924:
129:
163:
948:
900:
708:
936:
912:
538:
190:(If an object is asymmetric about its principal axis of rotation, the moment of inertia with respect to each coordinate direction will change with time, while preserving angular momentum), and has a timescale of about 26,000 years. Nutation occurs because the forces are not constant, and vary as the Earth
194:
around the Sun, and the Moon revolves around the Earth. Basically, there are also torques from other planets that cause planetary precession which contributes to about 2% of the total precession. Because periodic variations in the torques from the sun and the moon, the wobbling (nutation) comes into
726:, a phenomenon that Bradley had unexpectedly discovered in 1725-6. However, there were some residual discrepancies in the stars' positions that were not explained by aberration, and Bradley suspected that they were caused by nutation taking place over the 18.6 year period of the revolution of the
703:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\Delta \alpha &=(\cos \epsilon +\sin \epsilon \sin \alpha \tan \delta )\Delta \psi -\cos \alpha \tan \delta \Delta \epsilon \\\Delta \delta &=\cos \alpha \sin \epsilon \Delta \psi +\sin \alpha \Delta \epsilon \end{aligned}}}
403:
234:), these effects combine to vary the inclination of the Moon's orbit to the equator by between 18.4° and 28.6° over the 18.6 year period. This causes the orientation of the Earth's axis to vary over the same period, with the true position of the
261:
Because nutation causes a change to the frame of reference, rather than a change in position of an observed object itself, it applies equally to all objects. Its magnitude at any point in time is usually expressed in terms of
733:
Although
Bradley's observations proved the existence of nutation and he intuitively understood that it was caused by the action of the Moon on the rotating Earth, it was left to later mathematicians,
543:
331:
730:. This was confirmed by his 20-year series of observations, in which he discovered that the celestial pole moved in a slightly flattened ellipse of 18 by 16 arcseconds about its mean position.
41:
forces of other nearby bodies acting upon the spinning object. Although they are caused by the same effect operating over different timescales, astronomers usually make a distinction between
326:
318:
89:
the shorter-term effects of nutation. It is then necessary to apply a further correction to take into account the effect of nutation, after which the position relative to the
530:
507:
722:
from a series of observations of stars conducted between 1727 and 1747. These observations were originally intended to demonstrate conclusively the existence of the annual
291:
232:
484:
460:
426:
432:
of the Moon's orbit. By way of reference, the sum of the absolute value of all the remaining terms is 1.4 arcseconds for longitude and 0.9 arcseconds for obliquity.
863:
104:
that can be estimated for only a few months into the future because it is influenced by rapidly and unpredictably varying things such as
74:. The effect of precession and nutation causes this frame of reference itself to change over time, relative to an arbitrary fixed frame.
147:
85:— defined by the orientation of the Earth's axis at a specified date, taking into account the long-term effect of precession, but
871:
249:
Smaller effects also contribute to nutation. These are caused by the monthly motion of the Moon around the Earth and its
398:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\Delta \psi &=-17.2\sin \Omega \\\Delta \epsilon &=9.2\cos \Omega \end{aligned}}}
782:
790:
206:. The orientation of this orbital plane varies over a period of about 18.6 years (this period is referred to as the
166:
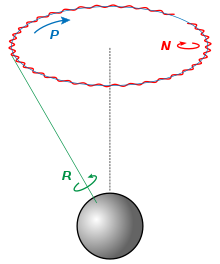
Nutation (N) of the Earth produces a slight axial wobble over the course of the 26,000 year precessional cycle (P)
81:
of an astronomical object. When calculating the position of an object, it is initially expressed relative to the
776:
71:
96:
Because the dynamic motions of the planets are so well known, their nutations can be calculated to within
890:
734:
320:) in seconds of arc. The largest term in nutation is expressed numerically (in arcseconds) as follows:
263:
300:
211:
512:
489:
438:
can then be used on any given object to convert these quantities into an adjustment in the object's
848:
827:
273:
210:). Because the Earth's equator is itself inclined at an angle of about 23.4° to the ecliptic (the
435:
217:
469:
445:
411:
250:
54:
An example of precession and nutation is the variation over time of the orientation of the
100:
over periods of many decades. There is another disturbance of the Earth's rotation called
8:
968:
952:
842:
750:
723:
179:
142:
137:
34:
821:
940:
928:
63:
786:
207:
199:
195:
place. You can think of precession as the average and nutation as the instantaneous.
187:
486:) For objects that are not close to a celestial pole, nutation in right ascension (
904:
239:
55:
43:
170:
Precession and nutation are caused principally by the gravitational forces of the
439:
738:
235:
78:
962:
719:
253:, and similar terms caused by the annual motion of the Earth around the Sun.
