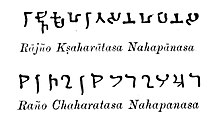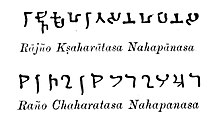711:
568:
466:
588:
502:
831:
759:
110:
482:
819:
807:
867:
795:
40:
2876:
702:
90:
454:
3178:
608:
257:
185:
262:
252:
247:
190:
180:
175:
567:
540:
have pointed out that
Gautamiputra Satakarni and Nahapana were not necessarily contemporaries, since Satakarni mentions that the areas conquered by him were ruled by Ushavadata, rather than Nahapana. According to Burgess, there might have been an interval of as much as a century between the reigns of
545:
dates this event to c. 124 CE, which according to him, was the 18th regnal year of
Gautamiputra. R.C.C. Fynes dates the event to sometime after 71 CE, in the same line, Shailendra Bhandare places the victory of Gautamiputra and the end of Nahapana's reign to the start of Saka era, 78 CE, in the year
481:
308:(which starts in 78 CE), some scholars have assigned his reign to 119-124 CE. Others believe that the years 41-46 are his regnal years, and assign his rule to a different period. For example, Krishna Chandra Sagar assigns his reign to 24-70 CE, while R.C.C. Fynes dates it to
391:
Nahapana is mentioned as a donator in inscriptions of numerous
Buddhist caves in northern India. The Nasik and Karle inscriptions refer to Nahapana's dynastic name (Kshaharata, for "Kshatrapa") but not to his ethnicity (Saka-Pahlava), which is known from other sources.
407:. Ushavadata was son of Dinika and had married Dakshamitra, daughter of Nahapana. According to the inscriptions, Ushavadata accomplished various charities and conquests on behalf of his father-in-law. He constructed rest-houses, gardens and tanks at Bharukachchha (
465:
676:
sixteen villages, who at the pure tirtha
Prabhasa gave eight wives to the Brahmanas, and who also fed annually a hundred thousand Brahmanas- there has been given the village of Karajika for the support of the ascetics living in the caves at
587:
858:, there is an inscription in three lines, of which, however, the first letters are obliterated; still it is possible make out that it was "Ayama, the minister of Mahakshatrapa Svami Nahapana." This inscription bears a
361:
oil and clarified butter, cotton and the Indian cloths made therefrom, of the coarser sorts. Very many cattle are pastured there, and the men are of great stature and black in color. The metropolis of this country is
2808:
An
Inscribed Silver Buddhist Reliquary of the Time of King Kharaosta and Prince Indravarman, Richard Salomon, Journal of the American Oriental Society, Vol. 116, No. 3 (Jul. - Sep., 1996), pp. 442
1152:
Bhandare, Shailendra, (1999). Historical
Analysis, pp. 168-178; Shimada, Akira, (2012). Early Buddhist Architecture in Context: The Great Stupa at Amaravati (ca 300 BCE - 300 CE), Brill, p. 51.
1347:
Bhandare, Shailendra, (1999). Historical
Analysis, pp. 168-178; Shimada, Akira, (2012). Early Buddhist Architecture in Context: The Great Stupa at Amaravati (ca 300 BCE - 300 CE), Brill, p.51.
1713:
491:
An arrow to the left and a lightning to the right. Legend in kharoshthi on the left: Rano
Chaharatasa Nahapanasa. Brahmi legend on the right: Rajna Kshaha (ratasa Nahapanasa).
3149:
2819:
A Kharosthī Reliquary
Inscription of the Time of the Apraca Prince Visnuvarma, by Richard Salomon, South Asian Studies 11 1995, Pages 27-32, Published online: 09 Aug 2010
1161:"The mention of 'Nambanus' whom the scholars have identified as Nahapana in the Periplus of the Erythrean Sea would help us to solve the problem of Nahapana's time.", in
1439:
rule in the western Deccan during the 1st century." in Guide to
Monuments of India 1: Buddhist, Jain, Hindu - by George Michell, Philip H. Davies, Viking - 1989 Page 374
1236:
668:, the son of Dinaka and the son-in-law of the king, the Khaharata, the Kshatrapa Nahapana, who gave three hundred thousand cows, who made gifts of gold and a
2525:
2432:
380:
coinage. The obverse of the coins consists of the profile of the ruler, within a legend in Greek. The reverse represents a thunderbolt and an arrow, within
304:
The exact period of Nahapana is not certain. A group of his inscriptions are dated to the years 41-46 of an unspecified era. Assuming that this era is the
3037:
2486:
3141:
3133:
2688:
2684:
1165:
541:
these two kings. However, most historians now agree that Gautamiputra and Nahapana were contemporaries, and that Gautamiputra defeated Nahapana.
862:
date of year 46, which is 124 CE. The inscription is located in the fourth excavation on the eastern side of Manmodi Hill, in Cave 7. It reads:
3157:
2696:
3061:
3053:
3021:
3013:
2603:
2541:
2537:
2498:
2494:
2478:
623:
The Western Satraps are known for the construction and dedication of numerous Buddhist caves in Central India, particularly in the areas of
3093:
2529:
2521:
2514:
3045:
2490:
2440:
2436:
1208:
2428:
2352:
529:
District. This suggests that Gautamiputra defeated Nahapana.The Nasik Cave No.3, inscription No.2 insription notes that Nahapana's
1708:
2855:
769:, son of Dinika, son-in- law of king Nahapana, the Kshaharata Kshatrapa, (...) inspired by (true) religion, in the Trirasmi hills at
2533:
1740:
349:, which is the beginning of the Kingdom of Nambanus and of all India. That part of it lying inland and adjoining Scythia is called
3204:
830:
653:, the largest in South Asia, was constructed and dedicated in 120 CE by Nahapana, according to several inscriptions in the cave.
1233:
1515:
1317:
1290:
1120:
1093:
1067:
1021:
710:
3209:
105:ΞΑΗΑΡΑΤΑ(Ϲ)", Prakrit for "King Kshaharata" rendered in corrupted Greek letters) on the obverse of the coinage of Nahapana.
