278:. Ampullary receptors respond to low-frequency stimulation less than 40 Hz and their role in the JAR is currently unknown. Tuberous receptors respond to higher frequencies, firing best near the fish's normal EOD frequency. Tuberous receptors themselves have two types, the T-unit and P-unit. The T-unit (T standing for time, meaning phase in the cycle) fires synchronously with the signal frequency by firing a spike on every cycle of the waveform. P-units (P standing for probability) tend to fire when the amplitude increases and fire less when it decreases. Under conditions of jamming, the P-unit fires on the amplitude peaks of the beat cycle where the two waves constructively interfere. So, a combined stimulus-EOD signal causes T-units to fire at the intermediate frequency, and causes P-unit firing to increase and decrease periodically with the beat.
241:
685:
22:
625:
557:
552:
131:
512:
680:
620:
1774:
3112:
2766:
2748:
517:
448:
453:
2778:
3124:
314:, which then projects onto two different pathways. Neurons selective for a positive difference (stimulus greater than EOD) stimulate the prepacemaker nucleus, while neurons selective for a negative difference (stimulus less than EOD) inhibit the sublemniscal prepacemaker nucleus. Both prepacemaker nuclei send projections to the pacemaker nucleus, which ultimately controls the frequency of the EOD.
302:. Phase and amplitude information are integrated here to determine whether the stimulus frequency is greater or less than the EOD frequency. Sign-selective neurons in the deeper layers of the torus semicircularis are selective to whether the frequency difference is positive or negative; any given sign-selective cell fires in one case but not in the other.
202:
To determine how close the stimulus frequency is to the discharge frequency, the fish compares the two frequencies using its electroreceptive organs, rather than comparing the discharge frequency to an internal pacemaker; in other words, the JAR relies only on sensory information. This was determined
290:
called spherical cells in the electrosensory lateral line lobe. By combining information from multiple T-units, the spherical cell is even more precise in its time coding. Amplitude-coding P-units converge onto pyramidal cells, also in the electrosensory lateral line lobe. Two types of pyramidal
198:
typically are within the electric field range of three to five other fish of the same species at any time. If many fish are located near each other, it is beneficial for each fish to distinguish between their own signal and those of others; this can be done by increasing the frequency difference
122:
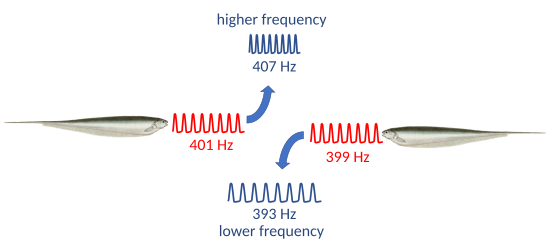
near the fish, if the stimulus frequency is within 5 Hz of the fish's electric organ discharge (EOD) frequency, the fish alters its EOD frequency to increase the difference between its own frequency and the stimulus frequency. Stimuli above the fish's EOD frequency push the EOD frequency
376:
most likely arose independently in the two lineages. Weakly electric fish are mostly pulse-dischargers, which do not perform the JAR, while some are wave-dischargers. Wave-discharge evolved in two taxa: the superfamily
Apteronotoidea (order
185:
to create electric fields, and they detect small distortions of these fields using special electroreceptive organs in the skin. All fish with the JAR are wave-discharging fish that emit steady quasi-sinusoidal discharges. For the genus
193:
If a neighboring sinusoidal electric field is discharging close to the fish's EOD frequency, it causes interference which results in sensory confusion in the fish and sufficient jamming to prevent it from electrolocating effectively.
123:
downwards, while frequencies below that of the fish push the EOD frequency upwards, with a maximum change of about ±6.5 Hz. This behavior was given the name "jamming avoidance response" several years later in 1972, in a paper by
207:, and then stimulating the fish with two external frequencies. The JAR, measured from the electromotor neurons in the spinal cord, depended only on the frequencies of the external stimuli, and not on the frequency of the pacemaker.
247:
sensory coding for jamming avoidance response. The fish avoids interference with its electrolocation signal by changing its frequency when a jamming signal is detected. This is mediated by a T-unit
291:
cells exist: excitatory E-units, which fire more when stimulated by P-units, and inhibitory I-units, which fire less when stimulated by inhibitory interneurons activated by P-units.
1335:
Kawasaki, M. (1975). "Independently evolved jamming avoidance responses in
Gymnotid and Gymnarchid electric fish: a case of convergent evolution of behavior and its sensory basis".
334:
are time coders, like the T-units in
Gymnotiformes. O-units code the signal's intensity, like P-units in Gymnotiformes, but respond over a narrower range of intensities. In
1147:"Phase and amplitude computations in the midbrain of an electric fish: Intracellular studies of neurons participating in the jamming avoidance response of Eigenmannia"
415:, omitting non-electric and strongly-electric fishes, shows major events in their evolution. In the tree, "sp" means "a species" and "spp" means "multiple species".
181:– they can locate objects by generating an electric field and detecting distortions in the field caused by interference from those objects. Electric fish use their
1235:(1975). "Comparison of the jamming avoidance responses in Gymnotid and Gymnarchid electric fish: A case of convergent evolution of behavior and its sensory basis".
