNA. It is the result of spontaneous hydrolysis and the activity of
2397:
2289:
1914:
186:
2754:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1891:
1724:
998:
932:
741:
new strands of DNA against complementary template strands. Most DNA polymerases comprise two different
630:
2740:
2727:
2714:
2701:
2688:
2675:
2662:
2624:
2151:
1707:
1132:
261:
216:
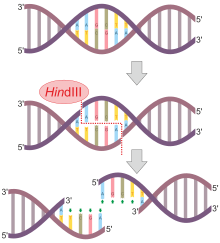
II enzyme always cuts directly in the center of this sequence (between the 3rd and 4th base pairs).
2634:
2588:
2531:
1899:
1748:
1662:
994:
225:
190:
19:
2536:
1768:
1638:
1613:
948:
841:
707:
2324:
1963:
898:
753:
540:
465:
391:
334:(positively charged) residues. It engages in extensive electrostatic interaction with the DNA.
202:
1562:"Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape, grip and blade of the DNA scissors"
1514:"Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape, grip and blade of the DNA scissors"
1473:"Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape, grip and blade of the DNA scissors"
1415:
Winkler FK, Banner DW, Oefner C, Tsernoglou D, Brown RS, Heathman SP, et al. (May 1993).
1376:"Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape, grip and blade of the DNA scissors"
1178:"Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape, grip and blade of the DNA scissors"
763:
inactivating or removing these nucleases increase rates of mutation and mortality in affected
170:". These enzymatic tools were important to scientists who were gathering the tools needed to "
2557:
2476:
2259:
2156:
1948:
1909:
1773:
1695:
1039:
1010:
888:
2629:
2442:
2277:
2272:
2205:
1865:
1690:
1282:
1127:
917:
719:
286:
194:
167:
1603:
146:
isolated examples of the two types of enzymes responsible for phage growth restriction in
8:
2593:
2297:
2267:
2071:
2066:
1990:
1926:
1712:
990:
978:
936:
856:
837:
760:
686:
88:
80:
64:
1608:
1341:
1286:
1020:
structures associated with double-strand breaks and subsequently joining both ends. The
2526:
2430:
2282:
1763:
1753:
1631:
1246:
1221:
1104:
982:
715:
323:
294:
24:
1441:
1416:
1305:
1270:
322:
forms far stronger associations by contrast. It draws DNA into the deep groove of its
2231:
2176:
2144:
2019:
1738:
1583:
1535:
1494:
1446:
1397:
1345:
1310:
1251:
1199:
1047:
823:
354:
237:
182:
115:
96:
2572:
2567:
2541:
2469:
2307:
1887:
1792:
1787:
1743:
1573:
1525:
1484:
1436:
1428:
1387:
1337:
1300:
1290:
1241:
1233:
1189:
800:
780:
585:
461:
331:
301:
interact with the chemical groups of the DNA. In the case of endonucleases such as
147:
92:
32:
901:
then degrades the site before DNA polymerase resynthesizes the gap in the strand.
293:. Such a nuclease diffuses along DNA until it encounters a target, upon which the
2784:
2619:
2603:
2516:
2409:
2223:
2139:
2134:
2129:
2042:
2037:
1797:
1675:
1021:
921:
913:
894:
731:
703:
159:
1623:
2768:
2657:
2598:
2382:
2377:
2372:
1758:
1733:
1729:
1702:
1685:
1275:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
852:
807:
745:
738:
735:
338:
1237:
499:
Not all restriction endonucleases cut symmetrically and leave blunt ends like
2778:
2562:
2521:
2123:
2032:
1782:
171:
2511:
2250:
2181:
1904:
1825:
1587:
1578:
1561:
1539:
1530:
1513:
1498:
1489:
1472:
1401:
1392:
1375:
1295:
1255:
1203:
1194:
1177:
1100:
1090:
155:
143:
119:
107:
72:
44:
1450:
1432:
1349:
1314:
2735:
2670:
2506:
2425:
2196:
2090:
1953:
1919:
1857:
1157:
1137:
875:
756:
711:
298:
245:
103:
870:
VSP repair is initiated by the endonuclease Vsr. It corrects a specific
2402:
1147:
1142:
944:
940:
879:
806:
from replication. Most such primers are excised from newly synthesized
803:
749:
669:
198:
84:
76:
68:
102:
There are two primary classifications based on the locus of activity.
