36:
66:
279:. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such as sodium and chloride. The mesenchyme develops into the tissues of the
1109:
1118:"Epithelial mesenchymal transition by c-Fos estrogen receptor activation involves nuclear translocation of beta-catenin and upregulation of beta-catenin/lymphoid enhancer binding factor-1 transcriptional activity"
1219:
686:
is sometimes used for the middle (mesenchymal) layer, in which the dense layer includes tissues derived from both ectoderm, and entomesoderm (true mesoderm, derived from
671:
In diploblasts (Cnidaria and
Ctenophora), the mesenchyme is fully ectodermally derived. This kind of mesenchyme is called ectomesodermal, and is not considered true
1270:
1260:
515:
Embryological mesenchyme is particularly transitory and soon differentiates after migration. Neural mesenchyme forms soon after primary mesenchyme formation.
812:
1403:
713:
cnidarians, the mesenchyme is perforated by gastrovascular channels continuous among colony members. This entire matrix of common basal material is called
118:
827:
1706:
1652:
361:(ECM). Epithelial–mesenchymal transition occurs in embryonic cells that require migration through or over tissue, and can be followed with a
1742:
1444:
1354:
785:
1279:"Expression of mesenchymal-related genes by the bovine trophectoderm following conceptus attachment to the endometrial epithelium"
1160:
1792:
596:. NCCs ingress into the embryo from the epithelial neuroectodermal layer and migrate throughout the body in order form multiple
1505:
1410:
Mareschi, K; Novara, M; Rustichelli, D; Ferrero, I; Guido, D; Carbone, E; Medico, E; Madon, E; Vercelli, A; Fagioli, F (2006).
922:
893:
734:
531:
362:
326:
316:
1412:"Neural differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells: Evidence for expression of neural markers and eag K+ channel types"
656:(non-triploblast animals usually are considered to lack "connective" tissue). In some cases, the mesoglea is noncellular.
644:), the term "mesenchyme" refers to a more-or-less solid but loosely organized tissue that consists of a gel matrix (the
2039:
1690:
1636:
860:
761:
2110:
1000:
835:
1735:
914:
40:
2087:
1492:
Stockdale, F. E.; Nikovits Jr, W; Christ, B (2000). "Molecular and cellular biology of avian somite development".
2056:
503:. Mesodermal tissue will continue to differentiate and/or migrate throughout the embryo to ultimately form most
398:
694:
When cellular material is sparse or densely packed, as in cnidarians, the mesenchyme may sometimes be called
593:
1577:
1453:"Wnt 6 regulates the epithelialisation process of the segmental plate mesoderm leading to somite formation"
292:
2004:
1916:
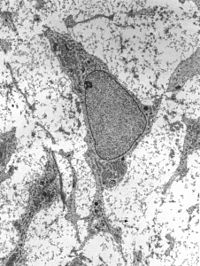
1728:
605:
101:
89:
2153:
495:
The tissue layers formed from the primitive streak invaginate together into the embryo and the induced
445:
Primary mesenchyme is the first embryonic mesenchymal tissue to emerge, and it is produced from EMT in
1584:
Trainor, P. A. (2005). "Specification of neural crest cell formation and migration in mouse embryos".
1363:"The mesenchymal cell, its role in the embryo, and the remarkable signaling mechanisms that create it"
417:
The first cells of the embryo to undergo EMT and form mesenchyme are the extra-embryonic cells of the
1169:"Beta-catenin signaling marks the prospective site of primitive streak formation in the mouse embryo"
597:
113:
1016:"Fibroblast-specific protein 1 identifies an inflammatory subpopulation of macrophages in the liver"
2095:
1987:
1528:
808:
522:
and somite-forming morphogenic factors cause some primary mesenchyme to form neural mesenchyme, or
1898:
401:. Specific markers of mesenchymal tissue include the additional expression of ECM factors such as
2031:
1996:
1211:
1682:
1628:
496:
252:
125:
71:
1277:
Yamakoshi, S; Bai, R; Chaen, T; Ideta, A; Aoyagi, Y; Sakurai, T; Konno, T; Imakawa, K (2012).
850:
1014:Österreicher, Christoph H.; Penz-Österreicher, Melitta; Grivennikov, Sergei I. (2011-01-04).
