1640:
the coordinating ion in the chlorophyll molecule. It is the intracellular compartmentalisation of Mg in plant cells that leads to additional complexity. Four compartments within the plant cell have reported interactions with Mg. Initially, Mg will enter the cell into the cytoplasm (by an as yet unidentified system), but free Mg concentrations in this compartment are tightly regulated at relatively low levels (≈2 mmol/L) and so any excess Mg is either quickly exported or stored in the second intracellular compartment, the vacuole. The requirement for Mg in mitochondria has been demonstrated in yeast and it seems highly likely that the same will apply in plants. The chloroplasts also require significant amounts of internal Mg, and low concentrations of cytoplasmic Mg. In addition, it seems likely that the other subcellular organelles (e.g., Golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.) also require Mg.
609:(EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL are defined the same as in the United States. For women and men ages 18 and older, the AIs are set at 300 and 350 mg/day, respectively. AIs for pregnancy and lactation are also 300 mg/day. For children ages 1–17 years, the AIs increase with age from 170 to 250 mg/day. These AIs are lower than the U.S. RDAs. The European Food Safety Authority reviewed the same safety question and set its UL at 250 mg/day - lower than the U.S. value. The magnesium UL is unique in that it is lower than some of the RDAs. It applies to intake from a pharmacological agent or dietary supplement only and does not include intake from food and water.
1469:
radioactive half-life of Mg, the most stable of the radioactive magnesium isotopes, is only 21 hours. This severely restricts the experiments involving the nuclide. Also, since 1990, no facility has routinely produced Mg, and the price per mCi is now predicted to be approximately US$ 30,000. The chemical nature of Mg is such that it is closely approximated by few other cations. However, Co, Mn and Ni have been used successfully to mimic the properties of Mg in some enzyme reactions, and radioactive forms of these elements have been employed successfully in cation transport studies. The difficulty of using metal ion replacement in the study of enzyme function is that the relationship between the enzyme activities with the replacement ion compared to the original is very difficult to ascertain.
20:
1786:, Ca, and Mn can all impede uptake.(Kurvits and Kirkby, 1980; In acid soils Al is a particularly strong inhibitor of Mg uptake. The inhibition by Al and Mn is more severe than can be explained by simple displacement, hence it is possible that these ions bind to the Mg uptake system directly. In bacteria and yeast, such binding by Mn has already been observed. Stress responses in the plant develop as cellular processes halt due to a lack of Mg (e.g. maintenance of ΔpH across the plasma and vacuole membranes). In Mg-starved plants under low light conditions, the percentage of Mg bound to chlorophyll has been recorded at 50%. Presumably, this imbalance has detrimental effects on other cellular processes.
423:(RDAs) for magnesium in 1997. If there is not sufficient information to establish EARs and RDAs, an estimate designated Adequate Intake (AI) is used instead. The current EARs for magnesium for women and men ages 31 and up are 265 mg/day and 350 mg/day, respectively. The RDAs are 320 and 420 mg/day. RDAs are higher than EARs so as to identify amounts that will cover people with higher than average requirements. RDA for pregnancy is 350 to 400 mg/day depending on age of the woman. RDA for lactation ranges 310 to 360 mg/day for same reason. For children ages 1–13 years, the RDA increases with age from 65 to 200 mg/day. As for safety, the IOM also sets
1677:, 1990), and is released at need. But for most cells it is death by senescence or injury that releases Mg and many of the other ionic constituents, recycling them into healthy parts of the plant. In addition, when Mg in the environment is limiting, some species are able to mobilise Mg from older tissues. These processes involve the release of Mg from its bound and stored states and its transport back into the vascular tissue, where it can be distributed to the rest of the plant. In times of growth and development, Mg is also remobilised within the plant as source and sink relationships change.
1560:, 2002). Thus, it is presumed that recognition of the Mg ion requires some mechanism to interact initially with the hydration shell of Mg, followed by a direct recognition/binding of the ion to the protein. Due to the strength of the inner sphere complexation between Mg and any ligand, multiple simultaneous interactions with the transport protein at this level might significantly retard the ion in the transport pore. Hence, it is possible that much of the hydration water is retained during transport, allowing the weaker (but still specific) outer sphere coordination.
1256:
sphere coordination, stabilising anions or reactive intermediates, also including binding to ATP and activating the molecule to nucleophilic attack. When interacting with enzymes and other proteins, Mg may bind using inner or outer sphere coordination, to either alter the conformation of the enzyme or take part in the chemistry of the catalytic reaction. In either case, because Mg is only rarely fully dehydrated during ligand binding, it may be a water molecule associated with the Mg that is important rather than the ion itself. The
1511:(AAS) determines the total magnesium content of a biological sample. This method is destructive; biological samples must be broken down in concentrated acids to avoid clogging the fine nebulising apparatus. Beyond this, the only limitation is that samples must be in a volume of approximately 2 mL and at a concentration range of 0.1 – 0.4 μmol/L for optimum accuracy. As this technique cannot distinguish between Mg already present in the cell and that taken up during the experiment, only content not uptaken can be quantified.
1774:
chloroplasts/chlorophyll. In pine trees, even before the visible appearance of yellowing and necrotic spots, the photosynthetic efficiency of the needles drops markedly. In Mg deficiency, reported secondary effects include carbohydrate immobility, loss of RNA transcription and loss of protein synthesis. However, due to the mobility of Mg within the plant, the deficiency phenotype may be present only in the older parts of the plant. For example, in Pinus radiata starved of Mg, one of the earliest identifying signs is the
1422:(Mn) is readily capable of replacing Mg, but only in a limited set of circumstances. Mn is very similar to Mg in terms of its chemical properties, including inner and outer shell complexation. Mn effectively binds ATP and allows hydrolysis of the energy molecule by most ATPases. Mn can also replace Mg as the activating ion for a number of Mg-dependent enzymes, although some enzyme activity is usually lost. Sometimes such enzyme metal preferences vary among closely related species: For example, the
1718:
631:
1751:
stroma on the addition of light. H is pumped out of the stroma (into both the cytoplasm and the lumen) leading to an alkaline pH. Mg (along with K) is released from the lumen into the stroma, in an electroneutralisation process to balance the flow of H. Finally, thiol groups on enzymes are reduced by a change in the redox state of the stroma. Examples of enzymes activated in response to these changes are fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, sedoheptulose bisphosphatase and
1165:
65:
297:. For other than pregnancy-related hypertension, a meta-analysis of 22 clinical trials with dose ranges of 120 to 973 mg/day and a mean dose of 410 mg, concluded that magnesium supplementation had a small but statistically significant effect, lowering systolic blood pressure by 3–4 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 2–3 mm Hg. The effect was larger when the dose was more than 370 mg/day.
1649:
highly mobile in both the xylem and phloem, the ions will be transported to the top of the plant and back down again in a continuous cycle of replenishment. Hence, uptake and release from vascular cells is probably a key part of whole plant Mg homeostasis. Figure 1 shows how few processes have been connected to their molecular mechanisms (only vacuolar uptake has been associated with a transport protein, AtMHX).
1653:
may be taken up into cells immediately (symplastic pathway) or may travel as far as the
Casparian band (4) before being absorbed into cells (apoplastic pathway; 2). The concentration of Mg in the root cells is probably buffered by storage in root cell vacuoles (3). Note that cells in the root tip do not contain vacuoles. Once in the root cell cytoplasm, Mg travels toward the centre of the root by
6101:
1106:. This suggests that different cell types may regulate influx and efflux of magnesium in different ways based on their unique metabolic needs. Interstitial and systemic concentrations of free magnesium must be delicately maintained by the combined processes of buffering (binding of ions to proteins and other molecules) and muffling (the transport of ions to storage or extracellular spaces).
1482:(2001) have described work into a new class of compounds that may prove more useful, having significantly better binding affinities for Mg. The use of the fluorescent dyes is limited to measuring the free Mg. If the ion concentration is buffered by the cell by chelation or removal to subcellular compartments, the measured rate of uptake will give only minimum values of km and Vmax.
1180:) is seen when the environmental availability of magnesium is low. In ruminant animals, particularly vulnerable to magnesium availability in pasture grasses, the condition is known as 'grass tetany'. Hypomagnesemia is identified by a loss of balance due to muscle weakness. A number of genetically attributable hypomagnesemia disorders have also been identified in humans.
427:(ULs) for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. In the case of magnesium the UL is set at 350 mg/day. The UL is specific to magnesium consumed as a dietary supplement, the reason being that too much magnesium consumed at one time can cause diarrhea. The UL does not apply to food-sourced magnesium. Collectively the EARs, RDAs and ULs are referred to as
1793:, 1990). However, if this is followed by drought then ionic concentrations within the cell can increase dramatically. High cytoplasmic Mg concentrations block a K channel in the inner envelope membrane of the chloroplast, in turn inhibiting the removal of H ions from the chloroplast stroma. This leads to an acidification of the stroma that inactivates key enzymes in
1636:). Plant cell walls and membranes carry a great number of negative charges, and the interactions of cations with these charges is key to the uptake of cations by root cells allowing a local concentrating effect. Mg binds relatively weakly to these charges, and can be displaced by other cations, impeding uptake and causing deficiency in the plant.
1410:(e.g., ATP), but also, what is more important, it is buffered by storage of Mg in intracellular compartments. The transport of Mg between intracellular compartments may be a major part of regulating enzyme activity. The interaction of Mg with proteins must also be considered for the transport of the ion across biological membranes.
1759:
active site and is directly involved in the catalytic reaction. The second class of enzymes includes those where the Mg is complexed to nucleotide di- and tri-phosphates (ADP and ATP), and the chemical change involves phosphoryl transfer. Mg may also serve in a structural maintenance role in these enzymes (e.g., enolase).
1657:, where it is loaded into the xylem (5) for transport to the upper parts of the plant. When the Mg reaches the leaves it is unloaded from the xylem into cells (6) and again is buffered in vacuoles (7). Whether cycling of Mg into the phloem occurs via general cells in the leaf (8) or directly from xylem to phloem via
119:. However, the unusual nature of ionic magnesium has also led to a major challenge in the use of the ion in biological systems. Biological membranes are impermeable to magnesium (and other ions), so transport proteins must facilitate the flow of magnesium, both into and out of cells and intracellular compartments.
2568:
Veronese N, Watutantrige-Fernando S, Luchini C, Solmi M, Sartore G, Sergi G, Manzato E, Barbagallo M, Maggi S, Stubbs B (2016). "Effect of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism in people with or at risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled
1758:
Two major classes of the enzymes that interact with Mg in the stroma during the light phase can be identified. Firstly, enzymes in the glycolytic pathway most often interact with two atoms of Mg. The first atom is as an allosteric modulator of the enzymes' activity, while the second forms part of the
1652:
The diagram shows a schematic of a plant and the putative processes of Mg transport at the root and leaf where Mg is loaded and unloaded from the vascular tissues. Mg is taken up into the root cell wall space (1) and interacts with the negative charges associated with the cell walls and membranes. Mg
1468:
The use of radioactive tracer elements in ion uptake assays allows the calculation of km, Ki and Vmax and determines the initial change in the ion content of the cells. Mg decays by the emission of a high-energy beta or gamma particle, which can be measured using a scintillation counter. However, the
1750:
The metabolic state of the chloroplast changes considerably between night and day. During the day, the chloroplast is actively harvesting the energy of light and converting it into chemical energy. The activation of the metabolic pathways involved comes from the changes in the chemical nature of the
1631:
can have a significant effect on the uptake of the ion.(Kurvits and Kirkby, 1980; The structure of root cell walls is highly permeable to water and ions, and hence ion uptake into root cells can occur anywhere from the root hairs to cells located almost in the centre of the root (limited only by the
1255:
The chemistry of the Mg ion, as applied to enzymes, uses the full range of this ion's unusual reaction chemistry to fulfill a range of functions. Mg interacts with substrates, enzymes, and occasionally both (Mg may form part of the active site). In general, Mg interacts with substrates through inner
1685:
pump H ions against their concentration gradient to maintain the pH differential that can be used for the transport of other ions and molecules. H ions are pumped out of the cytoplasm into the extracellular space or into the vacuole. The entry of Mg into cells may occur through one of two pathways,
1672:
When a Mg ion has been absorbed by a cell requiring it for metabolic processes, it is generally assumed that the ion stays in that cell for as long as the cell is active. In vascular cells, this is not always the case; in times of plenty, Mg is stored in the vacuole, takes no part in the day-to-day
1639:
Within individual plant cells, the Mg requirements are largely the same as for all cellular life; Mg is used to stabilise membranes, is vital to the utilisation of ATP, is extensively involved in the nucleic acid biochemistry, and is a cofactor for many enzymes (including the ribosome). Also, Mg is
1539:
The chemical and biochemical properties of Mg present the cellular system with a significant challenge when transporting the ion across biological membranes. The dogma of ion transport states that the transporter recognises the ion then progressively removes the water of hydration, removing most or
1734:
Mg is probably taken up into chloroplasts to the greatest extent during the light-induced development from proplastid to chloroplast or etioplast to chloroplast. At these times, the synthesis of chlorophyll and the biogenesis of the thylakoid membrane stacks absolutely require the divalent cation.
617:
For U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of daily value (%DV). For magnesium labeling purposes, 100% of the daily value was 400 mg, but as of May 27, 2016, it was revised to 420 mg to bring it into agreement with the RDA. A
1498:
Third, the technique of patch-clamp uses isolated sections of natural or artificial membrane in much the same manner as voltage-clamp but without the secondary effects of a cellular system. Under ideal conditions the conductance of individual channels can be quantified. This methodology gives the
1490:
First, ion-specific microelectrodes can be used to measure the internal free ion concentration of cells and organelles. The major advantages are that readings can be made from cells over relatively long periods of time, and that unlike dyes very little extra ion buffering capacity is added to the
1477:
A number of chelators of divalent cations have different fluorescence spectra in the bound and unbound states. Chelators for Ca are well established, have high affinity for the cation, and low interference from other ions. Mg chelators lag behind and the major fluorescence dye for Mg (mag-fura 2)
1648:
Once in the cytoplasmic space of root cells Mg, along with the other cations, is probably transported radially into the stele and the vascular tissue. From the cells surrounding the xylem the ions are released or pumped into the xylem and carried up through the plant. In the case of Mg, which is
1610:
The previous sections have dealt in detail with the chemical and biochemical aspects of Mg and its transport across cellular membranes. This section will apply this knowledge to aspects of whole plant physiology, in an attempt to show how these processes interact with the larger and more complex
1454:
An article investigating the structural basis of interactions between clinically relevant antibiotics and the 50S ribosome appeared in Nature in
October 2001. High-resolution X-ray crystallography established that these antibiotics associate only with the 23S rRNA of a ribosomal subunit, and no
1401:
activity on and off by changes in the local concentration of Mg. Although the concentration of free cytoplasmic Mg is on the order of 1 mmol/L, the total Mg content of animal cells is 30 mmol/L and in plants the content of leaf endodermal cells has been measured at values as high as
1226:
appear in virtually every metabolic pathway: Specific binding of Mg to biological membranes is frequently observed, Mg is also used as a signalling molecule, and much of nucleic acid biochemistry requires Mg, including all reactions that require release of energy from ATP. In nucleotides, the
1730:
Mg is the coordinating metal ion in the chlorophyll molecule, and in plants where the ion is in high supply about 6% of the total Mg is bound to chlorophyll. Thylakoid stacking is stabilised by Mg and is important for the efficiency of photosynthesis, allowing phase transitions to occur.
1494:
Second, the technique of two-electrode voltage-clamp allows the direct measurement of the ion flux across the membrane of a cell. The membrane is held at an electric potential and the responding current is measured. All ions passing across the membrane contribute to the measured current.
