1182:
944:
713:
the nutrient and energy stores. "Organisms usually extract energy in the form of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. These polymers have a dual role as supplies of energy as well as building blocks; the part that functions as energy supply results in the production of nutrients (and carbon dioxide, water, and heat). Excretion of nutrients is, therefore, basic to metabolism." The units in energy flow webs are typically a measure mass or energy per m per unit time. Different consumers are going to have different metabolic assimilation efficiencies in their diets. Each trophic level transforms energy into biomass. Energy flow diagrams illustrate the rates and efficiency of transfer from one trophic level into another and up through the hierarchy.
1231:
referred to as cliques, hubs, compartments, cohesive sub-groups, or modules...Within food webs, especially in aquatic systems, nestedness appears to be related to body size because the diets of smaller predators tend to be nested subsets of those of larger predators (Woodward & Warren 2007; YvonDurocher et al. 2008), and phylogenetic constraints, whereby related taxa are nested based on their common evolutionary history, are also evident (Cattin et al. 2004)." "Compartments in food webs are subgroups of taxa in which many strong interactions occur within the subgroups and few weak interactions occur between the subgroups. Theoretically, compartments increase the stability in networks, such as food webs."
1373:
863:
Phytoplankton live just a few days, whereas the zooplankton eating the phytoplankton live for several weeks and the fish eating the zooplankton live for several consecutive years. Aquatic predators also tend to have a lower death rate than the smaller consumers, which contributes to the inverted pyramidal pattern. Population structure, migration rates, and environmental refuge for prey are other possible causes for pyramids with biomass inverted. Energy pyramids, however, will always have an upright pyramid shape if all sources of food energy are included and this is dictated by the
611:
of primary production in plants. Although the predators do not eat the plants directly, they regulate the population of herbivores that are directly linked to plant trophism. The net effect of direct and indirect relations is called trophic cascades. Trophic cascades are separated into species-level cascades, where only a subset of the food-web dynamic is impacted by a change in population numbers, and community-level cascades, where a change in population numbers has a dramatic effect on the entire food-web, such as the distribution of plant biomass.
561:. The basis of trophic dynamics is the transfer of energy from one part of the ecosystem to another. The trophic dynamic concept has served as a useful quantitative heuristic, but it has several major limitations including the precision by which an organism can be allocated to a specific trophic level. Omnivores, for example, are not restricted to any single level. Nonetheless, recent research has found that discrete trophic levels do exist, but "above the herbivore trophic level, food webs are better characterized as a tangled web of omnivores."
589:
992:- emphasizes the functional significance of certain connections having strong interaction strength and greater bearing on community organization, more so than energy flow pathways. Functional webs have compartments, which are sub-groups in the larger network where there are different densities and strengths of interaction. Functional webs emphasize that "the importance of each population in maintaining the integrity of a community is reflected in its influence on the growth rates of other populations."
1345:
6479:
446:
1199:
methods for measuring network complexity. Connectance is "the fraction of all possible links that are realized in a network". These concepts were derived and stimulated through the suggestion that complexity leads to stability in food webs, such as increasing the number of trophic levels in more species rich ecosystems. This hypothesis was challenged through mathematical models suggesting otherwise, but subsequent studies have shown that the premise holds in real systems.
1211:
interaction in which specialists interact with species that form perfect subsets of the species with which generalists interact", "—that is, the diet of the most specialized species is a subset of the diet of the next more generalized species, and its diet a subset of the next more generalized, and so on." Until recently, it was thought that food webs had little nested structure, but empirical evidence shows that many published webs have nested subwebs in their assembly.
696:
569:. Alternatively to the top-down hypothesis, not all plant material is edible and the nutritional quality or antiherbivore defenses of plants (structural and chemical) suggests a bottom-up form of regulation or control. Recent studies have concluded that both "top-down" and "bottom-up" forces can influence community structure and the strength of the influence is environmentally context dependent. These complex multitrophic interactions involve more than two
784:
1387:
1012:
31:
1359:
298:
663:
549:) is set at zero. Ecologists identify feeding relations and organize species into trophic species through extensive gut content analysis of different species. The technique has been improved through the use of stable isotopes to better trace energy flow through the web. It was once thought that omnivory was rare, but recent evidence suggests otherwise. This realization has made trophic classifications more complex.
816:
824:
940:. It is explicitly understood that natural systems are 'sloppy' and that food web trophic positions simplify the complexity of real systems that sometimes overemphasize many rare interactions. Most studies focus on the larger influences where the bulk of energy transfer occurs. "These omissions and problems are causes for concern, but on present evidence do not present insurmountable difficulties."
506:
854:
become further removed from the source of production is one of several patterns that is repeated amongst the planets ecosystems. The size of each level in the pyramid generally represents biomass, which can be measured as the dry weight of an organism. Autotrophs may have the highest global proportion of biomass, but they are closely rivaled or surpassed by microbes.
1248:
760:
length depending on what parameters of the food web dynamic are being considered: connectance, energy, or interaction. In its simplest form, the length of a chain is the number of links between a trophic consumer and the base of the web. The mean chain length of an entire web is the arithmetic average of the lengths of all chains in a food web.
1239:. "This leads to anomalies, such as food web calculations determining that an ecosystem can support one half of a top carnivore, without specifying which end." Nonetheless, real differences in structure and function have been identified when comparing different kinds of ecological food webs, such as terrestrial vs. aquatic food webs.
1057:(number of species), biomass (the dry weight of plants and animals), productivity (rates of conversion of energy and nutrients into growth), and stability (food webs over time). A food web diagram illustrating species composition shows how change in a single species can directly and indirectly influence many others.
1008:. These characterizations stem from the ecosystem concept, which assumes that the phenomena under investigation (interactions and feedback loops) are sufficient to explain patterns within boundaries, such as the edge of a forest, an island, a shoreline, or some other pronounced physical characteristic.
1202:
At different levels in the hierarchy of life, such as the stability of a food web, "the same overall structure is maintained in spite of an ongoing flow and change of components." The farther a living system (e.g., ecosystem) sways from equilibrium, the greater its complexity. Complexity has multiple
1165:
where, S(S-1)/2 is the maximum number of binary connections among S species. "Connectance (C) is the fraction of all possible links that are realized (L/S) and represents a standard measure of food web complexity..." The distance (d) between every species pair in a web is averaged to compute the mean
759:
A common metric used to quantify food web trophic structure is food chain length. Food chain length is another way of describing food webs as a measure of the number of species encountered as energy or nutrients move from the plants to top predators. There are different ways of calculating food chain
161:
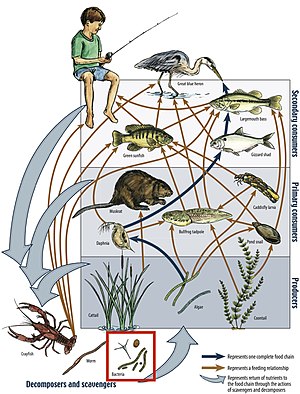
The linkages in a food web illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other heterotrophs. The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. There are
1320:
and his terminology, including an "entangled bank", "web of life", "web of complex relations", and in reference to the decomposition actions of earthworms he talked about "the continued movement of the particles of earth". Even earlier, in 1768 John
Bruckner described nature as "one continued web of
947:
Paleoecological studies can reconstruct fossil food-webs and trophic levels. Primary producers form the base (red spheres), predators at top (yellow spheres), the lines represent feeding links. Original food-webs (left) are simplified (right) by aggregating groups feeding on common prey into coarser
893:
web energy pathways. Ecologists employ stoichiometry to analyze the ratios of the main elements found in all organisms: carbon (C), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P). There is a large transitional difference between many terrestrial and aquatic systems as C:P and C:N ratios are much higher in terrestrial
853:
place the primary producers at the base. They can depict different numerical properties of ecosystems, including numbers of individuals per unit of area, biomass (g/m), and energy (k cal m yr). The emergent pyramidal arrangement of trophic levels with amounts of energy transfer decreasing as species
712:
Biomass represents stored energy. However, concentration and quality of nutrients and energy is variable. Many plant fibers, for example, are indigestible to many herbivores leaving grazer community food webs more nutrient limited than detrital food webs where bacteria are able to access and release
610:
by suppressing herbivores. Links in a food-web illustrate direct trophic relations among species, but there are also indirect effects that can alter the abundance, distribution, or biomass in the trophic levels. For example, predators eating herbivores indirectly influence the control and regulation
862:
as exists in the woody trees of terrestrial ecosystems. However, they are able to reproduce quickly enough to support a larger biomass of grazers. This inverts the pyramid. Primary consumers have longer lifespans and slower growth rates that accumulates more biomass than the producers they consume.
513:
terrestrial ecosystem. The trophic pyramid roughly represents the biomass (usually measured as total dry-weight) at each level. Plants generally have the greatest biomass. Names of trophic categories are shown to the right of the pyramid. Some ecosystems, such as many wetlands, do not organize as a
1299:
subsequently pioneered the concept of food cycles, food chains, and food size in his classical 1927 book "Animal
Ecology"; Elton's 'food cycle' was replaced by 'food web' in a subsequent ecological text. After Charles Elton's use of food webs in his 1927 synthesis, they became a central concept in
1072:
While the complexity of real food webs connections are difficult to decipher, ecologists have found mathematical models on networks an invaluable tool for gaining insight into the structure, stability, and laws of food web behaviours relative to observable outcomes. "Food web theory centers around
1024:
In a detrital web, plant and animal matter is broken down by decomposers, e.g., bacteria and fungi, and moves to detritivores and then carnivores. There are often relationships between the detrital web and the grazing web. Mushrooms produced by decomposers in the detrital web become a food source
1230:
in ecology), and small path length compared to a regular lattice. "Ecological networks, especially mutualistic networks, are generally very heterogeneous, consisting of areas with sparse links among species and distinct areas of tightly linked species. These regions of high link density are often
1210:
Several concepts have emerged from the study of complexity in food webs. Complexity explains many principals pertaining to self-organization, non-linearity, interaction, cybernetic feedback, discontinuity, emergence, and stability in food webs. Nestedness, for example, is defined as "a pattern of
1198:
is a term that conveys the mental intractability of understanding all possible higher-order effects in a food web. Sometimes in food web terminology, complexity is defined as product of the number of species and connectance., though there have been criticisms of this definition and other proposed
1189:
in eutrophic (green) and oligotrophic (blue) summer conditions. In the Green system state, both copepods and microzooplankton exert a strong grazing pressure on phytoplankton, while in the Blue state, copepods increase their predation over microzooplankton, which in turn shifts its predation from
763:
In a simple predator-prey example, a deer is one step removed from the plants it eats (chain length = 1) and a wolf that eats the deer is two steps removed from the plants (chain length = 2). The relative amount or strength of influence that these parameters have on the food web address questions
699:
An expanded three link energy food chain (1. plants, 2. herbivores, 3. carnivores) illustrating the relationship between food flow diagrams and energy transformity. The transformity of energy becomes degraded, dispersed, and diminished from higher quality to lesser quantity as the energy within a
857:
Pyramid structure can vary across ecosystems and across time. In some instances biomass pyramids can be inverted. This pattern is often identified in aquatic and coral reef ecosystems. The pattern of biomass inversion is attributed to different sizes of producers. Aquatic communities are often
704:
Food webs depict energy flow via trophic linkages. Energy flow is directional, which contrasts against the cyclic flows of material through the food web systems. Energy flow "typically includes production, consumption, assimilation, non-assimilation losses (feces), and respiration (maintenance
564:
A central question in the trophic dynamic literature is the nature of control and regulation over resources and production. Ecologists use simplified one trophic position food chain models (producer, carnivore, decomposer). Using these models, ecologists have tested various types of ecological
1048:
Ecologists collect data on trophic levels and food webs to statistically model and mathematically calculate parameters, such as those used in other kinds of network analysis (e.g., graph theory), to study emergent patterns and properties shared among ecosystems. There are different ecological
311:
Food webs are the road-maps through Darwin's famous 'entangled bank' and have a long history in ecology. Like maps of unfamiliar ground, food webs appear bewilderingly complex. They were often published to make just that point. Yet recent studies have shown that food webs from a wide range of
541:. The top level has top (or apex) predators which no other species kills directly for its food resource needs. The intermediate levels are filled with omnivores that feed on more than one trophic level and cause energy to flow through a number of food pathways starting from a basal species.
544:
In the simplest scheme, the first trophic level (level 1) is plants, then herbivores (level 2), and then carnivores (level 3). The trophic level is equal to one more than the chain length, which is the number of links connecting to the base. The base of the food chain (primary producers or
689:
The Law of
Conservation of Mass dates from Antoine Lavoisier's 1789 discovery that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. In other words, the mass of any one element at the beginning of a reaction will equal the mass of that element at the end of the reaction.
1835:
728:
increases. About eighty to ninety percent of the energy is expended for the organism's life processes or is lost as heat or waste. Only about ten to twenty percent of the organism's energy is generally passed to the next organism. The amount can be less than one percent in
666:
Energy flow diagram of a frog. The frog represents a node in an extended food web. The energy ingested is utilized for metabolic processes and transformed into biomass. The energy flow continues on its path if the frog is ingested by predators, parasites, or as a decaying
1234:
Food webs are also complex in the way that they change in scale, seasonally, and geographically. The components of food webs, including organisms and mineral nutrients, cross the thresholds of ecosystem boundaries. This has led to the concept or area of study known as
918:
create and cycle nutrients and biominerals. Food web models and nutrient cycles have traditionally been treated separately, but there is a strong functional connection between the two in terms of stability, flux, sources, sinks, and recycling of mineral nutrients.
1036:, dead wood, aquatic macrophytes, algae), animal tissue (carrion), dead microbes, faeces (manure, dung, faecal pellets, guano, frass), as well as products secreted, excreted or exuded from organisms (e.g. extra-cellular polymers, nectar, root exudates and
641:
that have developed a tolerance for these compounds and are able to consume the foliage of these plants. These sequestered iridoid glycosides then confer chemical protection against bird predators to the butterfly larvae. Another example of this sort of
245:
and his terminology, including an "entangled bank", "web of life", "web of complex relations", and in reference to the decomposition actions of earthworms he talked about "the continued movement of the particles of earth". Even earlier, in 1768
523:, including "decomposing organic material and its associated microorganisms which we defined as detritus, micro-inorganic material and associated microorganisms (MIP), and vascular plant material." Most autotrophs capture the sun's energy in
514:
strict pyramid, because aquatic plants are not as productive as long-lived terrestrial plants such as trees. Ecological trophic pyramids are typically one of three kinds: 1) pyramid of numbers, 2) pyramid of biomass, or 3) pyramid of energy.
1851:
927:
Food webs are necessarily aggregated and only illustrate a tiny portion of the complexity of real ecosystems. For example, the number of species on the planet are likely in the general order of 10, over 95% of these species consist of
565:
control mechanisms. For example, herbivores generally have an abundance of vegetative resources, which meant that their populations were largely controlled or regulated by predators. This is known as the top-down hypothesis or
5074:
Riede, J. O.; Rall, B. C.; Banasek-Richter, C.; Navarrete, S. A.; Wieters, E. A.; Emmerson, M. C.; et al. (2010). "Scaling of food web properties with diversity and complexity across ecosystems.". In
Woodwoard, G. (ed.).
902:
as they flow through organisms. Most of the primary production in an ecosystem is not consumed, but is recycled by detritus back into useful nutrients. Many of the Earth's microorganisms are involved in the formation of
518:
Food webs have trophic levels and positions. Basal species, such as plants, form the first level and are the resource limited species that feed on no other living creature in the web. Basal species can be autotrophs or
1263:
Food webs serve as a framework to help ecologists organize the complex network of interactions among species observed in nature and around the world. One of the earliest descriptions of a food chain was described by a
1324:
Interest in food webs increased after Robert Paine's experimental and descriptive study of intertidal shores suggesting that food web complexity was key to maintaining species diversity and ecological stability. Many
1698:
220:
pioneered the concept of food cycles, food chains, and food size in his classical 1927 book "Animal
Ecology"; Elton's 'food cycle' was replaced by 'food web' in a subsequent ecological text. Elton organized
996:
Within these categories, food webs can be further organized according to the different kinds of ecosystems being investigated. For example, human food webs, agricultural food webs, detrital food webs,
305:) linked to decomposers. The movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic, whereas the movement of energy is unidirectional and noncyclic. Trophic species are encircled as nodes and arrows depict the links.
1207:) is defined by the "properties emerging from the interplay of behavioral, biological, physical, and social interactions that affect, sustain, or are modified by living organisms, including humans".
2585:
5597:
1040:, dissolved organic matter, extra-cellular matrix, mucilage). The relative importance of these forms of detritus, in terms of origin, size and chemical composition, varies across ecosystems."
1159:
858:
dominated by producers that are smaller than the consumers that have high growth rates. Aquatic producers, such as planktonic algae or aquatic plants, lack the large accumulation of
1892:
1760:
269:
dynamics. Using these models they can measure and test for generalized patterns in the structure of real food web networks. Ecologists have identified non-random properties in the
5120:
2519:
158:), which are autotrophic organisms that partially obtain organic matter from sources other than the atmosphere, and complete heterotrophs that must feed to obtain organic matter.
