106:
54:
188:, lifting heavy objects) that can induce mechanical trauma or injury. Generally, the muscle or tendon overstretches and is placed under more physical stress than it can withstand. Strains commonly result in a partial or complete tear of a tendon or muscle, or they can be severe in the form of a complete tendon rupture. Strains most commonly occur in the
140:. Generally, the muscle or tendon overstretches and partially tears, under more physical stress than it can withstand, often from a sudden increase in duration, intensity, or frequency of an activity. Strains most commonly occur in the foot, leg, or back. Immediate treatment typically includes four steps abbreviated as
361:
and ibuprofen, affect platelet function (this is why they are known as "blood thinners") and should not be taken during the period when tissue is bleeding because they will tend to increase blood flow, inhibit clotting, and thereby increase bleeding and swelling. After the bleeding has stopped,
541:
Mueller-Wohlfahrt, Hans-Wilhelm; Haensel, Lutz; Mithoefer, Kai; Ekstrand, Jan; English, Bryan; McNally, Steven; Orchard, John; Dijk, C. Niek van; Kerkhoffs, Gino M.; Schamasch, Patrick; Blottner, Dieter; Swaerd, Leif; Goedhart, Edwin; Ueblacker, Peter (1 October 2012).
372:
It is recommended that the person injured should consult a medical provider if the injury is accompanied by severe pain, if the limb cannot be used, or if there is noticeable tenderness over an isolated spot. These can be signs of a broken or
888:
869:
603:
200:
Acute strains are more closely associated with recent mechanical trauma or injury. Chronic strains typically result from repetitive movement of the muscles and tendons over a long period of time.
274:
Although strains are not restricted to athletes and can happen while doing everyday tasks, people who play sports are more at risk for developing a strain. It is common for an
221:
To establish a uniform definition amongst healthcare providers, in 2012 a
Consensus Statement on suggested new terminology and classification of muscle injuries was published.
942:
684:
321:
Elevation: Keep the strained area as close to the level of the heart as is possible in order to promote venous blood return to the systemic circulation.
228:
The major difference suggested was the use of "indirect" muscle injury verse "grade 1" to provide subclassifications when advanced images were negative.
935:
1296:
928:
214:
Second degree – torn muscle or tendon tissues; painful, limited motion; possibly some swelling or depression at the spot of the injury.
528:
502:
217:
Third degree (most severe) – limited or no movement; severe acute pain, though sometimes painless straight after the initial injury
705:
204:
636:
1130:
613:
1177:
699:
263:
STRUCTURAL MUSCLE INJURY (Positive MSK US & MRI) • Type 3: Partial Muscle Tear • Type 4: (Sub) total tear
722:
1301:
346:
427:
903:
400:
369:(PRP) injections which have been shown to accelerate recovery from non-surgical muscular injuries.
330:
307:, which will reduce blood flow to the site of injury. Never ice for more than 20 minutes at a time.
176:. A strain can range from mild overstretching to severe tears, depending on the extent of injury.
1266:
1261:
1034:
920:
390:
334:
20:
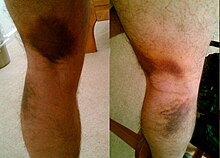
278:
to develop when there is a sudden increase in duration, intensity, or frequency of an activity.
211:
First degree (mildest) – little tissue tearing; mild tenderness; pain with full range of motion.
105:
1081:
338:
544:"Terminology and classification of muscle injuries in sport: The Munich consensus statement"
1140:
366:
8:
1028:
1002:
892:
837:
1038:
1024:
997:
814:
781:
576:
543:
475:
450:
275:
121:
86:
79:
897:
1217:
1171:
951:
819:
801:
695:
665:
609:
581:
563:
480:
462:
300:
Rest: Rest is necessary to accelerate healing and reduce the potential for re-injury.
118:
74:
648:
Järvinen, T.A.H.; et al. (April 2007). "Muscle injuries: optimising recovery".
1239:
1145:
1125:
809:
793:
760:
657:
571:
555:
470:
395:
350:
342:
304:
184:
A strain can occur as a result of improper body mechanics with any activity (e.g.,
1103:
908:
765:
748:
559:
311:
165:
1167:
1054:
661:
451:"Current Concepts of Muscle and Tendon Adaptation to Strength and Conditioning"
882:
878:
797:
53:
1290:
1135:
805:
782:"The role of platelet-rich plasma in inducing musculoskeletal tissue healing"
567:
466:
374:
354:
185:
362:
NSAIDs can be used with some effectiveness to reduce inflammation and pain.
