20:
217:
494:" are used interchangeably, typically referring to the way in which the drug interacts and produces a medical effect. However, in actuality, a mode of action describes functional or anatomical changes, at the cellular level, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance. This differs from a mechanism of action since it is a more specific term that focuses on the interaction between the drug itself and an
294:
Direct biochemical methods include methods in which a protein or a small molecule, such as a drug candidate, is labeled and is traced throughout the body. This proves to be the most direct approach to find target protein that will bind to small targets of interest, such as a basic representation of a
357:
abolishes the pharmacological effect of the compound. On the other hand, transcriptomics and proteomics profiles of the compound can be used to compare with profiles of compounds with known targets. Thanks to computation inference, it is then possible to make hypotheses about the mechanism of action
312:
of the drug molecule, the profiling method of pattern recognition can be carried out where a new target is identified. This provides an insight at a possible mechanism of action since it is known what certain functional components of the drug are responsible for when interacting with a certain area
307:
Typically, computation inference methods are primarily used to predict protein targets for small molecule drugs based on computer based pattern recognition. However, this method could also be used for finding new targets for existing or newly developed drugs. By identifying the
402:
Some drug mechanisms of action are still unknown. However, even though the mechanism of action of a certain drug is unknown, the drug still functions; it is just unknown or unclear how the drug interacts with receptors and produces its therapeutic effect.
129:
By knowing the interaction between a certain site of a drug and a receptor, other drugs can be formulated in a way that replicates this interaction, thus producing the same therapeutic effects. Indeed, this method is used to create new
1087:
266:
is being inhibited. Other antibacterial agent-induced changes include ovoid cell formation, pseudomulticellular forms, localized swelling, bulge formation, blebbing, and peptidoglycan thickening. In the case of
518:. Furthermore, the term "mechanism of action" is the main term that is primarily used in pharmacology, whereas "mode of action" will more often appear in the field of microbiology or certain aspects of biology.
70:
Drugs that do not bind to receptors produce their corresponding therapeutic effect by simply interacting with chemical or physical properties in the body. Common examples of drugs that work in this way are
967:
Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Allen, B.; Antal, T.; Chatterjee, K.; Shah, P.; Moon, Y.S.; Yaqubie, A.; Kelly, N.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Chapman, P.B.; Diaz, L.A.; Vogelstein, B.; Nowak, M.A. (2013).
299:
of the drug. Due to the physical interactions between the labeled molecule and a protein, biochemical methods can be used to determine the toxicity, efficacy, and mechanism of action of the drug.
1078:
1152:
1410:
1333:
Tóth, L.; Muszbek, L.; Komaromi, I. (2013). "Mechanism of the irreversible inhibition of human cyclooxygenase-1 by aspirin as predicted by QM/MM calculations".
341:, to identify the potential targets of the compound of interest. Reverse genetics and genomics approaches, for instance, uses genetic perturbation (e.g.
2402:
67:. Receptor sites have specific affinities for drugs based on the chemical structure of the drug, as well as the specific action that occurs there.
175:
drug acts upon, it is possible to administer a cocktail that inhibits multiple targets simultaneously, thereby reducing the risk that a single
2281:
282:
A current limitation of this approach is the time required to manually generate and interpret data, but advances in automated microscopy and
1086:. New Frontiers in Neuroscience and Methods of Transdisciplinary Education Workshop, Tel Aviv University, Israel: Tel Aviv University.
619:
Grant, R.L.; Combs, A.B.; Acosta, D. (2010) "Experimental Models for the
Investigation of Toxicological Mechanisms". In McQueen, C.A.
86:
describes functional or anatomical changes, at the cellular level, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance.
1403:
1298:
Wecke, T.; Mascher, T. (2011). "Antibiotic research in the age of omics: from expression profiles to interspecies communication".
728:
Chang, C.C.; Slavin, M.A.; Chen, S.C. (2017). "New developments and directions in the clinical application of the echinocandins".
171:
in such a way that the likelihood of drug resistance emerging is reduced. By knowing what cellular structure an anti-infective or
149:
can be screened for the presence of this molecule to determine whether or not the patient will benefit from trastuzumab therapy.