2709:
2683:
2315:
2114:
2027:
1654:
1017:
867:
of the non-methylated strand (the more recently synthesized strand).
815:
742:
680:
they will bond to each other—they are "sticky" for each other.
342:
233:
163:
787:. Deletions of which causes UV or methylation damage sensitivity in
2763:
2360:
2355:
2350:
1806:
1658:
1029:
436:
249:
285:
Nonspecific endonucleases involved in DNA repair can scan DNA for
268:
2367:
2345:
2340:
1958:
1117:
986:
909:
819:
811:
764:
531:
440:
432:
428:
151:
28:
2722:
2492:
2387:
2320:
2213:
1811:
1719:
1122:
1051:
1043:
1002:
955:
681:
476:
241:
60:
2696:
2329:
2080:
2076:
1414:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1006:
967:
963:
959:
788:
784:
621:
576:
469:
454:
310:
306:
302:
1328:
Arber W, Linn S (1969). "DNA modification and restriction".
2061:
1938:
1931:
1875:
1870:
1078:
1058:
848:
826:
2461:
1038:
Homologous recombination, on the other hand, involves two
829:
also participates in the processing of
Okazaki fragments.
230:
175:
127:
123:
114:
of target molecules. They are further subcategorized as
2752:
924:, which effect single strand breaks around the site.
676:
encounters another unpaired length with the sequence
326:. This results in significant deformation of the DNA
1222:"Enzymes used in molecular biology: a useful guide"
882:cytosines to thymines. Vsr recognizes the sequence
31:cleaving a double-stranded DNA molecule at a valid
1215:
1213:
1169:
219:
1949:Fructose 6-P,2-kinase:fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase
1653:
178:molecules in a predictable and reproducible way.
2776:
205:bacteria, this group isolated an enzyme, called
1559:
1511:
1470:
1373:
1210:
1175:
272:Crystal structure of EcoRV in complex with DNA.
1466:
1464:
1462:
1460:
1081:processes Holliday junctions in mitochondria.
794:
348:
236:(EC-number 3). The nucleases belong just like
193:in 1968, isolated and characterized the first
2477:
1639:
973:
927:
799:A ubiquitous task in cells is the removal of
360:
197:whose functioning depended on a specific DNA
1219:
330:and is accomplished with a surfaces rich in
1457:
1226:Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling
725:
16:Class of enzymes which cleave nucleic acids
2484:
2470:
1646:
1632:
1555:
1553:
1551:
1549:
1369:
1367:
1365:
1363:
1361:
1359:
1321:
1262:
770:
1577:
1529:
1488:
1440:
1391:
1327:
1304:
1294:
1268:
1245:
1193:
154:) bacteria. One of these enzymes added a
95:. Nucleases are also extensively used in
87:. Defects in certain nucleases can cause
1153:Serratia marcescens nuclease (benzonase)
267:
18:
1839:Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1
1560:Nishino T, Morikawa K (December 2002).
1546:
1512:Nishino T, Morikawa K (December 2002).
1471:Nishino T, Morikawa K (December 2002).
1374:Nishino T, Morikawa K (December 2002).
1356:
1176:Nishino T, Morikawa K (December 2002).
993:, which are primarily repaired through
954:In bacteria, both cuts executed by the
904:
464:RY13 bacteria, while HindII comes from
2777:
1619:Nucleases (Main source of the page...)
1099:One unique family of nucleases is the
228:of the "Nomenclature Committee of the
2465:
2419:either deoxy- or ribo-
1627:
1604:Examples of Restriction Enzymes Chart
1016:V(D)J recombination involves opening
1009:. Mutations of Mre11 can precipitate
224:Most nucleases are classified by the
2000:Protein serine/threonine phosphatase
494:
106:digest nucleic acids from the ends.
2101:Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase
2095:Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin
1896:Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase
1342:10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002343
947:(generated by ultraviolet light or
874:mismatch caused by the spontaneous
810:DNA by endonucleases of the family
276:
181:An important development came when
13:
1944:Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase
1609:Restriction Enzyme Action of EcoRI
1050:. In bacteria, endonucleases like
970:affect the same respective nicks.
844:(VSP repair) associated proteins.