411:
nearly identical neural computational mechanisms and behavioral responses to avoid jamming, with only minor differences. The phylogeny of the weakly electric fish
51:
are very similar, each fish shifts its discharge frequency to increase the difference between the two. By doing this, both fish prevent jamming of their sense of
1444:(1977) Principles of Electrolocation and Jamming Avoidance in Electric Fish: A Neuroethological Approach. Studies of Brain Function, Vol. 1. Berlin-New York:
996:
Tan, E.; Nizar, J.; Carrera-G, E.; Fortune, E. (2005). "Electrosensory interference in naturally occurring aggregates of a species of weakly electric fish,
949:"The complexity of high-frequency electric fields degrades electrosensory inputs: implications for the jamming avoidance response in weakly electric fish"
1380:
Lavoué, Sébastien; Miya, Masaki; Arnegard, Matthew E.; Sullivan, John P.; Hopkins, Carl D.; Nishida, Mutsumi (2012-05-14). Murphy, William J. (ed.).
190:, frequencies range from 240 to 600 Hz. The EOD frequency is very steady, typically with less than 0.3% variation over a 10-minute time span.
104:
The jamming avoidance response (JAR) was discovered by Akira
Watanabe and Kimihisa Takeda in 1963. The fish they used was an unspecified species of
338:, phase differences between EOD and stimulus are calculated in the electrosensory lateral line lobe rather than in the torus semicircularis.
1052:; Hamstra, R. Jr. (1973). "Coding properties of two classes of afferent nerve fibers: high-frequency electroreceptors in the electric fish,
263:, and the electroreceptive organs perceive a single wave with an intermediate frequency. In addition, the combined stimulus-EOD wave has a
2478:
1675:
2220:
2816:
1494:
199:
between their discharges. Therefore, it seems to be the function of the JAR to avoid sensory confusion among neighboring fish.
1277:"The phylogenetic distribution of electroreception: Evidence for convergent evolution of a primitive vertebrate sense modality"
1196:
Kramer, Berndt (15 May 1999). "Waveform discrimination, phase sensitivity and jamming avoidance in a wave-type electric fish".
2844:
2047:
1517:
1104:
871:
869:(1975). "Electrolocation and jamming avoidance in the electric fish Gymnarchus niloticus (Gymnarchidae, Mormyriformes)".
796:
768:
684:
2861:
2077:
1337:
1237:
831:
1382:"Comparable Ages for the Independent Origins of Electrogenesis in African and South American Weakly Electric Fishes"
259:
When the stimulus frequency and discharge frequency are close to each other, the two amplitude-time waves undergo
1731:
1668:
260:
3150:
3128:
3060:
44:
624:
251:
which fires at the signal frequency, and a P-unit tuberous receptor which fires fastest near the peak of the
240:
2782:
1816:
407:. Though they evolved the JAR separately, the South American and African taxa (boldface in the tree) have
178:
92:
to have its neural circuitry completely specified. As such, it holds special significance in the field of
2809:
1716:
1487:
1151:
829:; Hamstra, R. Jr.; Scheich, H. (1972). "The jamming avoidance response of high frequency electric fish".
788:
3065:
2468:
2195:
2165:
1661:
1276:
1058:
1002:
2866:
2741:
2734:
2701:
2443:
2115:
1796:
1632:
3070:
2751:
2510:
1538:
182:
2923:
2729:
2711:
2273:
2022:
1773:
1049:
826:
124:
21:
18:
Behavior performed by weakly electric fish to prevent jamming of their sense of electroreception
3155:
3116:
3080:
2839:
2802:
2691:
2515:
2500:
2323:
2042:
1931:
1480:
2896:
2721:
2706:
2215:
2032:
1546:
556:
330:
is nearly identical to that of the
Gymnotiformes, with a few minor differences. S-units in
2973:
2906:
2886:
2881:
2716:
2012:
1393:
408:
383:
295:
157:
152:
139:
84:
267:, with the beat frequency equal to the frequency difference between the stimulus and EOD.
8:
3040:
2978:
2928:
2505:
2448:
2248:
2135:
1924:
1441:
1232:
1142:
1099:
912:
866:
147:
88:. The jamming avoidance response was one of the first complex behavioral responses in a
2963:
1397:
3003:
2933:
2901:
2876:
2087:
1466:
1416:
1381:
1362:
1317:
1254:
1173:
1164:
1146:
1121:
1027:
973:
948:
929:
888:
848:
643:
271:
35:
meet, one fish shifts its frequency upward and the other shifts its frequency downward.
224:
Most of the JAR pathway in the South
American Gymnotiformes has been worked out using
3024:
2433:
2338:
2243:
2155:
2150:
2097:
1904:
1711:
1701:
1452:
1421:
1354:
1309:
1295:
1213:
1178:
1075:
1019:
978:
486:
388:
365:
275:
248:
135:
1366:
1321:
1258:
1125:
1031:
892:
852:
3090:
3085:
2998:
2175:
2120:
2082:
2037:
1995:
1919:
1706:
1642:
1615:
1603:
1411:
1401:
1346:
1299:
1291:
1246:
1205:
1168:
1160:
1113:
1067:
1011:
968:
960:
921:
880:
840:
805:
667:
373:
264:
252:
52:
47:. It occurs when two electric fish with wave discharges meet – if their discharge
3055:
2958:
2953:
2392:
2372:
2200:
2187:
2170:
2125:
2007:
1946:
1870:
1865:
1801:
1788:
1758:
1609:
1445:
1406:
906:
Hopkins, C. (1974). "Electric communication: functions in the social behavior of
397:
353:
64:
1465:
Kawasaki, M. (2009) Evolution of time-coding systems in weakly electric fishes.