1453:
191:
628:
604:
1545:
1510:
854:
391:
59:. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targets to which the drug binds, such as an
2239:
2274:
1793:
2229:
652:"Morphological and ultrastructural changes in bacterial cells as an indicator of antibacterial mechanism of action"
390:, thus reducing pain and inflammation. This mechanism of action is specific to aspirin and is not constant for all
557:
Ogrodowczyk, M.; Dettlaff, K.; Jelinska, A. (2016). "Beta-blockers: Current state of knowledge and perspectives".
2169:
1662:
199:
102:
development, the information permits anticipation of problems relating to clinical safety. Drugs disrupting the
2224:
1920:
1831:
1697:
375:
1368:
Sharma, S.; Sharma, S. C. (1997). "An update on eicosanoids and inhibitors of cyclooxygenase enzyme systems".
1113:
707:
2149:
1774:
153:
2433:
2267:
1702:
1892:
2357:
1627:
1446:
1176:
Dubovskii, P.V.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Feofanov, A.V.; Grishin, E.V.; Efremov, R.G. (2015).
255:
99:
2428:
2139:
1887:
1881:
94:
Elucidating the mechanism of action of novel drugs and medications is important for several reasons:
28:
24:
2204:
1906:
107:
1955:
1717:
1712:
1622:
1540:
499:
64:
2342:
2091:
1852:
1827:
1762:
1651:
1535:
56:
2423:
2362:
2199:
1991:
1470:
1439:
350:
2234:
2096:
2006:
1847:
1727:
1495:
1031:
737:
443:
103:
1175:
133:
It can help identify which patients are most likely to respond to treatment. Because the
23:
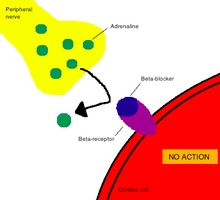
Beta blockers exert their pharmacological effect, decreased heart rate, by binding to and
8:
2377:
2291:
2144:
2032:
2001:
1647:
1530:
515:
272:
168:
1202:
1177:
1035:
741:
686:
366:
There are many drugs in which the mechanism of action is known. One example is aspirin.
19:
2114:
2064:
1965:
1778:
1757:
1657:
1578:
1490:
1272:
1239:
1215:
1054:
1019:
995:
968:
944:
917:
761:
699:
1240:"Target identification and mechanism of action in chemical biology and drug discovery"
570:
2352:
2109:
1970:
1960:
1788:
1782:
1617:
1385:
1377:
1350:
1315:
1277:
1259:
1207:
1144:
1059:
1000:
949:
898:
846:
805:
753:
691:
624:
600:
574:
1219:
765:
223:(top right) can indicate that an antibacterial agent is targeting PBP3, FtsZ or DNA.
2387:
2382:
2347:
2332:
2154:
2042:
2037:
1837:
1807:
1593:
1573:
1555:
1342:
1307:
1267:
1251:
1197:
1189:
1136:
1128:
1049:
1039:
990:
980:
939:
929:
888:
836:
795:
745:
703:
681:
671:
663:
566:
532:
503:
326:
48:
156:
because the drug's effects on the target pathway can be monitored in the patient.
2307:
2194:
2069:
1897:
1857:
1842:
1550:
1500:
1044:
893:
876:
537:
428:
413:
334:
322:
2259:
1752:
824:
16:
Biochemical interaction through which a drug produces its pharmacological effect
2372:
2337:
2184:
2164:
2083:
1925:
1667:
1612:
1346:
841:
527:
491:
433:
379:
283:
83:
1193:
749:
667:
394:(NSAIDs). Rather, aspirin is the only NSAID that irreversibly inhibits COX-1.
2417:
2397:
2322:
2312:
2189:
1676:
1583:
1381:
1263:
969:"Evolutionary dynamics of cancer in response to targeted combination therapy"
934:
825:"Escalating and de-escalating treatment in HER2-positive early breast cancer"
453:
383:
354:
309:
296:
276:
263:
251:
247:
220:
186:
It may allow other indications for the drug to be identified. Discovery that
134:
115:
160:
dosage, for example, is usually determined by measuring the patient's blood
2392:
2159:
2119:
2020:
1944:
1822:
1505:
1462:
1354:
1319:
1281:
1211:
1148:
1063:
1004:
953:
902:
850:
809:
757:
695:
578:
438:
268:
172:
36:
1389:
1326:
1255:
1111:
2327:
2244:
1731:
1707:
1311:
478:
458:
448:
423:
418:
408:
387:
243:
195:
161:
119:
1140:
985:
353:) in combination with the compound to identify genes whose knockdown or
235:
and that can give insight into the mechanism of action of the compound.
