523:
740:
31:
772:
760:
556:) twice. This means that the sternocleidomastoid is controlled by the brain on the same side of the body. Contraction of the stenocleidomastoid fibres turns the head to the opposite side, the net effect meaning that the head is turned to the side of the brain receiving visual information from that area. The cranial component of the accessory nerve, on the other hand, provides motor control to the muscles of the soft palate, larynx and pharynx.
548:. The trapezius muscle controls the action of shrugging the shoulders, and the sternocleidomastoid the action of turning the head. Like most muscles, control of the trapezius muscle arises from the opposite side of the brain. Contraction of the upper part of the trapezius muscle elevates the scapula. The nerve fibres supplying sternocleidomastoid, however, are thought to change sides (
609:) of the body being assessed. Weakness in head-turning suggests injury to the contralateral spinal accessory nerve: a weak leftward turn is indicative of a weak right sternocleidomastoid muscle (and thus right spinal accessory nerve injury), while a weak rightward turn is indicative of a weak left sternocleidomastoid muscle (and thus left spinal accessory nerve).
739:
716:, and it came to pass that these fibres were increasingly viewed as part of the vagus nerve itself. Consequently, the term "accessory nerve" was and is increasingly used to denote only fibres from the spinal cord; the fact that only the spinal portion could be tested clinically lent weight to this opinion.
612:
Hence, weakness of shrug on one side and head-turning on the other side may indicate damage to the accessory nerve on the side of the shrug weakness, or damage along the nerve pathway at the other side of the brain. Causes of damage may include trauma, surgery, tumours, and compression at the jugular
711:
described the nerve as the "spinal nerve accessory to the vagus", recognizing that while a minor component of the nerve joins with the larger vagus nerve, the majority of accessory nerve fibres originate in the spinal cord. In 1893 it was recognised that the heretofore named nerve fibres "accessory"
350:
to assess function of the spinal accessory nerve. Poor strength or limited movement are suggestive of damage, which can result from a variety of causes. Injury to the spinal accessory nerve is most commonly caused by medical procedures that involve the head and neck. Injury can cause wasting of the
501:
and briefly connects with the spinal accessory component before branching off of the nerve to join the vagus nerve. A study, published in 2007, of twelve subjects suggests that in the majority of individuals, this cranial component does not make any distinct connection to the spinal component; the
647:
excision. It can also occur as a result of blunt or penetrating trauma, and in some causes spontaneously. Damage at any point along the nerve's course will affect the function of the nerve. The nerve is intentionally removed in "radical" neck dissections, which are attempts at exploring the neck
651:
Injury to the accessory nerve can result in neck pain and weakness of the trapezius muscle. Symptoms will depend on at what point along its length the nerve was severed. Injury to the nerve can result in shoulder girdle depression, atrophy, abnormal movement, a protruding scapula, and weakened
423:
After leaving the skull, the cranial component detaches from the spinal component. The spinal accessory nerve continues alone and heads backwards and downwards. In the neck, the accessory nerve crosses the internal jugular vein around the level of the posterior belly of digastric muscle. As it
474:, is located in the lateral aspect of the anterior horn of the spinal cord, and stretches from where the spinal cord begins (at the junction with the medulla) through to the level of about C6. The lateral horn of high cervical segments appears to be continuous with the
339:, and there is ongoing debate about whether the cranial part should be considered part of the accessory nerve proper. Consequently, the term "accessory nerve" usually refers only to nerve supplying the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, also called the
1276:
The upper trapezius elevates, the middle trapezius retracts, and the lower trapezius depresses. In unison, the pri- mary function of the trapezius is to up- wardly rotate the scapula during shoulder elevation, forming a force couple with the serratus
328:. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves because part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, whereas the trapezius muscle, connecting to the
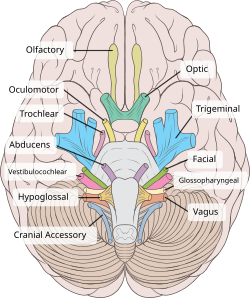
753:, and accessory nerves. The accessory nerve (top left) travels down through the jugular foramen with the other two nerves, and then passes down, usually over the internal jugular vein, to supply the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
602:. The trapezius muscle is tested by asking the patient to shrug their shoulders with and without resistance. The sternocleidomastoid muscle is tested by asking the patient to turn their head to the left or right against resistance.
564:
Among researchers there is disagreement regarding the terminology used to describe the type of information carried by the accessory nerve. As the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles are derived from the
771:
668:
may be needed to confirm a suspected injury. Outcomes with surgical treatment appear to be better than conservative management, which entails physiotherapy and pain relief. Surgical management includes
420:. The spinal accessory nerve is notable for being the only cranial nerve to both enter and exit the skull. This is due to it being unique among the cranial nerves in having neurons in the spinal cord.
