269:
519:
610:
697:
392:
1703:
198:
183:
2695:
2677:
601:, which evolved out of a clade of bony fishes that breathe through their skin or lungs, than they are to the sharks, rays, and the other cartilaginous fish. Their kind of gill respiration is shared by the "fishes" because it was present in their common ancestor and lost in the other living vertebrates. But based on this shared trait, we cannot infer that bony fish are more closely related to sharks and rays than they are to terrestrial vertebrates.
58:
33:
404:
463:. Countercurrent exchange means the flow of water over the gills is in the opposite direction to the flow of blood through the capillaries in the lamellae. The effect of this is that the blood flowing in the capillaries always encounters water with a higher oxygen concentration, allowing diffusion to occur all the way along the lamellae. As a result the gills can extract over 80% of the oxygen available in the water.
2707:
326:
efficient enough to sustain life. Rather than using lungs "Gaseous exchange takes place across the surface of highly vascularised gills over which a one-way current of water is kept flowing by a specialised pumping mechanism. The density of the water prevents the gills from collapsing and lying on top of each other, which is what happens when a fish is taken out of water."
450:
579:
Most sharks rely on ram ventilation, forcing water into the mouth and over the gills by rapidly swimming forward. In slow-moving or bottom dwelling species, especially among skates and rays, the spiracle may be enlarged, and the fish breathes by sucking water through this opening, instead of through
426:
is an
Ancient Greek word for gills). The great majority of bony fish species have five pairs of gills, although a few have lost some over the course of evolution. The operculum can be important in adjusting the pressure of water inside of the pharynx to allow proper ventilation of the gills, so that
325:
the oxygen content is 8 cm per litre compared to 210 in the same volume of air. Water is 777 times more dense than air and is 100 times more viscous. Oxygen has a diffusion rate in air 10,000 times greater than in water. The use of sac-like lungs to remove oxygen from water would not be
628:
of higher fish, each pouch contains two gills. In some cases, the openings may be fused together, effectively forming an operculum. Lampreys have seven pairs of pouches, while hagfishes may have six to fourteen, depending on the species. In the hagfish, the pouches connect with the pharynx
249:, which help increase their surface area for oxygen exchange. When a fish breathes, it draws in a mouthful of water at regular intervals. Then it draws the sides of its throat together, forcing the water through the gill openings, so that it passes over the gills to the outside. The
673:, only breathe air if they need to and can otherwise rely on their gills for oxygen. Most air breathing fish are facultative air breathers that avoid the energetic cost of rising to the surface and the fitness cost of exposure to surface predators.
1448:
Pozdnyakov, S. E. & Gibson, D. I. (2008). Family
Didymozoidae Monticelli, 1888. In R. A. Bray, D. I. Gibson & A. Jones (Eds.), Keys to the Trematoda, Vol. 3 (pp. 631-734). London: CAB International and The Natural History
474:
of their internal fluids. Seawater contains more osmolytes than the fish's internal fluids, so marine fishes naturally lose water through their gills via osmosis. To regain the water, marine fishes drink large amounts of
491:). Conversely, freshwater has less osmolytes than the fish's internal fluids. Therefore, freshwater fishes must utilize their gill ionocytes to attain ions from their environment to maintain optimal blood osmolarity.
1158:
Evans, David H.; Piermarini, Peter M.; Choe, Keith P. (January 2005). "The
Multifunctional Fish Gill: Dominant Site of Gas Exchange, Osmoregulation, Acid-Base Regulation, and Excretion of Nitrogenous Waste".
113:
Fish exchange gases by pulling oxygen-rich water through their mouths and pumping it over their gills. Within the gill filaments, capillary blood flows in the opposite direction to the water, causing
446:
associated with it often remains, being located at the base of the operculum. This is, however, often greatly reduced, consisting of a small mass of cells without any remaining gill-like structure.
506:
in most amphibians. Some amphibians retain the external larval gills in adulthood, the complex internal gill system as seen in fish apparently being irrevocably lost very early in the evolution of
68:
The fish draws oxygen-rich water in through the mouth (left). It then pumps it over gills so oxygen enters the bloodstream, and allows oxygen-depleted water to exit through the gill slits (right)
1538:
Evans, D H; Piermarini, P M; Choe, K P (2005). "The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste".
613:
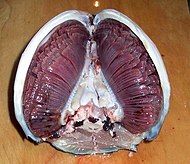
Outline of a hagfish, showing above the two ventral openings (h) by which the water escapes from the gills, and in the dissection below the spherical pouches which contain the gills
629:
internally. In adult lampreys, a separate respiratory tube develops beneath the pharynx proper, separating food and water from respiration by closing a valve at its anterior end.
94:. These filaments have many functions including the transfer of ions and water, as well as the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, acids and ammonia. Each filament contains a
1257:
Laurin M. (1998): The importance of global parsimony and historical bias in understanding tetrapod evolution. Part I-systematics, middle ear evolution, and jaw suspension.
