137:
908:
226:. In contrast, the double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond, and a triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 396). The number of component bonds is what determines the strength disparity. It stands to reason that the single bond is the weakest of the three because it consists of only a sigma bond, and the double bond or triple bond consist not only of this type of component bond but also at least one additional bond.
149:
122:
25:
902:
914:
229:
The single bond has the capacity for rotation, a property not possessed by the double bond or the triple bond. The structure of pi bonds does not allow for rotation (at least not at 298 K), so the double bond and the triple bond which contain pi bonds are held due to this property. The sigma bond is
233:
Another property comparison can be made in bond length. Single bonds are the longest of the three types of covalent bonds as interatomic attraction is greater in the two other types, double and triple. The increase in component bonds is the reason for this attraction increase as more electrons are
211:. A single bond is weaker than either a double bond or a triple bond. This difference in strength can be explained by examining the component bonds of which each of these types of covalent bonds consists (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 393).
200:, a single bond is denoted as AːA or A-A, for which A represents an element. In the first rendition, each dot represents a shared electron, and in the second rendition, the bar represents both of the electrons shared in the single bond.
421:
1001:
230:
not so restrictive, and the single bond is able to rotate using the sigma bond as the axis of rotation (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 396-397).
196:
in which it originated. Rather, both of the two electrons spend time in either of the orbitals which overlap in the bonding process. As a
1119:
1046:
727:
659:
414:
89:
1041:
61:
262:
Single bonds are also seen in molecules made up of more than two atoms. Examples of this use of single bonds include:
452:
108:
966:
407:
68:
790:
298:(Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 334). The names of specific molecules which belong to this group end with the suffix
981:
817:
778:
768:
46:
773:
690:
219:
75:
720:
42:
57:
1145:
1036:
1026:
1016:
991:
961:
680:
664:
807:
639:
1068:
971:
943:
713:
35:
290:
larger than methane. The type of covalent bonding in hydrocarbons is extremely important in the
1112:
1073:
599:
594:
291:
192:. When shared, each of the two electrons involved is no longer in the sole possession of the
1107:
1031:
922:
785:
744:
565:
8:
933:
797:
763:
685:
579:
365:"Chemistry: The Molecular Science (Moore, John W.; Stanitski, Conrad L.; Jurs, Peter C.)"
342:
267:
82:
1097:
852:
1083:
872:
832:
822:
654:
447:
386:
238:
1124:
864:
837:
376:
181:
1102:
976:
847:
604:
294:
of these molecules. Hydrocarbons containing only single bonds are referred to as
197:
125:
144:. Note depiction of the four single bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms.
136:
1011:
812:
547:
531:
526:
442:
193:
1139:
1060:
1020:
953:
907:
882:
755:
736:
620:
560:
555:
536:
430:
390:
189:
173:
157:
1006:
311:
399:
1092:
842:
521:
516:
287:
208:
204:
364:
503:
487:
477:
381:
323:
307:
215:
827:
802:
625:
165:
24:
901:
492:
249:
242:
185:
129:
234:
shared between the bonded atoms (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 343).
705:
482:
277:
223:
141:
148:
303:
295:
153:
121:
188:
where the bond forms. Therefore, a single bond is a type of
299:
177:
913:
256:
286:
Single bonding even appears in molecules as complex as
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1137:
241:. Examples of this use of single bonds include
721:
415:
429:
728:
714:
422:
408:
380:
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
1120:Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory
362:
147:
135:
120:
184:. That is, the atoms share one pair of
1138:
709:
403:
156:. Note that all the bonds are single
132:. Note depiction of the single bond.
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
363:Steehler, Jack K. (December 2001).
13:
735:
314:(Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 335).
