294:
This is because the removal of the mains transformer means that the load has electrical continuity with the input. For industrial ovens and furnaces the input is often the national grid AC, which is itself electrically referenced to ground. With the controller's output referenced to ground, a user need only be in contact with earth and one of the output terminals to risk receiving an electrical shock. With many high-power items of equipment running from three-phase 415 V, high-current inputs and having any enclosure or framework present earthed (grounded), this is a serious risk that must be carefully assessed.
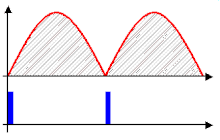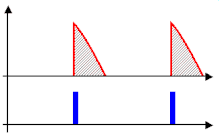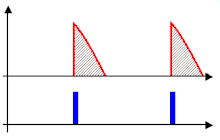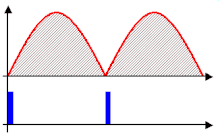
257:, is only able to deliver an output voltage not exceeding its input, minus any losses occurring in the control elements themselves. Provided the modulation during each cycle is predictable or repetitive, as it is on the national grid's AC mains, to obtain an output lower than its input, a phase-fired control simply switches off for a given phase angle of the input's modulation cycle. By triggering the device into conduction at a phase angle greater than 0 degrees, a point after the modulation cycle starts, a fraction of the total energy within each cycle is present at the output.
160:
323:
94:
25:
17:
289:
were used as the supplies for such elements, with the corresponding winding tap being connected to the element to produce the desired temperature. This limited the temperature resolution to the number of tap combinations available. They often find their way into controllers designed for equipment
273:
loads, such as heating elements. Over time, the resistance of heating elements can increase. To account for this, a phase-fired control must be able to provide some degree of extra voltage to draw the same heating current through the element. The only way of achieving this is to purposely design
265:
To achieve a "boost"-like effect, the PFC designs must be derated such that the maximum present at the input is higher than the nominal output requirements. When the supply is first turned on or operating under nominal conditions, the controller will continually be delivering less than 100% of its
229:
waveform that the national grid outputs. Here, it becomes important for the supply to pulse on and off at the correct position in the modulation cycle for a known value to be achieved; for example, the controller could turn on at the peak of a waveform or at its base if the cycle's time base were
293:
In modern, usually high-power, equipment, the transformer is replaced with phase-fired controllers connecting the load directly to the mains, resulting in a substantially cheaper and lighter system. However, the method is usually limited to use in equipment that would be unrealistic without it.
26:
27:
233:
Phase-fired controllers take their name from the fact that they trigger a pulse of output at a certain phase of the input's modulation cycle. In essence, a PFC is a controller that can synchronise itself with the modulation present at the input.
217:
feeds to its load. It does this to create an average value at its output. If the supply has a DC output, its time base is of no importance in deciding when to pulse the supply on or off, as the value that will be pulsed on and off is continuous.
29:
274:
the supply to require less than 100% of the input's modulation cycle when the elements are first put in place, progressively opening the supply up towards delivering 100% of the input modulation cycle as the elements age.
306:
rectifiers with control grids became available. Because of the limitations of mercury-arc valves this method of voltage regulation was not common at the time. It became widespread with the invention of solid-state
28:
241:, allowing the controller to not only decide when to switch the output on but when to turn it off, rather than having to wait for the waveform to return to the next
359:. M. H. Hamza, G. K. F. Lee, IEEE Control Systems Society, International Society for Mini-Microcomputers. Anaheim, Calif.: ACTA Press. 1986. p. 2.
237:
Most phase-fired controllers use thyristors or other solid-state switching devices as their control elements. Thyristor-based controllers may use
115:
302:
The first patent for phase-fired controllers derives from 1912. However, realization was first possible in the 1920s, when
266:
input. When a boost is required, the controller delivers a percentage closer to 100% of the maximum input available.
454:
444:
364:
141:
123:
449:
119:
61:
181:
459:
388:
254:
172:
424:
104:
335:
269:
Derating of mains-powered phase-fired controllers is important as they are often used to control
238:
108:
177:
222:
403:
411:
270:
225:(PWM) in that it addresses supplies that output a modulated waveform, such as the sinusoidal
8:
226:
53:
382:
328:
370:
360:
303:
285:
For industrial applications previously, extremely expensive and heavy multi-tapped
206:
282:
The most common application is in dimmer switches for domestic lighting control.