1371:
has also been shown to bind Na, K, Mn and Fe. The transport of ions is dependent on both the concentration gradient of the ion and the electric potential (ΔΨ) across the membrane, which will be affected by the charge on the membrane surface. For example, the specific binding of Mg to the
1773:
Plant stress responses can be observed in plants that are under- or over-supplied with Mg. The first observable signs of Mg stress in plants for both starvation and toxicity is a depression of the rate of photosynthesis, it is presumed because of the strong relationships between Mg and
692:
Although many foods contain magnesium, it is usually found in low levels. As with most nutrients, daily needs for magnesium are unlikely to be met by one serving of any single food. Eating a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains will help ensure adequate intake of magnesium.
1619:
Mg is essential for plant growth and is present in higher plants in amounts on the order of 80 μmol g dry weight. The amounts of Mg vary in different parts of the plant and are dependent upon nutritional status. In times of plenty, excess Mg may be stored in vascular cells (Stelzer
1709:
take Mg by a similar system. The mechanism and the molecular basis for the release of Mg from vacuoles and from the cell is not known. Likewise, the light-regulated Mg concentration changes in chloroplasts are not fully understood, but do require the transport of H ions across the
1525:(AES) modifications also allows the determination of the total ion content of biological samples. These techniques are more sensitive than flame AAS and are capable of measuring the quantities of multiple ions simultaneously. However, they are also significantly more expensive.
1563:
In spite of the mechanistic difficulty, Mg must be transported across membranes, and a large number of Mg fluxes across membranes from a variety of systems have been described. However, only a small selection of Mg transporters have been characterised at the molecular level.
1312:
contain large amounts of Mg and the stabilisation provided is essential to the complexation of this ribo-protein. A large number of enzymes involved in the biochemistry of nucleic acids bind Mg for activity, using the ion for both activation and catalysis. Finally, the
5868:
Findling, R. L.; Maxwell, K; Scotese-Wojtila, L; Huang, J; Yamashita, T; Wiznitzer, M (1997). "High-dose pyridoxine and magnesium administration in children with autistic disorder: an absence of salutary effects in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study".
1356:
are polyanionic surfaces. This has important implications for the transport of ions, in particular because it has been shown that different membranes preferentially bind different ions. Both Mg and Ca regularly stabilize membranes by the cross-linking of
1746:
had stated in their paper that older pea chloroplasts showed less significant changes in Mg content than those used to form their conclusions. The relative proportion of immature chloroplasts present in the preparations may explain these observations.
1781:
A Mg deficit can be caused by the lack of the ion in the media (soil), but more commonly comes from inhibition of its uptake. Mg binds quite weakly to the negatively charged groups in the root cell walls, so that excesses of other cations such as K,
1540:
all of the water at a selective pore before releasing the ion on the far side of the membrane. Due to the properties of Mg, large volume change from hydrated to bare ion, high energy of hydration and very low rate of ligand exchange in the inner
4296:
Schlünzen, Frank; Zarivach, Raz; Harms, Jörg; Bashan, Anat; Tocilj, Ante; Albrecht, Renate; Yonath, Ada; Franceschi, François (2001). "Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria".
2785:
Dai, Qi; Zhu, Xiangzhu; Manson, JoAnn E; Song, Yiqing; Li, Xingnan; Franke, Adrian A; Costello, Rebecca B; Rosanoff, Andrea; Nian, Hui; Fan, Lei; Murff, Harvey; Ness, Reid M; Seidner, Douglas L; Yu, Chang; Shrubsole, Martha J (2018-12-01).
5583:
Ishijima, S.; Uchibori, A.; Takagi, H.; Maki, R.; Ohnishi, M. (2003). "Light-induced increase in free Mg concentration in spinach chloroplasts: Measurement of free Mg by using a fluorescent probe and intensity of stromal alkalinization".
1478:
actually has a higher affinity for Ca. This limits the application of this dye to cell types where the resting level of Ca is < 1 μM and does not vary with the experimental conditions under which Mg is to be measured. Recently, Otten
1680:
The homeostasis of Mg within single plant cells is maintained by processes occurring at the plasma membrane and at the vacuole membrane (see Figure 2). The major driving force for the translocation of ions in plant cells is ΔpH.
6176:- Includes full text papers and textbook chapters by leading magnesium authorities Mildred Seelig, Jean Durlach, Burton M. Altura and Bella T. Altura. Links to over 300 articles discussing magnesium and magnesium deficiency.
1270:
11.4) is used to allow both hydrolysis and condensation reactions (most common ones being phosphate ester hydrolysis and phosphoryl transfer) that would otherwise require pH values greatly removed from physiological values.
6046:
Mousain-Bosc M, Roche M, Polge A, Pradal-Prat D, Rapin J, Bali JP (Mar 2006). "Improvement of neurobehavioral disorders in children supplemented with magnesium-vitamin B6. I. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders".
6068:
Mousain-Bosc M, Roche M, Polge A, Pradal-Prat D, Rapin J, Bali JP (Mar 2006). "Improvement of neurobehavioral disorders in children supplemented with magnesium-vitamin B6. II. Pervasive developmental disorder-autism".
1109:
In plants, and more recently in animals, magnesium has been recognized as an important signaling ion, both activating and mediating many biochemical reactions. The best example of this is perhaps the regulation of
1548:
has been shown to be a Mg channel. The mechanisms of Mg transport by the remaining proteins are beginning to be uncovered with the first three-dimensional structure of a Mg transport complex being solved in 2004.
700:
has twice as much magnesium as white bread because the magnesium-rich germ and bran are removed when white flour is processed. The table of food sources of magnesium suggests many dietary sources of magnesium.
49:(ATP), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all
1156:
molecule. The later effects of magnesium deficiency on plants are a significant reduction in growth and reproductive viability. Magnesium can also be toxic to plants, although this is typically seen only in
3799:
Weber S, Schneider L, Peters M, Misselwitz J, Rönnefarth G, Böswald M, Bonzel KE, Seeman T, Suláková T, Kuwertz-Bröking E, Gregoric A, Palcoux JB, Tasic V, Manz F, Schärer K, Seyberth HW, Konrad M (2001).
3274:
Stelzer, R.; Lehmann, H.; Krammer, D.; Luttge, U. (1990). "X-Ray microprobe analysis of vacuoles of spruce needle mesophyll, endodermis and transfusion parenchyma cells at different seasons of the year".
169:) is rare, and is more common as a drug side-effect (such as chronic alcohol or diuretic use) than from low food intake per se, but it can occur in people fed intravenously for extended periods of time.
5730:
Dorenstouter, H.; Pieters, G.A.; Findenegg, G. R. (1985). "Distribution of magnesium between chloroplhyll and other photosynthetic functions in magnesium deficient 'sun' and 'shade' leaves of poplar".
2843:
Maggio, Marcello; De Vita, Francesca; Lauretani, Fulvio; Nouvenne, Antonio; Meschi, Tiziana; Ticinesi, Andrea; Dominguez, Ligia J.; Barbagallo, Mario; Dall'Aglio, Elisabetta; Ceda, Gian Paolo (2014).
2679:
Maggio, Marcello; De Vita, Francesca; Lauretani, Fulvio; Nouvenne, Antonio; Meschi, Tiziana; Ticinesi, Andrea; Dominguez, Ligia J.; Barbagallo, Mario; Dall'Aglio, Elisabetta; Ceda, Gian Paolo (2014).
1742:(1984) found that Mg did move in and out of isolated chloroplasts from young pea plants, but Gupta and Berkowitz (1989) were unable to reproduce the result using older spinach chloroplasts. Deshaies
3758:
Weber S, Hoffmann K, Jeck N, Saar K, Boeswald M, Kuwertz-Broeking E, Meij II, Knoers NV, Cochat P, Suláková T, Bonzel KE, Soergel M, Manz F, Schaerer K, Seyberth HW, Reis A, Konrad M (2000).
1705:
by AtMHX). Transport of Mg into cells may use either the negative ΔΨ or the ΔpH. The transport of Mg into mitochondria probably uses ΔΨ as in the mitochondria of yeast, and it is likely that
1665:
6123:
6623:
305:
Higher dietary intakes of magnesium correspond to lower diabetes incidence. For people with diabetes or at high risk of diabetes, magnesium supplementation lowers fasting glucose.
244:) is erratic and of poorer efficiency, since it depends on the neutralization and solution of the salt by the acid of the stomach, which may not be (and usually is not) complete.
236:. Magnesium is absorbed with reasonable efficiency (30% to 40%) by the body from any soluble magnesium salt, such as the chloride or citrate. Magnesium is similarly absorbed from
2519:"Dose-Response Relationship between Dietary Magnesium Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies"
1282:(adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must be bound to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP.
696:
Because magnesium readily dissolves in water, refined foods, which are often processed or cooked in water and dried, in general, are poor sources of the nutrient. For example,
5150:
Scott, B. J.; Robson, A. D. (1990b). "Changes in the content and form of magnesium in the first trifoliate leaf of subterranean clover under altered or constant root supply".
1594:
and thus exert greater pull on water molecules, preventing passage through the channel (even though the magnesium itself is smaller). Thus, Mg ions block Ca channels such as (
6009:
Tolbert, L.; Haigler, T; Waits, MM; Dennis, T (1993). "Brief report: lack of response in an autistic population to a low dose clinical trial of pyridoxine plus magnesium".
115:. This availability, in combination with a useful and very unusual chemistry, may have led to its utilization in evolution as an ion for signaling, enzyme activation, and
1324:
Magnesium ions can be critical in maintaining the positional integrity of closely clustered phosphate groups. These clusters appear in numerous and distinct parts of the
210:
is very rare. Infants, which have less ability to excrete excess magnesium even when healthy, should not be given magnesium supplements, except under a physician's care.
1455:
interactions are formed with a subunit's protein portion. The article stresses that the results show "the importance of putative Mg ions for the binding of some drugs".
111:
A balance of magnesium is vital to the well-being of all organisms. Magnesium is a relatively abundant ion in Earth's crust and mantle and is highly bioavailable in the
5239:
Lu YK, Chen YR, Yang CM, Ifuku K (1995). "Influence of Fe- and Mg-deficiency on the thylakoid membranes of a chlorophyll-deficient ch5 mutant of
Arabidopsis thaliana".
722:
as described above, with irregular heartbeats, high blood pressure (a sign in humans but not some experimental animals such as rodents), insomnia, and muscle spasms (
5356:
Heldt, H.W.; Werdan, K.; Milovancev, M.; Geller, G. (1973). "Alkalization of the chloroplast stroma caused by light-dependent proton flux into the thylakoid space".
3179:
Seiler, R. H.; Ramirez, O.; Brest, A. N.; Moyer, J. H. (1966). "Serum and erythrocytic magnesium levels in congestive heart failure: effect of hydrochlorothiazide".
1148:
Plants deficient in magnesium show stress responses. The first observable signs of both magnesium starvation and overexposure in plants is a decrease in the rate of
5935:
Lelord, G.; Muh, JP; Barthelemy, C; Martineau, J; Garreau, B; Callaway, E (1981). "Effects of pyridoxine and magnesium on autistic symptoms--initial observations".
1778:
in the needles on the lower branches of the tree. This is because Mg has been recovered from these tissues and moved to growing (green) needles higher in the tree.
711:
contains less of the ion. Dietary surveys do not assess magnesium intake from water, which may lead to underestimating total magnesium intake and its variability.
329:
are often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell" because their primary role is generating energy for cellular processes. They achieve this by breaking down
1556:
of the Mg ion has a very tightly bound inner shell of six water molecules and a relatively tightly bound second shell containing 12–14 water molecules (Markham
7055:
1810:
1738:
Whether Mg is able to move into and out of chloroplasts after this initial developmental phase has been the subject of several conflicting reports. Deshaies
4890:
Heenan, D.P.; Campbell, L.C. (1981). "Influence of potassium and manganese on growth and uptake of magnesium by soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr. cv Bragg".
1376:
envelope has been implicated in a loss of photosynthetic efficiency by the blockage of K uptake and the subsequent acidification of the chloroplast stroma.
206:
prevent the occurrence of diarrhea. Since the kidneys of adult humans excrete excess magnesium efficiently, oral magnesium poisoning in adults with normal
5906:
Green, V.; Pituch, K.; Itchon, J.; Choi, A.; O'Reilly, M.; Sigafoos, J. (2006). "Internet Survey of
Treatments Used by Parents of Children with Autism".
240:, although the sulfate in these salts adds to their laxative effect at higher doses. Magnesium absorption from the insoluble oxide and hydroxide salts (
5452:"Effect of ionophores A-23187 and nigericin on the light induced redistribution of magnesium potassium and hydrogen ions across the thylakoid membrane"
2383:
Slutsky, I.; Abumaria, N.; Wu, L. J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.; Govindarajan, A.; Zhao, M. G.; Zhuo, M.; Tonegawa, S.; Liu, G. (2010).
5759:"Surface Charge-Mediated Effects of Mg2+ on K+ Flux across the Chloroplast Envelope Are Associated with Regulation of Stromal pH and Photosynthesis"
1694:
transporter (such as AtMHX). The H-ATPases are dependent on Mg (bound to ATP) for activity, so that Mg is required to maintain its own homeostasis.
2145:
6179:
4963:"The bacterial magnesium transporter CorA can functionally substitute for its putative homologue Mrs2p in the yeast inner mitochondrial membrane"
5045:"Effects of Magnesium on Intact Chloroplasts: I. EVIDENCE FOR ACTIVATION OF (SODIUM) POTASSIUM/PROTON EXCHANGE ACROSS THE CHLOROPLAST ENVELOPE"
3760:"Familial hypomagnesaemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis maps to chromosome 3q27 and is associated with mutations in the PCLN-1 gene"
5499:
Krause, G. H. (1977). "Light-induced movement of magnesium ions in intact chloroplasts. Spectroscopic determination with
Eriochrome Blue SE".
6630:
3651:"Leaf Phosphate Status, Photosynthesis, and Carbon Partitioning in Sugar Beet: III. Diurnal Changes in Carbon Partitioning and Carbon Export"
1701:
maintain a constant ΔpH across the plasma membrane and the vacuole membrane. Mg is transported into the vacuole using the energy of ΔpH (in
3731:
Paunier, L.; Radde, I. C.; Kooh, S.W.; Conen, P.E.; Fraser, D. (1968). "Primary hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia in an infant".
4470:
Raju, B.; Murphy, E.; Levy, L. A.; Hall, R. D.; London, R. E. (1989). "A fluorescent indicator for measuring cytosolic free magnesium".
1102:, it has been shown that different cell types maintain different concentrations of magnesium. It seems likely that the same is true for
6212:
2992:"Overview on Dietary Reference Values for the EU population as derived by the EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies"
1247:, who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1915 for the purification and structure of chlorophyll binding with sixth number of carbon
188:
2959:, pp.190-249 in "Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride". National Academy Press. 1997.
2622:
Liu, Man; Jeong, Euy-Myoung; Liu, Hong; Xie, An; So, Eui Young; Shi, Guangbin; Jeong, Go Eun; Zhou, Anyu; Dudley, Samuel C. (2019).
1789:
Mg toxicity stress is more difficult to develop. When Mg is plentiful, in general the plants take up the ion and store it (Stelzer
4548:
Otten, P.A.; London, R.E.; Levy, L. A. (2001). "4-Oxo-4H-quinolizine-3-carboxylic acids as Mg selective, fluorescent indicators".
6397:
5972:
Martineau, J.; et al. (1985). "Vitamin B6, magnesium, and combined B6-Mg: therapeutic effects in childhood autism." Biol".
1199:
30-100mM (bound), 0.01-1mM (free), in budding yeast 50mM, in mammalian cell 10mM (bound), 0.5mM (free) and in blood plasma 1mM.