1018:
Ryan S, Blyth P, Duggan N, Wild M, Al-Ali S (2007). "Is the cranial accessory nerve really a portion of the accessory nerve? Anatomy of the cranial nerves in the jugular foramen".
1459:
Davis, Matthew C.; Griessenauer, Christoph J.; Bosmia, Anand N.; Tubbs, R. Shane; Shoja, Mohammadali M. (January 2014). "The naming of the cranial nerves: A historical review".
404:, to the level of about C6. These fibres join together to form rootlets, roots, and finally the spinal accessory nerve itself. The formed nerve enters the skull through the
759:
134:
605:
One-sided weakness of the trapezius may indicate injury to the nerve on the same side of an injury to the spinal accessory nerve on the same side (Latin:
2496:
1180:
Saman M, Etebari P, Pakdaman MN, Urken ML (2010). "Anatomic relationship between the spinal accessory nerve and the jugular vein: a cadaveric study".
2491:
2420:
2275:
833:
2255:
1223:
Skórzewska, A; Bruska, M; Woźniak, W (1994). "The development of the spinal accessory nerve in human embryos during 5th week (stages 14 and 15)".
287:
2260:
1861:
110:
106:
2438:
2265:
581:(GSE) information. Still others believe it is reasonable to conclude that the spinal accessory nerve contains both SVE and GSE components.
2212:
2207:
335:
Traditional descriptions of the accessory nerve divide it into a spinal part and a cranial part. The cranial component rapidly joins the
2270:
2080:
1871:
1250:
Kelley, Martin J.; Kane, Thomas E.; Leggin, Brian G. (February 2008). "Spinal
Accessory Nerve Palsy: Associated Signs and Symptoms".
939:
Kelley, Martin J.; Kane, Thomas E.; Leggin, Brian G. (February 2008). "Spinal
Accessory Nerve Palsy: Associated Signs and Symptoms".
2486:
1799:
1637:
974:
Weglowski, M.; Woźniak, W.; Piotrowski, A.; Bruska, M.; Weglowska, J.; Sobański, J.; Grzymisławska, M.; Łupicka, J. (28 May 2015).
673:, nerve end-to-end suturing, and surgical replacement of affected trapezius muscle segments with other muscle groups, such as the
2070:
648:
surgically for the presence and extent of cancer. Attempts are made to spare it in other forms of less aggressive dissection.
2592:
2065:
1531:
1091:
864:
Neuroanatomy and the
Neurologic Exam: A Thesaurus of Synonyms, Similar-Sounding Non-Synonyms, and Terms of Variable Meanings
573:(SVE) information. This is in line with the observation that the spinal accessory nucleus appears to be continuous with the
2647:
1596:
2085:
1808:
1794:
494:, in front of the vein in about 80% of people, and behind it in about 20%, and in one reported case, piercing the vein.
280:
2443:
2075:
2053:
1327:
1298:
871:
725:
2560:
2391:
2386:
2342:
2337:
2048:
141:
2368:
2363:
578:
387:
2565:
2476:
383:
340:
618:
490:
In the neck, the accessory nerve crosses the internal jugular vein around the level of the posterior belly of
2517:
2481:
614:
273:
129:
2632:
2627:
1784:
1630:
497:
Traditionally, the accessory nerve is described as having a small cranial component that descends from the
1565:
825:
2296:
408:, the large opening at the skull's base. The nerve travels along the inner wall of the skull towards the
1740:
1701:
1547:
599:
527:
429:
425:
61:
2415:
2113:
2038:
1866:
1561:
570:
511:
367:
522:
2617:
2553:
2408:
2403:
2398:
1993:
1876:
1589:
665:
634:
471:
453:
347:
89:
30:
2637:
2622:
2127:
1623:
1604:
765:
Side of the neck, with accessory nerve seen between the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
260:
219:
2185:
2015:
2000:
1988:
569:, some researchers believe the spinal accessory nerve that innervates them must carry specific
467:
413:
225:
117:
101:
502:
roots of these distinct components were separated by a fibrous sheath in all but one subject.
2456:
2243:
2451:
2173:
2103:
2028:
781:
specimen. The accessory nerve can be seen as a number of rootlets arising from the medulla.
674:
8:
2584:
1968:
1886:
1526:. editor-in-chief, Susan Standring (40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. 2008.
