383:
the chromosome region that contains the genetic code for it. p53 acts to prevent the propagation of tumor cells and is considered a major tumor suppressor protein. p53 works by either halting progression through the cell cycle when uncontrolled cell division is sensed or it can promote cell death through apoptosis in the presence of irreparable DNA damage. Mitotic catastrophe can occur in a p53 independent fashion and thus presents a therapeutic avenue of interest. Furthermore, doses of DNA damaging drugs lower than lethal levels have been shown to induce mitotic catastrophe. This would allow for administration of a drug while the patient has fewer side effects.
265:
more than two centrosomes present in mitosis they can pull chromosomes in incorrect directions resulting in daughter cells that are inviable. Many cancers have excessive numbers of centrosomes, but to prevent inviable daughter cells, the cancer cells have developed mechanisms to cluster their centrosomes. When the centrosomes are clustered to two poles of the dividing cell, the chromosomes are segregated properly and two daughter cells are formed. Thus, cancers that are able to adapt to a higher number of centrosomes are able to are able to prevent mitotic catastrophe and propagate in the presence of their extra centrosomes.
83:
237:
20:
301:
256:
segregation errors that result in mitotic catastrophe. Cells that become aneuploid often are prevented from further cell growth and division by the activation of tumor suppressor pathways such as p53 which drives the cell to a non-proliferating state known as cellular senescence. Given that aneuploid cells can often become tumorigenic, this mechanism prevents the propagation of these cells and thus prevents the development of cancers in the organism.
216:
147:
323:
worse patient outcomes than those cancers which have lower levels of genomic instability. Cells have gained mechanisms that resist increased genomic instability in cells. Mitotic catastrophe is one way in which cells prevent the propagation of genomically unstable cells. If mitotic catastrophe fails for cells whose genome has become unstable they can propagate uncontrollably and potentially become tumorigenic.
371:
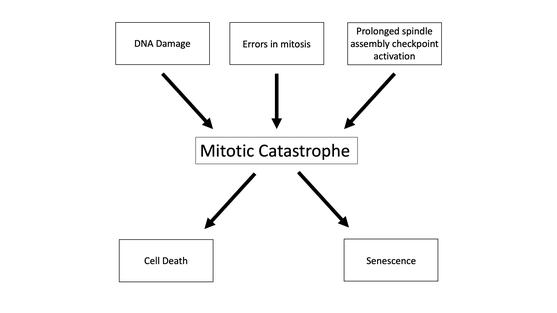
179:. This mechanism is important to ensure that the DNA within the cell is divided equally between the two daughter cells. When the spindle assembly checkpoint is activated, it arrests the cell in mitosis until all chromosomes are properly attached and aligned. If the checkpoint is activated for a prolonged period it can lead to mitotic catastrophe.
306:
305:
302:
307:
133:
Cells that undergo mitotic catastrophe death can lack activation of pathways of the traditional death pathways such as apoptosis. While more recent definitions of mitotic catastrophe do not use it to describe a bona fide cell death mechanism, some publications describe it as a mechanism of cell death.
232:
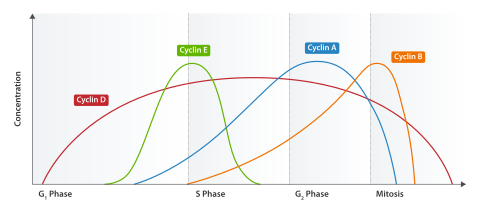
to control this progression and the complex is known as the mitotic promoting factor. While the mitotic promoting factor is utilized to guide the cells entry into mitosis, its destruction also guides the cells exit from mitosis. Normally, cyclin B1 degradation is initiated by the anaphase promoting
95:
has occurred. This definition of this mechanism has been described by the
International Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death. Under this definition, cells that undergo mitotic catastrophe either senesce and stop dividing or undergo a regulated form of cell death during mitosis or another form of cell
322:
cells and promotes genetic changes (both large chromosomal changes as well as individual nucleotide changes) in cancer cells which can lead to increased levels of tumor progression through genetic variation in the tumor cell. Cancers with a higher level of genomic instability have been shown to have
264:
are cellular organelles that acts to organize the mitotic spindle assembly in the cell during mitosis and thus guide the segregation of chromosomes during mitosis. Normally, cells will have two centrosomes that guide sister chromatids to opposite poles of the dividing cell. However, when there are
132:
Another usage of the term mitotic catastrophe is to describe a mode of cell death that occurs during mitosis. This cell death can occur due to an accumulation of DNA damage in the presence of improperly functioning DNA structure checkpoints or an improperly functioning spindle assembly checkpoint.
61:
that demonstrated abnormal segregation of chromosomes. The term has been used to define a mechanism of cellular death that occurs while a cell is in mitosis or as a method of oncosuppression that prevents potentially tumorigenic cells from dividing. This oncosuppression is accomplished by initiating
382:
Cancer cells have been found to be more sensitive to mitotic catastrophe induction than non-cancerous cells in the body. Tumors cells often have inactivated the machinery that is required for apoptosis such as the p53 protein. This is usually achieved by mutations in the p53 protein or by loss of
960:
Galluzzi, Lorenzo; Vitale, Ilio; Aaronson, Stuart A.; Abrams, John M.; Adam, Dieter; Agostinis, Patrizia; Alnemri, Emad S.; Altucci, Lucia; Amelio, Ivano; Andrews, David W.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, Margherita; Antonov, Alexey V.; Arama, Eli; Baehrecke, Eric H.; Barlev, Nickolai A. (March 2018).
