617:
750:
701:
659:
608:
149:
741:
692:
650:
157:
128:
1054:
577:, and other IEC variants. The Electric, Oil, Gas, and Water Utilities are slow to respond to newer networking technologies which may be due to large investments in capital equipment that has useful service life measured in decades. Serial ports and null modem cables are still widely used in these industries with Ethernet just slowly becoming a widely available option.
20:
585:
Connecting two DTE devices together requires a null modem that acts as a DCE between the devices by swapping the corresponding signals (TD-RD, DTR-DSR, and RTS-CTS). This can be done with a separate device and two cables, or using a cable wired to do this. If devices require
Carrier Detect, it can be
113:
machines which could communicate with each other over phone lines. Each teleprinter would be physically connected to its modem via an RS-232 connection and the modems could call each other to establish a remote connection between the teleprinters. If a user wished to connect two teleprinters directly
564:
Another context where these cables can be useful is when administering "headless" devices providing a serial administration console (i.e. managed switches, rackmount server units, and various embedded systems). An example of embedded systems that widely use null modems for remote monitoring include
478:
The original application of a null modem was to connect two teleprinter terminals directly without using modems. As the RS-232 standard was adopted by other types of equipment, designers needed to decide whether their devices would have DTE-like or DCE-like interfaces. When an application required
673:
Because of the compatibility issues and potential problems with a simple null modem cable, a solution was developed to trick the software into thinking there was handshaking available. However, the cable pin out merely loops back, and does not physically support the hardware flow control.
556:
for
Windows can be used to remotely debug systems, for example. This can also provide a serial console through which the in-kernel debugger can be dropped to in case of kernel panics, in which case the local monitor and keyboard may not be usable anymore (the
764:
This cable is incompatible with the previous types of cables' hardware flow control, due to a crossing of its RTS/CTS pins. With suitable software, the cable is capable of much higher speeds than its predecessors. It also supports software flow control.
677:
This cable could be used with more software but it had no actual enhancements over its predecessor. The software would work thinking it had hardware flow control but could suddenly stop when higher speeds were reached and with no identifiable reason.
135:
A null modem cable is a RS-232 serial cable where the transmit and receive lines are crosslinked. In some cables there are also handshake lines crosslinked. In many situations a straight-through serial cable is used, together with a null modem
635:
has to be implemented in the software. The use of this cable is restricted to data-traffic only on its cross-connected Rx and Tx lines. This cable can also be used in devices that do not need or make use of modem control signals.
118:
may also refer to the cable or adapter itself as well as the connection method. Null modem cables were a popular method for transferring data between the early personal computers from the 1980s to the early 1990s.
727:(CD) signal (at pin 1 on a DE-9 cable and pin 8 on a DB-25 cable). As a result, only specially designed software could make use of this partial handshaking. Software flow control still worked with this cable.
69:
communication refers to using a crossed-over RS-232 cable to connect the teleprinters directly to one another without the modems. It is also used to serially connect a computer to a printer, since both are
631:
The simplest type of serial cable has no hardware handshaking. This cable has only the data and signal ground wires connected. All of the other pins have no connection. With this type of cable
170:
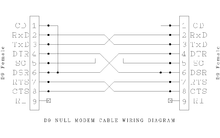
Below is a very common wiring diagram for a null modem cable to interconnect two DTEs (e.g. two PCs) providing full handshaking, which works with software relying on proper assertion of the
785:
solution which emulates a hardware null modem within the computer. All features of a hardware null modem are available in a virtual null modem as well. There are some advantages to this:
828:
interface to user applications, including virtual serial controls. Two such ptys may easily be linked together by an application to form a virtual null modem communication path.
569:, device controllers, and smart sensing devices. These devices tend to reside in close proximity and lend themselves to short run serial communication through protocols such as
723:(CTS) flow control but has no actual functionality. The only way the flow control signal would reach the other device is if the opposite device checked for a
532:
mode development, since it allows the user to remotely debug a kernel with a minimum of device drivers and code (a serial driver mainly consists of two
1025:
586:
simulated by connecting DSR and DCD internally in the connector, thus obtaining CD from the remote DTR signal. One feature of the
101:
lines are crosslinked. Several wiring layouts are in use because the null modem connection is not covered by the RS-232 standard.
