691:) innervate the structures derived from the corresponding processes of the first arch. In some lower animals, each arch is supplied by two cranial nerves. The nerve of the arch itself runs along the cranial side of the arch and is called post-trematic nerve of the arch. Each arch also receives a branch from the nerve of the succeeding arch called the pre-trematic nerve which runs along the caudal border of the arch. In human embryo, a double innervation is seen only in the first pharyngeal arch. The mandibular nerve is the post-trematic nerve of the first arch and
134:
120:
329:. These project forward from the back of the embryo toward the front of the face and neck. Each arch develops its own artery, nerve that controls a distinct muscle group, and skeletal tissue. The arches are numbered from 1 to 6, with 1 being the arch closest to the head of the embryo, and arch 5 existing only transiently.
299:
and jaw support. In fish, the other posterior arches contribute to the branchial skeleton, which support the gills; in tetrapods the anterior arches develop into components of the ear, tonsils, and thymus. The genetic and developmental basis of pharyngeal arch development is well characterized. It
1075:
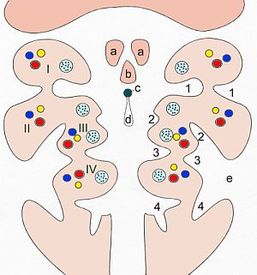
Amniotes have five arches, numbered 1 to 5. Older literature reports the fifth arch as the sixth arch, the fifth being absent. More is known about the fate of the first arch than the remaining four. The first three contribute to structures above the larynx, whereas the last two contribute to the
1091:
are produced from the nerve of arch 5, and the laryngeal cartilages from arches 4 and 5. The superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve arises from arch 4. Its arteries, which project between the nerves of the fourth and fifth arches, become the left-side arch of the aorta and the right
148:
29:
290:
such as bone and cartilage. However, the existence of pharyngeal structures before neural crest cells evolved is indicated by the existence of neural crest-independent mechanisms of pharyngeal arch development. The first, most anterior
400:
The development of the pharyngeal arches provides a useful landmark with which to establish the precise stage of embryonic development. Their formation and development corresponds to
747:
Cartilage in the second pharyngeal arch is referred to as
Reichert's cartilage and contributes to many structures in the fully developed adult. In contrast to the
2249:
2396:
771:
before being incorporated into the middle ear cavity, while the ventral portion ossifies to form the lesser cornu and upper part of the body of the
1047:
All the pharyngeal muscles of the fourth and sixth arches are innervated by the superior laryngeal and the recurrent laryngeal branches of the
1761:
755:, it does not constitute a continuous element, and instead is composed of two distinct cartilaginous segments joined by a faint layer of
2032:
2242:
695:(branch of facial nerve) is the pre-trematic nerve. This double innervation is reflected in the nerve supply of anterior two-thirds of
732:
1470:
1805:
Higashiyama, Hiroki; Koyabu, Daisuke; Hirasawa, Tatsuya; Werneburg, Ingmar; Kuratani, Shigeru; Kurihara, Hiroki (November 2, 2021).
436:(corresponding to the first branchial arch of fish), is the first of six pharyngeal arches that develops during the fourth week of
1735:
1561:
90:
2469:
2235:
1104:. During growth, these arteries descend into their ultimate positions in the chest, creating the elongated recurrent paths.
2066:
1967:
2165:
2137:
1793:
1718:
664:
1423:
589:
2434:
1096:. On the right side, the artery of arch 5 is obliterated while, on the left side, the artery persists as the
409:
362:
332:
These grow and join in the ventral midline. The first arch, as the first to form, separates the mouth pit or
161:
381:
region to separate the arches. In fish, the pouches line up with the clefts, and these thin segments become
340:. By differential growth the neck elongates and new arches form, so the pharynx has six arches ultimately.
2474:
1220:
594:
217:
2459:
1277:
1100:; circulatory changes immediately following birth cause the vessel to close down, leaving a remnant, the
644:
49:
2464:
1427:
1285:
1186:
1088:
948:
579:
520:
85:
1035:. The stylopharyngeus and other structures from the third pharyngeal arch are all innervated by the
416:. Although there are six pharyngeal arches, in humans the fifth arch exists only transiently during
2376:
2292:
1370:
1281:
1253:
956:
826:
792:
780:
621:
73:
2391:
2297:
1765:
1202:
617:
445:
1655:
Fraser GJ, Hulsey D, Bloomquist RF, Uyesugi K, Manley NR, Streelman T (2009). Jernvall J (ed.).
