406:
presented rats with levers that triggered the release of a cinnamon flavored solution. After the rats learned to press the lever, the researchers changed the value of the outcome (the rats were taught to dislike the flavor either by being given too much of the flavor, or by making the rats ill after drinking the solution) and the effects were observed. Normal rats pressed the lever less frequently, while rats with lesions in the caudate did not suppress the behavior as effectively. In this way, the study demonstrates the link between the caudate and goal-directed behavior; rats with damaged caudate nuclei had difficulty assessing the changing value of the outcome. In a 2003-human behavioral study, a similar process was repeated, but the decision this time was whether or not to trust another person when money was at stake. While here the choice was far more complex––the subjects were not simply asked to press a lever, but had to weigh a host of different factors––at the crux of the study was still behavioral selection based on changing values of outcomes.
911:. This can result in enduring cognitive and behavioral deficits, which can result in significant functional limitations, being overlooked. The symptoms of caudate strokes are usually more severe and persistent when they are bilateral rather than unilateral. In addition, they are more severe when other adjacent structures are also involved. Mendez et al. (1989) categorized caudate stroke patients into three groups based on stroke location and patterns of clinical symptoms: (1) apathetic or abulic, with difficulties perseverating in tasks (dorsolateral caudate); (2) restless, agitated, hyperactive, disinhibited, inappropriate, impulsive, distractible, and/or inattentive (ventromedial caudate); and (3) affective disturbances (
1105:) which are later combined with various cognitive deficiencies, including dementia. Parkinson's disease depletes dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal tract, a dopamine pathway that is connected to the head of the caudate. As such, many studies have correlated the loss of dopaminergic neurons that send axons to the caudate nucleus and the degree of dementia in Parkinson's patients. And while a relationship has been drawn between the caudate and Parkinson's motor deficiencies, the caudate has also been associated with Parkinson's concomitant cognitive impairments. One review contrasts the performance of patients with Parkinson's and patients that strictly had frontal-lobe damage in the
276:
1142:. The authors used MR images to compare the relative volumes of the caudate nuclei (as the caudate is a bilateral structure), and drew a connection between any asymmetries and symptoms of ADHD: "The degree of caudate asymmetry significantly predicted cumulative severity ratings of inattentive behaviors." This correlation is congruent with previous associations of the caudate with attentional functioning. A more recent 2018 study replicated these findings, and demonstrated that the caudate asymmetries related to ADHD were more pronounced in the dorsal medial regions of the caudate.
1471:
1459:
1635:
compromised by the death of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (Chapter 17). Patients with
Parkinson disease have normal declarative memory (unless they have a co-occurring dementia as may occur in Lewy body disease.) However, they have marked impairments of stimulus-response learning. Patients with Parkinson disease or other basal ganglia disorders such as Huntington disease (in which caudate neurons themselves are damaged) have deficits in other procedural learning tasks, such as the acquisition of new motor programs.
1435:
1109:. The differences in performance between the two types of patients (in a test that, in short, requires subjects to select appropriate intermediate goals with a larger goal in mind) draws a link between the caudate and goal-directed action. However, the studies are not conclusive. While the caudate has been associated with executive function (see "Goal-Directed Action"), it remains "entirely unclear whether executive deficits in reflect pre-dominantly their cortical or subcortical damage."
1255:
1303:
1411:
1375:
1423:
1279:
41:
1291:
29:
1351:
1339:
1327:
226:
1363:
1315:
1447:
1399:
1387:
552:
trilingual subject with a lesion to the caudate was observed. The patient maintained language comprehension in her three languages, but when asked to produce language, she involuntarily switched between the three languages. In short, "these and other findings with bilingual patients suggest that the left caudate is required to monitor and control lexical and language alternatives in production tasks."
3312:
give cortical signs . The smaller restricted striatocapsular infarct, also due to embolism as is the larger variety, usually does not give cortical signs and is an underacknowledged entity . There are other subcortical strokes, including internal borderzone (watershed) infarction, considered most likely due to hypoperfusion and others with even less certain patho-etiologies (TABLE 1) .
360:
greater in the caudate nucleus when the activity immediately preceded a motor response. These results indicate that the caudate nucleus could be involved in coding a motor response. With this in mind, the caudate nucleus could be involved in the recruitment of the motor system to support working memory performance by the mediation of sensory-motor transformations.
982:, and gaze abnormalities, among others. Caudate hemorrhages are due to rupture of penetrating arteries. Aside from additional acute subarachnoid hemorrhage-like symptoms, symptoms of caudate hemorrhages are similar to those of caudate infarcts, including features like behavioral abnormalities, dysarthria, movement disorders, language disorders, and memory problems.
631:. A 2002 review described 108 patients with 119 caudate infarcts that had been characterized, with three of the largest series having a total of 64 patients. In the 1994 meta-analysis, there were 43 patients with lesions confined to the caudate nucleus and 129 patients with lesions involving both the caudate and other structures, with 172 patients in total.
658:, which are small and are due to a single perforating artery occlusion, or can be striatocapsular (caudate–putamen–internal capsule) infarcts, which are larger and are due to multiple perforating artery occlusion. Caudate nucleus strokes infrequently affect only the caudate, but usually also involve neighboring areas like the anterior portion of the
610:(CT) scanning in the 1970s and early 1980s. Major studies of caudate strokes have included Stein et al. (1984), Weisberg et al. (1984), Mendez et al. (1989), Caplan et al. (1990), Caplan & Helgason (1995), Bokura & Robinson (1997), Kumral et al. (1999), Gnanashanmugam (2011), and Kumral et al. (2023). A number of
3727:
progression of small-vessel disease is a typical feature of the lacunar infarcts. For this reason, lacunar infarction should be regarded as a potentially severe condition rather than a relatively benign disorder and, therefore, lacunar stroke patients require adequate and rigorous management and follow-up.
3831:
infarcts have commonly been regarded as benign vascular lesions with a favourable long-term prognosis. However, recent studies have shown that this is only the case early in the disease course. A few years after infarct, there is an increased risk of death, mainly from cardiovascular causes. The risk
3726:
Lacunar infarcts show a paradoxical clinical course with a favorable prognosis in the short term, characterized by a low early mortality and reduced functional disability on hospital discharge, but with an increased risk of death, stroke recurrence and dementia in the mid- and long term. Asymptomatic
1167:
A 2014 study found Type I Bipolar patients had relatively higher volume of gray and white matter in the caudate nucleus and other areas associated with reward processing and decision making, compared to controls and
Bipolar II subjects. Overall the amount of gray and white matter in Bipolar patients
998:
years. People with caudate strokes only rarely die, and generally because of underlying heart disease or other problems rather than the stroke itself. However, although having favorable prognosis in the short-term, and having previously thought to be relatively benign, lacunar strokes in general are
376:
to the caudate nucleus and the resulting lesions produced, a "leaping or forward movement" was observed in monkeys. Due to its association with damage to the caudate, this movement demonstrates the inhibitory nature of the caudate nucleus. The "motor release" observed as a result of this procedure
3753:
In a follow-up study, patients with lacunar infarcts are diagnosed with dementia 4 to 12 times more frequently than the average population. Post-stroke dementia in accumulated lacunar infarct is common despite their small size and association with small vessel disease. Lacunar strokes are a common
555:
Local shape deformations of the medial surface of the caudate have been correlated with verbal learning capacity for females and the number of perseverance errors on spatial and verbal fluency working memory tasks for males. Specifically, a larger caudate nucleus volume has been linked with better
3311:
Clinical diagnosis of subcortical infarction, chiefly lacunar stroke, Subcortical infarction is unfortunately often considered synonymous with lacunar stroke, Not all subcortical strokes are lacunes. The large striatocapsular infarct, even though confined to subcortical structures, usually does
1634:
Evidence that the caudate nucleus and putamen influence stimulus-response learning comes from lesion studies in rodents and primates and from neuroimaging studies in humans and from studies of human disease. In
Parkinson disease, the dopaminergic innervation of the caudate and putamen is severely
1088:
patients and the caudate nucleus. MRI images were used to estimate the volume of caudate nuclei in patients with
Alzheimer's and normal volunteers. The study found a "significant reduction in the caudate volume" in Alzheimer's patients when compared to the normal volunteers. While the correlation
906:
The sizes, locations, and involvements of neighboring structures define the symptoms of caudate lesions. Damage to the caudate nucleus usually presents with cognitive and behavioral symptoms rather than with neurological signs. Cognitive and behavioral symptoms are more common than motor problems
359:
analysis techniques. Activity in the caudate nucleus was demonstrated to be greater during tasks featuring spatial and motoric memory demands than those that involved nonspatial tasks. Specifically, spatial working memory activity has been observed, via fMRI studies of delayed recognition, to be
245:, so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not as a result of structural differences, but merely due to the topographical distribution of function.
3272:
The occurrence of stroke involving only the caudate nucleus seems overall rather uncommon. In one register study 23, it was reported that patients with caudate stroke constituted only 1% of a total number of 3050 stroke patients (2450 ischaemic stroke and 600 haemorrhagic stroke). In the present
1125:
gene which encodes for Htt protein. The Htt protein interacts with over 100 other proteins, and appears to have multiple biological functions. The behavior of this mutated protein is not completely understood, but it is toxic to certain cell types, particularly in the brain. Early damage is most
985:
The prognosis of caudate strokes has been considered good and benign, with majorities of individuals recovering and becoming independent. However, patients with caudate strokes can have residual deficits and dependency needs, can worsen clinically with time, or can require institutionalization.
551:
Neuroimaging studies reveal that people who can communicate in multiple languages activate exactly the same brain regions regardless of the language. A 2006 publication studies this phenomenon and identifies the caudate as a center for language control. In perhaps the most illustrative case, a
405:
Meanwhile, behavioral studies provide another layer to the argument: recent studies suggest that the caudate is fundamental to goal-directed action, that is, "the selection of behavior based on the changing values of goals and a knowledge of which actions lead to what outcomes." One such study
462:
In a 2005 study, subjects were asked to learn to categorize visual stimuli by classifying images and receiving feedback on their responses. Activity associated with successful classification learning (correct categorization) was concentrated to the body and tail of the caudate, while activity
422:
patients. Functional imaging has shown activation of this subcortical loop during working memory tasks in primates and healthy human subjects. The caudate may be affiliated with deficits involving working memory from before illness onset as well. Caudate nucleus volume has been found to be
368:
The caudate nucleus contributes importantly to body and limbs posture and the speed and accuracy of directed movements. Deficits in posture and accuracy during paw usage tasks were observed following the removal of caudate nuclei in felines. A delay in initiating performance and the need to
534:
Approach-attachment behavior and affect are also controlled by the caudate nucleus. Cats with bilateral removal of the caudate nuclei persistently approached and followed objects, attempting to contact the target, while exhibiting a friendly disposition by the elicitation of treading of the
681:. About 25 to 30% of lesions are confined exclusively to the caudate. Caudate strokes are usually unilateral, but can also be bilateral, affecting both the left and right caudate nuclei. In the 1994 meta-analysis, 90% of isolated caudate infarcts were unilateral and 10% were bilateral.
402:) and anatomical studies expose a strong relationship between the caudate and cortical areas associated with executive functioning: "non-invasive measures of anatomical and functional connectivity in humans demonstrate a clear link between the caudate and executive frontal areas."