551:
3075:
2948:
2943:
2891:
2668:
2641:
2533:
2525:
2458:
2428:
2367:
2349:
2303:
2293:
1897:
1850:
432:
229:
1102:(1980). "Neural correlates of the jamming avoidance response of Eigenmannia".
1015:
511:
3144:
2938:
2871:
2825:
2770:
2673:
2587:
2407:
2382:
2377:
2333:
2328:
2283:
2278:
2258:
2130:
1909:
1828:
1575:
1503:
763:
597:
378:
361:
357:
347:
299:
169:
93:
69:
59:
1209:
1071:
925:
789:"The change of discharge frequency by A.C. stimulus in a weak electric fish"
679:
3095:
3045:
2983:
2663:
2487:
2402:
2362:
2263:
2205:
2145:
2072:
2067:
2057:
1973:
1963:
1892:
1875:
1782:
1743:
1736:
1637:
1581:
1569:
1551:
1425:
1217:
1023:
982:
964:
657:
649:
619:
566:
534:
526:
469:
311:
118:. They found that when a sinusoidal electrical stimulus is emitted from an
31:
perform the jamming avoidance response: When two fish with around the same
1358:
1313:
1182:
1079:
130:
3019:
2988:
2968:
2646:
2634:
2560:
2318:
2313:
2288:
2268:
2210:
2105:
2000:
1978:
1968:
1941:
1811:
1763:
1304:
403:
106:
74:
27:
809:
2993:
2696:
2495:
2463:
2397:
2387:
2308:
2298:
1983:
1951:
1936:
1882:
1855:
1838:
1597:
1591:
1350:
1250:
1117:
933:
884:
844:
541:
516:
502:
496:
438:
422:
89:
2453:
2438:
2423:
2253:
1914:
1860:
1845:
1823:
1806:
1753:
1459:
119:
111:
48:
32:
310:
Sign-selective cells input into the nucleus electrosensorius in the
2856:
2656:
2597:
2543:
2538:
2357:
2225:
1887:
1833:
1748:
255:
caused by the interference of two signals with similar frequencies.
1270:
1268:
341:
2629:
2624:
2602:
2575:
2570:
2565:
2110:
2062:
1956:
1726:
1721:
452:
447:
287:
2794:
1472:
2850:
2548:
1265:
369:
204:
79:
1043:
1041:
821:
819:
270:
Gymnotiforms have two classes of electroreceptive organs, the
2651:
2580:
1990:
412:
392:
115:
317:
2553:
2140:
1693:
1684:
1093:
1091:
1089:
1038:
816:
1379:
1275:
Bullock, T. H.; Bodznick, D. A.; Northcutt, R. G. (1983).
1230:
2592:
2160:
1373:
739:
462:
215:
203:
experimentally by silencing a fish's electric organ with
1274:
1137:
1135:
1086:
995:
294:
Spherical cells and pyramidal cells then project to the
1653:
156:, the African knifefish, showing that the behavior had
1458:
Heiligenberg, W. (1991) Neural Nets in
Electric fish.
58:
The behavior has been most intensively studied in the
1132:
1047:
825:
1097:
1451:Heiligenberg, W. (1990) Electric Systems in Fish.
940:
3142:
1141:
947:Shifman, Aaron R.; Lewis, John E. (2018-01-04).
859:
298:, a structure with many laminae (layers) in the
342:Phylogeny and evolution of weakly electric fish
786:
2810:
1669:
1488:
946:
865:
1189:
395:in Apteronotoidea that perform JAR include
127:, Robert Hamstra Jr., and Henning Scheich.
2817:
2803:
1676:
1662:
1495:
1481:
787:Watanabe, Akira; Takeda, Kimihisa (1963).
281:
150:discovered a JAR in the distantly-related
2221:Tradeoffs for locomotion in air and water
1415:
1405:
1303:
1172:
972:
1334:
239:
129:
20:
905:
138:also has a jamming avoidance response,
3143:
1195:
953:Journal of the Royal Society Interface
286:The time-coding T-units converge onto
2798:
1657:
1476:
3123:
2777:
2048:Electroreception and electrogenesis
1518:Electroreception and electrogenesis
1105:Journal of Comparative Physiology A
872:Journal of Comparative Physiology A
797:The Journal of Experimental Biology
769:Electroreception and electrogenesis
177:and other weakly electric fish use
13:
1435:
1165:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00515.1985
14:
3167:
2824:
1502:
1338:Journal of Comparative Physiology
1238:Journal of Comparative Physiology
832:Journal of Comparative Physiology
608:S. American knifefishes
235:
43:is a behavior of some species of
3122:
3111:
3110:
2776:
2765:
2764:
2747:
2746:
1772:
683:
678:
623:
618:
555:
550:
515:
510:
451:
446:
2867:Central pattern generator (CPG)
1732:Environmental impact of fishing
1328:
1224:
1198:Journal of Experimental Biology
210:
68:. It is also present in other
3061:Frog hearing and communication
989:
899:
780:
1:
774:
326:The neural pathway of JAR in
1817:intramembranous ossification
1407:10.1371/journal.pone.0036287
1296:10.1016/0165-0173(83)90003-6
114:wave discharge of about 300
99:
7:
1462:: Cambridge, Massachusetts.
1152:The Journal of Neuroscience
757:
163:
10:
3172:
3066:Infrared sensing in snakes
3051:Jamming avoidance response
2196:Fin and flipper locomotion
2166:Sequential hermaphroditism
2053:Jamming avoidance response
1770:
1578:(S. American knifefishes)
1523:Jamming avoidance response
1231:Bullock, T.; Behrend, K.;
1059:Journal of Neurophysiology
1003:Behavioural Brain Research
345:
167:
160:in two separate lineages.