489:
2309:
2304:
1902:"Morphogenesis of the second pharyngeal arch cartilage (Reichert's cartilage) in human embryos"
1458:
1317:
1136:
1064:
1036:
976:
606:
574:
184:
97:
2324:
2319:
2036:
1739:
1410:
1345:
1323:
1182:
1101:
752:
748:
649:
500:
292:
2412:
2314:
1818:
1465:
1414:
1361:
1352:
1152:
1052:
992:
971:
that come from the first pharyngeal arch are innervated by the mandibular divisions of the
457:
413:
190:
8:
2479:
1475:
1406:
1397:
1337:
1265:
952:
832:
800:
437:
417:
240:
172:
1822:
2211:
2186:
2107:
2009:
1984:
1926:
1901:
1841:
1806:
1683:
1656:
1637:
1573:
1530:
1081:
968:
735:
during the fourth week of development and assists in forming the side and front of the
461:
279:
165:
543:
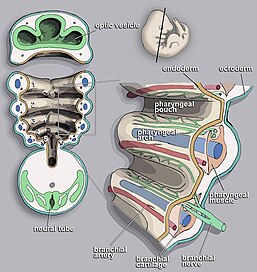
The skeletal elements and muscles are derived from mesoderm of the pharyngeal arches.
359:. Arches do not develop simultaneously but instead possess a "staggered" development.
2417:
2381:
2216:
2202:
2161:
2133:
2099:
2062:
2014:
1963:
1931:
1917:
1846:
1789:
1714:
1688:
1629:
1565:
1522:
1443:
1402:
1376:
1357:
1244:
1240:
1097:
1093:
860:
370:
2187:"The role of the endoderm in the development and evolution of the pharyngeal arches"
2111:
1641:
1577:
1534:
468:
of the lower two-thirds of the face and the jaw. The maxillary process becomes the
2358:
2227:
2206:
2198:
2091:
2004:
1996:
1921:
1913:
1836:
1826:
1678:
1668:
1619:
1557:
1514:
1480:
1439:
1433:
1327:
1289:
1198:
1192:
1144:
1056:
984:
972:
937:
914:
878:
712:
684:
638:
633:
310:
are important for patterning the anterior/posterior and dorsal/ventral axes of the
229:
196:
178:
1003:
All of the pharyngeal muscles of the second pharyngeal arch are innervated by the
1673:
1419:
1299:
1130:
1060:
1032:
933:
660:
401:
306:
287:
78:
44:
504:
374:
366:
318:, which develop using the same genetic pathways involved in oral jaw formation.
33:
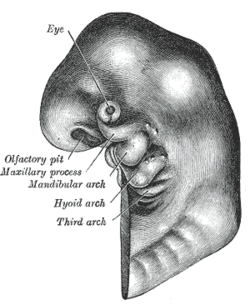
Schematic of developing human fetus with first, second and third arches labelled
2422:
2386:
2353:
1166:
1162:
1148:
1008:
988:
855:
692:
569:
524:
481:
315:
311:
1788:
William J. Larsen (2001). Human embryology. Edinburgh: Churchill
Livingstone.
351:
component that differentiates from the cartilaginous tissue, an artery, and a
2453:
2279:
1206:
1170:
1122:
910:
796:
784:
708:
584:
352:
322:
252:
1831:
1624:
1607:
1591:
Kardong KV (2003). "Vertebrates: Comparative
Anatomy, Function, Evolution".
944:, pharyngeal muscles are developmentally formed from the pharyngeal arches.
2220:
2103:
2018:
1935:
1850:
1692:
1633:
1569:
1526:
1271:
1004:
898:
838:
760:
696:
528:
236:
2336:
1518:
1381:
1366:
1341:
1048:
337:
275:
271:
1051:. These muscles include all the muscles of the palate (exception of the
314:. Some fish species have a second set of jaws in their throat, known as
103:
2095:
1304:
1257:
1236:
1224:
1214:
1016:
871:
842:
788:
772:
768:
756:
626:
560:
516:
356:
221:
2000:
1985:"A reappraisal and revision of the numbering of the pharyngeal arches"
133:
2284:
1562:
10.1002/1521-1878(200101)23:1<54::AID-BIES1007>3.0.CO;2-5
1232:
1140:
1020:
1012:
980:
883:
441:
344:
333:
259:
1657:"An Ancient Gene Network Is Co-opted for Teeth on Old and New Jaws"
1308:
1261:
1228:
866:
672:
668:
612:
394:
390:
386:
301:
244:
1804:
2127:
1178:
1165:(only as a model for mandible not actual formation of mandible),
1158:
951:) is pharyngeal. Exceptions include, but are not limited to, the
947:
Most of the skeletal musculature supplied by the cranial nerves (
941:
565:
552:
531:
using Meckel's cartilage as a 'template', but the maxillary does
512:
469:
405:
248:
955:
and some of the muscles of the tongue. These exceptions receive
2368:
2345:
1393:
1312:
1249:
1077:
820:
776:
764:
507:
of the mandibular process and eventually regresses to form the
477:
348:
326:
1548:
Graham A, Smith A (2001). "Patterning the pharyngeal arches".