885:
878:
201:
51:
1674:
1620:
1068:
2019:
2014:
1869:
1485:
1027:
358:
208:
55:
8:
695:
43:
1032:
777:
1888:
1700:
1646:
1566:
1517:
1392:
1343:
1250:
1198:
1144:
1117:
1052:
1015:
969:
942:
565:
287:
systems, as well as the musculoskeletal system. This latter system is characterized as
284:
256:
1751:
1686:
1675:
1632:
1621:
1601:
1558:
1509:
1474:
1433:
1384:
1335:
1300:
1242:
1190:
1149:
1098:
1093:
1076:
1057:
974:
918:
889:
856:
757:
551:
523:
504:
338:
288:
204:
1570:
1521:
1396:
1347:
1203:
1880:
1593:
1548:
1501:
1464:
1423:
1374:
1327:
1290:
1255:
1234:
1180:
1139:
1129:
1088:
1047:
1037:
964:
954:
710:
609:
454:
394:
280:
244:
241:
148:
936:
934:
738:
393:
associated with the down-regulation of epithelial cadherin. Both formation of the
1911:
1597:
1451:
Schmidt, C; Stoeckelhuber, M; McKinnell, I; Putz, R; Christ, B; Patel, K (2004).
1428:
1411:
581:
559:
370:
260:
248:
84:
1553:
1536:
1469:
1452:
2009:
1842:
1817:
931:
875:
334:
47:
2147:
1923:
756:(11th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins. p. 70.
577:
569:
458:
418:
342:
264:
1042:
1605:
1513:
1478:
1437:
1388:
1304:
1246:
1194:
1153:
1061:
978:
653:
621:
573:
474:
322:
263:, which lack mobility, are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are
1562:
1339:
1134:
1102:
800:
381:, which is indicative of their shared properties with the migratory adult
2071:
1822:
1765:
992:
832:
School of
Anatomy and Human Biology - The University of Western Australia
714:
698:, or parenchyma in flatworms. When no cellular material is present as in
641:
637:
601:
426:
406:
402:
382:
354:
350:
35:
1295:
1278:
1013:
1855:
1832:
1807:
1379:
1362:
1331:
1185:
1168:
683:
633:
589:
585:
422:
366:
346:
330:
224:
96:
1506:
10.1002/1097-0177(2000)9999:9999<::AID-DVDY1057>3.0.CO;2-5
2118:
2044:
1948:
1943:
1933:
1850:
1827:
1812:
1116:
Eger, A; Stockinger, A; Schaffhauser, B; Beug, H; Foisner, R (2000).
959:
649:
572:, instead of the primary mesenchyme, from morphogenic signals of the
555:
296:
1720:
1537:"Neural crest cell formation and migration in the developing embryo"
1238:
648:) with various cellular and fibrous inclusions, located between the
131:
2061:
1906:
1770:
1668:
1666:
1664:
1662:
703:
699:
687:
679:
672:
645:
629:
625:
588:
from the cell surface. NCCs additionally require the repression of
539:
519:
500:
489:
466:
462:
450:
446:
434:
390:
357:
cytoskeleton loses shape, enabling mesenchyme to migrate along the
276:
1960:
1955:
1928:
1450:
1220:"Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions"
665:
543:
480:
The formation of primary mesenchyme depends on the expression of
304:
20:
1659:
1409:
2066:
2049:
852:
Histology and Cell
Biology: An Introduction to Pathology E-Book
661:
547:
527:
430:
300:
1115:
792:
192:
186:
2128:
1077:"Early role of Fsp1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation"
884:. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p.
485:
386:
216:
65:
1075:
Okada, H; Danoff, T. M.; Kalluri, R; Neilson, E. G. (1997).
876:
Strum, Judy M.; Gartner, Leslie P.; Hiatt, James L. (2007).
2123:
1938:
1775:
535:
481:
240:
Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent
220:
212:
172:
163:
157:
1491:
329:(EMT) process. This transition occurs through the loss of
227:
help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo.
1074:
19:"Mucoid" redirects here. For the Ninjago characters, see
735:"MESENCHYME English Definition and Meaning | Lexico.com"
550:
tissue migrates later in development to form structural
433:
in order to contribute to the formation of the anchored
546:. These structures will undergo a secondary EMT as the
484:. Other deficiencies in signaling pathways, such as in
310:
1276:
855:(4 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 123.