1170:. These formulas are the basis for comparing and investigating the nature of non-random patterns in the structure of food web networks among many different types of ecosystems.
1061:
are used to simplify food web research into semi-isolated units such as small springs, decaying logs, and laboratory experiments using organisms that reproduce quickly, such as
5982:
Hardy, AC (1924). "The herring in relation to its animate environment. Part 1. The food and feeding habits of the herring with special reference to the east coast of
England".
4885:
2122:
1203:
meanings in the life sciences and in the public sphere that confuse its application as a precise term for analytical purposes in science. Complexity in the life sciences (or
1166:
distance between all nodes in a web (D) and multiplied by the total number of links (L) to obtain link-density (LD), which is influenced by scale-dependent variables such as
2233:
1275:: "All animals, in short, cannot exist without food, neither can the hunting animal escape being hunted in his turn." The earliest graphical depiction of a food web was by
5187:
1729:
277:
are of variable quality with omissions. However, the number of empirical studies on community webs is on the rise and the mathematical treatment of food webs using
618:
has elucidated multitrophic interactions that entail the transfer of defensive compounds across multiple trophic levels. For example, certain plant species in the
3957:
471:. Trophic species are functional groups that have the same predators and prey in a food web. Common examples of an aggregated node in a food web might include
3497:
843:), will be supported by a much larger number of separate producers. There is usually a maximum of four or five links in a food chain, although food chains in
150:. These trophic levels are not binary, but form a gradient that includes complete autotrophs, which obtain their sole source of carbon from the atmosphere,
4760:
4699:
3956:
Koch, P. L.; Fox-Dobbs, K.; Newsom, S. D. "The isotopic ecology of fossil vertebrates and conservation paleobiology". In Diet, G. P.; Flessa, K. W. (eds.).
2624:
3993:
Moore, J. C.; Berlow, E. L.; Coleman, D. C.; de Ruiter, P. C.; Dong, Q.; Hastings, A.; et al. (2004). "Detritus, trophic dynamics and biodiversity".
4854:
Elser, J.; Hayakawa, K.; Urabe, J. (2001). "Nutrient
Limitation Reduces Food Quality for Zooplankton: Daphnia Response to Seston Phosphorus Enrichment".
3781:
5644:
4624:
4195:"Seasonal seawater temperature as the major determinant for populations of culturable bacteria in the sediments of an intact mangrove in an arid region"
1541:"Autotrophic fixation of geogenic CO2 by microorganisms contributes to soil organic matter formation and alters isotope signatures in a wetland mofette"
700:
food chain flows from one trophic species into another. Abbreviations: I=input, A=assimilation, R=respiration, NU=not utilized, P=production, B=biomass.
671:
in soil. This energy flow diagram illustrates how energy is lost as it fuels the metabolic process that transform the energy and nutrients into biomass.
4245:
DeAngelis, D. L.; Mulholland, P. J.; Palumbo, A. V.; Steinman, A. D.; Huston, M. A.; Elwood, J. W. (1989). "Nutrient dynamics and food-web stability".
6101:
2170:
3363:
3808:
2452:
2050:
5076:
5718:
7604:
6857:
3413:
2383:
1218:. As networks, they exhibit similar structural properties and mathematical laws that have been used to describe other complex systems, such as
509:
A trophic pyramid (a) and a simplified community food web (b) illustrating ecological relations among creatures that are typical of a northern
5539:
1799:
1190:
phytoplankton to bacterial plankton or picoplankton. These trophic mechanisms stabilize the delivery of organic matter from copepods to fish.
1181:
943:
4282:"Regeneration, recycling, and trophic transfer of trace metals by microbial food-web organisms in the pelagic surface waters of Lake Erie"
3221:
1939:
7748:
4801:
5159:
4438:"Colloquium Paper: Where does biodiversity go from here? A grim business-as-usual forecast and a hopeful portfolio of partial solutions"
2560:
745:
or trophic pyramids. The transfer of energy from primary producers to top consumers can also be characterized by energy flow diagrams.
7818:
257:, which are functional groups of species that have the same predators and prey in a food web. Ecologists use these simplifications in
6055:
Stauffer, R. C. (1960). "Ecology in the long manuscript version of Darwin's "Origin of
Species" and Linnaeus' "Oeconomy of Nature"".
3386:
1226:. The small world attribute refers to the many loosely connected nodes, non-random dense clustering of a few nodes (i.e., trophic or
1058:
7390:
4924:
4322:
3899:
3440:
1454:
7355:
2145:
1491:
643:
2272:
1316:'s classic and landmark paper in 1942 on trophic dynamics. The notion of a food web has a historical foothold in the writings of
531:) obtain energy by the chemical oxidation of inorganic compounds and can grow in dark environments, such as the sulfur bacterium
7828:
7556:
898:
are the material resources that organisms need for growth, development, and vitality. Food webs depict the pathways of mineral
417:). Feeding connections in the web are called trophic links. The number of trophic links per consumer is a measure of food web
6203:
6111:
6013:
5277:
5242:
5089:
4838:
4811:
4146:
González-Muñoz, M. T.; Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Martínez-Ruiz, F.; Arias, J. M.; Merroun, M. L.; Rodriguez-Gallego, M. (2010).
3791:
3764:
3678:
3507:
3450:
3423:
3396:
2914:
2790:
1964:
1845:
1678:
1073:
the idea of connectance." Quantitative formulas simplify the complexity of food web structure. The number of trophic links (t
449:
6084:
4828:
7833:
5267:
1032:"Detritus can be broadly defined as any form of non-living organic matter, including different types of plant tissue (e.g.
8021:
889:(or mineral nutrients) are contained within the tissues and diets of organisms. Hence, mineral and nutrient cycles trace
724:
decreases from the base of the chain to the top. This is because energy is lost to the environment with each transfer as
598:
larvae sequester defensive compounds from specific types of plants they consume to protect themselves from bird predators
7774:
7597:
7438:
6850:
6705:
2780:
1436:
163:
5505:
Michener, W. K.; Baerwald, T. J.; Firth, P.; Palmer, M. A.; Rosenberger, J. L.; Sandlin, E. A.; Zimmerman, H. (2001).
3966:
7110:
6695:
6690:
6305:
3096:
1608:
1668:
6700:
17:
7571:
4783:
1083:
7853:
7566:
7433:
7145:
6222:
4732:
2300:
2008:
1869:
1333:
and Stuart Pimm, were prompted by this discovery and others to examine the mathematical properties of food webs.
1330:
425:
are nested within the trophic links of food webs. Food chains are linear (noncyclic) feeding pathways that trace
6198:. Monographs in Population Biology. Vol. 11. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. pp. xv+1–190.
4867:
4779:
2935:"Preference, performance, and chemical defense in an endangered butterfly using novel and ancestral host plants"
8238:
8111:
5015:
Banasek-Richter, C.; Bersier, L. L.; Cattin, M.; Baltensperger, R.; Gabriel, J.; Merz, Y.; et al. (2009).
5523:
5506:
5314:
5297:
2806:
Babikova, Zdenka; Gilbert, Lucy; Bruce, Toby; Dewhirst, Sarah; Pickett, John A.; Johnson, David (April 2014).
1173:
Scaling laws, complexity, chaos, and pattern correlates are common features attributed to food web structure.
8284:
7883:
7838:
7590:
6843:
5920:
4671:
1413:
7370:
285:, for example, predict a relationship between the topology of food web predator-prey linkages and levels of
7716:
3898:
Elser, J. J.; Fagan, W. F.; Donno, R. F.; Dobberfuhl, D. R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; et al. (2000).
864:
847:
are more often longer than those on land. Eventually, all the energy in a food chain is dispersed as heat.
807:
trophic levels are not drawn to scale and the pyramid of numbers excludes microorganisms and soil animals.
574:
8073:
6964:
5882:
4700:"Toward an integration of landscape and food web ecology: The dynamics of spatially subsidized food webs"
3670:
2693:
831:
In a pyramid of numbers, the number of consumers at each level decreases significantly, so that a single
360:. Heterotrophs consume rather than produce biomass energy as they metabolize, grow, and add to levels of
253:
Food webs are limited representations of real ecosystems as they necessarily aggregate many species into
5883:"A history of the ecological sciences, part 6: Arabic language science: Origins and zoological writings"
4193:
Gonzalez-Acosta, B.; Bashan, Y.; Hernandez-Saavedra, N. Y.; Ascencio, F.; De la Cruz-Agüero, G. (2006).
3959:
Conservation paleobiology: Using the past to manage for the future, Paleontological
Society short course
3839:
2491:
8138:
7858:
7345:
7062:
6959:
6685:
6314:
6162:
5791:
Montoya, J. M.; Blüthgen, N; Brown, L.; Dormann, C. F.; Edwards, F.; Figueroa, D.; et al. (2009).
2808:"Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and aphids interact by changing host plant quality and volatile emission"
2694:"Turning up the head: Temperature influences the relative importance of top-down and bottom-up effects"
2097:
1514:
1459:
1305:
557:
The trophic level concept was introduced in a historical landmark paper on trophic dynamics in 1942 by
226:
91:
5095:
8319:
7931:
7823:
7681:
7666:
7661:
7340:
7052:
6824:
5767:
4498:
Dunne, J. A.; Williams, R. J.; Martinez, N. D.; Wood, R. A.; Erwin, D. H.; Dobson, Andrew P. (2008).
1508:
635:
594:
394:
The base or basal species in a food web are those species without prey and can include autotrophs or
266:
233:'s classic and landmark paper in 1942 on trophic dynamics. Lindeman emphasized the important role of
6835:
2422:
8409:
8309:
8304:
8274:
8078:
7541:
7423:
6272:
4194:
3054:
Lehtonen, Päivi; Helander, Marjo; Wink, Michael; Sporer, Frank; Saikkonen, Kari (12 October 2005).
2171:"The importance of temporal resolution in food web analysis: Evidence from a detritus-based stream"
1401:
1296:
1288:
1252:
768:
the identity or existence of a few dominant species (called strong interactors or keystone species)
217:
7582:
7213:
5947:
Summerhayes, VS; Elton, CS (1923). "Contributions to the
Ecology of Spitsbergen and Bear Island".
5572:
1540:
491:, each containing many species in a web that can otherwise be connected to other trophic species.
8153:
8016:
7926:
7794:
7676:
7646:
7503:
7468:
7188:
7155:
7130:
6804:
2856:
2657:
1624:
Briand, F.; Cohen, J.E. (19 January 1984). "Community food webs have scale-invariant structure".
6086:
The formation of vegetable mould, through the action of worms, with observations on their habits
3222:"Production and use of detritus in various freshwater, estuarine, and coastal marine ecosystems"
811:
P=Producers, C1=Primary consumers, C2=Secondary consumers, C3=Tertiary consumers, S=Saprotrophs.
8299:
8243:
8178:
8041:
7976:
7911:
7473:
7261:
6969:
6949:
6057:
3244:
1280:
1236:
566:
480:
376:
329:
with food web. Ecologists can broadly group all life forms into one of two trophic layers, the
3566:
Paine, R. T. (1980). "Food webs: Linkage, interaction strength and community infrastructure".
2520:"Cause-effect relationships in energy flow, trophic structure, and interspecific interactions"
8203:
8148:
8011:
7996:
7779:
7736:
7726:
7721:
7478:
7458:
7314:
7304:
7246:
7241:
7077:
6929:
6449:
6298:
5558:
2757:
1451: – Processes by which nutritional substances are grown, raised, packaged and distributed
1378:
1326:
682:
676:
484:
380:
258:
4553:
3526:
Worm, B.; Duffy, J.E. (2003). "Biodiversity, productivity and stability in real food webs".
3273:"Dynamic energy budget representations of stoichiometric constraints on population dynamics"
654:
living within a grass host to a hemiparasitic plant that is also using the grass as a host.
8329:
8294:
8289:
8213:
8208:
8163:
8061:
8031:
8026:
7878:
7741:
7731:
7276:
7115:
6904:
6732:
6236:
5743:
5681:
5612:
5471:
5386:
5202:
5135:
5028:
4966:
4900:
4639:
4568:
4449:
4402:
4337:
4293:
4209:
4159:
4045:
4002:
3914:
3823:
3707:
3575:
3535:
3287:
3127:
3067:
3006:
2946:
2871:
2819:
2708:
2600:
2467:
2398:
2335:
2248:
2185:
2065:
1979:
1907:
1775:
1633:
1590:
1555:
1430:
959:- one or more node(s), all of their predators, all the food these predators eat, and so on.
361:
357:
318:
75:
5462:
Peters, R. H. (1988). "Some general problems for ecology illustrated by food web theory".
4147:
977:- quantified fluxes of energy between nodes along links between a resource and a consumer.
741:. Graphic representations of the biomass or productivity at each tropic level are called
8:
8379:
8354:
8218:
8188:
8133:
8046:
7936:
7921:
7868:
7701:
7636:
7518:
7448:
7380:
6979:
6819:
6673:
6039:
4369:
4148:"Bacterial biomineralization: new insights from Myxococcus-induced mineral precipitation"
3272:
1963:
Azam, F.; Fenche, T.; Field, J. G.; Gra, J. S.; Meyer-Reil, L. A.; Thingstad, F. (1983).
1497:
1479:
1219:
1050:
819:
A four level trophic pyramid sitting on a layer of soil and its community of decomposers.
6240:
5747:
5685:
5616:
5475:
5390:
5206:
5139:
5032:
4970:
4904:
4643:
4572:
4453:
4406:
4341:
4297:
4213:
4163:
4049:
4006:
3918:
3876:
3827:
3711:
3579:
3539:
3291:
3131:
3071:
3056:"Transfer of endophyte-origin defensive alkaloids from a grass to a hemiparasitic plant"
3010:
2950:
2875:
2823:
2712:
2604:
2471:
2402:
2339:
2252:
2189:
2069:
1983:
1911:
1779:
1637:
1559:
631:
8390:
8339:
8334:
8143:
8106:
7848:
7804:
7769:
7626:
7551:
7453:
7385:
7375:
7309:
7256:
7067:
7012:
6974:
6899:
6814:
6464:
6260:
6144:
6065:
5964:
5858:
5833:
5733:
5636:
5487:
5234:
4916:
4663:
4602:
4526:
4499:
4472:
4437:
4361:
4262:
4175:
4128:
4112:
4077:
4061:
4018:
3938:
3880:
3642:
3599:
3591:
3339:
3314:
3169:
3153:
3022:
2967:
2934:
2837:
2761:
2674:
2616:
2552:
2483:
2361:
2211:
2089:
1931:
1791:
1649:
1470:
1442:
1350:
1223:
1215:
1005:
850:
844:
771:
the total number of species and food-chain length (including many weak interactors) and
742:
418:
372:
338:
5409:
5374:
4989:
4954:
3482:
2883:
2649:
2141:
965:- one or more node(s), all of their prey, all the food that these prey eat, and so on.
8279:
8248:
8036:
7863:
7671:
7536:
7513:
7251:
7027:
6939:
6924:
6909:
6889:
6809:
6454:
6264:
6252:
6227:
6209:
6199:
6175:
6107:
6009:
5863:
5814:
5809:
5792:
5759:
5699:
5628:
5414:
5352:
5273:
5226:
5151:
5085:
5056:
4994:
4834:
4807:
4718:
4655:
4594:
4531:
4477:
4418:
4353:
4227:
4222:
4179:
4120:
4069:
4014:
3930:
3787:
3760:
3735:
3730:
3695:
3674:
3646:
3634:
3503:
3446:
3419:
3392:
3344:
3240:
3161:
3080:
3055:
3030:
2972:
2910:
2887:
2786:
2726:
2414:
2353:
2264:
2260:
2093:
2081:
2031:
1923:
1841:
1721:
1674:
1604:
1503:
1433: – Chemical transfer pathway between Earth's biological and non-biological parts
1418:
908:
895:
573:
in a food web. For example, such interactions have been discovered in the context of
454:
342:
312:
terrestrial, freshwater, and marine communities share a remarkable list of patterns.
187:
155:
143:
135:
119:
35:
6148:
5934:
5238:
4953:
Williams, R. J.; Berlow, E. L.; Dunne, J. A.; Barabási, A.; Martinez, N. D. (2002).
4667:
4365:
4258:
4132:
4081:
3835:
3603:
3173:
2765:
2678:
2556:
1935:
8233:
8096:
8088:
8006:
7888:
7873:
7809:
7789:
7706:
7696:
7691:
7656:
7488:
7428:
7299:
7100:
7042:
6954:
6914:
6678:
6459:
6291:
6244:
6136:
5956:
5916:
5853:
5845:
5804:
5751:
5689:
5620:
5562:
5554:
5518:
5479:
5444:
5404:
5394:
5342:
5309:
5218:
5210:
5143:
5046:
5036:
4984:
4974:
4908:
4863:
4826:
4775:
4761:"Is it time to bury the ecosystem concept? (With full military honors, of course!)"
4722:
4714:
4647:
4606:
4584:
4576:
4552:
Krause, A. E.; Frank, K. A.; Mason, D. M.; Ulanowicz, R. E.; Taylor, W. W. (2003).