393:
not only remain intact but also continue to be separated by a
278:(the primary layers of cells that form during embryogenesis).
147:
1654:
1174:
920:
556:
508:
296:
283:
61:
2082:
Higashiyama H, Kuratani S (2014). "On the maxillary nerve".
282:
enter these arches where they contribute to features of the
2271:
2263:
2259:
2160:. Hagerstown, Maryland: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
1031:
There is only one muscle of the third pharyngeal arch, the
736:
476:, although there are large differences among animals), and
465:
382:
378:
325:, a series of pharyngeal arch pairs form in the developing
251:. The vasculature of the pharyngeal arches is known as the
225:
1983:
Graham, Anthony; Poopalasundaram, Subathra (11 Aug 2019).
731:
is the second of fifth pharyngeal arches that develops in
119:
1505:
Graham A (2003). "Development of the pharyngeal arches".
295:
gives rise to the oral jaw. The second arch becomes the
224:
that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In
125:
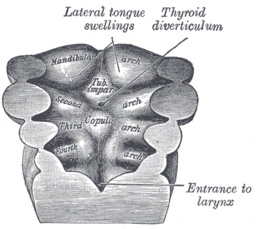
Floor of the pharynx of human embryo at about 26 days old
28:
1784:
1782:
2061:. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 366–372.
1962:. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 366–369.
2132:. Teterboro, N.J: Icon Learning Systems. p. 227.
535:
arise from direct ossification of Meckel's cartilage.
239:, the arches are first seen during the fourth week of
1982:
1779:
1713:. New York: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 318–323.
1605:
2257:
2123:
2121:
1899:
2081:
274:, the pharyngeal arches are derived from all three
2184:
1871:
1869:
795:will not remain as development continues, but its
2118:
2451:
1608:"Specification of jaw subdivisions by Dlx genes"
2155:
1866:
519:, the anterior ligament of the malleus and the
1877:Last's anatomy: Regional and applied (9th ed).
917:in some mammals but atrophies in most humans.
2243:
816:From the cartilage of the second arch arises
683:The mandibular and maxillary branches of the
243:. They appear as a series of outpouchings of
16:Embryonic precursor structures in vertebrates
2128:Netter, Frank H.; Cochard, Larry R. (2002).
1704:
1702:
909:The artery of the second arch is the second
775:. Caudal to what will eventually become the
1889:Embryology for Medical Students 2nd edition
1807:"Mammalian face as an evolutionary novelty"
1547:
2250:
2236:
1753:
1606:Depew MJ, Lufkin T, Rubenstein JL (2002).
1590:
1584:
1059:), all the muscles of the pharynx (except
1042:
921:Muscles derived from the pharyngeal arches
707:The artery of the first arch is the first
464:, giving rise to structures including the
258:In fish, the branchial arches support the
2210:
2008:
1925:
1840:
1830:
1699:
1682:
1672:
1623:
1471:Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck
480:while the mandibular process becomes the
91:arch_by_E5.4.2.0.0.0.2 E5.4.2.0.0.0.2
1504:
1863:Inderbir Sing, G.P Pal-Human Embryology
759:. Dorsal ends of Reichert's cartilage
742:
2452:
2151:
2149:
2056:
1957:
1762:"Text for Pharyngeal Arch Development"
1708:
1541:
1067:), and all the muscles of the larynx.
779:, Reichert's cartilage also forms the
699:which is derived from the first arch.
304:and other developmental genes such as
2231:
2185:Graham A, Okabe M, Quinlan R (2005).
1953:
1951:
1949:
1947:
1945:
1500:
1498:
1496:
1019:muscle, the auricular muscle and the
495:
1893:
1733:
2146:
2057:Sadler, Thomas W. (February 2009).
1958:Sadler, Thomas W. (February 2009).
1764:. Temple University. Archived from
1738:. Howard University. Archived from
1648:
527:or lower jaw forms by perichondral
488:. This arch also gives rise to the
13:
2130:Netter's Atlas of human embryology
2075:
2050:
1942:
1759:
1599:
1493:
711:, which partially persists as the
373:(or clefts) form from the lateral
14:
2491:
2178:
1736:"Lecture 24. Branchial Apparatus"
975:. These muscles include all the
904:
893:
665:anterior two thirds of the tongue
355:. Each of these is surrounded by
321:During human, and all vertebrate
2203:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00472.x
1918:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00524.x
1241:posterior belly of the digastric
998:
806:
247:on both sides of the developing
146:
132:
118:
27:
2025:
1976:
1881:
1857:
1798:
962:
940:that developmentally come from
763:during development to form the
702:
678:
153:Scheme of the pharyngeal arches
139:Scheme of the pharyngeal arches
1727:
718:
590:squamous part of temporal bone
538:
228:, the arches are known as the
1:
1900:Rodríguez-Vázquez JF (2008).