189:
169:
166:
160:
1681:(2nd ed.). Sunderland, Massachusetts. p.
1627:(2nd ed.). Sunderland, Massachusetts. p.
1166:
183:
180:
175:
154:
151:
877:
1167:Mohamed, O. A.; Clarke, H. J.; Dufort, D (2004).
993:"S100A4 - Protein S100-A4 - Homo sapiens (Human)"
943:"The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition"
2145:
869:
848:
321:The first emergence of mesenchyme occurs during
1020:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
940:
1534:
849:Kierszenbaum, Abraham L.; Tres, Laura (2015).
530:formation. Neural mesenchyme soon undergoes a
1736:
1311:
1217:
488:(a TGF-beta protein), will lead to defective
1672:
1618:
1586:Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology
1318:Bellairs, R (1986). "The primitive streak".
941:Kalluri, Raghu; Weinberg, Robert A. (2009).
604:. Migration of NCCs is primarily induced by
397:and mesenchymal tissue is dependent on the
1743:
1729:
1705:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
1651:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
369:. Embryological mesenchymal cells express
223:. The interactions between mesenchyme and
16:Type of animal embryonic connective tissue
1552:
1468:
1427:
1378:
1294:
1254:
1202:
1184:
1143:
1133:
1092:
1051:
1041:
1031:
968:
958:
1317:
211:that give rise to most tissues, such as
200:) is a type of loosely organized animal
1583:
985:
902:
798:
2146:
1218:Thiery, J. P.; Sleeman, J. P. (2006).
908:
751:
678:In triploblastic acoelomates (such as
1750:
1724:
1227:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
842:
828:"Blue Histology - Connective Tissues"
825:
745:
440:
421:. These migrate from the body of the
1007:
510:
311:Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
1673:Brusca, R.C.; Brusca, G.J. (2003).
1619:Brusca, R.C.; Brusca, G.J. (2003).
1360:
275:The mesenchyme originates from the
13:
1081:The American Journal of Physiology
1003:from the original on Nov 21, 2021.
815:from the original on Jan 20, 2024.
303:of mesenchymal cells is a type of
70:Mesenchyme (pointer) stained with
14:
2165:
2040:Dense irregular connective tissue
947:Journal of Clinical Investigation
915:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
788:from the original on Feb 4, 2024.
770:
532:mesenchymal–epithelial transition
363:mesenchymal–epithelial transition
327:epithelial–mesenchymal transition
317:Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
267:in an apical-basal orientation).
1094:10.1152/ajprenal.1997.273.4.F563
702:), the layer is properly called
615:
576:. The EMT occurs as a result of
469:from a transitory tissue called
349:. The surface molecules undergo
247:containing a loose aggregate of
147:
64:
34:
2057:Dense regular connective tissue
1612:
412:
819:
727:
270:
230:
1:
720:
594:neural cell adhesion molecule
291:throughout the body, such as
46:of mesenchyme displaying the
1598:10.1016/j.semcdb.2005.06.007
1429:10.1016/j.exphem.2006.06.020
911:Langman's Medical Embryology
799:MacCord, Kate (2012-09-14).
754:Langman's medical embryology
235:
7:
1554:10.1096/fasebj.8.10.8050668
1470:10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.03.016
1122:The Journal of Cell Biology
805:Embryo Project Encyclopedia
664:, the mesenchyme is called
379:fibroblast-specific protein
10:
2170:
1535:Bronner-Fraser, M (1994).
880:Cell biology and histology
778:"Definition of MESENCHYME"
499:will ingress and form the
314:
18:
2109:
2086:
2030:
1995:
1986:
1979:
1897:
1879:
1868:
1841:
1800:
1791:
1784:
1758:
598:peripheral nervous system
124:
112:
107:
95:
83:
78:
63:
33:
28:
809:Arizona State University
255:. Mesenchymal cells can
1416:Experimental Hematology
1043:10.1073/pnas.1017547108
534:under the influence of
453:, it is induced by the
259:easily (in contrast to
1494:Developmental Dynamics
1367:Developmental Dynamics
1320:Anatomy and Embryology
1173:Developmental Dynamics
752:Sadler, T. W. (2010).
741:on September 29, 2019.