105:
916:
806:
755:
429:
101:
864:"The Nodding Sphere and the Bird's Beak: D'Alembert's Dispute with Euler"
463:
109:
741:, to develop a more detailed theoretical explanation of the phenomenon.
66:
for measurement of the positions of astronomical objects is the Earth's
727:
112:
77:
Nutation is one of the corrections which must be applied to obtain the
97:
238:
describing a small ellipse around their mean position. The maximum
203:
51:, which is the combined effect of similar shorter-term variations.
30:
20:
47:, which is a steady long-term change in the axis of rotation, and
183:
67:
38:
198:
The largest contributor to nutation is the inclination of the
162:
256:
191:
59:
29:
is a phenomenon which causes the orientation of the axis of
171:
911:
202:
around the Earth, at slightly over 5° to the plane of the
175:
108:, wind systems, and hypothesised motions in the liquid
888:
541:
515:
492:
472:
448:
414:
329:
303:
276:
220:
186:
over a very long period of time, and a time-varying
62:. This is important because the most commonly used
778:Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac
702:
524:
501:
478:
454:
420:
397:
312:
285:
226:
960:
532:) can be calculated approximately as follows:
868:The MAA Mathematical Sciences Digital Library
861:
182:. Precession is the effect of these forces
136:It has been suggested that this section be
774:
257:Effect on position of astronomical objects
161:
19:For broader coverage of this topic, see
819:
807:"NeoProgrammics - Science Computations"
768:
37:to vary over time. It is caused by the
961:
840:
781:. University Science Books. pp.
140:out into another article titled
775:Seidelmann, P. Kenneth, ed. (1992).
122:
872:Mathematical Association of America
823:A Compendium of Spherical Astronomy
118:
13:
690:
672:
641:
631:
604:
546:
516:
493:
415:
388:
366:
359:
334:
304:
277:
14:
980:
428:is the ecliptic longitude of the
946:
934:
922:
910:
898:
313:{\displaystyle \Delta \epsilon }
246:, approximately 9.2 arcseconds.
127:
855:
834:
813:
799:
601:
559:
525:{\displaystyle \Delta \delta }
502:{\displaystyle \Delta \alpha }
178:acting upon the non-spherical
1:
761:
844:A Short History of Astronomy
286:{\displaystyle \Delta \psi }
72:equatorial coordinate system
7:
744:
718:Nutation was discovered by
16:Type of motion in astronomy
10:
985:
713:
18:
728:nodes of the Moon's orbit
227:{\displaystyle \epsilon }
212:obliquity of the ecliptic
847:. John Murray. pp.
293:) in seconds of arc and
91:true equinox and equator
83:mean equinox and equator
820:Newcomb, Simon (1906).
479:{\displaystyle \delta }
455:{\displaystyle \alpha }
421:{\displaystyle \Omega }
242:of this ellipse is the
113:outer core of the Earth
841:Berry, Arthur (1898).
826:. Macmillan. pp.
704:
526:
503:
480:
456:
436:Spherical trigonometry
422:
399:
314:
287:
228:
167:
705:
527:
504:
481:
457:
423:
400:
315:
295:nutation in obliquity
288:
268:nutation in longitude
229:
165:
27:Astronomical nutation
539:
513:
490:
470:
446:
412:
327:
301:
274:
264:ecliptic coordinates
251:orbital eccentricity
244:constant of nutation
218:
862:Robert E. Bradley.