279:
233:
151:
132:
45:
Silver coin of Nahapana, with ruler profile and pseudo-Greek legend "ΡΑΝΝΙΩ ΞΑΗΑΡΑΤΑϹ ΝΑΗΑΠΑΝΑϹ", transliteration of the
1396:
World Heritage Monuments and Related Edifices in India, Volume 1 ʻAlī Jāvīd, Tabassum Javeed, Algora Publishing, 2008
212:, in northwestern India, who ruled during the 1st or 2nd century CE. According to one of his coins, he was the son of
1685:
1376:
1263:
952:
925:
1703:
1423:
Southern India: A Guide to Monuments Sites & Museums, by George Michell, Roli Books Private Limited, 1 mai 2013
1001:
Catalogue of the Coins of the Andhra Dynasty, the Western Kṣatrapas, the Traikūṭaka Dynasty, and the "Bodhi" Dynasty
779:
581:
symbol and three arched mountain symbol struck respectively on the obverse and reverse of a drachm of Nahapana.
325:
501:
3085:
2848:
1718:
1183:"The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea: Travel and Trade in the Indian Ocean by a Merchant of the First Century"
537:
1733:
1538:
594:
574:
1463:
758:
333:. This person has been identified as Nahapana by modern scholars. The text describes Nambanus as follows:
1457:
109:
1636:
818:
1162:
1013:
806:
475:
Bust of the king crowned with a diadem on the right. Legend in Greek: ΡΑΝΝΙ (ω ΙΑΗΑΡΑΤΑϹ) ΝΑΗΑΠΑ (ΝΑϹ)
974:
2809:
3199:
2841:
2820:
1844:
453:
1507:
1503:
888:
Prime Minister to the king, the great Satrap, the Lord Nahapana, made for merit, in the year 46."
3005:
2417:
1914:
1726:
1497:
794:
1597:
944:
Transregional Trade and Traders: Situating Gujarat in the Indian Ocean from Early Times to 1900
553:
Nahapana was founder of one of the two major Saka Satrap dynasties in north-western India, the
522:
510:
1618:
1412:
1366:
1280:
1253:
1110:
1059:
915:
866:
2113:
2097:
1698:
1477:
1424:
1397:
1307:
1217:
1009:
942:
113:
Nahapana Brahmi and Kharoshthi legends on his coinage "RAJNO KSHAHARATASA NAHAPANASA "Of the
968:
8:
2875:
1055:
39:
1569:
1532:
2833:
2726:
2558:
1924:
1828:
1648:
1186:
1182:
381:
205:
89:
1591:
1411:
Foreign Influence on Ancient India, Krishna Chandra Sagar, Northern Book Centre, 1992
701:
550:'s ascension to the throne, and considers Gautamiputra's whole reign to ca. 60-85 CE.
435:
district). He also campaigned in the north under the orders of Nahapana to rescue the
2797:
1681:
1612:
1511:
1372:
1313:
1286:
1259:
1255:
A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th Century
1116:
1089:
1063:
1017:
999:
948:
921:
669:
1041:
1037:
2185:
2017:
1669:
542:
444:
400:
1673:
3077:
2864:
2780:
2506:
2285:
2085:
2052:
1963:
1553:
1240:
1169:
1083:
1049:
533:
race' was rooted out, which means all his possible heirs might have been killed.
530:
1489:
1449:
3165:
2773:
2756:
2549:
2322:
2245:
2048:
1931:
1896:
1045:
770:
420:
266:
209:
50:
30:
1748:
3193:
3117:
2957:
2632:
2397:
2180:
1811:
1806:
1787:
1749:
1502:. Vol. 8. Kolkata: Government of India Central Printing Office. p.
1462:. Vol. 7. Kolkata: Government of India Central Printing Office. p.
851:
739:
681:
without any distinction of sect or origin, for all who would keep the varsha.
436:
396:
338:
315:-71 CE, and Shailendra Bhandare regards 78 CE as the last year of his reign.
286:
169:
125:
1040:(1999). "Languages and scripts in Graeco-Bactria and the Saka Kingdoms". In
719:
Great Chaitya inscription 13 of Nahapana, at the right of the main entrance.
3125:
2981:
2973:
2942:
2759:
2752:
2680:
2654:
2598:
2582:
2510:
2405:
2393:
2365:
2037:
2009:
1956:
1950:
995:
94:
3177:
1660:
R.C.C. Fynes (1995). "The Religious Patronage of the Satavahana Dynasty".
1555:
The history and inscriptions of the Sātavāhanas and the Western Kshatrapas
3101:
2719:
2658:
2616:
2572:
2348:
2118:
2102:
2061:
2041:
1858:
1851:
1782:
1493:
1453:
749:
731:
678:
657:
650:
640:
624:
616:
447:) in the Trirashmi hill near Nasik and offered it to the Buddhist monks.
2451:
1652:
3069:
2989:
2715:
2662:
2609:
2553:
2502:
2461:
2409:
2297:
2191:
2157:
2149:
2079:
1946:
1918:
1476:
Buddhist Critical Spirituality: Prajñā and Śūnyatā, by Shōhei Ichimura
1436:
766:
665:
518:
506:
385:
377:
354:
607:
3109:
2997:
2965:
2927:
2711:
2706:
2692:
2636:
2628:
2577:
2563:
2413:
2401:
2389:
2370:
2289:
2218:
2197:
2163:
2137:
2108:
2073:
2056:
2021:
1984:
1881:
1791:
656:
An important inscription relates to Nahapana in the Great Chaitya at
558:
547:
363:
305:
270:
144:
138:
3029:
2912:
2888:
2743:
2646:
2482:
2456:
2377:
2358:
2314:
2124:
2067:
1999:
1874:
1801:
1778:
859:
412:
376:
He also established the Kshatrapa coinage, in a style derived from
330:
256:
184:
81:
1558:. Maharashtra State Board for Literature and Culture. p. 113.
1331:
1329:
2896:
2738:
2339:
2143:
2003:
1816:
1005:
883:
673:
646:
628:
612:
440:
408:
342:
261:
251:
246:
213:
189:
179:
174:
98:
71:
46:
602:
49:"Raño Kshaharatasa Nahapanasa" (or "King Kshaharata Nahapana").