625:
Galluzzi, Lorenzo; Vitale, Ilio; Aaronson, Stuart A.; Abrams, John M.; Adam, Dieter; Agostinis, Patrizia; Alnemri, Emad S.; Altucci, Lucia; Amelio, Ivano; Andrews, David W.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, Margherita; Antonov, Alexey V.; Arama, Eli; Baehrecke, Eric H.; Barlev, Nickolai A. (March 2018).
386:
Cancer therapies can induce mitotic catastrophe by either damaging the cells DNA or inhibiting spindle assembly. Drugs, known as spindle poisons, affect the polymerization or depolymerization of microtubule spindles and thus interfere with the correct formation of the mitotic spindles. When this
186:
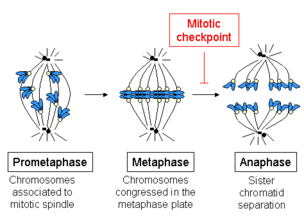
Normally, activation of the anaphase promoting complex leads to the separation of sister chromatids and the cell exiting mitosis. The mitotic checkpoint complex acts as a negative regulator of the anaphase promoting complex. Unattached kinetochores promote the formation of the mitotic checkpoint
286:
is no longer present in the cell. The response to DNA damage present during mitosis is different from the response to DNA damage detected during the rest of the cell cycle. Cells can detect DNA defects during the rest of the cell cycle and either repair them if possible or undergo apoptosis of
223:
Some cells can have an erroneous mitosis yet survive and undergo another cell division which puts the cell at a higher likelihood to undergo mitotic catastrophe. For instance, cells can undergo a process called mitotic slippage where cells exit mitosis too early before the process of mitosis is
259:
Cells that undergo multipolar divisions, or in other words split into more than 2 daughter cells, are at a higher risk of mitotic catastrophe as well. While many of the progeny of multipolar divisions do not survive do to highly imbalanced chromosome numbers, most of the cells that survive and
255:
to split into two daughter cells and thus remain as one cell. Aneuploid cells are cells that have an incorrect number of chromosomes including whole additions of chromosomes or complete losses of chromosomes. Cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes are more likely to have chromosome
304:
233:
complex after all of the kinetochores have been properly attached by mitotic spindle fibers. However, when cyclin B1 levels are degraded too fast this can result in the cell exiting mitosis prematurely resulting in potential mitotic errors including missegregation of chromosomes.
277:
do not have the ability to prevent progression through the cell cycle even when there is DNA damage present in the cell's genome. The G2 checkpoint normally functions to stop cells that have damaged DNA from progressing to mitosis. The
90:
One usage of the term mitotic catastrophe is to describe an oncosuppressive mechanism (i.e. a mechanism to prevent the proliferation of cancerous cells and the development of tumors) that occurs when cells undergo and detect a defective
224:
finished. In this case, the cell finishes mitosis in the presence of spindle assembly checkpoint signaling which would normally prevent the cell from exiting mitosis. This phenomenon is caused by improper degradation of
162:
or mitotic checkpoint. The spindle assembly checkpoint verifies that mitotic spindles have properly attached to the kinetochores of each pair of chromosomes before the chromosomes segregate during cell division. If the
303:
115:
still present in the cell at the time of cell death indicating the cell never finished mitosis. Mitotic catastrophe can also lead to the cell being fated for cell death by apoptosis or necrosis following
219:
Expression of cyclin levels during different phases of the cell cycle. Cyclin B promotes progression to mitosis and once the cell is in mitosis normally prevents the cell from exiting mitosis prematurely.
228:
and can result in chromosome missegregation events. Cyclin B1 is a major regulator of the cell cycle and guides the cells progression from G2 to M phase. Cyclin B1 works with its binding partner
378:
Promotion of mitotic catastrophe in cancer cells is an area of cancer therapeutic research that has garnered interest and is seen as a potential target to overcome resistance developed to current
150:
Mitotic checkpoint (also known as spindle assembly checkpoint) prevents the cell progressing from metaphase to anaphase if not all of the chromosomes are properly attached by mitotic spindles.
124:
The least common outcome of mitotic catastrophe is senescence in which the cell stops dividing and enters a permanent cell cycle arrest that prevents the cell from proliferating any further.
326:
The level of genomic instability is different across cancer types with epithelial cancers being more genomically unstable than cancers of hematological or mesenchymal origin.
120:
of the cell cycle. However, the timing of cell death can vary from hours after mitosis completes to years later which has been witnessed in human tissues treated with
34:
has been defined as either a cellular mechanism to prevent potentially cancerous cells from proliferating or as a mode of cellular death that occurs following improper
54:
Multiple attempts to specifically define mitotic catastrophe have been made since the term was first used to describe a temperature dependent lethality in the yeast,
42:, errors in mitosis, or DNA damage and operates to prevent genomic instability. It is a mechanism that is being researched as a potential therapeutic target in
260:
undergo a subsequent mitosis are likely to experience mitotic catastrophe. These multipolar divisions occur due to the presence of more than two centrosomes.