41:jamming avoidance response
3106:
3033:
3012:
2916:
2832:
2760:
2684:
2617:
2524:
2486:
2477:
2416:
2347:
2234:
2186:
2096:
2021:
1781:
1691:
1633:History of bioelectricity
1625:
1562:
1531:
1510:
1016:10.1016/j.bbr.2005.06.014
671:
661:
611:
601:
591:
584:
538:
500:
490:
480:
473:
436:
426:
356:of weakly electric fish,
305:
3071:Caridoid escape reaction
1683:
2924:Theodore Holmes Bullock
2712:Glossary of ichthyology
2274:Diel vertical migration
1210:10.1242/jeb.202.10.1387
1072:10.1152/jn.1973.36.1.39
926:10.1163/156853974X00499
282:Processing in the brain
3081:Surface wave detection
2078:Surface wave detection
2043:Hydrodynamic reception
1717:Diseases and parasites
1284:Brain Research Reviews
965:10.1098/rsif.2017.0633
256:
179:active electrolocation
143:
36:
3151:Animal nervous system
2897:Anti-Hebbian learning
2216:Undulatory locomotion
2033:Ampullae of Lorenzini
1547:Ampullae of Lorenzini
998:Eigenmannia virescens
908:Eigenmannia virescens
668:Electric catfish
346:Further information:
243:
226:Eigenmannia virescens
168:Further information:
133:
65:Eigenmannia virescens
24:
2974:Bernhard Hassenstein
2907:Ultrasound avoidance
2882:Fixed action pattern
2845:Coincidence detector
2444:Genetically modified
1606:(electric catfishes)
1233:Heiligenberg, Walter
1143:Heiligenberg, Walter
1100:Heiligenberg, Walter
1050:Bullock, Theodore H.
867:Heiligenberg, Walter
827:Bullock, Theodore H.
441:(skates) (~200 spp)
409:convergently evolved
384:Gymnarchus niloticus
296:torus semicircularis
158:convergently evolved
153:Gymnarchus niloticus
140:evolved convergently
110:, which has a quasi-
85:Gymnarchus niloticus
78:, as well as in the
45:weakly electric fish
3041:Animal echolocation
2979:Werner E. Reichardt
2929:Walter Heiligenberg
2249:Aquatic respiration
2136:Life history theory
1572:(African knifefish)
1398:2012PLoSO...736287L
1145:; Rose, G. (1985).
810:10.1242/jeb.40.1.57
381:), and the species
352:There are two main
322:(Osteoglossiformes)
272:ampullary receptors
148:Walter Heiligenberg
3004:Fernando Nottebohm
2902:Sound localization
2877:Lateral inhibition
2088:Weberian apparatus
1467:Zoological Science
1351:10.1007/BF00209614
1251:10.1007/BF01380047
1118:10.1007/BF00656908
885:10.1007/bf01380044
845:10.1007/BF00696517
276:tuberous receptors
257:
144:
37:
3138:
3137:
3025:Slice preparation
2887:Krogh's Principle
2862:Feature detection
2792:
2791:
2702:Fish common names
2613:
2612:
2244:Aquatic predation
2068:Capacity for pain
1797:Age determination
1651:
1650:
1543:Electroreceptors
1204:(10): 1387–1398.
959:(138): 20170633.
754:
753:
745:
744:
732:
731:
723:
722:
714:
713:
705:
704:
696:
695:
636:
635:
573:
572:
542:African knifefish
487:Osteoglossiformes
389:Osteoglossiformes
366:Osteoglossiformes
249:tuberous receptor
136:African knifefish
3163:
3126:
3125:
3114:
3113:
3091:Mechanoreception
3086:Electroreception
2999:Masakazu Konishi
2964:Jörg-Peter Ewert
2819:
2812:
2805:
2796:
2795:
2780:
2779:
2768:
2767:
2750:
2749:
2484:
2483:
1776:
1707:Ethnoichthyology
1678:
1671:
1664:
1655:
1654:
1643:Magnetoreception
1594:(elephantfishes)
1497:
1490:
1483:
1474:
1473:
1442:Heiligenberg, W.
1430:
1429:
1419:
1409:
1377:
1371:
1370:
1332:
1326:
1325:
1307:
1281:
1272:
1263:
1262:
1228:
1222:
1221:
1193:
1187:
1186:
1176:
1139:
1130:
1129:
1095:
1084:
1083:
1045:
1036:
1035:
993:
987:
986:
976:
944:
938:
937:
920:(3/4): 270–305.
903:
897:
896:
863:
857:
856:
823:
814:
813:
793:
784:
687:
682:
664:
663:
627:
622:
604:
603:
594:
593:
587:
586:
559:
554:
519:
514:
493:
492:
483:
482:
476:
475:
470:Bony fishes
455:
450:
429:
428:
419:
418:
374:Electroreception
125:Theodore Bullock
53:electroreception
25:Two neighboring
3171:
3170:
3166:
3165:
3164:
3162:
3161:
3160:
3141:
3140:
3139:
3134:
3102:
3056:Vision in toads
3029:
3008:
2959:Erich von Holst
2954:Karl von Frisch
2912:
2828:
2823:
2793:
2788:
2756:
2680:
2609:
2520:
2473:
2412:
2343:
2236:
2230:
2182:
2126:Ichthyoplankton
2092:
2024:
2017:
2013:Digital Library
2008:Teleost leptins
1947:Shark cartilage
1871:pharyngeal slit
1866:pharyngeal arch
1802:Anguilliformity
1787:
1785:
1777:
1768:
1687:
1682:
1652:
1647:
1621:
1612:(electric rays)
1610:Torpediniformes
1586:(electric eels)
1558:
1527:
1506:
1501:
1446:Springer Verlag
1438:
1436:Further reading
1433:
1378:
1374:
1333:
1329:
1279:
1273:
1266:
1245:(103): 97–121.