497:mesenchymal stem cells
473:during the process of
253:mesenchymal stem cells
209:undifferentiated cells
126:Anatomical terminology
1457:Developmental Biology
1135:10.1083/jcb.148.1.173
909:Sadler, T.W. (2006).
518:The interaction with
399:Wnt/β-catenin pathway
365:to produce secondary
526:, and contribute to
507:layers of the body.
359:extracellular matrix
1361:Hay, E. D. (2005).
1296:10.1530/REP-11-0364
1087:(4 Pt 2): F563–74.
1033:2011PNAS..108..308O
608:and its inhibitor,
580:, the influence of
331:epithelial cadherin
44:electron micrograph
1380:10.1002/dvdy.20345
1332:10.1007/bf00318331
1186:10.1002/dvdy.20135
917:. pp. 68–70.
566:Neural crest cells
441:Primary mesenchyme
367:epithelial tissues
339:adherens junctions
289:connective tissues
251:and unspecialized
119:E5.16.4.0.3.0.18
2154:Connective tissue
2141:
2140:
2137:
2136:
2082:
2081:
1975:
1974:
1971:
1970:
1864:
1863:
1752:Connective tissue
924:978-0-7817-9485-5
895:978-0-7817-8577-8
826:Slomianka, Lutz.
568:(NCCs) form from
552:connective tissue
524:paraxial mesoderm
511:Neural mesenchyme
505:connective tissue
205:connective tissue
140:
139:
135:
2161:
1993:
1992:
1984:
1983:
1912:Reticular fibers
1881:Ground substance
1877:
1876:
1798:
1797:
1789:
1788:
1745:
1738:
1731:
1722:
1721:
1711:
1710:
1704:
1696:
1680:
1670:
1657:
1656:
1650:
1642:
1626:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1581:
1575:
1574:
1556:
1532:
1526:
1525:
1489:
1483:
1482:
1472:
1448:
1442:
1441:
1431:
1407:
1401:
1400:
1382:
1358:
1352:
1351:
1315:
1309:
1308:
1298:
1274:
1268:
1267:
1266:on Jun 26, 2013.
1265:
1259:. Archived from
1258:
1224:
1215:
1209:
1208:
1206:
1188:
1164:
1158:
1157:
1147:
1137:
1113:
1107:
1106:
1096:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1055:
1045:
1035:
1011:
1005:
1004:
989:
983:
982:
972:
962:
960:10.1172/JCI39104
938:
929:
928:
906:
900:
899:
883:
873:
867:
866:
846:
840:
839:
834:. Archived from
823:
817:
816:
796:
790:
789:
774:
768:
767:
749:
743:
742:
737:. Archived from
731:
600:(PNS) cells and
584:and the loss of
455:primitive streak
395:primitive streak
377:) also known as
347:epithelial cells
261:epithelial cells
249:reticular fibers
242:ground substance
199:
198:
195:
194:
191:
188:
185:
182:
178:
177:
174:
171:
168:
165:
162:
159:
156:
153:
132:edit on Wikidata
129:
102:Lateral mesoderm
68:
38:
26:
25:
2169:
2168:
2164:
2163:
2162:
2160:
2159:
2158:
2144:
2143:
2142:
2133:
2105:
2078:
2026:
1967:
1907:Collagen fibers
1893:
1871:
1860:
1843:Wandering cells
1837:
1780:
1754:
1749:
1715:
1714:
1698:
1697:
1693:
1671:
1660:
1644:
1643:
1639:
1617:
1613:
1582:
1578:
1547:(10): 699–706.
1533:
1529:
1490:
1486:
1449:
1445:
1422:(11): 1563–72.
1408:
1404:
1359:
1355:
1316:
1312:
1275:
1271:
1263:
1239:10.1038/nrm1835
1222:
1216:
1212:
1165:
1161:
1114:
1110:
1073:
1069:
1012:
1008:
991:
990:
986:
939:
932:
925:
907:
903:
896:
874:
870:
863:
847:
843:
838:on Mar 7, 2020.