653:
538:
321:
2642:
2043:
1963:
1779:
1541:
1484:
1441:
1393:
1368:
1205:
1140:
1113:
1043:
905:
888:
696:
in 1664 first described the accessory nerve, choosing to use "accessory" (described in
459:
613:
foramen. Weakness in both muscles may point to a more general disease process such as
440:(entering at the junction of the middle and lower third of the anterior border of the
2575:
2161:
2156:
2139:
1829:
1527:
1476:
1445:
1433:
1398:
1323:
1316:
1294:
1267:
1232:
1197:
1145:
1087:
1035:
1031:
997:
956:
910:
867:
713:
498:
479:
401:
360:
243:
40:
1488:
1209:
1047:
639:
Injury to the spinal accessory nerve commonly occurs during neck surgery, including
2548:
2522:
2512:
2301:
2291:
2168:
2108:
1927:
1906:
1896:
1849:
1803:
1767:
1468:
1425:
1388:
1380:
1259:
1189:
1135:
1125:
1027:
987:
948:
900:
746:
574:
531:
491:
475:
437:
325:
201:
189:
65:
2238:
2144:
1901:
1820:
1716:
1689:
1503:
657:
640:
566:
409:
195:
177:
94:
2233:
2151:
2060:
2005:
1918:
1711:
1655:
1647:
1608:
1508:. Vol. 2 (5th ed.). London: Taylor, Walton, and Maberly. p. 812.
661:
549:
405:
356:
255:
207:
171:
161:
1384:
1193:
2611:
2355:
2326:
2248:
2225:
2196:
2010:
1667:
1577:
1429:
1130:
1001:
693:
622:
317:
122:
1263:
952:
412:. Leaving the skull, the nerve travels through the jugular foramen with the
1980:
1947:
1750:
1480:
1437:
1402:
1271:
1201:
1149:
1039:
960:
433:
213:
1236:
975:
914:
537:
The spinal component of the accessory nerve provides motor control of the
2315:
1755:
1728:
1582:
992:
708:
681:
463:
417:
397:
336:
231:
183:
36:
976:"Early development of the facial nerve in human embryos at stages 13–15"
830:
Structure of the Human body, Loyola
University Medical Education Network
1571:
670:
644:
482:, from which the cranial component of the accessory nerve is derived.
147:
1615:
1472:
1343:
Joshi SS, Joshi SD (2001). "Muscle Dorso-Fascialis — A Case Report".
656:. Weakness of the shoulder girdle can lead to traction injury of the
595:
542:
441:
44:
1163:
1161:
1159:
577:
of the medulla. Others consider the spinal accessory nerve to carry
808:
806:
804:
802:
800:
798:
796:
352:
2468:
1156:
778:
329:
1580:
at The
Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (
1369:"Scapular winging: anatomical review, diagnosis, and treatments"
973:
793:
594:
The accessory nerve is tested by evaluating the function of the
2430:
1524:
Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice
545:
393:
371:
1574:
at The
Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
458:
The fibres that form the spinal accessory nerve are formed by
750:
697:
400:, from where the spinal cord begins at the junction with the
392:
The fibres of the spinal accessory nerve originate solely in
77:
1458:
2378:
1502:
Jones Quain (1848). Richard Quain; William
Sharpey (eds.).
1318:
Neuroanatomy: an atlas of structures, sections, and systems
1291:
346:
Strength testing of these muscles can be measured during a
1179:
1222:
1322:. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
712:
to the vagus originated from the same nucleus in the
1293:. Washington, DC: Taylor & Francis. p. 12.
1288:
1252:
941:
47:, and is visible at the bottom of the image in blue.
1367:Martin, Ryan M.; Fish, David E. (2 November 2007).
1017:
861:
436:branches, then continues down until it reaches the
1522:
1315:
1167:
893:Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England
812:
444:) to provide motor innervation to its upper part.
424:courses downwards, the nerve pierces through the
39:from below. The accessory nerve emerges from the
16:Cranial nerve XI, for head and shoulder movements
2609:
1249:
1111:
938:
1313:
1107:
1105:
1103:
886:
704:) meaning in association with the vagus nerve.
857:
855:
853:
851:
1631:
1362:
1360:
1358:
281:
1112:Finsterer, Josef; Grisold, Wolfgang (2015).
1100:
934:
932:
930:
928:
926:
924:
1501:
1373:Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine
848:
1638:
1624:
1452:
1366:
1355:
1345:Journal of the Anatomical Society of India
1342:
1118:Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice
288:
274:
29:
1392:
1139:
1129:
1086:. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 424–5.
1077:
991:
921:
904:
866:. Boca Raton: CRC-Press. pp. 69–73.
359:, and weakness of shoulder abduction and
1075:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1059:
1057:
726:List of anatomy mnemonics#Cranial nerves
584:
521:
514:of the embryonic spinal segments C1–C6.
510:The accessory nerve is derived from the
366:The accessory nerve is derived from the
1415:
1114:"Disorders of the lower cranial nerves"
2610:
1645:
1081:
1013:
1011:
1619:
1173:
1054:
880:
777:The brain and upper spinal cord in a
462:located in the upper segments of the
1592:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
887:London J, London NJ, Kay SP (1996).
731:
1008:
889:"Iatrogenic accessory nerve injury"
13:
1416:Tomczak, K (2013). "Torticollis".