1229:
1225:
1194:
1190:
1140:
1133:
1096:
1087:
1046:
1039:
994:
990:
945:
941:
904:
900:
864:
860:
824:
817:
791:
785:
781:
777:
760:
755:
746:
733:
724:
715:
706:
697:
637:
574:
350:
344:
324:
308:
284:
238:
222:
220:(Gymnotiformes)
213:
172:
166:
102:
19:
12:
11:
5:
3169:
3159:
3158:
3153:
3136:
3135:
3133:
3132:
3120:
3107:
3104:
3103:
3101:
3100:
3099:
3098:
3088:
3083:
3078:
3076:Vocal learning
3073:
3068:
3063:
3058:
3053:
3048:
3043:
3037:
3035:
3031:
3030:
3028:
3027:
3022:
3016:
3014:
3010:
3009:
3007:
3006:
3001:
2996:
2991:
2986:
2981:
2976:
2971:
2966:
2961:
2956:
2951:
2949:Donald Kennedy
2946:
2944:Donald Griffin
2941:
2936:
2934:Niko Tinbergen
2931:
2926:
2920:
2918:
2914:
2913:
2911:
2910:
2904:
2899:
2894:
2892:Hebbian theory
2889:
2884:
2879:
2874:
2869:
2864:
2859:
2854:
2847:
2842:
2836:
2834:
2830:
2829:
2822:
2821:
2814:
2807:
2799:
2790:
2789:
2787:
2786:
2774:
2761:
2758:
2757:
2755:
2754:
2744:
2739:
2738:
2737:
2732:
2724:
2719:
2714:
2709:
2704:
2699:
2694:
2688:
2686:
2682:
2681:
2679:
2678:
2677:
2676:
2671:
2661:
2660:
2659:
2654:
2649:
2639:
2638:
2637:
2632:
2621:
2619:
2615:
2614:
2611:
2610:
2608:
2607:
2606:
2605:
2600:
2595:
2585:
2584:
2583:
2578:
2573:
2568:
2558:
2557:
2556:
2551:
2546:
2541:
2530:
2528:
2526:Wild fisheries
2522:
2521:
2519:
2518:
2513:
2508:
2503:
2498:
2492:
2490:
2481:
2475:
2474:
2472:
2471:
2466:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2449:Hallucinogenic
2446:
2441:
2436:
2431:
2426:
2420:
2418:
2414:
2413:
2411:
2410:
2405:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2354:
2352:
2345:
2344:
2342:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2324:Schooling fish
2321:
2316:
2311:
2306:
2301:
2296:
2291:
2286:
2284:Filter feeders
2281:
2276:
2271:
2266:
2261:
2259:Bottom feeders
2256:
2251:
2246:
2240:
2238:
2232:
2231:
2229:
2228:
2223:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2198:
2192:
2190:
2184:
2183:
2181:
2180:
2179:
2178:
2168:
2163:
2158:
2153:
2148:
2143:
2138:
2133:
2128:
2123:
2118:
2113:
2108:
2102:
2100:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2090:
2085:
2080:
2075:
2070:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2050:
2045:
2040:
2035:
2029:
2027:
2019:
2018:
2016:
2015:
2010:
2005:
2004:
2003:
1998:
1988:
1987:
1986:
1981:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1960:
1959:
1949:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1928:
1927:
1917:
1912:
1907:
1905:Leydig's organ
1902:
1901:
1900:
1898:pharyngeal jaw
1895:
1885:
1880:
1879:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1853:
1851:branchial arch
1843:
1842:
1841:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1820:
1819:
1814:
1804:
1799:
1793:
1791:
1779:
1778:
1771:
1769:
1767:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1751:
1746:
1741:
1740:
1739:
1734:
1729:
1719:
1714:
1709:
1704:
1698:
1696:
1689:
1688:
1681:
1680:
1673:
1666:
1658:
1649:
1648:
1646:
1645:
1640:
1635:
1629:
1627:
1623:
1622:
1620:
1619:
1613:
1607:
1604:Malapteruridae
1601:
1595:
1589:
1588:
1587:
1573:
1566:
1564:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1556:
1555:
1554:
1549:
1541:
1539:Electric organ
1535:
1533:
1529:
1528:
1526:
1525:
1520:
1514:
1512:
1508:
1507:
1500:
1499:
1492:
1485:
1477:
1471:
1470:
1463:
1456:
1449:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1431:
1372:
1327:
1264:
1223:
1188:
1159:(2): 515–531.
1131:
1112:(2): 135–152.
1085:
1037:
1010:(164): 83–92.