86:
to breathe underwater. Most fish exchange gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide using gills that are protected under gill covers (operculum) on both sides of the
641:
accounts for 5 to 40 per cent of the total respiration, depending on temperature. Cutaneous respiration is more important in species that breathe air, such as
1459:
Justine, JL. (September 2004). "Three new species of
Huffmanela Moravec, 1987 (Nematoda: Trichosomoididae) from the gills of marine fish off New Caledonia".
502:
bear external gills, branching off from the gill arches. These are reduced in adulthood, their function taken over by the gills proper in fishes and by
470:
also use their gills to excrete osmolytes (e.g. Na⁺, Cl). The gills' large surface area tends to create a problem for fish that seek to regulate the
427:
bony fish do not have to rely on ram ventilation (and hence near constant motion) to breathe. Valves inside the mouth keep the water from escaping.
954:
545:
that open directly to the outside of the body, though some more primitive sharks have six or seven pairs. Adjacent slits are separated by a
790:
169:) has shown potential evidence supporting the claim that gills from all current fish species have in fact evolved from a common ancestor.
2407:
1604:
242:
system to enhance the diffusion of substances in and out of the gill, with blood and water flowing in opposite directions to each other.
624:
do not have gill slits as such. Instead, the gills are contained in spherical pouches, with a circular opening to the outside. Like the
2149:
1089:"Vestiges of the natural history of development: Historical holdovers reveal the dynamic interaction between ontogeny and phylogeny"
586:
differ from other cartilagenous fish, having lost both the spiracle and the fifth gill slit. The remaining slits are covered by an
1129:
1410:"Spatial and temporal variations of the ectoparasites of seven reef fish species from Lizard Island and Heron Island, Australia"
859:
572:
that resembles a gill in structure, but only receives blood already oxygenated by the true gills. The spiracle is thought to be
1398:
Kearn, G. C. (2004). Leeches, Lice and
Lampreys. A natural history of skin and gill parasites of fishes. Dordrecht: Springer.
985:
882:
1976:
2006:
1280:
1139:
1047:
892:
869:
318:
1349:
1660:
1597:
218:. The gills are carried right behind the head, bordering the posterior margins of a series of openings from the
1296:
667:, are obligated to breathe air periodically or they suffocate. Facultative air breathers, such as the catfish
2711:
1745:
129:
have a single gill opening on each side. This opening is hidden beneath a protective bony cover called the
2743:
1645:
711:
117:. The gills push the oxygen-poor water out through openings in the sides of the pharynx. Some fish, like
438:, so that the gills alone project from the arch, supported by individual gill rays. Some species retain
2397:
2124:
2094:
1981:
1590:
391:
2738:
2670:
2663:
2630:
2372:
2044:
1725:
1573:
321:. The concentration of oxygen in water is lower than air and it diffuses more slowly. In a litre of
2680:
2439:
840:
593:
The shared trait of breathing via gills in bony fish and cartilaginous fish is a famous example of
403:
2658:
2640:
2202:
1951:
1702:
460:
459:
Fish transfer oxygen from the sea water to their blood using a highly efficient mechanism called
268:
239:
114:
2620:
2444:
2429:
2252:
1971:
1860:
669:
565:
191:
gills inside the head. The head is oriented snout-down with the view looking towards the mouth.
1350:"Modifications of the Digestive Tract for Holding Air in Loricariid and Scoloplacid Catfishes"
977:
970:
2733:
2650:
2635:
2144:
1961:
948:
638:
527:
211:
2645:
1941:
1421:
918:
333:
151:
of gills was thought to have occurred through two diverging lines: gills formed from the
8:
2434:
2377:
2177:
2064:
1853:
1472:
815:
777:
1425:
922:
2016:
1484:
1374:
1327:
1315:
1227:
1219:
1110:
573:
553:, partly supported by a further piece of cartilage called the gill ray. The individual
329:
254:
609:
518:
2362:
2267:
2172:
2084:
2079:
2026:
1833:
1640:
1630:
1555:
1476:
1319:
1276:
1184:
1176:
1135:
1043:
981:
936:
888:
865:
557:
of the gills lie on either side of the septum. The base of the arch may also support
554:
290:
1488:
1331:
1231:
1114:
2104:
2049:
2011:
1966:
1924:
1848:
1635:
1547:
1515:
1468:
1429:
1366:
1311:
1297:"Cutaneous gas exchange in vertebrates: design, patterns, control and implications"
1211:
1168:
1100:
926:
763:
664:
587:
419:
302:
286:
130:
91:
90:(throat). Gills are tissues that are like short threads, protein structures called
20:
2321:
2301:
2129:
2116:
2099:
2054:
1936:
1875:
1799:
1794:
1730:
1717:
1687:
1202:
Szarski, Henryk (1957). "The Origin of the Larva and
Metamorphosis in Amphibia".
594:
484:
377:
373:
79:
652:
Fish from multiple groups can live out of the water for extended time periods.