832:
791:, in addition to meiotic defects.
14:
2796:
1844:4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase
1597:
692:
2762:
1220:Rittié L, Perbal B (June 2008).
1084:
920:. These AP sites are removed by
507:RI has the recognition sequence
485:
2162:N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase
2050:Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase
220:Numerical Classification System
1971:Inositol-phosphate phosphatase
1834:Palmitoyl protein thioesterase
1505:
1408:
1269:Linn S, Arber W (April 1968).
863:sites and cleaves next to the
847:The MutSLH system (comprising
138:In the late 1960s, scientists
1:
2334:RNA-induced silencing complex
1330:Annual Review of Biochemistry
1163:
697:
75:. Nucleases variously affect
2438:Serratia marcescens nuclease
2005:Dual-specificity phosphatase
1995:Protein tyrosine phosphatase
255:
7:
2491:
1915:Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
1111:
916:as an intermediary step in
851:, MutL, and MutH) corrects
795:Okazaki fragment processing
349:Structure specific nuclease
51:(also archaically known as
10:
2801:
1088:
999:non-homologous end joining
974:Double-strand break repair
933:Nucleotide excision repair
928:Nucleotide excision repair
631:Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
361:Sequence specific nuclease
133:
2648:
2640:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
2612:
2581:
2550:
2499:
2418:
2306:
2258:
2244:
2222:
2204:
2190:
2170:
2152:Galactosamine-6 sulfatase
2109:
2013:
1852:
1820:
1708:6-phosphogluconolactonase
1670:
1238:10.1007/s12079-008-0026-2
1133:Nuclease protection assay
426:
2532:Diffusion-limited enzyme
1900:Purple acid phosphatases
1073:cleave the D-loops, and
995:homologous recombination
779:stop progression of the
726:Replication proofreading
226:Enzyme Commission number
191:Johns Hopkins University
63:capable of cleaving the
949:reactive oxygen species
842:very short patch repair
771:Halted replication fork
708:reactive oxygen species
201:sequence. Working with
158:to the DNA, generating
2325:Microprocessor complex
1964:Beta-propeller phytase
1579:10.1038/sj.onc.1206135
1531:10.1038/sj.onc.1206135
1490:10.1038/sj.onc.1206135
1393:10.1038/sj.onc.1206135
1296:10.1073/pnas.59.4.1300
1195:10.1038/sj.onc.1206135
1042:duplexes connected by
541:Haemophilus influenzae
466:Haemophilus influenzae
392:Haemophilus influenzae
319:site-specific nuclease
273:
203:Haemophilus influenzae
110:act on regions in the
40:
2625:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
2558:Allosteric regulation
2260:Endodeoxyribonuclease
2157:Iduronate-2-sulfatase
1910:Glucose 6-phosphatase
1696:Butyrylcholinesterase
1011:ataxia-telangiectasia
271:
122:. The former acts on
22:
2635:Lineweaver–Burk plot
2443:Micrococcal nuclease
2278:Deoxyribonuclease IV
2273:Deoxyribonuclease II
2206:Exodeoxyribonuclease
1866:Alkaline phosphatase
1691:Acetylcholinesterase
1128:Micrococcal nuclease
979:Double-strand breaks
918:base excision repair
905:Base excision repair
767:and cancer in mice.