1271:
1076:
1044:
823:
669:
585:
484:
173:
153:
955:
540:
287:
333:. Cold compression therapy acts to reduce swelling and pain by reducing
985:
315:
291:
197:
861:
1253:
1209:
1117:
1049:
1016:
62:
19:
This article is about the kind of muscle injury. For other uses, see
1205:
1012:
976:
780:
Halpern, Brian C.; Chaudhury, Salma; Rodeo, Scott A. (2012-07-01).
630:
597:
595:
169:
141:
133:
950:
1068:
531:. American College of Sports Medicine. Retrieved 5 December 2020.
358:
157:
592:
1196:
1191:
959:
873:
378:
297:
Protection: Apply soft padding to minimize impact with objects.
232:
Indirect Muscle Injury FUNCTIONAL (Negative MSK US & MRI)
137:
129:
125:
66:
27:
605:
Magnetic
Resonance Imaging in Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine
1231:
1155:
1095:
1064:
971:
326:
1249:
1159:
1113:
989:
189:
161:
349:
enzymes, which are the enzymes responsible for converting
1227:
1091:
193:
341:
work to reduce the immediate inflammation by inhibiting
325:
Immediate treatment is usually an adjunctive therapy of
286:
The first-line treatment for a muscular strain in the
779:
747:
Day, Richard O.; Graham, Garry G. (1 December 2004).
266:
DIRECT MUSCLE INJURY • Bump or Cut: Contact-related
851:
749:"The Vascular Effects of COX-2 selective inhibitors"
650:
Best
Practice & Research: Clinical Rheumatology
99:
Excessive stress and/or repeated injury on a muscle
723:"Clinical Studies on Cold and Compression Therapy"
449:Brumitt, Jason; Cuddeford, Tyler (November 2015).
16:Injury due to slight tearing of a muscle or tendon
503:"Sprains, Strains and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries"
1288:
455:International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy
448:
365:A new treatment for acute strains is the use of
69:. One of the pictures was shot through a mirror.
936:
430:. National Institutes of Health. January 2015
236:Type 1: Overexertion-related Muscle Disorder
164:, functional loss of the involved structure,
310:Compression: Wrap the strained area with a
943:
929:
509:. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
52:
813:
764:
746:
575:
474:
47:Muscle strain, pulled muscle, torn muscle
682:
647:
500:
248:• Type 2: Neuromuscular muscle disorder
203:Degrees of Injury (as classified by the
104:
601:
1289:
337:into the injured area. NSAIDs such as
132:, or both. The equivalent injury to a
91:Bruise, swelling, redness and soreness
924:
608:. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
290:include five steps commonly known as
147:
144:: rest, ice, compression, elevation.
61:Two images of the same strain to the
496:
494:
422:
420:
418:
416:
224:The classifications suggested were:
205:American College of Sports Medicine
13:
14:
1313:
1297:Dislocations, sprains and strains
1131:Anterior cruciate ligament injury
847:
491:
413:
838:"Natural Treatment for Injuries"
830:
773:
740:
715:
692:Principles of Athletic Training
501:Mulcahey, Mary K. (June 2020).
428:"Sprains and Strains: In-Depth"
318:and promote lymphatic drainage.
269:
676:
641:
622:
534:
521:
442:
1:
728:. Endomed, Inc. December 2007
683:Prentice, William E. (2014).
406:
381:, or a complete muscle tear.
357:. However, NSAIDs, including
109:3D animation depicting strain
840:. Retrieved 5 December 2020.
766:10.18773/austprescr.2004.119
560:10.1136/bjsports-2012-091448
529:"Sprains, Strains and Tears"
281:
7:
685:"Tissue Response to Injury"
554:(6): bjsports–2012–091448.
384:
10:
1318:
662:10.1016/j.berh.2006.12.004
602:Stoller, David W. (2007).
25:
18:
1248:
1226:
1204:
1190:
1154:
1112:
1090:
1063:
1011:
984:
970:
855:
798:10.1007/s11420-011-9239-7
303:Ice: Apply ice to induce
95:
85:
73:
60:
51:
43:
38:
527:Millar, A. Lynn (2011).
401:Repetitive strain injury
331:Cold compression therapy
239:Type 1a: Fatigue induced
179:
26:Not to be confused with
1267:Achilles tendon rupture
1262:Patellar tendon rupture
391:Achilles tendon rupture
335:leukocyte extravasation
257:Type 2b: Muscle-Related
21:Strain (disambiguation)
254:Type 2a: Spine-Related
110:
753:Australian Prescriber
339:Ibuprofen/paracetamol
108:
1141:Patellar dislocation
836:Neustaedter, Randy.