2317:
2124:
2056:
1948:
1723:
1132:
966:
800:
783:
649:
556:
507:
338:
239:
232:
187:
52:
676:
1902:
473:
463:
228:
138:
202:
treatment, since PDE-5 is expressed in pulmonary hypertensive lungs.
2024:
1996:
1983:
1672:
1018:
Tari, L.; Vo, N.; Liang, S.; Patel, J.; Baral, C.; Cai, J. (2012).
651:
468:
330:
275:
formation can be an indication that the compound is disrupting the
176:
146:
142:
111:
76:
490:
In some literature articles, the terms "mechanism of action" and "
216:
1485:
727:
511:
72:
1020:"Identifying novel drug indications through automated reasoning"
1017:
1431:
1332:
495:
342:
157:
60:
1238:
Schenone, M.; Dančík, V.; Wagner, B.K.; Clemons, P.A. (2013).
2302:
1877:
1770:
1766:
1568:
1237:
868:
346:
259:
114:
problems than those targeting components of the cell wall (
1943:
2217:
1112:
Fetz, V.; Prochnow, H.; Brönstrup, M.; Sasse, F. (2016).
816:
180:
123:
2019:
1080:
Why is it important to know the mode of action of drugs?
915:
594:
502:
and its particular form of interaction, whether through
231:
changes in target cells, changes that are observable by
2177:
909:
721:
1639:
874:
650:
Cushnie, T.P.; O’Driscoll, N.H.; Lamb, A.J. (2016).
321:
Omics based methods use omics technologies, such as
313:
on a protein, thus leading to a therapeutic effect.
1601:
358:of the compound, which can subsequently be tested.
183:
will lead to drug resistance and treatment failure.
2289:
781:
550:
2415:
302:
877:"Current status and prospects of HIV treatment"
378:involves irreversible inhibition of the enzyme
194:proteins, for example, enabled this drug to be
1070:
2275:
2082:
1447:
289:
126:, structures which are absent in human cells.
2403:Quantitative structure–activity relationship
1367:
1297:
1178:"Latarcins: versatile spider venom peptides"
777:
775:
1335:Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling
1011:
918:"Antimalarial drug resistance: An overview"
822:
211:
2282:
2268:
1454:
1440:
382:; therefore suppressing the production of
254:of target cells can be an indication that
2055:
1523:
1478:
1271:
1201:
1114:"Target identification by image analysis"
1053:
1043:
994:
984:
960:
943:
933:
892:
840:
799:
772:
685:
675:
590:
588:
397:
1409:. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
215:
110:, for example, are more likely to cause
18:
1982:
1690:
361:
295:drug outline, in order to identify the
2416:
1815:
1745:
1404:"Mechanisms and mode of dioxin action"
1370:Indian Journal of Experimental Biology
585:
316:
2263:
1435:
1416:from the original on 28 December 2016
1300:Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
1293:
1291:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1107:
1105:
623:(2nd ed.). Oxford: Elsevier. p. 204.
47:) refers to the specific biochemical
1870:
1182:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
656:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
645:
643:
641:
639:
637:
392:nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
242:, the conversion of target cells to
916:Antony, H.A.; Parija, S.C. (2016).
595:Spratto, G.R.; Woods, A.L. (2010).
559:Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry
13:
2240:Minimum bactericidal concentration
1288:
1226:
1169:
1102:
1090:from the original on 18 March 2017
250:synthesis is being inhibited, and
14:
2445:
634:
571:10.2174/1389557515666151016125948
485:
2230:Minimum inhibitory concentration
1461:
875:Cihlar, T.; Fordyce, M. (2016).
286:software may help resolve this.