1141:
strains of bacteria, healthy rates are maintained only with exposure to very high external concentrations of the ion. In yeast,
3843:"Disruption of TRPM6/TRPM7 complex formation by a mutation in the TRPM6 gene causes hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia"
3008:
213:
2036:
5854:
5826:
4670:
4644:
3715:
3258:
2904:"Effects of magnesium supplementation on testosterone levels of athletes and sedentary subjects at rest and after exhaustion"
2292:
2121:
2080:
2017:
1183:
Overexposure to magnesium may be toxic to individual cells, though these effects have been difficult to show experimentally.
4104:"Quantitation of cation binding to wheat germ ribosomes: influences on subunit association equilibria and ribosome activity"
1406:, 1990), much of which buffered in storage compartments. The cytoplasmic concentration of free Mg is buffered by binding to
19:
5004:"Effect of divalent cations on cation fluxes across the chloroplast envelope and on photosynthesis of intact chloroplasts"
2104:
Romani, Andrea, M.P. (2013). "Magnesium in Health and
Disease". In Astrid Sigel; Helmut Sigel; Roland K. O. Sigel (eds.).
1697:
A schematic of a plant cell is shown including the four major compartments currently recognised as interacting with Mg.
5536:"Evidence of a Low Stromal Mg2+ Concentration in Intact Chloroplasts in the Dark: I. STUDIES WITH THE IONOPHORE A23187"
4933:
Hope, A. B.; Stevens, P. G. (1952). "Electrical potential differences in bean roots on their relation to salt uptake".
3489:"Magnesium transport in Salmonella typhimurium: genetic characterization and cloning of three magnesium transport loci"
1911:
1768:
2991:
1168:
Space-filling model of the chlorophyll a molecule, with the magnesium ion (bright-green) visible at the center of the
6149:
3910:
394:
Overall, maintaining adequate levels of both magnesium and vitamin D is essential for optimal health and well-being.
3981:
Romani, A. M. P.; Maguire, M. E. (2002). "Hormonal regulation of Mg transport and homeostasis in eukaryotic cells".
1227:
triple-phosphate moiety of the compound is invariably stabilized by association with Mg in all enzymatic processes.
726:). However, as noted, symptoms of low magnesium from pure dietary deficiency are thought to be rarely encountered.
37:
is an essential element in biological systems. Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg ion. It is an essential mineral
3841:
Chubanov V, Waldegger S, Mederos y
Schnitzler M, Vitzthum H, Sassen MC, Seyberth HW, Konrad M, Gudermann T (2004).
3802:"Novel paracellin-1 mutations in 25 families with familial hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis"
3028:"Federal Register May 27, 2016 Food Labeling: Revision of the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels. FR page 33982"
6184:
5309:"Development and Use of Chlorotetracycline Fluorescence as a Measurement Assay of Chloroplast Envelope-Bound Mg2+"
5177:
Fork, D.C. (1986). "The control by state transitions of the distribution of excitation energy in photosynthesis".
4202:"Hexahydrated magnesium ions bind in the deep major groove and at the outer mouth of A-form nucleic acid duplexes"
3132:"Spectrochemical Analysis of Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Copper, and Zinc in Normal Human Erythrocytes"
1755:. During the dark period, if these enzymes were active a wasteful cycling of products and substrates would occur.
261:
In 2021, magnesium salts were the 211th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2
6821:
6552:
2788:"Magnesium status and supplementation influence vitamin D status and metabolism: results from a randomized trial"
1841:
411:
Studies have shown that significant gains in testosterone occur after taking 10 mg magnesium/kg body weight/day.
217:
4024:
Black, C. B.; Cowan, J.A. (1995). J.A. Cowan (ed.). "Magnesium-dependent enzymes in nucleic acid biochemistry".
408:
It is theorized that the process of making testosterone from cholesterol, needs magnesium to function properly.
6716:
6205:
1508:
1218:) and the most abundant free divalent cation — as a result, it is deeply and intrinsically woven into cellular
1191:
function. Healthy animals rapidly excrete excess magnesium in the urine and stool. Urinary magnesium is called
606:
420:
273:
Magnesium can affect muscle relaxation through direct action on cell membranes. Mg ions close certain types of
3579:"The nuclear gene MRS2 is essential for the excision of group II introns from yeast mitochondrial transcripts
3538:"Overexpression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae magnesium transport system confers resistance to aluminum ion"
6994:
2974:
1435:
1321:(enzymes containing only RNA) is Mg dependent (e.g. the yeast mitochondrial group II self splicing introns).
4200:
Robinson, Howard; Gao, Yi-Gui; Sanishvili, Ruslan; Joachimiak, Andrzej; Wang, Andrew H.-J. (15 April 2000).
384:
They contribute to muscle contraction and relaxation, impacting physical performance and overall well-being.
361:
have a synergistic relationship in the body, meaning they work together to optimize each other's functions:
6616:
1522:
424:
4583:
Gunzel, D.; Schlue, W.-R. (2002). "Determination of i - an update on the use of Mg-selective electrodes".
2415:
7060:
6187:- description of research studies regarding supplementation with magnesium and other therapies for autism
4153:"Cloning and characterization of MgtE, a putative new class of Mg2+ transporter from Bacillus firmus OF4"
4044:
Black, C.B.; Cowan, J. A. (1995). J.A. Cowan (ed.). "Magnesium-dependent enzymes in general metabolism".
3069:
2249:
Stepura OB, Martynow AI (February 2008). "Magnesium orotate in severe congestive heart failure (MACH)".
7019:
3112:
2371:
2341:"Enhancement of Synaptic Plasticity through Chronically Reduced Ca2+ Flux during Uncorrelated Activity"
1514:
1389:
1261:
5648:"Competitive Al3+ Inhibition of Net Mg2+ Uptake by Intact Lolium multiflorum Roots : I. Kinetics"
1544:, these steps are probably more difficult than for most other ions. To date, only the ZntA protein of
7045:
6874:
6198:
1337:
285:. With an excess of magnesium, more channels will be blocked and nerve cells activity will decrease.
5716:
5225:
4456:
4418:
3967:
1624:, 1990; and in times of starvation Mg is redistributed, in many plants, from older to newer leaves.
6588:
6131:
6127:
6111:
428:
251:
2969:
343:. This process ultimately produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy currency.
6593:
3027:
5862:
6886:
6455:
6225:
5809:
Romani, Andrea M.P. (2013). "Magnesium
Homeostasis in Mammalian Cells". In Banci, Lucia (ed.).
4755:
Warren, M. A.; Kucharski, L. M.; Veenstra, A.; Shi, L.; Grulich, P. F.; Maguire, M. E. (2004).
1279:
619:
435:
320:
138:
46:
27:
6119:
1244:
6826:
6701:
6570:
6361:
6325:
6242:
1628:
1423:
1257:
3305:
Shaul, O.; Hilgemann, D. W.; de-Almeida-Engler, J.; Van, M.M.; Inze, D.; Galili, G. (1999).
1137:, low levels of magnesium manifests in greatly reduced growth rates. In magnesium transport
6999:
6711:
6671:
6661:
6544:
6304:
6299:
6294:
5404:
4899:
4813:
4709:
4306:
3854:
3367:
1862:
1587:
1236:
339:
128:
5393:"Light-Dependent Redistribution of Ions in Suspensions of Chloroplast Thylakoid Membranes"
4059:
Cowan, J. A. (2002). "Structural and catalytic chemistry of magnesium-dependent enzymes".
2624:"Magnesium supplementation improves diabetic mitochondrial and cardiac diastolic function"
8:
7040:
6869:
6836:
6796:
6696:
6168:
2845:"The Interplay between Magnesium and Testosterone in Modulating Physical Function in Men"
2681:"The Interplay between Magnesium and Testosterone in Modulating Physical Function in Men"
1868:
1541:
1534:
203:
162:
146:
5408:
4903:
4817:
4713:
4310:
3858:
3444:
Shaul, O. (2002). "Magnesium transport and function in plants: the tip of the iceberg".
3371:
7050:
7004:
6963:
6788:
6666:
6580:
6034:
5997:
5960:
5894:
5783:
5758:
5704:
5672:
5647:
5476:
5451:
5333:
5308:
5284:
5259:
5213:
5119:
Scott, B. J.; Robson, A. D. (1990). "Distribution of magnesium in subterranean clover (
5025:
4915:
4608:
4530:
4444:
4406:
4376:
4330:
4278:
4084:
4006:
3955:
3675:
3650:
3635:
3469:
3393:
3331:
3306:
3288:
3231:
2939:
2879:
2844:
2820:
2787:
2715:
2680:
2656:
2623:
2604:
2545:
2518:
2453:
2428:
2226:
2201:
2139:
1850:
1815:
1599:
1583:
419:
The U.S. Institute of
Medicine (IOM) updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and
278:
30:
ionic mixture, what is often just called adenosine triphosphate colloquially in biology
5597:
5560:
5535:
5427:
5392:
5069:
5044:
4825:
4781:
4756:
4732:
4697:
4226:
4201:
4177:
4152:
4128:
4103:
3911:"Cell Biology by the Numbers: What are the concentrations of different ions in cells?"
3877:
3842:
3707:
3599:
3578:
3513:
3488:
3156:
3131:
2314:
2161:"Magnesium, calcium, potassium, and sodium intakes and risk of stroke in male smokers"
1964:
6973:
6943:
6911:
6906:
6891:
6864:
6811:
6801:
6706:
6686:
6681:
6651:
6526:
6078:
6056:
6026:
5989:
5985:
5952:
5923:
5886:
5858:
5850:
5840:
5832:
5822:
5788:
5677:
5601:
5565:
5516:
5512:
5481:
5467:
5432:
5373:
5369:
5338:
5289:
5190:
5074:
4984:
4872:
4855:
4829:
4786:
4772:
4737:
4666:
4640:
4631:
4600:
4565:
4522:
4487:
4368:
4334:
4322:
4270:
4231:
4182:
4133:
4076:
3998:
3882:
3823:
3781:
3740:
3711:
3680:
3604:
3559:
3518:
3461:
3423:
3385:
3336:
3254:
3223:
3192:
3161:
2931:
2923:
2902:
Cinar, Vedat; Polat, Yahya; Baltaci, Abdulkerim Kasim; Mogulkoc, Rasim (April 2011).
2884:
2866:
2825:
2807:
2767:
2759:
2720:
2702:
2661:
2643:
2596:
2550:
2499:
2458:
2406:
2362:
2266:
2231:
2182:
2127:
2117:
2086:
2076:
2064:
Dietary
Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride
2013:
1969:
1907:
1874:
1821:
1591:
1518:
1085:
929:
697:
247:
229:
200:
6038:
5898:
5029:
4919:
4856:"Physiological impacts of Mg deficiency in Pinus radiata: growth and photosynthesis"
4612:
4534:
4483:
4380:
4282:
4168:
4088:
4010:
3504:
3473:
3235:
2943:
2608:
6938:
6896:
6442:
6233:
6018:
5981:
5964:
5944:
5915:
5878:
5814:
5778:
5770:
5739:
5667:
5659:
5593:
5555:
5547:
5508:
5471:
5463:
5422:
5412:
5365:
5328:
5320:
5279:
5271:
5186:
5159:
5132:
5064:
5056:
5015:
4974:
4907:
4867:
4821:
4776:
4768:
4727:
4717:
4592:
4557:
4514:
4479:
4360:
4314:
4262:
4221:
4213:
4172:
4164:
4123:
4115:
4068:
3990:
3872:
3862:
3813:
3771:
3703:
3670:
3662:
3631:
3594:
3549:
3508:
3500:
3487:
Hmiel, S. P.; Snavely, M. D.; Florer, J. B.; Maguire, M. E.; Miller, C. G. (1989).
3453:
3397:
3375:
3326:
3318:
3304:
3284:
3215:
3188:
3151:
3143:
3044:
2915:
2874:
2856:
2815:
2799:
2751:
2710:
2692:
2651:
2635:
2586:
2578:
2540:
2530:
2489:
2448:
2444:
2440:
2396:
2352:
2258:
2221:
2213:
2172:
2109:
2068:
2040:
1959:
1899:
1579:
241:
192:
6001:
2284:
7009:
6901:
6841:
6806:
6691:
6676:
6534:
6480:
6316:
3414:
Berkowitz, G. A.; Wu, W. (1993). "Magnesium, potassium flux and photosynthesis".
2517:
Fang X, Han H, Li M, Liang C, Fan Z, Aaseth J, He J, Montgomery S, Cao Y (2016).
2401:
2384:
2357:
2340:
2262:
2217:
1794:
1633:
1627:
Mg is taken up into plants via the roots. Interactions with other cations in the
1553:
1362:
1301:
stabilises structure; this can be observed in the increased melting temperature (
1184:
638:
255:
5818:
5622:
Sharkey, T. D. (1998). A. Raghavendra (ed.). "Photosynthetic carbon reduction".
3208:
Ergebnisse der Physiologie Biologischen Chemie und Experimentellen Pharmakologie
2956:
2113:
6953:
6948:
6933:
6921:
6262:
6190:
5919:
5397:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
4266:
3847:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
3322:
2639:
2177:
2160:
1903:
1658:
1177:
1149:
983:
719:
674:
221:
207:
166:
100:
42:
5882:
5743:
4596:
4518:
4364:
4072:
3994:
3486:
3457:
2919:
1947:
7034:
7014:
6978:
6968:
6926:
6916:
6460:
6409:
5836:
5697:
Root-induced changes in the availability of micronutrients in the rhizosphere
5260:"Permeability of Chloroplast Envelopes to Mg2+: Effects on Protein Synthesis"
4979:
4962:
3840:
3622:
Kaiser, W. M. (1987). "Effects of water deficit on photosynthetic capacity".
2927:
2870:
2811:
2763:
2706:
2647:
1798:
1698:
1682:
1654:
1358:
1349:
1314:
961:
723:
326:
314:
294:
274:
84:
require the presence of magnesium ions for their catalytic action, including
72:
molecule, with the magnesium ion (bright-green) visible at the center of the
69:
50:
6958:
4351:
Maguire, M.E.; Cowan, J. A. (2002). "Magnesium chemistry and biochemistry".
4217:
4119:
3867:
3776:
3759:
2903:
2739:
1927:
Leroy, J. (1926). "Necessite du magnesium pour la croissance de la souris".
250:
may be used as adjuvant therapy in patients on optimal treatment for severe
6831:
6335:
6163:
6082:
6060:
5927:
5844:
5792:
5681:
5605:
5569:
5417:
5342:
5293:
5078:
5020:
5003:
4988:
4833:
4790:
4741:
4722:
4604:
4569:
4526:
4372:
4326:
4235:
4080:
4002:
3886:
3827:
3785:
3684:
3554:
3537:
3465:
3340:
3165:
2935:
2888:
2829:
2771:
2724:
2665:
2600:
2554:
2503:
2462:
2429:"Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia"
2410:
2366:
2270:
2235:
2186:
2131:
2090:
1856:
1827:
1664:
1595:
1325:
1290:
1235:
In photosynthetic organisms, Mg has the additional vital role of being the
1187:, an overabundance of magnesium in the blood, is usually caused by loss of
1142:
1119:
670:
403:
233:
196:
158:
6030:
5993:
5956:
5890:
5436:
5377:
4698:"An exchanger-like protein underlies the large Mg2+ current in Paramecium"
4491:
4399:
Metal substitution as a probe of the biological chemistry of magnesium ion
4274:
4186:
4137:
3744:
3608:
3563:
3522:
3427:
3389:
3227:
2861:
2803:
2755:
2697:
2582:
2062:
1973:
1717:
1129:
causes disease of the affected organism. In single-cell organisms such as
6879:
6816:
6517:
6424:
6419:
6392:
6290:
6285:
5729:
5663:
5520:
4961:
Bui, D.M.; Gregan, J.; Jarosch, E.; Ragnini, A.; Schweyen, R. J. (1999).
