206:
168:
156:
125:
40:
129:
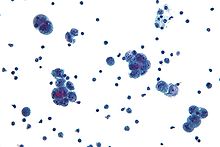
to single cells) should be over 5 mm in size to distinguish it from a borderline serous tumor. Calcifications often form psammoma bodies. Right picture shows higher magnification, including hobnailing which is individual cells protruding into the lumen of glands. Cells may have up to moderate atypia: They may have conspicuous nucleoli, and up to 3x variation in nuclear sizes compared to each other. More atypical features indicate a high-grade serous carcinoma.
167:
128:
Histopathology of invasive low-grade serous carcinoma of ovary with typical features. H&E stain. The left image shows lower magnification, including inverted macropapillae which are with broad fibrovascular cores surrounded by clear (white) clefts. Invasion (characterized by small irregular nests
133:
The "low grade" classification of serous tumors includes benign and borderline tumors, as well as low grade malignant tumors. Benign serous tumors are distinguished from borderline tumors by the absence of cellular stratification. Stromal invasion distinguishes borderline tumors from low grade
219:
C and D. Immunohistochemistry of p53 shows that high-grade serous carcinoma cells are diffusely positive for p53, a pattern consistent with a missense TP53 mutation while the adjacent epithelial cells from the background serous borderline tumor are only focally and weakly positive, a pattern
155:
250:
Beginning in the year 2000, the fallopian tube, specifically the fimbriated end, has emerged as an origin for many "ovarian" high-grade serous carcinomas. This discovery has been facilitated by pathology dissection protocols such as the
149:. On gross examination, the serous tumor may present as either a cystic lesion in which the papillary epithelium is contained within a few fibrous walled cysts, or the papillary projections may be away from the surface epithelium.
161:
Histopathology of serous cystadenoma of the ovary, which is benign. It shows admixed scattered ciliated cells. This case closely resembles normal surface endometrial epithelium of the uterus.
177:: Hierarchical branching, exfoliated cell clusters, calcifications, up to moderate atypia, and pseudostratified, crowded epithelium with hobnailing. H&E stain.
215:
A. Low-magnification view shows a focal high-grade serous carcinoma developing from the papillae (square) in a background of a typical serous borderline tumor.
205:
423:
389:
92:. They are common neoplasms with a strong tendency to occur bilaterally, and they account for approximately a quarter of all ovarian tumors.
137:
Benign serous tumors include serous cystadenomas, cystadenofibromas, and adenofibromas. Benign and borderline serous tumours are commonly
217:
B. Higher magnification demonstrates enlarged and atypical high-grade serous carcinoma cells that organize in a papillary architecture.
352:"Pulmonary papillary serous adenocarcinoma with intraperitoneal and ovarian tumors: identification of primary site. A case report"
255:, which play close attention to the distal fallopian tube and have revealed early serous cancers and precancers in this region.
72:
that typically has papillary to solid formations of tumor cells with crowded nuclei, and which typically arises on the modified
557:
190:, but stromal invasion is absent, and nuclear stratification is present. Approximately 15% of serous tumors are borderline.
321:. Unlike the more common low-grade endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma, uterine serous carcinoma does not develop from
85:
463:"Adenocarcinoma of Mullerian origin: review of pathogenesis, molecular biology, and emerging treatment paradigms"
124:
612:
197:
are often found. Serous psammocarcinoma is a low grade variant in which massive psammoma bodies are present.
405:
182:
In borderline lesions, the cyst or surface is lined by papillary structures, which are often very complex.
104:
17:
461:
Cobb, Lauren
Patterson; Gaillard, Stephanie; Wang, Yihong; Shih, Ie-Ming; Secord, Angeles Alvarez (2015).
134:
malignant tumors. Surgery is curative for benign tumors, and likely curative for other low grade tumors.
330:
99:, which typically arises in postmenopausal women. Rarely, serous tumors arise from other parts of the
318:
301:
142:
96:
322:
383:
224:
High grade serous tumors often involve both ovaries. The tumors are solid and cystic with
8:
540:
Gründker C, Günthert AR, Emons G (2008). "Hormonal
Heterogeneity of Endometrial Cancer".
497:
462:
314:
310:
563:
553:
502:
484:
417:
371:
367:
73:
545:
512:- "Figure 3- available via license: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International"
492:
474:
363:
275:
Stage IV- Tumour involving one or both ovaries with presence of distant metastasis.
252:
174:
51:
549:
544:. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 630. pp. 166–88.
258:
Unsurprisingly, 5-year survival decreases as the stage increases. There is a 25%
237:
194:
187:
77:
285:
479:
272:
Stage III - Tumour involving one or both ovaries with implants outside pelvis.
606:
488:
259:
89:
313:
that typically arises in postmenopausal women. It is typically diagnosed on
232:. They are morphologically heterogenous. Serous carcinomas often have bulky
39:
567:
506:
375:
351:
210:
592:
289:
225:
141:. Benign tumors contain clear fluid and have a smooth lining composed of
244:
240:
233:
183:
138:
100:
47:
325:
and is not hormone-sensitive. It arises in the setting of endometrial
269:
Stage II - Growth involving one or both ovaries with pelvic extension.
403:
229:
107:. Even more rarely they arise in other body locations, such as the
69:
349:
326:
146:
108:
81:
173:
Histopathology of the typical features of an ovarian serous
95:
Rarely, serous tumors arise from within the uterus, notably
209:
A high-grade serous carcinoma arising from a borderline
292:
have been identified as risk factors for the disease.