523:Recognition Sequence
374:Recognition Sequence
195:restriction nuclease
168:restriction nuclease
65:phosphodiester bonds
2298:UvrABC endonuclease
2268:Deoxyribonuclease I
1991:Protein phosphatase
1927:Protein phosphatase
1725:Bile salt-dependent
1713:PAF acetylhydrolase
1433:10.2210/pdb4rve/pdb
1287:1968PNAS...59.1300L
991:V(D)J recombination
838:DNA mismatch repair
687:genetic engineering
185:, K.W. Wilcox, and
166:" and the other a "
89:genetic instability
2594:Enzyme superfamily
2527:Enzyme promiscuity
2431:Mung bean nuclease
2290:Restriction enzyme
2283:Restriction enzyme
1105:Genome engineering
1048:Holliday junctions
983:ionizing radiation
716:ionizing radiation
328:tertiary structure
324:DNA-binding domain
274:
116:deoxyribonucleases
53:nucleodepolymerase
41:
37:5'–A|AGCTT–3'
25:restriction enzyme
2750:
2749:
2459:
2458:
2455:
2454:
2451:
2450:
2240:
2239:
2232:Oligonucleotidase
2177:deoxyribonuclease
2145:Steroid sulfatase
2020:Phosphodiesterase
1749:Hormone-sensitive
824:flap endonuclease
665:
664:
495:Staggered cutting
446:
445:
355:flap endonuclease
262:primary structure
238:phosphodiesterase
97:molecular cloning
71:together to form
23:Depiction of the
2792:
2767:
2766:
2758:
2630:Hanes–Woolf plot
2573:Enzyme activator
2568:Enzyme inhibitor
2542:Enzyme catalysis
2486:
2479:
2472:
2463:
2462:
2308:Endoribonuclease
2294:
2288:
2256:
2255:
2202:
2201:
2188:
2187:
1888:Acid phosphatase
1769:Monoacylglycerol
1679:ester hydrolases
1648:
1641:
1634:
1625:
1624:
1592:
1591:
1581:
1557:
1544:
1543:
1533:
1509:
1503:
1502:
1492:
1468:
1455:
1454:
1444:
1421:The EMBO Journal
1412:
1406:
1405:
1395:
1371:
1354:
1353:
1325:
1319:
1318:
1308:
1298:
1266:
1260:
1259:
1249:
1217:
1208:
1207:
1197:
1173:
1013:-like disorder.
922:AP endonucleases
914:DNA glycosylases
892:
873:
866:
862:
801:Okazaki fragment
781:replication fork
679:
675:
659:
656:
650:
647:
614:
611:
605:
602:
586:Escherichia coli
569:
566:
560:
557:
514:
513:
510:
462:Escherichia coli
420:
417:
411:
408:
365:
364:
353:For details see
321:
320:
287:target sequences
277:Site recognition
148:Escherichia coli
126:, the latter on
93:immunodeficiency
57:polynucleotidase
38:
33:restriction site
2800:
2799:
2795:
2794:
2793:
2791:
2790:
2789:
2775:
2774:
2773:
2761:
2753:
2751:
2746:
2658:Oxidoreductases
2644:
2620:Enzyme kinetics
2608:
2604:List of enzymes
2577:
2546:
2517:Catalytic triad
2495:
2490:
2460:
2447:
2414:
2302:
2292:
2286:
2249:
2236:
2224:Exoribonuclease
2218:
2195:
2179:
2175:
2166:
2140:Arylsulfatase L
2135:Arylsulfatase B
2130:Arylsulfatase A
2105:
2018:
2009:
1848:
1816:
1678:
1666:
1652:
1614:Enzyme glossary
1600:
1595:
1572:(58): 9022–32.
1558:
1547:
1524:(58): 9022–32.
1510:
1506:
1483:(58): 9022–32.
1469:
1458:
1413:
1409:
1386:(58): 9022–32.
1372:
1357:
1326:
1322:
1267:
1263:
1218:
1211:
1188:(58): 9022–32.
1174:
1170:
1166:
1114:
1093:
1087:
1033:
1025:
1005:complexed with
976:
930:
907:
883:
871:
864:
860:
853:point mutations
835:
833:Mismatch repair
797:
773:
736:DNA polymerases
732:DNA replication
728:
704:DNA replication
700:
695:
677:
673:
661:
657:
654:
652:
648:
645:
640:
638:
616:
612:
609:
607:
603:
600:
595:
593:
571:
567:
564:
562:
558:
555:
550:
548:
508:
497:
488:
418:
415:
413:
409:
406:
399:
363:
351:
318:
317:
279:
258:
222:
136:
36:
27:(endonuclease)
17:
12:
11:
5:
2798:
2788:
2787:
2772:
2771:
2748:
2747:
2745:
2744:
2731:
2718:
2705:
2692:
2679:
2666:
2652:
2650:
2646:
2645:
2643:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2616:
2614:
2610:
2609:
2607:
2606:
2601:
2596:
2591:
2585:
2583:
2582:Classification
2579:
2578:
2576:
2575:
2570:
2565:
2560:
2554:
2552:
2548:
2547:
2545:
2544:
2539:
2534:
2529:
2524:
2519:
2514:
2509:
2503:
2501:
2497:
2496:
2489:
2488:
2481:
2474:
2466:
2457:
2456:
2453:
2452:
2449:
2448:
2446:
2445:
2440:
2435:
2434:
2433:
2422:
2420:
2416:
2415:
2413:
2412:
2407:
2406:
2405:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2364:
2363:
2358:
2353:
2348:
2338:
2337:
2336:
2327:
2312:
2310:
2304:
2303:
2301:
2300:
2295:
2280:
2275:
2270:
2264:
2262:
2253:
2242:
2241:
2238:
2237:
2235:
2234:
2228:
2226:
2220:
2219:
2217:
2216:
2210:
2208:
2199:
2185:
2168:
2167:
2165:
2164:
2159:
2154:
2149:
2148:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2132:
2119:
2117:
2107:
2106:
2104:
2103:
2098:
2088:
2083:
2074:
2069:
2064:
2059:
2058:
2057:
2047:
2046:
2045:
2040:
2030:
2024:
2022:
2011:
2010:
2008:
2007:
2002:
1997:
1988:
1987:
1986:
1968:
1967:
1966:
1956:
1951:
1946:
1941:
1936:
1935:
1934:
1924:
1923:
1922:
1912:
1907:
1902:
1885:
1884:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1862:
1860:
1850:
1849:
1847:
1846:
1841:
1836:
1830:
1828:
1818:
1817:
1815:
1814:
1809:
1803:
1802:
1801:
1800:
1795:
1790:
1779:
1778:
1777:
1776:
1774:Diacylglycerol
1771:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1751:
1746:
1741:
1736:
1727:
1716:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1703:Pectinesterase
1700:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1686:Cholinesterase
1682:
1680:
1668:
1667:
1651:
1650:
1643:
1636:
1628:
1622:
1621:
1616:
1611:
1606:
1599:
1598:External links
1596:
1594:
1593:
1545:
1504:
1456:
1427:(5): 1781–95.
1407:
1355:
1320:
1261:
1232:(1–2): 25–45.
1209:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1160:
1155:
1150:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1130:
1125:
1120:
1113:
1110:
1089:Main article:
1086:
1083:
1040:homologous DNA
1031:
1023:
975:
972:
929:
926:
906:
903:
834:
831:
808:lagging strand
796:
793:
775:Many forms of
772:
769:
727:
724:
699:
696:
694:
693:Role in nature
691:
663:
662:
643:
641:
636:
634:
627:
618:
617:
598:
596:
591:
589:
582:
573:
572:
553:
551:
546:
544:
537:
528:
527:
524:
521:
518:
496:
493:
487:
484:
444:
443:
424:
423:
402:
395:
388:
379:
378:
375:
372:
369:
362:
359:
350:
347:
278:
275:
257:
254:
221:
218:
160:methylated DNA
135:
132:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2797:
2786:
2783:
2782:
2780:
2770:
2765:
2760:
2759:
2756:
2742:
2738:
2737:
2732:
2729:
2725:
2724:
2719:
2716:
2712:
2711:
2706:
2703:
2699:
2698:
2693:
2690:
2686:
2685:
2680:
2677:
2673:
2672:
2667:
2664:
2660:
2659:
2654:
2653:
2651:
2647:
2641:
2638:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2617:
2615:
2611:
2605:
2602:
2600:
2599:Enzyme family
2597:
2595:
2592:
2590:
2587:
2586:
2584:
2580:
2574:
2571:
2569:
2566:
2564:
2563:Cooperativity
2561:
2559:
2556:
2555:
2553:
2549:
2543:
2540:
2538:
2535:
2533:
2530:
2528:
2525:
2523:
2522:Oxyanion hole
2520:
2518:
2515:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2504:
2502:
2498:
2494:
2487:
2482:
2480:
2475:
2473:
2468:
2467:
2464:
2444:
2441:
2439:
2436:
2432:
2429:
2428:
2427:
2424:
2423:
2421:
2417:
2411:
2408:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2385:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2362:
2359:
2357:
2354:
2352:
2349:
2347:
2344:
2343:
2342:
2339:
2335:
2331:
2328:
2326:
2322:
2319:
2318:
2317:
2314:
2313:
2311:
2309:
2305:
2299:
2296:
2291:
2284:
2281:
2279:
2276:
2274:
2271:
2269:
2266:
2265:
2263:
2261:
2257:
2254:
2252:
2247:
2243:
2233:
2230:
2229:
2227:
2225:
2221:
2215:
2212:
2211:
2209:
2207:
2203:
2200:
2198:
2193:
2189:
2186:
2183:
2178:
2173:
2169:
2163:
2160:
2158:
2155:
2153:
2150:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2136:
2133:
2131:
2128:
2127:
2126:
2125:
2124:arylsulfatase
2121:
2120:
2118:
2116:
2112:
2108:
2102:
2099:
2096:
2092:
2089:
2087:
2084:
2082:
2078:
2075:
2073:
2070:
2068:
2065:
2063:
2060:
2056:
2053:
2052:
2051:
2048:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2035:
2034:
2033:Phospholipase
2031:
2029:
2026:
2025:
2023:
2021:
2016:
2012:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1998:
1996:
1992:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1974:
1973:
1972:
1969:
1965:
1962:
1961:
1960:
1957:
1955:
1952:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1940:
1937:
1933:
1930:
1929:
1928:
1925:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1916:
1913:
1911:
1908:
1906:
1903:
1901:
1897:
1893:
1889:
1886:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1868:
1867:
1864:
1863:
1861:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1845:
1842:
1840:
1837:
1835:
1832:
1831:
1829:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1804:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1791:
1789:
1786:
1785:
1784:
1783:Phospholipase
1781:
1780:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1755:
1752:
1750:
1747:
1745:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1735:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1722:
1721:
1718:
1717:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1697:
1694:
1692:
1689:
1688:
1687:
1684:
1683:
1681:
1677:
1673:
1669:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1649:
1644:
1642:
1637:
1635:
1630:
1629:
1626:
1620:
1617:
1615:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1589:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1556:
1554:
1552:
1550:
1541:
1537:
1532:
1527:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1508:
1500:
1496:
1491:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1467:
1465:
1463:
1461:
1452:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1411:
1403:
1399:
1394:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1370:
1368:
1366:
1364:
1362:
1360:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1324:
1316:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1297:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1281:(4): 1300–6.
1280:
1276:
1272:
1265:
1257:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1216:
1214:
1205:
1201:
1196:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1172:
1168:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1151:
1149:
1146:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1131:
1129:
1126:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1115:
1109:
1106:
1102:
1101:meganucleases
1097:
1092:
1085:Meganucleases
1082:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1036:
1034:
1027:
1022:Artemis-DNAPK
1019:
1014:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
984:
980:
971:
969:
965:
961:
957:
952:
950:
946:
942:
938:
934:
925:
923:
919:
915:
911:
902:
900:
896:
890:
887:
881:
877:
868:
858:
854:
850:
845:
843:
839:
830:
828:
825:
821:
817:
813:
809:
805:
802:
792:
790:
786:
782:
778:
768:
766:
762:
758:
755:
751:
747:
744:
740:
737:
733:
723:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
690:
688:
683:
671:
642:
635:
633:
632:
628:
626:
624:
620:
619:
597:
590:
588:
587:
583:
581:
579:
575:
574:
552:
545:
543:
542:
538:
536:
534:
530:
529:
525:
522:
519:
516:
515:
512:
506:
502:
492:
486:Endonucleases
483:
481:
479:
474:
472:
467:
463:
459:
457:
451:
442:
438:
434:
430:
425:
422:
403:
401:
400:3'–CARYTG–5'
396:
394:
393:
389:
387:
385:
381:
380:
376:
373:
370:
367:
366:
358:
356:
346:
344:
340:
335:
333:
329:
325:
314:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
283:
270:
266:
263:
253:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
217:
215:
211:
209:
204:
200:
196:
192:
189:, working at
188:
184:
179:
177:
173:
172:cut and paste
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
131:
129:
125:
121:
120:ribonucleases
117:
113:
109:
108:Endonucleases
105:
100:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
73:nucleic acids
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
34:
30:
26:
21:
2736:Translocases
2733:
2720:
2707:
2694:
2681:
2671:Transferases
2668:
2655:
2512:Binding site
2293:}}
2287:{{
2251:Endonuclease
2182:ribonuclease
2171:
2122:
1905:Nucleotidase
1826:Thioesterase
1569:
1565:
1521:
1517:
1507:
1480:
1476:
1424:
1420:
1410:
1383:
1379:
1333:
1329:
1323:
1278:
1274:
1264:
1229:
1225:
1185:
1181:
1171:
1098:
1094:
1091:meganuclease
1054:
1037:
1015:
977:
953:
937:crosslinking
931:
908:
885:
869:
846:
836:
798:
774:
754:proofreading
729:
701:
689:technology.