2224:
2168:
1978:
1796:
1326:
855:
735:
578:
526:
513:. Nahapana's profile and coin legend are still clearly visible.
428:
358:
350:
346:
1356:
Bhandare, Shailendra, (1999). Historical Analysis, pp. 168-178
2730:
2251:
1900:
1772:
660:(Valukura is thought to be an ancient name for Karla Caves):
432:
424:
416:
404:
276:
129:
114:
1136:
1134:
1132:
2666:
1371:. Vol. 4. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2000. p. 375.
557:("Satraps"); the other dynasty included the one founded by
366:, from which much cotton cloth is brought down to Barygaza.
224:
Nahapana's name appears on his coins in the Kharosthi form
1129:
773:, has caused this cave to be made and these cisterns...."
738:
caves also have inscriptions of Nahapana, as well as the
2863:
1700:, by Durga Prasad, with numerous references to Nahapana.
357:. It is a fertile country, yielding wheat and rice and
1680:
R.C. Senior "Indo-Scythian coins and history" Vol IV,
734:
also were carved during the time of Nahapana, and the
395:
Nahapana had a son-in-law named Ushavadata (Sanskrit:
329:
mentions one Nambanus as the ruler of the area around
239:
225:
199:
193:
163:
157:
1108:
1641:
Annals of the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute
577:
struck over a drachm of Nahapana. Circa 167-196 CE.
1639:(1996). "Sātavāhana Chronology: A Re-examination".
850:In a Buddhist cave of the Bhimasankar group of the
496:
879:yadhama cha ḍhi maṭapo cha puñathaya vase 46 kato
3191:
1635:
1530:
1335:
1285:. Cambridge University Press. pp. 266–268.
517:Overstrikes of Nahapana's coins by the powerful
2556:, Sassanid king and "Kushanshah" (c. 230 – 250)
672:on the river Banasa, who gave to the Devas and
597:, which was struck over the coinage of Nahapana
1435:"This hall is assigned to the brief period of
1305:
619:was built and dedicated by Nahapana in 120 CE.
290:
231:
149:
2849:
1734:
1524:
940:
603:Construction and dedication of Buddhist caves
1659:
1140:
1448:
941:Alpers, Edward A.; Goswami, Chhaya (2019).
725:
525:have been found in a hoard at Jogalthambi,
2856:
2842:
1741:
1727:
1585:
1583:
1581:
1088:. British Museum Press. 2000. p. 42.
970:Seaby's Coin and Medal Bulletin: July 1980
845:
399:), whose inscriptions were incised in the
38:
1531:Fergusson, James; Burgess, James (1880).
1258:. Pearson Education India. p. 383.
1051:History of civilizations of Central Asia
1036:
990:
988:
986:
984:
973:. Seaby Publications Ltd. 1980. p.
886:and cistern by Ayama of the Vatsa-gotra,
865:
757:
606:
500:
108:
88:
2709:Sassanid king and "Kushanshah" (c. 325)
1610:
1589:
1578:
1551:
1278:
1085:Buddhist Reliquaries from Ancient India
947:. Oxford University Press. p. 99.
909:
907:
893:Inscription of Nahapana, Manmodi Caves.
296:, which means "protector of the clan".
3192:
1614:Archaeological Survey Of Western India
1593:Archaeological Survey Of Western India
1571:Archaeological Survey of Western India
1488:
994:
439:who had been attacked by the Malayas (
2837:
1722:
1407:
1405:
1392:
1390:
1388:
1251:
1210:History of the Andrhas: Up to 1565 AD
1115:. Northern Book Centre. p. 133.
981:
913:
748:Cave No.10 "Nahapana Vihara" at the
686:Inscription of Nahapana, Karla Caves.
2724:Peroz III "Kushanshah" (c. 350 –360)
1056:Motilal Banarsidass Publishing House
904:
1312:. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 77.
1309:Some Early Dynasties of South India
505:A coin of Nahapana restruck by the
443:). He excavated a cave (one of the
13:
3176:
2874:
2796:From the dated inscription on the
1752:kings, territories and chronology
1429:
1417:
1402:
1385:
1216:. P. G. Publishers. Archived from
1206:
1112:Foreign Influence on Ancient India
204:;), was an important ruler of the
14:
3221:
1692:
1574:. Government Central Press. 1879.
1306:Chattopadhyaya, Sudhakar (1974).
593:Regular design of the coinage of
1552:Mirashi, Vasudev Vishnu (1981).
1234:Maharastra.gov.in Ancient Period
829:
817:
805:
793:
709:
700:
586:
566:
497:Defeat by Gautamiputra Satakarni
480:
464:
452:
345:and the coast of the country of
260:
255:
250:
245:
188:
183:
178:
173:
101:title "RANNIO KSAHARATA" ("ΡΑΝΝΙ
18:2nd century Western Satrap ruler
2813:
2802:
2790:
1628:
1604:
1562:
1545:
1537:. London : Allen. p.
1482:
1470:
1442:
1359:
1350:
1341:
1299:
1272:
1245:
1227:
1200:
1174:
1155:
3205:Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
2649:, "Kushanshah" (c. 300 – 325)
2612:, "Kushanshah" (c. 295 – 300)
1619:Plate LIV No.11 (Junnar No.32)
1146:
1109:Krishna Chandra Sagar (1992).
1102:
1076:
1030:
961:
934:
877:mātyasa Vachhasagotasa Ayamasa
634:
487:A silver drachma of Nahapana.
471:A silver drachma of Nahapana.
326:Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
285:), which are derived from the
1:
2946:
2931:
2916:
2566:, "Kushanshah" (c. 265 – 295)
2561:, "Kushanshah" (c. 250 – 265)
1674:10.1080/02666030.1995.9628494
898:
873:jmahākhatapasa sāminahapānasa
780:inscription No.10 of Nahapana
309:
2722:"Kushanshahs" (c. 325 – 350)
2283:Indo-Scythian dynasty of the
2035:Indo-Scythian dynasty of the
2015:Indo-Scythian dynasty of the
595:Gautamiputra Yajna Satakarni
575:Gautamiputra Yajna Satakarni
271:
240:
226:
200:
194:
164:
158:
139:
7:
3210:2nd-century Indian monarchs
882:"The meritorious gift of a
10:
3226:
2464:(c. 190 – to at least 230)
1368:Students' Britannica India
920:. Routledge. p. 310.