206:
2170:WHO list of essential medicines
1663:Non-specific effect of vaccines
1396:
1361:
1158:from the original on 2020-06-02
857:from the original on 2019-08-05
710:from the original on 2017-10-07
200:pulmonary arterial hypertension
2225:Antimicrobial pharmacodynamics
613:
376:mechanism of action of aspirin
1:
2150:Functional analog (chemistry)
543:
303:Computation inference methods
89:
1703:Hill equation (biochemistry)
1045:10.1371/journal.pone.0040946
894:10.1016/j.coviro.2016.03.004
597:Delmar Nurse's Drug Handbook
7:
881:Current Opinion in Virology
521:
227:Bioactive compounds induce
192:phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5)
141:is known to target protein
10:
2452:
2218:Antimicrobial pharmacology
1698:Dose–response relationship
1628:Desensitization (medicine)
1347:10.1016/j.jmgm.2012.12.013
842:10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.11.002
782:No authors listed (2010).
369:
290:Direct biochemical methods
246:can be an indication that
27:a type of receptor called
25:competitively antagonising
2298:
2140:Coinduction (anesthetics)
2133:
1934:
1806:
1592:
1469:
1194:10.1007/s00018-015-2016-x
1084:(Conference presentation)
750:10.1007/s00204-016-1916-3
668:10.1007/s00018-016-2302-2
2205:Multiple drug resistance
2178:Tolerance and resistance
1546:Physiological antagonist
935:10.4103/2229-5070.175081
829:Cancer Treatment Reviews
621:Comprehensive Toxicology
212:Microscopy-based methods
108:electron transport chain
2358:Lipinski's rule of five
1956:Neuropsychopharmacology
1718:Cheng-Prussoff Equation
1713:Del Castillo Katz model
1640:Other effects of ligand
1623:Receptor (biochemistry)
1541:Irreversible antagonist
1244:Nature Chemical Biology
1121:Natural Product Reports
55:substance produces its
2092:Classical pharmacology
1853:Plasma protein binding
1828:Volume of distribution
1536:Competitive antagonist
1077:Hayardeny, L. (2014).
730:Archives of Toxicology
398:Drugs with unknown MOA
224:
179:in microbial or tumor
57:pharmacological effect
32:
2363:Lipophilic efficiency
2200:Antibiotic resistance
1992:Clinical pharmacology
1511:Physiological agonist
1471:Ligand (biochemistry)
1256:10.1038/nchembio.1199
1030:(7): Article e40946.
979:: Article ID e00747.
922:Tropical Parasitology
219:
152:It can enable better
22:
2097:Reverse pharmacology
2007:Pharmacoepidemiology
1848:Biological half-life
1728:Ligand binding assay
1602:Activity at receptor
1496:Irreversible agonist
823:Joensuu, H. (2017).
599:. Cengage Learning.
528:Mode of action (MoA)
362:Drugs with known MOA
240:antibacterial agents
169:drugs to be combined
104:cytoplasmic membrane
84:mode of action (MoA)
2434:Medicinal chemistry
2378:New chemical entity
2368:Mechanism of action
2292:medicinal chemistry
2145:Combination therapy
2033:Pharmacoinformatics
2002:Medicinal chemistry
1608:Mechanism of action
1036:2012PLoSO...740946T
986:10.7554/eLife.00747
784:"Mechanism matters"
742:2017ArTox..91.1613C
317:Omics based methods
100:anti-infective drug
41:mechanism of action
2115:Immunopharmacology
2065:Pharmacotoxicology
1966:Psychopharmacology
1758:Intrinsic activity
1658:Pleiotropy (drugs)
1579:Agonist-antagonist
1491:Endogenous agonist
1312:10.1093/jac/dkr373
1133:10.1039/c5np00113g
801:10.1038/nm0410-347
225:
33:
29:beta adrenoceptors
2411:
2410:
2353:Ligand efficiency
2257:
2256:
2253:
2252:
2213:
2212:
2110:Photopharmacology
2105:
2104:
2078:
2077:
2051:
2050:
2015:
2014:
1978:
1977:
1971:Electrophysiology
1961:Neuropharmacology
1916:
1915:
1866:
1865:
1802:
1801:
1789:Therapeutic index
1741:
1740:
1686:
1685:
1635:
1634:
1564:
1563:
1519:
1518:
1376:(10): 1025–1031.
1306:(12): 2689–2704.
1188:(23): 4501–4522.
662:(23): 4471–4492.