14:
1157:
453:Introduction to quantum mechanics
343:"covalent bonding - single bonds"
912:
906:
900:
23:
237:Single bonds are often seen in
34:needs additional citations for
16:Chemical bond between two atoms
356:
335:
203:A covalent bond can also be a
1:
369:Journal of Chemical Education
329:
214:Usually, a single bond is a
7:
317:
10:
1162:
818:Metal–ligand multiple bond
1082:
1059:
990:
952:
932:
921:
898:
881:
863:
754:
743:
673:
647:
638:
613:
587:
578:
545:
501:
470:
463:
438:
640:Molecular orbital theory
152:Lewis structure for an
218:. An exception is the
161:
145:
133:
151:
139:
124:
808:Coordinate (dipolar)
140:Lewis structure for
43:improve this article
982:C–H···O interaction
764:Electron deficiency
580:Valence bond theory
302:. Examples include
967:Resonance-assisted
382:10.1021/ed078p1598
239:diatomic molecules
162:
146:
134:
1133:
1132:
1084:Electron counting
1055:
1054:
944:London dispersion
896:
895:
873:Metal aromaticity
703:
702:
699:
698:
674:Constituent units
655:Molecular orbital
634:
633:
614:Constituent units
574:
573:
448:Quantum mechanics
345:. Chemguide.co.uk
182:valence electrons
119:
118:
111:
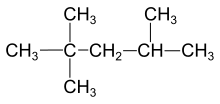
93:
1153:
1146:Chemical bonding
1125:Jemmis mno rules
977:Dihydrogen bonds
930:
929:
916:
910:
904:
838:Hyperconjugation
752:
751:
730:
723:
716:
707:
706:
645:
644:
585:
584:
566:Exchange-coupled
468:
467:
431:Chemical bonding
424:
417:
410:
401:
400:
395:
394:
384:
360:
354:
353:
351:
350:
339:
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
1161:
1160:
1156:
1155:
1154:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1136:
1135:
1134:
1129:
1078:
1051:
994:
986:
948:
935:
925:
917:
911:
905:
892:
877:
859:
747:
739:
734:
704:
695:
669:
630:
609:
605:Lewis structure
570:
541:
497:
459:
434:
428:
398:
361:
357:
348:
346:
341:
340:
336:
332:
320:
281:
276:All 4 bonds in
271:
253:
246:
220:bond in diboron
198:Lewis structure
126:Lewis structure
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1159:
1149:
1148:
1131:
1130:
1128:
1127:
1122:
1117:
1116:
1115:
1110:
1105:
1100:
1089:
1087:
1080:
1079:
1077:
1076:
1071:
1065:
1063:
1057:
1056:
1053:
1052:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1014:
1009:
1004:
998:
996:
988:
987:
985:
984:
979:
974:
969:
964:
958:
956:
950:
949:
947:
946:
940:
938:
927:
923:Intermolecular
919:
918:
899:
897:
894:
893:
891:
890:
887:
885:
879:
878:
876:
875:
869:
867:
861:
860:
858:
857:
856:
855:
850:
840:
835:
830:
825:
820:
815:
810:
805:
800:
795:
794:
793:
783:
782:
781:
776:
771:
760:
758:
749:
745:Intramolecular
741:
740:
737:Chemical bonds
733:
732:
725:
718:
710:
701:
700:
697:
696:
694:
693:
691:Antibonding MO
688:
686:Non-bonding MO
683:
677:
675:
671:
670:
668:
667:
662:
657:
651:
649:
642:
636:
635:
632:
631:
629:
628:
623:
617:
615:
611:
610:
608:
607:
602:
597:
595:Hybrid orbital
591:
589:
582:
576:
575:
572:
571:
569:
568:
563:
558:
552:
550:
543:
542:
540:
539:
534:
529:
524:
519:
514:
508:
506:
499:
498:
496:
495:
490:
485:
480:
474:
472:
465:
464:Types of bonds
461:
460:
458:
457:
456:
455:
445:
443:Atomic orbital
439:
436:
435:
427:
426:
419:
412:
404:
397:
396:
355:
333:
331:
328:
327:
326:
319:
316:
308:2-methylbutane
284:
283:
279:
274:
269:
266:Both bonds in
251:
244:
222:, which is a
180:involving two
158:covalent bonds
128:for molecular
117:
116:
99:September 2023
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1158:
1147:
1144:
1143:
1141:
1126:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1098:Hückel's rule
1096:
1095:
1094:
1091:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1081:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1066:
1064:
1062:
1061:Bond cleavage
1058:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1027:Intercalation
1025:
1022:
1018:
1017:Metallophilic
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
999:
997:
993:
989:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
968:
965:
963:
960:
959:
957:
955:
951:
945:
942:
941:
939:
937:
934:Van der Waals
931:
928:
924:
920:
915:
909:
903:
889:
888:
886:
884:
880:
874:
871:
870:
868:
866:
862:
854:
851:
849:
846:
845:
844:
841:
839:
836:
834:
831:
829:
826:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
792:
789:
788:
787:
784:
780:
777:
775:
772:
770:
767:
766:
765:
762:
761:
759:
757:
753:
750:
746:
742:
738:
731:
726:
724:
719:
717:
712:
711:
708:
692:
689:
687:
684:
682:
679:
678:
676:
672:
666:
663:
661:
658:
656:
653:
652:
650:
646:
643:
641:
637:
627:
624:
622:
621:Covalent bond
619:
618:
616:
612:
606:
603:
601:
598:
596:
593:
592:
590:
586:
583:
581:
577:
567:
564:
562:
559:
557:
554:
553:
551:
549:
544:
538:
535:
533:
532:5 (quintuple)
530:
528:
527:4 (quadruple)
525:
523:
520:
518:
515:
513:
510:
509:
507:
505:
500:
494:
491:
489:
486:
484:
481:
479:
476:
475:
473:
469:
466:
462:
454:
451:
450:
449:
446:
444:
441:
440:
437:
432:
425:
420:
418:
413:
411:
406:
405:
402:
392:
388:
383:
378:
374:
370:
366:
359:
344:
338:
334:
325:
322:
321:
315:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
282:
275:
273:
265:
264:
263:
260:
258:
254:
247:
240:
235:
231:
227:
225:
221:
217:
212:
210:
206:
201:
199:
195:
191:
190:covalent bond
187:
183:
179:
175:
174:chemical bond
171:
167:
159:
155:
150:
143:
138:
131:
127:
123:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
58:"Single bond"
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
1103:Baird's rule
823:Charge-shift
786:Hypervalence
537:6 (sextuple)
511:
504:multiplicity
375:(12): 1598.
372:
368:
358:
347:. Retrieved
337:
312:cyclopentane
292:nomenclature
288:hydrocarbons
285:
261:
236:
232:
228:
213:
202:
176:between two
169:
163:
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
1093:Aromaticity
1069:Heterolysis
1047:Salt bridge
992:Noncovalent
962:Low-barrier
843:Aromaticity
833:Conjugation
813:Pi backbond
471:By symmetry
209:triple bond
205:double bond
170:single bond
1021:aurophilic
1002:Mechanical
681:Bonding MO
665:MO diagram
522:3 (triple)
517:2 (double)
512:1 (single)
349:2012-08-12
330:References
324:Bond order
216:sigma bond
69:newspapers
1113:spherical
1074:Homolysis
1037:Cation–pi
1012:Chalcogen
972:Symmetric
828:Hapticity
626:Lone pair
600:Resonance
488:Delta (δ)
478:Sigma (σ)
391:0021-9584
186:electrons
166:chemistry
1140:Category
1042:Anion–pi
1032:Stacking
954:Hydrogen
865:Metallic
756:Covalent
748:(strong)
648:Concepts
588:Concepts
318:See also
130:hydrogen
1007:Halogen
853:bicyclo
798:Agostic
561:Singlet
556:Triplet
493:Phi (φ)
296:alkanes
224:pi bond
194:orbital
142:methane
83:scholar
1108:Möbius
936:forces
926:(weak)
483:Pi (π)
433:theory
389:
310:, and
304:ethane
255:, and
154:alkane
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
1086:rules
995:other
883:Ionic
791:3c–4e
779:8c–2e
774:4c–2e
769:3c–2e
207:or a
178:atoms
172:is a
90:JSTOR
76:books
848:homo
803:Bent
660:LCAO
548:spin
387:ISSN
300:-ane
168:, a
62:news
546:By
502:By
377:doi
257:HCl
164:In
45:by
1142::
385:.
373:78
371:.
367:.
306:,
278:CH
259:.
248:,
1023:)
1019:(
729:e
722:t
715:v
423:e
416:t
409:v
393:.
379::
352:.
280:4
272:O
270:2
268:H
252:2
250:F
245:2
243:H
160:.
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.