525:
Inhibitor which perturbs the movement of chromosomes during mitosis. This perturbation results in cells dying in mitosis or in the subsequent interphase.
207:
When the mitotic checkpoint complex is formed, it binds to the anaphase promoting complex and prevents its ability to promote cell cycle progression.
2094:
Triarico, Silvia; Romano, Alberto; Attinà, Giorgio; Capozza, Michele
Antonio; Maurizi, Palma; Mastrangelo, Stefano; Ruggiero, Antonio (2021-04-16).
273:
High levels of DNA damage that are not repaired before the cell enters mitosis can result in a mitotic catastrophe. Cells that have a compromised
430:
Promotes microtubule spindle assembly and prevents the detachment of microtubules preventing the cell from properly entering or exiting mitosis.
251:
cells are at higher risk of mitotic catastrophe. Tetraploid cells are cells that have duplicated their genetic material, but have not undergo
240:
An example of a normal mitosis on the left and a multipolar mitosis on the right. Microtubules are in red and the centrosomes are in yellow.
2096:"Vincristine-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (VIPN) in Pediatric Tumors: Mechanisms, Risk Factors, Strategies of Prevention and Treatment"
287:
senescence. Given that when this happens the cell does not progress into mitosis it is not considered a mitotic catastrophe.
19:
1693:
111:
When the cell undergoes cell death during mitosis this is known as mitotic death. This is characterized by high levels of
387:
happens, the spindle assembly checkpoint becomes activated and the transition from metaphase to anaphase is inhibited.
690:
Castedo, Maria; Perfettini, Jean-Luc; Roumier, Thomas; Andreau, Karine; Medema, Rene; Kroemer, Guido (April 2004).
573:
421:
343:
507:
491:
351:
2069:
536:
359:
2158:"Eg5 targeting agents: From new anti-mitotic based inhibitor discovery to cancer therapy and resistance"
374:
Chemical structure of
Paclitaxel (Taxol), an anticancer therapeutic that can induce mitotic catastrophe.
522:
279:
274:
183:
1400:
963:"Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018"
628:"Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018"
1335:"The balance between mitotic death and mitotic slippage in acute leukemia: a new therapeutic window?"
229:
56:
355:
906:
Denisenko, Tatiana V.; Sorokina, Irina V.; Gogvadze, Vladimir; Zhivotovsky, Boris (January 2016).
27:
and had a catastrophic mitosis. The cell has become multinucleated after an unsuccessful mitosis.
2215:"Past, present, and future of Bcr-Abl inhibitors: from chemical development to clinical efficacy"
1960:
1144:
Sazonova, Elena V.; Petrichuk, Svetlana V.; Kopeina, Gelina S.; Zhivotovsky, Boris (2021-12-09).
319:
2044:
1513:"Let's huddle to prevent a muddle: centrosome declustering as an attractive anticancer strategy"
912:
Drug
Resistance Updates: Reviews and Commentaries in Antimicrobial and Anticancer Chemotherapy
471:
445:
331:
38:
progression or entrance. Mitotic catastrophe can be induced by prolonged activation of the
8:
2334:
606:
562:
inhibitor which disrupts the movement of chromosomes and the cytoskeleton during mitosis
413:
71:
82:
2306:
2273:
2249:
2214:
2195:
2130:
2095:
2021:
1986:
1937:
1902:
1873:
1840:
1813:
1780:
1761:
1607:
1545:
1512:
1493:
1369:
1334:
1333:
Ghelli
Luserna di Rorà, Andrea; Martinelli, Giovanni; Simonetti, Giorgia (2019-11-26).
1301:
1268:
1244:
1211:
1180:
1145:
1126:
1063:
1028:
995:
962:
855:
729:
660:
627:
315:
159:
105:
86:
Diagram showing events that can lead to mitotic catastrophe and the potential outcomes.
39:
2311:
2293:
2254:
2236:
2199:
2187:
2179:
2135:
2117:
2026:
2008:
1942:
1924:
1878:
1860:
1818:
1800:
1765:
1753:
1745:
1699:
1689:
1654:
1646:
1611:
1599:
1591:
1550:
1532:
1497:
1485:
1477:
1428:
1420:
1374:
1356:
1306:
1288:
1249:
1231:
1185:
1167:
1130:
1118:
1110:
1068:
1050:
1000:
982:
935:
927:
847:
839:
721:
713:
665:
647:
467:
164:
121:
859:
733:
104:
of the cell cycle. The function of this mechanism is to prevent cells from accruing
2339:
2301:
2285:
2244:
2226:
2169:
2125:
2107:
2016:
1998:
1932:
1914:
1868:
1852:
1808:
1792:
1735:
1681:
1638:
1581:
1540:
1524:
1467:
1459:
1412:
1364:
1346:
1296:
1280:
1239:
1223:
1175:
1157:
1102:
1058:
1040:
990:
974:
919:
831:
703:
655:
639:
540:
463:
2289:
1796:
1284:
2344:
1740:
1723:
1227:
1146:"A link between mitotic defects and mitotic catastrophe: detection and cell fate"
559:
555:
475:
459:
441:
2274:"Review: Recent advances of cell cycle inhibitor therapies for pediatric cancer"
1685:
236:
1162:
1106:
1089:
Fu, Xiao; Li, Mu; Tang, Cuilian; Huang, Zezhi; Najafi, Masoud (December 2021).