629:978-0-08-046884-6
606:978-1-4390-5616-5
269:anticancer agents
2441:
2429:Pharmacodynamics
2388:Pharmacokinetics
2383:Pharmacodynamics
2348:Enzyme inhibitor
2333:Drug development
2284:
2277:
2270:
2261:
2260:
2215:
2214:
2175:
2174:
2155:Polypharmacology
2080:
2079:
2053:
2052:
2043:Pharmacogenomics
2038:Pharmacogenetics
2017:
2016:
1980:
1979:
1941:
1940:
1868:
1867:
1838:Rate of infusion
1813:
1812:
1808:Pharmacokinetics
1743:
1742:
1688:
1687:
1637:
1636:
1599:
1598:
1594:Pharmacodynamics
1574:Neurotransmitter
1556:Enzyme inhibitor
1521:
1520:
1476:
1475:
1456:
1449:
1442:
1433:
1432:
1426:
1425:
1423:
1421:
1415:
1408:
1400:
1394:
1393:
1365:
1359:
1358:
1330:
1324:
1323:
1295:
1286:
1285:
1275:
1235:
1224:
1223:
1205:
1173:
1167:
1166:
1164:
1163:
1157:
1118:
1109:
1100:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1085:
1074:
1068:
1067:
1057:
1047:
1015:
1009:
1008:
998:
988:
964:
958:
957:
947:
937:
913:
907:
906:
896:
872:
866:
865:
863:
862:
844:
820:
814:
813:
803:
779:
770:
769:
736:(4): 1613–1621.
725:
719:
718:
716:
715:
689:
679:
647:
632:
617:
611:
610:
592:
583:
582:
554:
533:Pharmacodynamics
327:reverse genetics
51:through which a
2451:
2450:
2444:
2443:
2442:
2440:
2439:
2438:
2414:
2413:
2412:
2407:
2308:Bioavailability
2294:
2288:
2258:
2249:
2209:
2195:Drug resistance
2173:
2129:
2101:
2074:
2070:Neurotoxicology
2047:
2011:
1974:
1936:
1930:
1912:
1862:
1858:Bioavailability
1843:Onset of action
1798:
1737:
1682:
1631:
1588:
1560:
1551:Inverse agonist
1515:
1501:Partial agonist
1465:
1460:
1430:
1429:
1419:
1417:
1413:
1406:
1402:
1401:
1397:
1366:
1362:
1331:
1327:
1296:
1289:
1236:
1227:
1174:
1170:
1161:
1159:
1155:
1116:
1110:
1103:
1093:
1091:
1083:
1076:
1075:
1071:
1016:
1012:
965:
961:
914:
910:
873:
869:
860:
858:
821:
817:
788:Nature Medicine
780:
773:
726:
722:
713:
711:
648:
635:
618:
614:
607:
593:
586:
555:
551:
546:
538:Chemoproteomics
524:
488:
483:
429:Cyclobenzaprine
414:Antidepressants
400:
372:
364:
335:transcriptomics
323:chemoproteomics
319:
305:
292:
277:plasma membrane
214:
209:
145:, for example,
98:In the case of
92:
82:In contrast, a
17:
12:
11:
5:
2449:
2448:
2437:
2436:
2431:
2426:
2409:
2408:
2406:
2405:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2373:Mode of action
2370:
2365:
2360:
2355:
2350:
2345:
2343:Drug targeting
2340:
2338:Drug discovery
2335:
2330:
2325:
2320:
2315:
2310:
2305:
2299:
2296:
2295:
2287:
2286:
2279:
2272:
2264:
2255:
2254:
2251:
2250:
2248:
2247:
2242:
2237:
2235:Bacteriostatic
2232:
2227:
2221:
2219:
2211:
2210:
2208:
2207:
2202:
2197:
2192:
2187:
2185:Drug tolerance
2181:
2179:
2172:
2167:
2165:Lists of drugs
2162:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2135:
2131:
2130:
2128:
2127:
2122:
2117:
2112:
2106:
2103:
2102:
2100:
2099:
2094:
2088:
2086:
2084:Drug discovery
2076:
2075:
2073:
2072:
2067:
2061:
2059:
2049:
2048:
2046:
2045:
2040:
2035:
2029:
2027:
2013:
2012:
2010:
2009:
2004:
1999:
1994:
1988:
1986:
1976:
1975:
1973:
1968:
1963:
1958:
1953:
1951:
1938:
1932:
1931:
1929:
1928:
1926:Bioequivalence
1923:
1917:
1914:
1913:
1911:
1910:
1900:
1895:
1890:
1885:
1874:
1872:
1864:
1863:
1861:
1860:
1855:
1850:
1845:
1840:
1835:
1825:
1819:
1817:
1810:
1804:
1803:
1800:
1799:
1797:
1796:
1791:
1786:
1760:
1755:
1749:
1747:
1739:
1738:
1736:
1735:
1720:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1700:
1694:
1692:
1684:
1683:
1681:
1680:
1670:
1668:Adverse effect
1665:
1660:
1655:
1643:
1641:
1633:
1632:
1630:
1625:
1620:
1615:
1613:Mode of action
1610:
1605:
1603:
1596:
1590:
1589:
1587:
1586:
1581:
1576:
1571:
1565:
1562:
1561:
1559:
1558:
1553:
1548:
1543:
1538:
1533:
1527:
1525:
1517:
1516:
1514:
1513:
1508:
1503:
1498:
1493:
1488:
1482:
1480:
1473:
1467:
1466:
1459:
1458:
1451:
1444:
1436:
1428:
1427:
1395:
1360:
1325:
1287:
1250:(4): 232–240.