931:) (dorsolateral caudate, with larger lesions and more often extending into adjacent areas). Sometimes, abulia can alternate with periods of disinhibition and agitation in people with caudate strokes. The symptoms of caudate infarcts are assumed to be due to interruption of
907:(e.g., respective rates of 39% vs. 20% in the 1994 meta-analysis). Due to the predominance of cognitive and behavioral symptoms over neurological symptoms, and frequent absence of classical stroke signs, people with caudate strokes can be misdiagnosed as having primarily
1071:
that has infiltrated the structure. Opinions in this area are mixed about resecting the caudate, with some authors reporting relatively few deficits upon caudate removal, and others recommending against removal due to poor cognitive and behavioral outcomes, for instance
811:(14–33%). Motor weakness is often absent, minor/slight, or transient, and reportedly does not occur with lesions confined exclusively to the caudate nucleus. Abulia is defined as decreased spontaneous verbal and motor activity and slowness, with symptoms including
3462:
Riahi, A., Derbali, H., Bedoui, I., Messelmani, M., Mansour, M., Zaouali, J., & Mrissa, R. (2016, June). Implication of
Caudate nucleus lacunar infarcts in post-stroke depression. European Journal of Neurology, 23(Suppl 2), 756–756 (abstract no. P32016).
535:
forelimbs and purring. The magnitude of the behavioral responses was correlated to the extent of the removal of the nuclei. Reports of human patients with selective damage to the caudate nucleus show unilateral caudate damage resulting in loss of drive,
4182:
Goehler H, Lalowski M, Stelzl U, Waelter S, Stroedicke M, Worm U, Droege A, Lindenberg KS, Knoblich M, Haenig C, Herbst M, Suopanki J, Scherzinger E, Abraham C, Bauer B, Hasenbank R, Fritzsche A, Ludewig AH, Büssow K, Buessow K, Coleman SH, Gutekunst CA,
409:
In short, neuroimagery and anatomical studies support the assertion that the caudate plays a role in executive functioning, while behavioral studies deepen our understanding of the ways in which the caudate guides some of our decision-making processes.
390:
A review of neuroimaging studies, anatomical studies of caudate connectivity, and behavioral studies reveals a role for the caudate in executive functioning. A study of
Parkinson's patients (see below) may also contribute to a growing body of evidence.
1130:, but as the disease progresses, other areas of the brain are also more conspicuously affected. Early symptoms are attributable to functions of the striatum and its cortical connections—namely control over movement, mood and higher cognitive function.
3792:
Recent studies have shown that the prognosis after lacunar infarcts is not benign; the risk of recurrent stroke is no lower than for other ischaemic stroke subtypes, and there is an increased risk for cognitive decline, dementia and death in the long
3475:
Riggi, F. F., Hommel, M., & Jaillard, A. (2018). Lesions in the dorsolateral caudate nucleus predict post stroke depression – a voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping study. Cerebrovascular
Diseases, 45(Suppl 1), 33–33 (abstract no. OP 025).
622:
lesions that included analysis of caudate lesions (Bhatia & Marsden, 1994). Caudate strokes are rare, representing only 1% of all strokes in one population of about 3,000 stroke patients. Caudate hemorrhages account for about 7% of all
2082:
Hannan KL, Wood SJ, Yung AR, Velakoulis D, Phillips LJ, Soulsby B, Berger G, McGorry PD, Pantelis C (June 2010). "Caudate nucleus volume in individuals at ultra-high risk of psychosis: a cross-sectional magnetic resonance imaging study".
3754:
cause of vascular dementia and mild cognitive impairment, often overlooked in clinical practice. Multiple silent lacunar strokes are documented on brain MRI, with patients presenting with mild cognitive impairment and early dementia.
1158:
to compare the relative volume of white matter in the caudate among schizophrenia patients. Those patients with the disorder have "smaller absolute and relative volumes of white matter in the caudate nucleus than healthy subjects."
579:. It is difficult to see how such a system can operate without some mechanism to prevent explosive activation. There is some indirect evidence that the caudate may perform this regulatory role by measuring the general activity of
3559:
Ruppert E, Hacquard A, Tatu L, Namer IJ, Wolff V, Kremer S, Lagha-Boukbiza O, Bataillard M, Bourgin P (April 2022). "Stroke-related restless legs syndrome: Clinical and anatomo-functional characterization of an emerging entity".
1100:
is likely the most studied basal ganglia disorder. Patients with this progressive neurodegenerative disorder often first experience movement related symptoms (the three most common being tremors at rest, muscular rigidity, and
290:. After the body travels briefly towards the back of the head, the tail curves back toward the anterior, forming the roof of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle. This means that a coronal (on a plane parallel to the
4414:
Maller, Jerome J.; Thaveenthiran, Prasanthan; Thomson, Richard H.; McQueen, Susan; Fitzgerald, Paul B. (2014). "Volumetric, cortical thickness and white matter integrity alterations in bipolar disorder type I and II".
4064:
Müller DM, Robe PA, Eijgelaar RS, Witte MG, Visser M, de Munck JC, Broekman ML, Seute T, Hendrikse J, Noske DP, Vandertop WP, Barkhof F, Kouwenhoven MC, Mandonnet E, Berger MS, De Witt Hamer PC (January 2019).
514:
measures during human sleep cycles has indicated that the caudate nucleus demonstrates reduced activity during non-REM sleep across all sleep stages. Additionally, studies of human caudate nuclei volume in
3273:
study, at least nine of the 925 patients initially included in the investigation had lesions involving an area in the superior part of the body of the left caudate nucleus and the adjacent corona radiata.
883:, and depression, have been particularly associated with caudate strokes relative to strokes occurring in other regions. Strokes in the caudate nucleus have also been strongly associated with post-stroke
486:
However, the effects of caudate nuclei removal on the sleep-wakefulness pattern of cats have not been permanent. Normalization has been discovered after a period of three months following caudate nuclei
4648:
2519:
Crinion J, Turner R, Grogan A, Hanakawa T, Noppeney U, Devlin JT, Aso T, Urayama S, Fukuyama H, Stockton K, Usui K, Green DW, Price CJ (June 2006). "Language control in the bilingual brain".
446:
on memory processing in the caudate nucleus has been demonstrated with the finding that lesions involving the connections between these two structures "block the memory-enhancing effects of
4271:
Schrimsher GW, Billingsley RL, Jackson EF, Moore BD (December 2002). "Caudate nucleus volume asymmetry predicts attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptomatology in children".
3077:
Gnanashanmugam, G. (2011). A Study on
Evaluation of Motor, Cognitive and Behavioral Manifestations of Basal Ganglia Infarcts (Doctoral dissertation, Madras Medical College, Chennai).
4363:
Takase K, Tamagaki C, Okugawa G, Nobuhara K, Minami T, Sugimoto T, Sawada S, Kinoshita T (2004). "Reduced white matter volume of the caudate nucleus in patients with schizophrenia".
999:
associated with greatly increased risk of stroke recurrence, cognitive impairment and dementia, and early death in the mid- to long-term. Treatment of caudate strokes may consist of
355:
have linked the caudate nucleus to spatial and nonspatial mnemonic processing. Spatially dependent motor preparation has been linked to the caudate nucleus through event-related
4613:
3436:
Tang, W.K.; Liang, H.J.; Chen, Y.K.; Chu, Winnie C.W.; Abrigo, Jill; Mok, V.C.T.; Ungvari, Gabor S.; Wong, K.S. (2013). "Poststroke fatigue is associated with caudate infarcts".
1712:
Functional neuroimaging in humans demonstrates activation of the prefrontal cortex and caudate nucleus (part of the striatum) in tasks that demand inhibitory control of behavior.
3994:Çırak M, Yağmurlu K, Kearns KN, Ribas EC, Urgun K, Shaffrey ME, Kalani MY (July 2020). "The Caudate Nucleus: Its Connections, Surgical Implications, and Related Complications".
3832:
of recurrent stroke after lacunar infarct is similar to that for most other types of stroke, and patients have an increased risk of developing cognitive decline and dementia.
1254:
450:
infused into the caudate nucleus". In a study involving rats given water-maze training, the caudate nucleus was discovered to enhance memory of visually cued training after
4641:
3149:
Pellizzaro Venti, Michele; Paciaroni, Maurizio; Caso, Valeria (2012). "Caudate
Infarcts and Hemorrhages". In Paciaroni, M.; Agnelli, G.; Caso, V.; Bogousslavsky, J. (eds.).
1302:
759:
Caudate nucleus strokes have been associated with a variety of clinical symptoms. In studies of patients with caudate infarcts, frequently occurring symptoms have included
272:). The caudate head receives its blood supply from the lenticulostriate artery while the tail of the caudate receives its blood supply from the anterior choroidal artery.
3844:
Grau-Olivares M, Arboix A (August 2009). "Mild cognitive impairment in stroke patients with ischemic cerebral small-vessel disease: a forerunner of vascular dementia?".
4634:
519:(CCHS) subjects established a correlation between CCHS and a significant reduction in left and right caudate volume. CCHS is a genetic disorder that affects the
3595:
Akaho R, Deguchi I, Kigawa H, Nishimura K (April 2019). "Obsessive-Compulsive
Disorder Following Cerebrovascular Accident: A Case Report and Literature Review".
2588:
Newberg AB, Wintering NA, Morgan D, Waldman MR (November 2006). "The measurement of regional cerebral blood flow during glossolalia: a preliminary SPECT study".
2032:"Differential response patterns in the striatum and orbitofrontal cortex to financial reward in humans: a parametric functional magnetic resonance imaging study"
1470:
543:
behavior, and hyperactivity. Most of these deficits can be classified as relating to approach-attachment behaviors, from approaching a target to romantic love.
2476:
Aron A, Fisher H, Mashek DJ, Strong G, Li H, Brown LL (July 2005). "Reward, motivation, and emotion systems associated with early-stage intense romantic love".
3489:
Wang XX, Feng Y, Tan EK, Ondo WG, Wu YC (February 2022). "Stroke-related restless legs syndrome: epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and pathophysiology".
503:(REMS) time that only lasted for about two months. However, afrontal cats had a permanent decrease in REMS time and only a temporary period of hyperactivity.
153:
1410:
596:
4114:
Jiji S, Smitha KA, Gupta AK, Pillai VP, Jayasree RS (September 2013). "Segmentation and volumetric analysis of the caudate nucleus in Alzheimer's disease".
2259:
Gogichadze M, Oniani MT, Nemsadze M, Oniani N (2009). "Sleep disorders and disturbances in memory processing related to the lesion of the caudate nucleus".
4314:
Douglas PK, Gutman B, Anderson A, Larios C, Lawrence KE, Narr K, Sengupta B, Cooray G, Douglas DB, Thompson PM, McGough JJ, Bookheimer SY (February 2018).
1458:
1374:
4605:
1446:
3630:
Satzer D, Bond DJ (May 2016). "Mania secondary to focal brain lesions: implications for understanding the functional neuroanatomy of bipolar disorder".
1787:
1434:
2126:
Levitt JJ, McCarley RW, Dickey CC, Voglmaier MM, Niznikiewicz MA, Seidman LJ, Hirayasu Y, Ciszewski AA, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA, Shenton ME (July 2002).
606:
Strokes can occur in the caudate nucleus and studies of patients with these kinds of strokes followed the introduction and widespread availability of
531:
The caudate nucleus has been implicated in responses to visual beauty, and has been suggested as one of the "neural correlates of romantic love".
1604:
4029:
Duffau H, Denvil D, Capelle L (August 2002). "Absence of movement disorders after surgical resection of glioma invading the right striatum".
2912:
Caplan LR, Schmahmann JD, Kase CS, Feldmann E, Baquis G, Greenberg JP, Gorelick PB, Helgason C, Hier DB (February 1990). "Caudate infarcts".
129:
1180:(OCD), in that it may perhaps be unable to properly regulate the transmission of information regarding worrying events or ideas between the
835:
items, verbal amnesia (33% of left-sided lesions), and visual amnesia (right-sided lesions), among other deficits. Less commonly, there are
418:
The dorsal-prefrontal cortex subcortical loop involving the caudate nucleus has been linked to deficits in working memory, specifically in
3093:
Kumral E, Çetin FE, Özdemir HN (2023). "A Neuropsychiatric and Neuroimaging Study of Unilateral and Bilateral Striatal Ischemic Lesions".