923:
908:"Mitotic catastrophe and cancer drug resistance: A link that must to be broken"
425:
339:
2231:
2174:
2157:
2003:
1856:
1642:
1586:
1569:
1463:
1416:
1351:
978:
643:
2328:
2297:
2240:
2183:
2121:
2012:
1928:
1864:
1804:
1749:
1650:
1595:
1536:
1481:
1424:
1360:
1292:
1235:
1171:
1114:
1054:
986:
931:
843:
818:
Vitale, Ilio; Galluzzi, Lorenzo; Castedo, Maria; Kroemer, Guido (June 2011).
717:
651:
499:
417:
335:
1919:
1673:
1626:
1447:
1090:
907:
2315:
2258:
2191:
2139:
2030:
1946:
1882:
1822:
1757:
1703:
1658:
1603:
1554:
1489:
1432:
1378:
1310:
1253:
1189:
1122:
1072:
1004:
939:
851:
725:
708:
691:
669:
379:
347:
327:
1045:
819:
2112:
1472:
1332:
485:
453:
252:
168:
146:
1528:
1672:
Stark, George R.; Taylor, William R. (2004), Schönthal, Axel H. (ed.),
1210:
Lara-Gonzalez, Pablo; Pines, Jonathon; Desai, Arshad (September 2021).
547:
448:, stomach adenocarcinoma, and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
407:
261:
248:
244:
155:
117:
35:
24:
1212:"Spindle assembly checkpoint activation and silencing at kinetochores"
171:
then the spindle assembly checkpoint will prevent the transition from
2213:
Rossari, Federico; Minutolo, Filippo; Orciuolo, Enrico (2018-06-20).
601:
567:
530:
514:
435:
225:
182:
Prolonged activation of the spindle assembly checkpoint inhibits the
172:
112:
63:
2272:
Mills, Christopher C.; Kolb, EA.; Sampson, Valerie B. (2017-12-01).
1781:"Genomic instability in cancer: Teetering on the limit of tolerance"
1091:"Targeting of cancer cell death mechanisms by resveratrol: a review"
905:
835:
215:
1678:
Checkpoint
Controls and Cancer: Volume 1: Reviews and Model Systems
1267:
Sinha, Debottam; Duijf, Pascal H.G.; Khanna, Kum Kum (2019-01-02).
1143:
820:"Mitotic catastrophe: a mechanism for avoiding genomic instability"
495:
176:
141:
97:
67:
311:
Video of a cell treated with taxol undergoing mitotic catastrophe.
1576:. Centrosomal Organization and Assemblies ● Folding and Binding.
591:
503:
92:
46:, and numerous approved therapeutics induce mitotic catastrophe.
1841:"The detection and implication of genome instability in cancer"
1399:
Ganem, Neil J; Storchova, Zuzana; Pellman, David (2007-04-01).
1029:"Targeting the Mitotic Catastrophe Signaling Pathway in Cancer"
689:
596:
43:
1625:
Doxsey, Stephen; Zimmerman, Wendy; Mikule, Keith (June 2005).
1328:
1326:
1324:
1322:
1320:
187:
complex which is composed of four different proteins known as
204:
192:
1987:"Progress in research on paclitaxel and tumor immunotherapy"
1839:
Pikor, Larissa; Thu, Kelsie; Vucic, Emily; Lam, Wan (2013).
959:
817:
624:
2093:
1779:
Andor, Noemi; Maley, Carlo C.; Ji, Hanlee P. (2017-05-01).
1680:, vol. 280, Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, pp. 51–82,
1317:
692:"Cell death by mitotic catastrophe: a molecular definition"
200:
196:
188:
2156:
Garcia-Saez, Isabel; Skoufias, Dimitrios A. (2021-02-01).
578:
Failed clinical trial for adult lymphomas and lung cancer
154:
Cells have a mechanism to prevent improper segregation of
77:
440:
Approved use: Breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer,
283:
370:
350:
cancer exhibit high levels of genomic instability while
2212:
1896:
1894:
1892:
1209:
1624:
1398:
1889:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1199:
399:
Approved uses / clinical trial phase / research use
295:
2155:
2151:
2149:
1903:"Treating p53 Mutant Aggregation-Associated Cancer"
1196:
955:
953:
951:
949:
901:
899:
897:
895:
893:
891:
889:
2326:
2271:
2146:
1838:
1269:"Mitotic slippage: an old tale with a new twist"
1266:
887:
885:
883:
881:
879:
877:
875:
873:
871:
869:
290:
142:Prolonged spindle assembly checkpoint activation
1900:
1511:Ogden, A; Rida, P C G; Aneja, R (August 2012).
1446:Ben-David, Uri; Amon, Angelika (January 2020).
