314:
33:
55:
174:
376:
332:
As part of a mating/copulation ritual, males and females fight each other. This allows the female to test the strength of the male to determine if they will produce viable offspring. During the fight, both release urine. The female's release of urine triggers a sexual response from the male. The
309:
is during early spring. After fertilisation, eggs develop inside the mother's body for 4 to 6 weeks. After that period, the eggs transition to the outside of the mother's body and rest on the female's tail. Then the eggs continue to develop and hatch in spring.
333:
male's release of urine is an aggressive response towards the fight with the female. When the male smells the female's urine, it will stop releasing its own, hoping the female will allow them to copulate.
1139:
363:
about that individual's strength. Individuals possessing larger chelae engage in more agonistic encounters and are also more likely to win. In a study of female C
977:
656:
526:
329:. Males tend to select copulation partners who have larger body sizes and are virgins. Opposed to females who were more dominant or had symmetrical chelipeds.
756:
746:
496:
967:
646:
556:
516:
466:
893:
566:
406:
396:
367:
chelae strength, researchers found that chelae size also indirectly indicated the dominance of the female because of its honest indication of strength.
863:
786:
726:
716:
626:
348:
In instances when displaying males have chelae of a similar size, they will engage in combat and those with the greater chelae closing force will win.
1167:
987:
913:
903:
826:
796:
776:
696:
686:
546:
486:
456:
923:
616:
446:
436:
426:
1720:
816:
736:
676:
636:
606:
576:
1394:
947:
706:
1197:
Aquiloni, L. & Gherardi, F. (2008). "Mutual mate choice in crayfish: Large body size is selected by both sexes, virginity by males only".
1759:
264:. Common yabbies are found in many ephemeral waterways, and can survive dry conditions for long periods of time (at least several years) by
536:
1694:
1733:
1440:
257:
336:
Once the female allows it, the male will position itself on its back, and deposit its sperm. Unlike other crayfish species, the
340:
does not use its cheliped to cage females during copulation. It is mainly used during mating when the males and females fight.
1738:
1432:
1406:
325:
are selective with copulation partners. Females tend to choose males with a larger central mass (abdomen and tail) and
1673:
1785:
1764:
1686:
1249:"To signal or not to signal? Chemical communication by urine-borne signals mirrors sexual conflict in crayfish"
1746:
1524:
1310:
1098:(Decapoda: Parastacidae), the first cave crayfish from the Southern Hemisphere (Papua Province, Indonesia)".
1364:
1175:
1642:
1629:
1647:
143:
1790:
1410:
1041:
1028:
Erichson (Decapoda: Parastacidae) in eastern
Australia re-examined using nucleotide sequences from
275:
crayfish are found widely in rivers, streams, and lakes, with a particularly high diversity in the
261:
54:
1356:"Weapon Size Is a Reliable Indicator of Strength and Social Dominance in Female Slender Crayfish (
260:
rivers and streams, lakes, swamps, and impoundments at low to medium altitude, largely within the
1818:
883:
1582:
873:
317:
Yabbies can inhabit shallow creeks during the wet season and burying themselves during droughts
1725:
1813:
313:
1777:
8:
204:
1302:"Mating Behavior and a Behavioral Assay for Female Receptivity in the Red-claw Crayfish
1329:
1277:
1248:
1226:
1199:
49:
1772:
1655:
1485:
1378:
1355:
1282:
1212:
1117:
1023:
957:
596:
295:
Some species are very colourful and sometimes seen in the freshwater aquarium trade.
1230:
1660:
1620:
1554:
1533:
1477:
1373:
1319:
1272:
1262:
1216:
1208:
1109:
1055:
766:
666:
586:
476:
1559:
836:
160:
32:
1751:
1681:
1668:
1605:
997:
933:
853:
416:
1634:
1538:
1507:
1481:
1113:
1807:
1144:
1074:
806:
506:
356:
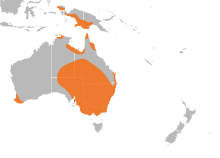
207:. Various species of cherax may be found in both still and flowing bodies of
359:
of strength, meaning the size of their chelae is a good indication to other
1489:
1286:
1267:
1121:
276:
249:
152:
126:
96:
41:
1707:
1614:
1253:
265:
116:
1075:
Freshwater Biotas of New Guinea and Nearby
Islands: Analysis of Endemism
1699:
1466:, a new crayfish (Decapoda: Parastacidae) from West Papua, Indonesia".