1225:
1168:
1127:(5): 655–667.
1101:
1069:
1010:
959:
908:
867:
815:
771:
720:
633:
612:
605:
584:
548:
547:
545:
542:
541:
540:
535:
530:
523:
520:
492:mode of action
487:
486:Mode of action
484:
482:
481:
476:
471:
466:
461:
456:
451:
446:
441:
436:
434:Demeclocycline
431:
426:
421:
416:
411:
405:
399:
396:
384:prostaglandins
380:cyclooxygenase
371:
368:
363:
360:
318:
315:
304:
301:
291:
288:
284:image analysis
213:
210:
208:
205:
204:
203:
184:
165:
150:
131:
127:
91:
88:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2447:
2446:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2427:
2425:
2422:
2421:
2419:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2398:Pharmacophore
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2354:
2351:
2349:
2346:
2344:
2341:
2339:
2336:
2334:
2331:
2329:
2326:
2324:
2323:Drug delivery
2321:
2319:
2316:
2314:
2313:Chemogenomics
2311:
2309:
2306:
2304:
2301:
2300:
2297:
2293:
2285:
2280:
2278:
2273:
2271:
2266:
2265:
2262:
2246:
2243:
2241:
2238:
2236:
2233:
2231:
2228:
2226:
2223:
2222:
2220:
2216:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2190:Tachyphylaxis
2188:
2186:
2183:
2182:
2180:
2176:
2171:
2168:
2166:
2163:
2161:
2158:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2136:
2132:
2126:
2123:
2121:
2118:
2116:
2113:
2111:
2108:
2107:
2098:
2095:
2093:
2090:
2089:
2087:
2085:
2081:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2062:
2060:
2058:
2054:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2030:
2028:
2026:
2022:
2018:
2008:
2005:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1989:
1987:
1985:
1981:
1972:
1969:
1967:
1964:
1962:
1959:
1957:
1954:
1952:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1939:
1933:
1927:
1924:
1922:
1919:
1918:
1908:
1904:
1901:
1899:
1896:
1894:
1891:
1889:
1886:
1883:
1879:
1876:
1875:
1873:
1869:
1859:
1856:
1854:
1851:
1849:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1839:
1836:
1833:
1829:
1826:
1824:
1821:
1820:
1818:
1814:
1811:
1809:
1805:
1795:
1792:
1790:
1787:
1784:
1780:
1776:
1772:
1768:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1756:
1754:
1751:
1750:
1748:
1744:
1733:
1729:
1725:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1699:
1696:
1695:
1693:
1689:
1678:
1677:Neurotoxicity
1674:
1671:
1669:
1666:
1664:
1661:
1659:
1656:
1653:
1649:
1646:Selectivity (
1645:
1644:
1642:
1638:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1619:
1616:
1614:
1611:
1609:
1606:
1604:
1600:
1597:
1595:
1591:
1585:
1584:Pharmacophore
1582:
1580:
1577:
1575:
1572:
1570:
1567:
1566:
1557:
1554:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1528:
1526:
1522:
1512:
1509:
1507:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1497:
1494:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1481:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1468:
1464:
1457:
1452:
1450:
1445:
1443:
1438:
1437:
1434:
1412:
1405:
1399:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1364:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1340:
1336:
1329:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1294:
1292:
1283:
1279:
1274:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1234:
1232:
1230:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1204:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1172:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1115:
1108:
1106:
1089:
1082:
1081:
1073:
1065:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1014:
1006:
1002:
997:
992:
987:
982:
978:
974:
970:
963:
955:
951:
946:
941:
936:
931:
927:
923:
919:
912:
904:
900:
895:
890:
886:
882:
878:
871:
856:
852:
848:
843:
838:
834:
830:
826:
819:
811:
807:
802:
797:
793:
789:
785:
778:
776:
767:
763:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
724:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
688:
683:
678:
673:
669:
665:
661:
657:
653:
646:
644:
642:
640:
638:
630:
626:
622:
616:
608:
602:
598:
591:
589:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
553:
549:
539:
536:
534:
531:
529:
526:
525:
519:
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
480:
477:
475:
472:
470:
467:
465:
462:
460:
457:
455:
454:Methocarbamol
452:
450:
447:
445:
442:
440:
437:
435:
432:
430:
427:
425:
422:
420:
417:
415:
412:
410:
407:
406:
404:
395:
393:
389:
385:
381:
377:
367:
359:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
314:
311:
310:pharmacophore
300:
298:
297:pharmacophore
287:
285:
280:
278:
274:
270:
265:
264:DNA synthesis
261:
257:
253:
252:filamentation
249:
248:peptidoglycan
245:
241:
236:
234:
230:
222:
221:Filamentation
218:
207:Determination
201:
197:
193:
189:
185:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
163:
159:
155:
151:
148:
144:
140:
136:
135:breast cancer
132:
128:
125:
121:
117:
116:peptidoglycan
113:
109:
105:
101:
97:
96:
95:
87:
85:
80:
78:
74:
68:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
30:
26:
21:
2424:Pharmacology
2393:Pharmacology
2367:
2160:Chemotherapy
2120:Cell biology
2021:Biochemistry
1945:Neuroscience
1893:Distribution
1823:Loading dose
1607:
1506:Superagonist
1463:Pharmacology
1418:. Retrieved
1398:
1373:
1369:
1363:
1338:
1334:
1328:
1303:
1299:
1247:
1243:
1185:
1181:
1171:
1160:. Retrieved
1141:10033/621283
1124:
1120:
1092:. Retrieved
1079:
1072:
1027:
1023:
1013:
976:
972:
962:
928:(1): 30–41.
925:
921:
911:
884:
880:
870:
859:. Retrieved
832:
828:
818:
791:
787:
733:
729:
723:
712:. Retrieved
659:
655:
620:
615:
596:
565:(1): 40–54.
562:
558:
552:
489:
439:Fabomotizole
401:
388:thromboxanes
373:
365:
320:
306:
293:
281:
244:spheroplasts
237:
226:
124:70S ribosome
93:
81:
69:
44:
40:
37:pharmacology
34:
2328:Drug design
2245:Bactericide
1921:Compartment
1732:Patch clamp
1708:Schild plot
479:Thalidomide
459:Paracetamol
449:Meprobamate
424:Cannabidiol
419:Armodafinil
409:Acamprosate
162:cholesterol
139:trastuzumab
137:medication
49:interaction
39:, the term
2418:Categories
2318:Drug class
2290:Topics in
2125:Physiology
2057:Toxicology
1949:psychology
1898:Metabolism
1888:Absorption
1882:Liberation
1724:Organ bath
1652:Functional
1531:Antagonist
1524:Inhibitory
1479:Excitatory
1341:: 99–109.
1162:2019-09-26
861:2017-10-07
794:(4): 347.
714:2017-10-07
677:10059/2129
544:References
516:antagonism
508:activation
504:inhibition
339:proteomics
233:microscopy
229:phenotypic
196:repurposed
188:sildenafil
173:anticancer
167:It allows
90:Importance
1907:Clearance
1903:Excretion
1722:Methods (
1382:0019-5189
1264:1552-4450
887:: 50–56.
474:Metformin
464:Phenytoin
190:inhibits
120:β-glucans
77:laxatives
2025:genetics
1997:Pharmacy
1984:Medicine
1794:Affinity
1753:Efficacy
1691:Analysis
1673:Toxicity
1411:Archived
1355:23384979
1320:21930574
1282:23508189
1220:14177431
1212:26286896
1203:11113828
1153:Archived
1149:26777141
1094:18 March
1088:Archived
1064:22911721
1024:PLOS ONE
1005:23805382
954:26998432
903:27023283
855:Archived
851:27866067
835:: 1–11.