1510:
946:
813:
811:
809:
807:
805:
803:
801:
799:
797:
795:
793:
791:
789:
787:
785:
783:
781:
779:
777:
775:
773:
771:
769:
767:
765:
763:
685:
683:
681:
679:
127:
1834:
1832:
1448:"Context is everything: aneuploidy in cancer"
1445:
1405:Current Opinion in Genetics & Development
1394:
1392:
1390:
1388:
1088:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1016:
1014:
866:
761:
759:
757:
755:
753:
751:
749:
747:
745:
743:
391:Cancer drugs that induce mitotic catastrophe
1778:
1216:Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology
618:
572:Phase I clinical trial: pediatric recurrent
2100:International Journal of Molecular Sciences
1671:
676:
1829:
1385:
1011:
740:
365:
2305:
2248:
2230:
2173:
2129:
2111:
2020:
2002:
1936:
1918:
1872:
1812:
1739:
1585:
1544:
1471:
1407:. Chromosomes and expression mechanisms.
1368:
1350:
1300:
1243:
1179:
1161:
1084:
1082:
1062:
1044:
994:
707:
659:
1991:Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters
1901:Kanapathipillai, Mathumai (2018-05-23).
369:
299:
235:
214:
145:
81:
18:
1985:Zhu, Linyan; Chen, Liqun (2019-06-13).
1984:
1721:
1570:"Centrosome organization and functions"
1567:
282:can be compromised if tumor suppressor
78:Mechanism to prevent cancer development
2327:
1627:"Centrosome control of the cell cycle"
1079:
1026:
1724:"Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions"
1574:Current Opinion in Structural Biology
824:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
446:head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
2219:Journal of Hematology & Oncology
1401:"Tetraploidy, aneuploidy and cancer"
1339:Journal of Hematology & Oncology
576:and pediatric advanced solid tumors
210:
13:
362:have lower levels of instability.
23:A cell that has been treated with
14:
2356:
1722:Hanahan, Douglas (January 2022).
574:atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors
296:Prevention of genomic instability
167:are not properly attached to the
108:which can lead to tumorigenesis.
967:Cell Death & Differentiation
632:Cell Death & Differentiation
2265:
2206:
2087:
2062:
2037:
1978:
1953:
1772:
1715:
1674:"Analyzing the G2/M Checkpoint"
1665:
1618:
1561:
1504:
1439:
1260:
1568:Bornens, Michel (2021-02-01).
1517:Cell Death and Differentiation
1137:
1:
2290:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2066
1845:Cancer and Metastasis Reviews
1797:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1553
1285:10.1080/15384101.2018.1559557
612:
508:central nervous system tumors
458:Approved use: Breast cancer,
291:Mitotic catastrophe in cancer
268:
62:a form of cell death such as
49:
1741:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059
1228:10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.06.009
1027:Mc Gee, Margaret M. (2015).
492:Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
352:acute lymphoblastic leukemia
7:
2070:"Vinblastine Sulfate - NCI"
585:
480:Depolymerizes microtubules
476:testicular germ cell tumors
412:Approved use: AIDS-related
360:myeloproliferative disorder
184:anaphase promoting complex.
160:spindle assembly checkpoint
128:Mechanism of cellular death
40:spindle assembly checkpoint
10:
2361:
1163:10.1186/s13062-021-00313-7
1107:10.1007/s10495-021-01689-7
924:10.1016/j.drup.2015.11.002
422:non-small cell lung cancer
344:non-small cell lung cancer
2232:10.1186/s13045-018-0624-2
2175:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114364
2004:10.1186/s11658-019-0164-y
1965:National Cancer Institute
1857:10.1007/s10555-013-9429-5
1686:10.1385/1-59259-788-2:051
1643:10.1016/j.tcb.2005.04.008
1587:10.1016/j.sbi.2020.11.002
1464:10.1038/s41576-019-0171-x
1417:10.1016/j.gde.2007.02.011
1352:10.1186/s13045-019-0808-4
1033:Mediators of Inflammation
979:10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
644:10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
554:
521:
479:
429:
136:
57:Schizosaccharomyces pombe
2162:Biochemical Pharmacology
1452:Nature Reviews. Genetics
537:Phase III clinical trial
1920:10.3390/cancers10060154
552:Pre-clinical research
366:Anticancer therapeutics
16:Mechanism of cell death
1631:Trends in Cell Biology
709:10.1038/sj.onc.1207528
375:
332:small-cell lung cancer
312:
241:
220:
151:
87:
28:
373:
310:
239:
218:
149:
85:
22:
2113:10.3390/ijms22084112
472:non-Hodgkin lymphoma
402:Mechanism of action
1529:10.1038/cdd.2012.61
1046:10.1155/2015/146282
392:
320:hallmarks of cancer
316:Genomic instability
106:genomic instability
72:cellular senescence
32:Mitotic catastrophe
1101:(11–12): 561–573.
466:, Kaposi sarcoma,
390:
376:
313:
242:
221:
152:
96:death in the next
88:
29:
2284:(23): 6489–6498.
2045:"Docetaxel - NCI"
1695:978-1-59259-788-8
702:(16): 2825–2837.
583:
582:
468:mycosis fungoides
308:
211:Errors in mitosis
2352:
2320:
2319:
2309:
2269:
2263:
2262:
2252:
2234:
2210:
2204:
2203:
2177:
2153:
2144:
2143:
2133:
2115:
2091:
2085:
2084:
2082:
2081:
2066:
2060:
2059:
2057:
2056:
2041:
2035:
2034:
2024:
2006:
1982:
1976:
1975:
1973:
1972:
1967:. 5 October 2006
1957:
1951:
1950:
1940:
1922:
1898:
1887:
1886:
1876:
1836:
1827:
1826:
1816:
1791:(9): 2179–2185.