1333:
1221:
280:
216:
208:
268:(lying dormant) in burrows sunk deep into muddy creek and swamp beds.
173:
1712:
1520:, a new crayfish (Decapoda: Parastacidae) from West Papua, Indonesia"
221:
212:
86:
66:
1576:
1324:
1301:
1073:
Polhemus, Dan A.; Englund, Ronald A. & Allen, Gerald R. (2004).
1059:
225:, it is also the largest crayfish genus in the Southern Hemisphere.
1599:
1080:(Report). Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum, Conservation International.
375:
326:
248:
The most common and widely distributed species in
Australia is the
200:
106:
1140:"Mysterious beautiful blue crayfish is new species from Indonesia"
1021:
Munasinghe, D. H. N.; Burridge, C. P. & Austin, C. M. (2004).
1468:
1100:
242:
76:
1354:
Bywater, C. L.; Angilletta, M. J. & Wilson, R. S. (2008).
1242:
1240:
238:
196:
1237:
234:
1454:
Patoka, Jiří; Bláha, Martin & Kouba, Antonín (2015). "
1506:
Patoka, Jiří; Bláha, Martin & Kouba, Antonín (2015).
1020:
1353:
1349:
1347:
1345:
1343:
1094:
Patoka, Jiří; Bláha, Martin; Kouba, Antonín (2017). "
1024:"The systematics of freshwater crayfish of the genus
1555:"New species of crayfish named after Edward Snowden"
1072:
1340:
1022:
1247:Berry, Fiona C. & Breithaupt, Thomas (2010).
1805:
1505:
1453:
1196:
1093:
1246:
1133:
1131:
1501:
1499:
1137:
431:Lukhaup, Eprilurahman & von Rintelen, 2018
1299:
1128:
1089:
1087:
279:. New Guinea is also home to the only known
233:Members of the cherax genus can be found in
1496:
1552:
172:
31:
1537:
1393:Fetzner, James W. Jr. (11 January 2010).
1377:
1323:
1300:Barki, Assaf & Karplus, Ilan (1999).
1276:
1266:
1220:
1084:
245:across most of Australia and New Guinea.
390:The genus contains at least 59 species:
374:
312:
1441:Integrated Taxonomic Information System
1392:
938:Lukhaup, Panteleit & Schrimpf, 2015
1806:
1002:Patoka, Akmal, Bláha & Kouba, 2023
1581:
1580:
1553:Dockterman, Eliana (25 August 2015).
1138:Blaszczak-Boxe, Agata (13 May 2015).
283:crayfish in the Southern Hemisphere,
195:in Australia, is the most widespread
1687:7cb61c3a-6bd7-4cc2-a5b8-aa516bfcd143
1425:
13:
1407:Carnegie Museum of Natural History
379:Cherax "Blue Moon" which could be
14:
1830:
1379:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01379.x
1213:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2007.00370.x
53:
1546:
1447:
1386:
631:Patoka, Bláha & Kouba, 2015
401:Patoka, Bláha & Kouba, 2017
298:
1293:
1190:
1160:
1066:
1014:
1:
1525:Journal of Crustacean Biology
1311:Journal of Crustacean Biology
1008:
290:
256:). It is generally found in
982:Eprilurahman / Lukhaup, 2022
343:
7:
821:Lukhaup & Herbert, 2008
451:Coughran & Hobson, 2012
10:
1835:
541:Coughran & Furse, 2012
370:
228:
1589:
1539:10.1163/1937240x-00002377
1482:10.11646/zootaxa.3964.5.2
1114:10.11646/zootaxa.4363.1.7
1062:– via ResearchGate.
