87:
31:
79:
66:, if the sediment is preserved in the rock record. In most cases, the environments associated with particular rock types or associations of rock types can be matched to existing analogues. However, the further back in geological time sediments were deposited, the more likely that direct modern analogues are not available (e.g.
148: – Rise and fall of the sea level under astronomical gravitational influences – processes due to tidal currents, creates tidal flats (fine-grained, ripple marks, cross-beds). Common sediments are silt and clay
164: – Area of loose particles at the edge of the sea or other body of water. Caused by waves and longshore currents. Creates beaches, spits, and sandbars with the common sediments of gravel and sand.
209: – Shoal of rock, coral, or other material lying beneath the surface of water caused by waves and tidal currents. Also creates adjacent basins. Common sediments are carbonates.
183:– processes due to waves and tidal currents, creates shelves and slopes, lagoons. Common sediments are carbonates (in tropical climates) or sand, silt, and clay (elsewhere)
154: – Shallow body of water separated from a larger one by a narrow landform. Little transportation, creates lagoon bottom environment. Common sediments are
268:
477:
107:– type of Fluvial deposit. Caused by moving water in a fan shape (Alluvial Fan) and containing mostly impermeable and nonporous sediments well sorted.
203: – Flat area on the deep ocean floor (abyssal plains) caused by ocean currents. Common sediments are clay, carbonate mud, silica mud.
142: – Silt deposition landform at the mouth of a river (possible cross beds, ripple marks) Common sediments are sand, silt, and clay.
17:
369:
129: – Sediment deposited by a lake – processes due to moving water, mainly lakes. Common sediments are sand, silt, and clay.
82:
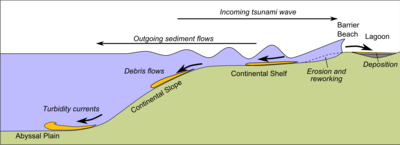
Diagram to show the different depositional environments in which tsunami deposits are formed – partly after
Shanmugam 2006
86:
113: – Processes due to wind activity. Often in deserts and coastal regions and well sorted, large scale cross-beds
180:
502:
441:
417:
393:
339:
482:
497:
272:
50:
describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the
189: – Portion of the seafloor that is shallow enough to be agitated by everyday wave action
123:– processes due to moving water, mainly streams. Common sediments are gravel, sand, and silt.
67:
313:
51:
8:
126:
317:
301:
263:
Depositional environments in ancient sediments are recognised using a combination of
110:
103: – Loose soil or sediment that is eroded and redeposited in a non-marine setting
222: – Water-soluble mineral deposit formed by evaporation from an aqueous solution
321:
59:
251:
192:
186:
30:
258:
78:
491:
200:
63:
280:
228: – Persistent body of ice that is moving downhill under its own weight
90:
Depositional environmental model of the
Araripe Basin formations, NE Brazil
370:"6.3 Depositional Environments and Sedimentary Basins – Physical Geology"
325:
139:
27:
Processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment
234:
Till – angular to rounded grains, poorly sorted, unstratified (massive)
219:
155:
283:
assemblages, as they indicate the environment in which they lived.
242:
100:
55:
225:
116:
39:
276:
264:
151:
259:
Recognition of depositional environments in ancient sediments
237:
Outwash – ripple marks, cross-beds, similar to stream channel
161:
119: – Sediment processes associated with rivers and streams
465:
Sedimentary
Environments: Processes, Facies and Stratigraphy
206:
167:
145:
245: – Rupture in a planet's crust where material escapes
247:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
230:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
121:
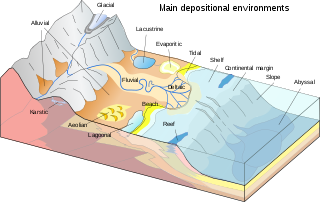
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
105:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
73:
170: – Large inland body of relatively still water
195: – Part of the seafloor undisturbed by waves
489:
254: – Sedimentary unit deposited by a tsunami
478:Sedimentary Environments Classification Charts
34:A diagram of various depositional environments
293:
299:
442:"Basics—Table of Depositional Environments"
418:"Basics—Table of Depositional Environments"
394:"Basics—Table of Depositional Environments"
340:"Basics—Table of Depositional Environments"
85:
77:
29:
14:
490:
367:
483:Depositional environments on e-notes
363:
361:
359:
24:
74:Types of depositional environments
25:
514:
471:
356:
368:Earle, Steven (September 2015).