4521:
4511:
4467:
4457:
4414:
4410:
4345:
4301:
4254:
4217:
4167:
4104:
4053:
4022:
4010:
3965:. The Paleontological Society Papers. Vol. 15. pp. 95–112. Archived from
3942:
3922:
3872:
3831:
3725:
3715:
3626:
3583:
3543:
3478:
3334:
3326:
3295:
3236:
3200:
3143:
3135:
3075:
3014:
2962:
2954:
2879:
2827:
2753:
2716:
2666:
2608:
2542:
2534:
2475:
2406:
2365:
2343:
2256:
2201:
2193:
2137:
2073:
2023:
1987:
1915:
1795:
1783:
1713:
1653:
1641:
1596:
1563:
1313:
1276:
1227:
1167:
1054:
899:
882:
859:
615:
558:
510:
286:
270:
230:
59:
5640:
4393:
Beattie, A.; Ehrlich, P. (2010). "The missing link in biodiversity conservation".
4349:
3139:
2995:"Hemiparasites can transmit indirect effects from their host plants to herbivores"
2384:"Trophic levels and trophic tangles: The prevalence of omnivory in real food webs"
8369:
8228:
8198:
8193:
8183:
8116:
8101:
7981:
7961:
7843:
7711:
7617:
7508:
7418:
7360:
6944:
6870:
6786:
6658:
6637:
5834:"All wet or dried up? Real differences between aquatic and terrestrial food webs"
4651:
4516:
4145:
3754:
1464:
997:
800:
603:
468:
262:
254:
139:
55:
8349:
8173:
8126:
8056:
8051:
7946:
7813:
7686:
7493:
7483:
7463:
7266:
7231:
7170:
7047:
7002:
6894:
6761:
6737:
6720:
6515:
4192:
3547:
2958:
1717:
1536:
1392:
1364:
1317:
1195:
1186:
1049:
dimensions that can be mapped to create more complicated food webs, including:
876:
705:
costs)." In a very general sense, energy flow (E) can be defined as the sum of
538:
350:
346:
278:
242:
131:
115:
99:
6028:
Elton CS (1927) Animal Ecology. Republished 2001. University of Chicago Press.
5935:"Animal Communities in Temperate America as Illustrated in the Chicago Region"
4306:
4281:
3759:. World Conservation Monitoring Centre, United Nations Environment Programme.
2027:
1600:
1279:
in 1880, followed independently by those of Pierce and colleagues in 1912 and
588:
8403:
8374:
7350:
7324:
7281:
7271:
7226:
7193:
7085:
6919:
6874:
6771:
6766:
6725:
6715:
6663:
6478:
6428:
6423:
6342:
6191:
5356:
5347:
5330:
2382:
Thompson, R. M.; Hemberg, M.; Starzomski, B. M.; Shurin, J. B. (March 2007).
1485:
1407:
1344:
1309:
1292:
1204:
1001:
933:
827:
A three layer trophic pyramid linked to the biomass and energy flow concepts.
738:
721:
570:
500:
430:
274:
247:
238:
199:
195:
87:
6248:
5214:
5147:
4462:
4108:
4057:
3720:
3630:
2832:
2807:
1919:
1568:
733:
consuming less digestible plants, and it can be as high as forty percent in
8359:
8344:
8001:
7971:
7916:
7799:
7764:
7641:
7140:
6791:
6668:
6556:
6377:
6367:
6256:
5867:
5849:
5818:
5763:
5755:
5703:
5632:
5418:
5399:
5230:
5060:
4998:
4979:
4659:
4598:
4535:
4481:
4422:
4357:
4231:
4124:
3934:
3638:
3348:
3330:
3165:
3034:
2976:
2891:
2730:
2418:
2357:
2085:
2035:
1927:
1725:
1424:
981:
832:
533:
520:
368:
334:
207:
95:
51:
5907:
Egerton, FN (2007). "Understanding food chains and food webs, 1700-1970".
5155:
4073:
3739:
7651:
7198:
7160:
7135:
7125:
7090:
7037:
7017:
6612:
6597:
6592:
6582:
6577:
6561:
6520:
6510:
6357:
6352:
6347:
6213:
5738:
5375:"Food-web structure and network theory: The role of connectance and size"
5051:
5014:
4589:
3756:
World Atlas of Biodiversity: Earth's Living Resources in the 21st Century
3205:
3188:
2268:
1448:
1033:
937:
734:
695:
607:
546:
524:
476:
426:
422:
398:
83:
5624:
4580:
3118:
Odum, H. T. (1988). "Self-organization, transformity, and information".
3026:
2994:
2933:
Haan, Nate L.; Bakker, Jonathan D.; Bowers, M. Deane (14 January 2021).
2841:
241:. The notion of a food web has a historical foothold in the writings of
8364:
7941:
7906:
7546:
7498:
7443:
7413:
7319:
7236:
7180:
7057:
7007:
6776:
6632:
6627:
6617:
6540:
6530:
6418:
6392:
6382:
5968:
5567:
5491:
4920:
4266:
4116:
4065:
3884:
3157:
2620:
2487:
2215:
1992:
836:
754:
706:
620:
528:
414:
402:
395:
388:
365:
354:
330:
326:
234:
211:
186:, provides energy. Autotrophs and heterotrophs come in all sizes, from
179:
175:
147:
71:
39:
6069:
5694:
5669:
5041:
5016:
4800:
Gönenç, I. Ethem; Koutitonsky, Vladimir G.; Rashleigh, Brenda (2007).
3148:
2721:
2547:
8269:
8223:
7951:
7395:
7365:
7165:
7120:
7095:
7032:
7022:
6997:
6989:
6934:
6865:
6781:
6710:
6653:
6622:
6602:
6587:
6535:
6525:
6505:
6500:
6487:
6397:
6387:
6372:
6362:
6322:
6283:
6223:"Collapse of terrestrial mammal food webs since the Late Pleistocene"
5540:"Plant-animal mutualistic networks: The architecture of biodiversity"
5448:
5222:
4803:
Assessment of the Fate and Effects of Toxic Agents on Water Resources
3926:
3018:
2077:
1787:
1645:
1268:
1026:
915:
783:
651:
488:
472:
384:
317:
Links in food webs map the feeding connections (who eats whom) in an
282:
171:
167:
151:
103:
79:
5960:
5483:
4912:
4727:
4171:
3595:
3364:"Secondary production, quantitative food webs, and trophic position"
3315:"Trophic and individual efficiencies of size-structured communities"
3299:
2612:
2479:
2410:
2348:
2323:
2206:
2197:
1011:
8324:
8253:
7784:
7612:
7203:
7150:
7105:
6607:
6495:
6140:
2744:
Schmitz, O. J. (2008). "Herbivory from individuals to ecosystems".
2670:
2538:
1386:
1272:
1265:
1037:
929:
912:
904:
886:
647:
626:
410:
30:
4244:
3617:
Raffaelli, D. (2002). "From Elton to mathematics and back again".
8314:
8121:
7991:
7986:
7613:
7561:
7221:
6866:
6747:
6433:
6413:
6337:
5073:
4886:"Road maps of interactions or grist for theoretical development?"
4095:
Warren, L. A.; Kauffman, M. E. (2003). "Microbial geoengineers".
3900:"Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs"
3587:
2993:
Haan, Nate L.; Bakker, Jonathan D.; Bowers, M. Deane (May 2018).
1554:(23). Copernicus Publications (published 2015-12-08): 7169–7183.
1445: – Representation of the biotic interactions in an ecosystem
1301:
1284:
1062:
730:
725:
717:
668:
662:
582:
552:
463:
Linkages connect to nodes in a food web, which are aggregates of
222:
107:
47:
5331:"SVD Entropy Reveals the High Complexity of Ecological Networks"
5329:
Strydom, Tanya; Dalla Riva, Giulio V.; Poisot, Timothée (2021).
4827:
Gil Nonato C. Santos; Alfonso C. Danac; Jorge P. Ocampo (2003).
2009:"Mineral weathering by bacteria: ecology, actors and mechanisms"
1535:
Nowak, M. E.; Beulig, F.; von Fischer, J.; Muhr, J.; Küsel, K.;
823:
815:
297:
6752:
6742:
6127:
Paine, RT (1966). "Food web complexity and species diversity".
6044:. Baltimore: The Williams & Wilkins Company and Associates.
3469:
Post, D. M. (1993). "The long and short of food-chain length".
2381:
606:, in which predators help to increase plant growth and prevent
301:
A simplified food web illustrating a three trophic food chain (
123:
5084:. Vol. 42. Burlington: Academic Press. pp. 139–170.
3809:"Modeling inverted biomass pyramids and refuges in ecosystems"
2006:
1257:
Arrows point to an organism being consumed by another organism
774:
how community structure, function and stability is determined.
2007:
Uroz, S.; Calvarus, C.; Turpault, M.; Frey-Klett, P. (2009).
1066:
840:
638:
630:
genera have been found to produce defensive compounds called
578:
505:
464:
349:
without the sun's energy or by capturing the sun's energy in
203:
191:
183:
43:
6161:
May RM (1973) Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems.
5186:
Neutel, A.; Heesterbeek, J. A. P.; de Ruiter, P. D. (2002).
2805:
1697:
Proulx, S. R.; Promislow, D. E. L.; Phillips, P. C. (2005).
1029:
eaten by robins are detritivores consuming decaying leaves.
986:- a web that reconstructs ecosystems from the fossil record.
971:- a group of nodes and all the connections of who eats whom.
894:
systems while N:P ratios are equal between the two systems.
273:
structure of food webs. Published examples that are used in
182:. Some of the organic matter eaten by heterotrophs, such as
5790:
5504:
4952:
4868:
10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[0898:NLRFQF]2.0.CO;2
4780:
10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[3275:IITTBT]2.0.CO;2
3992:
890:
799:
pyramid of energy. The terrestrial forest (summer) and the
406:
5185:
4799:
3863:
Pomeroy, L. R. (1970). "The strategy of mineral cycling".
3053:
2909:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 10, 72.
1534:
1247:
1004:, Arctic (or polar) food webs, terrestrial food webs, and
787:
Illustration of a range of ecological pyramids, including
78:. Ecologists can broadly define all life forms as either
6106:(2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 423.
5524:
10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[1018:daub]2.0.co;2
5315:
10.1641/0006-3568(2005)055[1065:ECAM]2.0.CO;2
4551:
4497:
4036:
H. A., Lowenstam (1981). "Minerals formed by organisms".
3897:
1965:"The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea"
1840:(5th ed.). Brooks/Cole, a part of Cengage Learning.
1517: – Type of aquatic ecosystem with flowing freshwater
1404: – Defensive feature of prey for selective advantage
127:
111:
5921:
10.1890/0012-9623(2007)88[50:UFCAFW]2.0.CO;2
4500:"Compilation and Network Analyses of Cambrian Food Webs"
1673:(4th ed.). New Jersey: Prentice-Hall. p. 559.
5373:
Dunne, J. A.; Williams, R. J.; Martinez, N. D. (2002).
5328:
3271:
Koijman, S. A. L. M.; Andersen, T.; Koo, B. W. (2004).
1696:
1595:. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer. p. 308.
1115:
1096:
1077:), for example, is converted into a connectance value:
74:
and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an
5831:
5188:"Stability in real food webs: Weak link in long loops"
4280:
Twiss, M. R.; Campbell, P. G. C.; Auclair, J. (1996).
3806:
2785:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 282.
2168:
1118:
1099:
1069:
grown under controlled environments in jars of water.
952:
There are different kinds or categories of food webs:
936:, and relatively few have been named or classified by
5832:
Shurin, J. B.; Gruner, D. S.; Hillebrand, H. (2006).
5372:
3807:
Wang, H.; Morrison, W.; Singh, A.; Weiss, H. (2009).
3312:
2586:"Food chain dynamics: The central theory of ecology?"
1890:
1086:
709:
production (P) and respiration (R), such that E=P+R.
5010:
5008:
4279:
3694:
Whitman, W. B.; Coleman, D. C.; Wieb, W. J. (1998).
3313:
Anderson, K. H.; Beyer, J. E.; Lundberg, P. (2009).
2746:
Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics
1475:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
1340:
90:, the position that they occupy in the food web. To
4698:Polis, G. A.; Anderson, W. B.; Hold, R. D. (1997).
1025:for deer, squirrels, and mice in the grazing web.
602:Another example of a multitrophic interaction is a
6279:. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
6221:Fricke, Evan C.; Hsieh, Chia; et al. (2022).
4853:
3752:
3693:
3270:
1962:
1153:
5596:Montoya, J. M.; Pimm, S. L.; Solé, R. V. (2006).
5005:
4697:
4186:
2904:
2778:
1759:Pimm, S. L.; Lawton, J. H.; Cohen, J. E. (1991).
1588:
433:, which is usually a larger predatory carnivore.
250:described nature as "one continued web of life".
8401:
5946:
5667:
4955:"Two degrees of separation in complex food webs"
4152:Geological Society, London, Special Publications
4139:
3189:"Energy flow in ecosystems: A historical review"
2992:
2932:
2162:
2048:
281:had identified patterns that are common to all.
6103:Nature's economy: A history of ecological ideas
5595:
5537:
5379:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
5121:"Environmental correlates of food chain length"
4959:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
4754:
4752:
4442:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
3955:
3783:The Science of Water: Concepts and Applications
3388:The Science of Water: Concepts and Applications
2905:Tscharntke, Teja; Hawkins, Bradford A. (2002).
2169:Tavares-Cromar, A. F.; Williams, D. D. (1996).
1758:
1500: – Underwater areas highly dense with kelp
4435:
4392:
4094:
2857:"When is a trophic cascade a trophic cascade?"
1891:Allesina, S.; Alonso, D.; Pascual, M. (2008).
1589:Cohen, J.E.; Briand, F.; Newman, C.M. (1990).
870:
553:Trophic dynamics and multitrophic interactions
7598:
6851:
6299:
5909:Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America
5890:Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America
5295:
4948:
4946:
4944:
4622:
4554:"Compartments revealed in food-web structure"
3746:
3660:
3658:
3656:
3266:
3264:
2779:Tscharntke, T.; Hawkins, B. A., eds. (2002).
2513:
2511:
2446:
2444:
2442:
2377:
2375:
1482: – Living and non-living things on Earth
1427: – Variety and variability of life forms
5670:"Food webs are built up with nested subwebs"
5291:
5289:
4749:
4618:
4616:
3094:
2772:
2650:"Food web complexity and community dynamics"
2294:
2292:
1439: – Dietary interactions between species
1154:{\displaystyle C={\cfrac {t_{L}}{S(S-1)/2}}}
6220:
6048:
5716:
5531:
5181:
5179:
5118:
4547:
4545:
4238:
4029:
3610:
3495:
3445:. Oxford University Press US. p. 510.
3418:. Oxford University Press US. p. 511.
2854:
2647:
1833:
1699:"Network thinking in ecology and evolution"
1623:
1410: – Predator at the top of a food chain
1176:
634:that are sequestered in the tissues of the
7819:Latitudinal gradients in species diversity
7605:
7591:
6858:
6844:
6306:
6292:
6093:
5999:
5997:
5498:
5430:
5428:
5368:
5366:
4941:
4879:
4877:
4758:
4693:
4691:
4493:
4491:
3988:
3986:
3653:
3561:
3559:
3557:
3306:
3261:
3095:Sterner, R. W.; Small, G. E.; Hood, J. M.
2577:
2508:
2439:
2372:
2042:
1761:"Food web patterns and their consequences"
1692:
1690:
1185:A simplified version of a food web in the
657:
134:, although a very small amount comes from
38:food web. The blue arrows show a complete
6076:
5874:
5857:
5808:
5784:
5737:
5710:
5693:
5668:Michio, K.; Kato, S.; Sakato, Y. (2010).
5598:"Ecological networks and their fragility"
5589:
5566:
5522:
5435:Capra, F. (2007). "Complexity and life".
5408:
5398:
5346:
5313:
5296:Proctor, J. D.; Larson, B. M. H. (2005).
5286:
5259:
5050:
5040:
4988:
4978:
4726:
4613:
4588:
4525:
4515:
4471:
4461:
4429:
4386:
4305:
4221:
3856:
3729:
3719:
3687:
3664:
3616:
3525:
3521:
3519:
3464:
3462:
3338:
3204:
3147:
3088:
3079:
2966:
2831:
2737:
2720:
2685:
2546:
2347:
2289:
2227:
2225:
2205:
2123:"The long and short of food chain length"
2049:Williams, R. J.; Martinez, N. D. (2000).
1991:
1884:
1863:
1861:
1660:
1567:
1488: – Complex living system in the soil
1043:
292:
7717:Predator–prey (Lotka–Volterra) equations
7356:Tritrophic interactions in plant defense
6054:
5984:Fisheries Investigation London Series II
5825:
5661:
5559:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095818
5455:
5176:
5112:
4707:Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics
4542:
4247:Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics
4088:
3865:Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics
3779:
3384:
2758:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.39.110707.173418
2583:
2517:
2450:
2315:
1893:"A general model for food web structure"
1829:
1827:
1825:
1823:
1821:
1819:
1754:
1752:
1750:
1748:
1746:
1744:
1742:
1666:
1492:Tritrophic interactions in plant defense
1287:were produced by Victor Summerhayes and
1246:
1180:
1010:
942:
822:
814:
782:
694:
661:
587:
504:
429:consumers from a base species up to the
296:
29:
7749:Random generalized Lotka–Volterra model
6099:
6031:
5994:
5906:
5793:"Ecological networks: beyond food webs"
5507:"Defining and unraveling biocomplexity"
5425:
5363:
5265:
5067:
4874:
4847:
4688:
4488:
4436:Ehrlich, P. R.; Pringle, R. M. (2008).