715:
In this cable the flow control lines are still looped back to the device. However, they are done so in a way that still permits
81:
The RS-232 standard is asymmetric as to the definitions of the two ends of the communications link, assuming that one end is a
1079:
518:
502:
86:
94:
533:
1084:
549:
862:
1058:
528:
made the use of null modem cables less common. In modern systems, such a cable can still be useful for
537:
529:
479:
that two DTEs (or two DCEs) needed to communicate with each other, then a null modem was necessary.
847:
494:
359:
82:
71:
31:
789:
Higher transmission speed of serial data, limited only by computer performance and network speed
561:
reserves those resources and dropping to the debugger in the case of a panic won't free them).
510:
893:
98:
774:
566:
219:
509:
on one computer as a network drive on the other computer. No
Ethernet hardware (such as a
8:
778:
632:
433:
417:
137:
43:
792:
Virtual connections over local network or
Internet, mitigating cable length restrictions
97:
and receive lines are crosslinked. Depending on the purpose, sometimes also one or more
1029:
980:
959:
487:
39:
490:
247:
594:" that just reverses pins 1 through 8 on one end to 8 through 1 on the other end.
1074:
837:
165:
114:
without modems (null modem) then they would crosslink the connections. The term
938:
857:
821:
591:
587:
524:
The popularity and availability of faster information exchange systems such as
389:
331:
303:
202:
1005:"Null-modem emulator | Download Null-modem emulator software for free at"
1068:
852:
483:
275:
616:
50:
1004:
1026:"BerliOS Developer: Project Summary - N8VB_vCOM Virtual Null Modem Cable"
917:
802:
749:
700:
658:
110:
58:
148:
825:
156:
607:
984:
842:
506:
140:. The adapter contains the necessary crosslinks between the signals.
127:
740:
691:
649:
782:
525:
35:
497:
can be used over a null modem connection. The later versions of
1053:
810:
574:
553:
498:
54:
47:
773:
A virtual null modem is a communication method to connect two
545:
514:
196:
90:
62:
19:
758:
Wiring pinouts for DB-25 (left) and DE-9 (right) connectors
709:
Wiring pinouts for DB-25 (left) and DE-9 (right) connectors
667:
Wiring pinouts for DB-25 (left) and DE-9 (right) connectors
625:
Wiring pinouts for DB-25 (left) and DE-9 (right) connectors
570:
541:
109:
Originally, the RS-232 standard was developed and used for
814:
558:
505:
program. Both pieces of software allow the mapping of a
781:. Unlike a null modem cable, a virtual null modem is a
517:
computer, a null modem connection was a common way of
894:"RS232 serial null modem cable wiring and tutorial"
486:between computers, or remote operation. Under the
30:is a communication method to directly connect two
795:Virtually unlimited number of virtual connections
1066:
887:
885:
883:
881:
879:
877:
912:
910:
53:. The name stems from the historical use of
874:
597:
590:standard is that a null modem cable is a "
65:in order to communicate with one another;
907:
513:or a modem) is required for this. On the
1028:. berlios.de. 2005-07-15. Archived from
891:
820:Another common example consists of Unix
155:
147:
126:
18:
639:
1067:
681:
580:
122:
981:"MS-DOS External commands - INTERLNK"
768:
16:Serial cable connecting two computers
730:
482:Null modems were commonly used for
93:. With a null modem connection the
13:
817:games to use virtual null modems.
143:
14:
1096:
1046:
1052:
960:"ADTPro - ADTPro Serial Cabling"
748:
739:
699:
690:
657:
648:
615:
606:
235:
232:
229:
941:. hardwarebook.info. 2006-12-27
824:(pty) which present a standard
473:
152:DB-25 null modem wiring diagram
1018:
997:
973:
952:
931:
160:DE-9 null modem wiring diagram
1:
962:. sourceforge.net. 2011-01-25
868:
863:Serial Line Internet Protocol
1080:Multiplayer null modem games
7:
920:. nullmodem.com. 2008-11-07
831:
10:
1103:
798:No need for a serial cable
163:
104:
538:interrupt service routine
519:playing multiplayer games
446:
443:
440:
437:
432:
411:
408:
405:
402:
193:Signal and abbreviations
192:
187:
182:
179:
801:The computer's physical
939:"Nullmodem (9-9) - HwB"
848:Direct cable connection
598:No hardware handshaking
495:direct cable connection
1085:Out-of-band management
521:between two machines.