4450:
516:
214:
2701:
Chung, Chin-Sang; Caplan, Louis R. (2012-07-12). "Caudate nucleus infarcts and hemorrhages". In Caplan, Louis R.; van Gijn, Jan (eds.).
4610:
1422:
2128:"MRI study of caudate nucleus volume and its cognitive correlates in neuroleptic-naive patients with schizotypal personality disorder"
1011:
like hypertension and diabetes mellitus to reduce the risk of additional strokes. On the basis of case reports and small case series,
899:, have been reported rarely in individuals with caudate strokes as well. In one case report of bilateral caudate head damage, severe
1987:
Grahn JA, Parkinson JA, Owen AM (April 2009). "The role of the basal ganglia in learning and memory: neuropsychological studies".
1278:
2570:
1227:
gyri. These findings contrast with those in people with other anxiety disorders, who evince decreased (rather than increased)
3337:
3166:
2784:
2718:
3201:
Bhatia KP, Marsden CD (August 1994). "The behavioural and motor consequences of focal lesions of the basal ganglia in man".
523:
due to a reduced drive to breathe. Therefore, the caudate nucleus has been suggested to play a role in human sleep cycles.
4555:"Meta-analytical comparison of voxel-based morphometry studies in obsessive-compulsive disorder vs other anxiety disorders"
4470:"The caudate nucleus in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Reduced metabolism following treatment with paroxetine: a PET study"
563:
showed a significant reduction in activity in the left caudate nucleus during glossolalia compared to singing in English.
463:
associated with feedback processing (the result of incorrect categorization) was concentrated to the head of the caudate.
2329:"Brain activation and hypothalamic functional connectivity during human non-rapid eye movement sleep: an EEG/fMRI study"
1935:
White NM (April 2009). "Some highlights of research on the effects of caudate nucleus lesions over the past 200 years".
1290:
4812:
4621:
4166:
1199:
found that the right caudate nucleus had the largest change in glucose metabolism after patients had been treated with
1012:
4067:"Comparing Glioblastoma Surgery Decisions Between Teams Using Brain Maps of Tumor Locations, Biopsies, and Resections"
3524:
Wu X, Xu J, Lu B (June 2020). "Acute post-stroke restless legs syndrome: the body of caudate nucleus considerations".
1815:"Dissociation of human caudate nucleus activity in spatial and nonspatial working memory: an event-related fMRI study"
1724:
Yeterian EH, Pandya DN (February 1995). "Corticostriatal connections of extrastriate visual areas in rhesus monkeys".
1350:
241:, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the
4802:
4626:
2288:"Counterpointing the functional role of the forebrain and of the brainstem in the control of the sleep-waking system"
1705:
1627:
1580:
1555:
1269:
1265:
888:
471:
Bilateral lesions in the head of the caudate nucleus in cats were correlated with a decrease in the duration of deep
3234:"Predominance of caudate nucleus lesions in acute ischaemic stroke patients with impairment in language and speech"
1649:"Linking dopaminergic reward signals to the development of attentional bias: A positron emission tomographic study"
729:
160:
3915:
752:. Additionally, a case report of lacunar infarction of the caudate and adjacent structures due to high-dose oral
3360:
Godfrey J (March 2009). "Safety of therapeutic methylphenidate in adults: a systematic review of the evidence".
475:
during the sleep-wakefulness cycle. With a decrease in total volume of deep slow wave sleep, the transition of
3665:
Canavero S, Fontanella M (1998). "Behavioral-attentional syndrome following bilateral caudate head ischaemia".
2175:
McGaugh JL (2004). "The amygdala modulates the consolidation of memories of emotionally arousing experiences".
1338:
1326:
1052:
2800:
Stein RW, Kase CS, Hier DB, Caplan LR, Mohr JP, Hemmati M, Henderson K (December 1984). "Caudate hemorrhage".
4904:
2877:
Mendez MF, Adams NL, Lewandowski KS (March 1989). "Neurobehavioral changes associated with caudate lesions".
1492:
1490:
1177:
987:
536:
339:
The caudate nucleus integrates spatial information with motor behavior formulation. Selective impairment of
148:
1791:
654:. In one series of patients, 80% of strokes were ischemic and 20% were hemorrhagic. Caudate infarcts can be
499:
activation. The cats with caudate removal, although permanently hyperactive, had a significant decrease in
1196:
395:
377:
indicates that the caudate nucleus inhibits the tendency for an animal to move forward without resistance.
4189:"A protein interaction network links GIT1, an enhancer of huntingtin aggregation, to Huntington's disease"
1487:
1314:
1308:
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view. The caudate nucleus can be seen above the optic nerve.
2963:
1362:
4899:
1155:
717:
635:
491:. This discovery could be due to the inter-related nature of the roles of the caudate nucleus and the
990:(MMSE), a short clinical test of basic cognitive function and impairment, during follow-up over 1 to 2
1240:
1224:
1211:
studies comparing people with OCD and healthy controls have found people with OCD to have increased
209:
of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the
104:
4988:
4807:
2984:
Bokura H, Robinson RG (May 1997). "Long-term cognitive impairment associated with caudate stroke".
823:, and lack of initiative for usual daily activities. Cognitive and memory impairment includes poor
624:
506:
Contrasting with associations between "deep", REM sleep and the caudate nucleus, a study involving
500:
369:
constantly shift body position were both observed in cats following partial removal of the nuclei.
87:
986:
Bokura & Robinson (1997) found that some individuals with caudate strokes deteriorated on the
4937:
4740:
4316:"Hemispheric brain asymmetry differences in youths with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder"
1768:
1208:
1118:
939:
725:
710:
663:
5149:
5114:
5006:
4932:
4868:
4846:
4745:
4184:
3608:
1150:
The volume of white matter in the caudate nucleus has been linked with patients diagnosed with
1097:
908:
884:
496:
344:
340:
294:) section that cuts through the tail will also cross the body and head of the caudate nucleus.
194:
136:
124:
4158:
3940:
Arnts H, van Erp WS, Lavrijsen JC, van Gaal S, Groenewegen HJ, van den Munckhof P (May 2020).
3325:
193:. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in
5109:
5030:
4976:
4861:
4396:
2370:"Reduced caudate nuclei volumes in patients with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome"
1647:
Anderson BA, Kuwabara H, Wong DF, Roberts J, Rahmim A, Brašić JR, Courtney SM (August 2017).
792:
776:
745:
286:
The head and body of the caudate nucleus form part of the floor of the anterior horn of the
2528:
2430:
2368:
Kumar R, Ahdout R, Macey PM, Woo MA, Avedissian C, Thompson PM, Harper RM (November 2009).
2327:
Kaufmann C, Wehrle R, Wetter TC, Holsboer F, Auer DP, Pollmächer T, Czisch M (March 2006).
2188:
1856:"Spatial working memory activity of the caudate nucleus is sensitive to frame of reference"
1236:
1220:
1219:, extending to the caudate nuclei, while decreased grey matter volumes in bilateral dorsal
1204:
1185:
1106:
694:
682:
303:
253:
202:
8:
5124:
5035:
4851:
2925:
2848:
2776:
1575:. Connors, Barry W.,, Paradiso, Michael A. (Fourth ed.). Philadelphia. p. 502.
1416:
Ventricles of brain and basal ganglia. Superior view, horizontal section, deep dissection
1064:
864:
607:
584:
572:
198:
2532:
2434:
1380:
Central part and anterior and posterior cornua of lateral ventricles exposed from above.
5072:
5067:
5062:
5057:
4726:
4388:
4340:
4315:
4296:
4253:
4091:
4066:
3258:
3233:
2613:
2552:
2501:
2453:
2418:
2394:
2385:
2369:
2236:
2211:
2152:
2127:
2108:
2056:
2047:
2031:
2012:
1960:
1749:
1673:
1648:
1598:
1523:
1514:
1498:
1232:
1216:
900:
702:
651:
323:
206:
4656:
4571:
4554:
4241:
3818:
3766:
Norrving B (August 2008). "Lacunar infarcts: no black holes in the brain are benign".
3285:
Gerraty RP (September 2003). "Clinical diagnosis of subcortical cerebral infarction".
2601:
2272:
2096:
1831:
1814:
4944:
4856:
4790:
4721:
4596:
4576:
4532:
4491:
4432:
4380:
4345:
4288:
4245:
4210:
4162:
4151:
4131:
4096:
4046:
4011:
3973:
3896:
3892:
3861:
3822:
3783:
3744:
3717:
3682:
3647:
3612:
3577:
3541:
3506:
3418:
3377:
3333:
3302:
3263:
3214:
3162:
3110:
3106:
3047:
3001:
2929:
2894:
2852:
2817:
2780:
2714:
2605:
2544:
2493:
2458:
2399:
2350:
2309:
2304:
2287:
2241:
2192:
2157:
2100:
2061:
2004:
1952:
1917:
1877:
1836:
1741:
1701:
1678:
1664:
1623:
1586:
1576:
1551:
1528:
1000:
880:
808:
796:
706:
698:
627:. Research on caudate strokes has consisted of small clinical series of patients and
611:
576:
476:
287:
4300:
4257:
3958:
3941:
2617:
2556:
2112:
2016:
1753:
1398:
1176:
It has been theorized that the caudate nucleus may be dysfunctional in persons with
1138:
A 2002 study draws a relationship between caudate asymmetry and symptoms related to
1089:
does not indicate causation, the finding may have implications for early diagnosis.
875:(9%, or 1 of 11 and with bilateral lesions). Among strokes in general, and/or among
780:
5011:
4833:
4797:
4716:
4566:
4522:
4481:
4424:
4392:
4372:
4335:
4327:
4280:
4237:
4200:
4123:
4086:
4078:
4038:
4003:
3963:
3953:
3888:
3853:
3814:
3775:
3709:
3674:
3639:
3604:
3569:
3533:
3498:
3445:
3408:
3369:
3294:
3253:
3245:
3206:
3154:
3102:
3037:
2993:
2921:
2886:
2844:
2809:
2772:
2706:
2597:
2536:
2485:
2448:
2438:
2389:
2381:
2340:
2299:
2268:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2184:
2147:
2139:
2092:
2051:
2043:
1996:
1964:
1944:
1867:
1826:
1733:
1668:
1660:
1518:
1510:
1386:
1040:
979:
916:
860:
816:
749:
733:
667:
480:
307:
256:
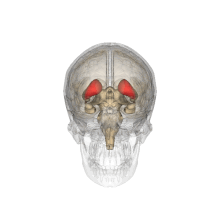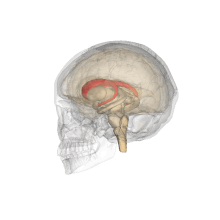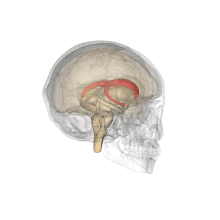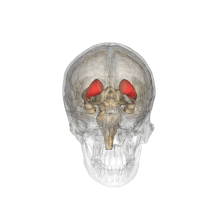
of the brain. Individually, they resemble a C-shape structure with a wider "head" (
242:
4511:"Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder"
2505:
197:, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including
4981:
4959:
4927:
4838:
4817:
4735:
4697:
4617:
4284:
4205:
4188:
3537:
2710:
2443:
1024:
1016:
959:
832:
828:
753:
678:
655:
643:
580:
472:
275:
248:
The caudate nuclei are located near the center of the brain, sitting astride the
238:
182:
117:
92:
63:
4400:
4127:
3740:
3502:
3078:
2143:
5119:
5084:
4909:
4882:
4826:
4331:
4042:
4007:
1769:"Cerebral vascular territories - Radiology Reference Article - Radiopaedia.org"
1235:/ caudate nuclei, while also decreased grey matter volumes in bilateral dorsal
1085:
994:
years, whereas patients with other subcortical lesions tended to improve over 2
971:
955:
932:
836:
737:
671:
492:
4527:
4510:
4486:
4469:
4428:
3449:
3413:
3396:
3210:
2000:
1948:
5143:
5079:
4671:
4658:
3779:
3713:
3373:
3298:
1590:
1151:
1004:
924:
892:
876:
804:
788:
784:
685:
or penetrating-branch disease is a major mechanism of caudate strokes. Major
619:
615:
540:
424:
419:
210:
186:
141:
46:
3042:
3025:
2997:
2966:. In Donnan, G. A.; Norrving, B.; Bamford, J. M.; Bogousslavsky, J. (eds.).
