31:
212:
of a vertical or diagonal edge where dark changes to light or vice versa, going from left to right, whereby the electron beam's intensity overshoots and undershoots the desired intensity there a few times instead of settling quickly. This bouncing could occur anywhere in the electronics or cabling
221:
Ringing can affect audio equipment in a number of ways. Audio amplifiers can produce ringing depending on their design, although the transients that can produce such ringing rarely occur in audio signals.
233:) can also ring. Mechanical ringing is more of a problem with loudspeakers as the moving masses are larger and less easily damped, but unless extreme they are difficult to audibly identify.
384:
348:
f. The action of a machine, instrument, system, etc., that is hunting (see hunt v. 7b); an undesirable oscillation about an equilibrium speed, position, or state.
113:. Ringing can be undesirable because it causes extra current to flow, thereby wasting energy and causing extra heating of the components; it can cause unwanted
188:, a resistor cannot simultaneously critically damp the response and perfectly match the impedance without losing some power on the series resistor, so a
19:
This article is about ringing in electronics and signals generally. For ringing artifacts in signal processing, particularly image processing, see
423:
144:
374:
408:
166:
or undershoot, and thus these related concepts are at times conflated. This ringing can be reduced by a slower
66:(the response to a sudden change in input). Often ringing is undesirable, but not always, as in the case of
278:
67:
114:
255:: spurious signals near sharp transitions. These have a number of causes, and occur for instance in
30:
428:
209:
110:
267:
185:
121:
for the desired final state; and it may cause unwanted triggering of bistable elements in
8:
314:
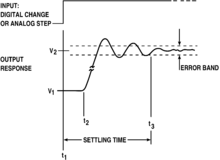
78:
24:
340:
319:
177:
163:
140:
35:
213:
and is often caused by or accentuated by a too high setting of the sharpness control.
252:
248:
242:
173:
51:
20:
290:
282:
201:
189:
82:
122:
274:
417:
264:
118:
63:
309:
230:
286:
226:
102:
94:
59:
47:
39:
167:
155:
147:
375:"Damping and Reflection Transfer with a Series Termination Resistor"
260:
151:
137:
159:
126:
106:
379:
170:
and possibly eliminated by critically dampening the resonance.
205:
256:
273:
Signals constructed as only a partial (not infinite)
361:
High-Speed
Digital Design: A Handbook of Black Magic
339:
208:circuit, electrical ringing causes closely spaced
184:While either issue can be addressed with a series
16:Oscillation of a signal, usually in step response
415:
346:(2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. 1989.
132:Two electrical sources of this ringing are:
125:. Ringy communications circuits may suffer
372:
29:
416:
88:
289:) create a ringing error called the
236:
81:, particularly in electricity or in
409:Microphony with older video cameras
373:Peterson, Zachariah (2023-01-09) .
154:in the circuit creating a resonant
13:
424:Transient response characteristics
332:
14:
440:
402:
62:of a signal, particularly in the
23:. For Ringing in telephony, see
387:from the original on 2023-01-30
216:
195:
117:to be emitted; it can increase
366:
353:
1:
325:
176:, which may be minimized by
7:
359:Johnson, H. and Graham, M.
303:
68:resonant inductive coupling
10:
445:
240:
38:, followed by ringing and
18:
342:Oxford English Dictionary
277:of a function containing
251:, "ringing" may refer to
115:electromagnetic radiation
283:brickwall lowpass filter
281:(e.g. when applying a
70:. It is also known as
43:
33:
300:each discontinuity.
186:termination resistor
158:. This is often the
77:It is also known as
315:Ripple (electrical)
259:compression and as
225:Transducers (i.e.,
162:response following
89:Electrical circuits
34:An illustration of
25:Ringing (telephony)
320:Impedance matching
192:may be preferred.
178:impedance matching
141:transient response
44:
363:. 1993. pp. 88–90
253:ringing artifacts
249:signal processing
243:Ringing artifacts
237:Signal processing
174:Signal reflection
143:due to undesired
52:signal processing
21:ringing artifacts
436:
396:
395:
393:
392:
370:
364:
357:
351:
350:
345:
336:
291:Gibbs phenomenon
202:cathode-ray tube
190:bypass capacitor
123:digital circuits
83:frequency domain
444:
443:
439:
438:
437:
435:
434:
433:
414:
413:
405:
400:
399:
390:
388:
371:
367:
358:
354:
338:
337:
333:
328:
306:
279:discontinuities
245:
239:
219:
210:repeated ghosts
198:
91:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
442:
432:
431:
426:
412:
411:
404:
403:External links
401:
398:
397:
365:
352:
330:
329:
327:
324:
323:
322:
317:
312:
305:
302:
275:Fourier series
241:Main article:
238:
235:
218:
215:
197:
194:
182:
181:
171:
90:
87:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
441:
430:
429:Filter theory
427:
425:
422:
421:
419:
410:
407:
406:
386:
382:
381:
376:
369:
362:
356:
349:
344:
343:
335:
331:
321:
318:
316:
313:
311:
308:
307:
301:
299:
295:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
271:
269:
266:
265:digital audio
262:
258:
254:
250:
244:
234:
232:
228:
223:
214:
211:
207:
203:
193:
191:
187:
179:
175:
172:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
146:
142:
139:
135:
134:
133:
130:
128:
124:
120:
119:settling time
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
86:
84:
80:
75:
73:
69:
65:
64:step response
61:
57:
54:, and video,
53:
49:
41:
37:
32:
26:
22:
389:. Retrieved
378:
368:
360:
355:
347:
341:
334:
310:Microphonics
297:
293:
272:
246:
231:loudspeakers
224:
220:
217:Analog audio
199:
196:Analog video
183:
148:capacitances
131:
98:
92:
76:
71:
55:
45:
287:square wave
268:compression
227:microphones
152:inductances
103:oscillation
60:oscillation
48:electronics
40:settle time
418:Categories
391:2024-01-09
326:References
97:circuits,
95:electrical
85:response.
168:slew rate
164:overshoot
156:frequency
145:parasitic
36:overshoot
385:Archived
304:See also
263:in some
261:pre-echo
138:resonant
160:damping
127:falsing
111:current
107:voltage
99:ringing
72:hunting
56:ringing
380:Altium
294:before
204:(CRT)
101:is an
79:ripple
298:after
285:to a
206:video
200:In a
105:of a
296:and
257:JPEG
229:and
150:and
247:In
109:or
93:In
58:is
46:In
420::
383:.
377:.
270:.
136:A
129:.
74:.
50:,
394:.
180:.
42:.
27:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.