148:
919:
237:. In contrast, the double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond, and a triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 396). The number of component bonds is what determines the strength disparity. It stands to reason that the single bond is the weakest of the three because it consists of only a sigma bond, and the double bond or triple bond consist not only of this type of component bond but also at least one additional bond.
160:
133:
36:
913:
925:
240:
The single bond has the capacity for rotation, a property not possessed by the double bond or the triple bond. The structure of pi bonds does not allow for rotation (at least not at 298 K), so the double bond and the triple bond which contain pi bonds are held due to this property. The sigma bond is
244:
Another property comparison can be made in bond length. Single bonds are the longest of the three types of covalent bonds as interatomic attraction is greater in the two other types, double and triple. The increase in component bonds is the reason for this attraction increase as more electrons are
222:. A single bond is weaker than either a double bond or a triple bond. This difference in strength can be explained by examining the component bonds of which each of these types of covalent bonds consists (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 393).
211:, a single bond is denoted as AːA or A-A, for which A represents an element. In the first rendition, each dot represents a shared electron, and in the second rendition, the bar represents both of the electrons shared in the single bond.
432:
1012:
241:
not so restrictive, and the single bond is able to rotate using the sigma bond as the axis of rotation (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 396-397).
207:
in which it originated. Rather, both of the two electrons spend time in either of the orbitals which overlap in the bonding process. As a
1130:
1057:
738:
670:
425:
100:
1052:
72:
273:
Single bonds are also seen in molecules made up of more than two atoms. Examples of this use of single bonds include:
463:
119:
977:
418:
79:
801:
309:(Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 334). The names of specific molecules which belong to this group end with the suffix
992:
828:
789:
779:
57:
784:
701:
230:
86:
731:
53:
17:
68:
1156:
1047:
1037:
1027:
1002:
972:
691:
675:
818:
650:
1079:
982:
954:
724:
46:
301:
larger than methane. The type of covalent bonding in hydrocarbons is extremely important in the
1123:
1084:
610:
605:
302:
203:. When shared, each of the two electrons involved is no longer in the sole possession of the
1118:
1042:
933:
796:
755:
576:
8:
944:
808:
774:
696:
590:
376:"Chemistry: The Molecular Science (Moore, John W.; Stanitski, Conrad L.; Jurs, Peter C.)"
353:
278:
93:
1108:
863:
1094:
883:
843:
833:
665:
458:
397:
249:
1135:
875:
848:
387:
192:
1113:
987:
858:
615:
305:
of these molecules. Hydrocarbons containing only single bonds are referred to as
208:
136:
155:. Note depiction of the four single bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms.
147:
1022:
823:
558:
542:
537:
453:
204:
1150:
1071:
1031:
964:
918:
893:
766:
747:
631:
571:
566:
547:
441:
401:
200:
184:
168:
1017:
322:
410:
1103:
853:
532:
527:
298:
219:
215:
375:
514:
498:
488:
392:
334:
318:
226:
838:
813:
636:
176:
35:
912:
503:
260:
253:
196:
140:
245:
shared between the bonded atoms (Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 343).
716:
493:
288:
234:
152:
159:
314:
306:
164:
132:
199:
where the bond forms. Therefore, a single bond is a type of
310:
188:
924:
267:
297:
Single bonding even appears in molecules as complex as
60:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1148:
252:. Examples of this use of single bonds include
732:
426:
440:
739:
725:
433:
419:
391:
120:Learn how and when to remove this message
1131:Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory
373:
158:
146:
131:
195:. That is, the atoms share one pair of
14:
1149:
720:
414:
167:. Note that all the bonds are single
143:. Note depiction of the single bond.
58:adding citations to reliable sources
29:
374:Steehler, Jack K. (December 2001).
24:
746:
325:(Moore, Stanitski, and Jurs 335).