4754:
4505:
Grubbs, R. D. (2002). "Intracellular magnesium and magnesium buffering".
3818:
3801:
3178:
2567:
1706:
1373:
1240:
1215:
1153:
1115:
891:
686:
650:
646:
630:
254:, increasing survival rate and improving clinical symptoms and patient's
237:
112:
96:
53:
compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of
5813:. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 12. Springer. pp. 69–118.
5774:
5551:
5485:
5324:
5275:
5060:
3730:
3095:"SELF Nutrition Data - Food Facts, Information & Calorie Calculator"
2591:
2494:
2478:"Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis"
2477:
1195:. Characteristic concentrations of magnesium in model organisms are: in
6767:
6414:
6281:
6221:
6022:
5948:
5355:
4911:
4677:
for descriptions of the methodology as applied to analytical chemistry.
4250:
3666:
3576:
3273:
3219:
3045:"Daily Value Reference of the Dietary Supplement Label Database (DSLD)"
2108:. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 13. Springer. pp. 49–79.
1691:
1686:
via channels using the ΔΨ (negative inside) across this membrane or by
1545:
1443:
1427:
1219:
1164:
1063:
782:
708:
704:
654:
177:
89:
64:
6608:
5582:
5163:
5136:
4561:
3147:
3129:
2535:
1690:
with H ions. To transport the Mg ion into the vacuole requires a Mg/H
1293:
have an important range of interactions with Mg. The binding of Mg to
390:
They support a healthy immune system and may help reduce inflammation.
6402:
6173:
4854:
Laing, W.; Greer, D.; Sun, O.; Beets, P.; Lowe, A.; Payn, T. (2000).
4695:
4318:
3380:
3355:
1836:
1775:
1711:
1687:
1572:
1442:
is typically dependent on Mg, whereas the analogous enzyme for other
1419:
1407:
1398:
1353:
1329:
1318:
1125:
Magnesium is very important in cellular function. Deficiency of the
999:
907:
766:
750:
358:
352:
225:
184:
116:
34:
23:
4469:
3248:
6851:
6759:
6743:
6383:
6370:
6340:
6330:
6276:
6251:
6130:
external links, and converting useful links where appropriate into
5867:
5257:
4960:
4437:
Physical methods for studying the biological chemistry of magnesium
1309:
1274:
1138:
1130:
1126:
1079:
330:
180:
173:
154:
142:
38:
2426:
2202:"Magnesium Sulfate for the Treatment of Eclampsia: A Brief Review"
2159:
Larsson S. C.; Virtanen M. J.; Mars M.; et al. (March 2008).
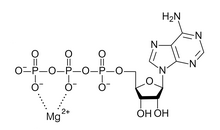
2158:
2072:
2067:. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. 1997. pp. 190–191.
6859:
6503:
6498:
6465:
6067:
6045:
4150:
3697:
2385:"Enhancement of Learning and Memory by Elevating Brain Magnesium"
1945:
1752:
1385:
1367:
1333:
1169:
1158:
1093:
1047:
1031:
967:
875:
846:
830:
824:
734:
715:
678:
642:
375:
334:
150:
73:
3353:
3094:
714:
Too much magnesium may make it difficult for the body to absorb
6775:
6751:
6735:
6726:
5695:
Marschner, H. (1991). Y. Waisel; A. Eshel; U. Kafikfai (eds.).
4199:
3307:"Cloning and characterization of a novel Mg(2+)/H(+) exchanger"
1643:
1223:
1188:
1111:
1103:
1099:
1075:
945:
662:
658:
282:
88:
enzymes utilizing or synthesizing ATP, or those that use other
81:
4853:
3798:
3070:"Top 10 Foods Highest in Magnesium + Printable One Page Sheet"
2842:
2678:
2106:
Interrelations between Essential Metal Ions and Human Diseases
1661:(9) is unknown. Mg may return to the roots in the phloem sap.
1598:) and have been shown to affect gap junction channels forming
729:
Following are some foods and the amount of magnesium in them:
6470:
6450:
5179:
Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology
1725:
1308:) of double-stranded DNA in the presence of Mg. In addition,
1208:
1134:
319:
Magnesium is essential as part of the process that generates
134:
5934:
5390:
4547:
4295:
3130:
Valberg, L. S.; Holt, J.M.; Paulson, E.; Szivek, J. (1965).
1614:
1458:
1152:. This is due to the central position of the Mg ion in the
6493:
6488:
6387:
6271:
5756:
4696:
Haynes, W. J.; Kung, C.; Saimi, Y.; Preston, R. R. (2002).
2427:
Duley L, Gülmezoglu AM, Henderson-Smart DJ, Chou D (2010).
1069:
1015:
913:
682:
666:
618:
table of the old and new adult Daily Values is provided at
172:
The most common symptom of excess oral magnesium intake is
3899:
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, Online Edition
3648:
3251:
The Elemental Composition of Human Tissues and Body Fluids
2738:
Uwitonze, Anne Marie; Razzaque, Mohammed S. (2018-03-01).
6008:
5449:
2901:
1575:
1439:
1431:
1365:
head groups of lipids. However, the envelope membrane of
1298:
1294:
1211:
58:
54:
4804:
Gardner, R. C. (2003). "Genes for magnesium transport".
4101:
3702:. Advances in Agronomy. Vol. 22. pp. 332–374.
3577:
Wiesenberger, G.; Waldherr, M.; Schweyen, R. J. (1992).
3535:
2740:"Role of Magnesium in Vitamin D Activation and Function"
5258:
Deshaies, R. J.; Fish, L. E.; Jagendorf, A. T. (1984).
4255:
Journal of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry
3249:
Iyengar, G.V.; Kollmer, W. E.; Bowen, H. J. M. (1978).
3010:
Tolerable Upper Intake Levels For Vitamins And Minerals
1846:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
1844: – Condition of low level of magnesium in the body
1832:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
1499:
most direct measurement of the action of ion channels.
2382:
2338:
2037:"Definition: magnesium from Online Medical Dictionary"
1397:≤ 10) and this can be exploited by the cell to switch
1332:. For instance, hexahydrated Mg ions bind in the deep
6360:
5905:
5645:
5306:
4151:
Smith, R. L.; Thompson, L.J.; Maguire, M. E. (1995).
3948:
Introduction to the biological chemistry of magnesium
3757:
3698:
Grunes, D. L.; Stout, P. R.; Brownwell, J.R. (1970).
2339:
Slutsky, I.; Sadeghpour, S.; Li, B.; Liu, G. (2004).
2031:
2029:
1801:
in the chloroplast that then cause oxidative damage.
133:
Inadequate magnesium intake frequently causes muscle
5206:
Structure and function of the photosynthesising cell
4889:
4397:
Tevelev, A.; Cowan, J. A. (1995). J.A. Cowan (ed.).
3980:
1946:
Lusk, J.E.; Williams, R.J.P.; Kennedy, E.P. (1968).
1929:
Comptes Rendus des Séances de la Société de Biologie
5501:
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics
5358:
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics
5149:
4935:
Australian Journal of Scientific Research, Series B
4582:
4396:
4350:
3354:Thomas, R.C.; Coles, J. A.; Deitmer, J. W. (1991).
2744:
The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association
2475:
1853: – Questionable IV vitamin alternative therapy
293:Intravenous magnesium sulphate is used in treating
95:In plants, magnesium is necessary for synthesis of
5723:
5118:
4932:
4630:
4430:
4428:
2026:
337:, through a series of chemical reactions known as
6114:may not follow Knowledge's policies or guidelines
5626:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 111–122.
5042:
5001:
4624:
4622:
4043:
3570:
3409:
3407:
3113:"Food Composition Databases Show Foods List12006"
2003:
300:
41:(i.e., element) for life and is present in every
7032:
6220:
5617:
5615:
4023:
2784:
2737:
2001:
1999:
1997:
1995:
1993:
1991:
1989:
1987:
1985:
1983:
1605:
1275:Essential role in the biological activity of ATP
5688:
5238:
4680:
4425:
4392:
4390:
4346:
4344:
4248:
3529:
3413:
2248:
228:. Such preparations are usually in the form of
6241:
5576:
4885:
4883:
4619:
4039:
4037:
4035:
3649:Rao, I. M.; Sharp, R. E.; Boyer, J.S. (1987).
3404:
2621:
2516:
1948:"Magnesium and the growth of Escherichia coli"
1797:, which all leads to the production of oxygen
1567:
1336:and at the outer mouth of A-form nucleic acid
1094:Biological range, distribution, and regulation
645:provide magnesium because of the abundance of
7056:Biology and pharmacology of chemical elements
6624:
6206:
5612:
5443:
5391:Hind, G.; Nakatani, H. Y.; Izawa, S. (1974).
5251:
4849:
4847:
4845:
4843:
4757:"The CorA Mg2+ Transporter Is a Homotetramer"
4095:
3941:
3939:
3937:
3935:
3933:
3931:
3834:
3806:Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
3439:
3437:
3300:
3298:
1980:
1811:Biology and pharmacology of chemical elements
1582:are usually in almost all senses opposite to
1502:
1449:
5757:Wu, W.; Peters, J.; Berkowitz, G.A. (1991).
5639:
5197:
4797:
4387:
4341:
3724:
3267:
3242:
3123:
2242:
2199:
2144:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1644:Distributing magnesium ions within the plant
1472:
1145:magnesium deficiency also leads to disease.
5527:
5492:
5450:Bulychev, A. A.; Vredenberg, W. J. (1980).
5152:Australian Journal of Agricultural Research
5143:
5125:Australian Journal of Agricultural Research
5112:
4995:
4880:
4748:
4689:
4576:
4498:
4032:
4017:
3974:
3691:
3615:
3347:
3206:Walser, M. (1967). "Magnesium metabolism".
3199:
3172:
2152:
1611:environment of the multicellular organism.
1343:
6631:
6617:
6213:
6199:
5349:
5300:
5036:
4840:
4541:
4435:Drakenberg, T. (1995). J. A. Cowan (ed.).
4434:
4144:
4102:Sperazza, J. M.; Spremulli, L. L. (1983).
4052:
3928:
3792:
3751:
3480:
3434:
3295:
2792:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
1726:Magnesium, chloroplasts and photosynthesis
1463:
414:
368:Vitamin D influences magnesium absorption.
214:Pharmaceutical preparations with magnesium
6150:Learn how and when to remove this message
5971:
5782:
5694:
5671:
5559:
5475:
5426:
5416:
5384:
5332:
5283:
5170:
5068:
5019:
4978:
4926:
4871:
4780:
4731:
4721:
4663:Atomic Absorption and Plasma Spectroscopy
4653:
4463:
4242:
4225:
4176:
4127:
3876:
3866:
3817:
3775:
3674:
3598:
3553:
3536:MacDiarmid, C.W.; Gardner, R. C. (1998).
3512:
3379:
3330:
3155:
2878:
2860:
2819:
2714:
2696:
2655:
2590:
2544:
2534:
2493:
2452:
2400:
2356:
2315:"Magnesium Salts - Drug Usage Statistics"
2225:
2176:
2007:
1963:
1920:
1673:metabolic processes of the cell (Stelzer
1615:Nutritional requirements and interactions
1459:Measuring magnesium in biological samples
5750:
5624:Photosynthesis: A Comprehensive Treatise
4954:
3642:
3049:Dietary Supplement Label Database (DSLD)
2193:
1939:
1716:
1663:
1384:The Mg ion tends to bind only weakly to
1163:
629:
63:
18:
6638:
6398:Iron-responsive element-binding protein
5621:
5586:Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics
5307:Gupta, A. S.; Berkowitz, G. A. (1989).
5232:
5203:
4803:
3946:Cowan, J. A. (1995). J.A. Cowan (ed.).
3908:
1485:
1202:
216:are used to treat conditions including
191:etc.) are much better-tolerated by the
7033:
5908:Research in Developmental Disabilities
5808:
5533:
5498:
4639:. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates Inc.
4504:
3621:
3205:
3020:
3016:, European Food Safety Authority, 2006
2849:International Journal of Endocrinology
2685:International Journal of Endocrinology
2476:Kass L, Weekes J, Carpenter L (2012).
2103:
1896:Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia
1668:Figure 1: Magnesium in the whole plant
1528:
1243:molecule. This role was discovered by
6612:
6194:
5241:Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica
4665:. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.
4637:Ionic channels of excitable membranes
4628:
4058:
4046:The Biological Chemistry of Magnesium
4026:The Biological Chemistry of Magnesium
3945:
3443:
3253:. Weinheim, New York: Verlag Chemie.
3062:
2200:Euser, A. G.; Cipolla, M. J. (2009).
1926:
1894:"Magnesium (In Biological Systems)".
1865: – Use of Potassium by organisms
1830: – Pore-forming membrane protein
1753:ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase
1721:Figure 2: Magnesium in the plant cell
45:type in every organism. For example,
6094:
5646:Rengel, Z.; Robinson, D. L. (1989).
5176:
4660:
4289:
4193:
2295:from the original on 15 January 2024
1898:. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2006.
1871: – Use of Selenium by organisms
910:, 70% cocoa (1 oz) = 73 mg
689:are also good sources of magnesium.
6729: (Core six elements)
1818: – Use of calcium by organisms
1762:
718:. Not enough magnesium can lead to
277:, which conduct positively charged
268:
199:of the older compounds used, while
13:
5456:American Journal of Neuroradiology
5043:Huber, S.C.; Maury, W. J. (1980).
3764:European Journal of Human Genetics
3636:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1987.tb04631.x
3289:10.1111/j.1438-8677.1990.tb00183.x
2039:. 25 December 2007. Archived from
2010:Mineral Nutrition in Higher Plants
1877: – Use of sodium by organisms
1837:Magnesium deficiency (agriculture)
1824: – Use of Iodine by organisms
1769:magnesium deficiency (agriculture)
1176:In animals, magnesium deficiency (
649:molecules, which contain the ion.
14:
7072:
6090:
3136:Journal of Clinical Investigation
2908:Biological Trace Element Research
6099:
5636:Section 8.5.6 of Marschner, 1995
5630:
5208:. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
5191:10.1146/annurev.arplant.37.1.335
5002:Demmig, B.; Gimmler, H. (1979).
4951:Section 8.5.2 in Marschner, 1995
4873:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00616.x
4806:Current Opinion in Plant Biology
4773:10.1128/JB.186.14.4605-4612.2004
4251:"Magnesium metabolism: a review"
1285:
707:can also provide magnesium, but
6553:Phosphoric acids and phosphates
6169:List of foods rich in Magnesium
5103:
5094:
5085:
4967:Journal of Biological Chemistry
4945:
4484:10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C540
4169:10.1128/jb.177.5.1233-1238.1995
3902:
3893:
3505:10.1128/jb.171.9.4742-4751.1989
3105:
3087:
3037:
3001:
2984:
2977:, Office of Dietary Supplements
2962:
2950:
2895:
2836:
2778:
2731:
2672:
2615:
2561:
2510:
2469:
2420:
2376:
2332:
2307:
2277:
1952:Journal of Biological Chemistry
1842:Magnesium deficiency (medicine)
1207:Mg is the fourth-most-abundant
625:
397:
378:absorption and bone metabolism.
308:
288:
137:, and has been associated with
122:
6717:Biological aspects of fluorine
5109:Section 2.4 in Marschner, 1995
5100:Section 3.3 in Marschner, 1995
5091:Section 2.7 in Marschner, 1995
5008:Zeitschrift für Naturforschung
4249:Ebel, H.; Gunther, T. (1980).
