142:
1332:, which expanded over an area much larger than that of any previous culture and Vietnamese archaeologists believe that it had multiple regional sources. For instance, while Đông Sơn bronzes are much the same in different regions of northern Viet Nam, the regional characters of the pottery are fairly marked. On the whole, Đông Sơn pottery has a high firing temperature and is varied in form, but decorative patterns are much reduced in comparison with preceding periods, and consist mainly of impressions from cord-wrapped or carved paddles. Incised decoration is virtually absent.
1894:'s shores are the present borders. From Zhouwu to the south there were the Wenlang people. They dwell in the wilderness, not houses, use large trees as their resting places, eat raw meat and fish, their profession is fragrance-gathering and they trade with other peoples at the markets. Like how people lived during the time of the Sovereigns. To the south of the prefecture there is the Wenlang rapid; its lower reach is a narrow flow."
1257:. The tidal irrigation of rice fields through an elaborate system of canals and dikes started by the sixth century BC. This type of sophisticated farming system would come to define Vietnamese society. It required tight-knit village communities to collectively manage their irrigation systems. These systems in turn produced crop yields that could sustain much higher population densities than competing methods of food production.
700:
43:
156:
741:
and Mã rivers. The
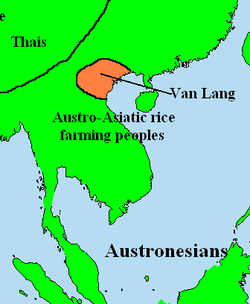
Vietnamese tribes were the primary tribes at this time. Their territory included modern meridional territories of China to the banks of the Hồng River in the northern territory of Vietnam. Centuries of developing a civilization and economy based on the cultivation of irrigated rice
1300:
cultures of southern
Vietnam. This period saw the appearance of wheel-made pottery, although the use of the paddle and anvil remained significant in manufacture. Vessel surfaces are usually smooth, often polished, and red slipping is common. Cord-marking is present in all cultures and forms a fairly
725:
reportedly dating back around half a million years ago. The prehistoric people had lived continuously in local caves since around 6000 BC, until more advanced material cultures developed. Some caves are known to have been the home of many generations of early humans. As northern
Vietnam was a
1245:
fashion with the aid of the Lạc Tướng, who controlled the communal settlements around each irrigated area, organized construction and maintenance of the dikes, and regulated the supply of water. Besides cultivating rice, the people of Văn Lang grew other grains and beans and raised stock, mainly
1283:
By about 1200 BC, the development of wet-rice cultivation and bronze casting in the Mã River and Red River plains led to the development of the Đông Sơn culture, notable for its elaborate bronze drums. The bronze weapons, tools, and drums of Đông Sơn sites show a
Southeast Asian influence that
1272:
1657:
p. 4 quote: "while the remaining sons followed their father to the sea in the South, except for the eldest who was assigned to succeed his father as the next King Hùng. King Hùng named his country Văn Lang with Phong Châu (Bạch Hạc district, Phú Thọ
1736:– 2001 Page 1 "At that time the civilization of northern Vietnam was known as Van Lang (van means beautiful, and lang means kind and healing, like a good doctor). The ruling house of Van Lang was called Hong Bang, which means a kind of huge bird."
1827:"峯州承化下... 古夜(!)郎國之地按今新昌縣界有夜(!)郎溪" translation: "Feng province, lower Shenghua... Territory of the ancient Ye(!)lang nation. Next to the border of the current Xinchang prefecture, there is the Ye(!)lang brook." Note: not to be confused with the
1301:
high percentage of sherdage. Complex incised decoration also developed with rich ornamental designs, and it is on the basis of incised decoration that
Vietnamese archaeologists distinguish the different cultures and phases one from another.
1288:. Some of the similarities between the Đông Sơn sites and other Southeast Asian sites include the presence of boat-shaped coffins and burial jars, stilt dwellings, and evidence of the customs of betel-nut-chewing and teeth-blackening.
830:
in
Vietnam's history. He is regarded as the ancestor of the Hùng kings, as the founding father of Vietnam, and as a Vietnamese cultural hero who is credited with teaching his people how to cultivate rice.
1810:" 《方輿志》曰:峰州,承化郡。古文郎國,有文郎水。亦陸梁地。" Translation: "'Geographical Almanacs' said: Feng province, Shenghua district. It was the ancient Wenlang nation; there was the Wenlang river; also a wanderers' land...
1296:
The period between the end of the third millennium and the middle of the first millennium BC produced increasingly sophisticated pottery of the pre-Dong Son cultures of northern Viet Nam and the pre-
1018:), the country was divided into 15 regions as in the table below. However, they're in fact taken from Sino-Vietnamese names of later commanderies established by the Chinese in northern Vietnam.
791:) appointed Đế Nghi as his successor, to govern the northern region, and conferred the title of Kinh Dương Vương upon him , to govern the southern region, known as the country of Xích Quỷ.
2606:
2576:
1324:, Vietnamese archaeologists also recognize three pre-Dong Son periods of cultural development: Con Chan Tien, Dong Khoi (Bai Man) and Quy Chu. In the areas stretching from the Red to the
1959:
1316:. The pottery of these three cultures, despite the use of different decorative styles, has features that suggest a continuity of cultural development in the Red River Valley. In the
754:. He consolidated the other tribes and succeeded in grouping all the vassal states (or autonomous communities) within his territory into a unified nation. Lộc Tục proclaimed himself
2444:
869:
The Hồng Bàng epoch finally ended in the middle of the third century BC on the advent of the military leader Thục Phán's conquest of Văn Lang, dethroning the last Hùng king.
1246:
buffaloes, chickens, and pigs. Pottery-making and bamboo-working were highly developed crafts, as were basketry, leather-working, and the weaving of hemp, jute, and silk.
1304:
The pottery from the successive cultural developments in the Red River Valley is the most well known. Vietnamese archaeologists here discern three pre-Đông Son cultures:
1360:. The dating of events is still a subject of research. The date ranges are conservative date estimates for the known periods: The lines of kings are in the order of the
1234:, and also included handicrafts, hunting and gathering, husbandry and fishing. Especially, the skill of bronze casting was at a high level. The most famous relics are
298:
1940:
1629:
1792:"峰州(今理嘉寧縣。)古文朗國,有文朗水。亦陸梁地。" translation: "Feng province (now Jianing prefecture) the ancient Wenlang nation; there was the Wenlang river; also a wanderers' land."