666:
639:3'–CCTAGG–5'
637:5'–GGATCC–3'
629:
622:
594:3'–CTTAAG–5'
592:5'–GAATTC-3'
584:
577:
549:3'–TTCGAA–5'
547:5'–AAGCTT–3'
539:
532:
509:5'—GAATTC—3'
504:
500:
498:
489:
477:
470:
455:
449:
447:
404:
398:5'–GTYRAC–3'
397:
390:
383:
352:
345:mismatches.
336:
315:
284:
282:DNA repair.
280:
259:
223:
213:
207:
180:
156:methyl group
144:Werner Arber
137:
111:
104:Exonucleases
101:
56:
52:
48:
45:biochemistry
42:
2507:Active site
2426:Nuclease S1
2197:Exonuclease
2091:Lecithinase
1920:Calcineurin
1858:Phosphatase
1764:Lipoprotein
1754:Endothelial
1336:: 467–500.
1158:S1 nuclease
1138:P1 nuclease
876:deamination
804:RNA primers
757:exonuclease
712:ultraviolet
670:sticky ends
460:comes from
299:active site
246:phosphatase
140:Stuart Linn
69:nucleotides
2710:Isomerases
2684:Hydrolases
2551:Regulation
1739:Pancreatic
1676:Carboxylic
1164:References
1148:Polymerase
1143:PIN domain
1018:stem-loops
880:methylated
861:5'—GATC—3'
855:and small
816:eukaryotes
777:DNA damage
750:polymerase
698:DNA repair
678:3'—TTAA—5'
674:5'—AATT—3'
234:hydrolases
199:nucleotide
187:T.J. Kelly
183:H.O. Smith
85:DNA repair
67:that link
2589:EC number
2316:RNase III
2174:(includes
2115:Sulfatase
2028:Autotaxin
1892:Prostatic
1744:Lysosomal
1659:esterases
1655:Hydrolase
956:UvrB-UvrC
761:Deletions
743:enzymatic
720:complexes
343:base pair
260:Nuclease
256:Structure
250:esterases
164:methylase
2779:Category
2613:Kinetics
2537:Cofactor
2500:Activity
2410:RNase T1
2172:Nuclease
1807:Cutinase
1588:12483517
1566:Oncogene
1540:12483517
1518:Oncogene
1499:12483517
1477:Oncogene
1402:12483517
1380:Oncogene
1256:18766469
1204:12483517
1182:Oncogene
1112:See also
765:microbes
739:elongate
339:backbone
295:residues
59:) is an
49:nuclease
2769:Biology
2723:Ligases
2493:Enzymes
2383:RNase E
2378:RNase Z
2373:RNase A
2368:RNase P
2341:RNase H
1959:Phytase
1759:Hepatic
1734:Lingual
1730:Gastric
1451:8491171
1350:4897066
1315:4870862
1283:Bibcode
1247:2570007
1118:HindIII
1055:resolve
1044:D-loops
1026:complex
987:meiosis
945:lesions
941:adducts
910:AP site
822:, the
820:archaea
818:and in
812:RNase H
746:domains
730:During
710:, near
297:of its
248:to the
152:E. coli
134:History
29:HindIII
2785:EC 3.1
2755:Portal
2697:Lyases
2321:Drosha
2246:3.1.21
2214:RecBCD
2192:3.1.11
1812:PETase
1720:Lipase
1586:
1538:
1497:
1449:
1442:413397
1439:
1400:
1348:
1313:
1306:224867
1303:
1254:
1244:
1202:
1123:Ligase
1069:, and
1030:DNA-PK
943:, and
895:ExoVII
752:and a
714:, and
682:Ligase
520:Source
517:Enzyme
435:; Y =
371:Source
368:Enzyme
311:B-form
291:damage
242:lipase
112:middle