2597:
2570:
2462:
2454:
2387:
2357:
2296:
2278:
2232:
2222:
1826:
1779:
1551:
1172:
861:
Fish
Physiology: Gills: Part A – Anatomy, gas transfer and acid-base regulation
696:
681:
261:
have seven. The vertebrate ancestor no doubt had more arches, as some of their
107:
1105:
1088:
2727:
2699:
2602:
2516:
2336:
2311:
2306:
2262:
2257:
2212:
2207:
2187:
2059:
1838:
1757:
1180:
748:
721:
685:
488:
341:
246:
43:
1244:
Clack, J. A. (2002): Gaining ground: the origin and evolution of tetrapods.
2592:
2416:
2331:
2291:
2192:
2134:
2074:
2001:
1996:
1986:
1902:
1892:
1821:
1804:
1711:
1672:
1665:
1559:
1480:
1188:
1035:
940:
756:
677:
569:
443:
415:
369:
298:
294:
258:
165:
160:
99:
1323:
736:, which can be extremely numerous. Other ectoparasites found on gills are
159:, as seen in jawed fish. However, recent studies on gill formation of the
140:
have external gills, a very primitive feature that they share with larval
2575:
2563:
2489:
2247:
2242:
2217:
2197:
2139:
2034:
1929:
1907:
1897:
1870:
1740:
1692:
1071:
786:
649:, and in such species can account for nearly half the total respiration.
642:
590:, developed from the septum of the gill arch in front of the first gill.
310:
278:
197:
1034:
637:
Some fish can at least partially respire without gills. In some species
182:
2625:
2424:
2392:
2326:
2316:
2237:
2227:
1912:
1880:
1865:
1811:
1784:
1767:
1434:
1409:
1378:
1223:
825:
799:
771:
741:
558:
538:
495:
471:
439:
322:
274:
227:
1520:
1503:
2382:
2367:
2352:
2182:
1843:
1789:
1752:
1735:
1682:
1000:
830:
820:
759:
729:
725:
700:
625:
598:
561:, small projecting elements that help to filter food from the water.
546:
542:
523:
476:
431:
250:
235:
223:
219:
148:
141:
126:
95:
39:
1370:
931:
906:
301:
of aquatic organisms as water contains only a small fraction of the
57:
2585:
2526:
2472:
2467:
2286:
2154:
1816:
1762:
1677:
1215:
1042:. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 316–327.
795:
766:
646:
583:
507:
442:. Though all but the most primitive bony fish lack a spiracle, the
361:
262:
222:
to the exterior. Each gill is supported by a cartilaginous or bony
156:
152:
2558:
2553:
2531:
2504:
2499:
2494:
2039:
1991:
1885:
1655:
1650:
744:
737:
733:
728:
attached to the gill but living out of it); the most commons are
717:
704:
621:
617:
467:
357:
231:
122:
87:
2477:
1357:
550:
435:
365:
353:
345:
137:
103:
32:
568:, lies in the back of the first gill slit. This bears a small
376:, as well as many other structures derived from the embryonic
2580:
2509:
1919:
534:
499:
215:
118:
2482:
2069:
1622:
1613:
904:
835:
803:
782:
752:
503:
480:
364:. Fish gill slits may be the evolutionary ancestors of the
314:
188:
83:
487:
ionocytes (formerly known as mitochondrion-rich cells and
2521:
2089:
1001:
Andrews, Chris; Adrian Exell; Neville
Carrington (2003).
418:, the gills lie in a branchial chamber covered by a bony
337:
306:
1294:
449:
155:, as seen in jawless fish species, or those form by the
1582:
884:
Fish
Physiology: Gills: Part B – Ion and water transfer
1072:
M. b. v. Roberts; Michael Reiss; Grace Monger (2000).
203:
The red gills detached from the tuna head on the left
1288:
336:, and lay the basis of essential structures such as
1579:. Updated: 11 June 2010. Retrieved 16 January 2012.
1537:
1157:
663:air breathers. Obligate air breathers, such as the
245:The gills are composed of comb-like filaments, the
1067:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1059:
969:
332:do not develop gills, the gill arches form during
1343:
1341:
479:while simultaneously expending energy to excrete
2725:
1270:
1259:Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Paris
549:gill arch from which projects a long sheet-like
1056:
238:opening to the exterior. Most species employ a
1338:
1295:Feder, Martin E.; Burggren, Warren W. (1985).
1238:
293:that have a highly folded surface to increase
257:have five to seven pairs, while the primitive
1598:
1275:, USA: Oxford University Press, p. 367,
1271:Cracraft, Joel; Donoghue, Michael J. (2004),
802:are also parasitic on gills, where they form
1501:
953:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
751:(parasites living inside the gills) include
265:relatives have more than 50 pairs of gills.
16:Organ that allows fish to breathe underwater
1502:Cannon, L. R. G.; Lester, R. J. G. (1988).
688:absorb air through their digestive tracts.
285:Gills usually consist of thin filaments of
125:, possess multiple gill openings. However,
1605:
1591:
1347:
781:which lives within the gill bone, and the
632:
576:to the ear opening in higher vertebrates.