671:Lukhaup & Pekny, 2006
481:Lukhaup & Pekny, 2008
171:
158:
151:
50:Scientific classification
48:
39:
30:
23:
1048:Invertebrate Systematics
884:Cherax quinquecarinatus
811:Short & Davie, 1993
1403:Crayfish Taxon Browser
1304:Cherax quadricarinatus
1268:10.1186/1741-7007-8-25
874:Cherax quadricarinatus
387:
318:
305:The mating season for
378:
316:
1682:Fauna Europaea (new)
978:Cherax wagenknechtae
657:Cherax gladstonensis
527:Cherax cartalacoolah
262:Murray–Darling Basin
187:, commonly known as
942:Cherax subterigneus
878:(von Martens, 1868)
757:Cherax neopunctatus
747:Cherax neocarinatus
497:Cherax buitendijkae
205:Southern Hemisphere
16:Genus of crayfishes
1365:Functional Ecology
1200:Journal of Zoology
968:Cherax urospinosus
647:Cherax glabrimanus
557:Cherax crassimanus
517:Cherax cairnsensis
467:Cherax bicarinatus
388:
319:
1801:
1800:
1773:Open Tree of Life
1583:Taxon identifiers
1096:Cherax acherontis
1003:
993:
983:
973:
963:
958:Cherax tenuimanus
953:
939:
929:
919:
909:
899:
894:Cherax rhynchotus
889:
879:
869:
859:
849:
842:
832:
822:
812:
802:
792:
782:
772:
762:
752:
742:
732:
722:
712:
702:
692:
682:
672:
662:
652:
642:
632:
622:
612:
602:
597:Cherax destructor
592:
582:
572:
567:Cherax cuspidatus
562:
552:
542:
532:
522:
512:
502:
492:
482:
472:
462:
452:
442:
432:
422:
412:
407:Cherax albertisii
402:
397:Cherax acherontis
357:honest signalling
199:of fully aquatic
180:
179:
147:
42:Cherax destructor
1826:
1794:
1793:
1781:
1780:
1768:
1767:
1755:
1754:
1752:NHMSYS0021196539
1742:
1741:
1729:
1728:
1716:
1715:
1703:
1702:
1690:
1689:
1677:
1676:
1664:
1663:
1651:
1650:
1638:
1637:
1625:
1624:
1623:
1610:
1609:
1608:
1578:
1577:
1572:
1571:
1569:
1567:
1550:
1544:
1543:
1541:
1503:
1494:
1493:
1451:
1445:
1444:
1429:
1423:
1422:
1420:
1418:
1409:. Archived from
1390:
1384:
1383:
1381:
1351:
1338:
1337:
1327:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1280:
1270:
1244:
1235:
1234:
1224:
1194:
1188:
1187:
1185:
1183:
1174:. Archived from
1172:www.dept.psu.edu
1164:
1158:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1135:
1126:
1125:
1091:
1082:
1081:
1079:
1070:
1064:
1063:
1045:
1038:
1018:
1001:
991:
981:
971:
961:
951:
937:
927:
917:
907:
897:
887:
877:
867:
864:Cherax punctatus
857:
847:
841:(Erichson, 1846)
840:
830:
820:
810:
800:
790:
787:Cherax paniaicus
780:
770:
767:Cherax nucifraga
760:
750:
740:
730:
727:Cherax monticola
720:
717:Cherax misolicus
710:
700:
690:
680:
670:
667:Cherax holthuisi
660:
650:
640:
630:
627:Cherax gherardii
620:
610:
600:
590:
587:Cherax depressus
580:
570:
560:
550:
540:
530:
520:
510:
500:
490:
480:
477:Cherax boesemani
470:
460:
450:
440:
430:
420:
410:
400:
219:. Together with
176:
161:Astacus preissii
142:
58:
57:
35:
21:
20:
1834:
1833:
1829:
1828:
1827:
1825:
1824:
1823:
1804:
1803:
1802:
1797:
1789:
1784:
1776:
1771:
1763:
1758:
1750:
1745:
1737:
1732:
1724:
1719:
1711:
1706:
1698:
1693:
1685:
1680:
1672:
1667:
1659:
1654:
1646:
1641:
1633:
1628:
1619:
1618:
1613:
1604:
1603:
1598:
1585:
1575:
1565:
1563:
1551:
1547:
1504:
1497:
1452:
1448:
1431:
1430:
1426:
1416:
1414:
1413:on 2 April 2015
1399:Erichson, 1846"
1391:
1387:
1352:
1341:
1325:10.2307/1549258
1298:
1294:
1245:
1238:
1195:
1191:
1181:
1179:
1178:on 18 July 2022
1166:
1165:
1161:
1151:
1149:
1148:. No. 3021
1136:
1129:
1092:
1085:
1077:
1071:
1067:
1060:10.1071/IS03012
1039:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1006:
988:Cherax wasselli