511:network interface card
501:were shipped with the
161:
153:
132:
57:cables to connect two
24:
775:computer applications
159:
151:
130:
22:
1061:at Wikimedia Commons
640:Loopback handshaking
166:Serial port: Pinouts
74:, and is known as a
23:A null modem adapter
779:virtual serial port
682:Partial handshaking
581:Types of null modem
434:Data Terminal Ready
418:Data Carrier Detect
172:Data Carrier Detect
123:Cables and adapters
85:and the other is a
813:has allowed older
769:Virtual null modem
162:
154:
133:
131:A null modem cable
25:
1057:Media related to
1007:. sourceforge.net
777:directly using a
488:Microsoft Windows
471:
470:
375:
46:, etc.) using an
1092:
1056:
1041:
1040:
1038:
1037:
1022:
1016:
1015:
1013:
1012:
1001:
995:
994:
992:
991:
977:
971:
970:
968:
967:
956:
950:
949:
947:
946:
935:
929:
928:
926:
925:
914:
905:
904:
902:
901:
896:. lammertbies.nl
889:
752:
743:
731:Full handshaking
703:
694:
661:
652:
619:
610:
491:operating system
373:
248:Transmitted Data
177:
176:
1102:
1101:
1095:
1094:
1093:
1091:
1090:
1089:
1065:
1064:
1049:
1044:
1035:
1033:
1024:
1023:
1019:
1010:
1008:
1003:
1002:
998:
989:
987:
979:
978:
974:
965:
963:
958:
957:
953:
944:
942:
937:
936:
932:
923:
921:
916:
915:
908:
899:
897:
890:
875:
871:
838:Crossover cable
834:
822:pseudoterminals
771:
762:
761:
760:
759:
755:
754:
753:
745:
744:
733:
717:Request To Send
713:
712:
711:
710:
706:
705:
704:
696:
695:
684:
671:
670:
669:
668:
664:
663:
662:
654:
653:
642:
629:
628:
627:
626:
622:
621:
620:
612:
611:
600:
583:
536:buffers and an
476:
304:Request To Send
184:
168:
146:
144:Wiring diagrams
125:
107:
61:devices or two
17:
12:
11:
5:
1100:
1099:
1088:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1063:
1062:
1048:
1047:External links
1045:
1043:
1042:
1017:
996:
972:
951:
930:
906:
892:Lammert Bies.
872:
870:
867:
866:
865:
860:
858:Rollover cable
855:
850:
845:
840:
833:
830:
809:For instance,
807:
806:
799:
796:
793:
790:
770:
767:
757:
756:
747:
746:
738:
737:
736:
735:
734:
732:
729:
725:Carrier Detect
708:
707:
698:
697:
689:
688:
687:
686:
685:
683:
680:
666:
665:
656:
655:
647:
646:
645:
644:
643:
641:
638:
624:
623:
614:
613:
605:
604:
603:
602:
601:
599:
596:
592:rollover cable
582:
579:
475:
472:
469:
468:
465:
462:
458:
457:
454:
451:
448:
445:
442:
439:
436:
430:
429:
426:
423:
420:
414:
413:
410:
407:
404:
401:
398:
395:
392:
390:Data Set Ready
386:
385:
382:
379:
376:
371:
368:
365:
362:
356:
355:
352:
349:
346:
343:
340:
337:
334:
328:
327:
324:
321:
318:
315:
312:
309:
306:
300:
299:
296:
293:
290:
287:
284:
281:
278:
272:
271:
268:
265:
262:
259:
256:
253:
250:
244:
243:
240:
237:
234:
231:
228:
225:
222:
216:
215:
212:
209:
206:
200:
194:
190:
189:
186:
181:
174:(DCD) signal:
145:
142:
124:
121:
106:
103:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1098:
1097:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1073:
1072:
1070:
1060:
1055:
1051:
1050:
1032:on 2013-12-26
1031:
1027:
1021:
1006:
1000:
986:
982:
976:
961:
955:
940:
934:
919:
913:
911:
895:
888:
886:
884:
882:
880:
878:
873:
864:
861:
859:
856:
854:
853:LapLink cable
851:
849:
846:
844:
841:
839:
836:
835:
829:
827:
823:
818:
816:
812:
804:
800:
797:
794:
791:
788:
787:
786:
784:
780:
776:
766:
751:
742:
728:
726:
722:
721:Clear To Send
718:
702:
693:
679:
675:
660:
651:
637:
634:
618:
609:
595:
593:
589:
578:
576:
572:
568:
562:
560:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
535:
531:
527:
522:
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
500:
496:
492:
489:
485:
484:file transfer
480:
466:
463:
460:
459:
455:
452:
449:
435:
431:
427:
424:
421:
419:
416:
415:
399:
396:
393:
391:
388:
387:
383:
380:
377:
372:
369:
366:
363:
361:
360:Signal Ground
358:
357:
353:
350:
347:
344:
341:
338:
335:
333:
332:Clear To Send
330:
329:
325:
322:
319:
316:
313:
310:
307:
305:
302:
301:
297:
294:
291:
288:
285:
282:
279:
277:
276:Received Data
274:
273:
269:
266:
263:
260:
257:
254:
251:
249:
246:
245:
241:
238:
226:
223:
221:
218:
217:
213:
210:
207:
204:
201:
198:
195:
191:
178:
175:
173:
167:
158:
150:
141:
139:
129:
120:
117:
112:
102:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
79:
77:
76:Printer Cable
73:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
29:
21:
1034:. Retrieved
1030:the original
1020:
1009:. Retrieved
999:
988:. Retrieved
975:
964:. Retrieved
954:
943:. Retrieved
933:
922:. Retrieved
918:"Null Modem"
898:. Retrieved
819:
808:
803:serial ports
772:
763:
724:
720:
716:
714:
676:
672:
633:flow control
630:
584:
563:
554:WinDbg or KD
523:
481:
477:
474:Applications
220:Frame Ground
171:
169:
134:
115:
108:
80:
75:
66:
51:serial cable
27:
26:
1059:Null modems
805:remain free
188:Other side
111:teleprinter
59:teleprinter
1069:Categories
1036:2013-12-26
1011:2013-12-26
990:2013-12-26
966:2013-12-26
945:2013-12-26
924:2013-12-26
900:2013-12-26
869:References
719:(RTS) and
548:, ddb for
211:DB-25 pin
185:direction
164:See also:
116:null modem
67:null modem
28:Null modem
985:Angelfire
843:Debugging
507:hard disk
208:DE-9 pin
180:One side
99:handshake
89:, e.g. a
832:See also
783:software
526:Ethernet
503:InterLnk
95:transmit
40:terminal
36:computer
422:DCD, CD
280:RxD, RD
252:TxD, TD
233:Common
214:Signal
138:adapter
105:Origins
44:printer
1075:Modems
811:DOSBox
575:Modbus
552:, and
530:kernel
499:MS-DOS
493:, the
374:Common
183:Signal
63:modems
55:RS-232
48:RS-232
546:Linux
515:Amiga
197:DB-25
91:modem
588:Yost
571:DNP3
567:RTUs
544:for
542:KGDB
534:FIFO
467:DSR
456:DCD
412:DTR
354:RTS
326:CTS
298:TxD
270:RxD
205:pin
203:DE-9
199:pin
32:DTEs
826:tty
815:DOS
559:GUI
550:BSD
540:).
438:DTR
394:DSR
384:SG
336:CTS
308:RTS
242:FG
87:DCE
83:DTE
72:DTE
1071::
983:.
909:^
876:^
573:,
447:→
444:4
441:20
428:1
409:20
403:←
400:6
370:5
364:SG
345:←
342:8
317:→
314:7
289:←
286:2
261:→
258:3
230:—
224:FG
78:.
42:,
38:,
1039:.
1014:.
993:.
969:.
948:.
927:.
903:.
464:6
461:6
453:8
450:1
425:8
406:4
397:6
381:7
378:5
367:7
351:4
348:7
339:5
323:5
320:8
311:4
295:2
292:3
283:3
267:3
264:2
255:2
239:1
236:—
227:1
34:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.