297:. The high surface area is crucial to the
2150:Tradeoffs for locomotion in air and water
1519:
1433:
1104:
930:
214:vertebrates (types of fish) breathe with
695:
608:
597:. Bony fish are more closely related to
517:
448:
267:
1458:
1407:
1201:
1076:. London, UK: Nelson. pp. 164–165.
907:"Evolutiom: Origin of vertebrate gills"
655:Air breathing fish can be divided into
604:
172:
48:Gills allow fish to breathe underwater.
2726:
1127:
230:typically develop in the walls of the
1586:
1531:
1504:"Two turbellarians parasitic in fish"
1153:
1151:
1086:
967:
691:
513:
1030:
1028:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1016:
1014:
1012:
905:Gillis, A. and Tidswell, O. (2017).
2706:
1977:Electroreception and electrogenesis
13:
1473:10.1023/B:SYPA.0000038442.25230.8b
1316:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1985.tb00416.x
1148:
1128:Sadler, T. W. (6 September 2018).
494:In some primitive bony fishes and
65:Respiratory mechanism in bony fish
14:
2755:
1567:
1093:Evolution: Education and Outreach
1009:
2705:
2694:
2693:
2676:
2675:
1701:
1348:Armbruster, Jonathan W. (1998).
732:and certain groups of parasitic
402:
390:
196:
181:
56:
31:
1661:Environmental impact of fishing
1574:Fish Dissection - Gills exposed
1495:
1452:
1442:
1401:
1392:
1264:
1251:
1195:
434:of bony fish typically have no
1414:Marine Ecology Progress Series
1248:, Bloomington, Indiana. 369 pp
1121:
1080:
994:
961:
898:
881:Hoar WS and Randall DJ (1984)
875:
858:Hoar WS and Randall DJ (1984)
852:
454:Most bony fish have five gills
289:, branches, or slender tufted
98:network that provides a large
1:
1508:Diseases of Aquatic Organisms
1210:(860). Essex Institute: 287.
1038:; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977).
976:. Walter de Gruyter. p.
846:
716:Fish gills are the preferred
541:typically have five pairs of
1746:intramembranous ossification
1131:Langman's Medical Embryology
1087:Werth, Alexander J. (2014).
972:Concise encyclopedia biology
740:and, in seawater, larvae of
530:; most sharks have only five
383:
253:have three pairs of arches,
7:
1273:Assembling the Tree of Life
809:
712:Fish diseases and parasites
10:
2760:
2125:Fin and flipper locomotion
2095:Sequential hermaphroditism
1982:Jamming avoidance response
1699:
1552:10.1152/physrev.00050.2003
1173:10.1152/physrev.00050.2003
709:
703:parasite on the gill of a
313:of air contains about 250
18:
2689:
2613:
2546:
2453:
2415:
2406:
2345:
2276:
2163:
2115:
2025:
1950:
1710:
1620:
1106:10.1186/s12052-014-0012-5
1612:
1261:, 13e Série 19: pp 1-42.
1246:Indiana University Press
841:Artificial gills (human)
676:Catfish of the families
240:counter-current exchange
115:counter-current exchange
2641:Glossary of ichthyology
2203:Diel vertical migration
1461:Systematic Parasitology
1408:Grutter, A. S. (1994).
1204:The American Naturalist
633:Breathing without gills
599:terrestrial vertebrates
564:A smaller opening, the
461:countercurrent exchange
2007:Surface wave detection
1972:Hydrodynamic reception
1646:Diseases and parasites
1036:Romer, Alfred Sherwood
968:Scott, Thomas (1996).
707:
670:Hypostomus plecostomus
614:
531:
456:
352:(corresponding to the
282:
2145:Undulatory locomotion
1962:Ampullae of Lorenzini
1540:Physiological Reviews
1161:Physiological Reviews
1003:Manual Of Fish Health
699:
639:cutaneous respiration
612:
528:bigeyed sixgill shark
521:
452:
397:Fish gill respiration
360:) and in mammals the
271:
2373:Genetically modified
605:Lampreys and hagfish
234:, along a series of
173:Breathing with gills
2178:Aquatic respiration
2065:Life history theory
1426:1994MEPS..115...21G
1040:The Vertebrate Body
923:2017Natur.542Q.394.