4273:
3983:
3891:
3862:
3554:
3378:
3355:
2988:
2986:
2848:
2743:
2691:
2641:
2453:"The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology"
2298:
1687:
1467: – Marine consumer-resource system
1242:
581:herbivores that utilize the same plant
387:from a productive base of self-feeding
14:
8402:
7557:Herbivore adaptations to plant defense
6313:
6082:
5461:
5017:"Complexity in quantitative food webs"
4623:Bormann, F. H.; Likens, G. E. (1967).
4323:"How many species are there on Earth?"
3949:
3800:
3516:
3459:
3213:
3180:
3111:
2928:
2926:
2321:
2222:
2114:
2051:"Simple rules yield complex food webs"
2000:
1956:
1858:
778:
27:Natural interconnection of food chains
7586:
6839:
6287:
6190:
6126:
6037:
6008:. London, UK.: Sidgwick and Jackson.
6003:
5981:
5434:
4883:
4314:
4035:
3753:Groombridge, B.; Jenkins, M. (2002).
3565:
3361:
1867:
1816:
1739:
1455:Food web of the San Francisco Estuary
922:
803:ecosystems exhibit inverted pyramids.
450:"Why you should care about parasites"
364:. A food web depicts a collection of
7572:Predator avoidance in schooling fish
5717:Montoya, J. M.; Solé, R. V. (2002).
5269:Ecology: From ecosystem to biosphere
3496:Odum, E. P.; Barrett, G. W. (2005).
3489:
3468:
3438:
3411:
3219:
3186:
3117:
2983:
2648:Polis, G. A.; Strong, D. R. (1996).
2231:
2120:
1834:Odum, E. P.; Barrett, G. W. (2005).
1592:Community Food Webs: Data and Theory
1528:
1421: – Superseded ecological theory
94:their bodies, grow, develop, and to
8022:Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
5880:
5719:"Small world patterns in food webs"
5298:"Ecology, complexity, and metaphor"
5272:. Science Publishers. p. 490.
4320:
3877:10.1146/annurev.es.01.110170.001131
2923:
1015:An illustration of a soil food web.
24:
7775:Ecological effects of biodiversity
6184:
5538:Bascompte, J.; Jordan, P. (2007).
5335:Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution
3696:"Prokaryotes: The unseen majority"
644:multitrophic interaction in plants
70:is the natural interconnection of
25:
8421:
7111:Generalist and specialist species
5119:Briand, F.; Cohen, J. E. (1987).
2855:Polis, G.A.; et al. (2000).
2301:"Ecologists build pyramids again"
1308:, which formed the basis for the
1255:'s 1923 food web of Bear Island (
1194:Food webs are extremely complex.
494:
261:(or mathematical representation)
166:that can be roughly divided into
7834:Occupancy–abundance relationship
6477:
6168:
6155:
6120:
5810:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01460.x
4719:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.28.1.289
4223:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2005.00019.x
4015:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00606.x
3241:10.4319/lo.1988.33.4_part_2.0910
3081:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00834.x
1385:
1371:
1357:
1343:
1310:trophic system of classification
969:Community (or connectedness) web
444:
239:trophic system of classification
7854:Relative abundance distribution
7567:Plant defense against herbivory
7434:Competitive exclusion principle
7146:Mesopredator release hypothesis
6022:
5975:
5940:
5927:
5900:
5322:
5078:Advances in Ecological Research
4820:
4793:
4259:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.20.1.71
3836:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.03.005
3773:
3528:Trends in Ecology and Evolution
3471:Trends in Ecology and Evolution
3432:
3405:
3047:
2907:Multitrophic Level Interactions
2898:
2864:Trends in Ecology and Evolution
2799:
2782:Multitrophic Level Interactions
2130:Trends in Ecology and Evolution
1706:Trends in Ecology and Evolution
1515:Trophic relationships in rivers
1498:Trophic ecology of kelp forests
1494: – Ecological interactions
1304:. Elton organized species into
1019:
303:producers-herbivores-carnivores
7439:Consumer–resource interactions
5937:. University of Chicago Press.
5726:Journal of Theoretical Biology
4833:. Rex Book Store. p. 58.
4415:10.1126/science.328.5976.307-c
2241:Theoretical Population Biology
1617:
1582:
1509:Trophic relationships in lakes
1437:Consumer–resource interactions
1135:
1123:
636:Taylor's checkerspot butterfly
164:consumer–resource interactions
126:, which mainly comes from the
13:
1:
8285:Biological data visualization
8112:Environmental niche modelling
7839:Population viability analysis
6041:Animal life and social growth
4350:10.1126/science.241.4872.1441
3665:Rickleffs, Robert E. (1996).
3483:10.1016/S0169-5347(02)02455-2
3140:10.1126/science.242.4882.1132
2884:10.1016/S0169-5347(00)01971-6
2142:10.1016/S0169-5347(02)02455-2
1522:
1414:Aquatic-terrestrial subsidies
1283:in 1913. Two food webs about
748:
646:is the transfer of defensive
7770:Density-dependent inhibition
4652:10.1126/science.155.3761.424
4517:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060102
3502:. Brooks Cole. p. 598.
2261:10.1016/0040-5809(79)90010-8
2234:"The structure of food webs"
865:second law of thermodynamics
575:arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
325:is an obsolete term that is
7:
8239:Liebig's law of the minimum
8074:Resource selection function
6965:Metabolic theory of ecology
5547:Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst
3780:Spellman, Frank R. (2008).
3671:University of Chicago Press
3385:Spellman, Frank R. (2008).
1473: – Biological food web
1336:
871:Material flux and recycling
527:, but some autotrophs (the
106:substances, including both
10:
8426:
8139:Niche apportionment models
7859:Relative species abundance
7063:Primary nutritional groups
6960:List of feeding behaviours
6174:Pimm SL (1982) Food Webs,
6163:Princeton University Press
4286:Limnology and Oceanography
3786:. CRC Press. p. 167.
3700:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
3548:10.1016/j.tree.2003.09.003
3391:. CRC Press. p. 165.
3368:Nature Education Knowledge
3101:Nature Education Knowledge
3097:"The conservation of mass"
2959:10.1038/s41598-020-80413-y
2299:Cousins, S. (1985-07-04).
1874:Nature Education Knowledge
1718:10.1016/j.tree.2005.04.004
1460:List of feeding behaviours
874:
752:
680:
674:
592:Multitrophic interaction:
498:
229:, which was the basis for
8388:
8320:Ecosystem based fisheries
8262:
8162:
8087:
7960:
7932:Interspecific competition
7897:
7824:Minimum viable population
7757:
7682:Maximum sustainable yield
7667:Intraspecific competition
7662:Effective population size
7625:
7542:Anti-predator adaptations
7527:
7406:
7333:
7290:
7212:
7179:
7076:
7053:Photosynthetic efficiency
6988:
6882:
6825:Category:Eating behaviors
6800:
6646:
6570:
6549:
6486:
6475:
6442:
6406:
6330:
6321:
6196:Food webs and niche space
5797:Journal of Animal Ecology
5266:Leveque, C., ed. (2003).
4806:. Springer. p. 279.
4307:10.4319/lo.1996.41.7.1425
4202:FEMS Microbiology Ecology
3568:Journal of Animal Ecology
2324:"Protecting biostructure"
2028:10.1016/j.tim.2009.05.004
1601:10.1007/978-3-642-83784-5
1511: – Type of ecosystem
595:Euphydryas editha taylori
443:
438:
267:consumer-resource systems
138:in wetlands, and mineral
8310:Ecological stoichiometry
8275:Alternative stable state
6277:NOAA Education Resources
5348:10.3389/fevo.2021.623141
2584:Fretwell, S. D. (1987).
2518:Hairston, N. G. (1993).
2451:Lindeman, R. L. (1942).
1667:Kormondy, E. J. (1996).
1402:Anti-predator adaptation
1177:Complexity and stability
948:grained trophic species.
911:. Bacteria that live in
795:pyramid of biomass, and
716:It is the case that the
567:'green-world' hypothesis
401:(i.e., the community of
8154:Ontogenetic niche shift
8017:Ideal free distribution
7927:Ecological facilitation
7677:Malthusian growth model
7647:Consumer-resource model
7504:Paradox of the plankton
7469:Energy systems language
7189:Chemoorganoheterotrophy
7156:Optimal foraging theory
7131:Heterotrophic nutrition
6805:Antipredator adaptation
6249:10.1126/science.abn4012
6129:The American Naturalist
5215:10.1126/science.1068326
5148:10.1126/science.3672136
4463:10.1073/pnas.0801911105
4109:10.1126/science.1072076
4058:10.1126/science.7008198
3721:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578
3631:10.1126/science.1072080
3499:Fundamentals of ecology
2833:10.1111/1365-2435.12181
2658:The American Naturalist
2527:The American Naturalist
1920:10.1126/science.1156269
1837:Fundamentals of Ecology
1569:10.5194/bg-12-7169-2015
1251:Victor Summerhayes and
658:Energy flow and biomass
353:, than they use during
8300:Ecological forecasting
8244:Marginal value theorem
8042:Landscape epidemiology
7977:Cross-boundary subsidy
7912:Biological interaction
7262:Microbial intelligence
6950:Green world hypothesis
6089:. London: John Murray.
6083:Darwin, C. R. (1881).
6058:Proc. Am. Philos. Soc.
5850:10.1098/rspb.2005.3377
5756:10.1006/jtbi.2001.2460
5400:10.1073/pnas.192407699
4980:10.1073/pnas.192448799
4759:O'Neil, R. V. (2001).
3439:Kent, Michael (2000).
3412:Kent, Michael (2000).
3331:10.1098/rspb.2008.0951
2016:Trends in Microbiology
1870:"Secondary production"
1327:theoretical ecologists
1260:
1237:cross-boundary subsidy
1214:Food webs are complex
1191:
1155:
1044:Quantitative food webs
1016:
949:
828:
820:
812:
701:
692:
672:
599:
515:
314:
306:
293:Taxonomy of a food web
63:
8305:Ecological humanities
8204:Ecological energetics
8149:Niche differentiation
8012:Habitat fragmentation
7780:Ecological extinction
7727:Small population size
7479:Feed conversion ratio
7459:Ecological succession
7391:San Francisco Estuary
7305:Ecological efficiency
7247:Microbial cooperation
6038:Allee, W. C. (1932).
6004:Elton, C. S. (1927).
5933:Shelford, V. (1913).
4884:Paine, R. T. (1988).
3667:The Economy of Nature
3362:Benke, A. C. (2011).
2178:Ecological Monographs
1868:Benke, A. C. (2010).
1379:Earth sciences portal
1250:
1224:scale free properties
1184:
1156:
1014:
1000:, aquatic food webs,
946:
826:
818:
786:
698:
687:
683:Ecological efficiency
677:Energy flow (ecology)
665:
591:
537:, which lives in hot
508:
309:
300:
98:, autotrophs produce
33:
8330:Evolutionary ecology
8295:Ecological footprint
8290:Ecological economics
8214:Ecological threshold
8209:Ecological indicator
8079:Source–sink dynamics
8032:Land change modeling
8027:Insular biogeography
7879:Species distribution
7618:Modelling ecosystems
7277:Microbial metabolism
7116:Intraguild predation
6905:Biogeochemical cycle
6871:Modelling ecosystems
6100:Worster, D. (1994).
3816:Ecological Modelling
3220:Mann, K. H. (1988).
3187:Odum, E. P. (1968).
2692:Hoekman, D. (2010).
2232:Pimm, S. L. (1979).
2121:Post, D. M. (2002).
1972:Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser
1431:Biogeochemical cycle
1243:History of food webs
1084:
907:in a process called
881:Many of the Earth's
791:pyramid of numbers,
362:secondary production
319:ecological community
76:ecological community
8380:Theoretical ecology
8355:Natural environment
8219:Ecosystem diversity
8189:Ecological collapse
8179:Bateman's principle
8134:Limiting similarity
8047:Landscape limnology
7869:Species homogeneity
7707:Population modeling
7702:Population dynamics
7519:Trophic state index
6820:Carnivorous protist
6674:Intraguild predator
6273:"Aquatic Food Webs"
6241:2022Sci...377.1008F
6235:(6609): 1008–1011.
5748:2002JThBi.214..405M
5686:2010Ecol...91.3123K
5625:10.1038/nature04927
5617:2006Natur.442..259M
5476:1988Ecol...69.1673P
5391:2002PNAS...9912917D
5385:(20): 12917–12922.
5207:2002Sci...296.1120N
5140:1987Sci...238..956B
5033:2009Ecol...90.1470B
4971:2002PNAS...9912913W
4965:(20): 12913–12916.
4905:1988Ecol...69.1648P
4644:1967Sci...155..424B
4581:10.1038/nature02115
4573:2003Natur.426..282K
4454:2008PNAS..10511579E
4448:(S1): 11579–11586.
4407:2010Sci...328..307B
4342:1988Sci...241.1441M
4336:(4872): 1441–1449.
4321:May, R. M. (1988).
4298:1996LimOc..41.1425T
4214:2006FEMME..55..311G
4164:2010GSLSP.336...31G
4103:(5609): 1027–1029.
4050:1981Sci...211.1126L
4044:(4487): 1126–1131.
4007:2004EcolL...7..584M
3919:2000Natur.408..578E
3828:2009EcMod.220.1376W
3712:1998PNAS...95.6578W
3625:(5570): 1035–1037.
3580:1980JAnEc..49..666P
3540:2003TEcoE..18..628W
3292:2004Ecol...85.1230K
3132:1988Sci...242.1132O
3126:(4882): 1132–1139.
3072:2005EcolL...8.1256L
3011:2018Ecol...99..399H
2951:2021NatSR..11..992H
2876:2000TEcoE..15..473P
2824:2014FuEco..28..375B
2713:2010Ecol...91.2819H
2605:1987Oikos..50..291F
2472:1942Ecol...23..399L
2403:2007Ecol...88..612T
2340:2007Natur.446...29M
2322:McCann, K. (2007).
2253:1979TPBio..16..144P
2190:1996EcoM...66...91T
2070:2000Natur.404..180W
1984:1983MEPS...10..257A
1912:2008Sci...320..658A
1780:1991Natur.350..669P
1670:Concepts of ecology
1638:1984Natur.307..264B
1560:2015BGeo...12.7169N
1480:Natural environment
1117:
1098:
1053:(type of species),
1051:species composition
1006:microbial food webs
851:Ecological pyramids
779:Ecological pyramids
743:ecological pyramids
559:Raymond L. Lindeman
162:different kinds of
8391:Outline of ecology
8340:Industrial ecology
8335:Functional ecology
8199:Ecological deficit
8144:Niche construction
8107:Ecosystem engineer
7884:Species–area curve
7805:Introduced species
7620:: Other components
7552:Deimatic behaviour
7454:Ecological network
7386:North Pacific Gyre
7371:hydrothermal vents
7310:Ecological pyramid
7257:Microbial food web
7068:Primary production
7013:Foundation species
6815:Carnivorous fungus
6465:Sexual cannibalism
6450:Animal cannibalism
6315:Feeding behaviours
6176:Chapman & Hall
5949:Journal of Ecology
5201:(550): 1120–1123.
4625:"Nutrient cycling"
3206:10.1093/icb/8.1.11
3193:American Zoologist
2939:Scientific Reports
2812:Functional Ecology
1993:10.3354/meps010257
1471:Microbial food web
1443:Ecological network
1351:Environment portal
1295:in 1923 and 1924.
1261:
1192:
1151:
1147:
1112:
1017:
950:
923:Kinds of food webs
845:aquatic ecosystems
829:
821:
813:
702:
673:
632:iridoid glycosides
600:
516:
307:
156:carnivorous plants
144:hydrothermal vents
120:chemical reactions
64:
8397:
8396:
8280:Balance of nature
8037:Landscape ecology
7922:Community ecology
7864:Species diversity
7800:Indicator species
7795:Gradient analysis
7672:Logistic function
7580:
7579:
7537:Animal coloration
7514:Trophic mutualism
7252:Microbial ecology
7043:Photoheterotrophs
7028:Myco-heterotrophy
6940:Ecosystem ecology
6925:Carrying capacity
6890:Abiotic component
6833:
6832:
6810:Carnivorous plant
6686:Aquatic predation
6473:
6472:
6455:Human cannibalism
6205:978-0-691-08202-8
6113:978-0-521-46834-3
6015:978-0-226-20639-4
5695:10.1890/09-2219.1
5680:(11): 3123–3130.
5611:(7100): 259–264.
5517:(12): 1018–1023.
5308:(12): 1065–1068.
5279:978-1-57808-294-0
5134:(4829): 956–960.
5091:978-0-12-381363-3
5042:10.1890/08-2207.1
4840:978-971-23-3563-1
4813:978-1-4020-5527-0
4774:(12): 3275–3284.
4638:(3761): 424–429.
4567:(6964): 282–285.
4401:(5976): 307–308.
3913:(6812): 578–580.
3822:(11): 1376–1382.