988:
939:
898:
858:
815:
778:
776:
773:
772:
771:
766:
759:
756:
752:
751:
748:
747:
743:
742:
735:
734:
730:
729:
726:
725:
721:
720:
717:
716:
712:
711:
708:
707:
703:
702:
699:
698:
694:
693:
690:
689:
670:
662:
660:
654:
653:
639:
638:
634:
633:
630:
629:
613:(>100 spp)
610:
602:
600:
592:
590:
585:
583:
580:
579:
576:
575:
571:
570:
562:
561:
537:
531:
530:
522:
521:
503:elephantfishes
499:
491:
489:
481:
479:
474:
472:
466:
465:
458:
457:
435:
433:Chondrichthyes
427:
425:
417:
343:
340:
323:
316:
307:
304:
283:
280:
237:
236:Sensory coding
234:
221:
214:
212:
209:
183:electric organ
165:
162:
101:
98:
60:South American
17:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3168:
3157:
3156:Neuroethology
3154:
3152:
3149:
3148:
3146:
3131:
3130:
3121:
3119:
3118:
3109:
3108:
3105:
3097:
3094:
3093:
3092:
3089:
3087:
3084:
3082:
3079:
3077:
3074:
3072:
3069:
3067:
3064:
3062:
3059:
3057:
3054:
3052:
3049:
3047:
3044:
3042:
3039:
3038:
3036:
3032:
3026:
3023:
3021:
3018:
3017:
3015:
3011:
3005:
3002:
3000:
2997:
2995:
2992:
2990:
2987:
2985:
2982:
2980:
2977:
2975:
2972:
2970:
2967:
2965:
2962:
2960:
2957:
2955:
2952:
2950:
2947:
2945:
2942:
2940:
2939:Konrad Lorenz
2937:
2935:
2932:
2930:
2927:
2925:
2922:
2921:
2919:
2915:
2908:
2905:
2903:
2900:
2898:
2895:
2893:
2890:
2888:
2885:
2883:
2880:
2878:
2875:
2873:
2872:NMDA receptor
2870:
2868:
2865:
2863:
2860:
2858:
2855:
2853:
2852:
2848:
2846:
2843:
2841:
2838:
2837:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2826:Neuroethology
2820:
2815:
2813:
2808:
2806:
2801:
2800:
2797:
2785:
2784:
2775:
2773:
2772:
2763:
2762:
2759:
2753:
2752:more lists...
2745:
2743:
2740:
2736:
2733:
2731:
2728:
2727:
2725:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2713:
2710:
2708:
2707:Fish families
2705:
2703:
2700:
2698:
2695:
2693:
2692:Aquarium life
2690:
2689:
2687:
2683:
2675:
2674:fleshy-finned
2672:
2670:
2667:
2666:
2665:
2662:
2658:
2655:
2653:
2650:
2648:
2645:
2644:
2643:
2642:Cartilaginous
2640:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2627:
2626:
2623:
2622:
2620:
2616:
2604:
2601:
2599:
2596:
2594:
2591:
2590:
2589:
2586:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2572:
2569:
2567:
2564:
2563:
2562:
2559:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2545:
2542:
2540:
2537:
2536:
2535:
2532:
2531:
2529:
2527:
2523:
2517:
2514:
2512:
2509:
2507:
2504:
2502:
2499:
2497:
2494:
2493:
2491:
2489:
2485:
2482:
2480:
2476:
2470:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2427:
2425:
2422:
2421:
2419:
2415:
2409:
2406:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2355:
2353:
2351:
2346:
2340:
2337:
2335:
2332:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2322:
2320:
2317:
2315:
2312:
2310:
2307:
2305:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2290:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2279:Electric fish
2277:
2275:
2272:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2242:
2241:
2239:
2233:
2227:
2224:
2222:
2219:
2217:
2214:
2212:
2209:
2207:
2204:
2202:
2199:
2197:
2194:
2193:
2191:
2189:
2185:
2177:
2174:
2173:
2172:
2169:
2167:
2164:
2162:
2159:
2157:
2154:
2152:
2149:
2147:
2144:
2142:
2139:
2137:
2134:
2132:
2129:
2127:
2124:
2122:
2119:
2117:
2114:
2112:
2109:
2107:
2104:
2103:
2101:
2099:
2095:
2089:
2086:
2084:
2081:
2079:
2076:
2074:
2071:
2069:
2066:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2030:
2028:
2026:
2020:
2014:
2011:
2009:
2006:
2002:
1999:
1997:
1994:
1993:
1992:
1989:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1976:
1975:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1958:
1955:
1954:
1953:
1950:
1948:
1945:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1933:
1930:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1921:
1918:
1916:
1913:
1911:
1910:Mauthner cell
1908:
1906:
1903:
1899:
1896:
1894:
1891:
1890:
1889:
1886:
1884:
1881:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1867:
1864:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1848:
1847:
1844:
1840:
1837:
1836:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1829:Chromatophore
1827:
1825:
1822:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1810:
1809:
1808:
1805:
1803:
1800:
1798:
1795:
1794:
1792:
1790:
1784:
1780:
1775:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1755:
1752:
1750:
1747:
1745:
1742:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1724:
1723:
1720:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1708:
1705:
1703:
1700:
1699:
1697:
1695:
1690:
1686:
1679:
1674:
1672:
1667:
1665:
1660:
1659:
1656:
1644:
1641:
1639:
1636:
1634:
1631:
1630:
1628:
1624:
1617:
1616:Uranoscopidae
1614:
1611:
1608:
1605:
1602:
1599:
1596:
1593:
1590:
1585:
1584:
1583:Electrophorus
1580:
1579:
1577:
1576:Gymnotiformes
1574:
1571:
1568:
1567:
1565:
1561:
1553:
1550:
1548:
1545:
1544:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1536:
1534:
1530:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1515:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1504:Electric fish
1498:
1493:
1491:
1486:
1484:
1479:
1478:
1475:
1468:
1464:
1461:
1457:
1454:
1450:
1447:
1443:
1440:
1439:
1427:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1392:(5): e36287.