1409:
818:
660:. Because diagnosis is difficult,
14:
2659:
1555:
836:from the original on 16 June 2007
559:
526:The accessory nerve supplies the
1566:GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cn11.htm
1032:10.1111/j.1447-073X.2006.00154.x
1020:Anatomical Science International
770:
758:
738:
142:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
1495:
1336:
1307:
1282:
1243:
1216:
1182:Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy
745:Course and distribution of the
388:Cranial root of accessory nerve
967:
680:Damage to the nerve can cause
589:
505:
384:Spinal root of accessory nerve
332:, acts to shrug the shoulder.
1:
2518:Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
1289:William T. Mosenthal (1995).
786:
615:amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
862:Terence R. Anthoney (1993).
485:
377:
7:
2648:Nerves of the head and neck
2297:Inferior salivatory nucleus
719:
600:sternocleidomastoid muscles
517:
10:
2664:
1741:lateral geniculate nucleus
1702:anterior olfactory nucleus
1418:Journal of Child Neurology
687:
632:
451:
447:
426:sternocleidomastoid muscle
381:
62:Sternocleidomastoid muscle
2574:
2535:
2505:
2467:
2429:
2421:Superior cervical cardiac
2377:
2353:
2324:
2314:
2284:
2223:
2194:
2184:
2126:
2114:Superior salivary nucleus
2096:
2026:
1977:
1956:
1946:
1917:
1867:spinal trigeminal nucleus
1848:
1819:
1766:
1727:
1688:
1654:
1385:10.1007/s12178-007-9000-5
1194:10.1007/s00276-010-0737-y
1082:Talley, Nicholas (2014).
628:
571:special visceral efferent
428:(approximately 1cm above
140:
128:
116:
100:
88:
76:
71:
57:
52:
28:
23:
2554:spinal accessory nucleus
1994:pterygopalatine ganglion
1785:Edinger–Westphal nucleus
1590:Anatomy photo:28:13-0115
1430:10.1177/0883073812469294
1314:Duane E. Haines (2004).
1131:10.4103/0976-3147.158768
826:"Spinal Accessory Nerve"
666:nerve conduction studies
635:Accessory nerve disorder
579:general somatic efferent
472:spinal accessory nucleus
454:Spinal accessory nucleus
348:neurological examination
1936:no significant branches
1838:no significant branches
1678:no significant branches
1605:Yale School of Medicine
1264:10.2519/jospt.2008.2454
953:10.2519/jospt.2008.2454
619:Guillain–Barré syndrome
374:spinal segments C1–C6.
2256:Stylopharyngeal branch
2016:submandibular ganglion
2001:Nerve to the stapedius
1546:: CS1 maint: others (
606:
553:
534:
396:situated in the upper
357:winging of the scapula
341:spinal accessory nerve
306:eleventh cranial nerve
585:Clinical significance
525:
2104:Facial motor nucleus
1800:parasympathetic root
1084:Clinical Examination
993:10.5603/fm.2015.0039
675:Eden-Lange procedure
304:, also known as the
2633:Human head and neck
2628:Otorhinolaryngology
2416:Recurrent laryngeal
2261:Pharyngeal branches
2039:Posterior auricular
1887:trigeminal ganglion
1505:Elements of Anatomy
1168:Gray's Anatomy 2008
813:Gray's Anatomy 2008
539:sternocleidomastoid
528:sternocleidomastoid
460:lower motor neurons
432:) while sending it
322:sternocleidomastoid
2399:Superior laryngeal
2266:Tonsillar branches
1964:Intermediate nerve
1780:oculomotor nucleus
1225:Folia Morphologica
980:Folia Morphologica
702:nervus accessorius
692:English anatomist
535:
468:cluster of neurons
320:that supplies the
83:nervus accessorius
2603:
2602:
2531:
2530:
2497:Posterior gastric
2392:pharyngeal plexus
2387:Pharyngeal branch
2310:
2309:
2174:Scarpa's ganglion
2162:lateral lemniscus
2157:striae medullares
2140:vestibular nuclei
2128:Vestibulocochlear
2122:
2121:
1533:978-0-8089-2371-8
1093:978-0-7295-4198-5
732:Additional images
714:medulla oblongata
567:pharyngeal arches
532:trapezius muscles
480:medulla oblongata
402:medulla oblongata
361:external rotation
326:trapezius muscles
298:
297:
220:Vestibulocochlear
156:
155:
151:
2655:
2549:nucleus ambiguus
2523:Solitary nucleus
2513:Nucleus ambiguus
2492:Anterior gastric
2439:Inferior cardiac
2369:Auricular branch
2364:Meningeal branch
2322:
2321:
2302:Solitary nucleus
2292:Nucleus ambiguus
2271:Lingual branches
2192:
2191:
2186:Glossopharyngeal
2109:Solitary nucleus
1989:Greater petrosal
1954:
1953:
1804:ciliary ganglion
1640:
1633:
1626:
1617:
1616:
1612:
1611:on 3 March 2016.