3793:978-1-4200-5544-3
3766:978-0-520-23668-4
3680:978-0-7167-3847-3
3509:978-0-534-42066-6
3452:978-0-19-914195-1
3425:978-0-19-914195-1
3398:978-1-4200-5544-3
3325:(1654): 109–114.
3066:(12): 1256–1263.
2916:978-0-511-06719-8
2792:978-0-521-79110-6
2722:10.1890/10-0260.1
2707:(10): 2819–2825.
2064:(6774): 180–183.
1906:(5876): 658–661.
1847:978-0-534-42066-6
1774:(6320): 669–674.
1680:978-0-13-478116-7
1632:(5948): 264–267.
1504:Trophic mutualism
1419:Balance of nature
1306:functional groups
1149:
1116:
1097:
1059:Microcosm studies
909:biomineralization
896:Mineral nutrients
461:
460:
455:Knowable Magazine
227:functional groups
136:bioelectrogenesis
86:, based on their
16:(Redirected from
8417:
8097:Ecological niche
8069:selection theory
7889:Umbrella species
7874:Species richness
7810:Invasive species
7790:Flagship species
7697:Population cycle
7692:Overexploitation
7657:Ecological yield
7607:
7600:
7593:
7584:
7583:
7489:Mesotrophic soil
7429:Climax community
7361:Marine food webs
7300:Biomagnification
7101:Chemoorganotroph
6955:Keystone species
6915:Biotic component
6860:
6853:
6846:
6837:
6836:
6679:Pursuit predator
6481:
6460:Self-cannibalism
6328:
6327:
6308:
6301:
6294:
6285:
6284:
6280:
6268:
6217:
6179:
6172:
6166:
6159:
6153:
6152:
6124:
6118:
6117:
6097:
6091:
6090:
6080:
6074:
6073:
6052:
6046:
6045:
6035:
6029:
6026:
6020:
6019:
6001:
5992:
5991:
5979:
5973:
5972:
5944:
5938:
5931:
5925:
5924:
5904:
5898:
5897:
5887:
5878:
5872:
5871:
5861:
5829:
5823:
5822:
5812:
5788:
5782:
5781:
5779:
5778:
5772:
5766:. Archived from
5741:
5739:cond-mat/0011195
5723:
5714:
5708:
5707:
5697:
5665:
5659:
5658:
5656:
5655:
5649:
5643:. Archived from
5602:
5593:
5587:
5586:
5584:
5583:
5577:
5571:. Archived from
5570:
5544:
5535:
5529:
5528:
5526:
5502:
5496:
5495:
5470:(6): 1673–1676.
5459:
5453:
5452:
5449:10.1002/sres.848
5432:
5423:
5422:
5412:
5402:
5370:
5361:
5360:
5350:
5326:
5320:
5319:
5317:
5293:
5284:
5283:
5263:
5257:
5256:
5254:
5253:
5247:
5241:. Archived from
5192:
5183:
5174:
5173:
5171:
5170:
5164:
5158:. Archived from
5125:
5116:
5110:
5109:
5107:
5106:
5100:
5094:. Archived from
5083:
5071:
5065:
5064:
5054:
5044:
5027:(6): 1470–1477.
5012:
5003:
5002:
4992:
4982:
4950:
4939:
4938:
4936:
4935:
4929:
4923:. Archived from
4899:(6): 1648–1654.
4890:
4881:
4872:
4871:
4851:
4845:
4844:
4824:
4818:
4817:
4797:
4791:
4790:
4788:
4782:. Archived from
4765:
4756:
4747:
4746:
4744:
4743:
4737:
4731:. Archived from
4730:
4704:
4695:
4686:
4685:
4683:
4682:
4676:
4670:. Archived from
4629:
4620:
4611:
4610:
4592:
4558:
4549:
4540:
4539:
4529:
4519:
4495:
4486:
4485:
4475:
4465:
4433:
4427:
4426:
4390:
4384:
4383:
4381:
4380:
4374:
4368:. Archived from
4327:
4318:
4312:
4311:
4309:
4292:(7): 1425–1437.
4277:
4271:
4270:
4242:
4236:
4235:
4225:
4199:
4190:
4184:
4183:
4143:
4137:
4136:
4092:
4086:
4085:
4033:
4027:
4026:
3990:
3981:
3980:
3978:
3977:
3971:
3964:
3953:
3947:
3946:
3927:10.1038/35046058
3904:
3895:
3889:
3888:
3860:
3854:
3853:
3851:
3850:
3844:
3838:. Archived from
3813:
3804:
3798:
3797:
3777:
3771:
3770:
3750:
3744:
3743:
3733:
3723:
3691:
3685:
3684:
3662:
3651:
3650:
3614:
3608:
3607:
3563:
3552:
3551:
3523:
3514:
3513:
3493:
3487:
3486:
3466:
3457:
3456:
3442:Advanced Biology
3436:
3430:
3429:
3415:Advanced Biology
3409:
3403:
3402:
3382:
3376:
3375:
3359:
3353:
3352:
3342:
3310:
3304:
3303:
3286:(5): 1230–1243.
3277:
3268:
3259:
3258:
3256:
3255:
3249:
3243:. Archived from
3229:Limnol. Oceanogr
3226:
3217:
3211:
3210:
3208:
3184:
3178:
3177:
3151:
3115:
3109:
3108:
3092:
3086:
3085:
3083:
3051:
3045:
3044:
3042:
3041:
3019:10.1002/ecy.2087
2990:
2981:
2980:
2970:
2930:
2921:
2920:
2902:
2896:
2895:
2861:
2852:
2846:
2845:
2835:
2803:
2797:
2796:
2776:
2770:
2769:
2741:
2735:
2734:
2724:
2698:
2689:
2683:
2682:
2654:
2645:
2639:
2638:
2636:
2635:
2629:
2623:. Archived from
2590:
2581:
2575:
2574:
2572:
2571:
2565:
2559:. Archived from
2550:
2524:
2515:
2506:
2505:
2503:
2502:
2496:
2490:. Archived from
2457:
2448:
2437:
2436:
2434:
2433:
2427:
2421:. Archived from
2388:
2379:
2370:
2369:
2351:
2319:
2313:
2312:
2296:
2287:
2286:
2284:
2283:
2277:
2271:. Archived from
2238:
2229:
2220:
2219:
2209:
2175:
2166:
2160:
2159:
2157:
2156:
2150:
2144:. Archived from
2127:
2118:
2112:
2111:
2109:
2108:
2102:
2096:. Archived from
2078:10.1038/35004572
2055:
2046:
2040:
2039:
2013:
2004:
1998:
1997:
1995:
1969:
1960:
1954:
1953:
1951:
1950:
1944:
1938:. Archived from
1897:
1888:
1882:
1881:
1865:
1856:
1855:
1850:. Archived from
1831:
1814:
1813:
1811:
1810:
1804:
1798:. Archived from
1788:10.1038/350669a0
1765:
1756:
1737:
1736:
1734:
1728:. Archived from
1703:
1694:
1685:
1684:
1664:
1658:
1657:
1646:10.1038/307264a0
1621:
1615:
1614:
1586:
1580:
1579:
1577:
1576:
1571:
1545:
1532:
1476:
1395:
1390:
1389:
1381:
1376:
1375:
1374:
1367:
1362:
1361:
1360:
1353:
1348:
1347:
1314:Raymond Lindeman
1277:Lorenzo Camerano
1228:keystone species
1168:species richness
1160:
1158:
1157:
1152:
1150:
1148:
1146:
1142:
1113:
1111:
1110:
1109:
1094:
998:marine food webs
900:nutrient cycling
860:secondary growth
616:chemical ecology
529:chemolithotrophs
448:
447:
436:
435:
287:species richness
231:Raymond Lindeman
60:great blue heron
21:
18:Trophic dynamics
8425:
8424:
8420:
8419:
8418:
8416:
8415:
8414:
8410:Trophic ecology
8400:
8399:
8398:
8393:
8384:
8370:Systems ecology
8258:
8229:Extinction debt
8194:Ecological debt
8184:Bioluminescence
8165:
8158:
8127:marine habitats
8102:Ecological trap
8083:
7963:
7956:
7899:
7893:
7849:Rapoport's rule
7844:Priority effect
7785:Endemic species
7753:
7712:Population size
7628:
7621:
7611:
7581:
7576:
7529:
7523:
7509:Trophic cascade
7419:Bioaccumulation
7402:
7329:
7286:
7208:
7175:
7072:
6984:
6945:Ecosystem model
6878:
6864:
6834:
6829:
6796:
6787:Surplus killing
6659:Ambush predator
6642:
6566:
6545:
6482:
6469:
6438:
6402:
6317:
6312:
6271:
6206:
6187:
6185:Further reading
6182:
6173:
6169:
6160:
6156:
6125:
6121:
6114:
6098:
6094:
6081:
6077:
6053:
6049:
6036:
6032:
6027:
6023:
6016:
6002:
5995:
5980:
5976:
5961:10.2307/2255864
5945:
5941:
5932:
5928:
5905:
5901:
5885:
5881:Egerton, F. N.
5879:
5875:
5838:Proc. R. Soc. B
5830:
5826:
5789:
5785:
5776:
5774:
5770:
5721:
5715:
5711:
5666:
5662:
5653:
5651:
5647:
5600:
5594:
5590:
5581:
5579:
5575:
5542:
5536:
5532:
5503:
5499:
5484:10.2307/1941145
5460:
5456:
5433:
5426:
5371:
5364:
5327:
5323:
5294:
5287:
5280:
5264:
5260:
5251:
5249:
5245:
5190:
5184:
5177:
5168:
5166:
5162:
5123:
5117:
5113:
5104:
5102:
5098:
5092:
5081:
5072:
5068:
5013:
5006:
4951:
4942:
4933:
4931:
4927:
4913:10.2307/1941141
4888:
4882:
4875:
4852:
4848:
4841:
4825:
4821:
4814:
4798:
4794:
4786:
4763:
4757:
4750:
4741:
4739:
4735:
4702:
4696:
4689:
4680:
4678:
4674:
4627:
4621:
4614:
4556:
4550:
4543:
4496:
4489:
4434:
4430:
4391:
4387:
4378:
4376:
4372:
4325:
4319:
4315:
4278:
4274:
4243:
4239:
4197:
4191:
4187:
4172:10.1144/SP336.3
4144:
4140:
4093:
4089:
4034:
4030:
3995:Ecology Letters
3991:
3984:
3975:
3973:
3969:
3962:
3954:
3950:
3902:
3896:
3892:
3861:
3857:
3848:
3846:
3842:
3811:
3805:
3801:
3794:
3778:
3774:
3767:
3751:
3747:
3706:(12): 6578–83.
3692:
3688:
3681:
3673:. p. 678.
3663:
3654:
3615:
3611:
3564:
3555:
3534:(12): 628–632.
3524:
3517:
3510:
3494:
3490:
3467:
3460:
3453:
3437:
3433:
3426:
3410:
3406:
3399:
3383:
3379:
3360:
3356:
3311:
3307:
3300:10.1890/02-0250
3275:
3269:
3262:
3253:
3251:
3247:
3224:
3218:
3214:
3185:
3181:
3116:
3112:
3093:
3089:
3060:Ecology Letters
3052:
3048:
3039:
3037:
2991:
2984:
2931:
2924:
2917:
2903:
2899:
2859:
2853:
2849:
2804:
2800:
2793:
2777:
2773:
2742:
2738:
2696:
2690:
2686:
2652:
2646:
2642:
2633:
2631:
2627:
2613:10.2307/3565489
2588:
2582:
2578:
2569:
2567:
2563:
2522:
2516:
2509:
2500:
2498:
2494:
2480:10.2307/1930126
2455:
2449:
2440:
2431:
2429:
2425:
2411:10.1890/05-1454
2386:
2380:
2373:
2349:10.1038/446029a
2320:
2316:
2297:
2290:
2281:
2279:
2275:
2236:
2230:
2223:
2198:10.2307/2963482
2173:
2167:
2163:
2154:
2152:
2148:
2125:
2119:
2115:
2106:
2104:
2100:
2053:
2047:
2043:
2011:
2005:
2001:
1967:
1961:
1957:
1948:
1946:
1942:
1895:
1889:
1885:
1866:
1859:
1848:
1832:
1817:
1808:
1806:
1802:
1763:
1757:
1740:
1732:
1701:
1695:
1688:
1681:
1665:
1661:
1622:
1618:
1611:
1587:
1583:
1574:
1572:
1543:
1537:Trumbore, S. E.
1533:
1529:
1525:
1520:
1474:
1465:Marine food web
1391:
1384:
1377:
1372:
1370:
1363:
1358:
1356:
1349:
1342:
1339:
1281:Victor Shelford
1245:
1179:
1138:
1119:
1114:
1105:
1101:
1100:
1095:
1093:
1085:
1082:
1081:
1076:
1046:
1022:
982:Paleoecological
975:Energy flow web
925:
879:
873:
801:English Channel
781:
757:
751:
693:
685:
679:
660:
604:trophic cascade
555:
503:
497:
469:trophic species
465:biological taxa
445:
439:External videos
371:consumers that
345:energy, either
315:
295:
255:trophic species
237:organisms in a
140:electron donors
130:and largely by
56:largemouth bass
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
8423:
8413:
8412:
8395:
8394:
8389:
8386:
8385:
8383:
8382:
8377:
8372:
8367:
8362:
8357:
8352:
8350:Microecosystem
8347:
8342:
8337:
8332:
8327:
8322:
8317:
8312:
8307:
8302:
8297:
8292:
8287:
8282:
8277:
8272:
8266:
8264:
8260:
8259:
8257:
8256:
8251:
8249:Thorson's rule
8246:
8241:
8236:
8231:
8226:
8221:
8216:
8211:
8206:
8201:
8196:
8191:
8186:
8181:
8176:
8174:Assembly rules
8170:
8168:
8160:
8159:
8157:
8156:
8151:
8146:
8141:
8136:
8131:
8130:
8129:
8119:
8114:
8109:
8104:
8099:
8093:
8091:
8085:
8084:
8082:
8081:
8076:
8071:
8059:
8057:Patch dynamics
8054:
8052:Metapopulation
8049:
8044:
8039:
8034:
8029:
8024:
8019:
8014:
8009:
8004:
7999:
7994:
7989:
7984:
7979:
7974:
7968:
7966:
7958:
7957:
7955:
7954:
7949:
7947:Storage effect
7944:
7939:
7934:
7929:
7924:
7919:
7914:
7909:
7903:
7901:
7895:
7894:
7892:
7891:
7886:
7881:
7876:
7871:
7866:
7861:
7856:
7851:
7846:
7841:
7836:
7831:
7829:Neutral theory
7826:
7821:
7816:
7814:Native species
7807:
7802:
7797:
7792:
7787:
7782:
7777:
7772:
7767:
7761:
7759:
7755:
7754:
7752:
7751:
7746:
7745:
7744:
7739:
7729:
7724:
7719:
7714:
7709:
7704:
7699:
7694:
7689:
7687:Overpopulation
7684:
7679:
7674:
7669:
7664:
7659:
7654:
7649:
7644:
7639:
7633:
7631:
7623:
7622:
7610:
7609:
7602:
7595:
7587:
7578:
7577:
7575:
7574:
7569:
7564:
7559:
7554:
7549:
7544:
7539:
7533:
7531:
7525:
7524:
7522:
7521:
7516:
7511:
7506:
7501:
7496:
7494:Nutrient cycle
7491:
7486:
7484:Feeding frenzy
7481:
7476:
7471:
7466:
7464:Energy quality
7461:
7456:
7451:
7446:
7441:
7436:
7431:
7426:
7424:Cascade effect
7421:
7416:
7410:
7408:
7404:
7403:
7401:
7400:
7399:
7398:
7393:
7388:
7383:
7378:
7373:
7368:
7358:
7353:
7348:
7343:
7337:
7335:
7331:
7330:
7328:
7327:
7322:
7317:
7312:
7307:
7302:
7296:
7294:
7288:
7287:
7285:
7284:
7279:
7274:
7269:
7267:Microbial loop
7264:
7259:
7254:
7249:
7244:
7239:
7234:
7232:Lithoautotroph
7229:
7224:
7218:
7216:
7214:Microorganisms
7210:
7209:
7207:
7206:
7201:
7196:
7191:
7185:
7183:
7177:
7176:
7174:
7173:
7171:Prey switching
7168:
7163:
7158:
7153:
7148:
7143:
7138:
7133:
7128:
7123:
7118:
7113:
7108:
7103:
7098:
7093:
7088:
7082:
7080:
7074:
7073:
7071:
7070:
7065:
7060:
7055:
7050:
7048:Photosynthesis
7045:
7040:
7035:
7030:
7025:
7020:
7015:
7010:
7005:
7003:Chemosynthesis
7000:
6994:
6992:
6986:
6985:
6983:
6982:
6977:
6972:
6967:
6962:
6957:
6952:
6947:
6942:
6937:
6932:
6927:
6922:
6917:
6912:
6907:
6902:
6897:
6895:Abiotic stress
6892:
6886:
6884:
6880:
6879:
6863:
6862:
6855:
6848:
6840:
6831:
6830:
6828:
6827:
6822:
6817:
6812:
6807:
6801:
6798:
6797:
6795:
6794:
6789:
6784:
6779:
6774:
6769:
6764:
6762:Hypercarnivore
6759:
6758:
6757:
6756:
6755:
6745:
6738:Cattle feeding
6735:
6730:
6729:
6728:
6723:
6721:Feeding frenzy
6718:
6713:
6708:
6706:Suction feeder
6703:
6698:
6693:
6683:
6682:
6681:
6676:
6671:
6666:
6661:
6650:
6648:
6644:
6643:
6641:
6640:
6635:
6630:
6625:
6620:
6615:
6610:
6605:
6600:
6595:
6590:
6585:
6580:
6574:
6572:
6568:
6567:
6565:
6564:
6559:
6553:
6551:
6547:
6546:
6544:
6543:
6538:
6533:
6528:
6523:
6518:
6516:Seed predation
6513:
6508:
6503:
6498:
6492:
6490:
6484:
6483:
6476:
6474:
6471:
6470:
6468:
6467:
6462:
6457:
6452:
6446:
6444:
6440:
6439:
6437:
6436:
6431:
6426:
6421:
6416:
6410:
6408:
6404:
6403:
6401:
6400:
6395:
6390:
6385:
6380:
6375:
6370:
6365:
6360:
6355:
6350:
6345:
6340:
6334:
6332:
6325:
6319:
6318:
6311:
6310:
6303:
6296:
6288:
6282:
6281:
6269:
6218:
6204:
6192:Cohen, Joel E.