2540:
40:
5101:
4998:
4919:
4782:
4580:
4536:
4495:
4436:
4384:
4349:
4292:
4249:
4214:
4135:
4100:
4050:
4015:
3977:
3900:
3865:
3826:
3787:
3748:
3721:
3651:
3616:
3581:
3545:
3510:
3422:
3381:
3306:
3267:
3114:
2813:
2609:
2548:
2497:
2462:
2403:
2354:
2345:
2328:
2313:
2245:
2196:
2161:
2104:
2065:
2008:
1956:
1921:
1881:
1840:
1682:
1532:
1192:
1020:
852:
690:
674:
628:
447:
3916:"Disorders of diminished motivation: What they are, and how to treat them"
3686:
3678:
3332:. Oxford medical publications. Oxford University Press. pp. 195–208.
3218:
3051:
3005:
2933:
2898:
2856:
2821:
2489:
1745:
1737:
571:
The brain contains large collections of neurons reciprocally connected by
5052:
5044:
5025:
4968:
4891:
4680:
4662:
4082:
3805:
Norrving B (April 2003). "Long-term prognosis after lacunar infarction".
3232:
Grönholm EO, Roll MC, Horne MA, Sundgren PC, Lindgren AG (January 2016).
2890:
1872:
1855:
1228:
1212:
1032:
1008:
963:
824:
686:
639:
560:
520:
451:
439:
268:). Sometimes a part of the caudate nucleus is referred to as the "knee" (
190:
4552:
859:(9–16%), as well as more severe cognitive and behavioral problems, like
166:
3968:
2705:(3 ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 397–404.
1200:
1048:
760:
99:
4376:
3857:
3643:
3573:
3249:
3158:
1440:
Caudate nuclei along with other subcortical structures, in glass brain
799:, minor speech or linguistic deficits (23–50% of left-sided lesions),
771:(40–100%), and cognitive/behavioral abnormalities (39–78%), including
5091:
4768:
4600:
4553:
Radua J, van den Heuvel OA, Surguladze S, Mataix-Cols D (July 2010).
1102:
1036:
1028:
920:
800:
764:
597:
Neurobiological effects of physical exercise § Structural growth
3914:
Spiegel DR, Warren A, Takakura W, Servidio L, Leu N (January 2018).
3477:
3464:
3144:
2630:
Braitenberg V. (1984) Vehicles. Experiments in synthetic psychology.
438:
and the caudate nucleus have direct and indirect projections to the
4763:
4689:
3879:
Marin RS, Wilkosz PA (2005). "Disorders of diminished motivation".
3142:
3140:
3138:
3136:
3134:
3132:
3130:
3128:
3126:
3124:
2212:"The roles of the caudate nucleus in human classification learning"
1698:
Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience
1696:
Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.).
1620:
Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience
1618:
Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.).
1548:
Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience
1546:
Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.).
1261:
1181:
1127:
1044:
951:
943:
928:
872:
856:
820:
768:
741:
721:
713:
488:
443:
435:
431:
352:
348:
319:
311:
249:
111:
1428:
Ventricles of brain and basal ganglia. Close-up of preceding image
879:
strokes specifically, certain sequelae, including apathy, abulia,
614:
on caudate nucleus strokes have been published, as well as a 1994
225:
28:
4702:
4413:
4270:
1550:(2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 147–148.
1476:
Caudate nucleus highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
975:
967:
912:
868:
844:
659:
647:
373:
315:
234:
3121:
1073:
1068:
947:
848:
840:
812:
772:
4597:
Stained brain slice images which include the "caudate nucleus"
3700:
Arboix A, Martí-Vilalta JL (February 2009). "Lacunar stroke".
2258:
1464:
Caudate nucleus highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
1284:
Coronal section through anterior cornua of lateral ventricles.
4362:
3939:
3913:
3148:
2587:
2125:
1452:
Caudate nucleus highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
896:
75:
4181:
3738:
2911:
2326:
1908:
Villablanca JR (2010). "Why do we have a caudate nucleus?".
1700:(2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 321.
1622:(2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 326.
1019:, secondary to stroke and other causes, may be treated with
4502:
4313:
3594:
2518:
1646:
1497:
Yager LM, Garcia AF, Wunsch AM, Ferguson SM (August 2015).
1139:
1133:
511:
434:
sends direct projections to the caudate nucleus. Both the
399:
356:
347:
and the knowledge of the disease's impact on the amount of
291:
16:
Structure of the striatum in the basal ganglia of the brain
4467:
2030:
Elliott R, Newman JL, Longe OA, Deakin JF (January 2003).
1499:"The ins and outs of the striatum: Role in drug addiction"
4468:
Hansen ES, Hasselbalch S, Law I, Bolwig TG (March 2002).
3942:"On the pathophysiology and treatment of akinetic mutism"
3231:
2771:. Oxford University PressNew York, NY. pp. 209–224.
1496:
507:
280:
279:
Transverse view of the caudate nucleus from a structural
4063:
3993:
3558:
2081:
2029:
3469:
3397:"Lacunar stroke associated with methylphenidate abuse"
2876:
2475:
2077:
2075:
938:
Caudate nucleus hemorrhages can mimic the symptoms of
4113:
3739:
Gore M, Bansal K, Khan Suheb MZ, Asuncion RM (2024).
3073:
3071:
3069:
3067:
3065:
3063:
3061:
2957:
2955:
2953:
2951:
2949:
2947:
2945:
2943:
1296:
Coronal section of brain through anterior commissure.
4474:
The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology
4157:(4th ed.). New York: Worth Publishers. p.
3429:
2970:. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 117–130.
2835:
Weisberg LA (September 1984). "Caudate hemorrhage".
1853:
1812:
903:
impairment was measured, along with other deficits.
634:
Caudate nucleus strokes can be diagnosed with CT or
4028:
3843:
3699:
3023:
2799:
2696:
2694:
2692:
2690:
2688:
2686:
2684:
2682:
2680:
2678:
2676:
2674:
2672:
2670:
2668:
2666:
2664:
2662:
2660:
2658:
2656:
2367:
2072:
1860:
Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience
1695:
1617:
1545:
1356:
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view.
4228:Walker FO (January 2007). "Huntington's disease".
4150:
4148:
3664:
3092:
3058:
2940:
2654:
2652:
2650:
2648:
2646:
2644:
2642:
2640:
2638:
2636:
1986:
935:such as cortico–striatal–thalamic–cortical loops.
394:A two-pronged approach of neuroimaging (including
3907:
1982:
1980:
1978:
1976:
1974:
322:. There are also additional inputs from various
314:and contains cell projections to the caudate and
5141:
4508:
3435:
3153:. Vol. 30. S. Karger AG. pp. 137–140.
1171:
3989:
3987:
3488:
3088:
3086:
2633:
2417:Ishizu T, Zeki S (May 2011). Warrant EJ (ed.).
1903:
1901:
1899:
1897:
1895:
1893:
1891:
33:Caudate nucleus (in red) shown within the brain
3196:
3194:
3192:
3190:
3188:
3186:
3184:
3182:
3180:
3178:
3024:Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K (January 1999).
3019:
3017:
3015:
2983:
2979:
2977:
2961:
2872:
2870:
2868:
2866:
2767:Caplan, L R (2002-04-11). "Caudate infarcts".
2762:
2760:
2758:
2756:
2754:
2752:
2750:
1971:
1723:
1611:
1539:
575:, thus forming large network of elements with
334:
260:in Latin) at the front, tapering to a "body" (
45:Transverse cut of brain (horizontal section),
4642:
3200:
3079:http://repository-tnmgrmu.ac.in/id/eprint/580
2748:
2746:
2744:
2742:
2740:
2738:
2736:
2734:
2732:
2730:
2571:"How bilingual brains switch between tongues"
2209:
4548:
4546:
4175:
4057:
4022:
3984:
3933:
3878:
3872:
3837:
3798:
3759:
3732:
3693:
3623:
3588:
3552:
3517:
3482:
3388:
3353:
3278:
3225:
3083:
2279:
1888:
1344:Deep dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
1332:Deep dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
454:was infused post-training into the caudate.
3658:
3317:
3175:
3012:
2974:
2905:
2863:
2828:
2793:
2700:
2285:
2119:
1907:
517:congenital central hypoventilation syndrome
215:cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop
4649:
4635:
4221:
3629:
3609:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.12.034
2727:
2416:
1689:
1603:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
1084:A 2013 study has suggested a link between
181:is one of the structures that make up the
39:
27:
4570:
4543:
4526:
4485:
4339:
4204:
4187:, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (September 2004).
4090:
3967:
3957:
3456:
3412:
3394:
3257:
3041:
2968:Lacunar and Other Subcortical Infarctions
2452:
2442:
2393:
2344:
2303:
2235:
2151:
2055:
1871:
1830:
1672:
1522:
887:(RLS). Other behavioral conditions, like
863:(loss of psychic self-activation) (12%),
252:. There is a caudate nucleus within each
4509:Radua J, Mataix-Cols D (November 2009).
3804:
3765:
2834:
1819:Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research
1134:Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
1023:agents and other medications, including
590:
427:errors on spatial working memory tasks.
274:
224:
3359:
3323:
3284:
3151:Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience
2962:Caplan, L. R.; Helgason, C. M. (1995).
2419:"Toward a brain-based theory of beauty"
2174:
1766:
1573:Neuroscience : exploring the brain
1320:Dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
1112:
795:or frontal system abnormalities (26%),
728:. Less common risk factors may include
689:and causes of caudate infarcts include
385:
5142:
4227:
3523:
2766:
2189:10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144157
1368:Dissection of brain-stem. Dorsal view.
1092:
1079:
380:
4630:
4153:An Introduction to Brain and Behavior
1934:
1854:Postle BR, D'Esposito M (June 2003).
1813:Postle BR, D'Esposito M (July 1999).
1264:(on the right side of the brain): A,
726:carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
363:
4149:Kolb, Bryan; Ian Q. Whishaw (2001).
3438:Journal of the Neurological Sciences
2926:10.1001/archneur.1990.00530020029011
2849:10.1001/archneur.1984.04050200077021
2210:Seger CA, Cincotta CM (March 2005).
1785:
1726:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1570:
1246:
1058:
566:
302:The caudate is highly innervated by
1121:, a genetic mutation occurs in the
970:, neuropsychological disturbances,
709:, large artery lesions, rupture of
638:(MRI) scanning. They are a type of
13:
4622:Neuroscience Information Framework
2777:10.1093/oso/9780192631572.003.0018
2386:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.07.038
2261:Parkinsonism and Related Disorders
2132:The American Journal of Psychiatry
2048:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-01-00303.2003
1515:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.033
1013:disorders of diminished motivation
329:
14:
5161:
4590:
4572:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.70
4515:The British Journal of Psychiatry
3478:https://doi.org/10.1159/000520354
3465:https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13094
2602:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.07.001
2286:Villablanca JR (September 2004).
2097:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.02.006
1162:
1063:The caudate nucleus is sometimes
601:
483:may also be affected negatively.