1607:. Archived from
1551:
1545:
1537:
1510:
1509:
1499:
1493:
1492:
1473:10.1002/ca.22345
1461:Clinical Anatomy
1456:
1450:
1449:
1413:
1407:
1406:
1396:
1364:
1353:
1352:
1340:
1334:
1333:
1321:
1311:
1305:
1304:
1286:
1280:
1279:
1247:
1241:
1240:
1220:
1214:
1213:
1177:
1171:
1165:
1154:
1153:
1143:
1133:
1109:
1098:
1097:
1079:
1052:
1051:
1015:
1006:
1005:
995:
971:
965:
964:
936:
919:
918:
908:
884:
878:
877:
859:
846:
845:
843:
841:
822:
816:
810:
774:
762:
747:glossopharyngeal
742:
575:nucleus ambiguus
492:digastric muscle
476:nucleus ambiguus
438:trapezius muscle
414:glossopharyngeal
310:cranial nerve XI
290:
283:
276:
226:Glossopharyngeal
158:
157:
148:edit on Wikidata
145:
66:trapezius muscle
33:
21:
20:
2663:
2662:
2658:
2657:
2656:
2654:
2653:
2652:
2618:Accessory nerve
2608:
2607:
2604:
2599:
2570:
2527:
2501:
2463:
2425:
2373:
2349:
2306:
2280:
2244:lesser petrosal
2239:tympanic plexus
2219:
2180:
2145:cochlear nuclei
2118:
2092:
2030:
2022:
1979:
1973:
1942:
1913:
1844:
1815:
1762:
1723:
1717:olfactory tract
1684:
1650:
1644:
1595:
1562:MedEd at Loyola
1558:
1539:
1538:
1534:
1514:
1513:
1500:
1496:
1457:
1453:
1414:
1410:
1365:
1356:
1341:
1337:
1330:
1312:
1308:
1301:
1287:
1283:
1248:
1244:
1221:
1217:
1178:
1174:
1166:
1157:
1110:
1101:
1094:
1080:
1055:
1016:
1009:
972:
968:
937:
922:
885:
881:
874:
860:
849:
839:
837:
824:
823:
819:
811:
794:
789:
782:
775:
766:
763:
754:
743:
734:
722:
690:
658:brachial plexus
641:neck dissection
637:
631:
592:
587:
562:
520:
508:
488:
456:
450:
410:jugular foramen
390:
380:
302:accessory nerve
294:
265:
152:
109:
48:
24:Accessory nerve
17:
12:
11:
5:
2661:
2651:
2650:
2645:
2640:
2638:Nervous system
2635:
2630:
2625:
2623:Cranial nerves
2620:
2601:
2600:
2598:
2597:
2596:
2595:
2587:
2581:
2579:
2572:
2571:
2569:
2568:
2563:
2558:
2557:
2556:
2551:
2542:
2540:
2533:
2532:
2529:
2528:
2526:
2525:
2520:
2515:
2509:
2507:
2503:
2502:
2500:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2484:
2479:
2473:
2471:
2465:
2464:
2462:
2461:
2460:
2459:
2454:
2446:
2441:
2435:
2433:
2427:
2426:
2424:
2423:
2418:
2413:
2412:
2411:
2406:
2396:
2395:
2394:
2383:
2381:
2375:
2374:
2372:
2371:
2366:
2360:
2358:
2351:
2350:
2348:
2347:
2346:
2345:
2340:
2331:
2329:
2319:
2312:
2311:
2308:
2307:
2305:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2288:
2286:
2282:
2281:
2279:
2278:
2273:
2268:
2263:
2258:
2253:
2252:
2251:
2246:
2241:
2230:
2228:
2221:
2220:
2218:
2217:
2216:
2215:
2210:
2201:
2199:
2189:
2182:
2181:
2179:
2178:
2177:
2176:
2166:
2165:
2164:
2159:
2152:Cochlear nerve
2149:
2148:
2147:
2142:
2133:
2131:
2124:
2123:
2120:
2119:
2117:
2116:
2111:
2106:
2100:
2098:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2090:
2089:
2088:
2083:
2078:
2073:
2068:
2061:Parotid plexus
2058:
2057:
2056:
2051:
2041:
2035:
2033:
2024:
2023:
2021:
2020:
2019:
2018:
2013:
2006:Chorda tympani
2003:
1998:
1997:
1996:
1985:
1983:
1975:
1974:
1972:
1971:
1966:
1960:
1958:
1951:
1944:
1943:
1941:
1940:
1939:
1938:
1930:
1924:
1922:
1915:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1910:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1891:
1890:
1889:
1881:
1880:
1879:
1874:
1869:
1864:
1855:
1853:
1846:
1845:
1843:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1832:
1826:
1824:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1813:
1812:
1811:
1806:
1797:
1789:
1788:
1787:
1782:
1773:
1771:
1764:
1763:
1761:
1760:
1759:
1758:
1753:
1745:
1744:
1743:
1734:
1732:
1725:
1724:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1719:
1714:
1712:olfactory bulb
1706:
1705:
1704:
1695:
1693:
1686:
1685:
1683:
1682:
1681:
1680:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1661:
1659:
1652:
1651:
1648:cranial nerves
1643:
1642:
1635:
1628:
1620:
1614:
1613:
1601:Cranial Nerves
1593:
1587:
1575:
1569:
1557:
1556:External links
1554:
1553:
1552:
1532:
1519:
1518:
1512:
1511:
1494:
1451:
1424:(3): 365–378.