6186:
6183:
6181:
6180:
6167:
6154:
6141:10.1086/282400
6135:(910): 65–75.
6119:
6112:
6092:
6075:
6064:(2): 235–241.
6047:
6030:
6021:
6014:
6006:Animal Ecology
5993:
5974:
5955:(2): 214–286.
5939:
5926:
5899:
5873:
5824:
5803:(1): 253–269.
5783:
5732:(3): 405–412.
5709:
5660:
5588:
5530:
5497:
5454:
5443:(5): 475–479.
5424:
5362:
5321:
5285:
5278:
5258:
5175:
5111:
5090:
5066:
5004:
4940:
4873:
4862:(3): 898–903.
4846:
4839:
4819:
4812:
4792:
4789:on 2012-04-25.
4748:
4687:
4612:
4541:
4487:
4428:
4385:
4313:
4272:
4237:
4208:(2): 311–321.
4185:
4138:
4087:
4028:
4001:(7): 584–600.
3982:
3948:
3890:
3855:
3799:
3792:
3772:
3765:
3745:
3686:
3679:
3652:
3609:
3574:(3): 666–685.
3553:
3515:
3508:
3488:
3477:(6): 269–277.
3458:
3451:
3431:
3424:
3404:
3397:
3377:
3354:
3305:
3260:
3235:(2): 910–930.
3212:
3179:
3110:
3087:
3046:
3005:(2): 399–410.
2982:
2922:
2915:
2897:
2847:
2818:(2): 375–385.
2798:
2791:
2771:
2736:
2684:
2671:10.1086/285880
2665:(5): 813–846.
2640:
2599:(3): 291–301.
2576:
2539:10.1086/285546
2533:(3): 379–411.
2507:
2466:(4): 399–417.
2438:
2397:(3): 612–617.
2371:
2314:
2288:
2247:(2): 144–158.
2221:
2161:
2136:(6): 269–277.
2113:
2041:
2022:(8): 378–387.
1999:
1955:
1883:
1857:
1854:on 2011-08-20.
1846:
1815:
1738:
1735:on 2011-08-15.
1712:(6): 345–353.
1686:
1679:
1659:
1616:
1609:
1581:
1548:Biogeosciences
1526:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1518:
1512:
1506:
1501:
1495:
1489:
1483:
1477:
1468:
1462:
1457:
1452:
1446:
1440:
1434:
1428:
1422:
1416:
1411:
1405:
1398:
1397:
1396:
1393:Biology portal
1382:
1368:
1365:Ecology portal
1354:
1338:
1335:
1331:Sir Robert May
1318:Charles Darwin
1271:scholar named
1244:
1241:
1187:Gulf of Naples
1178:
1175:
1163:
1162:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1134:
1131:
1128:
1125:
1122:
1108:
1104:
1092:
1089:
1074:
1045:
1042:
1021:
1018:
1002:soil food webs
994:
993:
990:Functional web
987:
978:
972:
966:
960:
924:
921:
877:Nutrient cycle
875:Main article:
872:
869:
809:Abbreviations:
780:
777:
776:
775:
772:
769:
753:Main article:
750:
747:
686:
675:Main article:
659:
656:
571:trophic levels
554:
551:
539:sulfur springs
499:Main article:
496:
495:Trophic levels
493:
459:
458:
452:, 12.14.2018,
441:
440:
381:flow of energy
351:photosynthesis
308:
294:
291:
279:network theory
265:of trophic or
243:Charles Darwin
200:giant redwoods
132:photosynthesis
116:carbon dioxide
100:organic matter
88:trophic levels
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
8422:
8411:
8408:
8407:
8405:
8392:
8387:
8381:
8378:
8376:
8375:Urban ecology
8373:
8371:
8368:
8366:
8363:
8361:
8358:
8356:
8353:
8351:
8348:
8346:
8343:
8341:
8338:
8336:
8333:
8331:
8328:
8326:
8323:
8321:
8318:
8316:
8313:
8311:
8308:
8306:
8303:
8301:
8298:
8296:
8293:
8291:
8288:
8286:
8283:
8281:
8278:
8276:
8273:
8271:
8268:
8267:
8265:
8261:
8255:
8252:
8250:
8247:
8245:
8242:
8240:
8237:
8235:
8234:Kleiber's law
8232:
8230:
8227:
8225:
8222:
8220:
8217:
8215:
8212:
8210:
8207:
8205:
8202:
8200:
8197:
8195:
8192:
8190:
8187:
8185:
8182:
8180:
8177:
8175:
8172:
8171:
8169:
8167:
8161:
8155:
8152:
8150:
8147:
8145:
8142:
8140:
8137:
8135:
8132:
8128:
8125:
8124:
8123:
8120:
8118:
8115:
8113:
8110:
8108:
8105:
8103:
8100:
8098:
8095:
8094:
8092:
8090:
8086:
8080:
8077:
8075:
8072:
8070:
8068:
8064:
8060:
8058:
8055:
8053:
8050:
8048:
8045:
8043:
8040:
8038:
8035:
8033:
8030:
8028:
8025:
8023:
8020:
8018:
8015:
8013:
8010:
8008:
8007:Foster's rule
8005:
8003:
8000:
7998:
7995:
7993:
7990:
7988:
7985:
7983:
7980:
7978:
7975:
7973:
7970:
7969:
7967:
7965:
7959:
7953:
7950:
7948:
7945:
7943:
7940:
7938:
7935:
7933:
7930:
7928:
7925:
7923:
7920:
7918:
7915:
7913:
7910:
7908:
7905:
7904:
7902:
7896:
7890:
7887:
7885:
7882:
7880:
7877:
7875:
7872:
7870:
7867:
7865:
7862:
7860:
7857:
7855:
7852:
7850:
7847:
7845:
7842:
7840:
7837:
7835:
7832:
7830:
7827:
7825:
7822:
7820:
7817:
7815:
7811:
7808:
7806:
7803:
7801:
7798:
7796:
7793:
7791:
7788:
7786:
7783:
7781:
7778:
7776:
7773:
7771:
7768:
7766:
7763:
7762:
7760:
7756:
7750:
7747:
7743:
7740:
7738:
7735:
7734:
7733:
7730:
7728:
7725:
7723:
7720:
7718:
7715:
7713:
7710:
7708:
7705:
7703:
7700:
7698:
7695:
7693:
7690:
7688:
7685:
7683:
7680:
7678:
7675:
7673:
7670:
7668:
7665:
7663:
7660:
7658:
7655:
7653:
7650:
7648:
7645:
7643:
7640:
7638:
7635:
7634:
7632:
7630:
7624:
7619:
7615:
7608:
7603:
7601:
7596:
7594:
7589:
7588:
7585:
7573:
7570:
7568:
7565:
7563:
7560:
7558:
7555:
7553:
7550:
7548:
7545:
7543:
7540:
7538:
7535:
7534:
7532:
7526:
7520:
7517:
7515:
7512:
7510:
7507:
7505:
7502:
7500:
7497:
7495:
7492:
7490:
7487:
7485:
7482:
7480:
7477:
7475:
7472:
7470:
7467:
7465:
7462:
7460:
7457:
7455:
7452:
7450:
7447:
7445:
7442:
7440:
7437:
7435:
7432:
7430:
7427:
7425:
7422:
7420:
7417:
7415:
7412:
7411:
7409:
7405:
7397:
7394:
7392:
7389:
7387:
7384:
7382:
7379:
7377:
7374:
7372:
7369:
7367:
7364:
7363:
7362:
7359:
7357:
7354:
7352:
7349:
7347:
7344:
7342:
7339:
7338:
7336:
7332:
7326:
7325:Trophic level
7323:
7321:
7318:
7316:
7313:
7311:
7308:
7306:
7303:
7301:
7298:
7297:
7295:
7293:
7289:
7283:
7282:Phage ecology
7280:
7278:
7275:
7273:
7272:Microbial mat
7270:
7268:
7265:
7263:
7260:
7258:
7255:
7253:
7250:
7248:
7245:
7243:
7240:
7238:
7235:
7233:
7230:
7228:
7227:Bacteriophage
7225:
7223:
7220:
7219:
7217:
7215:
7211:
7205:
7202:
7200:
7197:
7195:
7194:Decomposition
7192:
7190:
7187:
7186:
7184:
7182:
7178:
7172:
7169:
7167:
7164:
7162:
7159:
7157:
7154:
7152:
7149:
7147:
7144:
7142:
7141:Mesopredators
7139:
7137:
7134:
7132:
7129:
7127:
7124:
7122:
7119:
7117:
7114:
7112:
7109:
7107:
7104:
7102:
7099:
7097:
7094:
7092:
7089:
7087:
7086:Apex predator
7084:
7083:
7081:
7079:
7075:
7069:
7066:
7064:
7061:
7059:
7056:
7054:
7051:
7049:
7046:
7044:
7041:
7039:
7036:
7034:
7031:
7029:
7026:
7024:
7021:
7019:
7016:
7014:
7011:
7009:
7006:
7004:
7001:
6999:
6996:
6995:
6993:
6991:
6987:
6981:
6978:
6976:
6973:
6971:
6968:
6966:
6963:
6961:
6958:
6956:
6953:
6951:
6948:
6946:
6943:
6941:
6938:
6936:
6933:
6931:
6928:
6926:
6923:
6921:
6920:Biotic stress
6918:
6916:
6913:
6911:
6908:
6906:
6903:
6901:
6898:
6896:
6893:
6891:
6888:
6887:
6885:
6881:
6876:
6872:
6868:
6861:
6856:
6854:
6849:
6847:
6842:
6841:
6838:
6826:
6823:
6821:
6818:
6816:
6813:
6811:
6808:
6806:
6803:
6802:
6799:
6793:
6790:
6788:
6785:
6783:
6780:
6778:
6775:
6773:
6772:Mesocarnivore
6770:
6768:
6767:Hypocarnivore
6765:
6763:
6760:
6754:
6751:
6750:
6749:
6746:
6744:
6741:
6740:
6739:
6736:
6734:
6731:
6727:
6726:Filter feeder
6724:
6722:
6719:
6717:
6716:Bottom feeder
6714:
6712:
6709:
6707:
6704:
6702:
6699:
6697:
6694:
6692:
6689:
6688:
6687:
6684:
6680:
6677:
6675:
6672:
6670:
6667:
6665:
6664:Apex predator
6662:
6660:
6657:
6656:
6655:
6652:
6651:
6649:
6645:
6639:
6636:
6634:
6631:
6629:
6626:
6624:
6621:
6619:
6616:
6614:
6611:
6609:
6606:
6604:
6601:
6599:
6596:
6594:
6591:
6589:
6586:
6584:
6581:
6579:
6576:
6575:
6573:
6569:
6563:
6560:
6558:
6555:
6554:
6552:
6548:
6542:
6539:
6537:
6534:
6532:
6529:
6527:
6524:
6522:
6519:
6517:
6514:
6512:
6509:
6507:
6504:
6502:
6499:
6497:
6494:
6493:
6491:
6489:
6485:
6480:
6466:
6463:
6461:
6458:
6456:
6453:
6451:
6448:
6447:
6445:
6443:cannibalistic
6441:
6435:
6432:
6430:
6429:Breastfeeding
6427:
6425:
6424:Placentophagy
6422:
6420:
6417:
6415:
6412:
6411:
6409:
6405:
6399:
6396:
6394:
6391:
6389:
6386:
6384:
6381:
6379:
6376:
6374:
6371:
6369:
6366:
6364:
6361:
6359:
6356:
6354:
6351:
6349:
6346:
6344:
6343:Egg predation
6341:
6339:
6336:
6335:
6333:
6329:
6326:
6324:
6320:
6316:
6309:
6304:
6302:
6297:
6295:
6290:
6289:
6286:
6278:
6274:
6270:
6266:
6262:
6258:
6254:
6250:
6246:
6242:
6238:
6234:
6230:
6229:
6224:
6219:
6215:
6211:
6207:
6201:
6197:
6193:
6189:
6188:
6177:
6171:
6164:
6158:
6150:
6146:
6142:
6138:
6134:
6130:
6123:
6115:
6109:
6105:
6104:
6096:
6088:
6087:
6079:
6071:
6067:
6063:
6060:
6059:
6051:
6043:
6042:
6034:
6025:
6017:
6011:
6007:
6000:
5998:
5989:
5985:
5978:
5970:
5966:
5962:
5958:
5954:
5950:
5943:
5936:
5930:
5922:
5918:
5914:
5910:
5903:
5896:(2): 142–146.
5895:
5891:
5884:
5877:
5869:
5865:
5860:
5855:
5851:
5847:
5844:(1582): 1–9.
5843:
5839:
5835:
5828:
5820:
5816:
5811:
5806:
5802:
5798:
5794:
5787:
5773:on 2011-09-05
5769:
5765:
5761:
5757:
5753:
5749:
5745:
5740:
5735:
5731:
5727:
5720:
5713:
5705:
5701:
5696:
5691:
5687:
5683:
5679:
5675:
5671:
5664:
5650:on 2010-07-06
5646:
5642:
5638:
5634:
5630:
5626:
5622:
5618:
5614:
5610:
5606:
5599:
5592:
5578:on 2009-10-25
5574:
5569:
5564:
5560:
5556:
5552:
5548:
5541:
5534:
5525:
5520:
5516:
5512:
5508:
5501:
5493:
5489:
5485:
5481:
5477:
5473:
5469:
5465:
5458:
5450:
5446:
5442:
5438:
5431:
5429:
5420:
5416:
5411:
5406:
5401:
5396:
5392:
5388:
5384:
5380:
5376:
5369:
5367:
5358:
5354:
5349:
5344:
5340:
5336:
5332:
5325:
5316:
5311:
5307:
5303:
5299:
5292:
5290:
5281:
5275:
5271:
5270:
5262:
5248:on 2011-09-28
5244:
5240:
5236:
5232:
5228:
5224:
5220:
5216:
5212:
5208:
5204:
5200:
5196:
5189:
5182:
5180:
5165:on 2012-04-25
5161:
5157:
5153:
5149:
5145:
5141:
5137:
5133:
5129:
5122:
5115:
5101:on 2011-07-24
5097:
5093:
5087:
5080:
5079:
5070:
5062:
5058:
5053:
5052:1969.1/178777
5048:
5043:
5038:
5034:
5030:
5026:
5022:
5018:
5011:
5009:
5000:
4996:
4991:
4986:
4981:
4976:
4972:
4968:
4964:
4960:
4956:
4949:
4947:
4945:
4930:on 2011-07-28
4926:
4922:
4918:
4914:
4910:
4906:
4902:
4898:
4894:
4887:
4880:
4878:
4869:
4865:
4861:
4857:
4850:
4842:
4836:
4832:
4831:
4823:
4815:
4809:
4805:
4804:
4796:
4785:
4781:
4777:
4773:
4769:
4762:
4755:
4753:
4738:on 2011-10-02
4734:
4729:
4724:
4720:
4716:
4712:
4708:
4701:
4694:
4692:
4677:on 2011-09-27
4673:
4669:
4665:
4661:
4657:
4653:
4649:
4645:
4641:
4637:
4633:
4626:
4619:
4617:
4608:
4604:
4600:
4596:
4591:
4590:2027.42/62960
4586:
4582:
4578:
4574:
4570:
4566:
4562:
4555:
4548:
4546:
4537:
4533:
4528:
4523:
4518:
4513:
4509:
4505:
4501:
4494:
4492:
4483:
4479:
4474:
4469:
4464:
4459:
4455:
4451:
4447:
4443:
4439:
4432:
4424:
4420:
4416:
4412:
4408:
4404:
4400:
4396:
4389:
4375:on 2013-05-11
4371:
4367:
4363:
4359:
4355:
4351:
4347:
4343:
4339:
4335:
4331:
4324:
4317:
4308:
4303:
4299:
4295:
4291:
4287:
4283:
4276:
4268:
4264:
4260:
4256:
4252:
4248:
4241:
4233:
4229:
4224:
4219:
4215:
4211:
4207:
4203:
4196:
4189:
4181:
4177:
4173:
4169:
4165:
4161:
4157:
4153:
4149:
4142:
4134:
4130:
4126:
4122:
4118:
4114:
4110:
4106:
4102:
4098:
4091:
4083:
4079:
4075:
4071:
4067:
4063:
4059:
4055:
4051:
4047:
4043:
4039:
4032:
4024:
4020:
4016:
4012:
4008:
4004:
4000:
3996:
3989:
3987:
3972:on 2016-03-04
3968:
3961:
3960:
3952:
3944:
3940:
3936:
3932:
3928:
3924:
3920:
3916:
3912:
3908:
3901:
3894:
3886:
3882:
3878:
3874:
3870:
3866:
3859:
3845:on 2011-10-07
3841:
3837:
3833:
3829:
3825:
3821:
3817:
3810:
3803:
3795:
3789:
3785:
3784:
3776:
3768:
3762:
3758:
3757:
3749:
3741:
3737:
3732:
3727:
3722:
3717:
3713:
3709:
3705:
3701:
3697:
3690:
3682:
3676:
3672:
3668:
3661:
3659:
3657:
3648:
3644:
3640:
3636:
3632:
3628:
3624:
3620:
3613:
3605:
3601:
3597:
3593:
3589:
3585:
3581:
3577:
3573:
3569:
3562:
3560:
3558:
3549:
3545:
3541:
3537:
3533:
3529:
3522:
3520:
3511:
3505:
3501:
3500:
3492:
3484:
3480:
3476:
3472:
3465:
3463:
3454:
3448:
3444:
3443:
3435:
3427:
3421:
3417:
3416:
3408:
3400:
3394:
3390:
3389:
3381:
3373:
3369:
3365:
3358:
3350:
3346:
3341:
3336:
3332:
3328:
3324:
3320:
3319:Proc Biol Sci
3316:
3309:
3301:
3297:
3293:
3289:
3285:
3281:
3274:
3267:
3265:
3250:on 2012-04-25
3246:
3242:
3238:
3234:
3230:
3223:
3216:
3207:
3202:
3198:
3194:
3190:
3183:
3175:
3171:
3167:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3150:
3145:
3141:
3137:
3133:
3129:
3125:
3121:
3114:
3106:
3102:
3098:
3091:
3082:
3077:
3073:
3069:
3065:
3061:
3057:
3050:
3036:
3032:
3028:
3024:
3020:
3016:
3012:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2996:
2989:
2987:
2978:
2974:
2969:
2964:
2960:
2956:
2952:
2948:
2944:
2940:
2936:
2929:
2927:
2918:
2912:
2908:
2901:
2893:
2889:
2885:
2881:
2877:
2873:
2870:(11): 473–5.