1486:
1026:
1011:, the posterior belly of the
1007:. These muscles include the
936:of the head and neck. Unlike
440:. It is located between the
423:
369:side between the arches, and
216:, are structures seen in the
2470:Animal developmental biology
2158:Gross Anatomy (Board Review)
2059:Langman's Medical Embryology
1960:Langman's Medical Embryology
1674:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000031
1221:Muscles of facial expression
1070:
1009:muscles of facial expression
979:, the anterior belly of the
913:, which gives origin to the
787:. The cartilage between the
595:anterior ligament of malleus
451:
265:
7:
1709:Larsen, William J. (1993).
1452:
1340:, all intrinsic muscles of
1278:Ascending pharyngeal artery
1063:which is innervated by the
1055:which is innervated by the
645:tensor veli palatini muscle
343:Each pharyngeal arch has a
10:
2496:
1456:
1089:recurrent laryngeal nerves
1023:muscle of the middle ear.
2405:
2367:
2344:
2335:
2270:
1595:. New York (McGraw Hill).
1428:recurrent laryngeal nerve
1392:All intrinsic muscles of
1380:Left fourth aortic arch:
1311:and lower part of body),
1264:and upper part of body),
1213:Second (also called the "
1187:sphenomandibular ligament
949:special visceral efferent
799:will eventually form the
622:lateral pterygoid muscles
580:sphenomandibular ligament
521:sphenomandibular ligament
456:This arch divides into a
410:Hamburger–Hamilton stages
96:
84:
72:
60:
55:
43:
38:
26:
21:
2377:Lateral lingual swelling
2156:Kyung Won Chung (2005).
1438:Left fifth aortic arch:
1371:superior laryngeal nerve
1282:Inferior tympanic artery
1254:temporal styloid process
1181:of the middle ear, also
1139:, anterior belly of the
957:general somatic efferent
827:Temporal styloid process
2392:Hypopharyngeal eminence
1832:10.1073/pnas.2111876118
1625:10.1126/science.1075703
1432:Right 5th aortic arch:
1375:Right 4th aortic arch:
1203:external carotid artery
1043:Fourth and sixth arches
446:first pharyngeal groove
157:I–IV: pharyngeal arches
2310:Frontonasal prominence
2305:Intermaxillary segment
1459:anatomical terminology
1318:Glossopharyngeal nerve
1286:primitive hyoid artery
1268:, Reichert's cartilage
1137:Muscles of mastication
1116:Skeletal contributions
1113:Muscular contributions
1065:glossopharyngeal nerve
1037:glossopharyngeal nerve
977:muscles of mastication
725:second pharyngeal arch
607:muscles of mastication
575:spine of sphenoid bone
490:muscles of mastication
98:Anatomical terminology
2320:Mandibular prominence
2084:Journal of Morphology
1411:corniculate cartilage
1346:levator veli palatini
1102:ligamentum arteriosum
753:first pharyngeal arch
650:tensor tympani muscle
430:first pharyngeal arch
218:embryonic development
2413:Pharyngeal apparatus
2315:Maxillary prominence
1519:10.1002/ajmg.a.10980
1466:Branchial cleft cyst
1415:cuneiform cartilages
1407:arytenoid cartilages
1362:epiglottic cartilage
1353:tensor veli palatini
1153:tensor veli palatini
1129:First (also called "
1053:tensor veli palatini
993:tensor veli palatini
743:Reichert's cartilage
300:has been shown that
191:Ductus thyreoglossus
2475:Otorhinolaryngology
2258:Development of the
1887:Sudhir, Sant, 2008.
1823:2021PNAS..11811876H
1817:(44): e2111876118.
1734:McKenzie, James C.
1476:First arch syndrome
1398:cricothyroid muscle
1338:Cricothyroid muscle
1266:stylohyoid ligament
1195:(part of V2 and V3)
953:extraocular muscles
877:Posterior belly of
833:Stylohyoid ligament
801:stylohyoid ligament
173:Tuberculum laterale
2460:Vertebrate anatomy
2325:Meckel's cartilage
2289:Nasal prominences
2096:10.1002/jmor.20193
1875:McMinn, R., 1994.
1760:Marino, Thomas A.