638:
353:, but the coast is called
277:
232:
150:
130:
117:Nahapana, the Kshaharata".
3174:
2883:
2872:
2779:
2777:
2772:
2769:
2750:
2736:
2704:
2702:
2678:
2675:
2652:
2644:
2642:
2626:
2623:
2615:
2607:
2602:
2597:
2594:
2570:
2547:
2519:
2476:
2473:
2449:
2426:
2387:
2384:
2363:
2356:
2347:
2338:
2335:
2330:
2327:
2320:
2318:
2313:
2310:
2305:
2302:
2295:
2293:
2282:
2279:
2274:
2271:
2269:
2267:
2264:
2259:
2256:
2249:
2244:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2232:
2229:
2222:
2217:
2215:
2213:
2210:
2205:
2202:
2195:
2190:
2179:
2177:
2174:
2167:
2162:
2155:
2148:
2135:
2133:
2130:
2123:
2112:
2107:
2096:
2094:
2091:
2084:
2071:
2060:
2047:
2034:
2032:
2030:
2014:
2007:
1998:
1996:
1989:
1982:
1977:
1975:
1968:
1961:
1954:
1945:
1943:
1936:
1929:
1922:
1913:
1911:
1904:
1895:
1893:
1890:
1886:
1879:
1872:
1870:
1863:
1856:
1849:
1842:
1840:
1833:
1826:
1824:
1760:
1534:The cave temples of India
1282:The Cave Temples of India
1048:; Etemadi, G. F. (eds.).
917:Indian Ocean In Antiquity
536:Earlier scholars such as
299:
77:
67:
59:
37:
28:
23:
1163:"History of the Andhras"
726:Nahapana vihara at Nasik
318:
2045:(ruled 12 BCE - 15 CE)
1279:Burgess, James (1880).
1252:Singh, Upinder (2008).
846:Nahapana cave in Junnar
292:
219:
3181:
2879:
1709:More coins of Nahapana
1054:. Vol. 2. Delhi:
896:
870:
785:
762:
689:
620:
523:Gautamiputra Satakarni
514:
511:Gautamiputra Satakarni
374:
118:
106:
3180:
2878:
2114:INDO-PARTHIAN KINGDOM
2098:INDO-PARTHIAN KINGDOM
2065:(ruled 10 BCE– 10 CE)
1897:INDO-SCYTHIAN KINGDOM
1611:Burgess, Jas (1883).
1590:Burgess, Jas (1883).
1336:M. K. Dhavalikar 1996
1168:13 March 2007 at the
869:
864:
836:Chaitya and Umbrellas
761:
756:
662:
610:
504:
335:
112:
92:
63:1st or 2nd century CE
3000:(restored) (197–199)
2984:(restored) (191–197)
2867:(1st c. CE - 395 CE)
1714:Coins with biography
1239:3 March 2007 at the
694:Nahapana inscription
649:cave complex of the
459:Nahapana coin hoard.
208:, descendant of the
1662:South Asian Studies
914:Cribb, Joe (2013).
782:, Cave No.10, Nasik
645:In particular, the
238:), the Brahmi form
3182:
2880:
2153:(ruled c.0-20 CE)
1829:INDO-GREEK KINGDOM
1187:Fordham University
871:
763:
621:
515:
427:) and Shorparaga (
206:Western Kshatrapas
119:
107:
3187:
3186:
2831:
2830:
2798:Rukhana reliquary
2786:
2785:
2459:(c. 160 – c. 190)
2454:(c. 140 – c. 160)
1704:Coins of Nahapana
1517:978-1-246-36021-9
1499:Epigraphia Indica
1459:Epigraphia Indica
1319:978-81-208-2941-1
1292:978-1-108-05552-9
1223:on 24 April 2015.
1141:R.C.C. Fynes 1995
1122:978-81-7211-028-4
1095:978-0-7141-1492-7
1069:978-8-120-81408-0
1023:978-1-332-41465-9
843:
842:
87:
86:
54:
3217:
3169:
3161:
3153:
3145:
3137:
3129:
3121:
3113:
3105:
3097:
3089:
3081:
3073:
3065:
3057:
3049:
3041:
3033:
3025:
3017:
3009:
3001:
2993:
2985:
2977:
2969:
2961:
2953:
2951:
2948:
2938:
2936:
2933:
2923:
2921:
2918:
2908:
2900:
2892:
2858:
2851:
2844:
2835:
2834:
2822:
2817:
2811:
2806:
2800:
2794:
2186:Kujula Kadphises
2018:NORTHERN SATRAPS
1763:
1762:
1743:
1736:
1729:
1720:
1719:
1677:
1656:
1647:(1/4): 133–140.
1637:M. K. Dhavalikar
1623:
1622:
1608:
1602:
1601:
1587:
1576:
1575:
1566:
1560:
1559:
1549:
1543:
1542:
1528:
1522:
1521:
1486:
1480:
1474:
1468:
1467:
1446:
1440:
1433:
1427:
1421:
1415:
1409:
1400:
1394:
1383:
1382:
1363:
1357:
1354:
1348:
1345:
1339:
1333:
1324:
1323:
1303:
1297:
1296:
1276:
1270:
1269:
1249:
1243:
1231:
1225:
1224:
1222:
1215:
1204:
1198:
1197:
1195:
1193:
1178:
1172:
1159:
1153:
1150:
1144:
1138:
1127:
1126:
1106:
1100:
1099:
1080:
1074:
1073:
1034:
1028:
1027:
1006:Longman & Co
992:
979:
978:
965:
959:
958:
938:
932:
931:
911:
894:
833:
821:
809:
797:
783:
765:"Success !