2869:
2865:
2858:
2851:
2843:
2839:
2834:
2829:
2825:
2821:
2817:
2813:
2809:
2802:
2794:
2788:
2784:
2783:
2775:
2767:
2763:
2759:
2755:
2751:
2747:
2740:
2732:
2728:
2723:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2706:
2702:
2695:
2688:
2680:
2676:
2672:
2668:
2664:
2660:
2659:
2651:
2644:
2630:on 2011-07-28
2626:
2622:
2618:
2614:
2610:
2606:
2602:
2598:
2594:
2587:
2580:
2566:on 2011-07-20
2562:
2558:
2554:
2549:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2521:
2514:
2512:
2497:on 2017-03-29
2493:
2489:
2485:
2481:
2477:
2473:
2469:
2465:
2461:
2454:
2447:
2445:
2443:
2428:on 2011-08-15
2424:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2404:
2400:
2396:
2392:
2385:
2378:
2376:
2367:
2363:
2359:
2355:
2350:
2345:
2341:
2337:
2333:
2329:
2325:
2318:
2310:
2306:
2305:New Scientist
2302:
2295:
2293:
2278:on 2011-09-27
2274:
2270:
2266:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2242:
2235:
2228:
2226:
2217:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2184:(1): 91–113.
2183:
2179:
2172:
2165:
2151:on 2011-07-28
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2124:
2117:
2103:on 2012-03-15
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2052:
2045:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2017:
2010:
2003:
1994:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1973:
1966:
1959:
1945:on 2011-09-28
1941:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1925:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1894:
1887:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1864:
1862:
1853:
1849:
1843:
1839:
1838:
1830:
1828:
1826:
1824:
1822:
1820:
1805:on 2010-06-10
1801:
1797:
1793:
1789:
1785:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1762:
1755:
1753:
1751:
1749:
1747:
1745:
1743:
1731:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1700:
1693:
1691:
1682:
1676:
1672:
1671:
1663:
1655:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1620:
1612:
1610:9783642837869
1606:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1593:
1585:
1570:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1542:
1538:
1531:
1527:
1516:
1513:
1510:
1507:
1505:
1502:
1499:
1496:
1493:
1490:
1487:
1486:Soil food web
1484:
1481:
1478:
1472:
1469:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1450:
1447:
1444:
1441:
1438:
1435:
1432:
1429:
1426:
1423:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1412:
1409:
1408:Apex predator
1406:
1403:
1400:
1399:
1394:
1388:
1383:
1380:
1369:
1366:
1355:
1352:
1346:
1341:
1334:
1332:
1328:
1322:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1300:the field of
1298:
1297:Charles Elton
1294:
1293:Alister Hardy
1290:
1289:Charles Elton
1286:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1267:
1258:
1254:
1253:Charles Elton
1249:
1240:
1238:
1232:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1212:
1208:
1206:
1205:biocomplexity
1200:
1197:
1188:
1183:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1143:
1139:
1132:
1129:
1126:
1120:
1106:
1102:
1090:
1087:
1080:
1079:
1078:
1070:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1041:
1039:
1035:
1030:
1028:
1013:
1009:
1007:
1003:
999:
991:
988:
985:
983:
979:
976:
973:
970:
967:
964:
961:
958:
955:
954:
953:
945:
941:
939:
935:
934:invertebrates
931:
920:
917:
914:
910:
906:
901:
897:
892:
888:
884:
878:
868:
866:
861:
855:
852:
848:
846:
842:
838:
834:
825:
817:
810:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
785:
773:
770:
767:
766:
765:
761:
756:
746:
744:
740:
739:phytoplankton
736:
732:
727:
723:
722:trophic level
719:
714:
710:
708:
697:
691:
684:
678:
670:
664:
655:
653:
649:
645:
640:
637:
633:
629:
628:
623:
622:
617:
614:The field of
612:
609:
605:
597:
596:
590:
586:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
562:
560:
550:
548:
542:
540:
536:
535:
530:
526:
522:
512:
507:
502:
501:Trophic level
492:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
457:
456:
451:
442:
437:
434:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
397:
392:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
369:heterotrophic
367:
363:
359:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
337:. Autotrophs
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
313:
304:
299:
290:
288:
284:
280:
276:
275:meta analysis
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
251:
249:
248:John Bruckner
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
219:
218:Charles Elton
215:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
196:cyanobacteria
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
159:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
34:A freshwater
32:
19:
8360:Regime shift
8345:Macroecology
8066:
8062:
8002:Edge effects
7972:Biogeography
7917:Commensalism
7765:Biodiversity
7642:Allee effect
7381:kelp forests
7334:Example webs
7291:
7199:Detritivores
7038:Organotrophs
7018:Kinetotrophs
6970:Productivity
6792:Trophallaxis
6696:Pivot feeder
6691:Lunge feeder
6669:Egg predator
6557:Phagocytosis
6407:reproductive
6378:Myrmecophagy
6368:Molluscivore
6276:
6232:
6226:
6195:
6170:
6157:
6132:
6128:
6122:
6102:
6095:
6085:
6078:
6061:
6056:
6050:
6040:
6033:
6024:
6005:
5987:
5983:
5977:
5952:
5948:
5942:
5929:
5912:
5908:
5902:
5893:
5889:
5876:
5841:
5837:
5827:
5800:
5796:
5786:
5775:. Retrieved
5768:the original
5729:
5725:
5712:
5677:
5673:
5663:
5652:. Retrieved
5645:the original
5608:
5604:
5591:
5580:. Retrieved
5573:the original
5550:
5546:
5533:
5514:
5510:
5500:
5467:
5463:
5457:
5440:
5436:
5382:
5378:
5338:
5334:
5324:
5305:
5301:
5268:
5261:
5250:. Retrieved
5243:the original
5198:
5194:
5167:. Retrieved
5160:the original
5131:
5127:
5114:
5103:. Retrieved
5096:the original
5077:
5069:
5024:
5020:
4962:
4958:
4932:. Retrieved
4925:the original
4896:
4892:
4859:
4855:
4849:
4830:E-Biology II
4829:
4822:
4802:
4795:
4784:the original
4771:
4767:
4740:. Retrieved
4733:the original
4710:
4706:
4679:. Retrieved
4672:the original
4635:
4631:
4564:
4560:
4507:
4504:PLOS Biology
4503:
4445:
4441:
4431:
4398:
4394:
4388:
4377:. Retrieved
4370:the original
4333:
4329:
4316:
4289:
4285:
4275:
4250:
4246:
4240:
4205:
4201:
4188:
4158:(1): 31–50.
4155:
4151:
4141:
4100:
4096:
4090:
4041:
4037:
4031:
3998:
3994:
3974:. Retrieved
3967:the original
3958:
3951:
3910:
3906:
3893:
3868:
3864:
3858:
3847:. Retrieved
3840:the original
3819:
3815:
3802:
3782:
3775:
3755:
3748:
3703:
3699:
3689:
3666:
3622:
3618:
3612:
3588:10.2307/4220
3571:
3567:
3531:
3527:
3498:
3491:
3474:
3470:
3441:
3434:
3414:
3407:
3387:
3380:
3371:
3367:
3357:
3322:
3318:
3308:
3283:
3279:
3252:. Retrieved
3245:the original
3232:
3228:
3215:
3199:(1): 11–18.
3196:
3192:
3182:
3123:
3119:
3113:
3104:
3100:
3090:
3063:
3059:
3049:
3038:. Retrieved
3002:
2998:
2945:(992): 992.
2942:
2938:
2906:
2900:
2867:
2863:
2850:
2815:
2811:
2801:
2781:
2774:
2749:
2745:
2739:
2704:
2700:
2687:
2662:
2656:
2643:
2632:. Retrieved
2625:the original
2596:
2592:
2579:
2568:. Retrieved
2561:the original
2530:
2526:
2499:. Retrieved
2492:the original
2463:
2459:
2430:. Retrieved
2423:the original
2394:
2390:
2334:(7131): 29.
2331:
2327:
2317:
2308:
2304:
2280:. Retrieved
2273:the original
2244:
2240:
2181:
2177:
2164:
2153:. Retrieved
2146:the original
2133:
2129:
2116:
2105:. Retrieved
2098:the original
2061:
2057:
2044:
2019:
2015:
2002:
1975:
1971:
1958:
1947:. Retrieved
1940:the original
1903:
1899:
1886:
1877:
1873:
1852:the original
1836:
1807:. Retrieved
1800:the original
1771:
1767:
1730:the original
1709:
1705:
1669:
1662:
1629:
1625:
1619:
1591:
1584:
1573:. Retrieved
1551:
1547:
1530:
1425:Biodiversity
1329:, including
1323:
1262:
1256:
1233:
1213:
1209:
1201:
1193:
1172:
1164:
1071:
1047:
1031:
1023:
1020:Detrital web
995:
989:
980:
974:
968:
962:
956:
951:
926:
880:
856:
849:
833:top consumer
830:
808:
804:
796:
792:
788:
762:
758:
715:
711:
703:
688:
650:produced by
625:
619:
613:
601:
593:
563:
556:
547:detritivores
543:
534:Thiobacillus
532:
521:detritivores
517:
475:, microbes,
462:
453:
431:top consumer
399:detritivores
393:
335:heterotrophs
322:
316:
310:
302:
283:Scaling laws
259:quantitative
252:
216:
208:bdellovibrio
160:
84:heterotrophs
67:
65:
52:gizzard shad
7997:Disturbance
7900:interaction
7722:Recruitment
7652:Depensation
7444:Copiotrophs
7315:Energy flow
7237:Lithotrophy
7181:Decomposers
7161:Planktivore
7136:Insectivore
7126:Heterotroph
7091:Bacterivore
7058:Phototrophs
7008:Chemotrophs
6980:Restoration
6930:Competition
6613:Planktivore
6598:Detritivore
6593:Coprophagia
6583:Bacterivore
6578:Microbivory
6562:Myzocytosis
6521:Nectarivore
6511:Graminivore
6358:Lepidophagy
6353:Insectivore
6348:Hematophagy
5568:10261/40177
5553:: 567–569.
4713:: 289–316.
4510:(4): e102.
3871:: 171–190.
2752:: 133–152.
1978:: 257–263.
1449:Food system
1220:small world
1065:feeding on
1034:leaf litter
938:taxonomists
835:, (e.g., a
735:zooplankton
608:overgrazing
525:chlorophyll
481:saprotrophs
477:decomposers
427:monophagous
423:Food chains
419:connectance
403:decomposers
396:saprophytic
366:polyphagous
358:respiration
271:topological
212:blue whales
202:, and from
188:microscopic
148:hot springs
72:food chains
8365:Sexecology
7942:Parasitism
7907:Antibiosis
7742:Resistance
7737:Resilience
7627:Population
7547:Camouflage
7499:Oligotroph
7414:Ascendency
7376:intertidal
7366:cold seeps
7320:Food chain
7121:Herbivores
7096:Carnivores
7023:Mixotrophs
6998:Autotrophs
6877:components
6777:Parasitism
6711:Bait balls
6701:Ram feeder
6633:Plastivore
6628:Lithotroph
6618:Saprophagy
6541:Osteophagy
6531:Palynivore
6488:Herbivores
6419:Paedophagy
6393:Spongivore
6383:Ophiophagy
6323:Carnivores
5990:(3): 1–53.
5777:2011-07-05
5654:2011-07-04
5582:2011-07-03
5511:BioScience
5302:BioScience
5252:2011-07-04
5169:2011-06-15
5105:2011-06-10
4934:2011-06-09
4742:2011-06-29
4681:2011-06-29
4379:2011-06-13
3976:2011-06-14
3849:2011-07-05
3254:2011-06-28
3149:11323/5713
3040:2022-05-02
2634:2011-06-14
2570:2011-06-14
2548:1813/57238
2501:2011-06-13
2432:2011-06-10
2282:2011-06-13
2155:2011-06-10
2107:2011-06-13
1949:2011-06-10
1809:2011-06-13
1575:2019-10-01
1523:References
1196:Complexity
1027:Earthworms
957:Source web
837:polar bear
755:food chain
749:Food chain
737:consuming
681:See also:
652:endophytes
621:Castilleja
415:periphyton
389:autotrophs
347:chemically
331:autotrophs
327:synonymous
323:Food cycle
235:decomposer
180:parasitism
176:scavenging
152:mixotrophs
80:autotrophs
40:food chain
8270:Allometry
8224:Emergence
7952:Symbiosis
7937:Mutualism
7732:Stability
7637:Abundance
7449:Dominance
7407:Processes
7396:tide pool
7292:Food webs
7166:Predation
7151:Omnivores
7078:Consumers
7033:Mycotroph
6990:Producers
6935:Ecosystem
6900:Behaviour
6782:Scavenger
6654:Predation
6623:Xenophagy
6603:Geophagia
6588:Fungivore
6536:Xylophagy
6526:Mellivory
6506:Frugivore
6501:Florivore
6398:Vermivore
6388:Piscivore
6373:Mucophagy
6363:Man-eater
6265:251843290
5915:: 50–69.
5437:Syst. Res
5357:2296-701X
5223:1874/8123
4253:: 71–95.
4180:130343033
3647:177263265
2094:205004984
1269:Afro-Arab
1130:−
1038:leachates
916:sediments
707:metabolic
648:alkaloids
489:predators
485:consumers
473:parasites
385:nutrients
355:metabolic
172:carnivory
168:herbivory
154:(such as
104:inorganic
96:reproduce
8404:Category
8325:Endolith
8254:Xerosere
8166:networks
7982:Ecocline
7528:Defense,
7204:Detritus
7106:Foraging
6975:Resource
6733:Browsing
6608:Omnivore
6550:Cellular
6496:Folivore
6257:36007038
6194:(1978).
6149:85265656
5868:16519227
5819:19120606
5764:11846598
5704:21141173
5633:16855581
5419:12235364
5239:34331654
5231:12004131
5061:19569361
4999:12235367
4728:1808/817
4668:35880562
4660:17737551
4599:14628050
4536:18447582
4482:18695214
4423:20395493
4366:34992724
4358:17790039
4232:16420638
4133:19993145
4125:12586932
4082:31036238
3935:11117743
3639:12004106
3604:55981512
3349:18782750
3174:27517361
3166:17799729
3107:(1): 11.
3035:29131311
3027:26624251
2977:33446768
2892:11050351
2842:24033672
2766:86686057
2731:21058543
2679:85155900
2557:55279332
2419:17503589
2358:17330028
2311:: 50–54.
2207:1807/768
2086:10724169
2036:19660952
1936:11536563
1928:18451301
1726:16701391
1539:(2015).