2591:
1058:
1048:
750:
Legend describes a significant political event occurred when Lộc Tục came into power in 2879 BC. Lộc Tục was recorded as a descendant of the mythical ruler
1890:
quote: "《林邑記》曰:渡比景至朱吾。朱吾縣浦,今之封界,朱吾以南,有文狼人,野居無室宅,依樹止宿,食生魚肉,採香為業,與人交市,若上皇之民矣。縣南有文狼究,下流逕通。" translation: "'Records of Linyi' said: Crossing Bijing to Zhouwu.
1861:
to the south there are the wild people of
Wenlang. They don't dwell in houses, use large trees as their resting places, eat raw meat; their profession is
1820:
1989:
1698:
859:
by carving on stones dates back to 2200–2000 BC. Parallel lines were carved on the stone tools as a counting instrument involving the lunar calendar.
89:
141:
2596:
1850:
1807:
1535:
1493:
1428:
2354:: 21–62, ed. W. G. Solheim II. Honolulu: Asian and Pacific Archaeology Series No. 2, Social Science Research Institute, University of Hawaii.
1956:
1624:
784:Đế Minh mới lập Đế Nghi là con nối ngôi, cai quản phương Bắc, phong cho vua làm Kinh Dương Vương, cai quản phương Nam, gọi là nước Xích Quỷ.
759:
369:
1541:
2527:
2448:
2389:
The
Cultural Dimensions of the Vietnamese Private Entrepreneurship, The IUP J. Entrepreneurship Development, Vol. VI, No. 3&4, 2009
491:
2586:
1904:
1249:
From 2000 BC, people in modern-day North
Vietnam developed a sophisticated agricultural society, probably through learning from the
505:
2601:
524:
679:
The earliest historical mentions of Văn Lang, however, just had been recorded in
Chinese-language documents, dated back to the
2302:. Hà Nội: Ban tư tưởng – văn hóa trung ương, Trung tâm thông tin công tác tư tưởng, 2005. 495 p. : col. ill.; 21 cm.
2020:
1340:
Contemporary Vietnamese historians have established the existence of various ethnic minorities now living in the highlands of
951:; usually the lạc tướng was a member of the Hùng kings' family. Bộ comprised the agricultural hamlets and villages based on a
2269:
2074:
397:
was the absolute monarch of the country and, at least in theory, wielded complete control of the land and its resources. The
1937:
1284:
indicates an indigenous origin for the bronze-casting technology. Many small, ancient copper mine sites have been found in
210:
2463:
2260:
Kelley, Liam C. (2016), "Inventing Traditions in Fifteenth-century Vietnam", in Mair, Victor H.; Kelley, Liam C. (eds.),
460:" assigned to this dynasty in early Vietnamese-written histories in Chinese; its meaning is supposedly a mythical giant (
1866:
931:
The first Hùng King established the first "Vietnamese" state in response to the needs of co-operation in constructing
2428:
2407:
2084:
2057:
2030:
795:
The name Xích Quỷ 赤鬼 is derived from Sino-Vietnamese xích 赤 "red" and quỷ 鬼 "demon". The meaning of the name is from
781:Đế Minh ư thị lập Đế Nghi vi tự, trị Bắc phương, phong vương vi Kinh Dương Vương, trị Nam phương, hiệu Xích Quỷ quốc.
2566:
839:
Starting from the third Hùng dynasty since 2524 BC, the kingdom was renamed Văn Lang, and the capital was set up at
31:
2476:
1604:
1883:
1571:
899:
tribes to overthrow the last Hùng king in approximately 258 BC. After conquering Văn Lang, Thục Phán united the
733:, the inhabitant populations grew and spread to every part of Vietnam. Most ancient people were living near the
691:). However, Chinese records also indicated that another people, who lived elsewhere, were also called Văn Lang.
2399:
155:
1440:
1309:
800:
585:
1235:
2502:
1997:
1706:
669:
983:
Semi-historical source described Văn Lang's northern border stretched to the southern part of present-day
1132:
17:
1891:
1380:
1188:
863:
816:
804:
755:
378:
349:
229:
1726:
1184:
878:
242:
1410:
1305:
1086:
450:
2571:
908:
886:
361:
68:
1576:
1517:
1329:
1266:
1238:
on which are depicted houses, clothing, customs, habits, and cultural activities of the Hùng era.
1150:
1110:
855:
begins from the foot of the mountains. The evidence that the Vietnamese knew how to calculate the
815:(a common motif of Vietnamese place names). Red 赤 is associated with Vermilion Bird of the South (
2420:
1121:
528:
1076:
1072:
1038:
848:
406:
393:), a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Vietnamese rulers of this period. The
1146:
1007:
726:
place with mountains, forests, and rivers, the number of tribes grew between 5000 and 3000 BC.
536:
532:
85:
2047:
1566:
2345:
The Archaeology of Central Philippines: A Study Chiefly of the Iron Age and its Relationships
1198:
1100:
1090:
796:
1321:
1208:
1164:
1154:
722:
2477:"Rediscovering the people's ethnic origins and ancestral lands during the Hùng kings' time"
1297:
1174:
1887:
1789:
1637:
826:
Lộc Tục inaugurated the earliest monarchical regime as well as the first ruling family by
8:
2144:
2132:(in Vietnamese). Ho Chi Minh City: Ho Chi Minh City General Publishing House. p. 18.
1911:
808:
712:
386:
333:
1619:
414:
2357:
1970a. Prehistoric archaeology in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia and the Philippines.
912:
94:
2424:
2403:
2265:
2080:
2053:
2026:
1858:
1824:
1487:
1313:
2516:
2232:
Bayard, D. T. 1977. Phu Wiang pottery and the prehistory of Northeastern Thailand.