824:
820:
797:
793:
782:Merriam-Webster
776:
775:
771:
764:
750:
746:
733:
732:
728:
723:
618:
560:skeletal muscle
513:
461:, and produces
443:
415:
371:Protein S100-A4
335:tight junctions
319:
313:
273:
238:
233:
179:
150:
146:
136:
74:
59:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2167:
2157:
2156:
2139:
2138:
2135:
2134:
2132:
2131:
2126:
2121:
2115:
2113:
2107:
2106:
2104:
2103:
2098:
2092:
2090:
2084:
2083:
2080:
2079:
2077:
2076:
2075:
2074:
2069:
2064:
2054:
2053:
2052:
2047:
2036:
2034:
2028:
2027:
2025:
2024:
2023:
2022:
2017:
2007:
2001:
1999:
1990:
1981:
1977:
1976:
1973:
1972:
1969:
1968:
1966:
1965:
1964:
1963:
1958:
1953:
1952:
1951:
1946:
1936:
1931:
1924:Elastic fibers
1921:
1920:
1919:
1909:
1903:
1901:
1895:
1894:
1892:
1891:
1885:
1883:
1874:
1870:Extracellular
1866:
1865:
1862:
1861:
1859:
1858:
1853:
1847:
1845:
1839:
1838:
1836:
1835:
1830:
1825:
1820:
1818:Reticular cell
1815:
1810:
1804:
1802:
1795:
1786:
1782:
1781:
1779:
1778:
1773:
1768:
1762:
1760:
1756:
1755:
1748:
1747:
1740:
1733:
1725:
1719:
1718:
1713:
1712:
1691:
1658:
1637:
1611:
1576:
1527:
1484:
1463:(1): 198–209.
1443:
1402:
1353:
1310:
1269:
1210:
1159:
1108:
1067:
1026:(1): 308–313.
1006:
984:
930:
923:
901:
894:
868:
861:
841:
818:
791:
769:
762:
744:
725:
724:
722:
719:
692:
691:
676:
669:
617:
614:
512:
509:
449:cells. In the
442:
439:
414:
411:
343:cell membranes
315:Main article:
312:
309:
299:. A malignant
272:
269:
237:
234:
232:
229:
138:
137:
128:
122:
121:
116:
110:
109:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
85:Carnegie stage
81:
80:
76:
75:
69:
61:
60:
48:ultrastructure
39:
31:
30:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2166:
2155:
2152:
2151:
2149:
2130:
2127:
2125:
2122:
2120:
2117:
2116:
2114:
2112:
2108:
2102:
2099:
2097:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2089:
2085:
2073:
2070:
2068:
2065:
2063:
2060:
2059:
2058:
2055:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2042:
2041:
2038:
2037:
2035:
2033:
2029:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2013:
2012:
2011:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2002:
2000:
1998:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1985:
1982:
1978:
1962:
1959:
1957:
1954:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1941:
1940:
1937:
1935:
1932:
1930:
1927:
1926:
1925:
1922:
1918:
1915:
1914:
1913:
1910:
1908:
1905:
1904:
1902:
1900:
1896:
1890:
1887:
1886:
1884:
1882:
1878:
1875:
1873:
1867:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1848:
1846:
1844:
1840:
1834:
1831:
1829:
1826:
1824:
1821:
1819:
1816:
1814:
1811:
1809:
1806:
1805:
1803:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1790:
1787:
1783:
1777:
1774:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1764:
1763:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1746:
1741:
1739:
1734:
1732:
1727:
1726:
1723:
1717:
1716:
1708:
1702:
1694:
1692:9780878930975
1688:
1684:
1679:
1678:
1677:Invertebrates
1669:
1667:
1665:
1663:
1654:
1648:
1640:
1638:9780878930975
1634:
1630:
1625:
1624:
1623:Invertebrates
1615:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1592:(6): 683–93.
1591:
1587:
1580:
1572:
1568:
1564:
1560:
1555:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1541:FASEB Journal
1538:
1531:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1500:(3): 304–21.
1499:
1495:
1488:
1480:
1476:
1471:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1447:
1439:
1435:
1430:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1406:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1373:(3): 706–20.
1372:
1368:
1364:
1357:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1314:
1306:
1302:
1297:
1292:
1289:(3): 377–87.
1288:
1284:
1280:
1273:
1262:
1257:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1236:
1233:(2): 131–42.
1232:
1228:
1221:
1214:
1205:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1187:
1182:
1179:(2): 416–24.
1178:
1174:
1170:
1163:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1131:
1128:(1): 173–88.