318:, utilizing the neurotransmitter
310:(SNc). The SNc is located in the
297:
3893:10.1097/00001199-200507000-00009
3107:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.21030083
3026:"Acute caudate vascular lesions"
2305:10.1111/j.1365-2869.2004.00412.x
1665:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.062
1469:
1457:
1445:
1433:
1421:
1409:
1397:
1385:
1373:
1361:
1349:
1337:
1325:
1313:
1301:
1289:
1277:
1253:
1145:
1007:agents and management of stroke
960:decreased level of consciousness
867:(10% with right-sided lesions),
730:non-valvular atrial fibrillation
229:Caudate nucleus within the skull
161:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
4461:
4443:
4407:
4356:
4307:
4264:
4142:
4107:
3959:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.02.006
3095:J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci
2624:
2581:
2563:
2512:
2469:
2410:
2361:
2320:
2252:
2203:
2168:
2023:
1928:
1847:
1806:
1053:acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
4559:Archives of General Psychiatry
4417:Journal of Affective Disorders
2228:10.1523/jneurosci.3401-04.2005
1779:
1760:
1717:
1640:
1564:
308:substantia nigra pars compacta
185:, which is a component of the
1:
4905:Anterior perforated substance
4242:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60111-1
4116:European Journal of Radiology
3819:10.1016/s1474-4422(03)00352-1
3395:Sadeghian H (February 2004).
2273:10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70639-X
2177:Annual Review of Neuroscience
1832:10.1016/s0926-6410(99)00010-5
1481:
1178:obsessive compulsive disorder
1172:Obsessive-compulsive disorder
988:mini-mental state examination
889:obsessive–compulsive disorder
642:stroke and are classified as
537:obsessive-compulsive disorder
372:Following the application of
213:and functions as part of the
4611:NIF Search - Caudate Nucleus
4451:"A Trip Into Bipolar Brains"
4285:10.1177/08830738020170122001
4206:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.016
3538:10.1016/j.sleep.2019.11.1253
2711:10.1017/cbo9781139093286.034
2444:10.1371/journal.pone.0021852
1260:Two views of a model of the
1197:positron emission tomography
556:verbal fluency performance.
220:
7:
4606:Diagram at uni-tuebingen.de
4128:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.03.012
3503:10.1016/j.sleep.2022.02.001
3205:. 117 ( Pt 4) (4): 859–76.
2216:The Journal of Neuroscience
2144:10.1176/appi.ajp.159.7.1190
2036:The Journal of Neuroscience
1015:, like apathy, abulia, and
718:arteriovenous malformations
546:
457:
335:Spatial mnemonic processing
10:
5166:
4900:Anterior olfactory nucleus
4332:10.1016/j.nicl.2018.02.020
4273:Journal of Child Neurology
4043:10.3171/jns.2002.97.2.0363
4008:10.1016/j.wneu.2020.04.027
3326:"Striatocapsular infarcts"
2478:Journal of Neurophysiology
1989:Behavioural Brain Research
1937:Behavioural Brain Research
1156:magnetic resonance imaging
636:magnetic resonance imaging
594:
526:
423:inversely associated with
5100:
5043:
5024:
4997:
4967:
4957:
4918:
4890:
4881:
4781:
4756:
4688:
4679:
4670:
4665:and associated structures
4528:10.1192/bjp.bp.108.055046
4487:10.1017/S1461145701002681
4429:10.1016/j.jad.2014.08.016
3450:10.1016/j.jns.2012.10.022
3414:10.1017/s0317167100002924
2292:Journal of Sleep Research
2001:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.11.020
1949:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.12.003
1910:Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars)
1168:was lower than controls.
732:, myocardial dyskinesia,
625:intracerebral hemorrhages
495:in controlling levels of
413:
159:
147:
135:
123:
110:
98:
86:
74:
69:
59:
54:
38:
26:
21:
4989:Nucleus of diagonal band
3780:10.1136/jnnp.2008.153601
3714:10.1586/14737175.9.2.179
3597:J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis
3374:10.1177/0269881108089809
3299:10.1586/14737175.3.5.703
756:use has been published.
559:A neurological study of
501:rapid eye movement sleep
466:
442:. The influence of the
306:that originate from the
237:, the caudate forms the
4938:Lateral olfactory stria
3328:. In Donnan, G. (ed.).
3211:10.1093/brain/117.4.859
3043:10.1161/01.str.30.1.100
2998:10.1161/01.str.28.5.970
2541:10.1126/science.1127761
1209:voxel-based morphometry
940:subarachnoid hemorrhage
711:internal carotid artery
5007:Diagonal band of Broca
4933:Medial olfactory stria
4869:Subthalamic fasciculus
4847:Pallidothalamic tracts
4071:JCO Clin Cancer Inform
2814:10.1212/wnl.34.12.1549
1571:Bear, Mark F. (2016).
885:restless legs syndrome
497:central nervous system
341:spatial working memory
283:
230:
5031:Hippocampal formation
4977:Substantia innominata
4862:Lenticular fasciculus
3946:Neurosci Biobehav Rev
3881:J Head Trauma Rehabil
3679:10.1007/s004150050226
2490:10.1152/jn.00838.2004
1738:10.1002/cne.903520309
1231:volumes in bilateral
1215:volumes in bilateral
793:executive dysfunction
591:Clinical significance
278:
228:
4320:NeuroImage: Clinical
4083:10.1200/CCI.18.00089
3846:Expert Rev Neurother
3702:Expert Rev Neurother
3324:Weiller, C. (2002).
3287:Expert Rev Neurother
2891:10.1212/wnl.39.3.349
2346:10.1093/brain/awh686
1873:10.3758/cabn.3.2.133
1794:on 30 September 2013
1186:orbitofrontal cortex
1154:. A 2004 study uses
1119:Huntington's disease
1113:Huntington's disease
1107:Tower of London test
695:hypercholesterolemia
683:Small vessel disease
583:and controlling the
386:Goal-directed action
324:association cortices
304:dopaminergic neurons
203:associative learning
5125:Schaffer collateral
5036:Hippocampus anatomy
4852:Thalamic fasciculus
2590:Psychiatry Research
2533:2006Sci...312.1537C
2435:2011PLoSO...621852I
2085:Psychiatry Research
1098:Parkinson's disease
1093:Parkinson's disease
1080:Alzheimer's disease
1065:surgically resected
909:psychogenic illness
608:computed tomography
585:threshold potential
573:excitatory synapses
381:Cognitive functions
345:Parkinson's disease
199:procedural learning
195:Parkinson's disease
5053:Hippocampus proper
4727:Olfactory tubercle
4616:2013-07-27 at the
4365:Neuropsychobiology
3923:Current Psychiatry
3330:Subcortical Stroke
2964:"Caudate infarcts"
2769:Subcortical Stroke
1788:"Substantia Nigra"
1241:anterior cingulate
1225:anterior cingulate
901:prospective memory
803:difficulties, and
746:Hodgkin's lymphoma
703:myocardial infarct
612:literature reviews
364:Directed movements
284:
233:Together with the
231:
207:inhibitory control
5137:
5136:
5133:
5132:
5020:
5019:
4953:
4952:
4945:Olfactory trigone
4877:
4876:
4857:Ansa lenticularis
4791:Centrum semiovale
4777:
4776:
4722:Nucleus accumbens
4601:BrainMaps project
4377:10.1159/000080956
3858:10.1586/ern.09.73
3644:10.1111/bdi.12387
3574:10.1111/ene.15207
3362:J Psychopharmacol
3339:978-0-19-263157-2
3250:10.1111/ene.12822
3168:978-3-8055-9910-8
3159:10.1159/000333616
2786:978-0-19-263157-2
2720:978-1-139-09328-6
2527:(5779): 1537–40.
1786:McDougal, David.
1247:Additional images
1217:lenticular nuclei
1205:SDM meta-analyses
1059:Caudate resection
1041:dopamine agonists
797:memory impairment
707:cigarette smoking
699:diabetes mellitus
577:positive feedback
567:Threshold control
539:, stimulus-bound
477:short-term memory
343:in subjects with
288:lateral ventricle
175:
174:
170:
5157:
5041:
5040:
5012:Stria terminalis
4965:
4964:
4888:
4887:
4834:External capsule
4798:Internal capsule
4717:Ventral striatum
4686:
4685:
4677:
4676:
4651:
4644:
4637:
4628:
4627:
4585:
4584:
4574:
4550:
4541:
4540:
4530:
4506:
4500:
4499:
4489:
4465:
4459:
4458:
4447:
4441:
4440:
4411:
4405:
4404:
4360:
4354:
4353:
4343:
4311:
4305:
4304:
4268:
4262:
4261:
4236:(9557): 218–28.
4225:
4219:
4218:
4208:
4185:Landwehrmeyer BG
4179:
4173:
4172:
4156:
4146:
4140:
4139:
4111:
4105:
4104:
4094:
4061:
4055:
4054:
4026:
4020:
4019:
3991:
3982:
3981:
3971:
3961:
3937:
3931:
3930:
3920:
3911:
3905:
3904:
3876:
3870:
3869:
3841:
3835:
3834:
3802:
3796:
3795:
3763:
3757:
3756:
3741:"Lacunar Stroke"
3736:
3730:
3729:
3697:
3691:
3690:
3662:
3656:
3655:
3627:
3621:
3620:
3592:
3586:
3585:
3568:(4): 1011–1016.
3556:
3550:
3549:
3521:
3515:
3514:
3486:
3480:
3473:
3467:
3460:
3454:
3453:
3444:(1–2): 131–135.
3433:
3427:
3426:
3416:
3401:Can J Neurol Sci
3392:
3386:
3385:
3357:
3351:
3350:
3348:
3346:
3321:
3315:
3314:
3282:
3276:
3275:
3261:
3229:
3223:
3222:
3198:
3173:
3172:
3146:
3119:
3118:
3090:
3081:
3075:
3056:
3055:
3045:
3021:
3010:
3009:
2981:
2972:
2971:
2959:
2938:
2937:
2909:
2903:
2902:
2874:
2861:
2860:
2832:
2826:
2825:
2797:
2791:
2790:
2764:
2725:
2724:
2703:Stroke syndromes
2698:
2631:
2628:
2622:
2621:
2585:
2579:
2578:
2575:newscientist.com
2567:
2561:
2560:
2516:
2510:
2509:
2473:
2467:
2466:
2456:
2446:
2414:
2408:
2407:
2397:
2365:
2359:
2358:
2348:
2339:(Pt 3): 655–67.
2324:
2318:
2317:
2307:
2283:
2277:
2276:
2256:
2250:
2249:
2239:
2207:
2201:
2200:
2172:
2166:
2165:
2155:
2123:
2117:
2116:
2079:
2070:
2069:
2059:
2027:
2021:
2020:
1984:
1969:
1968:
1932:
1926:
1925:
1905:
1886:
1885:
1875:
1851:
1845:
1844:
1834:
1810:
1804:
1803:
1801:
1799:
1790:. Archived from
1783:
1777:
1776:
1767:D'Souza, Donna.
1764:
1758:
1757:
1721:
1715:
1714:
1693:
1687:
1686:
1676:
1644:
1638:
1637:
1615:
1609:
1608:
1602:
1594:
1568:
1562:
1561:
1543:
1537:
1536:
1526:
1494:
1473:
1461:
1449:
1437:
1425:
1413:
1401:
1389:
1377:
1365:
1353:
1341:
1329:
1317:
1305:
1293:
1281:
1257:
1025:psychostimulants
997:
993:
980:mental confusion
942:and can include
917:bipolar disorder
861:psychic akinesia
817:flattened affect
750:Moyamoya disease
734:cardiac aneurysm
722:cardiac embolism
668:internal capsule
656:lacunar infarcts
481:long-term memory
351:supplied to the
264:) and a "tail" (
243:internal capsule
167:edit on Wikidata
164:
81:nucleus caudatus
43:
31:
19:
18:
5165:
5164:
5160:
5159:
5158:
5156:
5155:
5154:
5140:
5139:
5138:
5129:
5096:
5034:
5029:
5016:
4993:
4982:Nucleus basalis
4960:basal forebrain
4949:
4928:Olfactory tract
4914:
4873:
4839:Extreme capsule
4818:Optic radiation
4773:
4752:
4736:Globus pallidus
4708:Caudate nucleus
4698:Dorsal striatum
4666:
4655:
4618:Wayback Machine
4593:
4588:
4551:
4544:
4507:
4503:
4466:
4462:
4457:. 14 June 2017.