1457:This article uses
1183:Meckel's cartilage
969:pharyngeal muscles
926:Pharyngeal muscles
749:Meckel's cartilage
663:and glands of the
501:Meckel's cartilage
496:Meckel's cartilage
462:mandibular process
371:pharyngeal grooves
363:Pharyngeal pouches
280:Neural crest cells
232:, or gill arches.
166:pharyngeal grooves
162:pharyngeal pouches
2465:Pharyngeal arches
2447:
2446:
2443:
2442:
2418:Pharyngeal groove
2397:Gustatory placode
2382:Median tongue bud
2001:10.1111/joa.13067
1618:(5592): 381–385.
1450:
1449:
1444:ductus arteriosus
1403:Cricoid cartilage
1377:subclavian artery
1358:Thyroid cartilage
1098:ductus arteriosus
1094:subclavian artery
930:branchial muscles
889:Auricular muscles
861:Occipitofrontalis
667:are derived from
458:maxillary process
385:. In mammals the
210:pharyngeal arches
112:
111:
107:
2487:
2435:Pharyngeal pouch
2359:Secondary palate
2342:
2341:
2252:
2245:
2238:
2229:
2228:
2224:
2214:
2172:
2171:
2153:
2144:
2143:
2125:
2116:
2115:
2079:
2073:
2072:
2054:
2048:
2047:
2045:
2044:
2035:. Archived from
2029:
2023:
2022:
2012:
1995:(6): 1019–1023.
1980:
1974:
1973:
1955:
1940:
1939:
1929:
1897:
1891:
1885:
1879:
1873:
1864:
1861:
1855:
1854:
1844:
1834:
1802:
1796:
1786:
1777:
1776:
1774:
1773:
1757:
1751:
1750:
1748:
1747:
1731:
1725:
1724:
1711:Human embryology
1706:
1697:
1696:
1686:
1676:
1667:(2): 0233–0247.
1652:
1646:
1645:
1627:
1603:
1597:
1596:
1588:
1582:
1581:
1545:
1539:
1538:
1507:Am J Med Genet A
1502:
1481:Splanchnocranium
1440:pulmonary artery
1434:pulmonary artery
1328:internal carotid
1290:Stapedial artery
1199:Maxillary artery
1193:Trigeminal nerve
1107:
1106:
1057:trigeminal nerve
973:trigeminal nerve
938:skeletal muscles
934:striated muscles
915:stapedial artery
879:digastric muscle
713:maxillary artery
685:trigeminal nerve
641:, anterior belly
639:digastric muscle
634:mylohyoid muscle
412:14 to 28 in the
312:branchial arches
230:branchial arches
212:, also known as
197:Sinus cervicalis
179:Tuberculum impar
164:(inside) and/or
150:
136:
122:
104:edit on Wikidata
101:
31:
19:
18:
2495:
2494:
2490:
2489:
2488:
2486:
2485:
2484:
2450:
2449:
2448:
2439:
2430:Pharyngeal arch
2401:
2363:
2331:
2266:
2256:
2181:
2176:
2175:
2168:
2154:
2147:
2140:
2126:
2119:
2080:
2076:
2069:
2055:
2051:
2042:
2040:
2031:
2030:
2026:
1981:
1977:
1970:
1956:
1943:
1898:
1894:
1886:
1882:
1874:
1867:
1862:
1858:
1803:
1799:
1787:
1780:
1771:
1769:
1758:
1754:
1745:
1743:
1732:
1728:
1721:
1707:
1700:
1653:
1649:
1604:
1600:
1589:
1585:
1546:
1542:
1503:
1494:
1489:
1462:
1455:
1436:
1420:Accessory nerve
1300:Stylopharyngeus
1131:mandibular arch
1110:Pharyngeal arch
1073:
1061:stylopharyngeus
1045:
1033:stylopharyngeus
1029:
1001:
965:
923:
907:
896:
809:
793:styloid process
781:styloid process
745:
721:
705:
681:
661:Mucous membrane
541:
498:
454:
434:mandibular arch
426:
402:Carnegie stages
377:surface of the
316:pharyngeal jaws
293:pharyngeal arch
288:facial skeleton
268:
214:visceral arches
206:
205:
204:
203:
202:
201:
151:
142:
141:
140:
137:
128:
127:
126:
123:
108:
67:arcus pharyngei
34:
22:Pharyngeal arch
17:
12:
11:
5:
2493:
2483:
2482:
2477:
2472:
2467:
2462:
2445:
2444:
2441:
2440:
2438:
2437:
2432:
2427:
2426:
2425:
2423:Cervical sinus
2415:
2409:
2407:
2403:
2402:
2400:
2399:
2394:
2389:
2387:Copula linguae
2384:
2379:
2373:
2371:
2365:
2364:
2362:
2361:
2356:
2354:Primary palate
2350:
2348:
2339:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2329:
2328:
2327:
2317:
2312:
2307:
2302:
2301:
2300:
2295:
2287:
2282:
2276:
2274:
2268:
2267:
2255:
2254:
2247:
2240:
2232:
2226:
2225:
2180:
2179:External links
2177:
2174:
2173:
2166:
2145:
2138:
2117:
2074:
2068:978-0781790697
2067:
2049:
2033:"marshall.edu"
2024:
1975:
1969:978-0781790697
1968:
1941:
1912:(2): 179–189.