25:
1168:
464:Introduction to quantum mechanics
354:"covalent bonding - single bonds"
923:
917:
911:
34:
248:Single bonds are often seen in
45:needs additional citations for
27:Chemical bond between two atoms
367:
346:
214:A covalent bond can also be a
13:
1:
380:Journal of Chemical Education
340:
225:Usually, a single bond is a
7:
328:
10:
1173:
829:Metal–ligand multiple bond
1093:
1070:
1001:
963:
943:
932:
909:
892:
874:
765:
754:
684:
658:
649:
624:
598:
589:
556:
512:
481:
474:
449:
651:Molecular orbital theory
163:Lewis structure for an
229:. An exception is the
172:
156:
144:
162:
150:
135:
819:Coordinate (dipolar)
151:Lewis structure for
54:improve this article
993:C–H···O interaction
775:Electron deficiency
591:Valence bond theory
313:. Examples include
978:Resonance-assisted
393:10.1021/ed078p1598
250:diatomic molecules
173:
157:
145:
1144:
1143:
1095:Electron counting
1066:
1065:
955:London dispersion
907:
906:
884:Metal aromaticity
714:
713:
710:
709:
685:Constituent units
666:Molecular orbital
645:
644:
625:Constituent units
585:
584:
459:Quantum mechanics
356:. Chemguide.co.uk
193:valence electrons
130:
129:
122:
104:
16:(Redirected from
1164:
1157:Chemical bonding
1136:Jemmis mno rules
988:Dihydrogen bonds
941:
940:
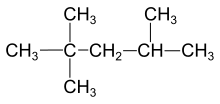
927:
921:
915:
849:Hyperconjugation
763:
762:
741:
734:
727:
718:
717:
656:
655:
596:
595:
577:Exchange-coupled
479:
478:
442:Chemical bonding
435:
428:
421:
412:
411:
406:
405:
395:
371:
365:
364:
362:
361:
350:
125:
118:
114:
111:
105:
103:
62:
38:
30:
21:
1172:
1171:
1167:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1162:
1161:
1147:
1146:
1145:
1140:
1089:
1062:
1005:
997:
959:
946:
936:
928:
922:
916:
903:
888:
870:
758:
750:
745:
715:
706:
680:
641:
620:
616:Lewis structure
581:
552:
508:
470:
445:
439:
409:
372:
368:
359:
357:
352:
351:
347:
343:
331:
292:
287:All 4 bonds in
282:
264:
257:
231:bond in diboron
209:Lewis structure
137:Lewis structure
126:
115:
109:
106:
63:
61:
51:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1170:
1160:
1159:
1142:
1141:
1139:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1127:
1126:
1121:
1116:
1111:
1100:
1098:
1091:
1090:
1088:
1087:
1082:
1076:
1074:
1068:
1067:
1064:
1063:
1061:
1060:
1055:
1050:
1045:
1040:
1035:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1009:
1007:
999:
998:
996:
995:
990:
985:
980:
975:
969:
967:
961:
960:
958:
957:
951:
949:
938:
934:Intermolecular
930:
929:
910:
908:
905:
904:
902:
901:
898:
896:
890:
889:
887:
886:
880:
878:
872:
871:
869:
868:
867:
866:
861:
851:
846:
841:
836:
831:
826:
821:
816:
811:
806:
805:
804:
794:
793:
792:
787:
782:
771:
769:
760:
756:Intramolecular
752:
751:
748:Chemical bonds
744:
743:
736:
729:
721:
712:
711:
708:
707:
705:
704:
702:Antibonding MO
699:
697:Non-bonding MO
694:
688:
686:
682:
681:
679:
678:
673:
668:
662:
660:
653:
647:
646:
643:
642:
640:
639:
634:
628:
626:
622:
621:
619:
618:
613:
608:
606:Hybrid orbital
602:
600:
593:
587:
586:
583:
582:
580:
579:
574:
569:
563:
561:
554:
553:
551:
550:
545:
540:
535:
530:
525:
519:
517:
510:
509:
507:
506:
501:
496:
491:
485:
483:
476:
475:Types of bonds
472:
471:
469:
468:
467:
466:
456:
454:Atomic orbital
450:
447:
446:
438:
437:
430:
423:
415:
408:
407:
366:
344:
342:
339:
338:
337:
330:
327:
319:2-methylbutane
295:
294:
290:
285:
280:
277:Both bonds in
262:
255:
233:, which is a
191:involving two
169:covalent bonds
139:for molecular
128:
127:
110:September 2023
42:
40:
33:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1169:
1158:
1155:
1154:
1152:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1129:
1125:
1122:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1109:Hückel's rule
1107:
1106:
1105:
1102:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1092:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1077:
1075:
1073:
1072:Bond cleavage
1069:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1049:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1039:
1038:Intercalation
1036:
1033:
1029:
1028:Metallophilic
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1010:
1008:
1004:
1000:
994:
991:
989:
986:
984:
981:
979:
976:
974:
971:
970:
968:
966:
962:
956:
953:
952:
950:
948:
945:Van der Waals
942:
939:
935:
931:
926:
920:
914:
900:
899:
897:
895:
891:
885:
882:
881:
879:
877:
873:
865:
862:
860:
857:
856:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
812:
810:
807:
803:
800:
799:
798:
795:
791:
788:
786:
783:
781:
778:
777:
776:
773:
772:
770:
768:
764:
761:
757:
753:
749:
742:
737:
735:
730:
728:
723:
722:
719:
703:
700:
698:
695:
693:
690:
689:
687:
683:
677:
674:
672:
669:
667:
664:
663:
661:
657:
654:
652:
648:
638:
635:
633:
632:Covalent bond
630:
629:
627:
623:
617:
614:
612:
609:
607:
604:
603:
601:
597:
594:
592:
588:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
565:
564:
562:
560:
555:
549:
546:
544:
543:5 (quintuple)
541:
539:
538:4 (quadruple)
536:
534:
531:
529:
526:
524:
521:
520:
518:
516:
511:
505:
502:
500:
497:
495:
492:
490:
487:
486:
484:
480:
477:
473:
465:
462:
461:
460:
457:
455:
452:
451:
448:
443:
436:
431:
429:
424:
422:
417:
416:
413:
403:
399:
394:
389:
385:
381:
377:
370:
355:
349:
345:
336:
333:
332:
326:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
293:
286:
284:
276:
275:
274:
271:
269:
265:
258:
251:
246:
242:
238:
236:
232:
228:
223:
221:
217:
212:
210:
206:
202:
201:covalent bond
198:
194:
190:
186:
185:chemical bond
182:
178:
170:
166:
161:
154:
149:
142:
138:
134:
124:
121:
113:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71: –
70:
69:"Single bond"
66:
65:Find sources:
59:
55:
49:
48:
43:This article
41:
37:
32:
31:
19:
1114:Baird's rule
834:Charge-shift
797:Hypervalence
548:6 (sextuple)
522:
515:multiplicity
386:(12): 1598.
383:
379:
369:
358:. Retrieved
348:
323:cyclopentane
303:nomenclature
299:hydrocarbons
296:
272:
247:
243:
239:
224:
213:
187:between two
180:
174:
116:
107:
97:
90:
83:
76:
64:
52:Please help
47:verification
44:
1104:Aromaticity
1080:Heterolysis
1058:Salt bridge
1003:Noncovalent
973:Low-barrier
854:Aromaticity
844:Conjugation
824:Pi backbond
482:By symmetry
220:triple bond
216:double bond
181:single bond
18:Single-bond
1032:aurophilic
1013:Mechanical
692:Bonding MO
676:MO diagram
533:3 (triple)
528:2 (double)
523:1 (single)
360:2012-08-12
341:References
335:Bond order
227:sigma bond
80:newspapers
1124:spherical
1085:Homolysis
1048:Cation–pi
1023:Chalcogen
983:Symmetric
839:Hapticity
637:Lone pair
611:Resonance
499:Delta (δ)
489:Sigma (σ)
402:0021-9584
197:electrons
177:chemistry
1151:Category
1053:Anion–pi
1043:Stacking
965:Hydrogen
876:Metallic
767:Covalent
759:(strong)
659:Concepts
599:Concepts
329:See also
141:hydrogen
1018:Halogen
864:bicyclo
809:Agostic
572:Singlet
567:Triplet
504:Phi (φ)
307:alkanes
235:pi bond
205:orbital
153:methane
94:scholar
1119:Möbius
947:forces
937:(weak)
494:Pi (π)
444:theory
400:
321:, and
315:ethane
266:, and
165:alkane
96:
89:
82:
75:
67:
1097:rules
1006:other
894:Ionic
802:3c–4e
790:8c–2e
785:4c–2e
780:3c–2e
218:or a
189:atoms
183:is a
101:JSTOR
87:books
859:homo
814:Bent
671:LCAO
559:spin
398:ISSN
311:-ane
179:, a
73:news
557:By
513:By
388:doi
268:HCl
175:In
56:by
1153::
396:.
384:78
382:.
378:.
317:,
289:CH
270:.
259:,
1034:)
1030:(
740:e
733:t
726:v
434:e
427:t
420:v
404:.
390::
363:.
291:4
283:O
281:2
279:H
263:2
261:F
256:2
254:H
171:.
123:)
117:(
112:)
108:(
98:·
91:·
84:·
77:·
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.