914:Cherax rotundus
904:Cherax robustus
848:McCulloch, 1914
845:Cherax angustus
837:Cherax preissii
827:Cherax plebejus
797:Cherax papuanus
777:Cherax pallidus
697:Cherax lorentzi
687:Cherax longipes
547:Cherax communis
487:Cherax boschmai
457:Cherax barretti
373:
346:
301:
293:
271:In New Guinea,
231:
211:across most of
167:
164:
141:
52:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1832:
1822:
1821:
1819:Decapod genera
1816:
1799:
1798:
1796:
1795:
1782:
1769:
1756:
1743:
1730:
1717:
1704:
1691:
1678:
1669:Fauna Europaea
1665:
1652:
1639:
1626:
1611:
1595:
1593:
1587:
1586:
1574:
1573:
1545:
1532:(6): 830–838.
1495:
1476:(5): 526–536.
1460:Astaconephrops
1446:
1424:
1385:
1372:(2): 311–316.
1339:
1318:(3): 493–497.
1292:
1236:
1207:(2): 171–179.
1189:
1159:
1127:
1108:(1): 137–144.
1083:
1065:
1054:(2): 215–225.
1012:
1010:
1007:
1005:
1004:
998:Cherax woworae
994:
984:
974:
964:
954:
952:Holthuis, 1949
944:
934:Cherax snowden
930:
924:Cherax setosus
920:
910:
900:
890:
880:
870:
860:
854:Cherax pulcher
850:
833:
823:
813:
803:
801:Holthuis, 1949
793:
791:Holthuis, 1949
783:
781:Holthuis, 1949
773:
763:
753:
743:
741:Holthuis, 1949
733:
731:Holthuis, 1950
723:
721:Holthuis, 1949
713:
711:Holthuis, 1996
703:
693:
691:Holthuis, 1949
683:
681:Coughran, 2005
673:
663:
653:
643:
633:
623:
617:Cherax esculus
613:
603:
593:
583:
573:
563:
553:
551:Holthuis, 1949
543:
533:
523:
513:
503:
501:Holthuis, 1949
493:
491:Holthuis, 1949
483:
473:
463:
453:
447:Cherax austini
443:
437:Cherax aruanus
433:
427:Cherax alyciae
423:
417:Cherax albidus
413:
403:
392:
372:
369:
345:
342:
321:Both sexes of
300:
297:
292:
289:
230:
227:
178:
177:
169:
168:
166:Erichson, 1846
165:
156:
155:
149:
148:
134:
130:
129:
124:
120:
119:
114:
110:
109:
104:
100:
99:
94:
90:
89:
84:
80:
79:
74:
70:
69:
64:
60:
59:
46:
45:
37:
36:
28:
27:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1831:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1811:
1809:
1792:
1787:
1783:
1779:
1774:
1770:
1766:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1735:
1731:
1727:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1683:
1679:
1675:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1631:
1627:
1622:
1616:
1612:
1607:
1601:
1597:
1596:
1594:
1592:
1588:
1584:
1579:
1562:
1561:
1556:
1549:
1540:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1526:
1521:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1502:
1500:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1470:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1450:
1442:
1438:
1436:
1428:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1398:
1389:
1380:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1366:
1361:
1359:
1358:Cherax dispar
1350:
1348:
1346:
1344:
1335:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1312:
1307:
1305:
1296:
1288:
1284:
1279:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1255:
1250:
1243:
1241:
1232:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1201:
1193:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1163:
1147:
1146:
1145:New Scientist
1141:
1134:
1132:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1102:
1097:
1090:
1088:
1076:
1069:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1043:
1037:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1017:
1013:
1000:
999:
995:
990:
989:
985:
980:
979:
975:
970:
969:
965:
962:(Smith, 1912)
960:
959:
955:
950:
949:
945:
943:
936:
935:
931:
926:
925:
921:
916:
915:
911:
906:
905:
901:
896:
895:
891:
886:
885:
881:
876:
875:
871:
866:
865:
861:
858:Lukhaup, 2015
856:
855:
851:
846:
839:
838:
834:
829:
828:
824:
819:
818:
817:Cherax peknyi
814:
809:
808:
807:Cherax parvus
804:
799:
798:
794:
789:
788:
784:
779:
778:
774:
769:
768:
764:
759:
758:
754:
749:
748:
744:
739:
738:
737:Cherax murido
734:
729:
728:
724:
719:
718:
714:
709:
708:
704:
699:
698:
694:
689:
688:
684:
679:
678:
677:Cherax leckii
674:
669:
668:
664:
659:
658:
654:
649:
648:
644:
639:
638:
637:Cherax glaber
634:
629:
628:
624:
619:
618:
614:
609:
608:
607:Cherax dispar
604:
599:
598:
594:
589:
588:
584:
579:
578:
577:Cherax davisi
574:
569:
568:
564:
559:
558:
554:
549:
548:
544:
539:
538:
534:
529:
528:
524:
519:
518:
514:
509:
508:
507:Cherax cainii
504:
499:
498:
494:
489:
488:
484:
479:
478:
474:
469:
468:
464:
459:
458:
454:
449:
448:
444:
439:
438:
434:
429:
428:
424:
419:
418:
414:
409:
408:
404:
399:
398:
394:
393:
391:
386:
382:
377:
368:
366:
362:
358:
354:
349:
341:
339:
338:Cherax dispar
334:
330:
328:
324:
315:
311:
308:
303:
296:
288:
286:
285:C. acherontis
282:
278:
274:
269:
267:
263:
259:
255:
254:C. destructor
251:
246:
244:
240:
236:
226:
224:
223:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
185:
175:
170:
163:
162:
157:
154:
150:
145:
140:
139:
135:
132:
131:
128:
125:
122:
121:
118:
115:
112:
111:
108:
105:
102:
101:
98:
95:
92:
91:
88:
85:
82:
81:
78:
75:
72:
71:
68:
65:
62:
61:
56:
51:
47:
44:
43:
38:
34:
29:
26:
22:
19:
1814:Parastacidae
1590:
1564:. Retrieved
1558:
1548:
1529:
1523:
1518:subterigneus
1517:
1513:
1509:
1473:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1455:
1449:
1434:
1427:
1415:. Retrieved
1411:the original
1402:
1396:
1388:
1369:
1363:
1357:
1315:
1309:
1303:
1295:
1258:
1252:
1204:
1198:
1192:
1180:. Retrieved
1176:the original
1171:
1162:
1150:. Retrieved
1143:
1105:
1099:
1095:
1068:
1051:
1047:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1016:
996:
986:
976:
966:
956:
948:Cherax solus
946:
941:
932:
928:(Riek, 1951)
922:
912:
902:
892:
888:(Gray, 1845)
882:
872:
862:
852:
844:
835:
831:(Hess, 1865)
825:
815:
805:
795:
785:
775:
765:
755:
745:
735:
725:
715:
707:Cherax minor
705:
695:
685:
675:
665:
655:
645:
635:
625:
615:
605:
595:
585:
575:
565:
555:
545:
535:
525:
515:
511:Austin, 2002
505:
495:
485:
475:
471:(Gray, 1845)
465:
455:
445:
435:
425:
421:Clarke, 1936
415:
411:Nobili, 1899
405:
395:
389:
385:C. holthuisi
384:
381:C. boesemani
380:
364:
360:
352:
350:
347:
337:
335:
331:
322:
320:
306:
304:
302:
299:Reproduction
294:
284:
277:Paniai Lakes
272:
270:
253:
250:common yabby
247:
232:
220:
192:
188:
183:
182:
181:
159:
153:Type species
137:
136:
127:Parastacidae
97:Malacostraca
40:
24:
18:
1708:iNaturalist
1615:Wikispecies
1417:24 November
1254:BMC Biology
1222:2158/252681
1036:rRNA genes"
918:Clark, 1941
868:Clark, 1936
771:Short, 1991
601:Clark, 1936
581:Clark, 1941
531:Short, 1993
461:Clark, 1941
281:cave-living
266:aestivating
117:Pleocyemata
1808:Categories
1168:"Crayfish"
1009:References
992:Riek, 1969
972:Riek, 1969
908:Riek, 1951
898:Riek, 1951
761:Riek, 1969
751:Riek, 1967
701:Roux, 1911
661:Riek, 1969
651:Riek, 1967
641:Riek, 1967
621:Riek, 1956
611:Riek, 1951
591:Riek, 1951
571:Riek, 1969
561:Riek, 1967
537:Cherax cid
521:Riek, 1969
441:Roux, 1911
291:Introduced
217:New Guinea
209:freshwater
113:Suborder:
87:Arthropoda
1566:25 August
1464:gherardii
1261:(1): 25.