1337:See also
1273:Al-Jahiz
1266:medieval
1216:networks
1055:richness
963:Sink web
930:microbes
913:detrital
905:minerals
887:minerals
883:elements
720:of each
627:Plantago
411:biofilms
333:and the
190:to many
122:require
118:. These
114:such as
108:minerals
92:maintain
68:food web
58:→
54:→
50:→
46:→
8315:Ecopath
8122:Habitat
7992:Ecotype
7987:Ecotone
7964:ecology
7962:Spatial
7898:Species
7758:Species
7629:ecology
7614:Ecology
7562:Mimicry
7530:counter
7474:f-ratio
7222:Archaea
6910:Biomass
6883:General
6875:Trophic
6867:Ecology
6748:Grazing
6647:Methods
6434:Weaning
6414:Oophagy
6338:Avivore
6237:Bibcode
6228:Science
5969:2255864
5859:1560001
5744:Bibcode
5682:Bibcode
5674:Ecology
5613:Bibcode
5492:1941145
5472:Bibcode
5464:Ecology
5387:Bibcode
5203:Bibcode
5195:Science
5156:3672136
5136:Bibcode
5128:Science
5029:Bibcode
5021:Ecology
4967:Bibcode
4921:1941141
4901:Bibcode
4893:Ecology
4856:Ecology
4768:Ecology
4640:Bibcode
4632:Science
4607:1752696
4569:Bibcode
4527:2689700
4473:2556413
4450:Bibcode
4403:Bibcode
4395:Science
4338:Bibcode
4330:Science
4294:Bibcode
4267:2097085
4210:Bibcode
4160:Bibcode
4117:3833546
4097:Science
4074:7008198
4066:1685216
4046:Bibcode
4038:Science
4023:2635427
4003:Bibcode
3943:4408787
3915:Bibcode
3885:2096770
3824:Bibcode
3740:9618454
3708:Bibcode
3619:Science
3576:Bibcode
3536:Bibcode
3374:(2): 2.
3340:2614255
3288:Bibcode
3280:Ecology
3158:1702630
3128:Bibcode
3120:Science
3068:Bibcode
3007:Bibcode
2999:Ecology
2968:7809109
2947:Bibcode
2872:Bibcode
2820:Bibcode
2709:Bibcode
2701:Ecology
2621:3565489
2601:Bibcode
2488:1930126
2468:Bibcode
2460:Ecology
2399:Bibcode
2391:Ecology
2366:4428058
2336:Bibcode
2249:Bibcode
2216:2963482
2186:Bibcode
2066:Bibcode
1980:Bibcode
1908:Bibcode
1900:Science
1880:(8): 5.
1796:4267587
1776:Bibcode
1654:4319708
1634:Bibcode
1556:Bibcode
1321:life".
1302:ecology
1285:herring
1063:daphnia
764:about:
731:animals
726:entropy
718:biomass
669:carcass
583:species
467:called
373:network
343:biomass
339:produce
223:species
204:viruses
194:- from
48:daphnia
36:aquatic
7346:Rivers
7242:Marine
6753:Forage
6743:Fodder
6571:Others
6263:
6255:
6214:683203
6212:
6202:
6147:
6110:
6070:985662
6068:
6012:
5967:
5866:
5856:
5817:
5762:
5702:
5641:592403
5639:
5631:
5605:Nature
5490:
5417:
5410:130560
5407:
5355:
5276:
5237:
5229:
5154:
5088:
5059:
4997:
4990:130559
4987:
4919:
4837:
4810:
4666:
4658:
4605:
4597:
4561:Nature
4534:
4524:
4480:
4470:
4421:
4364:
4356:
4265:
4230:
4178:
4131:
4123:
4115:
4080:
4072:
4064:
4021:
3941:
3933:
3907:Nature
3883:
3790:
3763:
3738:
3728:
3677:
3645:
3637:
3602:
3594:
3506:
3449:
3422:
3395:
3347:
3337:
3172:
3164:
3156:
3033:
3025:
2975:
2965:
2913:
2890:
2840:
2789:
2764:
2729:
2677:
2619:
2555:
2486:
2417:
2364:
2356:
2328:Nature
2269:538731
2267:
2214:
2092:
2084:
2058:Nature
2034:
1934:
1926:
1844:
1794:
1768:Nature
1724:
1677:
1652:
1626:Nature
1607:
797:bottom
793:middle
639:larvae
511:Boreal
413:, and
263:models
192:tonnes
184:sugars
178:, and
124:energy
8263:Other
8164:Other
8117:Guild
8089:Niche
7341:Lakes
6331:adult
6261:S2CID
6145:S2CID
6066:JSTOR
5965:JSTOR
5886:(PDF)
5771:(PDF)
5734:arXiv
5722:(PDF)
5648:(PDF)
5637:S2CID
5601:(PDF)
5576:(PDF)
5543:(PDF)
5488:JSTOR
5246:(PDF)
5235:S2CID
5191:(PDF)
5163:(PDF)
5124:(PDF)
5099:(PDF)
5082:(PDF)
4928:(PDF)
4917:JSTOR
4889:(PDF)
4787:(PDF)
4764:(PDF)
4736:(PDF)
4703:(PDF)
4675:(PDF)
4664:S2CID
4628:(PDF)
4603:S2CID
4557:(PDF)
4373:(PDF)
4362:S2CID
4326:(PDF)
4263:JSTOR
4198:(PDF)
4176:S2CID
4129:S2CID
4113:JSTOR
4078:S2CID
4062:JSTOR
4019:S2CID
3970:(PDF)
3963:(PDF)
3939:S2CID
3903:(PDF)
3881:JSTOR
3843:(PDF)
3812:(PDF)
3731:33863
3643:S2CID
3600:S2CID
3592:JSTOR
3276:(PDF)
3248:(PDF)
3225:(PDF)
3170:S2CID
3154:JSTOR
3023:JSTOR
2860:(PDF)
2838:JSTOR
2762:S2CID
2697:(PDF)
2675:S2CID
2653:(PDF)
2628:(PDF)
2617:JSTOR
2593:Oikos
2589:(PDF)
2564:(PDF)
2553:S2CID
2523:(PDF)
2495:(PDF)
2484:JSTOR
2456:(PDF)
2426:(PDF)
2387:(PDF)
2362:S2CID
2276:(PDF)
2237:(PDF)
2212:JSTOR
2174:(PDF)
2149:(PDF)
2126:(PDF)
2101:(PDF)
2090:S2CID
2054:(PDF)
2012:(PDF)
1968:(PDF)
1943:(PDF)
1932:S2CID
1896:(PDF)
1803:(PDF)
1792:S2CID
1764:(PDF)
1733:(PDF)
1702:(PDF)
1650:S2CID
1544:(PDF)
1067:algae
841:human
839:or a
805:Note:
579:aphid
487:, or
377:cycle
341:more
225:into
112:gases
102:from
44:algae
7351:Soil
6638:Pica
6253:PMID
6210:PMID
6200:ISBN
6108:ISBN
6010:ISBN
5864:PMID
5815:PMID
5760:PMID
5700:PMID
5629:PMID
5415:PMID
5353:ISSN
5274:ISBN
5227:PMID
5152:PMID
5086:ISBN
5057:PMID
4995:PMID
4835:ISBN
4808:ISBN
4656:PMID
4595:PMID
4532:PMID
4478:PMID
4419:PMID
4354:PMID
4228:PMID
4121:PMID
4070:PMID
3931:PMID
3788:ISBN
3761:ISBN
3736:PMID
3675:ISBN
3635:PMID
3596:4220
3504:ISBN
3447:ISBN
3420:ISBN
3393:ISBN
3345:PMID
3162:PMID
3031:PMID
2973:PMID
2911:ISBN
2888:PMID
2787:ISBN
2727:PMID
2415:PMID
2354:PMID
2309:1463
2265:PMID
2082:PMID
2032:PMID
1924:PMID
1842:ISBN
1722:PMID
1675:ISBN
1605:ISBN
1291:and
1222:and
932:and
891:food
885:and
624:and
577:and
407:soil
383:and
379:the
375:and
206:and
146:and
110:and
6245:doi
6233:377
6137:doi
6133:100
6062:104
5957:doi
5917:doi
5854:PMC
5846:doi
5842:273
5805:doi
5752:doi
5730:214
5690:doi
5621:doi
5609:442
5563:hdl
5555:doi
5519:doi
5480:doi
5445:doi
5405:PMC
5395:doi
5343:doi
5310:doi
5219:hdl
5211:doi
5199:295
5144:doi
5132:238
5047:hdl
5037:doi
4985:PMC
4975:doi
4909:doi
4864:doi
4776:doi
4723:hdl
4715:doi
4648:doi
4636:155
4585:hdl
4577:doi
4565:426
4522:PMC
4512:doi
4468:PMC
4458:doi
4446:105
4411:doi
4399:328
4346:doi
4334:241
4302:doi
4255:doi
4218:doi
4168:doi
4156:336
4105:doi
4101:299
4054:doi
4042:211
4011:doi
3923:doi
3911:408
3873:doi
3832:doi
3820:220
3726:PMC
3716:doi
3627:doi
3623:296
3584:doi
3544:doi
3479:doi
3335:PMC
3327:doi
3323:276
3296:doi
3237:doi
3201:doi
3144:hdl
3136:doi
3124:242
3076:doi
3015:doi
2963:PMC
2955:doi
2880:doi
2828:doi
2754:doi
2717:doi
2667:doi
2663:147
2609:doi
2543:hdl
2535:doi
2531:142
2476:doi
2407:doi
2344:doi
2332:446
2257:doi
2202:hdl
2194:doi
2138:doi
2074:doi
2062:404
2024:doi
1988:doi
1916:doi
1904:320
1784:doi
1772:350
1714:doi
1642:doi
1630:307
1597:doi
1564:doi
1312:in
984:web
789:top
585:.
405:in
210:to
198:to
142:in
128:Sun
82:or
8406::
7812:/
7616::
6873::
6869::
6275:.
6259:.
6251:.
6243:.
6231:.
6225:.
6208:.
6143:.
6131:.
5996:^
5986:.
5963:.
5953:11
5951:.
5913:88
5911:.
5894:83
5892:.
5888:.
5862:.
5852:.
5840:.
5836:.
5813:.
5801:78
5799:.
5795:.
5758:.
5750:.
5742:.
5728:.
5724:.
5698:.
5688:.
5678:91
5676:.
5672:.
5635:.
5627:.
5619:.
5607:.
5603:.
5561:.
5551:38
5549:.
5545:.
5515:51
5513:.
5509:.
5486:.
5478:.
5468:69
5466:.
5441:24
5439:.
5427:^
5413:.
5403:.
5393:.
5383:99
5381:.
5377:.
5365:^
5351:.
5341:.
5337:.
5333:.
5306:55
5304:.
5300:.
5288:^
5233:.
5225:.
5217:.
5209:.
5197:.
5193:.
5178:^
5150:.
5142:.
5130:.
5126:.
5055:.
5045:.
5035:.
5025:90
5023:.
5019:.
5007:^
4993:.
4983:.
4973:.
4963:99
4961:.
4957:.
4943:^
4915:.
4907:.
4897:69
4895:.
4891:.
4876:^
4860:82
4858:.
4772:82
4770:.
4766:.
4751:^
4721:.
4711:28
4709:.
4705:.
4690:^
4662:.
4654:.
4646:.
4634:.
4630:.
4615:^
4601:.
4593:.
4583:.
4575:.
4563:.
4559:.
4544:^
4530:.
4520:.
4506:.
4502:.
4490:^
4476:.
4466:.
4456:.
4444:.
4440:.
4417:.
4409:.
4397:.
4360:.
4352:.
4344:.
4332:.
4328:.
4300:.
4290:41
4288:.
4284:.
4261:.
4251:20
4249:.
4226:.
4216:.
4206:55
4204:.
4200:.
4174:.
4166:.
4154:.
4150:.
4127:.
4119:.
4111:.
4099:.
4076:.
4068:.
4060:.
4052:.
4040:.
4017:.
4009:.
3997:.
3985:^
3937:.
3929:.
3921:.
3909:.
3905:.
3879:.
3867:.
3830:.
3818:.
3814:.
3734:.
3724:.
3714:.
3704:95
3702:.
3698:.
3669:.
3655:^
3641:.
3633:.
3621:.
3598:.
3590:.
3582:.
3572:49
3570:.
3556:^
3542:.
3532:18
3530:.
3518:^
3475:17
3473:.
3461:^
3370:.
3366:.
3343:.
3333:.
3321:.
3317:.
3294:.
3284:85
3282:.
3278:.
3263:^
3233:33
3231:.
3227:.
3195:.
3191:.
3168:.
3160:.
3152:.
3142:.
3134:.
3122:.
3103:.
3099:.
3074:.
3062:.
3058:.
3029:.
3021:.
3013:.
3003:99
3001:.
2997:.
2985:^
2971:.
2961:.
2953:.
2943:11
2941:.
2937:.
2925:^
2886:.
2878:.
2868:15
2866:.
2862:.
2836:.
2826:.
2816:28
2814:.
2810:.
2760:.
2750:39
2748:.
2725:.
2715:.
2705:91
2703:.
2699:.
2673:.
2661:.
2655:.
2615:.
2607:.
2597:50
2595:.
2591:.
2551:.
2541:.
2529:.
2525:.
2510:^
2482:.
2474:.
2464:23
2462:.
2458:.
2441:^
2413:.
2405:.
2395:88
2393:.
2389:.
2374:^
2360:.
2352:.
2342:.
2330:.
2326:.
2307:.
2303:.
2291:^
2263:.
2255:.
2245:16
2243:.
2239:.
2224:^
2210:.
2200:.
2192:.
2182:66
2180:.
2176:.
2134:17
2132:.
2128:.
2088:.
2080:.
2072:.
2060:.
2056:.
2030:.
2020:17
2018:.
2014:.
1986:.
1976:10
1974:.
1970:.
1930:.
1922:.
1914:.
1902:.
1898:.
1876:.
1872:.
1860:^
1818:^
1790:.
1782:.
1770:.
1766:.
1741:^
1720:.
1710:20
1708:.
1704:.
1689:^
1648:.
1640:.
1628:.
1603:.
1562:.
1552:12
1550:.
1546:.
1259:).
867:.
483:,
479:,
421:.
409:,
391:.
321:.
289:.
214:.
174:,
170:,
66:A
8067:K
8065:/
8063:r
7606:e
7599:t
7592:v
6859:e
6852:t
6845:v
6307:e
6300:t
6293:v
6267:.
6247::
6239::
6216:.
6178:.
6165:.
6151:.
6139::
6116:.
6072:.
6018:.
5988:7
5971:.
5959::
5923:.
5919::
5870:.
5848::
5821:.
5807::
5780:.
5754::
5746::
5736::
5706:.
5692::
5684::
5657:.
5623::
5615::
5585:.
5565::
5557::
5527:.
5521::
5494:.
5482::
5474::
5451:.
5447::
5421:.
5397::
5389::
5359:.
5345::
5339:9
5318:.
5312::
5282:.
5255:.
5221::
5213::
5205::
5172:.
5146::
5138::
5108:.
5063:.
5049::
5039::
5031::
5001:.
4977::
4969::
4937:.
4911::
4903::
4870:.
4866::
4843:.
4816:.
4778::
4745:.
4725::
4717::
4684:.
4650::
4642::
4609:.
4587::
4579::
4571::
4538:.
4514::
4508:6
4484:.
4460::
4452::
4425:.
4413::
4405::
4382:.
4348::
4340::
4310:.
4304::
4296::
4269:.
4257::
4234:.
4220::
4212::
4182:.
4170::
4162::
4135:.
4107::
4084:.
4056::
4048::
4025:.
4013::
4005::
3999:7
3979:.
3945:.
3925::
3917::
3887:.
3875::
3869:1
3852:.
3834::
3826::
3796:.
3769:.
3742:.
3718::
3710::
3683:.
3649:.
3629::
3606:.
3586::
3578::
3550:.
3546::
3538::
3512:.
3485:.
3481::
3455:.
3428:.
3401:.
3372:2
3351:.
3329::
3302:.
3298::
3290::
3257:.
3239::
3209:.
3203::
3197:8
3176:.
3146::
3138::
3130::
3105:2
3084:.
3078::
3070::
3064:8
3043:.
3017::
3009::
2979:.
2957::
2949::
2919:.
2894:.
2882::
2874::
2844:.
2830::
2822::
2795:.
2768:.
2756::
2733:.
2719::
2711::
2681:.
2669::
2637:.
2611::
2603::
2573:.
2545::
2537::
2504:.
2478::
2470::
2435:.
2409::
2401::
2368:.
2346::
2338::
2285:.
2259::
2251::
2218:.
2204::
2196::
2188::
2158:.
2140::
2110:.
2076::
2068::
2038:.
2026::
1996:.
1990::
1982::
1952:.
1918::
1910::
1878:1
1812:.
1786::
1778::
1716::
1683:.
1656:.
1644::
1636::
1613:.
1599::
1578:.
1566::
1558::
1161:,
1144:2
1140:/
1136:)
1133:1
1127:S
1124:(
1121:S
1107:L
1103:t
1091:=
1088:C
1075:L
62:)
42:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.