46:
363:
is completed, the cell enters a relatively brief period of nuclear and cellular division, composed of mitosis and cytokinesis, respectively. After the successful completion of mitosis and cytokinesis, both resulting
595:
Shibata A. Regulation of repair pathway choice at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks. Mutat Res. 2017 Oct;803-805:51-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Review. PMID 28781144
299:
The duration of time spent in interphase and in each stage of interphase is variable and depends on both the type of cell and the species of organism it belongs to. Most cells of adult
34:
278:(Gap 2), in which the cell resumes its growth in preparation for division. The cell continues to grow until mitosis begins. In plants, chloroplasts divide during G2.
303:
spend about 24 hours in interphase; this accounts for about 90%-96% of the total time involved in cell division. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases.
338:
repair (HRR), is more accurate than NHEJ in repairing double-strand breaks. However HRR is only active during the S and G2 phases of interphase when
642:
399:, which, in some circumstances, may then end and be followed by the remaining stages of interphase. After the successful completion of the
934:
828:
265:(S), in which the cell synthesizes its DNA and the amount of DNA is doubled but the number of chromosomes remains constant (via
580:
874:
522:
635:
190:
cells of the body, go through mitosis in order to reproduce themselves through cell division, whereas diploid
628:
538:
400:
266:
230:
checks the accuracy of the stage's completion before proceeding to the next. The stages of interphase are:
944:
1085:
788:
319:
783:
778:
773:
768:
763:
758:
753:
748:
743:
335:
735:
606:
117:
27:
343:
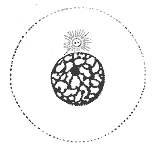
1145:
1067:
818:
447:
227:
45:
20:
240:(Gap 1), in which the cell grows and functions normally. During this time, a high amount of
241:
113:
57:
of this cell or the neighboring cell is not visible (top-left), which is currently in the
8:
125:
1080:
885:
1075:
576:
518:
1140:
426:
phase where the cell is neither dividing nor preparing to divide, or as a distinct
862:
339:
97:
281:
In addition, some cells that do not divide often or ever, enter a stage called
137:
427:
1134:
1014:
388:
365:
226:
There are three stages of cellular interphase, with each phase ending when a
288:(Gap zero), which is either a stage separate from interphase or an extended
112:. Calling it so would be misleading since a cell in interphase is very busy
1036:
613:. Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of California, Berkeley. 1999.
493:
468:
342:
is either partially or fully accomplished, since HRR requires two adjacent
195:
183:
164:
26:
This article is about the phase in the cell cycle. For the video game, see
1057:
1026:
607:"Re: Are the cells in the G0 (g zero) phase of mitosis really suspended?"
488:
412:
384:
308:
121:
93:
651:
376:
315:
149:
141:
133:
77:
41:
has not yet condensed, and the cell is undergoing its normal functions.
620:
1101:
1051:
1041:
724:
720:
710:
706:
702:
692:
688:
678:
674:
483:
473:
451:
380:
249:
245:
244:
occurs and the cell grows (to about double its original size) – more
191:
58:
54:
38:
349:
1106:
1046:
1031:
1000:
986:
716:
698:
684:
670:
478:
463:
408:
392:
331:
323:
289:
282:
272:
253:
234:
168:
145:
129:
109:
89:
81:
318:
during interphase by two principal processes. The first process,
1115:
1022:
995:
654:
443:
391:. In alternative fashion, interphase is sometimes interrupted by
327:
304:
262:
207:
203:
187:
179:
175:
160:
153:
101:
85:
62:
159:
A common misconception is that interphase is the first stage of
954:
870:
856:
852:
848:
840:
798:
793:
662:
575:(9th ed.). Boston, MA, USA: McGraw Hill Higher Education.
439:
300:
199:
128:, to name just a few activities. The cell is quiescent only in
50:
929:
924:
813:
808:
803:
252:
increases. If the cell is not to divide again, it will enter
211:
140:
spends most of its life. Interphase is the "daily living" or
33:
958:
949:
919:
898:
836:
407:, the final checkpoint in interphase, the cell proceeds to
215:
66:
560:(10th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. pp. 28–29.
433:
939:
903:
893:
866:
844:
104:, respectively. Interphase was formerly called the "
322:(NHEJ), can join the two broken ends of DNA in the
152:them, grows, replicates its DNA in preparation for
350:Interphase within sequences of cellular processes
1132:
354:
53:) currently in interphase (likely G1). Note:
430:stage which occurs outside of the cell cycle.
174:In interphase, the cell gets itself ready for
156:, and conducts other "normal" cell functions.
65:. Image taken using an optical microscope and
636:
144:phase of the cell, in which the cell obtains
108:," but the cell in interphase is not simply
163:, but since mitosis is the division of the
643:
629:
515:Essentials of human anatomy and physiology
334:phases of interphase. The second process,
218:) for the purpose of sexual reproduction.
935:Cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein
506:
450:, interphase is followed or preempted by
311:, however, are separate from interphase.
555:
44:
32:
650:
543:The Biology Project – Cell Biology
539:"The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Tutorial"
442:production, interphase is succeeded by
434:Interphase and other cellular processes
422:phase is viewed as either an extended G
415:, which is the first stage of mitosis.
221:
1133:
512:
624:
570:
558:Human Heredity: Principles and Issues
16:G1, S and G2 phases of the cell cycle
517:. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings.
248:are produced and the volume of the
49:An image of the nucleus of a cell (
37:An illustration of interphase. The
13:
14:
1157:
132:. Interphase is the phase of the
604:
314:DNA double-strand breaks can be
122:engulfing extracellular material
598:
589:
564:
549:
531:
1:
499:
355:Interphase and the cell cycle
171:is actually the first stage.
76:is the active portion of the
379:, interphase is preceded by
267:semiconservative replication
7:
945:Maturation promoting factor
457:
206:in order to create haploid
10:
1162:
1086:Postreplication checkpoint
336:homologous recombinational
320:non-homologous end joining
25:
18:
1094:
1066:
1013:
977:
968:
912:
884:
827:
734:
661:
118:transcribing DNA into RNA
545:. University of Arizona.
19:Not to be confused with
92:phases, where the cell
28:Interphase (video game)
1068:Cell cycle checkpoints
344:homologous chromosomes
70:
42:
1095:Other cellular phases
819:CDK-activating kinase
448:programmed cell death
114:synthesizing proteins
48:
36:
21:Interface (chemistry)
556:Cummings MR (2014).
222:Stages of interphase
228:cellular checkpoint
136:in which a typical
100:, and prepares for
1081:Spindle checkpoint
886:P53 p63 p73 family
611:MadScience Network
411:, or in plants to
126:processing signals
98:replicates its DNA
80:that includes the
71:
43:
1128:
1127:
1124:
1123:
1076:Restriction point
582:978-0-07-325839-3
571:Mader SS (2007).
513:Marieb E (2000).
242:protein synthesis
1153:
975:
974:
645:
638:
631:
622:
621:
615:
614:
602:
596:
593:
587:
586:
568:
562:
561:
553:
547:
546:
535:
529:
528:
510:
69:staining of DNA.
1161:
1160:
1156:
1155:
1154:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1131:
1130:
1129:
1120:
1110:
1090:
1062:
1009:
1004:
990:
970:
964:
908:
880:
823:
730:
657:
649:
619:
618:
603:
599:
594:
590:
583:
569:
565:
554:
550:
537:
536:
532:
525:
511:
507:
502:
460:
436:
425:
421:
404:
396:
372:of interphase.
371:
362:
357:
352:
340:DNA replication
293:
286:
276:
257:
238:
224:
194:(i.e., primary
31:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1159:
1149:
1148:
1143:
1126:
1125:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1118:
1113:
1108:
1104:
1098:
1096:
1092:
1091:
1089:
1088:
1083:
1078:
1072:
1070:
1064:
1063:
1061:
1060:
1055:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1019:
1017:
1011:
1010:
1008:
1007:
1002:
998:
993:
988:
983:
981:
972:
966:
965:
963:
962:
952:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
922:
916:
914:
910:
909:
907:
906:
901:
896:
890:
888:
882:
881:
879:
878:
860:
833:
831:
825:
824:
822:
821:
816:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
786:
781:
776:
771:
766:
761:
756:
751:
746:
740:
738:
732:
731:
729:
728:
714:
696:
682:
667:
665:
659:
658:
648:
647:
640:
633:
625:
617:
616:
597:
588:
581:
563:
548:
530:
524:978-0805349405
523:
504:
503:
501:
498:
497:
496:
491:
486:
481:
476:
471:
466:
459:
456:
435:
432:
423:
419:
402:
394:
369:
366:daughter cells
360:
356:
353:
351:
348:
297:
296:
291:
284:
279:
274:
270:
260:
255:
236:
223:
220:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1158:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1138:
1136:
1117:
1114:
1112:
1105:
1103:
1100:
1099:
1097:
1093:
1087:
1084:
1082:
1079:
1077:
1074:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1065:
1059:
1056:
1053:
1050:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1024:
1021:
1020:
1018:
1016:
1012:
1006:
999:
997:
994:
992:
985:
984:
982:
980:
976:
973:
967:
960:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
926:
923:
921:
918:
917:
915:
911:
905:
902:
900:
897:
895:
892:
891:
889:
887:
883:
876:
872:
868:
864:
861:
858:
854:
850:
846:
842:
838:
835:
834:
832:
830:
829:CDK inhibitor
826:
820:
817:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
785:
782:
780:
777:
775:
772:
770:
767:
765:
762:
760:
757:
755:
752:
750:
747:
745:
742:
741:
739:
737:
733:
726:
722:
718:
715:
712:
708:
704:
700:
697:
694:
690:
686:
683:
680:
676:
672:
669:
668:
666:
664:
660:
656:
653:
646:
641:
639:
634:
632:
627:
626:
623:
612:
608:
601:
592:
584:
578:
574:
567:
559:
552:
544:
540:
534:
526:
520:
516:
509:
505:
495:
492:
490:
487:
485:
482:
480:
477:
475:
472:
470:
467:
465:
462:
461:
455:
453:
449:
445:
441:
431:
429:
416:
414:
410:
406:
398:
390:
386:
382:
378:
373:
367:
347:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
312:
310:
306:
302:
294:
287:
280:
277:
271:
268:
264:
261:
258:
251:
247:
243:
239:
233:
232:
231:
229:
219:
217:
213:
209:
205:
202:) go through
201:
197:
196:spermatocytes
193:
189:
185:
184:Somatic cells
181:
177:
172:
170:
166:
162:
157:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
106:resting phase
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
47:
40:
35:
29:
22:
1146:Cell biology
1037:Prometaphase
978:
610:
600:
591:
572:
566:
557:
551:
542:
533:
514:
508:
494:Cytoskeleton
469:Prometaphase
437:
417:
374:
358:
313:
298:
225:
198:and primary
186:, or normal
173:
158:
105:
73:
72:
1058:Cytokinesis
1027:Preprophase
971:checkpoints
489:Cytokinesis
413:preprophase
385:cytokinesis
309:cytokinesis
150:metabolizes
1135:Categories
979:Interphase
969:Phases and
652:Cell cycle
500:References
405:checkpoint
377:cell cycle
368:re-enter G
246:organelles
192:germ cells
134:cell cycle
78:cell cycle
74:Interphase
1102:Apoptosis
1052:Telophase
1042:Metaphase
837:INK4a/ARF
484:Telophase
474:Metaphase
452:apoptosis
428:quiescent
381:telophase
263:Synthesis
250:cytoplasm
146:nutrients
142:metabolic
59:telophase
55:Cytoplasm
39:chromatin
1047:Anaphase
1032:Prophase
655:proteins
605:Cram E.
479:Anaphase
464:Prophase
458:See also
409:prophase
316:repaired
169:prophase
1141:Mitosis
1116:Meiosis
1023:Mitosis
1015:M phase
996:S phase
863:cip/kip
573:Biology
444:meiosis
389:M phase
387:of the
375:In the
305:Mitosis
301:mammals
210:(i.e.,
208:gametes
204:meiosis
200:oocytes
188:diploid
180:meiosis
176:mitosis
165:nucleus
161:mitosis
154:mitosis
110:dormant
102:mitosis
63:mitosis
955:Cullin
841:p14arf
663:Cyclin
579:
521:
440:gamete
359:When G
124:, and
88:, and
51:HT1080
1111:phase
1005:phase
991:phase
930:Cdc42
925:Cdc25
913:Other
695:, B3)
446:. In
397:phase
212:sperm
94:grows
959:CUL7
920:Cdc2
577:ISBN
519:ISBN
383:and
330:and
307:and
214:and
148:and
138:cell
67:DAPI
950:Wee
940:E2F
904:p73
899:p63
894:p53
875:p57
871:p27
867:p21
857:p19
853:p18
849:p15
845:p16
799:11B
794:11A
736:CDK
438:In
216:ova
178:or
61:of
1137::
873:,
869:,
855:,
851:,
847:,
814:14
809:13
804:12
789:10
725:E2
723:,
721:E1
711:D3
709:,
707:D2
705:,
703:D1
693:B2
691:,
689:B1
679:A2
677:,
675:A1
609:.
541:.
454:.
346:.
332:G2
326:,
324:G1
269:).
182:.
167:,
130:G0
120:,
116:,
96:,
90:G2
84:,
82:G1
1109:0
1107:G
1054:)
1025:(
1003:2
1001:G
989:1
987:G
961:)
957:(
877:)
865:(
859:)
843:/
839:(
784:9
779:8
774:7
769:6
764:5
759:4
754:3
749:2
744:1
727:)
719:(
717:E
713:)
701:(
699:D
687:(
685:B
681:)
673:(
671:A
644:e
637:t
630:v
585:.
527:.
424:1
420:0
418:G
403:2
401:G
395:0
393:G
370:1
361:2
328:S
295:.
292:1
290:G
285:0
283:G
275:2
273:G
259:.
256:0
254:G
237:1
235:G
86:S
30:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.