1032:rRNA and
361:C. dispar
353:C. dispar
344:Behaviour
222:Euastacus
213:Australia
73:Kingdom:
67:Eukaryota
1606:Q2702517
1600:Wikidata
1490:26249463
1287:20353555
1231:84513148
1122:29245414
365:. dispar
327:cheliped
201:crayfish
144:Erichson
123:Family:
107:Decapoda
83:Phylum:
77:Animalia
63:Domain:
1739:1133542
1726:1069681
1700:4417557
1469:Zootaxa
1395:"Genus
1334:1549258
1278:2867775
1101:Zootaxa
371:Species
351:Female
258:lowland
243:streams
229:Habitat
203:in the
193:yabbies
133:Genus:
103:Order:
93:Class:
1791:877788
1674:238450
1635:Cherax
1621:Cherax
1591:Cherax
1514:Cherax
1510:Cherax
1488:
1456:Cherax
1435:Cherax
1397:Cherax
1332:
1285:
1275:
1229:
1182:27 May
1152:28 May
1120:
1026:Cherax
323:Cherax
307:Cherax
273:Cherax
241:, and
239:rivers
184:Cherax
146:, 1846
138:Cherax
25:Cherax
1786:WoRMS
1778:79854
1721:IRMNG
1713:87399
1661:7NSKZ
1330:JSTOR
1227:S2CID
1078:(PDF)
940:syn.
843:syn.
355:uses
235:lakes
197:genus
189:yabby
1765:6722
1760:NCBI
1734:ITIS
1695:GBIF
1648:5592
1643:BOLD
1568:2015
1560:Time
1486:PMID
1474:3964
1419:2015
1283:PMID
1184:2022
1154:2015
1118:PMID
1106:4363
215:and
1747:NBN
1656:CoL
1630:AFD
1534:doi
1478:doi
1374:doi
1320:doi
1273:PMC
1263:doi
1217:hdl
1209:doi
1205:274
1110:doi
1056:doi
1042:PDF
1034:16S
1030:12S
383:or
1810::
1788::
1775::
1762::
1749::
1736::
1723::
1710::
1697::
1684::
1671::
1658::
1645::
1632::
1617::
1602::
1557:.
1530:35
1528:.
1522:.
1516:)
1498:^
1484:.
1472:.
1462:)
1439:.
1405:.
1401:.
1370:22
1368:.
1362:.
1360:)"
1342:^
1328:.
1316:19
1314:.
1308:.
1281:.
1271:.
1257:.
1251:.
1239:^
1225:.
1215:.
1203:.
1170:.
1142:.
1130:^
1116:.
1104:.
1086:^
1052:18
1050:.
1046:.
287:.
237:,
1570:.
1542:.
1536::
1512:(
1508:"
1492:.
1480::
1458:(
1443:.
1437:"
1433:"
1421:.
1382:.
1376::
1336:.
1322::
1306:"
1289:.
1265::
1259:8
1233:.
1219::
1211::
1186:.
1156:.
1124:.
1112::
1058::
1044:)
1040:(
252:(
191:/
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.