1776:
1770:
1769:
1743:
1728:Cancer Discovery
1719:
1713:
1712:
1711:
1710:
1669:
1663:
1662:
1622:
1616:
1615:
1589:
1565:
1559:
1558:
1548:
1523:(8): 1255–1267.
1508:
1502:
1501:
1475:
1443:
1437:
1436:
1396:
1383:
1382:
1372:
1354:
1330:
1315:
1314:
1304:
1264:
1258:
1257:
1247:
1207:
1194:
1193:
1183:
1165:
1141:
1135:
1134:
1086:
1077:
1076:
1066:
1048:
1024:
1009:
1008:
998:
957:
944:
943:
903:
864:
863:
815:
738:
737:
711:
687:
674:
673:
663:
622:
541:multiple myeloma
464:Hodgkin lymphoma
393:
389:
309:
165:mitotic spindles
2360:
2359:
2355:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2350:
2349:
2325:
2324:
2323:
2278:Cancer Research
2270:
2266:
2211:
2207:
2154:
2147:
2092:
2088:
2079:
2077:
2068:
2067:
2063:
2054:
2052:
2043:
2042:
2038:
1983:
1979:
1970:
1968:
1959:
1958:
1954:
1899:
1890:
1837:
1830:
1785:Cancer Research
1777:
1773:
1720:
1716:
1708:
1706:
1696:
1670:
1666:
1623:
1619:
1566:
1562:
1509:
1505:
1444:
1440:
1397:
1386:
1331:
1318:
1265:
1261:
1208:
1197:
1142:
1138:
1087:
1080:
1025:
1012:
958:
947:
904:
867:
836:10.1038/nrm3115
816:
741:
688:
677:
623:
619:
615:
588:
460:Choriocarcinoma
442:prostate cancer
380:chemotherapies.
368:
300:
298:
293:
271:
213:
144:
139:
130:
101:
80:
70:or by inducing
52:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2358:
2348:
2347:
2342:
2337:
2322:
2321:
2264:
2205:
2145:
2086:
2074:www.cancer.gov
2061:
2049:www.cancer.gov
2036:
1977:
1952:
1888:
1851:(3): 341–352.
1828:
1771:
1714:
1694:
1664:
1637:(6): 303–311.
1617:
1560:
1503:
1438:
1411:(2): 157–162.
1384:
1316:
1259:
1195:
1150:Biology Direct
1136:
1078:
1010:
973:(3): 486–541.
945:
865:
830:(6): 385–392.
739:
675:
638:(3): 486–541.
616:
614:
611:
610:
609:
604:
599:
594:
587:
584:
581:
580:
570:
564:
563:
553:
550:
544:
543:
534:
527:
526:
520:
517:
511:
510:
490:Approved use:
488:
482:
481:
478:
456:
450:
449:
438:
432:
431:
428:
426:ovarian cancer
414:Kaposi sarcoma
410:
404:
403:
400:
397:
367:
364:
356:myelodysplasia
318:is one of the
297:
294:
292:
289:
270:
267:
212:
209:
143:
140:
138:
135:
129:
126:
99:
79:
76:
51:
48:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2357:
2346:
2343:
2341:
2338:
2336:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2317:
2313:
2308:
2303:
2299:
2295:
2291:
2287:
2283:
2279:
2275:
2268:
2260:
2256:
2251:
2246:
2242:
2238:
2233:
2228:
2224:
2220:
2216:
2209:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2181:
2176:
2171:
2167:
2163:
2159:
2152:
2150:
2141:
2137:
2132:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2114:
2109:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2090:
2075:
2071:
2065:
2050:
2046:
2040:
2032:
2028:
2023:
2018:
2014:
2010:
2005:
2000:
1996:
1992:
1988:
1981:
1966:
1962:
1956:
1948:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1897:
1895:
1893:
1884:
1880:
1875:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1835:
1833:
1824:
1820:
1815:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1775:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1742:
1737:
1733:
1729:
1725:
1718:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1691:
1687:
1683:
1679:
1675:
1668:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1621:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1564:
1556:
1552:
1547:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1507:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1479:
1474:
1473:1721.1/126231
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1442:
1434:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1395:
1393:
1391:
1389:
1380:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1353:
1348:
1344:
1340:
1336:
1329:
1327:
1325:
1323:
1321:
1312:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1263:
1255:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1191:
1187:
1182:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1140:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1085:
1083:
1074:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1047:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1023:
1021:
1019:
1017:
1015:
1006:
1002:
997:
992:
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
968:
964:
956:
954:
952:
950:
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
902:
900:
898:
896:
894:
892:
890:
888:
886:
884:
882:
880:
878:
876:
874:
872:
870:
861:
857:
853:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
829:
825:
821:
814:
812:
810:
808:
806:
804:
802:
800:
798:
796:
794:
792:
790:
788:
786:
784:
782:
780:
778:
776:
774:
772:
770:
768:
766:
764:
762:
760:
758:
756:
754:
752:
750:
748:
746:
744:
735:
731:
727:
723:
719:
715:
710:
705:
701:
697:
693:
686:
684:
682:
680:
671:
667:
662:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
629:
621:
617:
608:
605:
603:
600:
598:
595:
593:
590:
589:
579:
575:
571:
569:
566:
565:
561:
557:
551:
549:
546:
545:
542:
538:
535:
532:
529:
528:
524:
519:Research use
518:
516:
513:
512:
509:
505:
501:
500:neuroblastoma
497:
493:
489:
487:
484:
483:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
455:
452:
451:
447:
443:
439:
437:
434:
433:
427:
423:
419:
418:breast cancer
415:
411:
409:
406:
405:
401:
398:
395:
394:
388:
384:
381:
372:
363:
361:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
324:
321:
317:
288:
285:
281:
280:G2 checkpoint
276:
275:G2 checkpoint
266:
263:
257:
254:
250:
247:or otherwise
246:
238:
234:
231:
227:
217:
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
185:
180:
178:
174:
170:
166:
161:
158:known as the
157:
148:
134:
125:
123:
122:radiotherapy.