3181:American Journal of Cardiology
2445:10.1002/14651858.CD000025.pub2
2097:
2055:
1887:
1509:atomic absorption spectroscopy
1230:
1072:, non fat (1 cup) = 27 mg
634:Some good sources of magnesium
607:European Food Safety Authority
421:Recommended Dietary Allowances
301:Diabetes and glucose tolerance
1:
6995:Composition of the human body
6286:Ferroportin (SLC11A3/SLC40A1)
5802:
5598:10.1016/S0003-9861(03)00038-9
4826:10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00032-3
3708:10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60272-2
3600:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)50522-1
2975:National Institutes of Health
2012:. San Diego: Academic Press.
1965:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)93417-4
1606:Plant physiology of magnesium
425:Tolerable upper intake levels
365:Magnesium activates vitamin D
16:Use of Magnesium by organisms
5986:10.1016/0006-3223(85)90019-8
5513:10.1016/0005-2728(77)90088-3
5468:10.1016/0005-2728(76)90006-2
5370:10.1016/0005-2728(73)90137-0
5123:L.) in relation to supply".
3193:10.1016/0002-9149(66)90372-9
2402:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.12.026
2358:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.11.013
2263:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.11.022
2218:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.527788
1523:atomic emission spectroscopy
1418:In biological systems, only
1413:
964:(2 tablespoons) = 50 mg
346:
7:
7005:Mineral (Essential element)
5819:10.1007/978-94-007-5561-1_4
2981:Updated: September 26, 2018
2114:10.1007/978-94-007-7500-8_3
1804:
1568:Ligand ion channel blockade
1379:
612:
374:They play crucial roles in
106:
92:to synthesize DNA and RNA.
68:Space-filling model of the
10:
7077:
7020:Uranium in the environment
5920:10.1016/j.ridd.2004.12.002
5732:Journal of Plant Nutrition
5699:. New York: Marcel Dekker.
5204:Gregory, R. P. F. (1989).
4267:10.1515/cclm.1980.18.5.257
2640:10.1172/jci.insight.123182
2433:Cochrane Database Syst Rev
2178:10.1001/archinte.168.5.459
1904:10.1002/0471743984.vse4741
1766:
1532:
1515:Inductively coupled plasma
1503:By absorption spectroscopy
1450:Importance in drug binding
1250:
401:
350:
312:
126:
6987:
6875:Acute beryllium poisoning
6850:
6787:
6725:
6644:
6579:
6561:
6543:
6525:
6516:
6479:
6441:
6379:
6353:
6315:
6261:
6250:
6232:
5744:10.1080/01904168509363409
4659:See Chapters 5 and 6 in
4472:Am J Physiol Cell Physiol
3909:Milo, Ron; Philips, Rob.
3700:Grass tetany of ruminants
2920:10.1007/s12011-010-8676-3
1859: – Skeletal disorder
1473:By fluorescent indicators
1402:100 mmol/L (Stelzer
827:(3 oz) = 103 mg
429:Dietary Reference Intakes
6589:Calcium-sensing receptor
6336:Calreticulin/mobilferrin
6180:Dietary Reference Intake
5811:Metallomics and the Cell
4980:10.1074/jbc.274.29.20438
3323:10.1093/emboj/18.14.3973
1881:
1344:Cell membranes and walls
1082:(1 oz) = 24 mg
252:congestive heart failure
165:. Acute deficiency (see
6594:Calcium-binding protein
5883:10.1023/A:1025861522935
4761:Journal of Bacteriology
4686:Hille, 1992. Chapter 11
4597:10.1023/A:1016074714951
4519:10.1023/A:1016026831789
4365:10.1023/A:1016058229972
4157:Journal of Bacteriology
4073:10.1023/A:1016022730880
3995:10.1023/A:1016082900838
3868:10.1073/pnas.0305252101
3777:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200475
3493:Journal of Bacteriology
3458:10.1023/A:1016091118585
1586:ions, because they are
1517:(ICP) using either the
1464:By radioactive isotopes
1222:. Indeed, Mg-dependent
415:Dietary recommendations
265:million prescriptions.
232:or chloride when given
176:. Supplements based on
6887:Chlorine gas poisoning
5534:Portis, A. R. (1981).
5418:10.1073/pnas.71.4.1484
5121:Trifolium subterranean
5021:10.1515/znc-1979-3-413
4723:10.1073/pnas.242603999
4550:Bioconjugate Chemistry
4206:Nucleic Acids Research
4108:Nucleic Acids Research
3555:10.1074/jbc.273.3.1727
3356:"Homeostatic muffling"
3099:nutritiondata.self.com
2008:Marschner, H. (1995).
1722:
1669:
1590:too, but have greater
1173:
1088:(1 slice) = 23 mg
635:
620:Reference Daily Intake
436:Reference Daily Intake
321:adenosine triphosphate
139:cardiovascular disease
77:
47:adenosine triphosphate
31:
28:adenosine triphosphate
6860:Argyria (Silver)
6702:Molybdenum in biology
6571:Magnesium transporter
6362:Iron-binding proteins
6326:Duodenal cytochrome B
6174:The Magnesium Website
4218:10.1093/nar/28.8.1760
4120:10.1093/nar/11.9.2665
3624:Physiologia Plantarum
2756:10.7556/jaoa.2018.037
2583:10.1038/ejcn.2016.154
2285:"The Top 300 of 2021"
1720:
1667:
1424:reverse transcriptase
1167:
1066:(1 Tbsp) = 32 mg
633:
402:Further information:
351:Further information:
313:Further information:
127:Further information:
67:
22:
7000:Lithium (medication)
6712:Arsenic biochemistry
6672:Manganese in biology
6662:Potassium in biology
6657:Magnesium in biology
6563:Magnesium metabolism
6545:Phosphate metabolism
6295:Transferrin receptor
6164:Magnesium Deficiency
6120:improve this article
5664:10.1104/pp.91.4.1407
4478:(3 Pt 1): C540–548.
3819:10.1681/ASN.V1291872
1863:Potassium in biology
1486:By electrophysiology
1203:Biological chemistry
602:* = Adequate intake
340:cellular respiration
218:magnesium deficiency
195:and do not have the
129:Magnesium deficiency
6870:Beryllium poisoning
6697:Selenium in biology
6639:Elements in biology
6132:footnote references
6011:J Autism Dev Disord
5937:J Autism Dev Disord
5871:J Autism Dev Disord
5775:10.1104/pp.97.2.580
5552:10.1104/pp.67.5.985
5409:1974PNAS...71.1484H
5325:10.1104/pp.89.3.753
5276:10.1104/pp.74.4.956
5061:10.1104/pp.65.2.350
4973:(29): 20438–20443.
4904:1981PlSoi..61..447H
4818:2003COPB....6..263G
4714:2002PNAS...9915717H
4708:(24): 15717–15722.
4661:Dean, J.R. (1997).
4311:2001Natur.413..814S
3915:book.bionumbers.org
3859:2004PNAS..101.2894C
3372:1991Natur.350R.564T
2862:10.1155/2014/525249
2804:10.1093/ajcn/nqy274
2698:10.1155/2014/525249
2495:10.1038/ejcn.2012.4
1869:Selenium in biology
1600:electrical synapses
1542:coordination sphere
1535:Magnesium transport
1529:Magnesium transport
1245:Richard Willstätter
862:Whole wheat flour (
439:
204:dietary supplements
163:cerebral infarction
147:high blood pressure
7061:Biological systems
6964:Thallium poisoning
6667:Calcium in biology
6581:Calcium metabolism
6185:Healing Thresholds
6023:10.1007/BF01066428
5949:10.1007/BF01531686
4912:10.1007/BF02182025
4629:Hille, B. (1992).
3667:10.1104/pp.92.1.29
3416:Magnesium Research
3220:10.1007/BF02269144
3074:HealthAliciousNess
1816:Calcium in biology
1723:
1670:
1174:
821:cup) = 107 mg
808:cup) = 110 mg
795:cup) = 125 mg
779:cup) = 151 mg
763:cup) = 162 mg
747:cup) = 303 mg
636:
460:Birth to 6 months
434:
78:
32:
7028:
7027:
6974:Toxic heavy metal
6959:Selenium toxicity
6944:Mercury poisoning
6912:Fluoride toxicity
6907:Cadmium poisoning
6892:Chromium toxicity
6865:Arsenic poisoning
6707:Iodine in biology
6687:Copper in biology
6682:Cobalt in biology
6652:Sodium in biology
6606:
6605:
6602:
6601:
6527:Sodium metabolism
6512:
6511:
6443:Copper metabolism
6437:
6436:
6433:
6432:
6349:
6348:
6160:
6159:
6152:
5855:978-94-007-5561-1
5828:978-94-007-5560-4
5738:(12): 1088–1101.
5164:10.1071/AR9900511
5137:10.1071/AR9900499
4767:(14): 4605–4612.
4672:978-0-471-97255-6
4646:978-0-87893-322-8
4562:10.1021/bc000087d
3717:978-0-12-000722-6
3593:(10): 6963–6969.
3317:(14): 3973–3980.
3260:978-0-89573-003-9
3148:10.1172/JCI105151
2577:(12): 1354–1359.
2536:10.3390/nu8110739
2165:Arch. Intern. Med
2123:978-94-007-7499-5
2082:978-0-309-06403-3
2019:978-0-12-473542-2
1958:(10): 2618–2624.
1875:Sodium in biology
1822:Iodine in biology
1592:electronegativity
1519:mass spectrometry
1086:Whole wheat bread
1060:cup) = 32 mg
1044:cup) = 36 mg
1028:cup) = 37 mg
1012:cup) = 39 mg
996:cup) = 41 mg
980:cup) = 46 mg
958:cup) = 59 mg
942:cup) = 60 mg
926:cup) = 73 mg
904:cup) = 75 mg
888:cup) = 79 mg
872:cup) = 83 mg
859:cup) = 89 mg
843:cup) = 99 mg
737:seeds, no hulls (
698:whole-wheat bread
600:
599:
248:Magnesium orotate
230:magnesium sulfate
201:sustained-release
7068:
7046:Plant physiology
6939:Lithium toxicity
6897:Cobalt poisoning
6633:
6626:
6619:
6610:
6609:
6523:
6522:
6358:
6357:
6259:
6258:
6248:
6247:
6239:
6238:
6234:Transition metal
6226:Metal metabolism
6215:
6208:
6201:
6192:
6191:
6155:
6148:
6144:
6141:
6135:
6103:
6102:
6095:
6086:
6064:
6042:
6005:
5968:
5931:
5902:
5849:electronic-book
5848:
5797:
5796:
5786:
5763:Plant Physiology
5754:
5748:
5747:
5727:
5721:
5720:
5714:
5710:
5708:
5700:
5692:
5686:
5685:
5675:
5658:(4): 1407–1413.
5652:Plant Physiology
5643:
5637:
5634:
5628:
5627:
5619:
5610:
5609:
5580:
5574:
5573:
5563:
5540:Plant Physiology
5531:
5525:
5524:
5496:
5490:
5489:
5479:
5447:
5441:
5440:
5430:
5420:
5403:(4): 1484–1488.
5388:
5382:
5381:
5353:
5347:
5346:
5336:
5313:Plant Physiology
5304:
5298:
5297:
5287:
5264:Plant Physiology
5255:
5249:
5248:
5236:
5230:
5229:
5223:
5219:
5217:
5209:
5201:
5195:
5194:
5174:
5168:
5167:
5147:
5141:
5140:
5116:
5110:
5107:
5101:
5098:
5092:
5089:
5083:
5082:
5072:
5049:Plant Physiology
5040:
5034:
5033:
5023:
5014:(3–4): 233–241.
4999:
4993:
4992:
4982:
4958:
4952:
4949:
4943:
4942:
4930:
4924:
4923:
4887:
4878:
4877:
4875:
4851:
4838:
4837:
4801:
4795:
4794:
4784:
4752:
4746:
4745:
4735:
4725:
4693:
4687:
4684:
4678:
4676:
4657:
4651:
4650:
4634:
4626:
4617:
4616:
4580:
4574:
4573:
4545:
4539:
4538:
4502:
4496:
4495:
4467:
4461:
4460:
4454:
4450:
4448:
4440:
4439:. New York: VCH.
4432:
4423:
4422:
4416:
4412:
4410:
4402:
4401:. New York: VCH.
4394:
4385:
4384:
4348:
4339:
4338:
4319:10.1038/35101544
4305:(6858): 814–21.
4293:
4287:
4286:
4246:
4240:
4239:
4229:
4212:(8): 1760–1766.
4197:
4191:
4190:
4180:
4163:(5): 1233–1238.
4148:
4142:
4141:
4131:
4114:(9): 2665–2679.
4099:
4093:
4092:
4056:
4050:
4049:
4048:. New York: VCH.
4041:
4030:
4029:
4028:. New York: VCH.
4021:
4015:
4014:
3978:
3972:
3971:
3965:
3961:
3959:
3951:
3950:. New York: VCH.
3943:
3926:
3925:
3923:
3921:
3906:
3900:
3897:
3891:
3890:
3880:
3870:
3853:(9): 2894–2899.
3838:
3832:
3831:
3821:
3812:(9): 1872–1881.
3796:
3790:
3789:
3779:
3755:
3749:
3748:
3728:
3722:
3721:
3695:
3689:
3688:
3678:
3655:Plant Physiology
3646:
3640:
3639:
3619:
3613:
3612:
3602:
3574:
3568:
3567:
3557:
3548:(3): 1727–1732.
3533:
3527:
3526:
3516:
3499:(9): 4742–4751.
3484:
3478:
3477:
3441:
3432:
3431:
3411:
3402:
3401:
3383:
3381:10.1038/350564b0
3351:
3345:
3344:
3334:
3302:
3293:
3292:
3271:
3265:
3264:
3246:
3240:
3239:
3203:
3197:
3196:
3176:
3170:
3169:
3159:
3127:
3121:
3120:
3117:ndb.nal.usda.gov
3109:
3103:
3102:
3091:
3085:
3084:
3082:
3080:
3066:
3060:
3059:
3057:
3055:
3041:
3035:
3034:
3032:
3024:
3018:
3017:
3015:
3005:
2999:
2998:
2996:
2988:
2982:
2980:
2966:
2960:
2954:
2948:
2947:
2899:
2893:
2892:
2882:
2864:
2840:
2834:
2833:
2823:
2798:(6): 1249–1258.
2782:
2776:
2775:
2735:
2729:
2728:
2718:
2700:
2676:
2670:
2669:
2659:
2619:
2613:
2612:
2594:
2565:
2559:
2558:
2548:
2538:
2514:
2508:
2507:
2497:
2473:
2467:
2466:
2456:
2439:(11): CD000025.
2424:
2418:
2414:
2404:
2380:
2374:
2370:
2360:
2336:
2330:
2329:
2327:
2325:
2311:
2305:
2304:
2302:
2300:
2281:
2275:
2274:
2246:
2240:
2239:
2229:
2212:(4): 1169–1175.