181:Shallow water marine environment
62:types that will be formed after
467:. Blackwell Publishing Limited.
306:Journal of Sedimentary Research
434:
410:
386:
332:
13:
1:
286:
201:Deep water marine environment
7:
10:
519:
463:Harold G. Reading. 1996.
54:of a particular type of
44:depositional environment
302:"The Tsunamite Problem"
158:(in tropical climates).
48:sedimentary environment
18:Sedimentary environment
273:sedimentary structures
91:
83:
68:banded iron formations
35:
300:Shanmugam G. (2006).
89:
81:
33:
503:Deposition (geology)
326:10.2110/jsr.2006.073
58:and, therefore, the
318:2006JSedR..76..718S
269:facies associations
265:sedimentary facies
92:
84:
36:
16:(Redirected from
510:
456:
455:
453:
452:
438:
432:
431:
429:
428:
414:
408:
407:
405:
404:
390:
384:
383:
381:
380:
374:Physical Geology
365:
354:
353:
351:
350:
336:
330:
329:
297:
248:
231:
122:
106:
21:
518:
517:
513:
512:
511:
509:
508:
507:
488:
487:
474:
460:
459:
450:
448:
446:commons.wvc.edu
440:
439:
435:
426:
424:
422:commons.wvc.edu
416:
415:
411:
402:
400:
398:commons.wvc.edu
392:
391:
387:
378:
376:
366:
357:
348:
346:
344:commons.wvc.edu
338:
337:
333:
298:
294:
289:
279:, particularly
261:
246:
229:
193:Lower shoreface
187:Upper shoreface
120:
104:
76:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
516:
506:
505:
500:
486:
485:
480:
473:
472:External links
470:
469:
468:
458:
457:
433:
409:
385:
355:
331:
312:(5): 718–730.
291:
290:
288:
285:
260:
257:
256:
255:
249:
240:
239:
238:
235:
223:
211:
210:
204:
198:
197:
196:
190:
172:
171:
165:
159:
149:
143:
131:
130:
124:
114:
108:
75:
72:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
515:
504:
501:
499:
498:Sedimentology
496:
495:
493:
484:
481:
479:
476:
475:
466:
462:
461:
447:
443:
437:
423:
419:
413:
399:
395:
389:
375:
371:
364:
362:
360:
345:
341:
335:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
296:
292:
284:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
253:
250:
244:
241:
236:
233:
232:
227:
224:
221:
218:
217:
216:
215:
208:
205:
202:
199:
194:
191:
188:
185:
184:
182:
179:
178:
177:
176:
169:
166:
163:
160:
157:
153:
150:
147:
144:
141:
138:
137:
136:
135:
128:
125:
118:
115:
112:
109:
102:
99:
98:
97:
96:
88:
80:
71:
69:
65:
64:lithification
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
32:
19:
464:
449:. Retrieved
445:
436:
425:. Retrieved
421:
412:
401:. Retrieved
397:
388:
377:. Retrieved
373:
347:. Retrieved
343:
334:
309:
305:
295:
281:trace fossil
262:
213:
212:
174:
173:
134:Transitional
133:
132:
94:
93:
47:
43:
37:
95:Continental
492:Categories
451:2020-01-13
427:2020-01-13
403:2020-01-13
379:2020-01-13
349:2020-01-13
287:References
156:carbonates
127:Lacustrine
52:deposition
220:Evaporite
243:Volcanic
152:Lagoonal
101:Alluvial
56:sediment
314:Bibcode
277:fossils
252:Tsunami
226:Glacial
140:Deltaic
117:Fluvial
111:Aeolian
40:geology
214:Others
175:Marine
162:Beach
275:and
207:Reef
168:Lake
146:Tide
60:rock
322:doi
70:).
46:or
38:In
494::
444:.
420:.
396:.
372:.
358:^
342:.
320:.
308:.
304:.
271:,
267:,
42:,
454:.
430:.
406:.
382:.
352:.
328:.
324::
316::
310:6
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.