2162:
1758:
Shorto, H. A Mon-Khmer Comparative Dictionary, Ed. Paul Sidwell, 2006. #692. p. 217
1341:
1285:
1000:
900:
734:
569:
550:
410:
892:
2581:
1963:
1944:
1345:
936:
852:
545:
430:
257:
844:
2347:. Manila: Monograph of the National Institute of Science and Technology No. 10.
1446:
1365:
977:
856:
812:
646:
618:
2467:
896:
820:
763:
688:
2560:
2542:
2529:
1845:
1802:
1398:
1386:
1250:
1068:
606:
472:
422:
58:
2305:
Peacock, B. A. V. 1959. A short description of Malayan prehistoric pottery.
1142:
935:
and in struggles against their enemies. This was a very primitive form of a
904:
840:
684:
465:
402:
291:
184:
2326:
Sieveking, G. de G. 1954. Excavations at Gua Cha, Kelantan, 1954 (Part 1).
1731:
1499:
1416:
1392:
1356:
The history of the Hồng Bàng period is split according to the rule of each
1325:
988:
966:
738:
680:
630:
599:
78:
1464:
1452:
1357:
827:
394:
382:
1505:
1458:
1276:
788:
718:
486:
2484:
1529:
2466:[New Light on a Forgotten Past] (in Vietnamese). Archived from
2447:[Đông Sơn ancient bronze tools] (in Vietnamese). Archived from
2336:
1959. Further notes on the Kalanay pottery complex in the Philippines.
1878:
1228:
952:
932:
882:
261:
2396:
The Colonial Bastille: A History of Imprisonment in Vietnam, 1862–1940
1747:
42nd International Conference on SinoTibetan Languages and Linguistics
742:
encouraged the development of tribal states and communal settlements.
638:
635:
595:
592:
577:
574:
479:
476:
461:
457:
454:
2284:
Lévy, P. 1943. Recherches préhistoriques dans la région de Mlu Prei.
1865:-gathering and they trade with other peoples, like people during the
1862:
1523:
996:
730:
2255:
The Dongson Culture and Cultural Centers in the Metal Age in Vietnam
947:. The country was composed of fifteen bộ "regions", each ruled by a
1784:
1317:
916:
751:
565:
265:
699:
2506:
1832:
1609:
Bảo Tàng Lịch Sử Quốc Gia (Vietnamese National Museum of History)
1422:
1271:
1231:
992:
965:
claimed that Hùng kings had named princesses as "mỵ nương" (From
418:
345:
316:
2364:
1970b. Northern Thailand, Southeast Asia, and world prehistory.
553:
people living in Vietnam and Laos; Ferlus suggests that Vietic *
1854:
1828:
1779:
1242:
434:
2241:
Cult, Culture, and Authority: Princess Liẽu Hạnh in Vietnamese
1328:
valleys, all the local cultures eventually developed into the
866:, which Văn Lang came out victorious thanks to general Gióng.
2319:
Phan Huy Lê, Trần Quốc Vượng, Hà Văn Tấn, Lương Ninh (1991),
2291:
Mourer, R. 1977. Laang Spean and the prehistory of Cambodia.
1361:
1003:. Such claims haven't been proved by archeological research.
984:
940:
920:
862:
According to Vietnamese legend, at one point, Văn Lang had a
426:
320:
1853:"《林邑記》曰:蒼梧以南有文郎野人,居無室宅,依樹止宿,食生肉,采香為業,與人交易,若上皇之人。'Records of
27:
Legendary, semi-mythical period in Vietnamese historiography
2607:
States and territories disestablished in the 3rd century BC
2577:
States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC
2183:
Phan Huy Lê, Trần Quốc Vượng, Hà Văn Tấn, Lương Ninh, p. 99
1745:
Michel Ferlus. "Formation of Ethnonyms in Southeast Asia".
1254:
348:
historiography, spanning from the beginning of the rule of
2264:, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, pp. 161–193,
2350:
1968. The Batungan Cave sites, Masbate, Philippines, in
2314:
Postcolonial Vietnam: New Histories of the National Past
903:
tribes with the Âu Việt tribes to form a new kingdom of
413:) and alleged that Văn Lang was bordered to the west by
717:
The area now known as Vietnam has been inhabited since
770:
2417:
Việt Nam: a history from earliest time to the present
2109:
1990:"Complete Book of the Historical Records of Đại Việt"
1761:
2161:
eHistory, Ohio State University. Guilmartin, John. "
1603:"Hùng kings' Jade Genealogies". Phan Duy Kha (2012)
621:; the kingdom's name is phonetically connected with
1957:
6,000-year-old tombs unearthed in northeast Vietnam
1821:
Yuanhe Maps and Records of Prefectures and Counties
2352:Anthropology at the Eight Pacific Science Congress
1933:
1931:
758:and called his newly born nation Xích Quỷ. In the
2046:Ray, Nick; et al. (2010), "Co Loa Citadel",
1597:Not in official histories, but in the unofficial
1348:during the early phase of the Hồng Bàng dynasty.
84:for phonetic transcriptions, with an appropriate
2558:
2145:"History of Vietnam from the Stone Age to today"
1950:
1598:
360:) in 2879 BC until the conquest of the state by
30:"Hồng Bàng" redirects here. For other uses, see
2079:. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 13, 14.
2022:Rice and Baguette: A History of Food in Vietnam
1928:
1905:"Mission Atlas Project – VIETNAM – Basic Facts"
1749:, Nov 2009, Chiang Mai, Thailand. 2009. pp. 4-5
2592:1st-millennium BC disestablishments in Vietnam
2216:
2214:
2212:
2210:
2127:
2106:Khâm định Việt sử thông giám cương mục, Vol. 1
2076:A History of Vietnam: From Hong Bang to Tu Duc
1670:
1630:Records about the Hồng Bàng clan - Hung Kings
1605:"'Decoding' the Hung Kings' Jade Genealogies"
2200:
2198:
851:) at the juncture of three rivers where the
527:ethnonyms across three linguistic families,
401:also recorded that the nation's capital was
2207:
987:, and the southern border stretched to the
980:word for Muong noble throughout the time).