816:Aquatic respiration
778:Huffmanela ossicola
409:Fish gill structure
42:bearing gills in a
2744:Respiratory system
2017:Weberian apparatus
1532:Further references
1435:10.3354/meps115021
1304:Biological Reviews
708:
692:Parasites on gills
659:air breathers and
615:
532:
514:Cartilaginous fish
457:
330:Higher vertebrates
283:
255:cartilaginous fish
166:Leucoraja erinacea
2721:
2720:
2631:Fish common names
2542:
2541:
2173:Aquatic predation
1997:Capacity for pain
1726:Age determination
1577:Australian Museum
1521:10.3354/dao005015
987:978-3-11-010661-9
378:branchial pouches
362:malleus and incus
334:fetal development
2751:
2739:Organs (anatomy)
2709:
2708:
2697:
2696:
2679:
2678:
2413:
2412:
1705:
1636:Ethnoichthyology
1607:
1600:
1593:
1584:
1583:
1563:
1526:
1525:
1523:
1499:
1493:
1492:
1456:
1450:
1446:
1440:
1439:
1437:
1405:
1399:
1396:
1390:
1389:
1387:
1385:
1354:
1345:
1336:
1335:
1301:
1292:
1286:
1285:
1268:
1262:
1255:
1249:
1242:
1236:
1235:
1199:
1193:
1192:
1155:
1146:
1145:
1125:
1119:
1118:
1108:
1084:
1078:
1077:
1074:Advanced Biology
1069:
1054:
1053:
1032:
1007:
1006:
1005:. Firefly Books.
998:
992:
991:
975:
965:
959:
958:
952:
944:
934:
902:
896:
887:Academic Press.
879:
873:
864:Academic Press.
856:
665:African lungfish
406:
394:
374:Eustachian tubes
303:dissolved oxygen
200:
185:
147:Previously, the
60:
35:
21:Fish respiration
2759:
2758:
2754:
2753:
2752:
2750:
2749:
2748:
2724:
2723:
2722:
2717:
2685:
2609:
2538:
2449:
2402:
2341:
2272:
2165:
2159:
2111:
2055:Ichthyoplankton
2021:
1953:
1946:
1942:Digital Library
1937:Teleost leptins
1876:Shark cartilage
1800:pharyngeal slit
1795:pharyngeal arch
1731:Anguilliformity
1716:
1714:
1706:
1697:
1616:
1611:
1570:
1534:
1529:
1500:
1496:
1457:
1453:
1447:
1443:
1406:
1402:
1397:
1393:
1383:
1381:
1371:10.2307/1447796
1352:
1346:
1339:
1299:
1293:
1289:
1283:
1269:
1265:
1256:
1252:
1243:
1239:
1200:
1196:
1156:
1149:
1142:
1126:
1122:
1085:
1081:
1070:
1057:
1050:
1033:
1010:
999:
995:
988:
966:
962:
946:
945:
932:10.1038/542394a
903:
899:
880:
876:
857:
853:
849:
812:
714:
694:
635:
607:
595:symplesiomorphy
516:
455:
410:
407:
398:
395:
386:
281:
226:. The gills of
208:
207:
206:
205:
204:
201:
193:
192:
186:
175:
102:for exchanging
73:
72:
71:
70:
69:
67:
61:
52:
51:
50:
49:
47:
36:
23:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2757:
2747:
2746:
2741:
2736:
2719:
2718:
2716:
2715:
2703:
2690:
2687:
2686:
2684:
2683:
2673:
2668:
2667:
2666:
2661:
2653:
2648:
2643:
2638:
2633:
2628:
2623:
2617:
2615:
2611:
2610:
2608:
2607:
2606:
2605:
2600:
2590:
2589:
2588:
2583:
2578:
2568:
2567:
2566:
2561:
2550:
2548:
2544:
2543:
2540:
2539:
2537:
2536:
2535:
2534:
2529:
2524:
2514:
2513:
2512:
2507:
2502:
2497:
2487:
2486:
2485:
2480:
2475:
2470:
2459:
2457:
2455:Wild fisheries
2451:
2450:
2448:
2447:
2442:
2437:
2432:
2427:
2421:
2419:
2410:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2378:Hallucinogenic
2375:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2355:
2349:
2347:
2343:
2342:
2340:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2289:
2283:
2281:
2274:
2273:
2271:
2270:
2265:
2260:
2255:
2253:Schooling fish
2250:
2245:
2240:
2235:
2230:
2225:
2220:
2215:
2213:Filter feeders
2210:
2205:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2188:Bottom feeders
2185:
2180:
2175:
2169:
2167:
2161:
2160:
2158:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2132:
2127:
2121:
2119:
2113:
2112:
2110:
2109:
2108:
2107:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2067:
2062:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2037:
2031:
2029:
2023:
2022:
2020:
2019:
2014:
2009:
2004:
1999:
1994:
1989:
1984:
1979:
1974:
1969:
1964:
1958:
1956:
1948:
1947:
1945:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1933:
1932:
1927:
1917:
1916:
1915:
1910:
1900:
1895:
1890:
1889:
1888:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1857:
1856:
1846:
1841:
1836:
1834:Leydig's organ
1831:
1830:
1829:
1827:pharyngeal jaw
1824:
1814:
1809:
1808:
1807:
1802:
1797:
1792:
1787:
1782:
1780:branchial arch
1772:
1771:
1770:
1760:
1755:
1750:
1749:
1748:
1743:
1733:
1728:
1722:
1720:
1708:
1707:
1700:
1698:
1696:
1695:
1690:
1685:
1680:
1675:
1670:
1669:
1668:
1663:
1658:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1633:
1627:
1625:
1618:
1617:
1610:
1609:
1602:
1595:
1587:
1581:
1580:
1569:
1568:External links
1566:
1565:
1564:
1533:
1530:
1528:
1527:
1494:
1451:
1441:
1400:
1391:
1365:(3): 663–675.