81:double
77:single
61:enzyme
2649:Types
2330:Dicer
2285:;see
2111:3.1.6
2081:PDE4B
2077:PDE4A
2015:3.1.4
1984:IMPA3
1980:IMPA2
1976:IMPA1
1854:3.1.3
1822:3.1.2
1672:3.1.1
1071:MUS81
1067:ERCC1
1007:Rad50
1003:Mre11
968:ERCC1
897:, or
891:GG—3'
857:turns
814:. In
789:yeast
785:MUS81
655:CCTAG
649:GATCC
610:CTTAA
604:AATTC
565:TTCGA
559:AGCTT
332:basic
307:BamHI
303:EcoRV
232:" as
2741:list
2734:EC7
2728:list
2721:EC6
2715:list
2708:EC5
2702:list
2695:EC4
2689:list
2682:EC3
2676:list
2669:EC2
2663:list
2656:EC1
2248:-31:
2194:-16:
2180:and
2086:PDE5
2072:PDE3
2067:PDE2
2062:PDE1
1954:PTEN
1939:OCRL
1932:PP2A
1881:ALPP
1876:ALPL
1871:ALPI
1665:3.1)
1584:PMID
1536:PMID
1495:PMID
1447:PMID
1398:PMID
1346:PMID
1311:PMID
1252:PMID
1200:PMID
1079:Ydc2
1075:Cce1
1059:FEN1
1052:RuvC
997:and
989:and
962:and
899:ExoI
884:5'—C
849:MutS
827:FEN1
748:: a
533:Hind
526:Cut
501:Hind
450:Hind
427:R =
421:–5'
384:Hind
377:Cut
244:and
214:Hind
208:Hind
142:and
118:and
79:and
47:, a
2403:4/5
1574:doi
1526:doi
1485:doi
1437:PMC
1429:doi
1388:doi
1338:doi
1301:PMC
1291:doi
1242:PMC
1234:doi
1190:doi
1063:XPF
1046:or
964:XPF
960:XPG
878:of
872:T/G
660:–5'
653:3'–
651:–3'
644:5'–
623:Bam
615:–5'
608:3'–
606:–3'
599:5'–
578:Eco
570:–5'
563:3'–
561:–3'
554:5'–
535:III
505:Eco
480:RII
478:Eco
471:Eco
456:Eco
439:or
431:or
419:YTG
416:CAR
414:3'–
412:–3'
410:RAC
407:GTY
405:5'–
341:by
289:or
176:DNA
128:RNA
124:DNA
91:or
55:or
43:In
2781::
2361:2C
2356:2B
2351:2A
2332::
2323::
2113::
1993::
1982:,
1978:,
1894:)/
1856::
1824::
1793:A2
1788:A1
1674::
1663:EC
1657::
1582:.
1570:21
1568:.
1564:.
1548:^
1534:.
1522:21
1520:.
1516:.
1493:.
1481:21
1479:.
1475:.
1459:^
1445:.
1435:.
1425:12
1423:.
1419:.
1396:.
1384:21
1382:.
1378:.
1358:^
1344:.
1334:38
1332:.
1309:.
1299:.
1289:.
1279:59
1277:.
1273:.
1250:.
1240:.
1228:.
1224:.
1212:^
1198:.
1186:21
1184:.
1180:.
1061:,
1032:cs
1024:cs
939:,
734:,
625:HI
580:RI
511:.
482:.
475:,
473:RI
458:RI
386:II
357:.
316:A
313:.
305:,
240:,
210:II
130:.
99:.
39:).
2757::
2743:)
2739:(
2730:)
2726:(
2717:)
2713:(
2704:)
2700:(
2691:)
2687:(
2678:)
2674:(
2665:)
2661:(
2485:e
2478:t
2471:v
2398:3
2393:2
2388:1
2346:1
2184:)
2097:)
2093:(
2079:/
2055:1
2043:D
2038:C
2017::
1898:/
1890:(
1798:B
1732:/
1661:(
1647:e
1640:t
1633:v
1590:.
1576::
1542:.
1528::
1501:.
1487::
1453:.
1431::
1404:.
1390::
1352:.
1340::
1317:.
1293::
1285::
1258:.
1236::
1230:2
1206:.
1192::
1077:/
1065:-
966:-
889:W
886:T
865:G
658:G
646:G
613:G
601:G
568:A
556:A
441:T
437:C
433:G
429:A
150:(
35:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.