2197:
2191:
2190:
2180:
2156:
2150:
2149:
2143:
2135:
2101:
2095:
2094:
2059:
2053:
2052:
2050:
2048:
2033:
2024:
2023:
2005:
1978:
1977:
1967:
1943:
1937:
1936:
1924:
1918:
1917:
1891:
1847:
1833:
1763:Magnesium stress
1580:cellular biology
1237:coordinating ion
1059:
1058:
1054:
1043:
1042:
1038:
1027:
1026:
1022:
1011:
1010:
1006:
995:
994:
990:
979:
978:
974:
957:
956:
952:
941:
940:
936:
925:
924:
920:
903:
902:
898:
887:
886:
882:
871:
870:
866:
858:
857:
853:
842:
841:
837:
820:
819:
815:
807:
806:
802:
794:
793:
789:
778:
777:
773:
762:
761:
757:
746:
745:
741:
639:Green vegetables
440:
433:
388:Immune function:
382:Muscle function:
275:calcium channels
269:Nerve conduction
264:
242:milk of magnesia
193:digestive system
7076:
7075:
7071:
7070:
7069:
7067:
7066:
7065:
7031:
7030:
7029:
7024:
7010:Oxygen toxicity
6983:
6902:Copper toxicity
6846:
6783:
6721:
6692:Zinc in biology
6677:Iron in biology
6640:
6637:
6607:
6598:
6575:
6557:
6539:
6508:
6481:Zinc metabolism
6475:
6429:
6375:
6345:
6317:Iron(III) oxide
6311:
6253:
6243:Iron metabolism
6228:
6219:
6156:
6145:
6139:
6136:
6117:
6108:This article's
6104:
6100:
6093:
5829:
5805:
5800:
5755:
5751:
5728:
5724:
5712:
5711:
5702:
5701:
5693:
5689:
5644:
5640:
5635:
5631:
5620:
5613:
5581:
5577:
5532:
5528:
5497:
5493:
5448:
5444:
5389:
5385:
5354:
5350:
5305:
5301:
5256:
5252:
5237:
5233:
5221:
5220:
5211:
5210:
5202:
5198:
5175:
5171:
5148:
5144:
5117:
5113:
5108:
5104:
5099:
5095:
5090:
5086:
5041:
5037:
5000:
4996:
4959:
4955:
4950:
4946:
4931:
4927:
4888:
4881:
4852:
4841:
4802:
4798:
4753:
4749:
4694:
4690:
4685:
4681:
4673:
4658:
4654:
4647:
4627:
4620:
4581:
4577:
4546:
4542:
4503:
4499:
4468:
4464:
4452:
4451:
4442:
4441:
4433:
4426:
4414:
4413:
4404:
4403:
4395:
4388:
4349:
4342:
4294:
4290:
4247:
4243:
4198:
4194:
4149:
4145:
4100:
4096:
4057:
4053:
4042:
4033:
4022:
4018:
3979:
3975:
3963:
3962:
3953:
3952:
3944:
3929:
3919:
3917:
3907:
3903:
3898:
3894:
3839:
3835:
3797:
3793:
3756:
3752:
3729:
3725:
3718:
3696:
3692:
3647:
3643:
3620:
3616:
3575:
3571:
3534:
3530:
3485:
3481:
3442:
3435:
3412:
3405:
3352:
3348:
3303:
3296:
3272:
3268:
3261:
3247:
3243:
3204:
3200:
3177:
3173:
3128:
3124:
3111:
3110:
3106:
3093:
3092:
3088:
3078:
3076:
3068:
3067:
3063:
3053:
3051:
3043:
3042:
3038:
3030:
3026:
3025:
3021:
3013:
3007:
3006:
3002:
2994:
2990:
2989:
2985:
2968:
2967:
2963:
2955:
2951:
2900:
2896:
2841:
2837:
2783:
2779:
2736:
2732:
2677:
2673:
2620:
2616:
2571:Eur J Clin Nutr
2566:
2562:
2515:
2511:
2482:Eur J Clin Nutr
2474:
2470:
2425:
2421:
2381:
2377:
2337:
2333:
2323:
2321:
2313:
2312:
2308:
2298:
2296:
2283:
2282:
2278:
2251:Int. J. Cardiol
2247:
2243:
2198:
2194:
2157:
2153:
2137:
2136:
2124:
2102:
2098:
2083:
2061:
2060:
2056:
2046:
2044:
2035:
2034:
2027:
2020:
2006:
1981:
1944:
1940:
1925:
1921:
1914:
1893:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1851:Myers' cocktail
1845:
1831:
1807:
1795:carbon fixation
1785:
1771:
1765:
1728:
1646:
1634:Casparian strip
1617:
1608:
1570:
1554:hydration shell
1537:
1531:
1505:
1488:
1475:
1466:
1461:
1452:
1416:
1395:
1382:
1346:
1307:
1288:
1277:
1268:
1253:
1233:
1205:
1185:Hypermagnesemia
1096:
1091:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1040:
1036:
1035:
1024:
1020:
1019:
1008:
1004:
1003:
992:
988:
987:
984:Sunflower seeds
976:
972:
971:
954:
950:
949:
938:
934:
933:
922:
918:
917:
900:
896:
895:
884:
880:
879:
868:
864:
863:
855:
851:
850:
839:
835:
834:
817:
813:
812:
804:
800:
799:
798:Oat bran, raw (
791:
787:
786:
775:
771:
770:
759:
755:
754:
743:
739:
738:
628:
615:
417:
406:
400:
355:
349:
317:
311:
303:
291:
271:
262:
256:quality of life
131:
125:
109:
17:
12:
11:
5:
7074:
7064:
7063:
7058:
7053:
7048:
7043:
7026:
7025:
7023:
7022:
7017:
7012:
7007:
7002:
6997:
6991:
6989:
6985:
6984:
6982:
6981:
6976:
6971:
6966:
6961:
6956:
6954:Nickel allergy
6951:
6949:Metal toxicity
6946:
6941:
6936:
6934:Lead poisoning
6931:
6930:
6929:
6922:Iron poisoning
6919:
6914:
6909:
6904:
6899:
6894:
6889:
6884:
6883:
6882:
6877:
6867:
6862:
6856:
6854:
6848:
6847:
6845:
6844:
6839:
6834:
6829:
6824:
6819:
6814:
6809:
6804:
6799:
6793:
6791:
6785:
6784:
6782:
6781:
6773:
6765:
6757:
6749:
6741:
6732:
6730:
6723:
6722:
6720:
6719:
6714:
6709:
6704:
6699:
6694:
6689:
6684:
6679:
6674:
6669:
6664:
6659:
6654:
6648:
6646:
6642:
6641:
6636:
6635:
6628:
6621:
6613:
6604:
6603:
6600:
6599:
6597:
6596:
6591:
6585:
6583:
6577:
6576:
6574:
6573:
6567:
6565:
6559:
6558:
6556:
6555:
6549:
6547:
6541:
6540:
6538:
6537:
6531:
6529:
6520:
6514:
6513:
6510:
6509:
6507:
6506:
6501:
6496:
6491:
6485:
6483:
6477:
6476:
6474:
6473:
6468:
6463:
6458:
6453:
6447:
6445:
6439:
6438:
6435:
6434:
6431:
6430:
6428:
6427:
6422:
6417:
6412:
6407:
6406:
6405:
6395:
6390:
6380:
6377:
6376:
6374:
6373:
6367:
6365:
6355:
6351:
6350:
6347:
6346:
6344:
6343:
6338:
6333:
6328:
6322:
6320:
6313:
6312:
6310:
6309:
6308:
6307:
6302:
6288:
6279:
6274:
6272:DMT1 (SLC11A2)
6268:
6266:
6263:Iron(II) oxide
6256:
6245:
6236:
6230:
6229:
6218:
6217:
6210:
6203:
6195:
6189:
6188:
6182:
6177:
6171:
6166:
6158:
6157:
6112:external links
6107:
6105:
6098:
6092:
6091:External links
6089:
6088:
6087:
6065:
6043:
6017:(1): 193–199.
6006:
5980:(5): 467–478.
5969:
5943:(2): 219–230.
5932:
5903:
5877:(4): 467–478.
5865:
5827:
5804:
5801:
5799:
5798:
5769:(2): 580–587.
5749:
5722:
5687:
5638:
5629:
5611:
5592:(1): 126–132.
5575:
5546:(5): 985–989.
5526:
5507:(3): 500–510.
5491:
5442:
5383:
5364:(2): 224–241.
5348:
5319:(3): 753–761.
5299:
5270:(4): 956–961.
5250:
5231:
5196:
5169:
5158:(3): 511–519.
5142:
5131:(3): 499–510.
5111:
5102:
5093:
5084:
5055:(2): 350–354.
5035:
4994:
4953:
4944:
4925:
4898:(3): 447–456.
4879:
4839:
4812:(3): 263–267.
4796:
4747:
4688:
4679:
4671:
4652:
4645:
4618:
4591:(3): 237–249.
4575:
4556:(2): 203–212.
4540:
4513:(3): 251–259.
4497:
4462:
4424:
4386:
4359:(3): 203–210.
4340:
4288:
4261:(5): 257–270.
4241:
4192:
4143:
4094:
4067:(3): 225–235.
4051:
4031:
4016:
3989:(3): 271–283.
3973:
3927:
3901:
3892:
3833:
3791:
3770:(6): 414–422.
3750:
3739:(2): 385–402.
3723:
3716:
3690:
3641:
3614:
3569:
3528:
3479:
3452:(3): 309–323.
3433:
3422:(3): 257–265.
3403:
3346:
3294:
3283:(4): 415–423.
3266:
3259:
3241:
3198:
3187:(6): 786–791.
3171:
3142:(3): 379–389.
3122:
3104:
3086:
3061:
3036:
3019:
3000:
2983:
2961:
2949:
2894:
2835:
2777:
2750:(3): 181–189.
2730:
2671:
2634:(1): e123182.
2614:
2560:
2509:
2468:
2419:
2375:
2331:
2306:
2276:
2241:
2192:
2151:
2122:
2096:
2081:
2054:
2025:
2018:
1979:
1938:
1919:
1913:978-0471743989
1912:
1885:
1883:
1880:
1879:
1878:
1872:
1866:
1860:
1854:
1848:
1839:
1834:
1825:
1819:
1813:
1806:
1803:
1783:
1767:Main article:
1764:
1761:
1727:
1724:
1659:transfer cells
1645:
1642:
1616:
1613:
1607:
1604:
1569:
1566:
1533:Main article:
1530:
1527:
1504:
1501:
1487:
1484:
1474:
1471:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1451:
1448:
1415:
1412:
1393:
1381:
1378:
1363:phosphorylated
1350:cell membranes
1345:
1342:
1305:
1287:
1284:
1276:
1273:
1266:
1252:
1249:
1232:
1229:
1214:in cells (per
1204:
1201:
1178:hypomagnesemia
1150:photosynthesis
1095:
1092:
1090:
1089:
1083:
1073:
1067:
1061:
1045:
1029:
1013:
997:
981:
965:
959:
943:
927:
911:
905:
889:
873:
860:
844:
828:
822:
811:Cocoa powder (
809:
796:
780:
764:
748:
731:
720:hypomagnesemia
675:dark chocolate
627:
624:
614:
611:
598:
597:
595:
593:
590:
587:
583:
582:
579:
576:
573:
570:
566:
565:
562:
559:
556:
553:
549:
548:
545:
542:
539:
536:
532:
531:
529:
527:
524:
521:
517:
516:
514:
512:
509:
506:
502:
501:
499:
497:
494:
491:
487:
486:
484:
482:
479:
476:
472:
471:
469:
467:
464:
461:
457:
456:
453:
450:
447:
444:
416:
413:
399:
396:
392:
391:
385:
379:
369:
366:
357:Magnesium and
348:
345:
310:
307:
302:
299:
290:
287:
270:
267:
222:hypomagnesemia
208:renal function
167:hypomagnesemia
124:
121:
108:
105:
101:photosynthesis
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
7073:
7062:
7059:
7057:
7054:
7052:
7049:
7047:
7044:
7042:
7039:
7038:
7036:
7021:
7018:
7016:
7015:Soil salinity
7013:
7011:
7008:
7006:
7003:
7001:
6998:
6996:
6993:
6992:
6990:
6986:
6980:
6979:Zinc toxicity
6977:
6975:
6972:
6970:
6969:Tin poisoning
6967:
6965:
6962:
6960:
6957:
6955:
6952:
6950:
6947:
6945:
6942:
6940:
6937:
6935:
6932:
6928:
6927:Iron overload
6925:
6924:
6923:
6920:
6918:
6917:Halotolerance
6915:
6913:
6910:
6908:
6905:
6903:
6900:
6898:
6895:
6893:
6890:
6888:
6885:
6881:
6878:
6876:
6873:
6872:
6871:
6868:
6866:
6863:
6861:
6858:
6857:
6855:
6853:
6849:
6843:
6840:
6838:
6835:
6833:
6830:
6828:
6825:
6823:
6820:
6818:
6815:
6813:
6810:
6808:
6805:
6803:
6800:
6798:
6795:
6794:
6792:
6790:
6786:
6780:
6778:
6774:
6772:
6770:
6766:
6764:
6762:
6758:
6756:
6754:
6750:
6748:
6746:
6742:
6740:
6738:
6734:
6733:
6731:
6728:
6724:
6718:
6715:
6713:
6710:
6708:
6705:
6703:
6700:
6698:
6695:
6693:
6690:
6688:
6685:
6683:
6680:
6678:
6675:
6673:
6670:
6668:
6665:
6663:
6660:
6658:
6655:
6653:
6650:
6649:
6647:
6643:
6634:
6629:
6627:
6622:
6620:
6615:
6614:
6611:
6595:
6592:
6590:
6587:
6586:
6584:
6582:
6578:
6572:
6569:
6568:
6566:
6564:
6560:
6554:
6551:
6550:
6548:
6546:
6542:
6536:
6533:
6532:
6530:
6528:
6524:
6521:
6519:
6515:
6505:
6502:
6500:
6497:
6495:
6492:
6490:
6487:
6486:
6484:
6482:
6478:
6472:
6469:
6467:
6464:
6462:
6461:Ceruloplasmin
6459:
6457:
6454:
6452:
6449:
6448:
6446:
6444:
6440:
6426:
6423:
6421:
6418:
6416:
6413:
6411:
6410:Ceruloplasmin
6408:
6404:
6401:
6400:
6399:
6396:
6394:
6391:
6389:
6385:
6382:
6381:
6378:
6372:
6369:
6368:
6366:
6363:
6359:
6356:
6352:
6342:
6339:
6337:
6334:
6332:
6329:
6327:
6324:
6323:
6321:
6318:
6314:
6306:
6303:
6301:
6298:
6297:
6296:
6292:
6289:
6287:
6283:
6280:
6278:
6275:
6273:
6270:
6269:
6267:
6264:
6260:
6257:
6255:
6252:Absorption in
6249:
6246:
6244:
6240:
6237:
6235:
6231:
6227:
6223:
6216:
6211:
6209:
6204:
6202:
6197:
6196:
6193:
6186:
6183:
6181:
6178:
6175:
6172:
6170:
6167:
6165:
6162:
6161:
6154:
6151:
6143:
6133:
6129:
6128:inappropriate
6125:
6121:
6115:
6113:
6106:
6097:
6096:
6084:
6080:
6076:
6072:
6066:
6062:
6058:
6054:
6050:
6044:
6040:
6036:
6032:
6028:
6024:
6020:
6016:
6012:
6007:
6003:
5999:
5995:
5991:
5987:
5983:
5979:
5975:
5970:
5966:
5962:
5958:
5954:
5950:
5946:
5942:
5938:
5933:
5929:
5925:
5921:
5917:
5913:
5909:
5904:
5900:
5896:
5892:
5888:
5884:
5880:
5876:
5872:
5866:
5864:
5860:
5856:
5852:
5846:
5842:
5838:
5834:
5830:
5824:
5820:
5816:
5812:
5807:
5806:
5794:
5790:
5785:
5780:
5776:
5772:
5768:
5764:
5760:
5753:
5745:
5741:
5737:
5733:
5726:
5718:
5706:
5698:
5691:
5683:
5679:
5674:
5669:
5665:
5661:
5657:
5653:
5649:
5642:
5633:
5625:
5618:
5616:
5607:
5603:
5599:
5595:
5591:
5587:
5579:
5571:
5567:
5562:
5557:
5553:
5549:
5545:
5541:
5537:
5530:
5522:
5518:
5514:
5510:
5506:
5502:
5495:
5487:
5483:
5478:
5473:
5469:
5465:
5461:
5457:
5453:
5446:
5438:
5434:
5429:
5424:
5419:
5414:
5410:
5406:
5402:
5398:
5394:
5387:
5379:
5375:
5371:
5367:
5363:
5359:
5352:
5344:
5340:
5335:
5330:
5326:
5322:
5318:
5314:
5310:
5303:
5295:
5291:
5286:
5281:
5277:
5273:
5269:
5265:
5261:
5254:
5246:
5242:
5235:
5227:
5215:
5207:
5200:
5192:
5188:
5184:
5180:
5173:
5165:
5161:
5157:
5153:
5146:
5138:
5134:
5130:
5126:
5122:
5115:
5106:
5097:
5088:
5080:
5076:
5071:
5066:
5062:
5058:
5054:
5050:
5046:
5039:
5031:
5027:
5022:
5017:
5013:
5009:
5005:
4998:
4990:
4986:
4981:
4976:
4972:
4968:
4964:
4957:
4948:
4940:
4936:
4929:
4921:
4917:
4913:
4909:
4905:
4901:
4897:
4893:
4886:
4884:
4874:
4869:
4865:
4861:
4857:
4850:
4848:
4846:
4844:
4835:
4831:
4827:
4823:
4819:
4815:
4811:
4807:
4800:
4792:
4788:
4783:
4778:
4774:
4770:
4766:
4762:
4758:
4751:
4743:
4739:
4734:
4729:
4724:
4719:
4715:
4711:
4707:
4703:
4699:
4692:
4683:
4674:
4668:
4664:
4656:
4648:
4642:
4638:
4633:
4625:
4623:
4614:
4610:
4606:
4602:
4598:
4594:
4590:
4586:
4579:
4571:
4567:
4563:
4559:
4555:
4551:
4544:
4536:
4532:
4528:
4524:
4520:
4516:
4512:
4508:
4501:
4493:
4489:
4485:
4481:
4477:
4473:
4466:
4458:
4446:
4438:
4431:
4429:
4420:
4408:
4400:
4393:
4391:
4382:
4378:
4374:
4370:
4366:
4362:
4358:
4354:
4347:
4345:
4336:
4332:
4328:
4324:
4320:
4316:
4312:
4308:
4304:
4300:
4292:
4284:
4280:
4276:
4272:
4268:
4264:
4260:
4256:
4252:
4245:
4237:
4233:
4228:
4223:
4219:
4215:
4211:
4207:
4203:
4196:
4188:
4184:
4179:
4174:
4170:
4166:
4162:
4158:
4154:
4147:
4139:
4135:
4130:
4125:
4121:
4117:
4113:
4109:
4105:
4098:
4090:
4086:
4082:
4078:
4074:
4070:
4066:
4062:
4055:
4047:
4040:
4038:
4036:
4027:
4020:
4012:
4008:
4004:
4000:
3996:
3992:
3988:
3984:
3977:
3969:
3957:
3949:
3942:
3940:
3938:
3936:
3934:
3932:
3916:
3912:
3905:
3896:
3888:
3884:
3879:
3874:
3869:
3864:
3860:
3856:
3852:
3848:
3844:
3837:
3829:
3825:
3820:
3815:
3811:
3807:
3803:
3795:
3787:
3783:
3778:
3773:
3769:
3765:
3761:
3754:
3746:
3742:
3738:
3734:
3727:
3719:
3713:
3709:
3705:
3701:
3694:
3686:
3682:
3677:
3672:
3668:
3664:
3660:
3656:
3652:
3645:
3637:
3633:
3629:
3625:
3618:
3610:
3606:
3601:
3596:
3592:
3588:
3587:J. Biol. Chem
3584:
3582:
3573:
3565:
3561:
3556:
3551:
3547:
3543:
3542:J. Biol. Chem
3539:
3532:
3524:
3520:
3515:
3510:
3506:
3502:
3498:
3494:
3490:
3483:
3475:
3471:
3467:
3463:
3459:
3455:
3451:
3447:
3440:
3438:
3429:
3425:
3421:
3417:
3410:
3408:
3399:
3395:
3391:
3387:
3382:
3377:
3373:
3369:
3366:(6319): 564.