2262:Imperial China and its southern neighbours
1849:"Provinces, Districts, and Divisions 18",
1806:"Provinces, Districts, and Divisions 18",
939:with the Hùng king on top and under him a
799:, where 鬼 quỷ refers to the constellation
154:
2464:"Ánh sáng mới trên một quá khứ lãng quên"
2204:Vuong Quan Hoang and Tran Tri Dung, p. 64
2195:
2163:America and Vietnam: The Fifteen Year War
1974:
1972:
1593:
1591:
721:times, with some archaeological sites in
683:(7th- to 9th-century), about the area of
668:There also exists a phonetically similar
2375:On the struggle for democracy in Vietnam
2253:Hoang Xuan Chinh and Bui Van Tien 1980.
2039:
2012:
1897:
1734:: First Zen Teacher in Vietnam and China
1667:Dror, p. 33 & 254 "Hồng Bàng period"
1270:
729:During a few thousand years in the Late
698:
2414:
2072:
2066:
1987:
1767:
1655:A brief chronology of Vietnam's history
1227:The economy was based predominantly on
972:, which means princess), and prince as
14:
2597:Former countries in Vietnamese history
2559:
2382:Oxford Encyclopedia of the Vietnam War
2259:
2115:
2102:
2100:
2098:
2096:
1969:
1687:Oxford Encyclopedia of the Vietnam War
1588:
1217:
762:(Vietnamese: Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư,
367:The 15th-century Vietnamese chronicle
2474:
2177:
1642:established his capital in Phong Châu
1383:(支乾) (Hùng Dynasty I, 2879 – 2794 BC)
377:) claimed that the period began with
2387:Vuong Quan Hoang and Tran Tri Dung.
2142:
1653:Anh Thư Hà, Hò̂ng Đức Trà̂n (2000).
1481:
1371:
625:, yet nothing further is conclusive.
344:, was a legendary ancient period in
36:
2093:
2045:
1449:(支兌) (Dynasty VIII, 1431 - 1332 BC)
911:and built his capital and citadel,
834:
745:
24:
2165:." 1991. New York: Military Press.
2018:
1544:(支癸) (Dynasty XVIII, 408 – 258 BC)
1431:(支坤) (Dynasty VII, 1631 – 1432 BC)
1413:(approximately 2000–1500 BC)
1395:(支艮) (Dynasty III, 2524 – 2253 BC)
1241:The Hùng Vươngs ruled Văn Lang in
1211:from Day River to Mount Tara Diep
955:clan relationship and headed by a
74:for transliterated languages, and
54:of its non-English content, using
25:
2618:
2437:
1538:(支壬) (Dynasty XVII, 568 – 409 BC)
1502:(支戊) (Dynasty XIII, 968 – 854 BC)
1496:(支丁) (Dynasty XII, 1054 – 969 BC)
1467:(支丙) (Dynasty XI, 1161 – 1055 BC)
1455:(支甲) (Dynasty IX, 1331 – 1252 BC)
1425:(支離) (Dynasty VI, 1712 – 1632 BC)
1401:(支震) (Dynasty IV, 2252 - 1913 BC)
1389:(支坎) (Dynasty II, 2793 – 2525 BC)
991:delta, including parts of modern
872:
634:(1342); in Chinese transcription
440:
2587:3rd-century BC disestablishments
2279:Vietnam, Now: A Reporter Returns
2143:Carr, Karen (October 15, 2017).
1532:(支辛) (Dynasty XVI, 660 – 569 BC)
1508:(支己) (Dynasty XIV, 853 – 755 BC)
1461:(支乙) (Dynasty X, 1251 – 1162 BC)
1419:(支巽) (Dynasty V, 1912 – 1713 BC)
864:war against Shang-China invasion
296:
140:
41:
2483:(in Vietnamese). Archived from
2186:
2168:
2155:
2136:
2121:
1981:
1884:Commentary on the Water Classic
1872:
1838:
1813:
1795:
1773:
1752:
1644:, (now in Bạch Hạc prefecture)"
1526:(支庚) (Dynasty XV, 754 – 661 BC)
1335:
1260:
959:, usually a male tribal elder.
926:
787:Đế Minh (Great-grandson of the
706:
2602:29th-century BC establishments
2400:University of California Press
2052:, Lonely Planet, p. 123,
1739:
1720:
1691:
1679:
1661:
1647:
1613:
1222:
963:The Tale of the Hồng Bàng Clan
557:is the "iambic late form" of *
375:Đại Việt, The Complete History
90:multilingual support templates
13:
1:
2475:Vương, Liêm (27 March 2011).
1582:
1443:(approximately 1500–1100 BC)
1351:
811:: sao Quỷ) which lies in the
609:in the 8th century, known as
451:Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation
2300:Sổ tay báo cáo viên năm 2005
1640:'s son (taboo name unknown)
1490:(approximately 1100–800 BC)
1377:Early period (2879–2000 BC)
943:consisted of advisors – the
7:
2246:Heekeren, H. R. van. 1972.
1560:
1520:(approximately 800–258 BC)
1035:Phong Châu (King's capital)
891:Văn Lang ended 258 BC when
760:Complete Annals of Đại Việt
10:
2623:
2321:Lịch sử Việt Nam, volume 1
2248:The Stone Age of Indonesia
2226:
1938:Ancient calendar unearthed
1699:"ĐVSKTT NK 1 - Viet Texts"
1291:
1264:
1016:A Brief History of Vietnam
876:
772:帝明於是立帝宜爲嗣、治北方、封王爲涇陽王、治南方、號
771:
710:
694:
123:(legendarily 2879–2524 BC)
32:Hồng Bàng (disambiguation)
29:
2513:
2500:
2494:
1636:〈今白鶴縣是也〉。" translation: "
573:
564:A kingdom north of today-
523:"human being, person" of
312:
271:
253:
249:
236:
223:
219:
209:
201:
193:
170:
162:
153:
137:
131:(legendarily 2524–258 BC)
116:
2220:Ngô Văn Thạo, p. 823-824
1851:Section: Lingnan Circuit
1808:Section: Lingnan Circuit
907:. He proclaimed himself
766:: 大越史記全書), states that,
2421:Oxford University Press
2394:Zinoman, Peter (2001).
2128:Trần Trọng Kim (2005).
2073:Chapuis, Oscar (1995).