4449:
4448:
4444:
4412:
4408:
4361:
4357:
4312:
4308:
4269:
4265:
4226:
4222:
4180:
4176:
4169:
4147:
4143:
4112:
4108:
4062:
4058:
4027:
4023:
3996:World Neurosurg
3992:
3985:
3938:
3934:
3929:(1): 10–18, 20.
3918:
3912:
3908:
3877:
3873:
3842:
3838:
3803:
3799:
3764:
3760:
3737:
3733:
3698:
3694:
3663:
3659:
3628:
3624:
3593:
3589:
3557:
3553:
3522:
3518:
3487:
3483:
3474:
3470:
3461:
3457:
3434:
3430:
3393:
3389:
3358:
3354:
3344:
3342:
3340:
3322:
3318:
3283:
3279:
3230:
3226:
3199:
3176:
3169:
3147:
3122:
3091:
3084:
3076:
3059:
3022:
3013:
2982:
2975:
2960:
2941:
2910:
2906:
2875:
2864:
2833:
2829:
2808:(12): 1549–54.
2798:
2794:
2787:
2765:
2728:
2721:
2699:
2634:
2629:
2625:
2586:
2582:
2569:
2568:
2564:
2517:
2513:
2474:
2470:
2415:
2411:
2366:
2362:
2325:
2321:
2284:
2280:
2257:
2253:
2222:(11): 2941–51.
2208:
2204:
2173:
2169:
2124:
2120:
2080:
2073:
2028:
2024:
1985:
1972:
1933:
1929:
1906:
1889:
1852:
1848:
1811:
1807:
1797:
1795:
1784:
1780:
1773:radiopaedia.org
1765:
1761:
1722:
1718:
1708:
1694:
1690:
1645:
1641:
1630:
1616:
1612:
1596:
1595:
1583:
1569:
1565:
1558:
1544:
1540:
1495:
1488:
1484:
1477:
1474:
1465:
1462:
1453:
1450:
1441:
1438:
1429:
1426:
1417:
1414:
1405:
1404:Caudate nucleus
1402:
1393:
1392:Caudate nucleus
1390:
1381:
1378:
1369:
1366:
1357:
1354:
1345:
1342:
1333:
1330:
1321:
1318:
1309:
1306:
1297:
1294:
1285:
1282:
1273:
1258:
1249:
1174:
1165:
1148:
1136:
1126:evident in the
1115:
1095:
1082:
1061:
1017:akinetic mutism
995:
991:
933:neural circuits
873:global dementia
839:(20–23%), like
837:motor disorders
815:, disinterest,
754:methylphenidate
679:globus pallidus
604:
599:
593:
581:cerebral cortex
569:
549:
529:
473:slow wave sleep
469:
460:
416:
388:
383:
366:
337:
332:
330:Motor functions
300:
239:dorsal striatum
223:
183:corpus striatum
179:caudate nucleus
171:
64:Dorsal striatum
50:
34:
22:Caudate nucleus
17:
12:
11:
5:
5163:
5153:
5152:
5135:
5134:
5131:
5130:
5128:
5127:
5122:
5120:Perforant path
5117:
5112:
5106:
5104:
5098:
5097:
5095:
5094:
5089:
5088:
5087:
5085:Fascia dentata
5077:
5076:
5075:
5070:
5065:
5060:
5049:
5047:
5038:
5022:
5021:
5018:
5017:
5015:
5014:
5009:
5003:
5001:
4995:
4994:
4992:
4991:
4986:
4985:
4984:
4973:
4971:
4962:
4955:
4954:
4951:
4950:
4948:
4947:
4942:
4941:
4940:
4935:
4924:
4922:
4916:
4915:
4913:
4912:
4910:Olfactory bulb
4907:
4902:
4896:
4894:
4885:
4883:Rhinencephalon
4879:
4878:
4875:
4874:
4872:
4871:
4866:
4865:
4864:
4859:
4842:
4841:
4836:
4830:
4829:
4827:Corona radiata
4823:
4822:
4821:
4820:
4815:
4813:Posterior limb
4810:
4805:
4794:
4793:
4787:
4785:
4779:
4778:
4775:
4774:
4772:
4771:
4766:
4760:
4758:
4754:
4753:
4751:
4750:
4749:
4748:
4743:
4732:
4731:
4730:
4729:
4724:
4713:
4712:
4711:
4710:
4705:
4694:
4692:
4683:
4674:
4668:
4667:
4654:
4653:
4646:
4639:
4631:
4625:
4624:
4608:
4603:
4592:
4591:External links
4589:
4587:
4586:
4542:
4521:(5): 393–402.
4501:
4460:
4442:
4406:
4371:(4): 296–300.
4355:
4306:
4279:(12): 877–84.
4263:
4220:
4193:Molecular Cell
4174:
4168:978-1429242288
4167:
4141:
4122:(9): 1525–30.
4106:
4056:
4021:
3983:
3932:
3906:
3871:
3852:(8): 1201–17.
3836:
3797:
3758:
3731:
3692:
3673:(6–7): 322–4.
3657:
3632:Bipolar Disord
3622:
3603:(4): e17–e21.
3587:
3551:
3516:
3481:
3468:
3455:
3428:
3387:
3368:(2): 194–205.
3352:
3338:
3316:
3277:
3224:
3174:
3167:
3120:
3082:
3057:
3011:
2973:
2939:
2904:
2862:
2827:
2792:
2785:
2726:
2719:
2632:
2623:
2580:
2562:
2511:
2468:
2409:
2360:
2319:
2298:(3): 179–208.
2278:
2251:
2202:
2167:
2118:
2071:
2022:
1970:
1927:
1887:
1846:
1805:
1778:
1759:
1716:
1706:
1688:
1639:
1628:
1610:
1581:
1563:
1556:
1538:
1485:
1483:
1480:
1479:
1478:
1475:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1456:
1454:
1451:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1420:
1418:
1415:
1408:
1406:
1403:
1396:
1394:
1391:
1384:
1382:
1379:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1360:
1358:
1355:
1348:
1346:
1343:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1312:
1310:
1307:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1288:
1286:
1283:
1276:
1274:
1259:
1252:
1248:
1245:
1237:medial frontal
1221:medial frontal
1173:
1170:
1164:
1163:Bipolar type I
1161:
1147:
1144:
1135:
1132:
1114:
1111:
1094:
1091:
1081:
1078:
1060:
1057:
972:disorientation
956:neck stiffness
925:hallucinations
915:, depression,
893:perseverations
769:motor weakness
738:mural thrombus
672:corona radiata
603:
602:Caudate stroke
600:
592:
589:
568:
565:
548:
545:
528:
525:
493:frontal cortex
468:
465:
459:
456:
415:
412:
387:
384:
382:
379:
365:
362:
336:
333:
331:
328:
299:
298:Neurochemistry
296:
222:
219:
173:
172:
163:
157:
156:
151:
145:
144:
139:
133:
132:
127:
121:
120:
115:
108:
107:
102:
96:
95:
90:
84:
83:
78:
72:
71:
67:
66:
61:
57:
56:
52:
51:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5162:
5151:
5150:Basal ganglia
5148:
5147:
5145:
5126:
5123:
5121:
5118:
5116:
5113:
5111:
5108:
5107:
5105:
5103:
5099:
5093:
5090:
5086:
5083:
5082:
5081:
5080:Dentate gyrus
5078:
5074:
5071:
5069:
5066:
5064:
5061:
5059:
5056:
5055:
5054:
5051:
5050:
5048:
5046:
5042:
5039:
5037:
5032:
5027:
5023:
5013:
5010:
5008:
5005:
5004:
5002:
5000:
4996:
4990:
4987:
4983:
4980:
4979:
4978:
4975:
4974:
4972:
4970:
4966:
4963:
4961:
4956:
4946:
4943:
4939:
4936:
4934:
4931:
4930:
4929:
4926:
4925:
4923:
4921:
4917:
4911:
4908:
4906:
4903:
4901:
4898:
4897:
4895:
4893:
4889:
4886:
4884:
4880:
4870:
4867:
4863:
4860:
4858:
4855:
4854:
4853:
4850:
4848:
4844:
4843:
4840:
4837:
4835:
4832:
4831:
4828:
4825:
4824:
4819:
4816:
4814:
4811:
4809:
4806:
4804:
4803:Anterior limb
4801:
4800:
4799:
4796:
4795:
4792:
4789:
4788:
4786:
4784:
4780:
4770:
4767:
4765:
4762:
4761:
4759:
4755:
4747:
4744:
4742:
4739:
4738:
4737:
4734:
4733:
4728:
4725:
4723:
4720:
4719:
4718:
4715:
4714:
4709:
4706:
4704:
4701:
4700:
4699:
4696:
4695:
4693:
4691:
4687:
4684:
4682:
4678:
4675:
4673:
4672:Basal ganglia
4669:
4664:
4660:
4659:basal ganglia
4652:
4647:
4645:
4640:
4638:
4633:
4632:
4629:
4623:
4619:
4615:
4612:
4609:
4607:
4604:
4602:
4598:
4595:
4594:
4582:
4578:
4573:
4568:
4565:(7): 701–11.
4564:
4560:
4556:
4549:
4547:
4538:
4534:
4529:
4524:
4520:
4516:
4512:
4505:
4497:
4493:
4488:
4483:
4479:
4475:
4471:
4464:
4456:
4452:
4446:
4438:
4434:
4430:
4426:
4422:
4418:
4410:
4402:
4398:
4394:
4390:
4386:
4382:
4378:
4374:
4370:
4366:
4359:
4351:
4347:
4342:
4337:
4333:
4329:
4325:
4321:
4317:
4310:
4302:
4298:
4294:
4290:
4286:
4282:
4278:
4274:
4267:
4259:
4255:
4251:
4247:
4243:
4239:
4235:
4231:
4224:
4216:
4212:
4207:
4202:
4199:(6): 853–65.
4198:
4194:
4190:
4186:
4178:
4170:
4164:
4160:
4155:
4154:
4145:
4137:
4133:
4129:
4125:
4121:
4117:
4110:
4102:
4098:
4093:
4088:
4084:
4080:
4076:
4072:
4068:
4060:
4052:
4048:
4044:
4040:
4036:
4032:
4025:
4017:
4013:
4009:
4005:
4002:: e428–e438.
4001:
3997:
3990:
3988:
3979:
3975:
3970:
3965:
3960:
3955:
3951:
3947:
3943:
3936:
3928:
3924:
3917:
3910:
3902:
3898:
3894:
3890:
3887:(4): 377–88.
3886:
3882:
3875:
3867:
3863:
3859:
3855:
3851:
3847:
3840:
3833:
3828:
3824:
3820:
3816:
3813:(4): 238–45.
3812:
3808:
3807:Lancet Neurol
3801:
3794:
3789:
3785:
3781:
3777:
3773:
3769:
3762:
3755:
3750:
3746:
3742:
3735:
3728:
3723:
3719:
3715:
3711:
3708:(2): 179–96.
3707:
3703:
3696:
3688:
3684:
3680:
3676:
3672:
3668:
3661:
3653:
3649:
3645:
3641:
3638:(3): 205–20.