1391:
1387:
1383:
1376:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1345:(1): 97–121.
1344:
1340:
1339:
1331:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1306:
1305:2027.42/25137
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1278:
1271:
1269:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1239:
1234:
1227:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1184:
1180:
1175:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1153:
1148:
1144:
1138:
1136:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1106:
1101:
1098:Bastian, J.;
1094:
1092:
1090:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1060:
1055:
1051:
1048:Scheich, H.;
1044:
1042:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1004:
999:
992:
984:
980:
975:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
950:
943:
935:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
914:
909:
902:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
873:
868:
862:
854:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
833:
828:
822:
820:
811:
807:
803:
799:
798:
790:
783:
779:
770:
767:
765:
764:Electric fish
762:
761:
750:
749:
741:
737:
736:
728:
727:
719:
718:
710:
709:
701:
700:
692:
691:
688:
686:
681:
676:
669:
666:
665:
659:
656:
655:
652:
651:
646:
645:
641:
640:
632:
631:
628:
626:
621:
616:
609:
606:
605:
599:
598:Gymnotiformes
596:
595:
589:
588:
582:
581:
578:
577:
569:
568:
567:knollenorgans
564:
563:
560:
558:
553:
548:
544:
543:
536:
533:
532:
529:
528:
527:knollenorgans
524:
523:
520:
518:
513:
508:
504:
498:
495:
494:
488:
485:
484:
478:
477:
471:
468:
467:
464:
460:
459:
456:
454:
449:
444:
440:
434:
431:
430:
424:
421:
420:
416:
414:
410:
406:
405:
400:
399:
394:
390:
386:
385:
380:
379:Gymnotiformes
375:
371:
367:
363:
362:South America
359:
358:Gymnotiformes
355:
349:
348:Electric fish
339:
337:
333:
329:
321:
315:
313:
303:
301:
300:mesencephalon
297:
292:
289:
279:
277:
273:
268:
266:
262:
254:
250:
246:
242:
233:
231:
227:
219:
208:
206:
200:
197:
191:
189:
184:
180:
176:
171:
170:Electric fish
161:
159:
155:
154:
149:
141:
137:
132:
128:
126:
121:
117:
113:
109:
108:
97:
95:
94:neuroethology
91:
87:
86:
81:
77:
76:
71:
70:Gymnotiformes
67:
66:
61:
56:
54:
50:
46:
42:
34:
30:
29:
23:
16:
3127:
3115:
3096:Lateral line
3050:
3046:Waggle dance
2984:Eric Knudsen
2849:
2781:
2769:
2669:spiny-finned
2618:Major groups
2339:Intelligence
2319:Scale eaters
2264:Cleaner fish
2146:Mouthbrooder
2098:Reproduction
2073:Schreckstoff
2058:Lateral line
2052:
1974:Swim bladder
1964:Spiral valve
1893:hyomandibula
1876:pseudobranch
1759:Hypoxia in -
1638:Lateral line
1618:(stargazers)
1582:
1570:Gymnarchidae
1552:Knollenorgan
1522:
1469:26: 587-599.
1389:
1385:
1375:
1342:
1336:
1330:
1290:(1): 25–46.
1287:
1283:
1242:
1236:
1226:
1201:
1197:
1191:
1156:
1150:
1109:
1103:
1066:(1): 39–60.
1063:
1057:
1053:
1007:
1001:
997:
991:
956:
952:
942:
917:
911:
907:
901:
879:(1): 55–67.
876:
870:
861:
836:
830:
801:
795:
782:
674:
672:
658:Siluriformes
648:
642:
614:
612:
607:
565:
546:
540:
539:
535:Gymnarchidae
525:
506:
501:
442:
437:
402:
396:
391:). Notable
382:
351:
335:
331:
327:
325:
319:
312:diencephalon
309:
293:
285:
269:
265:beat pattern
261:interference
258:
244:
230:model system
225:
223:
217:
211:Neurobiology
201:
195:
192:
187:
174:
173:
151:
145:
105:
103:
83:
73:
63:
57:
40:
38:
26:
15:
3020:Patch clamp
2989:Eric Kandel
2969:Franz Huber
2840:Feedforward
2783:WikiProject
2742:Prehistoric
2726:Threatened
2417:Other types
2314:Sardine run
2289:Forage fish
2269:Corallivory
2121:Development
2106:Bubble nest
1979:physoclisti
1969:Suckermouth
1942:Root effect
1764:Ichthyology
1054:Eigenmannia
839:(1): 1–22.
505:(~200 spp)
423:Vertebrates
404:Apteronotus
398:Eigenmannia
318:Pathway in
245:Eigenmannia
218:Eigenmannia
216:Pathway in
196:Eigenmannia
188:Eigenmannia
175:Eigenmannia
107:Eigenmannia
75:Apteronotus
49:frequencies
28:Eigenmannia
3145:Categories
2994:Nobuo Suga
2909:in insects
2398:Groundfish
2393:Freshwater
2388:Euryhaline
2373:Coral reef
2309:Salmon run
2299:Paedophagy
2201:Amphibious
2188:Locomotion
1996:pharyngeal
1984:physostome
1937:Photophore
1883:Glossohyal
1856:gill raker
1839:dorsal fin
1789:physiology
1598:Rajiformes
1592:Mormyridae
1511:Physiology
1455:6:196-206.