1966:. Retrieved 2014-01-19.
1947:. Retrieved 2014-01-05.
1625:Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư
605:A kingdom subjected by
399:Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư
370:Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư
2543:21.28167°N 105.44194°E
2281:. PublicAffairs, 2008.
2019:Vu, Hong Lien (2016).
1599:
1280:
793:
703:
664:"human being, person".
517:) in the word-family *
429:), to the east by the
390:
337:
197:Animism, folk religion
2445:"Đồ đồng cổ Đông Sơn"
2415:Kiernan, Ben (2019).
2373:Tăng Dực Đào (1994).
2298:Ngô Văn Thạo (2005).
2250:. The Hague: Nijhoff.
1632:" quote: "貉龍君之子也〈缺諱〉。
1275:Image on the Ngoc Lu
1274:
1265:Further information:
1236:Đông Sơn Bronze Drums
1120:Quảng Yên (a part of
1030:Present-day location
797:Twenty-Eight Mansions
768:
702:
613:in Pre-Angkorian and
2312:Pelley, Patricia M.
1087:Thái Nguyên Province
1077:Tuyên Quang Province
1022:Regions of Văn Lang
915:, in the modern-day
628:The ethnonym မြန်မာ
433:and to the south by
352:over the kingdom of
225:• 2879–2794 BC
188:(2524 – 258 BC)
147:Đông Sơn bronze drum
52:specify the language
50:This article should
2548:21.28167; 105.44194
2539: /
2384:(hardback edition).
2380:Tucker, Spencer C.
2239:Dror, Olga (2007).
1600:Ngọc phả Hùng Vương
1567:Văn Lang University
1411:Phùng Nguyên Period
1218:Culture and economy
1185:Quảng Bình Province
1122:Quảng Ninh Province
1023:
713:Prehistoric Vietnam
421:), to the north by
340:), also called the
176:(2879 BC – 2524 BC)
2481:www.newvietart.com
2333:Solheim II, W. G.
2192:Tăng Dực Đào, p. 7
2174:Hoang and Bui 1980
2025:. Reaktion Books.
2000:on 15 October 2020
1962:2014-02-11 at the
1943:2014-01-03 at the
1322:Thanh Hóa Province
1281:
1189:Quảng Trị Province
1165:Thanh Hóa Province
1155:Ninh Bình Province
1133:Hải Dương Province
1021:
723:Thanh Hóa Province
704:
356:(initially called
238:• 408–258 BC
2567:Hồng Bàng dynasty
2523:
2522:
2514:Succeeded by
2511:c. 2879 – 258 BC
2271:978-9-81462-055-0
1892:Zhouwu prefecture
1859:Cangwu Commandery
1831:Kingdom in today
1557:
1556:
1478:
1477:
1215:
1214:
1181:Việt Thường (越 裳)
1151:Nam Định Province
1147:Hưng Yên Province
1111:Lạng Sơn Province
1101:Bắc Ninh Province
1091:Cao Bằng Province
933:hydraulic systems
917:Dong Anh district
539:, together with:
342:Hồng Bàng dynasty
338:thời kỳ Hồng Bàng
326:
325:
308:
307:
304:
303:
189:
182:
177:
126:State of Văn Lang
118:State of Xích Quỷ
112:
111:
92:may also be used.
16:(Redirected from
2614:
2554:
2553:
2551:
2550:
2549:
2544:
2540:
2537:
2536:
2535:
2532:
2495:Preceded by
2492:
2491:
2488:
2487:on 1 April 2011.
2471:
2459:
2457:
2456:
2434:
2330:I and II:75–138.
2274:
2221:
2218:
2205:
2202:
2193:
2190:
2184:
2181:
2175:
2172:
2166:
2159:
2153:
2152:
2140:
2134:
2133:
2130:Việt Nam sử lược
2125:
2119:
2113:
2107:
2104:
2091:
2090:
2070:
2064:
2062:
2043:
2037:
2036:
2016:
2010:
2009:
2007:
2005:
1996:. Archived from
1985:
1979:
1976:
1967:
1954:
1948:
1935:
1926:
1925:
1923:
1922:
1916:
1910:. Archived from
1909:
1901:
1895:
1876:
1870:
1842:
1836:
1817:
1811:
1799:
1793:
1777:
1771:
1765:
1759:
1756:
1750:
1743:
1737:
1724:
1718:
1717:
1715:
1714:
1705:. Archived from
1703:sites.google.com
1695:
1689:
1683:
1677:
1674:
1668:
1665:
1659:
1651:
1645:
1617:
1611:
1602:
1595:
1577:Đông Sơn culture
1572:Việt Nam sử lược
1482:
1372:
1330:Đông Sơn culture
1286:northern Vietnam
1267:Đông Sơn culture
1199:Hà Tĩnh Province
1175:Nghệ An Province
1129:Dương Tuyên (陽泉)
1073:Phú Thọ Province
1059:Sơn Tây Province
1049:Sơn Tây Province
1039:Phú Thọ Province
1024:
1020:
1012:Việt Nam sử lược
1001:Northern Vietnam
835:Văn Lang Kingdom
778:
777:
775:
756:Kinh Dương Vương
746:Xích Quỷ Kingdom
580:
475:(2009) includes
471:French linguist
411:northern Vietnam
407:Phú Thọ Province
405:(in present-day
379:Kinh Dương Vương
350:Kinh Dương Vương
330:Hồng Bàng period
300:
299:
288:
287:
273:
272:
243:Hùng Vương XVIII
187:
180:
175:
158:
144:
132:
124:
114:
113:
107:
104:
98:
83:
77:
73:
67:
63:
57:
45:
44:
37:
21:
2622:
2621:
2617:
2616:
2615:
2613:
2612:
2611:
2572:Ancient Vietnam
2557:
2556:
2547:
2545:
2541:
2538:
2533:
2530:
2528:
2526:
2525:
2519:
2510:
2498:
2462:
2454:
2452:
2443:
2440:
2431:
2340:3 (2): 157–166.
2309:3 (2): 121–156.