1127:
1123:
1119:
1112:
1104:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1071:
1063:
1059:
1054:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1010:
1002:
998:
994:
988:
980:
976:
971:
966:
961:
956:
953:(6): 1420–8.
952:
948:
944:
937:
935:
926:
920:
916:
912:
905:
897:
891:
887:
882:
881:
872:
864:
862:9780323313353
858:
854:
853:
845:
837:
833:
829:
822:
814:
810:
806:
802:
795:
787:
783:
779:
773:
765:
763:9780781790697
759:
755:
748:
740:
736:
730:
726:
718:
716:
712:
707:
705:
701:
697:
689:
685:
681:
677:
674:
670:
667:
663:
659:
658:
657:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
622:invertebrates
616:Invertebrates
613:
611:
607:
606:BMP signaling
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
583:
579:
578:Wnt signaling
575:
571:
570:neuroectoderm
567:
563:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
516:
508:
506:
502:
498:
493:
491:
487:
483:
478:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
459:Wnt signaling
456:
452:
448:
438:
436:
432:
429:layer of the
428:
424:
420:
419:trophectoderm
410:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
318:
308:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
268:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
243:
228:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
203:
197:
144:
133:
127:
123:
120:
117:
115:
111:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
77:
73:
67:
62:
57:
53:
50:of a typical
49:
45:
42:
37:
32:
27:
22:
2100:
1889:Tissue fluid
1676:
1622:
1614:
1589:
1585:
1579:
1544:
1540:
1530:
1497:
1493:
1487:
1460:
1456:
1446:
1419:
1415:
1405:
1370:
1366:
1356:
1323:
1319:
1313:
1286:
1283:Reproduction
1282:
1272:
1261:the original
1230:
1226:
1213:
1176:
1172:
1162:
1125:
1121:
1111:
1084:
1080:
1070:
1023:
1019:
1009:
996:
987:
950:
946:
910:
904:
879:
871:
851:
844:
836:the original
831:
821:
804:
801:"Mesenchyme"
794:
781:
772:
753:
747:
739:the original
729:
708:
693:
682:), the term
654:gastrodermis
640:(namely the
638:triploblasts
619:
574:neural crest
564:
538:produced by
517:
514:
494:
479:
475:gastrulation
470:
444:
416:
413:Implantation
378:
374:
323:gastrulation
320:
274:
239:
142:
141:
41:Transmission
2111:Specialized
2101:Mesenchymal
2072:Aponeurosis
1823:Tendon cell
1785:Composition
1766:Soft tissue
1326:(1): 1–14.
715:coenenchyme
696:collenchyma
642:acoelomates
636:, and some
602:melanocytes
492:formation.
471:mesendoderm
427:endometrial
407:vitronectin
403:fibronectin
383:fibroblasts
355:microtubule
351:endocytosis
285:circulatory
271:Development
231:Vertebrates
108:Identifiers
1856:Macrophage
1833:Melanocyte
1808:Fibroblast
1759:Physiology
721:References
684:parenchyma
634:Ctenophora
624:, such as
590:N-cadherin
586:E-cadherin
423:blastocyst
225:epithelium
143:Mesenchyme
29:Mesenchyme
2119:Cartilage
2088:Embryonic
2045:Submucosa
2005:Reticular
1934:Fibrillin
1851:Mast cell
1828:Adipocyte
1813:Fibrocyte
1701:cite book
1647:cite book
680:flatworms
650:epidermis
582:Sox genes
556:cartilage
425:into the
325:from the
297:cartilage
281:lymphatic
265:polarized
236:Structure
202:embryonic
97:Precursor
2148:Category
2062:Ligament
1801:Resident