751:Aberration of light
724:aberration of light
509:) and declination (
180:figure of the Earth
35:astronomical object
700:
698:
522:
499:
476:
452:
418:
395:
393:
310:
283:
224:
168:
64:frame of reference
200:orbit of the Moon
188:moment of inertia
160:
159:
155:
976:
951:
950:
949:
939:
938:
937:
927:
926:
925:
915:
914:
903:
902:
901:
894:
883:
882:
880:
878:
859:
853:
852:
838:
832:
831:
817:
811:
810:
803:
797:
796:
772:
709:
707:
706:
701:
699:
531:
529:
528:
523:
508:
506:
505:
500:
485:
483:
482:
477:
461:
459:
458:
453:
427:
425:
424:
419:
404:
402:
401:
396:
394:
319:
317:
316:
311:
292:
290:
289:
284:
233:
231:
230:
225:
151:
143:Earth's nutation
131:
130:
123:
119:Earth's nutation
70:— the so-called
56:axis of rotation
984:
983:
979:
978:
977:
975:
974:
973:
959:
958:
957:
947:
945:
935:
933:
923:
921:
909:
899:
897:
889:
887:
886:
876:
874:
860:
856:
839:
835:
818:
814:
805:
804:
800:
793:
773:
769:
764:
747:
716:
697:
696:
647:
638:
637:
552:
542:
540:
537:
536:
514:
511:
510:
491:
488:
487:
471:
468:
467:
447:
444:
443:
440:right ascension
413:
410:
409:
392:
391:
372:
363:
362:
340:
330:
328:
325:
324:
302:
299:
298:
275:
272:
271:
259:
236:celestial poles
219:
216:
215:
156:
132:
128:
121:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
982:
972:
971:
956:
955:
943:
931:
919:
907:
885:
884:
854:
833:
812:
798:
791:
766:
765:
763:
760:
759:
758:
753:
746:
743:
715:
712:
711:
710:
695:
692:
689:
686:
683:
680:
677:
674:
671:
668:
665:
662:
659:
656:
653:
650:
648:
646:
643:
640:
639:
636:
633:
630:
627:
624:
621:
618:
615:
612:
609:
606:
603:
600:
597:
594:
591:
588:
585:
582:
579:
576:
573:
570:
567:
564:
561:
558:
555:
553:
551:
548:
545:
544:
521:
518:
498:
495:
475:
451:
430:ascending node
417:
406:
405:
390:
387:
384:
381:
378:
375:
373:
371:
368:
365:
364:
361:
358:
355:
352:
349:
346:
343:
341:
339:
336:
333:
332:
309:
306:
282:
279:
258:
255:
223:
158:
157:
153:(October 2020)
135:
133:
126:
120:
117:
106:ocean currents
79:apparent place
33:of a spinning
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
981:
970:
967:
966:
964:
954:
944:
942:
932:
930:
920:
918:
913:
908:
906:
896:
895:
892:
873:
869:
865:
858:
850:
846:
845:
837:
829:
825:
824:
816:
808:
802:
794:
792:0-935702-68-7
788:
784:
780:
779:
771:
767:
757:
754:
752:
749:
748:
742:
740:
736:
731:
729:
725:
721:
720:James Bradley
693:
687:
684:
681:
678:
675:
669:
666:
663:
660:
657:
654:
651:
649:
644:
634:
628:
625:
622:
619:
616:
613:
610:
607:
598:
595:
592:
589:
586:
583:
580:
577:
574:
571:
568:
565:
562:
556:
554:
549:
535:
534:
533:
519:
496:
473:
465:
449:
441:
437:
433:
431:
385:
382:
379:
376:
374:
369:
356:
353:
350:
347:
344:
342:
337:
323:
322:
321:
307:
296:
280:
269:
265:
254:
252:
247:
245:
241:
237:
221:
213:
209:
205:
201:
196:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
164:
154:
149:
145:
144:
139:
134:
125:
124:
116:
114:
111:
107:
103:
99:
94:
93:is obtained.
92:
88:
84:
80:
75:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
52:
50:
46:
45:
40:
39:gravitational
36:
32:
28:
22:
953:Solar System
875:. Retrieved
867:
857:
843:
836:
822:
815:
801:
777:
770:
756:Polar motion
732:
717:
434:
407:
294:
267:
260:
248:
243:
197:
169:
152:
141:
102:polar motion
95:
90:
86:
82:
76:
53:
48:
42:
26:
25:
941:Outer space
929:Spaceflight
464:declination
110:nickel-iron
969:Astrometry
762:References
735:d'Alembert
98:arcseconds
44:precession
905:Astronomy
694:ϵ
691:Δ
688:α
685:
676:ψ
673:Δ
670:ϵ
667:
661:α
658:
645:δ
642:Δ
635:ϵ
632:Δ
629:δ
626:
620:α
617:
611:−
608:ψ
605:Δ
599:δ
596:
590:α
587:
581:ϵ
578:
569:ϵ
566:
550:α
547:Δ
520:δ
517:Δ
497:α
494:Δ
474:δ
450:α
416:Ω
389:Ω
386:
370:ϵ
367:Δ
360:Ω
357:
348:−
338:ψ
335:Δ
308:ϵ
305:Δ
281:ψ
278:Δ
222:ϵ
963:Category
877:21 April
745:See also
204:ecliptic
192:revolves
184:averaged
49:nutation
31:rotation
21:Nutation
891:Portals
714:History
148:Discuss
68:equator
58:of the
789:
785:–120.
462:) and
408:where
240:radius
917:Stars
851:–269.
830:–292.
739:Euler
266:, as
208:saros
138:split
60:Earth
879:2014
787:ISBN
737:and
351:17.2
174:and
172:Moon
849:265
828:289
682:sin
664:sin
655:cos
623:tan
614:cos
593:tan
584:sin
575:sin
563:cos
383:cos
380:9.2
354:sin
176:Sun
146:. (
87:not
965::
870:.
866:.
783:99
214:,
150:)
115:.
893::
881:.
809:.
795:.
679:+
652:=
602:)
572:+
560:(
557:=
466:(
442:(
377:=
345:=
297:(
270:(
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.