745:
744:
713:
704:
687:
615:cave complex at
590:
570:
543:M. K. Dhavalikar
484:
468:
456:
445:Pandavleni Caves
401:Pandavleni Caves
372:
314:
311:
295:
284:
283:
282:
274:
264:
259:
254:
249:
243:
237:
236:
229:
203:
197:
192:
187:
182:
177:
167:
161:
155:
154:
142:
137:
136:
135:
44:
42:
21:
20:
3225:
3224:
3220:
3219:
3218:
3216:
3215:
3214:
3200:Western Satraps
3190:
3189:
3188:
3183:
3172:
3164:
3156:
3148:
3140:
3132:
3124:
3116:
3108:
3100:
3092:
3084:
3078:Damajadasri III
3076:
3068:
3060:
3052:
3044:
3036:
3028:
3020:
3012:
3004:
2996:
2988:
2980:
2972:
2964:
2956:
2949:
2941:
2934:
2926:
2919:
2911:
2903:
2895:
2887:
2881:
2868:
2865:Western Satraps
2862:
2832:
2827:
2826:
2825:
2818:
2814:
2807:
2803:
2795:
2791:
2781:Chandragupta II
2764:
2755:
2747:
2742:
2725:
2723:
2710:
2699:
2695:
2691:
2687:
2683:
2670:
2669:(c. 310? – 325)
2665:
2661:
2657:
2639:
2635:
2631:
2619:(c. 275 – 310)
2589:
2586:
2581:
2576:
2567:
2562:
2557:
2552:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2524:
2513:
2509:
2507:Damajadasri III
2505:
2501:
2497:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2481:
2468:
2465:
2460:
2455:
2446:
2443:
2439:
2435:
2431:
2423:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2404:
2400:
2396:
2392:
2375:
2373:
2368:
2351:
2342:
2288:
2286:WESTERN SATRAPS
2284:
2183:
2152:
2141:
2116:
2100:
2066:
2064:
2055:
2053:Patika Kusulaka
2051:
2044:
2040:
2036:
2028:25 BCE – 10 CE
2020:
2016:
2002:
1949:
1917:
1899:
1790:
1781:
1767:
1756:
1747:
1695:
1690:
1631:
1626:
1609:
1605:
1588:
1579:
1568:
1567:
1563:
1550:
1546:
1529:
1525:
1518:
1487:
1483:
1475:
1471:
1447:
1443:
1434:
1430:
1422:
1418:
1410:
1403:
1395:
1386:
1379:
1365:
1364:
1360:
1355:
1351:
1346:
1342:
1334:
1327:
1320:
1304:
1300:
1293:
1277:
1273:
1266:
1250:
1246:
1241:Wayback Machine
1232:
1228:
1220:
1213:
1207:Prasad, Durga.
1205:
1201:
1191:
1189:
1181:
1179:
1175:
1170:Wayback Machine
1160:
1156:
1151:
1147:
1139:
1130:
1123:
1107:
1103:
1096:
1082:
1081:
1077:
1070:
1042:Harmatta, János
1038:Harmatta, János
1035:
1031:
1024:
993:
982:
967:
966:
962:
955:
939:
935:
928:
912:
905:
901:
895:
892:
887:
881:
880:
878:
874:
848:
837:
834:
825:
822:
813:
810:
801:
798:
784:
777:
728:
723:
722:
721:
720:
716:
715:
714:
706:
705:
696:
695:
688:
685:
643:
637:
605:
598:
591:
582:
571:
499:
492:
485:
476:
469:
460:
457:
373:
370:
321:
312:
302:
278:
222:
131:
104:
55:
19:
12:
11:
5:
3223:
3213:
3212:
3207:
3202:
3185:
3184:
3175:
3173:
3171:
3170:
3166:Rudrasimha III
3162:
3154:
3146:
3138:
3130:
3122:
3114:
3106:
3098:
3090:
3082:
3074:
3066:
3058:
3050:
3042:
3038:Damajadasri II
3034:
3026:
3018:
3010:
3002:
2994:
2986:
2978:
2970:
2962:
2954:
2939:
2924:
2909:
2901:
2893:
2884:
2882:
2873:
2870:
2869:
2861:
2860:
2853:
2846:
2838:
2829:
2828:
2824:
2823:
2812:
2801:
2788:
2787:
2784:
2783:
2778:
2776:
2774:Rudrasimha III
2771:
2767:
2766:
2757:Chandragupta I
2749:
2746:(c. 345 – 375)
2741:(c. 325 – 345)
2735:
2703:
2701:
2677:
2673:
2672:
2651:
2643:
2641:
2625:
2621:
2620:
2614:
2606:
2601:
2596:
2592:
2591:
2585:(c. 250 – 275)
2580:(c. 240 – 250)
2575:(c. 230 – 240)
2569:
2550:INDO-SASANIANS
2546:
2518:
2487:Damajadasri II
2475:
2471:
2470:
2448:
2425:
2386:
2382:
2381:
2362:
2355:
2346:
2337:
2333:
2332:
2329:
2326:
2323:Vima Kadphises
2319:
2317:
2312:
2308:
2307:
2304:
2301:
2294:
2292:
2281:
2277:
2276:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2266:
2262:
2261:
2258:
2255:
2248:
2243:
2241:
2239:
2235:
2234:
2231:
2228:
2221:
2216:
2214:
2212:
2208:
2207:
2204:
2201:
2194:
2189:
2178:
2176:
2172:
2171:
2166:
2161:
2154:
2147:
2134:
2132:
2128:
2127:
2122:
2111:
2106:
2095:
2093:
2089:
2088:
2083:
2070:
2059:
2049:Liaka Kusulaka
2046:
2033:
2031:
2029:
2025:
2024:
2013:
2006:
1997:
1995:
1991:
1990:
1988:
1981:
1976:
1974:
1970:
1969:
1967:
1960:
1953:
1944:
1942:
1938:
1937:
1935:
1932:Apollodotus II
1928:
1921:
1912:
1910:
1906:
1905:
1903:
1894:
1892:
1888:
1887:
1885:
1878:
1871:
1869:
1865:
1864:
1862:
1855:
1848:
1841:
1839:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1825:
1823:
1820:
1819:
1814:
1812:Eastern Punjab
1809:
1807:Western Punjab
1804:
1799:
1794:
1785:
1775:
1769:
1761:
1758:
1757:
1746:
1745:
1738:
1731:
1723:
1717:
1716:
1711:
1706:
1701:
1694:
1693:External links
1691:
1689:
1688:
1678:
1657:
1632:
1630:
1627:
1625:
1624:
1603:
1577:
1561:
1544:
1523:
1516:
1481:
1469:
1441:
1428:
1416:
1401:
1384:
1377:
1358:
1349:
1340:
1338:, p. 135.