810:20376007
766:31029386
758:28180946
708:Archived
696:27392605
687:11108400
579:26471965
522:See also
500:receptor
469:PRL-8-53
355:knockout
331:genomics
177:mutation
112:toxicity
73:antacids
65:receptor
1935:Related
1878:(L)ADME
1832:Initial
1816:Metrics
1763:Potency
1746:Metrics
1648:Binding
1618:Binding
1486:Agonist
1420:11 June
1390:9475035
1273:5543995
1055:3402456
1032:Bibcode
996:3691570
945:4778180
738:Bibcode
704:2065821
512:agonism
444:Lithium
370:Aspirin
164:levels.
1937:fields
1388:
1380:
1353:
1318:
1280:
1270:
1262:
1218:
1210:
1200:
1147:
1062:
1052:
1003:
993:
952:
942:
901:
849:
808:
764:
756:
702:
694:
684:
627:
603:
577:
496:enzyme
343:CRISPR
337:, and
158:Statin
154:dosing
147:tumors
130:drugs.
61:enzyme
2134:Other
1871:LADME
1414:(PDF)
1407:(PDF)
1216:S2CID
1156:(PDF)
1117:(PDF)
973:eLife
762:S2CID
700:S2CID
514:, or
351:siRNA
262:, or
238:With
122:) or
2303:ADME
2023:and
1947:and
1783:TD50
1779:LD50
1775:ED50
1771:IC50
1767:EC50
1569:Drug
1422:2012
1386:PMID
1378:ISSN
1351:PMID
1316:PMID
1278:PMID
1260:ISSN
1208:PMID
1145:PMID
1096:2017
1060:PMID
1001:PMID
950:PMID
899:PMID
847:PMID
806:PMID
754:PMID
692:PMID
625:ISBN
601:ISBN
575:PMID
386:and
374:The
347:Cas9
329:and
273:bleb
260:FtsZ
198:for
143:HER2
75:and
53:drug
1880:: (
1343:doi
1308:doi
1268:PMC
1252:doi
1198:PMC
1190:doi
1137:hdl
1129:doi
1050:PMC
1040:doi
991:PMC
981:doi
940:PMC
930:doi
889:doi
837:doi
796:doi
746:doi
682:PMC
672:hdl
664:doi
567:doi
498:or
349:or
258:3,
256:PBP
181:DNA
118:or
106:or
63:or
45:MOA
35:In
2420::
1781:,
1777:,
1773:,
1769:,
1730:,
1726:,
1650:,
1384:.
1374:35
1372:.
1349:.
1339:40
1337:.
1314:.
1304:66
1302:.
1290:^
1276:.
1266:.
1258:.
1246:.
1242:.
1228:^
1214:.
1206:.
1196:.
1186:72
1184:.
1180:.
1151:.
1143:.
1135:.
1125:33
1123:.
1119:.
1104:^
1058:.
1048:.
1038:.
1026:.
1022:.
999:.
989:.
975:.
971:.
948:.
938:.
924:.
920:.
897:.
885:18
883:.
879:.
853:.
845:.
833:52
831:.
827:.
804:.
792:16
790:.
786:.
774:^
760:.
752:.
744:.
734:91
732:.
706:.
698:.
690:.
680:.
670:.
660:73
658:.
654:.
636:^
587:^
573:.
563:16
561:.
510:,
506:,
333:,
325:,
279:.
271:,
79:.
2283:e
2276:t
2269:v
1909:)
1905:(
1884:)
1834:)
1830:(
1785:)
1765:(
1734:)
1679:)
1675:(
1654:)
1455:e
1448:t
1441:v
1424:.
1392:.
1357:.
1345::
1322:.
1310::
1284:.
1254::
1248:9
1222:.
1192::
1165:.
1139::
1131::
1098:.
1066:.
1042::
1034::
1028:7
1007:.
983::
977:2
956:.
932::
926:6
905:.
891::
864:.
839::
812:.
798::
768:.
748::
740::
717:.
674::
666::
631:.
609:.
581:.
569::
345:-
43:(
31:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.