36:
292:
373:
scanning technology to create digital endocasts without damaging valuable specimens. This gives a 3D representation of the brain. Brain size and complexity can then be determined.
249:
were rather complex, and contained in addition to the bones mentioned above several small cartilaginous components that are fused to temporal and occipital bones in mammals:
361:(braincase), providing a replica of the brain with most of the details of its outer surface. Endocasts can also form naturally, when sediments fill the empty
271:
254:
258:
233:
occur as one or more stout bony elements in several mammal groups. The occipital bone is also found as several bony elements in
472:
446:
190:
121:
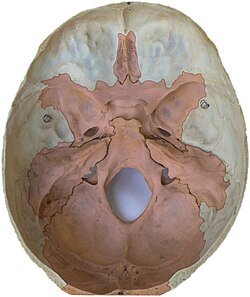
Structurally, the endocranium consists of a boxlike shape, open at the top. The posterior margin exhibit the
463:
496:
339:, the skull is only loosely joined, and the endocranial elements do not form a unit with the skull roof.
441:
Kent, G.C & Miller, L. (1997): Comparative
Anatomy of the Vertebrates. Wm. C. Brown Publishers.
68:
370:
171:(including humans), the endocranium is composed of only five bony elements (from front to back):
225:
is much reduced in relative size and number of bones compared to the condition in the ancestral
491:
459:
140:
136:
331:
dermal elements, their whole cranium being composed of the endocranium, properly called a
8:
90:
353:
An endocast or endocranial cast is a cast made of the mold formed by the impression the
464:
Colbert's
Evolution of the Vertebrates: A History of the Backboned Animals Through Time
275:
167:, that ossifies from several centers. Several of these bones merge, and in the adult
468:
442:
160:
144:
394:
246:
263:
389:
332:
324:
230:
201:
132:
123:
485:
413:
The
American Heritage Medical Dictionary, 2004. Houghton Mifflin Company, USA
183:
110:
94:
425:
358:
336:
164:
128:
98:
135:, and the anterior margin holds a spongy construction, allowing for the
74:
328:
316:
312:
245:
is generally reduced with a simplified endocranium. The skull of early
106:
320:
242:
194:
348:
308:
303:
While the endocranium is an integral part of the skull in mammals,
238:
226:
131:. The floor of the endocranium has several paired openings for the
20:
176:
168:
102:
366:
222:
156:
35:
362:
354:
304:
296:
291:
267:, fused to the petrous part of the temporal bones in mammals.
234:
56:
216:
139:
to pass through. All bones of the structure derive from the
467:. 4th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York -
105:. The term is also applied to the outer layer of the
365:, after which the skull is destroyed and the cast
376:Endocasts were used for looking at the brains of
150:
483:
421:
419:
101:and it represents the basal, inner part of the
40:Human endocranium (pink fields), inner surface.
432:5th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia. (6th ed. 1985)
186:, underlying the forward portion of the brain
416:
286:
34:
19:For the internal cast of the cranium, see
217:Endocranial components in other tetrapods
369:. Scientists are increasingly utilizing
290:
282:, part of the occipital bone in mammals.
484:
16:The lower and inner parts of the skull
380:to find hemispheric specialization.
13:
315:of the skull is more loose in the
191:petrous part of the temporal bones
14:
508:
295:The loosely connected skull of a
342:
211:
159:, the endocranium forms during
452:
435:
407:
151:Endocranial elements in humans
1:
400:
428:. & T.S. Parsons. 1977.
241:, while the skull of modern
179:bone, lying behind the nose.
116:
7:
383:
357:makes on the inside of the
10:
513:
462:& Morales, M. (2001):
346:
18:
67:
55:
50:
45:
33:
28:
311:, its connection to the
69:Anatomical terms of bone
371:computerized tomography
287:The endocranium in fish
327:, the skull lacks the
300:
274:medially and a single
294:
137:external nasal nerves
127:, an opening for the
430:The Vertebrate Body.
155:In humans and other
141:cranial neural crest
221:The endocranium in
163:as a cartilaginous
91:comparative anatomy
497:Vertebrate anatomy
301:
276:basioccipital bone
204:, surrounding the
473:978-0-471-38461-8
317:lower vertebrates
272:exoccipital bones
261:bones above each
193:, containing the
161:fetal development
145:fetal development
93:is a part of the
83:
82:
78:
504:
476:
456:
450:
439:
433:
423:
414:
411:
395:Splanchnocranium
227:land vertebrates
75:edit on Wikidata
72:
38:
26:
25:
512:
511:
507:
506:
505:
503:
502:
501:
482:
481:
480:
479:
457:
453:
440:
436:
424:
417:
412:
408:
403:
386:
351:
345:
289:
264:fenestra ovalis
247:labyrinthodonts
219:
214:
153:
119:
79:
41:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
510:
500:
499:
494:
478:
477:
451:
434:
415:
405:
404:
402:
399:
398:
397:
392:
390:Dermatocranium
385:
382:
347:Main article:
344:
341:
333:chondrocranium
325:Chondrichthyes
288:
285:
284:
283:
280:foramen magnum
268:
231:occipital bone
218:
215:
213:
210:
209:
208:
206:foramen magnum
202:occipital bone
198:
187:
180:
152:
149:
133:cranial nerves
124:foramen magnum
118:
115:
81:
80:
71:
65:
64:
59:
53:
52:
48:
47:
43:
42:
39:
31:
30:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
509:
498:
495:
493:
492:Human anatomy
490:
489:
487:
474:
470:
466:
465:
461:
460:Colbert, E.H.
455:
448:
447:0-697-24378-8
444:
438:
431:
427:
422:
420:
410:
406:
396:
393:
391:
388:
387:
381:
379:
374:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
350:
343:Fossilization
340:
338:
334:
330:
326:
322:
318:
314:
313:roofing parts
310:
306:
298:
293:
281:
277:
273:
269:
266:
265:
260:
256:
252:
251:
250:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
229:, though the
228:
224:
212:Other animals
207:
203:
199:
196:
192:
188:
185:
184:sphenoid bone
181:
178:
174:
173:
172:
170:
166:
162:
158:
148:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
126:
125:
114:
112:
111:human anatomy
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
76:
70:
66:
63:
60:
58:
54:
49:
44:
37:
32:
27:
22:
458:
454:
437:
429:
409:
378:Homo sapiens
377:
375:
359:neurocranium
352:
337:Osteichthyes
302:
279:
262:
220:
205:
200:Most of the
165:neurocranium
154:
122:
120:
86:
84:
61:
129:spinal cord
99:vertebrates
87:endocranium
62:endocranium
51:Identifiers
29:Endocranium
486:Categories
426:Romer, A.S
401:References
367:fossilized
335:. In most
329:skull roof
278:below the
259:opisthotic
243:amphibians
197:structures
107:dura mater
95:skull base
321:Agnathans
195:inner ear
117:Structure
384:See also
349:Endocast
309:reptiles
239:reptiles
169:primates
21:Endocast
270:Paired
255:prootic
253:Paired
223:mammals
189:Paired
177:ethmoid
157:mammals
143:during
103:cranium
46:Details
471:
445:
363:skull
355:brain
319:. In
305:birds
297:perch
235:birds
73:[
57:Latin
469:ISBN
443:ISBN
323:and
307:and
257:and
237:and
182:The
175:The
85:The
109:in
97:in
89:in
488::
418:^
147:.
113:.
475:.
449:.
299:.
77:]
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.