1325:
1318:
1298:
1291:
1271:
1264:
1244:
1226:
1199:
1173:
1154:
1145:
1128:
1121:
1101:
1094:
1075:
1068:
1029:
1022:
980:
960:
953:
933:
926:
902:
900:
897:
890:
847:
844:
841:
840:
839:
838:
835:
828:
826:
823:
816:
814:
811:
804:
802:
799:
792:
787:
786:
775:
753:
752:
727:
724:
718:
717:
708:
707:
699:
698:
697:
693:
692:
691:
690:
683:
639:Main article:
636:
633:
604:
601:
600:
599:
592:
585:
583:
572:
565:
498:
495:
494:
493:
486:
479:
477:
470:
463:
461:
458:
451:
411:), Dashapura (
368:
339:gulf of Baraca
320:
317:
301:
298:
221:
218:
210:Indo-Scythians
102:
85:
84:
79:
75:
74:
69:
65:
64:
61:
57:
56:
51:British Museum
43:
35:
34:
31:Western Satrap
26:
25:
17:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3222:
3211:
3208:
3206:
3203:
3201:
3198:
3197:
3195:
3179:
3167:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3151:
3147:
3143:
3142:Rudrasena III
3139:
3135:
3134:Rudradaman II
3131:
3127:
3123:
3119:
3118:Rudrasimha II
3115:
3111:
3107:
3103:
3099:
3095:
3091:
3087:
3083:
3079:
3075:
3071:
3067:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3047:
3043:
3039:
3035:
3031:
3027:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3011:
3007:
3003:
2999:
2995:
2991:
2987:
2983:
2979:
2975:
2971:
2967:
2963:
2959:
2958:Damajadasri I
2955:
2944:
2940:
2929:
2925:
2914:
2910:
2906:
2902:
2898:
2894:
2890:
2886:
2885:
2877:
2871:
2866:
2859:
2854:
2852:
2847:
2845:
2840:
2839:
2836:
2821:
2816:
2810:
2805:
2799:
2793:
2789:
2782:
2775:
2768:
2765:
2762:
2761:
2758:
2754:
2748:
2745:
2740:
2734:
2732:
2728:
2721:
2717:
2713:
2708:
2700:
2698:
2694:
2690:
2689:Rudrasena III
2686:
2685:Rudradaman II
2682:
2674:
2671:
2668:
2664:
2660:
2656:
2650:
2648:
2640:
2638:
2634:
2633:Rudrasimha II
2630:
2622:
2618:
2613:
2611:
2605:
2600:
2593:
2590:
2587:
2584:
2579:
2574:
2568:
2565:
2560:
2555:
2551:
2545:
2543:
2539:
2535:
2531:
2527:
2523:
2517:
2516:
2512:
2508:
2504:
2500:
2496:
2492:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2472:
2469:
2466:
2463:
2458:
2453:
2447:
2444:
2442:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2424:
2421:
2419:
2415:
2411:
2407:
2403:
2399:
2398:Damajadasri I
2395:
2391:
2383:
2380:
2379:
2372:
2367:
2364:Great Satrap
2361:
2360:
2354:
2350:
2345:
2341:
2334:
2325:
2324:
2316:
2309:
2300:
2299:
2291:
2287:
2278:
2263:
2254:
2253:
2247:
2236:
2227:
2226:
2220:
2209:
2200:
2199:
2193:
2188:
2187:
2182:
2181:KUSHAN EMPIRE
2173:
2170:
2165:
2160:
2159:
2151:
2146:
2145:
2140:
2139:
2129:
2126:
2121:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2104:
2099:
2090:
2087:
2082:
2081:
2076:
2075:
2069:
2063:
2058:
2054:
2050:
2043:
2039:
2027:
2026:
2023:
2019:
2012:
2011:
2005:
2001:
1993:
1992:
1987:
1986:
1980:
1972:
1971:
1966:
1965:
1959:
1958:
1952:
1948:
1940:
1939:
1934:
1933:
1927:
1926:
1920:
1916:
1908:
1907:
1902:
1898:
1889:
1884:
1883:
1877:
1876:
1867:
1866:
1861:
1860:
1854:
1853:
1847:
1846:
1837:
1836:
1831:
1830:
1822:
1821:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1803:
1800:
1798:
1795:
1793:
1789:
1788:Paropamisadae
1786:
1784:
1780:
1776:
1774:
1770:
1765:
1764:
1759:
1755:
1751:
1750:Indo-Scythian
1744:
1739:
1737:
1732:
1730:
1725:
1724:
1721:
1715:
1712:
1710:
1707:
1705:
1702:
1699:
1697:
1696:
1687:
1686:0-9709268-6-3
1683:
1679:
1675:
1671:
1667:
1663:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1634:
1633:
1620:
1616:
1615:
1607:
1599:
1595:
1594:
1586:
1584:
1582:
1573:
1572:
1565:
1557:
1556:
1548:
1540:
1536:
1535:
1527:
1519:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1500:
1495:
1491:
1485:
1479:
1473:
1465:
1461:
1460:
1455:
1452:(1902–1903).
1451:
1445:
1438:
1432:
1426:
1420:
1414:
1408:
1406:
1399:
1393:
1391:
1389:
1380:
1378:9780852297605
1374:
1370:
1369:
1362:
1353:
1344:
1337:
1332:
1330:
1321:
1315:
1311:
1310:
1302:
1294:
1288:
1284:
1283:
1275:
1267:
1265:9788131711200
1261:
1257:
1256:
1248:
1242:
1238:
1235:
1230:
1219:
1212:
1211:
1203:
1188:
1184:
1177:
1171:
1167:
1164:
1158:
1149:
1143:, p. 44.