1337:
1287:
1281:
1263:
1250:
1237:
1216:10.1086/281990
1194:
1147:
1140:
1120:
1079:
1055:
1048:
1008:
993:
986:
960:
897:
874:
850:
848:
845:
844:
843:
838:
833:
828:
823:
818:
811:
808:
764:trichosomoidid
693:
690:
682:Callichthyidae
634:
631:
606:
603:
515:
512:
489:chloride cells
453:
412:
411:
408:
401:
399:
396:
389:
385:
382:
272:
202:
195:
194:
187:
180:
179:
178:
177:
176:
174:
171:
108:carbon dioxide
63:
62:
55:
54:
53:
38:
37:
30:
29:
28:
27:
26:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2756:
2745:
2742:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2731:
2729:
2714:
2713:
2704:
2702:
2701:
2692:
2691:
2688:
2682:
2681:more lists...
2674:
2672:
2669:
2665:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2656:
2654:
2652:
2649:
2647:
2644:
2642:
2639:
2637:
2636:Fish families
2634:
2632:
2629:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2621:Aquarium life
2619:
2618:
2616:
2612:
2604:
2603:fleshy-finned
2601:
2599:
2596:
2595:
2594:
2591:
2587:
2584:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2573:
2572:
2571:Cartilaginous
2569:
2565:
2562:
2560:
2557:
2556:
2555:
2552:
2551:
2549:
2545:
2533:
2530:
2528:
2525:
2523:
2520:
2519:
2518:
2515:
2511:
2508:
2506:
2503:
2501:
2498:
2496:
2493:
2492:
2491:
2488:
2484:
2481:
2479:
2476:
2474:
2471:
2469:
2466:
2465:
2464:
2461:
2460:
2458:
2456:
2452:
2446:
2443:
2441:
2438:
2436:
2433:
2431:
2428:
2426:
2423:
2422:
2420:
2418:
2414:
2411:
2409:
2405:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2354:
2351:
2350:
2348:
2344:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2308:
2305:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2288:
2285:
2284:
2282:
2280:
2275:
2269:
2266:
2264:
2261:
2259:
2256:
2254:
2251:
2249:
2246:
2244:
2241:
2239:
2236:
2234:
2231:
2229:
2226:
2224:
2221:
2219:
2216:
2214:
2211:
2209:
2208:Electric fish
2206:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2196:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2176:
2174:
2171:
2170:
2168:
2162:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2136:
2133:
2131:
2128:
2126:
2123:
2122:
2120:
2118:
2114:
2106:
2103:
2102:
2101:
2098:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2041:
2038:
2036:
2033:
2032:
2030:
2028:
2024:
2018:
2015:
2013:
2010:
2008:
2005:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1968:
1965:
1963:
1960:
1959:
1957:
1955:
1949:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1921:
1918:
1914:
1911:
1909:
1906:
1905:
1904:
1901:
1899:
1896:
1894:
1891:
1887:
1884:
1883:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1867:
1864:
1862:
1859:
1855:
1852:
1851:
1850:
1847:
1845:
1842:
1840:
1839:Mauthner cell
1837:
1835:
1832:
1828:
1825:
1823:
1820:
1819:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1810:
1806:
1803:
1801:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1791:
1788:
1786:
1783:
1781:
1778:
1777:
1776:
1773:
1769:
1766:
1765:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1758:Chromatophore
1756:
1754:
1751:
1747:
1744:
1742:
1739:
1738:
1737:
1734:
1732:
1729:
1727:
1724:
1723:
1721:
1719:
1713:
1709:
1704:
1694:
1691:
1689:
1686:
1684:
1681:
1679:
1676:
1674:
1671:
1667:
1664:
1662:
1659:
1657:
1654:
1653:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1632:
1629:
1628:
1626:
1624:
1619:
1615:
1608:
1603:
1601:
1596:
1594:
1589:
1588:
1585:
1578:
1575:
1572:
1571:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1546:(1): 97–177.
1545:
1541:
1536:
1535:
1522:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1498:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1455:
1445:
1436:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1404:
1395:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1359:
1351:
1344:
1342:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1298:
1291:
1284:
1282:0-19-517234-5
1278:
1274:
1267:
1260:
1254:
1247:
1241:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1198:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1167:(1): 97–177.
1166:
1162:
1154:
1152:
1143:
1141:9781496383921
1137:
1133:
1132:
1124:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1083:
1075:
1068:
1066:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1051:
1049:0-03-910284-X
1045:
1041:
1037:
1031:
1029:
1027:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1019:
1017:
1015:
1013:
1004:
997:
989:
983:
979:
974:
973:
964:
956:
950:
942:
938:
933:
928:
924:
920:
917:(7642): 394.