1408:
1354:
1335:
1328:
1306:
1299:
1281:
1242:
1215:
1188:(2): 175–179.
1172:
1170:, p. 460.
1155:
1099:
1092:
1053:
1007:
986:(2): 252–257.
966:
920:
879:
872:
847:
817:
815:, p. 459.
791:
790:
788:
785:
784:
783:
776:
769:
767:
764:
757:
755:
744:
737:
733:
730:
729:
728:
721:
718:
689:
686:
662:electromyogram
633:Main article:
630:
627:
591:
588:
586:
583:
561:
560:Classification
558:
519:
516:
507:
504:
487:
484:
452:Main article:
449:
446:
406:foramen magnum
379:
376:
296:
295:
293:
292:
285:
278:
270:
267:
266:
264:
263:
258:
252:
249:
248:
247:
246:
240:
234:
228:
222:
216:
210:
204:
198:
192:
186:
180:
174:
165:
164:
162:Cranial nerves
154:
153:
144:
138:
137:
132:
126:
125:
120:
114:
113:
104:
98:
97:
92:
86:
85:
80:
74:
73:
69:
68:
59:
55:
54:
50:
49:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2660:
2649:
2646:
2644:
2641:
2639:
2636:
2634:
2631:
2629:
2626:
2624:
2621:
2619:
2616:
2615:
2613:
2606:
2594:
2591:
2590:
2588:
2586:
2583:
2582:
2580:
2577:
2573:
2567:
2564:
2562:
2559:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2546:
2544:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2534:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2514:
2511:
2510:
2508:
2504:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2490:
2488:
2485:
2483:
2480:
2478:
2475:
2474:
2472:
2470:
2466:
2458:
2455:
2453:
2450:
2449:
2448:Vagal trunks
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2436:
2434:
2432:
2428:
2422:
2419:
2417:
2414:
2410:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2401:
2400:
2397:
2393:
2390:
2389:
2388:
2385:
2384:
2382:
2380:
2376:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2361:
2359:
2357:
2356:jugular fossa
2352:
2344:
2341:
2339:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2328:
2327:jugular fossa
2323:
2320:
2317:
2313:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2289:
2287:
2283:
2277:
2276:Carotid sinus
2274:
2272:
2269:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2250:
2249:otic ganglion
2247:
2245:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2236:
2235:
2232:
2231:
2229:
2227:
2226:jugular fossa
2222:
2214:
2211:
2209:
2206:
2205:
2203:
2202:
2200:
2198:
2197:jugular fossa
2193:
2190:
2187:
2183:
2175:
2172:
2171:
2170:
2167:
2163:
2160:
2158:
2155:
2154:
2153:
2150:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2137:
2135:
2134:
2132:
2129:
2125:
2115:
2112:
2110:
2107:
2105:
2102:
2101:
2099:
2095:
2087:
2084:
2082:
2079:
2077:
2074:
2072:
2069:
2067:
2064:
2063:
2062:
2059:
2055:
2052:
2050:
2047:
2046:
2045:
2042:
2040:
2037:
2036:
2034:
2032:
2025:
2017:
2014:
2012:
2011:lingual nerve
2009:
2008:
2007:
2004:
2002:
1999:
1995:
1992:
1991:
1990:
1987:
1986:
1984:
1982:
1976:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1961:
1959:
1955:
1952:
1949:
1945:
1937:
1934:
1933:
1931:
1929:
1926:
1925:
1923:
1920:
1916:
1908:
1905:
1903:
1900:
1898:
1895:
1894:
1892:
1888:
1885:
1884:
1882:
1878:
1875:
1873:
1870:
1868:
1865:
1863:
1860:
1859:
1857:
1856:
1854:
1851:
1847:
1839:
1836:
1835:
1833:
1831:
1828:
1827:
1825:
1822:
1818:
1810:
1807:
1805:
1801:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1792:
1790:
1786:
1783:
1781:
1778:
1777:
1775:
1774:
1772:
1769:
1765:
1757:
1754:
1752:
1749:
1748:
1746:
1742:
1739:
1738:
1736:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1726:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1700:
1699:
1697:
1696:
1694:
1691:
1687:
1679:
1676:
1675:
1673:
1669:
1668:septal nuclei
1666:
1665:
1663:
1662:
1660:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1641:
1636:
1634:
1629:
1627:
1622:
1621:
1618:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1591:
1588:
1585:
1584:
1579:
1578:cranialnerves
1576:
1573:
1570:
1568:
1567:
1563:
1560:
1559:
1549:
1543:
1535:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1520:
1516:
1515:
1507:
1506:
1498:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1455:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1412:
1404:
1400:
1395:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1363:
1361:
1359:
1351:(2): 159–160.