1892:
1880:
1865:
1856:
1797:
1778:
1752:
1726:
1719:
1698:
1647:
1598:
1583:
1540:
1513:(3): 251–256.
1491:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1484:
1483:
1478:
1473:
1468:
1454:
1451:
1448:
1447:
1430:
1417:
1400:
1390:
1386:
1385:
1373:
1364:
1355:
1335:
1331:
1330:
1324:common carotid
1321:
1315:
1302:
1297:
1293:
1292:
1275:
1269:
1247:
1218:
1210:
1209:
1196:
1190:
1169:, part of the
1167:zygomatic bone
1155:
1149:tensor tympani
1134:
1126:
1125:
1120:
1117:
1114:
1111:
1072:
1069:
1044:
1041:
1028:
1025:
1000:
997:
989:tensor tympani
964:
961:
922:
919:
906:
903:
895:
892:
891:
890:
887:
881:
875:
869:
864:
858:
856:Facial muscles
847:
846:
836:
830:
824:
808:
805:
744:
741:
720:
717:
704:
701:
693:chorda tympani
680:
677:
653:
652:
647:
642:
636:
631:
630:
629:
624:
615:
598:
597:
592:
587:
582:
577:
572:
563:
540:
537:
497:
494:
453:
450:
425:
422:
267:
264:
200:
199:
193:
187:
181:
175:
169:
158:
154:
152:
145:
144:
143:
138:
131:
130:
129:
124:
117:
116:
115:
114:
113:
110:
109:
100:
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
64:
58:
57:
53:
52:
47:
45:Carnegie stage
41:
40:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2492:
2481:
2478:
2476:
2473:
2471:
2468:
2466:
2463:
2461:
2458:
2457:
2455:
2436:
2433:
2431:
2428:
2424:
2421:
2420:
2419:
2416:
2414:
2411:
2410:
2408:
2404:
2398:
2395:
2393:
2390:
2388:
2385:
2383:
2380:
2378:
2375:
2374:
2372:
2370:
2366:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2351:
2349:
2347:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2334:
2326:
2323:
2322:
2321:
2318:
2316:
2313:
2311:
2308:
2306:
2303:
2299:
2296:
2294:
2291:
2290:
2288:
2286:
2283:
2281:
2280:Nasal placode
2278:
2277:
2275:
2273:
2269:
2265:
2261:
2253:
2248:
2246:
2241:
2239:
2234:
2233:
2230:
2222:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2204:
2200:
2197:(5): 479–87.
2196:
2192:
2188:
2183:
2182:
2169:
2167:0-7817-5309-0
2163:
2159:
2152:
2150:
2141:
2139:0-914168-99-1
2135:
2131:
2124:
2122:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2078:
2070:
2064:
2060:
2053:
2039:on 2009-02-27
2038:
2034:
2028:
2020:
2016:
2011:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1986:
1979:
1971:
1965:
1961:
1954:
1952:
1950:
1948:
1946:
1937:
1933:
1928:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1896:
1890:
1884:
1878:
1872:
1870:
1860:
1852:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1812:
1808:
1801:
1795:
1794:0-443-06583-7
1791:
1785:
1783:
1768:on 2007-09-09
1767:
1763:
1756:
1742:on 2003-05-02
1741:
1737:
1730:
1722:
1720:0-443-08724-5
1716:
1712:
1705:
1703:
1694:
1690:
1685:
1680:
1675:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1651:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1626:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1602:
1594:
1593:Third Edition
1587:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1544:
1536:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1501:
1499:
1497:
1492:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1463:
1460:
1446:
1445:
1441:
1435:
1431:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1401:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1388:
1387:
1384:
1383:
1378:
1374:
1372:
1368:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1329:
1325:
1322:
1319:
1316:
1314:
1310:
1309:greater horns
1306:
1303:
1301:
1298:
1295:
1294:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1276:
1273:
1270:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1219:
1216:
1212:
1211:
1208:
1207:Vidian artery
1204:
1200:
1197:
1194:
1191:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1171:temporal bone
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1135:
1132:
1128:
1127:
1124:
1121:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1109:
1108:
1105:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1083:
1079:
1068:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1040:
1038:
1034:
1024:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
996:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
974:
970:
960:
959:innervation.