916:
912:
908:
901:
894:
893:9780080585321
890:
886:
885:
878:
871:
870:9780080585314
867:
863:
862:
855:
851:
842:
839:
837:
834:
832:
829:
827:
824:
822:
819:
817:
814:
813:
807:
805:
801:
797:
793:
792:
788:
784:
780:
779:
774:
773:
769:of the genus
768:
765:
761:
758:
754:
750:
749:Endoparasites
746:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
723:
722:ectoparasites
719:
713:
706:
702:
698:
689:
687:
686:Scoloplacidae
683:
679:
674:
672:
671:
666:
662:
658:
653:
650:
648:
644:
640:
630:
627:
623:
619:
611:
602:
600:
596:
591:
589:
585:
581:
577:
575:
571:
567:
562:
560:
556:
552:
548:
547:cartilaginous
544:
540:
536:
529:
525:
520:
511:
509:
505:
501:
497:
492:
490:
486:
482:
478:
473:
469:
464:
462:
451:
447:
445:
441:
437:
433:
428:
425:
421:
417:
405:
400:
393:
388:
387:
381:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
343:
342:thyroid gland
339:
335:
331:
327:
324:
320:
317:of oxygen at
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
280:
276:
270:
266:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
247:gill lamellae
243:
241:
237:
233:
229:
225:
221:
217:
213:
199:
190:
184:
170:
168:
167:
162:
158:
154:
150:
145:
143:
139:
134:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
111:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
66:
59:
45:
41:
34:
25:
22:
2734:Fish anatomy
2710:
2698:
2598:spiny-finned
2547:Major groups
2268:Intelligence
2248:Scale eaters
2193:Cleaner fish
2075:Mouthbrooder
2027:Reproduction
2002:Schreckstoff
1987:Lateral line
1903:Swim bladder
1893:Spiral valve
1822:hyomandibula
1805:pseudobranch
1774:
1688:Hypoxia in -
1576:
1543:
1539:
1511:
1507:
1497:
1467:(1): 29–37.
1464:
1460:
1454:
1444:
1417:
1413:
1403:
1394:
1382:. Retrieved
1362:
1356:
1307:
1303:
1290:
1272:
1266:
1258:
1253:
1245:
1240:
1207:
1203:
1197:
1164:
1160:
1130:
1123:
1096:
1092:
1082:
1073:
1039:
1002:
996:
971:
963:
949:cite journal
914:
910:
900:
883:
877:
860:
854:
789:
787:turbellarian
776:
775:, including
770:
715:
678:Loricariidae
675:
668:
660:
656:
654:
651:
636:
616:
592:
582:
578:
570:pseudobranch
563:
533:
493:
483:through the
465:
458:
444:pseudobranch
429:
423:
413:
370:thymus gland
349:
328:
299:gas exchange
295:surface area
284:
273:Pharynx and
259:jawless fish
244:
209:
164:
161:little skate
146:
135:
112:
100:surface area
75:
74:
64:
24:
2712:WikiProject
2671:Prehistoric
2655:Threatened
2346:Other types
2243:Sardine run
2218:Forage fish
2198:Corallivory
2050:Development
2035:Bubble nest
1908:physoclisti
1898:Suckermouth
1871:Root effect
1693:Ichthyology
1310:(1): 1–45.
730:monogeneans
661:facultative
643:mudskippers
580:the mouth.
559:gill rakers
485:Na/K-ATPase
440:gill rakers
432:gill arches
311:cubic meter
279:estuary cod
275:gill rakers
228:vertebrates
82:that allow
40:Gill arches
2728:Categories
2327:Groundfish
2322:Freshwater
2317:Euryhaline
2302:Coral reef
2238:Salmon run
2228:Paedophagy
2130:Amphibious
2117:Locomotion
1925:pharyngeal
1913:physostome
1866:Photophore
1812:Glossohyal
1785:gill raker
1768:dorsal fin
1718:physiology
847:References
826:Gill raker
800:Myxosporea
794:. Various
791:Paravortex
785:parasitic
772:Huffmanela
760:trematodes
757:didymozoid
710:See also:
701:Monogenean
626:gill slits
574:homologous
543:gill slits
524:gill slits
496:amphibians
472:osmolarity
323:freshwater
236:gill slits
142:amphibians
76:Fish gills
19:See also:
2576:chimaeras
2463:Predatory
2440:Salmonids
2398:Whitefish
2388:Poisonous
2363:Diversity
2297:Coldwater
2233:Predatory
2223:Migratory
2183:Bait ball
2166:behaviour
2085:Pregnancy
2080:Polyandry
1854:papillare
1849:Operculum
1844:Meristics
1790:gill slit
1753:Cleithrum
1683:Fish kill
1673:Fear of -
1666:- as food
1656:Fisheries
1641:Evolution
1631:Diversity
1514:: 15–22.
1420:: 21–30.