3637:
3633:
3626:
3618:
3614:
3610:
3606:
3602:
3598:
3591:
3583:
3579:
3575:
3571:
3567:
3563:
3555:
3547:
3543:
3539:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3520:
3512:
3508:
3504:
3500:
3496:
3492:
3485:
3479:
3472:
3466:
3459:
3451:
3447:
3443:
3439:
3432:
3424:
3420:
3415:
3410:
3407:(1): 109–11.
3406:
3402:
3398:
3391:
3383:
3379:
3375:
3371:
3367:
3363:
3356:
3341:
3335:
3331:
3327:
3320:
3313:
3308:
3304:
3300:
3296:
3293:(5): 703–11.
3292:
3288:
3281:
3274:
3269:
3265:
3260:
3255:
3251:
3247:
3244:(1): 148–53.
3243:
3239:
3235:
3228:
3220:
3216:
3212:
3208:
3204:
3197:
3195:
3193:
3191:
3189:
3187:
3185:
3183:
3181:
3179:
3170:
3164:
3160:
3156:
3152:
3145:
3143:
3141:
3139:
3137:
3135:
3133:
3131:
3129:
3127:
3125:
3116:
3112:
3108:
3104:
3100:
3096:
3089:
3087:
3080:
3074:
3072:
3070:
3068:
3066:
3064:
3062:
3053:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3035:
3031:
3027:
3020:
3018:
3016:
3007:
3003:
2999:
2995:
2991:
2987:
2980:
2978:
2969:
2965:
2958:
2956:
2954:
2952:
2950:
2948:
2946:
2944:
2935:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2920:(2): 133–43.
2919:
2915:
2908:
2900:
2896:
2892:
2888:
2885:(3): 349–54.
2884:
2880:
2873:
2871:
2869:
2867:
2858:
2854:
2850:
2846:
2842:
2838:
2831:
2823:
2819:
2815:
2811:
2807:
2803:
2796:
2788:
2782:
2778:
2774:
2770:
2763:
2761:
2759:
2757:
2755:
2753:
2751:
2749:
2747:
2745:
2743:
2741:
2739:
2737:
2735:
2733:
2731:
2722:
2716:
2712:
2708:
2704:
2697:
2695:
2693:
2691:
2689:
2687:
2685:
2683:
2681:
2679:
2677:
2675:
2673:
2671:
2669:
2667:
2665:
2663:
2661:
2659:
2657:
2655:
2653:
2651:
2649:
2647:
2645:
2643:
2641:
2639:
2637:
2627:
2619:
2615:
2611:
2607:
2603:
2599:
2595:
2591:
2584:
2576:
2572:
2566:
2558:
2554:
2550:
2546:
2542:
2538:
2534:
2530:
2526:
2522:
2515:
2507:
2503:
2499:
2495:
2491:
2487:
2484:(1): 327–37.
2483:
2479:
2472:
2464:
2460:
2455:
2450:
2445:
2440:
2436:
2432:
2429:(7): e21852.
2428:
2424:
2420:
2413:
2405:
2401:
2396:
2391:
2387:
2383:
2380:(4): 1373–9.
2379:
2375:
2371:
2364:
2356:
2352:
2347:
2342:
2338:
2334:
2330:
2323:
2315:
2311:
2306:
2301:
2297:
2293:
2289:
2282:
2274:
2270:
2267:: S167–S168.
2266:
2262:
2255:
2247:
2243:
2238:
2233:
2229:
2225:
2221:
2217:
2213:
2206:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2171:
2163:
2159:
2154:
2149:
2145:
2141:
2138:(7): 1190–7.
2137:
2133:
2129:
2122:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2102:
2098:
2094:
2091:(3): 223–30.
2090:
2086:
2078:
2076:
2067:
2063:
2058:
2053:
2049:
2045:
2041:
2037:
2033:
2026:
2018:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1983:
1981:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1931:
1923:
1919:
1916:(1): 95–105.
1915:
1911:
1904:
1902:
1900:
1898:
1896:
1894:
1892:
1883:
1879:
1874:
1869:
1866:(2): 133–44.
1865:
1861:
1857:
1850:
1842:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1825:(2): 107–15.
1824:
1820:
1816:
1809:
1793:
1789:
1782:
1774:
1770:
1763:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1732:(3): 436–57.
1731:
1727:
1720:
1713:
1709:
1707:9780071481274
1703:
1699:
1692:
1684:
1680:
1675:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1643:
1636:
1631:
1629:9780071481274
1625:
1621:
1614:
1606:
1600:
1592:
1588:
1584:
1582:9780781778176
1578:
1574:
1567:
1559:
1557:9780071481274
1553:
1549:
1542:
1534:
1530:
1525:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1493:
1491:
1486:
1472:
1467:
1460:
1455:
1448:
1443:
1436:
1431:
1424:
1419:
1412:
1407:
1400:
1395:
1388:
1383:
1376:
1371:
1364:
1359:
1352:
1347:
1340:
1335:
1328:
1323:
1316:
1311:
1304:
1299:
1292:
1287:
1280:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1256:
1251:
1250:
1244:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1189:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1169:
1160:
1157:
1153:
1152:schizophrenia
1146:Schizophrenia
1143:
1141:
1131:
1129:
1124:
1120:
1110:
1108:
1104:
1099:
1090:
1087:
1077:
1075:
1070:
1066:
1056:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1005:anticoagulant
1002:
989:
983:
981:
977:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
941:
936:
934:
930:
926:
922:
918:
914:
910:
904:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
877:basal ganglia
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
789:disinhibition
786:
785:hyperactivity
782:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
757:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
723:
719:
716:, rupture of
715:
712:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
673:
669:
665:
664:anterior limb
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
632:
630:
626:
621:
620:basal ganglia
617:
616:meta-analysis
613:
609:
598:
588:
586:
582:
578:
574:
564:
562:
557:
553:
544:
542:
541:perseverative
538:
532:
524:
522:
518:
513:
509:
504:
502:
498:
494:
490:
484:
482:
478:
474:
464:
455:
453:
449:
445:
441:
437:
433:
428:
426:
425:perseverative
421:
420:schizophrenic
411:
407:
403:
401:
397:
392:
378:
375:
370:
361:
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
327:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
295:
293:
289:
282:
277:
273:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
246:
244:
240:
236:
227:
218:
216:
212:
211:reward system
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
187:basal ganglia
184:
180:
168:
162:
158:
155:
152:
150:
146:
143:
140:
138:
134:
131:
128:
126:
122:
119:
116:
113:
109:
106:
103:
101:
97:
94:
91:
89:
85:
82:
79:
77:
73:
68:
65:
62:
58:
53:
48:
47:basal ganglia
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
5102:White matter
4999:White matter
4920:White matter
4845:
4783:White matter
4707:
4562:
4558:
4518:
4514:
4504:
4477:
4473:
4463:
4454:
4445:
4420:
4416:
4409:
4368:
4364:
4358:
4323:
4319:
4309:
4276:
4272:
4266:
4233:
4229:
4223:
4196:
4192:
4177:
4152:
4144:
4119:
4115:
4109:
4074:
4070:
4059:
4037:(2): 363–9.
4034:
4030:
4024:
3999:
3995:
3949:
3945:
3935:
3926:
3922:
3909:
3884:
3880:
3874:
3849:
3845:
3839:
3830:
3810:
3806:
3800:
3791:
3774:(4): 222–8.
3771:
3768:Pract Neurol
3767:
3761:
3752:
3734:
3725:
3705:
3701:
3695:
3670:
3666:
3660:
3635:
3631:
3625:
3600:
3596:
3590:
3565:
3562:Eur J Neurol
3561:
3554:
3529:
3525:
3519:
3494:
3490:
3484:
3471:
3458:
3441:
3437:
3431:
3404:
3400:
3390:
3365:
3361:
3355:
3343:. Retrieved
3329:
3319:
3310:
3290:
3286:
3280:
3271:
3241:
3238:Eur J Neurol
3237:
3227:
3202:
3150:
3101:(1): 48–58.
3098:
3094:
3036:(1): 100–8.
3033:
3029:
2992:(5): 970–5.
2989:
2985:
2967:
2917:
2913:
2907:
2882:
2878:
2843:(9): 971–4.
2840:
2836:
2830:
2805:
2801:
2795:
2768:
2702:
2626:
2596:(1): 67–71.
2593:
2589:
2583:
2574:
2565:
2524:
2520:
2514:
2481:
2477:
2471:
2426:
2422:
2412:
2377:
2374:Neuroscience
2373:
2363:
2336:
2332:
2322:
2295:
2291:
2281:
2264:
2260:
2254:
2219:
2215:
2205:
2180:
2176:
2170:
2135:
2131:
2121:
2088:
2084:
2042:(1): 303–7.
2039:
2035:
2025:
1995:(1): 53–60.
1992:
1988:
1940:
1936:
1930:
1913:
1909:
1863:
1859:
1849:
1822:
1818:
1808:
1796:. Retrieved
1792:the original
1781:
1772:
1762:
1729:
1725:
1719:
1711:
1697:
1691:
1656:
1652:
1642:
1633:
1619:
1613:
1572:
1566:
1547:
1541:
1506:
1503:Neuroscience
1502:
1193:neuroimaging
1190:
1175:
1166:
1149:
1137:
1122:
1116:
1096:
1083:
1062:
1021:dopaminergic
1009:risk factors
1001:antiplatelet
984:
937:
905:
871:(2–5%), and
855:(2–3%), and
853:parkinsonism
805:mood changes
781:restlessness
758:
691:hypertension
687:risk factors
675:white matter
633:
629:case reports
605:
570:
558:
554:
550:
533:
530:
505:
485:
470:
461:
448:oxotremorine
429:
417:
408:
404:
393:
389:
371:
367:
338:
301:
285:
269:
265:
261:
257:
247:
232:
178:
176:
130:A14.1.09.502
118:birnlex_1373
80:
5045:Grey matter
5026:Archicortex
4969:Grey matter
4892:Grey matter
4681:Grey matter
4663:human brain
4480:(1): 1–10.
4423:: 118–127.
4077:(3): 1–12.
4031:J Neurosurg
3969:2066/225901
3952:: 270–278.
3497:: 238–248.
2914:Arch Neurol
2837:Arch Neurol
1943:(1): 3–23.
1509:: 529–541.
1268:aspect; B,
1229:grey matter
1213:grey matter
1195:study with
1086:Alzheimer's
1033:atomoxetine
964:hemiparesis
825:free recall
701:, previous
670:, adjacent
662:, adjacent
652:hemorrhagic
640:subcortical
561:glossolalia
521:sleep cycle
452:amphetamine
440:hippocampus
191:human brain
70:Identifiers
4326:: 744–52.
3345:9 December
1798:5 December
1653:NeuroImage
1482:References
1233:lenticular
1203:. Recent
1201:paroxetine
1049:selegiline
923:features (
809:depression
775:(26–48%),
767:(61–86%),
761:dysarthria
595:See also:
254:hemisphere
100:NeuroNames
5092:Subiculum
4769:Claustrum
4455:psmag.com
4401:293981781
3532:: 66–70.
3526:Sleep Med
3491:Sleep Med
2879:Neurology
2802:Neurology
1659:: 27–33.