958:
954:
950:
945:
943:
939:
935:
931:
927:
918:
916:
912:
902:
900:
888:
885:
882:
880:
876:
873:
870:
868:
865:
862:
859:
857:
854:
853:
852:
851:
844:
840:
837:
834:
831:
828:
825:
822:
819:
818:
817:
814:
813:
804:
802:
798:
797:perichondrium
794:
790:
786:
785:temporal bone
782:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
750:
740:
738:
734:
730:
726:
716:
714:
710:
700:
698:
694:
690:
686:
676:
675:of the arch.
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
657:
651:
648:
646:
643:
640:
637:
635:
632:
628:
625:
623:
619:
616:
614:
611:
610:
608:
605:
604:
603:
602:
596:
593:
591:
588:
586:
585:palatine bone
583:
581:
578:
576:
573:
571:
567:
564:
562:
558:
554:
551:
550:
549:
548:
544:
536:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
503:forms in the
502:
493:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
449:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
421:
419:
418:embryogenesis
415:
411:
407:
403:
398:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
358:
354:
353:cranial nerve
350:
346:
345:cartilaginous
341:
339:
335:
330:
328:
324:
319:
317:
313:
309:
308:
303:
298:
294:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
263:
261:
256:
254:
253:aortic arches
250:
246:
242:
238:
233:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
198:
194:
192:
188:
186:
185:Foramen cecum
182:
180:
176:
174:
170:
167:
163:
159:
156:
155:
149:
135:
121:
105:
99:
95:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
68:
65:
63:
59:
54:
51:
48:
46:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
2429:
2194:
2190:
2157:
2129:
2090:(1): 17–38.
2087:
2083:
2077:
2058:
2052:
2041:. Retrieved
2037:the original
2027:
1992:
1988:
1978:
1959:
1909:
1905:
1895:
1888:
1883:
1876:
1859:
1814:
1810:
1800:
1770:. Retrieved
1766:the original
1755:
1744:. Retrieved
1740:the original
1729:
1710:
1664:
1661:PLOS Biology
1660:
1650:
1615:
1611:
1601:
1592:
1586:
1556:(1): 54–61.
1553:
1549:
1543:
1510:
1506:
1437:
1424:Cranial root
1379:
1349:
1272:Facial nerve
1262:lesser horns
1157:Premaxilla,
1086:
1074:
1046:
1030:
1005:facial nerve
1002:
966:
946:
929:
925:
924:
908:
905:Blood supply
899:Facial nerve
897:
894:Nerve supply
849:
848:
839:Lesser cornu
815:
811:
810:
746:
728:
724:
722:
706:
703:Blood supply
688:
682:
679:Nerve supply
659:
655:
654:
600:
599:
546:
545:
542:
532:
529:ossification
499:
485:
473:
455:
433:
429:
427:
404:10 to 16 in
399:
365:form on the
361:
342:
331:
320:
305:
269:
257:
237:human embryo
234:
213:
209:
207:
66:
1396:except the
1382:aortic arch
1367:Vagus nerve
1344:(including
1342:soft palate
1049:vagus nerve
999:Second arch
967:All of the
911:aortic arch
807:Derivatives
719:Second arch
709:aortic arch
539:Derivatives
438:development
338:pericardium
323:development
276:germ layers
272:vertebrates
241:development
222:vertebrates
56:Identifiers
2480:Embryology
2454:Categories
2043:2007-09-09
1772:2007-09-09
1746:2007-09-09
1487:References
1305:Hyoid bone
1258:hyoid bone
1237:stylohyoid
1225:buccinator
1215:hyoid arch
1177:, and the
1027:Third arch
1017:stylohyoid
963:First arch
872:Stylohyoid
843:hyoid bone
789:hyoid bone
773:hyoid bone
769:middle ear
757:mesenchyme
733:fetal life
729:hyoid arch
627:temporalis
609:(chewing)
561:middle ear
517:middle ear
424:First arch
375:ectodermal
367:endodermal
357:mesenchyme
2285:Nasal pit
1550:BioEssays
1245:auricular
1233:stapedius
1145:mylohyoid
1141:digastric
1071:In humans
1021:stapedius
1013:digastric
985:mylohyoid
981:digastric
901:(CN VII)
884:Stapedius
486:lower jaw
474:upper jaw
452:Processes
442:stomodeum
347:stick, a
336:from the
334:stomodeum
302:Hox genes
266:Structure
168:(outside)
2221:16313389
2112:32707087
2104:24151219
2019:31402457
1936:16441562
1851:34716275
1693:19215146
1642:10274300
1634:12193642
1578:10792335
1570:11135309
1535:28318053
1527:12784288
1453:See also
1426:) (XI),
1229:platysma
1185:and the
1163:mandible
867:Platysma
812:Skeletal
673:endoderm
669:ectoderm
613:masseter
570:mandible
547:Skeletal
525:mandible
505:mesoderm
482:mandible
444:and the
395:mesoderm
391:ectoderm
387:endoderm
245:mesoderm
2406:General
2293:Lateral
2212:1571564
2191:J. Anat
2010:6875933
1989:J. Anat
1927:2100189
1906:J. Anat
1842:8673075
1819:Bibcode
1684:2637924
1612:Science
1179:malleus
1173:, the
1159:maxilla
1082:trachea
942:somites
850:Muscles
841:of the
783:of the
767:of the
751:of the
601:Muscles
566:maxilla
559:of the
553:malleus
515:of the
513:malleus
470:maxilla
432:, also
414:chicken
406:mammals
397:layer.