1181:0031-9333
831:Gill slit
821:Book lung
767:nematodes
726:parasites
588:operculum
584:Chimaeras
508:tetrapods
477:sea water
420:operculum
416:bony fish
384:Bony fish
350:columella
291:processes
251:bony fish
224:gill arch
220:esophagus
149:evolution
136:Juvenile
131:operculum
127:bony fish
96:capillary
92:filaments
2700:Category
2651:Smallest
2564:lampreys
2527:flatfish
2517:Demersal
2473:mackerel
2468:billfish
2408:Commerce
2337:Tropical
2312:Demersal
2307:Deep-sea
2263:Venomous
2155:RoboTuna
2105:triggers
2100:Spawning
2060:Juvenile
2045:Egg case
1678:FishBase
1560:15618479
1489:29105973
1481:15318018
1332:40158158
1232:85231736
1189:15618479
1115:16350360
941:28230134
810:See also
796:protists
783:encysted
762:, a few
753:encysted
742:gnathiid
734:copepods
720:of many
657:obligate
647:reedfish
618:Lampreys
566:spiracle
555:lamellae
468:teleosts
424:branchia
309:does. A
263:chordate
157:ectoderm
153:endoderm
123:lampreys
2646:Largest
2559:hagfish
2554:Jawless
2532:pollock
2505:sardine
2500:herring
2495:anchovy
2445:Tilapia
2435:Octopus
2430:Catfish
2417:Farming
2332:Pelagic
2292:Coastal
2279:habitat
2135:Walking
2040:Clasper
1992:Otolith
1954:systems
1952:Sensory
1886:ganoine
1861:Papilla
1712:Anatomy
1651:Fishing
1449:Museum.
1422:Bibcode
1384:25 June
1379:1447796
1324:3919777
1224:2458911
919:Bibcode
745:isopods
738:leeches
718:habitat
705:grouper
622:hagfish
466:Marine
366:tonsils
358:mammals
232:pharynx
138:bichirs
88:pharynx
2664:sharks
2581:sharks
2510:sprats
2490:Forage
2478:salmon
2358:Coarse
2140:Flying
2012:Vision
1967:Barbel
1881:Scales
1741:dermal
1621:About
1558:
1487:
1479:
1377:
1358:Copeia
1330:
1322:
1279:
1230:
1222:
1187:
1179:
1138:
1113:
1046:
984:
939:
911:Nature
891:
868:
755:adult
684:, and
551:septum
535:Sharks
500:larvae
498:, the
436:septum
372:, and
354:stapes
348:, the
346:larynx
344:, the
340:, the
287:tissue
277:in an
119:sharks
104:oxygen
80:organs
2626:Blind
2614:Lists
2393:Rough
2258:Sleep
2164:Other
1930:shark
1920:Teeth
1485:S2CID
1375:JSTOR
1353:(PDF)
1328:S2CID
1300:(PDF)
1228:S2CID
1220:JSTOR
1111:S2CID
804:cysts
526:in a
504:lungs
315:grams
305:that
216:gills
212:basal
2659:rays
2593:Bony
2586:rays
2483:tuna
2425:Carp
2383:Oily
2368:Game
2353:Bait
2287:Cave
2070:Milt
1775:Gill
1763:Fins
1736:Bone
1623:fish
1614:Fish
1556:PMID
1477:PMID
1386:2009
1363:1998
1320:PMID
1277:ISBN
1185:PMID
1177:ISSN
1136:ISBN
1044:ISBN
982:ISBN
955:link
937:PMID
889:ISBN
866:ISBN
836:Lung
798:and
645:and
620:and
539:rays
537:and
522:Six
481:salt
430:The
338:jaws
210:All
189:Tuna
121:and
106:and
84:fish
78:are
44:pike
2522:cod
2277:By
2090:Roe
1817:Jaw
1715:and
1548:doi
1516:doi
1469:doi
1430:doi
1418:115
1367:doi
1312:doi
1212:doi
1169:doi
1101:doi
978:542
927:doi
915:542
414:In
356:in
319:STP
307:air
2730::
1554:.
1544:85
1542:.
1510:.
1506:.
1483:.
1475:.
1465:59
1463:.
1428:.
1416:.
1412:.
1373:.
1361:.
1355:.
1340:^
1326:.
1318:.
1308:60
1306:.
1302:.
1226:.
1218:.
1208:91
1206:.
1183:.
1175:.
1165:85
1163:.
1150:^
1134:.
1109:.
1099:.
1095:.
1091:.
1058:^
1011:^
980:.
951:}}
947:{{
935:.
925:.
913:.
909:.
806:.
747:.
680:,
510:.
380:.
368:,
144:.
133:.
110:.
1606:e
1599:t
1592:v
1562:.
1550::
1524:.
1518::
1512:5
1491:.
1471::
1438:.
1432::
1424::
1388:.
1369::
1334:.
1314::
1234:.
1214::
1191:.
1171::
1144:.
1117:.
1103::
1097:7
1052:.
990:.
957:)
943:.
929::
921::
895:.
872:.
724:(
422:(
163:(
46:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.