2272:
2229:
2224:
2219:
2208:
2203:
2196:
2191:
2187:
2182:
2178:
2173:
2169:
2160:
2156:
2141:
2137:
2126:
2122:
2114:
2110:
2105:
2094:
2087:
2071:
2067:
2060:
2044:
2040:
2033:
2017:
2013:
2003:
2001:
1986:
1982:
1977:
1970:
1964:Wayback Machine
1955:
1951:
1945:Wayback Machine
1936:
1929:
1920:
1918:
1914:
1907:
1903:
1902:
1898:
1877:
1873:
1843:
1839:
1818:
1814:
1800:
1796:
1778:
1774:
1766:
1762:
1757:
1753:
1744:
1740:
1732:Master Tang Hoi
1727:Thích Nhất Hạnh
1725:
1721:
1712:
1710:
1697:
1696:
1692:
1684:
1680:
1675:
1671:
1666:
1662:
1652:
1648:
1618:
1614:
1596:
1589:
1585:
1563:
1558:
1518:Đông Sơn Period
1479:
1441:Đồng Đậu Period
1354:
1346:Central Vietnam
1338:
1294:
1269:
1263:
1225:
1220:
937:sovereign state
929:
889:
877:Main articles:
875:
853:Red River Delta
837:
817:Sino-Vietnamese
805:Sino-Vietnamese
773:
748:
715:
709:
697:
670:Proto-Mon-Khmer
525:Southeast Asian
453:of characters "
443:
319:
297:
258:Ancient history
239:
226:
183:
178:
149:
148:
145:
133:
130:
128:
127:
125:
122:
120:
119:
108:
102:
99:
93:
81:
75:
71:
69:transliteration
65:
61:
55:
46:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2620:
2610:
2609:
2604:
2599:
2594:
2589:
2584:
2579:
2574:
2569:
2521:
2520:
2515:
2512:
2499:
2496:
2490:
2489:
2472:
2470:on 2012-09-13.
2460:
2439:
2438:External links
2436:
2429:
2412:
2411:
2392:
2385:
2378:
2371:
2370:
2369:
2362:
2355:
2348:
2341:
2331:
2324:
2317:
2310:
2303:
2296:
2289:
2282:
2275:
2270:
2257:
2251:
2244:
2237:
2228:
2225:
2223:
2222:
2206:
2194:
2185:
2176:
2167:
2154:
2135:
2120:
2118:, p. 172.
2108:
2092:
2085:
2065:
2058:
2038:
2031:
2011:
1980:
1968:
1949:
1927:
1896:
1871:
1837:
1812:
1794:
1772:
1760:
1751:
1738:
1719:
1690:
1678:
1676:Pelley, p. 151
1669:
1660:
1646:
1612:
1586:
1584:
1581:
1580:
1579:
1574:
1569:
1562:
1559:
1555:
1554:
1549:
1548:
1547:
1546:
1545:
1539:
1533:
1527:
1513:
1512:
1511:
1510:
1509:
1503:
1497:
1480:
1476:
1475:
1471:
1470:
1469:
1468:
1462:
1456:
1450:
1436:
1435:
1434:
1433:
1432:
1426:
1420:
1406:
1405:
1404:
1403:
1402:
1396:
1390:
1384:
1370:
1366:Heavenly Stems
1353:
1350:
1337:
1334:
1293:
1290:
1262:
1259:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1213:
1212:
1206:
1202:
1201:
1196:
1192:
1191:
1182:
1178:
1177:
1172:
1171:Hoài Hoan (懷驩)
1168:
1167:
1162:
1158:
1157:
1140:
1136:
1135:
1130:
1126:
1125:
1118:
1114:
1113:
1108:
1104:
1103:
1098:
1094:
1093:
1084:
1080:
1079:
1066:
1062:
1061:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1046:
1045:Châu Diên (朱鳶)
1042:
1041:
1036:
1032:
1031:
1028:
1008:Trần Trọng Kim
928:
925:
913:Cổ Loa Citadel
909:An Dương Vương
887:An Dương Vương
879:Hùng Duệ Vương
874:
873:Âu Lạc Kingdom
871:
857:lunar calendar
836:
833:
747:
744:
711:Main article:
708:
705:
696:
693:
666:
665:
658:
626:
603:
562:
442:
441:Origin of name
439:
362:An Dương Vương
324:
323:
314:
310:
309:
306:
305:
302:
301:
294:
285:
282:
281:
276:
269:
268:
255:
254:Historical era
251:
250:
247:
246:
240:
237:
234:
233:
227:
224:
221:
220:
217:
216:
213:
207:
206:
203:
199:
198:
195:
191:
190:
172:
168:
167:
164:
160:
159:
151:
150:
146:
139:
138:
135:
134:
117:
110:
109:
88:. Knowledge's
49:
47:
40:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2619:
2608:
2605:
2603:
2600:
2598:
2595:
2593:
2590:
2588:
2585:
2583:
2580:
2578:
2575:
2573:
2570:
2568:
2565:
2564:
2562:
2555:
2552:
2518:
2509:
2508:
2504:
2493:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2473:
2469:
2465:
2461:
2451:on 2009-04-30
2450:
2446:
2442:
2441:
2435:
2432:
2430:9780190053796
2426:
2422:
2418:
2409:
2408:9780520224124
2405:
2401:
2397:
2393:
2390:
2386:
2383:
2379:
2376:
2372:
2367:
2363:
2360:
2356:
2353:
2349:
2346:
2342:
2339:
2335:
2334:
2332:
2329:
2325:
2322:
2318:
2315:
2311:
2308:
2304:
2301:
2297:
2294:
2290:
2287:
2283:
2280:
2277:Lamb, David.
2276:
2273:
2267:
2263:
2258:
2256:
2252:
2249:
2245:
2242:
2238:
2235:
2231:
2230:
2217:
2215:
2213:
2211:
2201:
2199:
2189:
2180:
2171:
2164:
2158:
2150:
2146:
2139:
2131:
2124:
2117:
2116:Kelley (2016)
2112:
2103:
2101:
2099:
2097:
2088:
2086:0-313-29622-7
2082:
2078:
2077:
2069:
2061:
2059:9781742203898
2055:
2051:
2050:
2042:
2034:
2032:9781780237046
2028:
2024:
2023:
2015:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1988:Ngô Sĩ Liên.