1599:cite book
1591:897825779
1103:akathisia
1067:to treat
1037:modafinil
1029:bupropion
929:delusions
921:psychotic
801:attention
791:(9–11%),
777:agitation
765:dysphonia
714:aneurysms
221:Structure
5144:Category
4764:Amygdala
4690:Striatum
4657:Rostral
4620:via the
4614:Archived
4581:20603451
4537:19880927
4496:12057027
4437:25189991
4397:ProQuest
4385:15539860
4350:29876263
4301:36086945
4293:12593459
4258:46151626
4250:17240289
4215:15383276
4136:23664648
4101:30673344
4051:12186465
4016:32311569
3978:32044373
3901:16030444
3866:19673608
3827:12849212
3788:18644908
3749:33085363
3722:19210194
3667:J Neurol
3652:27112231
3617:30638936
3582:34889000
3546:32229419
3511:35219214
3423:15038480
3382:18515459
3307:19810969
3268:26268364
3115:35872616
2618:17079826
2610:17046214
2557:10445511
2549:16763154
2498:15928068
2463:21755004
2423:PLOS ONE
2404:19632307
2355:16339798
2314:15339255
2246:15772354
2197:15217324
2183:: 1–28.
2162:12091198
2113:35678217
2105:20488675
2066:12514228
2017:15685091
2009:19059285
1957:19111791
1922:20407491
1882:12943328
1841:10407200
1754:42928601
1683:28572059
1533:26116518
1262:striatum
1184:and the
1182:thalamus
1128:striatum
1045:levodopa
952:vomiting
944:headache
857:dystonia
843:(6–7%),
833:semantic
829:episodic
821:lethargy
742:syphilis
648:infarcts
644:ischemic
547:Language
489:ablation
458:Learning
444:amygdala
436:amygdala
432:amygdala
353:striatum
349:dopamine
320:dopamine
312:midbrain
281:MR image
250:thalamus
112:NeuroLex
5115:Fimbria
4703:Putamen
4661:of the
4599:at the
4393:7921315
4341:5988460
4092:6873995
3687:9669482
3259:5042068
3219:7922471
3052:9880396
3006:9158635
2934:2405818
2899:2927642
2857:6477232
2822:6504325
2529:Bibcode
2521:Science
2454:3130765
2431:Bibcode
2395:2761724
2237:6725143
2153:2826363
2057:6742125
1965:3717092
1746:7706560
1674:5600829
1524:4523218
1272:aspect.
1266:lateral
976:aphasia
968:aphasia
919:) with
913:anxiety
881:fatigue
869:aphasia
865:neglect
845:ballism
779:(29%),
736:with a
666:of the
660:putamen
527:Emotion
374:cocaine
316:putamen
235:putamen
189:in the
93:D002421
60:Part of
55:Details
49:is blue
5110:Alveus
4958:Other
4579:
4535:
4494:
4435:
4399:
4391:
4383:
4348:
4338:
4299:
4291:
4256:
4248:
4230:Lancet
4213:
4165:
4134:
4099:
4089:
4049:
4014:
3976:
3899:
3864:
3825:
3786:
3747:
3720:
3685:
3650:
3615:
3580:
3544:
3509:
3421:
3380:
3336:
3305:
3266:
3256:
3217:
3165:
3113:
3050:
3030:Stroke
3004:
2986:Stroke
2932:
2897:
2855:
2820:
2783:
2717:
2616:
2608:
2555:
2547:
2506:396612
2504:
2496:
2461:
2451:
2402:
2392:
2353:
2312:
2244:
2234:
2218:. 11.
2195:
2160:
2150:
2111:
2103:
2064:
2054:
2015:
2007:
1963:
1955:
1920:
1880:
1839:
1752:
1744:
1704:
1681:
1671:
1626:
1589:
1579:
1554:
1531:
1521:
1270:medial
1243:gyri.
1074:abulia
1069:glioma
1051:, and
996:
992:
948:nausea
895:, and
849:tremor
841:chorea
813:apathy
773:abulia
748:, and
724:, and
677:, and
414:Memory
262:corpus
4757:Other
4389:S2CID
4297:S2CID
4254:S2CID
3919:(PDF)
3793:term.
3203:Brain
2614:S2CID
2553:S2CID
2502:S2CID
2333:Brain
2109:S2CID
2013:S2CID
1961:S2CID
1750:S2CID
897:mania
650:) or
467:Sleep
266:cauda
258:caput
165:[
154:61833
76:Latin
4808:Genu
4577:PMID
4533:PMID
4492:PMID
4433:PMID
4381:PMID
4346:PMID
4289:PMID
4246:PMID
4211:PMID
4163:ISBN
4132:PMID
4097:PMID
4047:PMID
4012:PMID
3974:PMID
3897:PMID
3862:PMID
3823:PMID
3784:PMID
3745:PMID
3718:PMID
3683:PMID
3648:PMID
3613:PMID
3578:PMID
3542:PMID
3507:PMID
3419:PMID
3378:PMID
3347:2023
3334:ISBN
3303:PMID
3264:PMID
3215:PMID
3163:ISBN
3111:PMID
3048:PMID
3002:PMID
2930:PMID
2895:PMID
2853:PMID
2818:PMID
2781:ISBN
2715:ISBN
2606:PMID
2545:PMID
2494:PMID
2459:PMID
2400:PMID
2351:PMID
2310:PMID
2242:PMID
2193:PMID
2158:PMID
2101:PMID
2062:PMID
2005:PMID
1953:PMID
1918:PMID
1878:PMID
1837:PMID
1800:2013
1742:PMID
1702:ISBN
1679:PMID
1624:ISBN
1605:link
1587:OCLC
1577:ISBN
1552:ISBN
1529:PMID
1140:ADHD
831:and
512:fMRI
510:and
430:The
400:fMRI
398:and
357:fMRI
292:face
270:genu
205:and
177:The
142:5561
125:TA98
88:MeSH
5073:CA4
5068:CA3
5063:CA2
5058:CA1
4746:GPi
4741:GPe
4567:doi
4523:doi
4519:195
4482:doi
4425:doi
4421:169
4373:doi
4336:PMC
4328:doi
4281:doi
4238:doi
4234:369
4201:doi
4159:590
4124:doi
4087:PMC
4079:doi
4039:doi
4004:doi
4000:139
3964:hdl
3954:doi
3950:112
3889:doi
3854:doi
3815:doi
3776:doi
3710:doi
3675:doi
3671:245
3640:doi
3605:doi
3570:doi
3534:doi
3499:doi
3446:doi
3442:324
3409:doi
3370:doi
3295:doi
3254:PMC
3246:doi
3207:doi
3155:doi
3103:doi
3038:doi
2994:doi
2922:doi
2887:doi
2845:doi
2810:doi
2773:doi
2707:doi
2598:doi
2594:148
2537:doi
2525:312
2486:doi
2449:PMC
2439:doi
2390:PMC
2382:doi
2378:163
2341:doi
2337:129
2300:doi
2269:doi
2232:PMC
2224:doi
2185:doi
2148:PMC
2140:doi
2136:159
2093:doi
2089:182
2052:PMC
2044:doi
1997:doi
1993:199
1945:doi
1941:199
1868:doi
1827:doi
1734:doi
1730:352
1669:PMC
1661:doi
1657:157
1519:PMC
1511:doi
1507:301
1207:of
1123:HTT
1117:In
1003:or
827:of
807:or
763:or
618:of
508:EEG
479:to
396:PET
149:FMA
137:TA2
105:226
5146::
4575:.
4563:67
4561:.
4557:.
4545:^
4531:.
4517:.
4513:.
4490:.
4476:.
4472:.
4453:.
4431:.
4419:.
4395:.
4387:.
4379:.
4369:50
4367:.
4344:.
4334:.
4324:18
4322:.
4318:.
4295:.
4287:.
4277:17
4275:.
4252:.
4244:.
4232:.
4209:.
4197:15
4195:.
4191:.
4161:.
4130:.
4120:82
4118:.
4095:.
4085:.
4073:.
4069:.
4045:.
4035:97
4033:.
4010:.
3998:.
3986:^
3972:.
3962:.
3948:.
3944:.
3927:17
3925:.
3921:.
3895:.
3885:20
3883:.
3860:.
3848:.
3829:.
3821:.
3809:.
3790:.
3782:.
3770:.
3751:.
3743:.
3724:.
3716:.
3704:.
3681:.
3669:.
3646:.
3636:18
3634:.
3611:.
3601:28
3599:.
3576:.
3566:29
3564:.
3540:.
3530:70
3528:.
3505:.
3495:90
3493:.
3440:.
3417:.
3405:31
3403:.
3399:.
3376:.
3366:23
3364:.
3309:.
3301:.
3289:.
3270:.
3262:.
3252:.
3242:23
3240:.
3236:.
3213:.
3177:^
3161:.
3123:^
3109:.
3099:35
3097:.
3085:^
3060:^
3046:.
3034:30
3032:.
3028:.
3014:^
3000:.
2990:28
2988:.
2976:^
2942:^
2928:.
2918:47
2916:.
2893:.
2883:39
2881:.
2865:^
2851:.
2841:41
2839:.
2816:.
2806:34
2804:.
2779:.
2729:^
2713:.
2635:^
2612:.
2604:.
2592:.
2573:.
2551:.
2543:.
2535:.
2523:.
2500:.
2492:.
2482:94
2480:.
2457:.
2447:.
2437:.
2425:.
2421:.
2398:.
2388:.
2376:.
2372:.
2349:.
2335:.
2331:.
2308:.
2296:13
2294:.
2290:.
2265:15
2263:.
2240:.
2230:.
2220:25
2214:.
2191:.
2181:27
2179:.
2156:.
2146:.
2134:.
2130:.
2107:.
2099:.
2087:.
2074:^
2060:.
2050:.
2040:23
2038:.
2034:.
2011:.
2003:.
1991:.
1973:^
1959:.
1951:.
1939:.
1914:70
1912:.
1890:^
1876:.
1862:.
1858:.
1835:.
1821:.
1817:.
1771:.
1748:.
1740:.
1728:.
1710:.
1677:.
1667:.
1655:.
1651:.
1632:.
1601:}}
1597:{{
1585:.
1527:.
1517:.
1505:.
1501:.
1489:^
1191:A
1188:.
1076:.
1055:.
1047:,
1043:,
1039:,
1035:,
1031:,
1027:,
978:,
974:,
966:,
962:,
958:,
954:,
950:,
946:,
927:,
891:,
851:,
847:,
819:,
787:,
783:,
744:,
740:,
720:,
705:,
697:,
693:,
587:.
326:.
217:.
201:,
114:ID
5033:/
5028::
4849::
4650:e
4643:t
4636:v
4583:.
4569::
4539:.
4525::
4498:.
4484::
4478:5
4439:.
4427::
4403:.
4375::
4352:.
4330::
4303:.
4283::
4260:.
4240::
4217:.
4203::
4171:.
4138:.
4126::
4103:.
4081::
4075:3
4053:.
4041::
4018:.
4006::
3980:.
3966::
3956::
3903:.
3891::
3868:.
3856::
3850:9
3817::
3811:2
3778::
3772:8
3712::
3706:9
3689:.
3677::
3654:.
3642::
3619:.
3607::
3584:.
3572::
3548:.
3536::
3513:.
3501::
3452:.
3448::
3425:.
3411::
3384:.
3372::
3349:.
3297::
3291:3
3248::
3221:.
3209::
3171:.
3157::
3117:.
3105::
3054:.
3040::
3008:.
2996::
2936:.
2924::
2901:.
2889::
2859:.
2847::
2824:.
2812::
2789:.
2775::
2723:.
2709::
2620:.
2600::
2577:.
2559:.
2539::
2531::
2508:.
2488::
2465:.
2441::
2433::
2427:6
2406:.
2384::
2357:.
2343::
2316:.
2302::
2275:.
2271::
2248:.
2226::
2199:.
2187::
2164:.
2142::
2115:.
2095::
2068:.
2046::
2019:.
1999::
1967:.
1947::
1924:.
1884:.
1870::
1864:3
1843:.
1829::
1823:8
1802:.
1775:.
1756:.
1736::
1685:.
1663::
1607:)
1593:.
1560:.
1535:.
1513::
1239:/
1223:/
646:(
169:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.