367:platelet rich plasma
312:soft-wrapped bandage
160:of a strain include
1029:Dislocated shoulder
1302:Muscular disorders
1082:Gamekeeper's thumb
1039:Separated shoulder
998:Dislocation of jaw
314:to reduce further
148:Signs and symptoms
122:soft tissue injury
111:
80:Emergency medicine
1284:
1283:
1280:
1279:
1218:Rotator cuff tear
1186:
1185:
1172:High ankle sprain
918:
917:
124:that occurs to a
103:
102:
33:Medical condition
1309:
1240:Pulled hamstring
1202:
1201:
1146:Knee dislocation
1126:Tear of meniscus
982:
981:
945:
938:
931:
922:
921:
853:
852:
841:
834:
828:
827:
817:
777:
771:
770:
768:
744:
738:
737:
735:
733:
727:
719:
713:
712:
710:
704:. Archived from
689:
680:
674:
673:
645:
639:
626:
620:
619:
599:
590:
589:
579:
538:
532:
525:
519:
518:
516:
514:
498:
489:
488:
478:
446:
440:
439:
437:
435:
424:
396:Pulled hamstring
351:arachidonic acid
305:vasoconstriction
172:, and localized
56:
36:
35:
1317:
1316:
1312:
1311:
1310:
1308:
1307:
1306:
1287:
1286:
1285:
1276:
1244:
1222:
1195:
1182:
1150:
1108:
1104:Hip dislocation
1086:
1059:
1007:
975:
966:
949:
919:
914:
913:
864:
850:
845:
844:
835:
831:
778:
774:
745:
741:
731:
729:
725:
721:
720:
716:
708:
702:
687:
681:
677:
646:
642:
627:
623:
616:
600:
593:
548:Br J Sports Med
539:
535:
526:
522:
512:
510:
499:
492:
447:
443:
433:
431:
426:
425:
414:
409:
387:
284:
272:
182:
166:muscle weakness
150:
117:is an acute or
65:and associated
34:
31:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1315:
1305:
1304:
1299:
1282:
1281:
1278:
1277:
1275:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1258:
1256:
1246:
1245:
1243:
1242:
1236:
1234:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1220:
1214:
1212:
1199:
1188:
1187:
1184:
1183:
1181:
1180:
1175:
1168:Sprained ankle
1164:
1162:
1152:
1151:
1149:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1122:
1120:
1110:
1109:
1107:
1106:
1100:
1098:
1088:
1087:
1085:
1084:
1079:
1073:
1071:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1057:
1055:Bankart lesion
1052:
1047:
1042:
1032:
1021:
1019:
1009:
1008:
1006:
1005:
1000:
994:
992:
979:
968:
967:
948:
947:
940:
933:
925:
916:
915:
912:
911:
900:
885:
865:
860:
859:
857:
856:Classification
849:
848:External links
846:
843:
842:
829:
792:(2): 137–145.
772:
759:(6): 142–145.
739:
714:
711:on 2017-10-31.
700:
675:
656:(2): 317–331.
640:
621:
614:
591:
533:
520:
490:
461:(6): 748–759.