1142:
1137:
1135:
1133:
1124:
1118:
1114:
1113:
1105:
1097:
1091:
1087:
1086:
1079:
1071:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1052:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1033:
1025:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1003:
1002:
997:
996:Rapson, E. J.
991:
989:
987:
985:
976:
972:
971:
964:
956:
954:9780199096138
950:
946:
945:
937:
929:
927:9781136155314
923:
919:
918:
910:
908:
903:
889:
885:
875:
868:
863:
861:
857:
853:
852:Manmodi Caves
832:
827:
820:
815:
808:
803:
796:
791:
790:
789:
788:
781:
774:
772:
768:
760:
755:
754:
751:
747:
746:
743:
741:
740:Manmodi Caves
737:
733:
730:Parts of the
712:
703:
682:
680:
675:
671:
667:
664:Success!! By
661:
659:
654:
652:
648:
642:
632:
630:
626:
618:
614:
609:
596:
589:
584:
580:
576:
569:
564:
563:
562:
560:
556:
551:
549:
544:
539:
538:James Burgess
534:
532:
528:
524:
520:
512:
508:
503:
490:
483:
478:
474:
467:
462:
455:
450:
449:
448:
446:
442:
438:
437:Uttamabhadras
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
397:Rishabhadatta
393:
389:
387:
383:
379:
367:
365:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
334:
332:
328:
327:
316:
307:
297:
294:
288:
281:
273:
268:
263:
258:
253:
248:
242:
235:
228:
217:
215:
211:
207:
202:
196:
191:
186:
181:
176:
171:
166:
160:
156:
153:
146:
141:
134:
127:
126:Ancient Greek
123:
116:
111:
100:
96:
91:
83:
80:
76:
73:
70:
66:
62:
58:
52:
48:
41:
36:
33:
32:
27:
22:
16:
3158:Rudrasena IV
3126:Yasodaman II
3086:Rudrasena II
2982:Rudrasimha I
2974:Rudrasimha I
2943:Rudradaman I
2904:
2815:
2804:
2792:
2763:
2760:Samudragupta
2753:GUPTA EMPIRE
2751:
2737:
2705:
2697:Rudrasena IV
2681:Yasodaman II
2679:
2655:Vasudeva III
2653:
2645:
2627:
2608:
2599:Bhratadarman
2588:
2583:Kanishka III
2571:
2548:
2520:
2511:Rudrasena II
2477:
2467:
2450:
2445:
2427:
2422:
2406:Rudrasimha I
2394:Rudradaman I
2388:
2376:
2366:Kharapallana
2357:
2343:
2321:
2296:
2250:
2223:
2196:
2184:
2156:
2142:
2136:
2117:
2101:
2078:
2072:
2038:APRACHARAJAS
2010:Apollophanes
2008:
1983:
1962:
1957:Hippostratos
1955:
1951:Spalagadames
1930:
1923:
1880:
1873:
1857:
1850:
1843:
1827:
1766:Territories/
1753:
1668:(1): 43–50.
1665:
1661:
1644:
1640:
1629:Bibliography
1613:
1606:
1592:
1570:
1564:
1554:
1547:
1533:
1526:
1498:
1494:Hultzsch, R.
1484:
1472:
1458:
1454:Hultzsch, E.
1444:
1431:
1419:
1367:
1361:
1352:
1343:
1308:
1301:
1281:
1274:
1254:
1247:
1229:
1218:the original
1209:
1202:
1190:. Retrieved
1176:
1157:
1148:
1111:
1104:
1084:
1078:
1050:
1032:
1000:
969:
963:
943:
936:
916:
876:
872:
849:
764:
729:
663:
655:
644:
622:
554:
552:
535:
516:
488:
472:
394:
390:
375:
336:
324:
322:
303:
223:
148:
121:
120:
29:
15:
3102:Bhartrdaman
3062:Yasodaman I
3054:Isvaradatta
3022:Samghadaman
3014:Prthivisena
3006:Rudrasena I
2891:(1st c. CE)
2770:388-395 CE
2727:HEPHTHALITE
2720:Varhran III
2676:320-388 CE
2659:Vasudeva IV
2624:300-320 CE
2617:Vasudeva II
2604:Datayola II
2595:280-300 CE
2573:Kanishka II
2542:Datarvharna
2538:Datarvharna
2499:Yasodaman I
2495:Isvaradatta
2479:Samghadaman
2474:230-280 CE
2418:Rudrasena I
2385:130-230 CE
2369:and Satrap
2349:PARATARAJAS
2311:100-120 CE
2119:Gondophares
2103:Gondophares
2062:Kharahostes
2042:Vijayamitra
1859:Artemidoros
1852:Menander II
1783:Balochistan
1046:Puri, B. N.
750:Nasik Caves
732:Nasik Caves
658:Karla Caves
651:Karla Caves
641:Karla caves
635:Karla caves
625:Maharashtra
617:Karla Caves
555:Kshaharatas
531:'Khakharata
371:Periplus 41
341:is that of
337:Beyond the
265:), and the
195:Na-ha-pā-na
159:Na-ha-pa-na
68:Predecessor
3194:Categories
3094:Visvasimha
3070:Vijayasena
2990:Satyadaman
2950: 130
2935: 130
2733:invasions
2716:Varhran II
2663:Vasudeva V
2610:Hormizd II
2554:Ardashir I
2530:Bhimarjuna
2522:Miratakhma
2515:Visvasimha
2503:Vijayasena
2462:Vasudeva I
2410:Satyadaman
2378:Kanishka I
2359:Kanishka I
2298:Vima Takto
2280:75-100 CE
2192:Indravarma
2158:Sarpedones
2150:Vispavarma
2080:Strato III
1994:55–35 BCE
1973:55–35 BCE
1947:Spalirises
1941:65–55 BCE
1919:Spalahores
1909:75–70 BCE
1891:85-60 BCE
1868:90–70 BCE
1838:90–85 BCE
1754:(in green)
1617:. p.
1596:. p.
1490:Senart, E.
1450:Senart, E.
1437:Kshatrapas
1180:quoted in
1058:. p.
1008:. p.