539:
582:
460:
402:
Image by Mikael Häggström, MD. Source for findings:
604:
84:in females. Such ovarian tumors are part of the
193:In borderline tumors and low grade carcinomas,
527:Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
450:(11 ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1367–1431.
422:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
388:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
262:with a stage III serous carcinoma. Staging:
343:
295:
266:Stage I - Tumour growth limited to ovaries.
186:, stromal papillae are covered by atypical
529:(9 ed.). Elsevier. pp. 991–1042.
467:Gynecologic Oncology Research and Practice
350:Chen MY, Jung SM, Ng KK, Chang TC (2006).
220:consistent with a wild-type TP53 sequence.
38:
496:
478:
404:Erna Forgó, M.D., Teri A. Longacre, M.D.
114:
204:
123:
520:
518:
448:Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology
442:
440:
438:
436:
434:
14:
605:
288:are serous tumors. Family history and
515:
431:
24:
542:Innovative Endocrinology of Cancer
25:
624:
578:
524:
284:25% of ovarian tumors and 40% of
86:surface epithelial-stromal tumour
368:10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00369.x
166:
154:
428:Last staff update: 23 July 2020
279:
533:
454:
396:
13:
1:
336:
200:
105:primary peritoneal carcinomas
550:10.1007/978-0-387-78818-0_11
406:"Low grade serous carcinoma"
119:
7:
10:
629:
331:type II endometrial cancer
299:
586:
480:10.1186/s40661-015-0008-z
143:columnar epithelial cells
46:
37:
32:
319:post-menopausal bleeding
307:Uterine serous carcinoma
302:Uterine serous carcinoma
296:Uterine serous carcinoma
97:uterine serous carcinoma
329:and is classified as a
323:endometrial hyperplasia
309:is an uncommon form of
221:
130:
115:Ovarian serous tumours
613:Gynaecological cancer
208:
127:
356:Int J Gynecol Cancer
243:, and spread to the
103:, including serous
410:Pathology Outlines
362:(Suppl 1): 231–5.
315:endometrial biopsy
311:endometrial cancer
222:
131:
80:that surround the
600:
599:
559:978-0-387-78817-3
62:
61:
27:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
620:
584:
583:
572:
571:
537:
531:
530:
522:
513:
510:
500:
482:
458:
452:
451:
444:
429:
427:
421:
413:
400:
394:
393:
387:
379:
347:
253:SEE-FIM Protocol
188:epithelial cells
175:borderline tumor
170:
158:
78:serous membranes
52:serous carcinoma
42:
30:
29:
21:
628:
627:
623:
622:
621:
619:
618:
617:
603:
602:
601:
596:
595:
581:
576:
575:
560:
538:
534:
523:
516:
511:
459:
455:
446:
445:
432:
415:
414:
401:
397:
381:
380:
348:
344:
339:
304:
298:
286:ovarian cancers
282:
218:
216:
214:
203:
195:psammoma bodies
184:Microscopically
178:
171:
162:
159:
122:
117:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
626:
616:
615:
598:
597:
591:
590:
588:
587:Classification
580:
579:External links
577:
574:
573:
558:
532:
525:Kumar, Vinay.
514:
453:
430:
395:
341:
340:
338:
335:
317:, prompted by
300:Main article:
297:
294:
281:
278:
277:
276:
273:
270:
267:
202:
199:
180:
179:
172:
165:
163:
160:
153:
121:
118:
116:
113:
90:ovarian tumors
60:
59:
44:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
625:
614:
611:
610:
608:
594:
589:
585:
569:
565:
561:
555:
551:
547:
543:
536:
528:
521:
519:
508:
504:
499:
494:
490:
486:
481:
476:
472:
468:
464:
457:
449:
443:
441:
439:
437:
435:
425:
419:
411:
407:
399:
391:
385:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
346:
342:
334:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
303:
293:
291:
287:
274:
271:
268:
265:
264:
263:
261:
260:survival rate
256:
254:
248:
247:is frequent.
246:
242:
239:
235:
231:
227:
212:
207:
198:
196:
191:
189:
185:
176:
169:
164:
157:
152:
151:
150:
148:
144:
140:
135:
126:
112:
110:
106:
102:
98:
93:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
66:serous tumour
57:
56:serous tumour
53:
49:
45:
41:
36:
33:Serous tumour
31:
19:
541:
535:
526:
470:
466:
456:
447:
409:
398:
384:cite journal
359:
355:
345:
306:
305:
283:
280:Epidemiology
257:
249:
223:
211:serous tumor
192:
181:
136:
132:
94:
65:
63:
55:
54:, a type of
18:Serous tumor
290:nulliparity
245:lymph nodes
226:haemorrhage
337:References
241:metastases
234:peritoneal
201:High grade
139:unilocular
101:peritoneum
48:Micrograph
489:2053-6844
120:Low grade
88:group of
76:-derived
74:Müllerian
607:Category
568:18637491
507:27231561
473:(1): 1.
418:cite web
376:16515596
230:necrosis
70:neoplasm
498:4880836
327:atrophy
238:omental
82:ovaries
566:
556:
505:
495:
487:
374:
147:cilia
145:with
109:lungs
68:is a
564:PMID
554:ISBN
503:PMID
485:ISSN
424:link
390:link
372:PMID
236:and
228:and
546:doi
493:PMC
475:doi
364:doi
50:of
609::
562:.
552:.
517:^
501:.
491:.
483:.
469:.
465:.
433:^
420:}}
416:{{
408:.
386:}}
382:{{
370:.
360:16
358:.
354:.
333:.
213::
111:.
64:A
593:D
570:.
548::
509:.
477::
471:2
426:)
412:.
392:)
378:.
366::
58:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.