3365:
3361:
3357:
3350:
3342:
3338:
3333:
3328:
3324:
3320:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3301:
3299:
3290:
3286:
3282:
3278:
3277:Botanica Acta
3270:
3262:
3256:
3252:
3245:
3237:
3233:
3229:
3225:
3221:
3217:
3213:
3209:
3202:
3194:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3175:
3167:
3163:
3158:
3153:
3149:
3145:
3141:
3137:
3133:
3126:
3118:
3114:
3108:
3100:
3096:
3090:
3075:
3071:
3065:
3050:
3046:
3040:
3029:
3023:
3012:
3011:
3004:
2993:
2987:
2978:
2976:
2971:
2965:
2958:
2953:
2945:
2941:
2937:
2933:
2929:
2925:
2921:
2917:
2913:
2909:
2905:
2898:
2890:
2886:
2881:
2876:
2872:
2868:
2863:
2858:
2854:
2850:
2846:
2839:
2831:
2827:
2822:
2817:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2801:
2797:
2793:
2789:
2781:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2761:
2757:
2753:
2749:
2745:
2741:
2734:
2726:
2722:
2717:
2712:
2708:
2704:
2699:
2694:
2690:
2686:
2682:
2675:
2667:
2663:
2658:
2653:
2649:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2633:
2629:
2625:
2618:
2610:
2606:
2602:
2598:
2593:
2588:
2584:
2580:
2576:
2572:
2564:
2556:
2552:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2528:
2524:
2520:
2513:
2505:
2501:
2496:
2491:
2487:
2483:
2479:
2472:
2464:
2460:
2455:
2450:
2446:
2442:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2423:
2417:
2412:
2408:
2403:
2398:
2395:(2): 165–77.
2394:
2390:
2386:
2379:
2373:
2368:
2364:
2359:
2354:
2351:(5): 835–49.
2350:
2346:
2342:
2335:
2320:
2316:
2310:
2294:
2290:
2286:
2280:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2260:
2256:
2252:
2245:
2237:
2233:
2228:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2196:
2188:
2184:
2179:
2174:
2171:(5): 459–65.
2170:
2166:
2162:
2155:
2147:
2141:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2100:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2078:
2074:
2073:10.17226/5776
2070:
2066:
2065:
2058:
2043:on 2007-12-25
2042:
2038:
2032:
2030:
2021:
2015:
2011:
2004:
2002:
2000:
1998:
1996:
1994:
1992:
1990:
1988:
1986:
1984:
1975:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1957:
1953:
1949:
1942:
1934:
1930:
1923:
1915:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1897:
1890:
1886:
1876:
1873:
1870:
1867:
1864:
1861:
1858:
1855:
1852:
1849:
1843:
1840:
1838:
1835:
1829:
1826:
1823:
1820:
1817:
1814:
1812:
1809:
1808:
1802:
1800:
1799:free radicals
1796:
1792:
1787:
1779:
1777:
1770:
1760:
1756:
1754:
1748:
1745:
1741:
1736:
1732:
1719:
1715:
1713:
1708:
1704:
1700:
1695:
1693:
1689:
1684:
1678:
1676:
1666:
1662:
1660:
1656:
1655:plasmodesmata
1650:
1641:
1637:
1635:
1630:
1625:
1623:
1612:
1603:
1601:
1597:
1596:NMDA channels
1593:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1574:
1565:
1561:
1559:
1555:
1550:
1547:
1543:
1536:
1526:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1510:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1483:
1481:
1470:
1456:
1447:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1411:
1409:
1405:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1387:
1377:
1375:
1370:
1369:
1364:
1360:
1355:
1351:
1341:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1322:
1320:
1316:
1315:autocatalysis
1311:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1291:Nucleic acids
1286:Nucleic acids
1283:
1281:
1272:
1269:
1265:
1259:
1258:Lewis acidity
1248:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1228:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1210:
1200:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1186:
1181:
1179:
1171:
1166:
1162:
1160:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1144:
1143:mitochondrial
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1123:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1107:
1105:
1101:
1087:
1084:
1081:
1077:
1074:
1071:
1068:
1065:
1062:
1049:
1046:
1033:
1030:
1017:
1014:
1001:
998:
985:
982:
969:
966:
963:
962:Peanut butter
960:
947:
944:
931:
928:
915:
912:
909:
906:
893:
890:
877:
874:
861:
848:
845:
832:
829:
826:
823:
810:
797:
784:
781:
768:
765:
752:
749:
736:
733:
732:
730:
727:
725:
724:fasciculation
721:
717:
712:
710:
706:
702:
699:
694:
690:
688:
684:
680:
676:
672:
671:pumpkin seeds
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
632:
623:
621:
610:
608:
603:
596:
594:
591:
588:
585:
584:
580:
577:
574:
571:
568:
567:
563:
560:
557:
554:
551:
550:
546:
543:
540:
537:
534:
533:
530:
528:
525:
522:
519:
518:
515:
513:
510:
507:
504:
503:
500:
498:
495:
492:
489:
488:
485:
483:
480:
477:
474:
473:
470:
468:
465:
462:
459:
458:
454:
451:
448:
445:
442:
441:
438:of magnesium
437:
432:
430:
426:
422:
412:
409:
405:
395:
389:
386:
383:
380:
377:
373:
370:
367:
364:
363:
362:
360:
354:
344:
342:
341:
336:
332:
328:
324:
322:
316:
315:Mitochondrion
306:
298:
296:
295:pre-eclampsia
286:
284:
280:
276:
266:
259:
257:
253:
249:
245:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
224:, as well as
223:
219:
215:
211:
209:
205:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
179:
175:
170:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
136:
130:
120:
118:
114:
104:
102:
98:
93:
91:
87:
83:
75:
71:
70:chlorophyll a
66:
62:
60:
56:
52:
51:polyphosphate
48:
44:
40:
36:
29:
25:
21:
6789:Deficiencies
6776:
6768:
6760:
6752:
6744:
6736:
6656:
6562:
6146:
6140:January 2018
6137:
6122:by removing
6109:
6077:(1): 53–62.
6074:
6070:
6055:(1): 46–52.
6052:
6048:
6014:
6010:
5977:
5973:
5940:
5936:
5914:(1): 70–84.
5911:
5907:
5874:
5870:
5810:
5766:
5762:
5752:
5735:
5731:
5725:
5696:
5690:
5655:
5651:
5641:
5632:
5623:
5589:
5585:
5578:
5543:
5539:
5529:
5504:
5500:
5494:
5462:(1): 48–58.
5459:
5455:
5445:
5400:
5396:
5386:
5361:
5357:
5351:
5316:
5312:
5302:
5267:
5263:
5253:
5244:
5240:
5234:
5205:
5199:
5182:
5178:
5172:
5155:
5151:
5145:
5128:
5124:
5120:
5114:
5105:
5096:
5087:
5052:
5048:
5038:
5011:
5007:
4997:
4970:
4966:
4956:
4947:
4938:
4934:
4928:
4895:
4891:
4863:
4859:
4809:
4805:
4799:
4764:
4760:
4750:
4705:
4701:
4691:
4682:
4662:
4655:
4636:
4588:
4584:
4578:
4553:
4549:
4543:
4510:
4506:
4500:
4475:
4471:
4465:
4436:
4398:
4356:
4352:
4302:
4298:
4291:
4258:
4254:
4244:
4209:
4205:
4195:
4160:
4156:
4146:
4111:
4107:
4097:
4064:
4060:
4054:
4045:
4025:
4019:
3986:
3982:
3976:
3947:
3918:. Retrieved
3914:
3904:
3895:
3850:
3846:
3836:
3809:
3805:
3794:
3767:
3763:
3753:
3736:
3732:
3726:
3699:
3693:
3661:(1): 29–36.
3658:
3654:
3644:
3627:
3623:
3617:
3590:
3586:
3580:
3572:
3545:
3541:
3531:
3496:
3492:
3482:
3449:
3445:
3419:
3415:
3363:
3359:
3349:
3314:
3311:EMBO Journal
3310:
3280:
3276:
3269:
3250:
3244:
3211:
3207:
3201:
3184:
3180:
3174:
3139:
3135:
3125:
3116:
3107:
3098:
3089:
3077:. Retrieved
3073:
3064:
3052:. Retrieved
3048:
3039:
3022:
3009:
3003:
2986:
2973:
2964:
2952:
2914:(1): 18–23.
2911:
2907:
2897:
2852:
2848:
2838:
2795:
2791:
2780:
2747:
2743:
2733:
2688:
2684:
2674:
2631:
2627:
2617:
2592:10447/297358
2574:
2570:
2563:
2526:
2522:
2512:
2488:(4): 411–8.
2485:
2481:
2471:
2436:
2432:
2422:
2392:
2388:
2378:
2348:
2344:
2334:
2322:. Retrieved
2318:
2309:
2297:. Retrieved
2288:
2279:
2257:(2): 293–5.
2254:
2250:
2244:
2209:
2205:
2195:
2168:
2164:
2154:
2105:
2099:
2063:
2057:
2045:. Retrieved
2041:the original
2009:
1955:
1951:
1941:
1932:
1928:
1922:
1895:
1889:
1857:Osteoporosis
1828:Ion channels
1790:
1788:
1780:
1772:
1757:
1749:
1743:
1739:
1737:
1733:
1729:
1707:chloroplasts
1702:
1696:
1679:
1674:
1671:
1651:
1647:
1638:
1626:
1621:
1618:
1609:
1571:
1562:
1557:
1551:
1538:
1513:
1506:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1479:
1476:
1467:
1453:
1446:prefers Mn.
1444:retroviruses
1428:lentiviruses
1417:
1403:
1390:
1383:
1366:
1359:carboxylated
1347:
1334:major groove
1326:cell nucleus
1323:
1302:
1289:
1278:
1263:
1254:
1234:
1206:
1196:
1192:
1182:
1175:
1161:conditions.
1147:
1124:
1120:Calvin cycle
1116:chloroplasts
1114:fixation in
1108:
1097:
728:
713:
709:"soft" water
705:"Hard" water
703:
695:
691:
687:whole grains
653:(especially
637:
626:Food sources
616:
604:
601:
592:320 mg
589:420 mg
581:320 mg
578:360 mg
575:320 mg
572:420 mg
569:31–50 years
564:310 mg
561:350 mg
558:310 mg
555:400 mg
552:19–30 years
547:360 mg
544:400 mg
541:360 mg
538:410 mg
535:14–18 years
526:240 mg
523:240 mg
511:130 mg
508:130 mg
481:75 mg*
478:75 mg*
475:7–12 months
466:30 mg*
463:30 mg*
418:
410:
407:
404:Testosterone
398:Testosterone
393:
387:
381:
372:Bone health:
371:
356:
338:
333:, primarily
327:Mitochondria
325:
318:
309:Mitochondria
304:
292:
289:Hypertension
279:calcium ions
272:
260:
246:
234:parenterally
212:
197:side-effects
171:
159:osteoporosis
132:
123:Human health
110:
94:
85:
79:
33:
6880:Berylliosis
6535:Na/K-ATPase
6518:Electrolyte
6425:Lactoferrin
6420:Hemosiderin
6393:Hemojuvelin
6291:Transferrin
6071:Magnes. Res
6049:Magnes. Res
5857:electronic-
5713:|work=
5222:|work=
5185:: 335–361.
4453:|work=
4415:|work=
3964:|work=
3630:: 142–149.
3214:: 185–296.
2970:"Magnesium"
2957:"Magnesium"
2628:JCI Insight
2529:(11): 739.
1703:A. thaliana
1629:rhizosphere
1374:chloroplast
1348:Biological
1241:chlorophyll
1231:Chlorophyll
1154:chlorophyll
930:Black beans
892:Swiss chard
783:Brazil nuts
685:, and some
655:Brazil nuts
647:chlorophyll
520:9–13 years
496:80 mg
493:80 mg
238:Epsom salts
153:disorders,
113:hydrosphere
97:chlorophyll
90:nucleotides
7041:Physiology
7035:Categories
6827:Molybdenum
6282:Hephaestin
6222:Metabolism
5974:Psychiatry
5803:References
4941:: 335–343.