1004:. London:
899:References
771:Govardhana
767:Ushavadata
666:Usabhadata
519:Satavahana
507:Satavahana
421:Govardhana
386:Kharoshthi
378:Indo-Greek
355:Syrastrene
3168:(388–415)
3160:(383–384)
3152:(380–385)
3150:Simhasena
3144:(348–378)
3136:(332–348)
3128:(317–332)
3120:(304–348)
3112:(293–304)
3110:Visvasena
3104:(282–295)
3096:(277–282)
3088:(255–277)
3080:(251–255)
3072:(239–250)
3056:(236–239)
3048:(234–238)
3046:Viradaman
3040:(232–239)
3032:(223–232)
3024:(222–223)
3008:(200–222)
2998:Jivadaman
2992:(197-198)
2976:(180–188)
2968:(178-181)
2966:Jivadaman
2960:(170–175)
2928:Jayadaman
2920: 78
2907:(119–124)
2712:Varhran I
2707:Shapur II
2693:Simhasena
2637:Jivadaman
2629:Visvasena
2578:Vashishka
2564:Hormizd I
2491:Viradaman
2441:Mirahvara
2437:Hvaramira
2414:Jivadaman
2402:Jivadaman
2390:Jayadaman
2371:Vanaspara
2265:50-75 CE
2238:45-50 CE
2219:Aspavarma
2211:40-45 CE
2198:Abdagases
2175:30-40 CE
2164:Bhadayasa
2138:Ubouzanes
2131:20-30 CE
2109:Indravasu
2092:10-20 CE
2074:Strato II
2057:Zeionises
2022:Hagamasha
1985:Zoilos II
1964:Dionysios
1925:Telephos
1882:Archebius
1792:Arachosia
674:Bramhanas
559:Chashtana
548:Chashtana
388:legends.
364:Minnagara
313: 66
306:Shaka era
145:Kharosthi
78:Successor
3030:Damasena
2913:Chastana
2905:Nahapana
2889:Abhiraka
2744:Kipunada
2647:Peroz II
2483:Damasena
2457:Huvishka
2452:Vāsishka
2429:Bagamira
2353:Yolamira
2344:Nahapana
2315:Abhiraka
2290:Chastana
2125:Rajuvula
2068:Mujatria
2000:Azilises
1875:Hermaeus
1802:Gandhara
1779:Pakistan
1777:Western
1771:Western
1653:41702166
1492:(1906).
1237:Archived
1166:Archived
998:(1908).
891:—
860:Saka era
824:Interior
778:Part of
776:—
684:—
679:Valuraka
573:Coin of
413:Mandasor
369:—
343:Barygaza
331:Barigaza
293:Nāhapānä
280:Ναηαπάνα
272:Nahapána
241:Nahapāna
234:𐨣𐨱𐨤𐨣
227:Nahapana
201:Nahapāna
165:Nahapana
152:𐨣𐨱𐨤𐨣
140:Nahapána
133:Ναηαπάνα
122:Nahapana
82:Chastana
24:Nahapana
2899:(?–119)
2897:Bhumaka
2739:Shaka I
2559:Peroz I
2340:Bhumaka
2336:120 CE
2144:Pakores
2004:Azes II
1915:Vonones
1817:Mathura
1496:(ed.).
1456:(ed.).
884:mandapa
812:Veranda
647:chaitya
629:Gujarat
613:Chaitya
441:Malavas
431:in the
409:Bharuch
214:Bhumaka
99:Prakrit
72:Bhumaka
47:Prakrit
2534:Koziya
2526:Kozana
2433:Arjuna
2225:Gadana
2169:Sodasa
2086:Hagana
1979:Azes I
1845:Nicias
1797:Bajaur
1768:dates
1684:
1651:
1514:
1375:
1316:
1289:
1262:
1192:11 May
1119:
1092:
1066:
1020:
951:
924:
856:Junnar
736:Junnar
670:tirtha
579:Ujjain
527:Nashik
429:Sopara
423:(near
382:Brahmi
359:sesame
351:Abiria
347:Ariaca
300:Period
170:Brahmi
3064:(239)
3016:(222)
2952:–150)
2922:-130)
2731:HUNAS
2252:Sases
2246:Sasan
1901:Maues
1773:India
1649:JSTOR
1413:p.150
1221:(PDF)
1214:(PDF)
800:Front
521:king
509:king
433:Thana
425:Nasik
417:Malva
405:Nasik
403:near
319:Reign
291:*
289:name
269:form
267:Greek
115:Rajah
95:Greco
60:Reign
2667:Chhu
2331:...
2328:...
2306:...
2303:...
2275:...
2272:...
2260:...
2257:...
2233:...
2230:...
2206:...
2203:...
2077:and
1682:ISBN
1512:ISBN
1478:p.40
1425:p.72
1398:p.42
1373:ISBN
1314:ISBN
1287:ISBN
1260:ISBN
1194:2013
1117:ISBN
1090:ISBN
1064:ISBN
1018:ISBN
949:ISBN
922:ISBN
627:and
611:The
489:Rev:
473:Obv:
384:and
323:The
287:Saka
220:Name
93:The
2374:for
1670:doi
1598:103
1539:261
1060:413
975:219
854:in
546:of
419:),
415:in
3196::
2947:c.
2932:c.
2917:c.
2729:/
2718:,
2714:,
1666:11
1664:.
1645:77
1643:.
1580:^
1510:.
1508:79
1504:78
1464:58
1404:^
1387:^
1328:^
1185:.
1131:^
1062:.
1044:;
1016:.
1014:67
1010:65
983:^
906:^
742:.
631:.
561:.
310:c.
216:.
198:,
172::
168:;
162:,
147::
143:;
128::
2945:(
2937:)
2930:(
2915:(
2857:e
2850:t
2843:v
1742:e
1735:t
1728:v
1676:.
1672::
1655:.
1621:.
1600:.
1541:.
1520:.
1506:-
1466:.
1381:.
1322:.
1295:.
1268:.
1196:.
1125:.
1098:.
1072:.
1026:.
1012:-
977:.
957:.
930:.
275:(
244:(
230:(
124:(
103:ω
97:-
53:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.