1350:
1346:
1339:
1331:
1329:0-7817-4677-9
1325:
1320:
1319:
1310:
1302:
1300:1-85070-587-9
1296:
1292:
1285:
1278:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1253:
1246:
1238:
1234:
1231:(3): 177–84.
1230:
1226:
1219:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1176:
1169:
1164:
1162:
1160:
1151:
1147:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1127:
1124:(3): 377–91.
1123:
1119:
1115:
1108:
1106:
1104:
1095:
1089:
1085:
1078:
1076:
1074:
1072:
1070:
1068:
1066:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1014:
1012:
1003:
999:
994:
989:
985:
981:
977:
970:
962:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
935:
933:
931:
929:
927:
925:
916:
912:
907:
902:
899:(2): 146–50.
898:
894:
890:
883:
875:
873:0-8493-8631-4
869:
865:
858:
856:
854:
852:
835:
831:
827:
821:
814:
809:
807:
805:
803:
801:
799:
797:
792:
780:
773:
768:
761:
756:
752:
748:
741:
736:
735:
727:
724:
723:
717:
715:
710:
705:
703:
699:
695:
694:Thomas Willis
685:
683:
678:
676:
672:
667:
663:
659:
655:
649:
646:
642:
636:
626:
624:
623:poliomyelitis
620:
616:
610:
608:
603:
601:
597:
582:
580:
576:
572:
568:
557:
555:
551:
547:
544:
540:
533:
529:
524:
515:
513:
503:
500:
495:
493:
483:
481:
477:
473:
470:, called the
469:
465:
461:
455:
445:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
421:
419:
415:
411:
407:
403:
399:
395:
389:
385:
375:
373:
369:
364:
362:
358:
354:
349:
344:
342:
338:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
318:cranial nerve
315:
311:
307:
303:
291:
286:
284:
279:
277:
272:
271:
269:
268:
262:
259:
257:
254:
253:
251:
250:
245:
241:
239:
235:
233:
229:
227:
223:
221:
217:
215:
211:
209:
205:
203:
199:
197:
193:
191:
187:
185:
181:
179:
175:
173:
169:
168:
167:
166:
163:
160:
159:
149:
143:
139:
136:
133:
131:
127:
124:
121:
119:
115:
112:
108:
105:
103:
99:
96:
93:
91:
87:
84:
81:
79:
75:
70:
67:
63:
60:
56:
51:
46:
42:
38:
32:
27:
22:
19:
2605:
2536:
2029:stylomastoid
1981:facial canal
1935:
1837:
1751:optic chiasm
1677:
1609:the original
1600:
1581:
1564:
1523:
1504:
1497:
1467:(1): 14–19.
1464:
1460:
1454:
1421:
1417:
1411:
1376:
1372:
1348:
1344:
1338:
1317:
1309:
1290:
1284:
1275:
1258:(2): 78–86.
1255:
1251:
1245:
1228:
1224:
1218:
1185:
1181:
1175:
1121:
1117:
1083:
1023:
1019:
983:
979:
969:
947:(2): 78–86.
944:
940:
896:
892:
882:
863:
838:. Retrieved
829:
820:
706:
701:
691:
679:
650:
638:
611:
604:
593:
563:
536:
509:
496:
489:
457:
422:
418:vagus nerves
391:
365:
345:
334:
313:
312:, or simply
309:
305:
301:
299:
237:
111:A14.1.02.112
107:A14.2.01.184
82:
35:View of the
18:
2576:Hypoglossal
1957:Near origin
1756:optic tract
1379:(1): 1–11.
709:Jones Quain
682:torticollis
607:ipsilateral
590:Examination
512:basal plate
506:Development
464:spinal cord
430:Erb's point
398:spinal cord
368:basal plate
337:vagus nerve
244:Hypoglossal
72:Identifiers
37:human brain
2612:Categories
2169:Vestibular
2081:mandibular
2054:stylohyoid
2044:Suprahyoid
1969:Geniculate
1907:mandibular
1897:ophthalmic
1850:Trigeminal
1768:Oculomotor
1026:(1): 1–7.