1776:Scarring
1771:Fibrosis
1606:16043371
1571:12161494
1522:32342256
1514:11066088
1479:15196961
1438:17046576
1397:22368548
1389:15937929
1348:33629601
1305:22157247
1247:16493418
1204:39908122
1195:15366019
1154:10629227
1062:21173249
1001:Archived
979:19487818
813:Archived
786:Archived
711:colonial
709:In some
704:mesoglea
700:Hydrozoa
688:entoderm
673:mesoderm
652:and the
646:mesoglea
630:Cnidaria
626:Porifera
620:In some
554:such as
542:to form
540:ectoderm
520:ectoderm
501:mesoderm
490:mesoderm
467:mesoderm
463:endoderm
457:through
451:epiblast
447:epiblast
435:placenta
391:oncogene
353:and the
277:mesoderm
2010:Adipose
1961:Elaunin
1956:EMILIN1
1929:Elastin
1563:8050668
1340:3518538
1256:8435009
1145:3207144
1103:9362334
1053:3017162
1028:Bibcode
997:UniProt
970:2689101
666:mesohyl
662:sponges
544:somites
341:on the
305:sarcoma
257:migrate
79:Details
72:H&E
21:Mucoids
2096:Mucoid
2067:Tendon
2050:Dermis
1988:Proper
1917:COL3A1
1899:Fibers
1872:matrix
1689:
1635:
1604:
1569:
1561:
1520:
1512:
1477:
1436:
1395:
1387:
1346:
1338:
1303:
1253:
1245:
1201:
1193:
1152:
1142:
1101:
1060:
1050:
977:
967:
921:
892:
859:
760:
610:Noggin
592:, and
548:somite
528:somite
431:uterus
385:, and
375:S100A4
337:, and
301:cancer
295:, and
245:matrix
56:matrix
2129:Blood
2032:Dense
2020:White
2015:Brown
1997:Loose
1980:Types
1793:Cells
1567:S2CID
1518:S2CID
1393:S2CID
1344:S2CID
1264:(PDF)
1251:S2CID
1223:(PDF)
1199:S2CID
486:Nodal
389:, an
387:c-Fos
217:blood
130:[
2124:Bone
1949:FBN3
1944:FBN2
1939:FBN1
1707:link
1687:ISBN
1653:link
1633:ISBN
1602:PMID
1559:PMID
1510:PMID
1475:PMID
1434:PMID
1385:PMID
1336:PMID
1301:PMID
1243:PMID
1191:PMID
1150:PMID
1099:PMID
1058:PMID
975:PMID
919:ISBN
890:ISBN
857:ISBN
758:ISBN
558:and
536:WNT6
482:WNT3
465:and
405:and
293:bone
283:and
221:bone
213:skin
54:and
52:cell
1683:220
1629:101
1594:doi
1549:doi
1502:doi
1498:219
1465:doi
1461:271
1424:doi
1375:doi
1371:233
1328:doi
1324:174
1291:doi
1287:143
1235:doi
1181:doi
1177:231
1140:PMC
1130:doi
1126:148
1089:doi
1085:273
1048:PMC
1038:doi
1024:108
965:PMC
955:doi
951:119
660:In
345:of
219:or
207:of
2150::
1703:}}
1699:{{
1685:.
1661:^
1649:}}
1645:{{
1631:.
1600:.
1590:16
1588:.
1565:.
1557:.
1543:.
1539:.
1516:.
1508:.
1496:.
1473:.
1459:.
1455:.
1432:.
1420:34
1418:.
1414:.
1391:.
1383:.
1369:.
1365:.
1342:.
1334:.
1322:.
1299:.
1285:.
1281:.
1249:.
1241:.
1229:.
1225:.
1197:.
1189:.
1175:.
1171:.
1148:.
1138:.
1124:.
1120:.
1097:.
1083:.
1079:.
1056:.
1046:.
1036:.
1022:.
1018:.
999:.
995:.
973:.
963:.
949:.
945:.
933:^
913:.
888:.
886:83
830:.
811:.
807:.
803:.
784:.
780:.
717:.
706:.
690:).
632:,
628:,
612:.
562:.
477:.
437:.
409:.
333:,
307:.
215:,
196:-/
193:ən
187:iː
173:aɪ
114:TE
90:6b
1744:e
1737:t
1730:v
1709:)
1695:.
1655:)
1641:.
1608:.
1596::
1573:.
1551::
1545:8
1524:.
1504::
1481:.
1467::
1440:.
1426::
1399:.
1377::
1350:.
1330::
1307:.
1293::
1237::
1231:7
1207:.
1183::
1156:.
1132::
1105:.
1091::
1064:.
1040::
1030::
981:.
957::
927:.
898:.
865:.
766:.
675:.
668:.
373:(
190:z
184:m
181:ˈ
176:m
170:k
167:n
164:ə
161:s
158:ɛ
155:m
152:ˈ
149:/
145:(
134:]
58:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.