119:
114:
109:
107:
103:
94:
84:
75:
73:
69:
65:
60:
58:
47:
45:
41:
37:
33:
26:
21:
2281:
2277:
2267:
2222:
2218:
2208:
2165:
2161:
2103:
2099:
2089:
2078:. Retrieved
2076:. 2011-02-03
2073:
2064:
2053:. Retrieved
2051:. 2006-10-05
2048:
2039:
1994:
1990:
1980:
1969:. Retrieved
1964:
1961:"Paclitaxel"
1955:
1910:
1906:
1848:
1844:
1788:
1784:
1774:
1734:(1): 31–46.
1731:
1727:
1717:
1707:, retrieved
1677:
1667:
1634:
1630:
1620:
1577:
1573:
1563:
1520:
1516:
1506:
1458:(1): 44–62.
1455:
1451:
1441:
1408:
1404:
1342:
1338:
1276:
1272:
1262:
1219:
1215:
1153:
1149:
1139:
1098:
1094:
1036:
1032:
970:
966:
915:
911:
827:
823:
699:
695:
635:
631:
620:
577:
533:(Filanesib)
385:
377:
328:Mesothelioma
325:
314:
272:
258:
243:
222:
181:
169:kinetochores
153:
131:
110:
89:
55:
53:
31:
30:
2106:(8): 4112.
1580:: 199–206.
1279:(1): 7–15.
486:Vinkristine
262:Centrosomes
253:cytokinesis
156:chromosomes
2335:Cell cycle
2329:Categories
2168:: 114364.
2080:2022-11-29
2055:2022-11-29
1971:2022-11-29
1913:(6): 154.
1709:2022-11-26
1345:(1): 123.
1273:Cell Cycle
1039:: 146282.
613:References
607:Senescence
454:Vinblastin
408:Paclitaxel
269:DNA damage
245:Tetraploid
118:interphase
50:Term usage
36:cell cycle
2298:0008-5472
2241:1756-8722
2225:(1): 84.
2200:229180081
2184:0006-2952
2122:1422-0067
2013:1425-8153
1929:2072-6694
1865:0167-7659
1805:0008-5472
1766:245916132
1750:2159-8290
1651:0962-8924
1612:229324538
1596:0959-440X
1537:1350-9047
1498:202746570
1482:1471-0064
1425:0959-437X
1361:1756-8722
1293:1538-4101
1236:1096-3634
1222:: 86–98.
1172:1745-6150
1156:(1): 25.
1131:237627882
1115:1573-675X
1095:Apoptosis
1055:1466-1861
987:1476-5403
932:1532-2084
844:1471-0080
718:1476-5594
652:1476-5403
602:Apoptosis
515:Monastrol
496:lymphomas
436:Docetaxel
249:aneuploid
226:cyclin B1
173:metaphase
113:cyclin B1
64:apoptosis
2316:29097609
2259:29925402
2192:33310050
2140:33923421
2031:31223315
1947:29789497
1883:23633034
1823:28432052
1758:35022204
1704:15187249
1659:15953548
1604:33338884
1555:22653338
1490:31548659
1433:17324569
1379:31771633
1311:30601084
1254:34210579
1190:34886882
1123:34561763
1073:26491220
1005:29362479
940:26830311
918:: 1–12.
860:22483746
852:21527953
734:28061417
726:15077146
696:Oncogene
670:29362479
586:See also
531:ARRY-520
504:sarcomas
177:anaphase
68:necrosis
2340:Mitosis
2307:5712276
2250:6011351
2131:8073828
2022:6567594
1938:6025594
1907:Cancers
1874:3843371
1814:5413432
1546:3392635
1370:6880427
1302:6343733
1245:8406419
1181:8656038
1064:4600505
996:5864239
661:5864239
592:Mitosis
568:MLN8237
340:ovarian
205:humans.
93:mitosis
44:cancers
2345:Cancer
2314:
2304:
2296:
2257:
2247:
2239:
2198:
2190:
2182:
2138:
2128:
2120:
2029:
2019:
2011:
1997:: 40.