1984:
1975:
1973:
1965:
1961:
1958:
1953:
1946:
1942:
1939:
1934:
1932:
1917:on 2012-09-15
1913:
1906:
1900:
1893:
1889:
1886:
1885:
1880:
1875:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1857:' said: From
1856:
1852:
1848:
1847:
1846:Taiping Yulan
1841:
1834:
1830:
1826:
1823:
1822:
1816:
1809:
1805:
1804:
1803:Taiping Yulan
1798:
1791:
1787:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1770:, p. 53.
1769:
1764:
1755:
1748:
1742:
1735:
1733:
1728:
1723:
1709:on 2020-10-15
1708:
1704:
1700:
1694:
1688:
1682:
1673:
1664:
1656:
1650:
1643:
1639:
1638:Lạc Long Quân
1635:
1631:
1627:
1626:
1621:
1616:
1610:
1607:. Publisher:
1606:
1601:
1594:
1592:
1587:
1578:
1575:
1573:
1570:
1568:
1565:
1564:
1553:
1550:
1543:
1540:
1537:
1534:
1531:
1528:
1525:
1522:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1515:
1514:
1507:
1504:
1501:
1498:
1495:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1488:Gò Mun Period
1486:
1485:
1484:
1483:
1474:
1466:
1463:
1460:
1457:
1454:
1451:
1448:
1445:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1438:
1437:
1430:
1427:
1424:
1421:
1418:
1415:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1408:
1407:
1400:
1397:
1394:
1391:
1388:
1385:
1382:
1379:
1378:
1376:
1375:
1374:
1373:
1369:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1349:
1347:
1343:
1333:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1302:
1299:
1289:
1287:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1258:
1256:
1252:
1251:Shang dynasty
1247:
1244:
1239:
1237:
1233:
1230:
1210:
1207:
1205:Bình Văn (平文)
1204:
1203:
1200:
1197:
1194:
1193:
1190:
1186:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1176:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1166:
1163:
1161:Cửu Chân (九真)
1160:
1159:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1141:
1139:Giao Chỉ (交趾)
1138:
1137:
1134:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1117:Ninh Hải (寧海)
1116:
1115:
1112:
1109:
1107:Lục Hải (陸 海)
1106:
1105:
1102:
1099:
1096:
1095:
1092:
1088:
1085:
1082:
1081:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1067:
1065:Tân Hưng (新興)
1064:
1063:
1060:
1057:
1055:Phúc Lộc (福祿)
1054:
1053:
1050:
1047:
1044:
1043:
1040:
1037:
1034:
1033:
1029:
1026:
1025:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1006:According to
1004:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
986:
981:
979:
975:
971:
968:
964:
960:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
938:
934:
924:
922:
918:
914:
910:
906:
902:
898:
894:
888:
884:
880:
870:
867:
865:
860:
858:
854:
850:
846:
842:
832:
829:
824:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
802:
798:
792:
790:
785:
782:
779:
767:
765:
761:
757:
753:
743:
740:
736:
732:
727:
724:
720:
714:
701:
692:
690:
686:
682:
677:
676:"man, male".
675:
671:
663:
659:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
637:
633:
632:
627:
624:
620:
617:in Angkorian
616:
612:
608:
607:Jayavarman II
604:
601:
597:
594:
591:
587:
583:
579:
576:
571:
567:
563:
560:
556:
552:
548:
547:
543:The ethnonym
542:
541:
540:
538:
534:
530:
529:Austroasiatic
526:
522:
521:
516:
512:
508:
507:
502:
498:
494:
493:
488:
484:
481:
478:
474:
473:Michel Ferlus
469:
467:
463:
459:
456:
452:
448:
438:
436:
432:
428:
424:
423:Dongting Lake
420:
417:(present-day
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
381:as the first
380:
376:
372:
371:
365:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
322:
318:
315:
313:Today part of
311:
295:
293:
290:
289:
286:
284:
283:
280:
277:
275:
274:
270:
267:
263:
259:
256:
252:
248:
244:
241:
235:
231:
228:
222:
218:
214:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
186:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
152:
143:
136:
115:
106:
96:
91:
87:
80:
70:
60:
53:
48:
39:
38:
33:
19:
2524:
2517:Thục dynasty
2501:
2497:New creation
2485:the original
2480:
2468:the original
2453:. Retrieved
2449:the original
2416:
2413:
2395:
2388:
2381:
2374:
2365:
2358:
2351:
2344:
2337:
2327:
2320:
2313:
2306:
2299:
2292:
2285:
2278:
2261:
2254:
2247:
2240:
2233:
2188:
2179:
2170:
2157:
2148:
2138:
2129:
2123:
2111:
2075:
2068:
2048:
2041:
2021:
2014:
2002:. Retrieved
1998:the original
1993:
1983:
1952:
1919:. Retrieved
1912:the original
1899:
1882:
1874:
1844:
1840:
1819:
1815:
1801:
1797:
1783:
1775:
1768:Kiernan 2019
1763:
1754:
1746:
1741:
1730:
1722:
1711:. Retrieved
1707:the original
1702:
1693:
1686:
1681:
1672:
1663:
1654:
1649:
1641:
1633:
1623:
1615:
1608:
1551:
1472:
1355:
1339:
1336:Demographics
1306:Phùng Nguyên
1303:
1295:
1282:
1261:Bronze tools
1248:
1240:
1226:
1195:Cửu Đức (九德)
1097:Vũ Ninh (武寧)
1083:Vũ Định (武定)
1015:
1011:
1005:
982:
973:
969:
962:
961:
956:
948:
944:
930:
927:Organization
890:
868:
861:
838:
825:
819:: Chu Tước,
794:
786:
783:
780:
769:
749:
728:
719:Palaeolithic
716:
707:Pre-dynastic
681:Tang dynasty
678:
673:
667:
661:
654:
650:
642:
629:
622:
614:
610:
589:
581:
558:
554:
544:
537:Austronesian
533:Sino-Tibetan
519:
518:
514:
510:
504:
500:
496:
490:
482:
470:
446:
444:
398:
374:
368:
366:
357:
353:
341:
329:
327:
279:Succeeded by
278:
230:Hùng Vương I
181:(29th c. BC)
100:
86:ISO 639 code
82:}}
76:{{
72:}}
66:{{
62:}}
56:{{
51:
2546: /
2534:105°26′31″E
2368:13:145–162.