775:References
497:Mormyridae
439:Rajiformes
336:Gymnarchus
332:Gymnarchus
328:Gymnarchus
320:Gymnarchus
253:beat cycle
112:sinusoidal
90:vertebrate
2647:chimaeras
2534:Predatory
2511:Salmonids
2469:Whitefish
2459:Poisonous
2434:Diversity
2368:Coldwater
2304:Predatory
2294:Migratory
2254:Bait ball
2237:behaviour
2156:Pregnancy
2151:Polyandry
1925:papillare
1920:Operculum
1915:Meristics
1861:gill slit
1824:Cleithrum
1754:Fish kill
1744:Fear of -
1737:- as food
1727:Fisheries
1712:Evolution
1702:Diversity
1460:MIT Press
913:Behaviour
804:: 57–66.
738:425
673:(11 spp)
644:ampullary
461:430
146:In 1975,
120:electrode
100:Discovery
33:frequency
3117:Category
2857:Instinct
2833:Concepts
2771:Category
2722:Smallest
2635:lampreys
2598:flatfish
2588:Demersal
2544:mackerel
2539:billfish
2479:Commerce
2408:Tropical
2383:Demersal
2378:Deep-sea
2334:Venomous
2226:RoboTuna
2176:triggers
2171:Spawning
2131:Juvenile
2116:Egg case
1749:FishBase
1600:(skates)
1426:22606250
1386:PLOS ONE
1367:27622365
1322:15603518
1259:20094087
1218:10210679
1126:26069930
1032:15744149
1024:16099058
983:29367237
893:42982465
853:19690508
758:See also
650:tuberous
274:and the
164:Behavior
82:species
72:such as
62:species
3129:Commons
3034:Systems
3013:Methods
2717:Largest
2630:hagfish
2625:Jawless
2603:pollock
2576:sardine
2571:herring
2566:anchovy
2516:Tilapia
2506:Octopus
2501:Catfish
2488:Farming
2403:Pelagic
2363:Coastal
2350:habitat
2206:Walking
2111:Clasper
2063:Otolith
2025:systems
2023:Sensory
1957:ganoine
1932:Papilla
1783:Anatomy
1722:Fishing
1626:Related
1532:Anatomy
1453:Synapse
1417:3351409
1394:Bibcode
1359:8366474
1314:6616267
1183:3973680
1174:6565201
1080:4705666
974:5805966
934:4533613
647:,
545:(1 sp)
387:(order
288:neurons
80:African
2917:People
2851:Umwelt
2735:sharks
2652:sharks
2581:sprats
2561:Forage
2549:salmon
2429:Coarse
2211:Flying
2083:Vision
2038:Barbel
1952:Scales
1812:dermal
1692:About
1563:Groups
1424:
1414:
1365:
1357:
1320:
1312:
1257:
1216:
1181:
1171:
1124:
1078:
1030:
1022:
981:
971:
932:
891:
851:
413:clades
393:genera
370:Africa
354:orders
306:Output
205:curare
2697:Blind
2685:Lists
2464:Rough
2329:Sleep
2235:Other
2001:shark
1991:Teeth
1363:S2CID
1318:S2CID
1280:(PDF)
1255:S2CID
1122:S2CID
1028:S2CID
930:JSTOR
889:S2CID
849:S2CID
792:(PDF)
675:Pulse
507:Pulse
443:Pulse
368:from
360:from
228:as a
2730:rays
2664:Bony
2657:rays
2554:tuna
2496:Carp
2454:Oily
2439:Game
2424:Bait
2358:Cave
2141:Milt
1846:Gill
1834:Fins
1807:Bone
1694:fish
1685:Fish
1422:PMID
1355:PMID
1310:PMID
1214:PMID
1179:PMID
1076:PMID
1020:PMID
979:PMID
615:Wave
547:Wave
401:and
364:and
134:The
39:The
2593:cod
2348:By
2161:Roe
1888:Jaw
1786:and
1412:PMC
1402:doi
1347:doi
1343:103
1300:hdl
1292:doi
1247:doi
1243:103
1206:doi
1202:202
1169:PMC
1161:doi
1114:doi
1110:136
1068:doi
1056:".
1012:doi
1008:164
1000:".
969:PMC
961:doi
922:doi
910:".
881:doi
877:103
841:doi
806:doi
740:mya
463:mya
372:.
3147::
1420:.
1410:.
1400:.
1388:.
1384:.
1361:.
1353:.
1341:.
1316:.
1308:.
1298:.
1286:.
1282:.
1267:^
1253:.
1241:.
1212:.
1200:.
1177:.
1167:.
1155:.
1149:.
1134:^
1120:.
1108:.
1088:^
1074:.
1064:36
1062:.
1040:^
1026:.
1018:.
1006:.
977:.
967:.
957:15
955:.
951:.
928:.
918:50
916:.
887:.
875:.
847:.
837:77
835:.
818:^
802:40
800:.
794:.
677::
617::
549::
509::
445::
232:.
116:Hz
96:.
55:.
2818:e
2811:t
2804:v
1677:e
1670:t
1663:v
1496:e
1489:t
1482:v
1448:.
1428:.
1404::
1396::
1390:7
1369:.
1349::
1324:.
1302::
1294::
1288:6
1261:.
1249::
1220:.
1208::
1185:.
1163::
1157:5
1128:.
1116::
1082:.
1070::
1034:.
1014::
985:.
963::
936:.
924::
895:.
883::
855:.
843::
812:.
808::
142:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.