1945:
1935:
1927:
1881:
1871:
1863:
1821:
1811:
1803:
1764:
1756:
1748:
1702:
1692:
1657:
1649:
1610:
1602:
1594:
1553:
1543:
1535:
1496:
1488:
1480:
1431:
1423:
1377:
1367:
1359:
1309:
1299:
1291:
1252:
1242:
1234:
1188:
1178:
1170:
1129:
1121:
1113:
1071:
1061:
1053:
1003:
993:
985:
938:
930:
858:
850:
842:
732:
724:
716:
668:
658:
650:
597:Cancer
548:VX-680
506:, and
424:, and
358:, and
346:, and
336:breast
199:, and
137:Causes
2196:S2CID
1762:S2CID
1608:S2CID
1494:S2CID
1127:S2CID
856:S2CID
730:S2CID
560:AURKB
556:AURKA
396:Drug
348:liver
197:BubR1
193:Cdc20
102:phase
25:taxol
2312:PMID
2294:ISSN
2255:PMID
2237:ISSN
2188:PMID
2180:ISSN
2136:PMID
2118:ISSN
2027:PMID
2009:ISSN
1943:PMID
1925:ISSN
1879:PMID
1861:ISSN
1819:PMID
1801:ISSN
1754:PMID
1746:ISSN
1700:PMID
1690:ISBN
1655:PMID
1647:ISSN
1600:PMID
1592:ISSN
1551:PMID
1533:ISSN
1486:PMID
1478:ISSN
1429:PMID
1421:ISSN
1375:PMID
1357:ISSN
1307:PMID
1289:ISSN
1250:PMID
1232:ISSN
1186:PMID
1168:ISSN
1119:PMID
1111:ISSN
1069:PMID
1051:ISSN
1037:2015
1001:PMID
983:ISSN
936:PMID
928:ISSN
848:PMID
840:ISSN
722:PMID
714:ISSN
666:PMID
648:ISSN
230:CDK1
201:Bub3
189:Mad2
2302:PMC
2286:doi
2245:PMC
2227:doi
2170:doi
2166:184
2126:PMC
2108:doi
2017:PMC
1999:doi
1933:PMC
1915:doi
1869:PMC
1853:doi
1809:PMC
1793:doi
1736:doi
1682:doi
1639:doi
1582:doi
1541:PMC
1525:doi
1468:hdl
1460:doi
1413:doi
1365:PMC
1347:doi
1297:PMC
1281:doi
1240:PMC
1224:doi
1220:117
1176:PMC
1158:doi
1103:doi
1059:PMC
1041:doi
991:PMC
975:doi
920:doi
832:doi
704:doi
656:PMC
640:doi
523:EG5
284:p53
203:in
175:to
66:or
2331::
2310:.
2300:.
2292:.
2282:77
2280:.
2276:.
2253:.
2243:.
2235:.
2223:11
2221:.
2217:.
2194:.
2186:.
2178:.
2164:.
2160:.
2148:^
2134:.
2124:.
2116:.
2104:22
2102:.
2098:.
2072:.
2047:.
2025:.
2015:.
2007:.
1995:24
1993:.
1989:.
1963:.
1941:.
1931:.
1923:.
1911:10
1909:.
1905:.
1891:^
1877:.
1867:.
1859:.
1849:32
1847:.
1843:.
1831:^
1817:.
1807:.
1799:.
1789:77
1787:.
1783:.
1760:.
1752:.
1744:.
1732:12
1730:.
1726:.
1698:,
1688:,
1676:,
1653:.
1645:.
1635:15
1633:.
1629:.
1606:.
1598:.
1590:.
1578:66
1572:.
1549:.
1539:.
1531:.
1521:19
1519:.
1515:.
1492:.
1484:.
1476:.
1466:.
1456:21
1454:.
1450:.
1427:.
1419:.
1409:17
1403:.
1387:^
1373:.
1363:.
1355:.
1343:12
1341:.
1337:.
1319:^
1305:.
1295:.
1287:.
1277:18
1275:.
1271:.
1248:.
1238:.
1230:.
1218:.
1214:.
1198:^
1184:.
1174:.
1166:.
1154:16
1152:.
1148:.
1125:.
1117:.
1109:.
1099:26
1097:.
1093:.
1081:^
1067:.
1057:.
1049:.
1035:.
1031:.
1013:^
999:.
989:.
981:.
971:25
969:.
965:.
948:^
934:.
926:.
916:24
914:.
910:.
868:^
854:.
846:.
838:.
828:12
826:.
822:.
742:^
728:.
720:.
712:.
700:23
698:.
694:.
678:^
664:.
654:.
646:.
636:25
634:.
630:.
558:/
539::
502:,
498:,
494:,
474:,
470:,
462:,
444:,
420:,
416:,
354:,
342:,
338:,
334:,
330:,
195:,
191:,
74:.
2318:.
2288::
2261:.
2229::
2202:.
2172::
2142:.
2110::
2083:.
2058:.
2033:.
2001::
1974:.
1949:.
1917::
1885:.
1855::
1825:.
1795::
1768:.
1738::
1684::
1661:.
1641::
1614:.
1584::
1557:.
1527::
1500:.
1470::
1462::
1435:.
1415::
1381:.
1349::
1313:.
1283::
1256:.
1226::
1192:.
1160::
1133:.
1105::
1075:.
1043::
1007:.
977::
942:.
922::
862:.
834::
736:.
706::
672:.
642::
100:1
98:G
59:,
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.