441:
411:
410:
408:
405:
404:
403:
398:
393:
386:
383:
375:fractured bone
323:
322:
319:
308:
301:
298:
283:
280:
271:
268:
261:
260:
259:
258:
255:
246:
245:
244:
243:
240:
230:
229:
219:
218:
215:
212:
186:contact sports
181:
178:
149:
146:
101:
100:
97:
93:
92:
89:
83:
82:
77:
71:
70:
58:
57:
49:
48:
45:
41:
40:
32:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1314:
1303:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1294:
1292:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1259:
1257:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1241:
1238:
1237:
1235:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1179:
1176:
1173:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1136:Unhappy triad
1134:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1123:
1121:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1105:
1102:
1101:
1099:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1083:
1080:
1078:
1075:
1074:
1072:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1046:
1043:
1040:
1036:
1033:
1030:
1026:
1023:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1004:
1001:
999:
996:
995:
993:
991:
987:
983:
980:
978:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
946:
941:
939:
934:
932:
927:
926:
923:
910:
906:
905:
901:
899:
895:
894:
890:
886:
884:
880:
876:
875:
871:
867:
866:
863:
858:
854:
839:
833:
825:
821:
816:
811:
807:
803:
799:
795:
791:
787:
783:
776:
767:
762:
758:
754:
750:
743:
724:
718:
707:
703:
697:
693:
686:
679:
671:
667:
663:
659:
655:
651:
644:
638:
634:
632:
625:
617:
615:9780781773577
611:
607:
606:
598:
596:
587:
583:
578:
573:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
537:
530:
524:
508:
504:
497:
495:
486:
482:
477:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
452:
445:
429:
423:
421:
419:
417:
412:
402:
399:
397:
394:
392:
389:
388:
382:
380:
376:
370:
368:
363:
360:
356:
355:prostaglandin
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
320:
317:
313:
309:
306:
302:
299:
296:
295:
294:
293:
289:
279:
277:
267:
264:
256:
253:
252:
251:
250:
249:
242:Type 1b: DOMS
241:
238:
237:
235:
234:
233:
227:
226:
225:
222:
216:
213:
210:
209:
208:
206:
201:
199:
195:
191:
187:
177:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
145:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
120:
116:
107:
98:
94:
90:
88:
84:
81:
78:
76:
72:
68:
64:
59:
55:
50:
46:
42:
37:
29:
22:
1272:Shin splints
1077:Pulled elbow
1045:ALPSA lesion
963:
956:subluxations
952:Dislocations
902:
887:
868:
832:
789:
785:
775:
756:
752:
742:
730:. Retrieved
717:
706:the original
691:
678:
653:
649:
643:
628:
624:
604:
551:
547:
536:
523:
511:. Retrieved
506:
458:
454:
444:
432:. Retrieved
371:
364:
324:
285:
273:
270:Risk factors
265:
262:
247:
231:
223:
220:
202:
183:
174:inflammation
151:
114:
112:
786:HSS Journal
288:acute phase
44:Other names
1291:Categories
732:5 December
701:0078022649
513:5 December
434:5 December
407:References
316:diapedesis
292:P.R.I.C.E.
1210:upper arm
1050:SLAP tear
1017:upper arm
977:ligaments
806:1556-3316
631:Mnemonics
568:0306-3674
507:OrthoInfo
467:2159-2896
282:Treatment
170:contusion
75:Specialty
63:hamstring
1206:Shoulder
1178:Turf toe
1013:Shoulder
1003:Whiplash
824:23874254
670:17512485
586:23080315
485:26618057
385:See also
158:symptoms
152:Typical
142:R.I.C.E.
134:ligament
87:Symptoms
67:bruising
1197:tendons
1192:Muscles
1069:forearm
964:strains
960:sprains
909:D013180
815:3715623
629:Medical
577:3607100
476:4637912
359:aspirin
119:chronic
972:Joints
822:
812:
804:
698:
668:
637:235
612:
584:
574:
566:
483:
473:
465:
379:sprain
327:NSAIDs
276:injury
138:sprain
130:tendon
126:muscle
115:strain
96:Causes
39:Strain
28:Sprain
1232:thigh
1156:Ankle
1096:thigh
1065:Elbow
898:848.9
883:T14.3
879:M62.6
726:(PDF)
709:(PDF)
688:(PDF)
353:into
347:Cox-2
343:Cox-1
198:back.
196:, or
180:Cause
154:signs
136:is a
1252:and
1250:Knee
1230:and
1208:and
1160:foot
1158:and
1116:and
1114:Knee
1094:and
1067:and
1015:and
990:neck
988:and
986:Head
962:and
904:MeSH
893:9-CM
820:PMID
802:ISSN
734:2020
696:ISBN
666:PMID
633:.com
610:ISBN
582:PMID
564:ISSN
515:2020
481:PMID
463:ISSN
436:2020
377:, a
345:and
329:and
190:foot
162:pain
156:and
1254:leg
1228:Hip
1194:and
1118:leg
1092:Hip
974:and
889:ICD
870:ICD
810:PMC
794:doi
761:doi
658:doi
572:PMC
556:doi
471:PMC
207:):
194:leg
1293::
1035:AC
1025:GH
958:,
907::
896::
881:,
877::
874:10
818:.
808:.
800:.
788:.
784:.
757:27
755:.
751:.
694:.
690:.
664:.
654:21
652:.
635::
594:^
580:.
570:.
562:.
552:47
550:.
546:.
505:.
493:^
479:.
469:.
459:10
457:.
453:.
415:^
192:,
168:,
128:,
113:A
1174:)
1170:(
1041:)
1037:(
1031:)
1027:(
954:/
944:e
937:t
930:v
891:-
872:-
862:D
826:.
796::
790:8
769:.
763::
736:.
672:.
660::
618:.
588:.
558::
517:.
487:.
438:.
30:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.