2004:30 December
1978:Lamb, p. 52
1620:Ngô Sĩ Liên
1277:bronze drum
1232:cultivation
1223:Agriculture
953:matriarchal
843:(in modern
789:Yan Emperor
653:→ Mandarin
487:Old Chinese
364:in 258 BC.
179:Nghĩa Lĩnh
2561:Categories
2531:21°16′54″N
2455:2008-07-05
1994:Viet Texts
1921:2012-10-07
1888:Chapter 36
1879:Li Daoyuan
1867:Sovereigns
1713:2018-12-30
1583:References
1352:Chronology
1320:Valley in
1279:'s surface
1229:rice paddy
841:Phong Châu
809:Vietnamese
807:: Quỷ tú,
735:Hồng (Red)
685:Phong Châu
643:moːɡ-raːŋs
602:documents;
588:and later
403:Phong Châu
391:Hùng Vương
387:Vietnamese
346:Vietnamese
334:Vietnamese
262:Bronze Age
202:Government
185:Phong Châu
174:Ngàn Hống
2361:13:47–58.
2236:3:57–102.
1863:fragrance
1536:Nhâm line
1524:Canh line
1494:Đinh line
1465:Bính line
1453:Giáp line
1447:Đoài line
1429:Khôn line
1399:Chấn line
1387:Khảm line
1358:Hùng king
1209:Ninh Binh
1071:(part of
1010:'s book,
997:Guangdong
974:quan lang
949:lạc tướng
893:Thục Phán
731:Stone Age
672:etymon: *
660:Malayic *
651:muk̚-lɑŋᴴ
586:Sānguózhì
582:Táng-míng
447:Hồng Bàng
445:The name
395:Hùng king
383:Hùng king
194:Religion
103:June 2021
2295:3:29–56.
2149:quatr.us
1960:Archived
1941:Archived
1869:' time.'
1790:Vol. 184
1785:Tongdian
1685:Tucker,
1561:See also
1542:Qúy line
1530:Tân line
1500:Mậu line
1417:Tốn line
1393:Cấn line
1381:Càn line
1326:Cả River
1318:Ma River
1310:Đồng Đậu
1298:Sa Huỳnh
1069:Hưng Hóa
989:Cả River
970:mae nang
957:bộ chính
901:Lạc Việt
895:led the
845:Việt Trì
752:Shennong
590:Dào-míng
566:Cambodia
483:Văn Lang
464:) bird (
431:East Sea
358:Xích Quỷ
354:Văn Lang
266:Iron Age
205:Monarchy
18:Văn Lang
2507:Vietnam
2503:Dynasty
2227:Sources
2049:Vietnam
1835:, China
1833:Guizhou
1825:vol .38
1506:Kỷ line
1459:Ất line
1423:Ly line
1292:Pottery
1255:Laotian
1253:or the
993:Guangxi
945:lạc hầu
897:Âu Việt
849:Phú Thọ
828:heirdom
823:: 朱雀).
821:chữ Hán
764:chữ Hán
695:History
689:Phú Thọ
674:t₂nra:ŋ
655:Mù-làng
570:Chinese
506:B&S
449:is the
419:Sichuan
317:Vietnam
232:(first)
171:Capital
166:Kingdom
95:See why
2582:258 BC
2427:
2406:
2343:1964.
2293:MQRSEA
2268:
2234:MQRSEA
2083:
2056:
2029:
1829:Yelang
1780:Du You
1552:
1473:
1362:baguas
1314:Gò Mun
1312:, and
1243:feudal
1143:Hà Nội
1075:) and
976:(From
905:Âu Lạc
885:, and
883:Cao Lỗ
641:: OC *
631:Mraṅmā
623:Maleng
615:Malyaṅ
572::
559:m.ra:ŋ
551:Vietic
546:Maleng
515:C.rˤaŋ
435:Champa
415:Ba-Shu
292:Âu Lạc
245:(last)
215:
163:Status
2316:2002.
2286:PEFEO
1915:(PDF)
1908:(PDF)
1855:Linyi
1342:North
985:Hunan
978:Muong
941:court
921:Hanoi
813:South
662:ʔuʀaŋ
619:Khmer
611:Maleṅ
555:m.leŋ
549:of a
520:-ra:ŋ
427:Hunan
321:China
2425:ISBN
2404:ISBN
2266:ISBN
2081:ISBN
2054:ISBN
2027:ISBN
2006:2018
1658:..."
1364:and
1344:and
1187:and
1153:and
1089:and
1027:Name
999:and
600:Tang
501:raːŋ
328:The
211:King
59:lang
2505:of
2328:FMJ
2288:30.
1634:都峯州
1628:, "
967:Tai
919:of
774:赤鬼國
598:in
584:in
497:mɯn
468:).
409:in
79:IPA
2563::
2479:.
2423:.
2419:.
2402:.
2398:.
2366:AP
2359:AP
2338:AP
2307:AP
2209:^
2197:^
2147:.
2095:^
1992:.
1971:^
1930:^
1881:,
1788:,
1782:,
1729:,
1701:.
1622:,
1590:^
1368:.
1308:,
1149:,
1145:,
1124:)
995:,
923:.
881:,
847:,
801:鬼宿
739:Cả
737:,
647:MC
645:→
568:,
535:,
531:,
511:mə
503:;
492:ZS
489::
437:.
389::
336::
264:,
260:,
129:文郎
121:赤鬼
64:,
2458:.
2433:.
2410:.
2391:.
2377:.
2323:.
2243:.
2151:.
2089:.
2063:.
2035:.
2008:.
1924:.
1716:.
1014:(
803:(
776:。
687:(
657:.
649:*
639:浪
636:木
596:明
593:道
578:明
575:堂
561:.
513:-
509:*
499:-
495:*
485:(
480:郎
477:文
466:鴻
462:龐
458:龐
455:鴻
425:(
385:(
373:(
332:(
105:)
101:(
97:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.