787:References
671:neurolysis
645:lymph node
382:See also:
218:CN VIII –
202:Trigeminal
190:Oculomotor
58:Innervates
2643:Neurology
2589:Branches
2537:Accessory
2457:posterior
2444:Pulmonary
2130:(CN VIII)
2071:zygomatic
2049:digastric
1932:Branches
1902:maxillary
1893:Branches
1834:Branches
1821:Trochlear
1791:Branches
1690:Olfactory
1542:cite book
1446:216099695
1002:1644-3284
707:In 1848,
654:abduction
596:trapezius
554:decussate
543:trapezius
486:Variation
442:trapezius
378:Structure
372:embryonic
355:muscles,
242:CN XII –
238:Accessory
212:CN VII –
196:Trochlear
188:CN III –
178:Olfactory
45:brainstem
2578:(CN XII)
2452:anterior
2409:internal
2404:external
2343:inferior
2338:superior
2334:Ganglia
2234:Tympanic
2213:inferior
2208:superior
2204:Ganglia
2086:cervical
2066:temporal
1950:(CN VII)
1919:Abducens
1809:inferior
1795:superior
1770:(CN III)
1656:Terminal
1489:15242391
1481:24323823
1438:23271760
1403:19468892
1277:anterior
1272:18560187
1210:24202845
1202:20959982
1150:26167022
1048:25032538
1040:17370444
961:18560187
834:Archived
720:See also
518:Function
353:shoulder
256:Overview
236:CN XI –
224:CN IX –
208:Abducens
206:CN VI –
194:CN IV –
182:CN II –
172:Terminal
2593:lingual
2585:Nucleus
2561:Cranial
2545:Nuclei
2539:(CN XI)
2487:Hepatic
2469:Abdomen
2325:Before
2195:Before
2188:(CN IX)
2136:Nuclei
2031:foramen
1928:Nucleus
1921:(CN VI)
1883:Course
1858:Nuclei
1830:Nucleus
1823:(CN IV)
1776:Nuclei
1747:Course
1737:Nuclei
1731:(CN II)
1708:Course
1698:Nuclei
1674:Course
1664:Nuclei
1572:lesson6
1394:2684151
1237:7883243
1141:4481793
915:8678450
906:2502542
840:17 June
779:cadaver
688:History
546:muscles
499:medulla
478:of the
466:. This
448:Nucleus
394:neurons
370:of the
330:scapula
316:, is a
230:CN X –
200:CN V –
176:CN I –
170:CN 0 –
95:D000055
53:Details
43:of the
41:medulla
2566:Spinal
2506:Nuclei
2477:Celiac
2431:Thorax
2354:After
2318:(CN X)
2285:Nuclei
2224:After
2097:Nuclei
2076:buccal
1978:Inside
1948:Facial
1852:(CN V)
1692:(CN I)
1658:(CN 0)
1597:"11-1"
1530:
1487:
1479:
1444:
1436:
1401:
1391:
1326:
1297:
1270:
1235:
1208:
1200:
1148:
1138:
1090:
1046:
1038:
1000:
959:
913:
903:
870:
629:Injury
214:Facial
2482:Renal
2316:Vagus
1729:Optic
1517:Books
1485:S2CID
1442:S2CID
1206:S2CID
1044:S2CID
751:vagus
698:Latin
550:Latin
434:motor
314:CN XI
261:Table
232:Vagus
184:Optic
146:[
78:Latin
2379:Neck
1646:The
1548:link
1528:ISBN
1477:PMID
1434:PMID
1399:PMID
1324:ISBN
1295:ISBN
1268:PMID
1233:PMID
1198:PMID
1146:PMID
1088:ISBN
1036:PMID
998:ISSN
957:PMID
911:PMID
868:ISBN
842:2007
643:and
598:and
541:and
530:and
416:and
386:and
324:and
300:The
135:6720
123:6352
102:TA98
90:MeSH
2027:At
1877:TMN
1862:PSN
1802:of
1469:doi
1426:doi
1389:PMC
1381:doi
1260:doi
1190:doi
1136:PMC
1126:doi
1028:doi
988:doi
949:doi
901:PMC
700:as
664:or
621:or
130:FMA
118:TA2
2614::
1872:MN
1603:.
1599:.
1583:XI
1544:}}
1540:{{
1483:.
1475:.
1465:27
1463:.
1440:.
1432:.
1422:28
1420:.
1397:.
1387:.
1375:.
1371:.
1357:^
1349:50
1347:.
1274:.
1266:.
1256:38
1254:.
1229:53
1227:.
1204:.
1196:.
1186:33
1184:.
1158:^
1144:.
1134:.
1120:.
1116:.
1102:^
1056:^
1042:.
1034:.
1024:82
1022:.
1010:^
996:.
984:74
982:.
978:.
955:.
945:38
943:.
923:^
909:.
897:78
895:.
891:.
850:^
832:.
828:.
795:^
749:,
684:.
677:.
625:.
617:,
552::
363:.
343:.
308:,
64:,
1639:e
1632:t
1625:v
1586:)
1550:)
1536:.
1491:.
1471::
1448:.
1428::
1405:.
1383::
1377:1
1332:.
1303:.
1262::
1239:.
1212:.
1192::
1152:.
1128::
1122:6
1096:.
1050:.
1030::
1004:.
990::
963:.
951::
917:.
876:.
844:.
289:e
282:t
275:v
150:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.