210:
438:
242:
77:
374:
214:
159:
354:
286:
16:
308:
69:
57:
93:
322:
202:
201:
Phase-fired control (PFC) is often used to control the amount of
73:
65:
76:-like devices into and out of conduction at a predetermined
356:
Software and hardware applications of microcomputers
318:
260:
33:Unrectified AC voltage regulated by phase control
436:
253:A phase-fired controller, like a buck-topology
248:
404:"ac power control in the Core Flow Test Loop"
52:, is a method for power limiting, applied to
20:Rectified voltage regulated by phase control
122:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
142:Learn how and when to remove this message
23:
15:
437:
290:such as electric ovens and furnaces.
401:
153:
120:adding citations to reliable sources
87:
56:voltages. It works by modulating a
13:
14:
471:
321:
158:
92:
277:
395:
347:
239:gate turn-off (GTO) thyristors
230:not taken into consideration.
1:
340:
7:
314:
249:Output reduction by bucking
171:to comply with Knowledge's
83:
10:
476:
297:
255:switched-mode power supply
311:at the end of the 1950s.
80:of the applied waveform.
455:Physical layer protocols
445:Telecommunication theory
184:may contain suggestions.
169:may need to be rewritten
402:D.W., McDonald (1980).
336:Burst-fired controllers
450:Radio modulation modes
419:Cite journal requires
387:: CS1 maint: others (
261:"Boosting" by derating
223:pulse-width modulation
72:, or other such gated
34:
21:
32:
19:
116:improve this section
50:phase-angle control
38:Phase-fired control
329:Electronics portal
35:
22:
460:Data transmission
304:mercury-arc valve
221:PFC differs from
199:
198:
173:quality standards
152:
151:
144:
30:
467:
429:
428:
422:
417:
415:
407:
399:
393:
392:
386:
378:
351:
331:
326:
325:
194:
191:
185:
162:
154:
147:
140:
136:
133:
127:
96:
88:
31:
475:
474:
470:
469:
468:
466:
465:
464:
435:
434:
433:
432:
420:
418:
409:
408:
400:
396:
380:
379:
367:
353:
352:
348:
343:
327:
320:
317:
300:
280:
263:
251:
195:
189:
186:
176:
163:
148:
137:
131:
128:
113:
97:
86:
44:), also called
24:
12:
11:
5:
473:
463:
462:
457:
452:
447:
431:
430:
421:|journal=
394:
365:
345:
344:
342:
339:
333:
332:
316:
313:
299:
296:
279:
276:
262:
259:
250:
247:
197:
196:
166:
164:
157:
150:
149:
100:
98:
91:
85:
82:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
472:
461:
458:
456:
453:
451:
448:
446:
443:
442:
440:
426:
413:
405:
398:
390:
384:
376:
372:
368:
366:0-88986-085-8
362:
358:
357:
350:
346:
338:
337:
330:
324:
319:
312:
310:
305:
295:
291:
288:
283:
275:
272:
267:
258:
256:
246:
244:
243:zero crossing
240:
235:
231:
228:
224:
219:
216:
212:
208:
204:
193:
183:
179:
174:
170:
167:This section
165:
161:
156:
155:
146:
143:
135:
125:
121:
117:
111:
110:
106:
101:This section
99:
95:
90:
89:
81:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
55:
51:
47:
46:phase cutting
43:
39:
18:
412:cite journal
397:
355:
349:
334:
301:
292:
287:transformers
284:
281:
278:Applications
268:
264:
252:
236:
232:
220:
215:power supply
200:
187:
178:You can help
168:
138:
129:
114:Please help
102:
49:
45:
41:
37:
36:
78:phase angle
439:Categories
341:References
309:thyristors
383:cite book
271:resistive
190:June 2023
182:talk page
132:June 2023
103:does not
70:thyratron
58:thyristor
375:24541232
315:See also
84:Overview
298:History
213:that a
207:current
203:voltage
124:removed
109:sources
373:
363:
180:. The
211:power
74:diode
66:triac
425:help
389:link
371:OCLC
361:ISBN
107:any
105:cite
209:or
118:by
62:SCR
48:or
42:PFC
441::
416::
414:}}
410:{{
385:}}
381:{{
369:.
245:.
227:AC
205:,
68:,
64:,
60:,
54:AC
427:)
423:(
406:.
391:)
377:.
192:)
188:(
175:.
145:)
139:(
134:)
130:(
126:.
112:.
40:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.