249:pharynx
235:In the
79:D001934
39:Details
2369:Tongue
2346:Palate
2298:Medial
2219:
2209:
2164:
2136:
2110:
2102:
2065:
2017:
2007:
1966:
1934:
1924:
1849:
1839:
1792:
1717:
1691:
1681:
1640:
1632:
1576:
1568:
1533:
1525:
1394:larynx
1350:except
1334:Fourth
1313:thymus
1250:Stapes
1123:Artery
1078:larynx
1015:, the
991:, and
983:, the
886:muscle
874:muscle
863:muscle
821:Stapes
777:stapes
765:stapes
761:ossify
697:tongue
618:medial
523:. The
478:palate
460:and a
408:, and
349:muscle
327:embryo
2337:Mouth
2108:S2CID
1638:S2CID
1574:S2CID
1531:S2CID
1389:Fifth
1369:(X),
1296:Third
1274:(VII)
1175:incus
1119:Nerve
835:, and
656:Other
557:incus
509:incus
466:bones
383:gills
297:hyoid
284:skull
260:gills
160:1–4:
102:[
62:Latin
2272:Face
2264:neck
2262:and
2260:head
2217:PMID
2162:ISBN
2134:ISBN
2100:PMID
2063:ISBN
2015:PMID
1964:ISBN
1932:PMID
1847:PMID
1811:PNAS
1790:ISBN
1715:ISBN
1689:PMID
1630:PMID
1566:PMID
1523:PMID
1511:119A
1442:and
1320:(IX)
1087:The
1080:and
932:are
791:and
737:neck
723:The
689:CN V
671:and
620:and
568:and
555:and
511:and
472:(or
428:The
389:and
379:neck
286:and
226:fish
208:The
74:MeSH
2207:PMC
2199:doi
2195:207
2092:doi
2088:275
2005:PMC
1997:doi
1993:235
1922:PMC
1914:doi
1910:208
1837:PMC
1827:doi
1815:118
1679:PMC
1669:doi
1620:doi
1616:298
1558:doi
1515:doi
928:or
727:or
533:not
484:or
307:DLX
270:In
220:of
195:e:
189:d:
183:c:
177:b:
171:a:
2456::
2215:.
2205:.
2193:.
2189:.
2148:^
2120:^
2106:.
2098:.
2086:.
2013:.
2003:.
1991:.
1987:.
1944:^
1930:.
1920:.
1908:.
1904:.
1868:^
1845:.
1835:.
1825:.
1813:.
1809:.
1781:^
1701:^
1687:.
1677:.
1663:.
1659:.
1636:.
1628:.
1614:.
1610:.
1572:.
1564:.
1554:23
1552:.
1529:.
1521:.
1509:.
1495:^
1413:,
1409:,
1405:,
1360:,
1348:)
1326:,
1288:,
1284:,
1280:,
1256:,
1252:,
1243:,
1239:,
1235:,
1231:,
1227:,
1223:,
1217:")
1205:,
1201:,
1161:,
1151:,
1147:,
1143:,
1133:")
1084:.
1039:.
995:.
987:,
803:.
739:.
715:.
492:.
448:.
420:.
262:.
255:.
86:TE
50:10
2251:e
2244:t
2237:v
2223:.
2201::
2170:.
2142:.
2114:.
2094::
2071:.
2046:.
2021:.
1999::
1972:.
1938:.
1916::
1853:.
1829::
1821::
1775:.
1749:.
1723:.
1695:.
1671::
1665:7
1644:.
1622::
1580:.
1560::
1537:.
1517::
1461:.
1422:(
1307:(
1260:(
1189:.
845:.
829:,
823:,
687:(
106:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.