4892:Plant Soil
4860:New Phytol
3733:Pediatrics
3079:17 January
2855:: 525249.
2691:: 525249.
2324:14 January
2299:14 January
2047:17 January
1935:: 431–433.
1714:membrane.
1546:Paramecium
1426:enzyme of
1354:cell walls
1220:metabolism
1193:magnesuria
1064:Fish sauce
1050:, cooked (
1034:, boiled (
1018:, boiled (
1002:, boiled (
986:, hulled (
948:, cooked (
932:, boiled (
894:, boiled (
878:, boiled (
751:Chia seeds
677:, roasted
586:51+ years
505:4–8 years
490:1–3 years
455:Lactation
452:Pregnancy
178:amino acid
7051:Magnesium
6822:Manganese
6817:Potassium
6771:hosphorus
6403:Aconitase
6124:excessive
5863:1868-0402
5837:1559-0836
5715:ignored (
5705:cite book
5224:ignored (
5214:cite book
4866:: 47–57.
4585:BioMetals
4507:BioMetals
4455:ignored (
4445:cite book
4417:ignored (
4407:cite book
4353:BioMetals
4335:205022511
4061:BioMetals
3983:BioMetals
3966:ignored (
3956:cite book
3446:BioMetals
2928:1559-0720
2871:1687-8337
2812:0002-9165
2764:1945-1997
2707:1687-8337
2648:2379-3708
2569:trials".
2523:Nutrients
2416:Full Text
2372:Full Text
2140:cite book
1776:chlorosis
1712:thylakoid
1699:H-ATPases
1683:H-ATPases
1573:Magnesium
1420:manganese
1414:Manganese
1408:chelators
1399:enzymatic
1330:cytoplasm
1319:ribozymes
1310:ribosomes
1000:Chickpeas
908:Chocolate
767:Buckwheat
359:vitamin D
353:Vitamin D
347:Vitamin D
331:nutrients
226:eclampsia
185:glycinate
183:(such as
155:migraines
117:catalysis
80:Over 300
35:Magnesium
24:Magnesium
6852:Toxicity
6837:Selenium
6797:Chromium
6645:Elements
6384:Hepcidin
6371:Ferritin
6341:Ferritin
6331:Integrin
6277:Ferritin
6254:duodenum
6083:16846101
6061:16846100
6039:21450498
5928:15919178
5899:39143708
5845:23595671
5793:16668438
5682:16667193
5606:12646275
5570:16661806
5343:16666617
5294:16663541
5079:16661188
5030:42750442
4989:10400670
4920:12271923
4834:12753976
4791:15231793
4742:12422021
4613:27877817
4605:12206390
4570:11312681
4535:20873166
4527:12206391
4381:31622669
4373:12206387
4327:11677599
4283:37427719
4236:10734195
4089:40446313
4081:12206389
4011:20835803
4003:12206393
3920:23 March
3887:14976260
3828:11518780
3786:10878661
3685:16667261
3474:32535554
3466:12206396
3341:10406802
3236:43703938
3166:14271298
2944:23626641
2936:20352370
2889:24723948
2830:30541089
2772:29480918
2725:24723948
2666:30626750
2609:24998868
2601:27530471
2555:27869762
2504:22318649
2463:21069663
2411:20152124
2367:15572114
2319:ClinCalc
2293:Archived
2289:ClinCalc
2271:18281113
2236:19211496
2187:18332289
2132:24470089
2091:23115811
1805:See also
1692:antiport
1588:bivalent
1578:(Mg) in
1521:(MS) or
1386:proteins
1380:Proteins
1338:duplexes
1317:of many
1139:knockout
1131:bacteria
1127:nutrient
1080:espresso
916:, firm (
679:soybeans
641:such as
613:Labeling
189:lysinate
181:chelates
174:diarrhea
143:diabetes
107:Function
39:nutrient
6988:Related
6763:itrogen
6747:ydrogen
6504:SLC39A4
6499:SLC30A1
6466:SLC31A1
6118:Please
6110:use of
6031:8463199
5994:3886023
5965:7898722
5957:6765503
5891:9261669
5784:1081046
5673:1062198
5477:8333438
5437:4524652
5405:Bibcode
5378:4747067
5334:1055918
5285:1066800
4900:Bibcode
4814:Bibcode
4710:Bibcode
4492:2923192
4307:Bibcode
4275:7000968
4187:7868596
4138:6856472
3855:Bibcode
3745:5637791
3676:1062243
3609:1551905
3581:in vivo
3564:9430719
3523:2548998
3428:8292500
3398:4346618
3390:2017256
3368:Bibcode
3332:1171473
3228:4865748
2997:. 2017.
2880:3958794
2821:6693398
2716:3958794
2657:6485371
2546:5133122
2454:7061250
2227:2663594
1974:4968384
1688:symport
1491:cells.
1368:E. coli
1260:of Mg (
1251:Enzymes
1239:in the
1224:enzymes
1197:E. coli
1170:chlorin
1159:drought
1118:in the
1100:animals
1055:⁄
1048:Oatmeal
1039:⁄
1032:Lentils
1023:⁄
1007:⁄
991:⁄
975:⁄
968:Walnuts
953:⁄
937:⁄
921:⁄
899:⁄
883:⁄
876:Spinach
867:⁄
854:⁄
847:Cashews
838:⁄
831:Almonds
825:Halibut
816:⁄
803:⁄
790:⁄
774:⁄
769:flour (
758:⁄
742:⁄
735:Pumpkin
716:calcium
669:(e.g.,
663:almonds
659:cashews
643:spinach
449:Female
376:calcium
335:glucose
283:neurons
151:anxiety
82:enzymes
74:chlorin
6832:Sodium
6812:Iodine
6802:Copper
6727:CHONPS
6081:
6059:
6037:
6029:
6002:631153
6000:
5992:
5963:
5955:
5926:
5897:
5889:
5861:
5853:
5843:
5835:
5825:
5791:
5781:
5680:
5670:
5604:
5568:
5561:425814
5558:
5521:880298
5519:
5484:
5474:
5435:
5428:388254
5425:
5376:
5341:
5331:
5292:
5282:
5077:
5070:440325
5067:
5028:
4987:
4918:
4832:
4789:
4782:438605
4779:
4740:
4733:137782
4730:
4669:
4643:
4611:
4603:
4568:
4533:
4525:
4490:
4379:
4371:
4333:
4325:
4299:Nature
4281:
4273:
4234:
4227:102818
4224:
4185:
4178:176728
4175:
4136:
4129:325916
4126:
4087:
4079:
4009:
4001:
3885:
3878:365716
3875:
3826:
3784:
3743:
3714:
3683:
3673:
3607:
3562:
3521:
3514:210275
3511:
3472:
3464:
3426:
3396:
3388:
3360:Nature
3339:
3329:
3257:
3234:
3226:
3164:
3157:292488
3154:
3054:16 May
2942:
2934:
2926:
2887:
2877:
2869:
2828:
2818:
2810:
2770:
2762:
2723:
2713:
2705:
2664:
2654:
2646:
2607:
2599:
2553:
2543:
2502:
2461:
2451:
2409:
2389:Neuron
2365:
2345:Neuron
2269:
2234:
2224:
2206:Stroke
2185:
2130:
2120:
2089:
2079:
2016:
1972:
1910:
1791:et al.
1744:et al.
1740:et al.
1675:et al.
1622:et al.
1558:et al.
1507:Flame
1480:et al.
1404:et al.
1189:kidney
1112:carbon
1104:plants
1076:Coffee
946:Quinoa
263:
161:, and
135:spasms
6779:ulfur
6755:xygen
6739:arbon
6471:ATOX1
6456:ATP7B
6451:ATP7A
6354:Other
6035:S2CID
5998:S2CID
5961:S2CID
5895:S2CID
5486:10009
5026:S2CID
4916:S2CID
4609:S2CID
4531:S2CID
4377:S2CID
4331:S2CID
4279:S2CID
4085:S2CID
4007:S2CID
3470:S2CID
3394:S2CID
3232:S2CID
3031:(PDF)
3014:(PDF)
2995:(PDF)
2940:S2CID
2605:S2CID
1882:Notes
1430:like
1216:moles
1209:metal
1172:group
1135:yeast
667:seeds
446:Male
281:into
76:group
6842:Zinc
6807:Iron
6494:TMC8
6489:TMC6
6388:HAMP
6305:TFR2
6300:TFR1
6079:PMID
6057:PMID
6027:PMID
5990:PMID
5953:PMID
5924:PMID
5887:PMID
5859:ISSN
5851:ISBN
5841:PMID
5833:ISSN
5823:ISBN
5789:PMID
5717:help
5678:PMID
5602:PMID
5566:PMID
5517:PMID
5482:PMID
5433:PMID
5374:PMID
5339:PMID
5290:PMID
5226:help
5075:PMID
4985:PMID
4830:PMID
4787:PMID
4738:PMID
4702:PNAS
4667:ISBN
4641:ISBN
4601:PMID
4566:PMID
4523:PMID
4488:PMID
4457:help
4419:help
4369:PMID
4323:PMID
4271:PMID
4232:PMID
4183:PMID
4134:PMID
4077:PMID
3999:PMID
3968:help
3922:2017
3883:PMID
3824:PMID
3782:PMID
3741:PMID
3712:ISBN
3681:PMID
3605:PMID
3560:PMID
3519:PMID
3462:PMID
3424:PMID
3386:PMID
3337:PMID
3255:ISBN
3224:PMID
3162:PMID
3081:2018
3056:2020
2932:PMID
2924:ISSN
2885:PMID
2867:ISSN
2853:2014
2826:PMID
2808:ISSN
2768:PMID
2760:ISSN
2721:PMID
2703:ISSN
2689:2014
2662:PMID
2644:ISSN
2597:PMID
2551:PMID
2500:PMID
2459:PMID
2437:2010
2407:PMID
2363:PMID
2326:2024
2301:2024
2267:PMID
2232:PMID
2183:PMID
2146:link
2128:PMID
2118:ISBN
2087:PMID
2077:ISBN
2049:2018
2014:ISBN
1970:PMID
1908:ISBN
1576:ions
1552:The
1438:and
1361:and
1352:and
1328:and
1297:and
1133:and
1070:Milk
1016:Kale
914:Tofu
683:bran
661:and
651:Nuts
605:The
443:Age
220:and
99:and
57:and
43:cell
6415:HFE
6293:to
6126:or
6019:doi
5982:doi
5945:doi
5916:doi
5879:doi
5815:doi
5779:PMC
5771:doi
5740:doi
5668:PMC
5660:doi
5594:doi
5590:412
5556:PMC
5548:doi
5509:doi
5505:460
5472:PMC
5464:doi
5460:449
5423:PMC
5413:doi
5366:doi
5362:314
5329:PMC
5321:doi
5280:PMC
5272:doi
5187:doi
5160:doi
5133:doi
5065:PMC
5057:doi
5016:doi
5012:24C
4975:doi
4971:274
4908:doi
4868:doi
4864:146
4822:doi
4777:PMC
4769:doi
4765:186
4728:PMC
4718:doi
4632:"2"
4593:doi
4558:doi
4515:doi
4480:doi
4476:256
4361:doi
4315:doi
4303:413
4263:doi
4222:PMC
4214:doi
4173:PMC
4165:doi
4161:177
4124:PMC
4116:doi
4069:doi
3991:doi
3873:PMC
3863:doi
3851:101
3814:doi
3772:doi
3704:doi
3671:PMC
3663:doi
3632:doi
3595:doi
3591:267
3550:doi
3546:273
3509:PMC
3501:doi
3497:171
3454:doi
3376:doi
3364:350
3327:PMC
3319:doi
3285:doi
3281:103
3216:doi
3189:doi
3152:PMC
3144:doi
2916:doi
2912:140
2875:PMC
2857:doi
2816:PMC
2800:doi
2796:108
2752:doi
2748:118
2711:PMC
2693:doi
2652:PMC
2636:doi
2587:hdl
2579:doi
2541:PMC
2531:doi
2490:doi
2449:PMC
2441:doi
2397:doi
2353:doi
2259:doi
2255:131
2222:PMC
2214:doi
2173:doi
2169:168
2110:doi
2069:doi
1960:doi
1956:243
1900:doi
1440:FIV
1436:SIV
1432:HIV
1299:RNA
1295:DNA
1280:ATP
1212:ion
1098:In
753:, (
673:),
665:),
86:all
59:RNA
55:DNA
7037::
6224::
6075:19
6073:.
6053:19
6051:.
6033:.
6025:.
6015:23
6013:.
5996:.
5988:.
5978:20
5976:.
5959:.
5951:.
5941:11
5939:.
5922:.
5912:27
5910:.
5893:.
5885:.
5875:27
5873:.
5839:.
5831:.
5821:.
5787:.
5777:.
5767:97
5765:.
5761:.
5734:.
5709::
5707:}}
5703:{{
5676:.
5666:.
5656:91
5654:.
5650:.
5614:^
5600:.
5588:.
5564:.
5554:.
5544:67
5542:.
5538:.
5515:.
5503:.
5480:.
5470:.
5458:.
5454:.
5431:.
5421:.
5411:.
5401:71
5399:.
5395:.
5372:.
5360:.
5337:.
5327:.
5317:89
5315:.
5311:.
5288:.
5278:.
5268:74
5266:.
5262:.
5245:36
5243:.
5218::
5216:}}
5212:{{
5183:37
5181:.
5156:41
5154:.
5129:41
5127:.
5073:.
5063:.
5053:65
5051:.
5047:.
5024:.
5010:.
5006:.
4983:.
4969:.
4965:.
4937:.
4914:.
4906:.
4896:61
4894:.
4882:^
4862:.
4858:.
4842:^
4828:.
4820:.
4808:.
4785:.
4775:.
4763:.
4759:.
4736:.
4726:.
4716:.
4706:99
4704:.
4700:.
4635:.
4621:^
4607:.
4599:.
4589:15
4587:.
4564:.
4554:12
4552:.
4529:.
4521:.
4511:15
4509:.
4486:.
4474:.
4449::
4447:}}
4443:{{
4427:^
4411::
4409:}}
4405:{{
4389:^
4375:.
4367:.
4357:15
4355:.
4343:^
4329:.
4321:.
4313:.
4301:.
4277:.
4269:.
4259:18
4257:.
4253:.
4230:.
4220:.
4210:28
4208:.
4204:.
4181:.
4171:.
4159:.
4155:.
4132:.
4122:.
4112:11
4110:.
4106:.
4083:.
4075:.
4065:15
4063:.
4034:^
4005:.
3997:.
3987:15
3985:.
3960::
3958:}}
3954:{{
3930:^
3913:.
3881:.
3871:.
3861:.
3849:.
3845:.
3822:.
3810:12
3808:.
3804:.
3780:.
3766:.
3762:.
3737:41
3735:.
3710:.
3679:.
3669:.
3659:92
3657:.
3653:.
3628:71
3626:.
3603:.
3589:.
3585:.
3558:.
3544:.
3540:.
3517:.
3507:.
3495:.
3491:.
3468:.
3460:.
3450:15
3448:.
3436:^
3418:.
3406:^
3392:.
3384:.
3374:.
3362:.
3358:.
3335:.
3325:.
3315:18
3313:.
3309:.
3297:^
3279:.
3230:.
3222:.
3212:59
3210:.
3185:17
3183:.
3160:.
3150:.
3140:44
3138:.
3134:.
3115:.
3097:.
3072:.
3047:.
2972:.
2938:.
2930:.
2922:.
2910:.
2906:.
2883:.
2873:.
2865:.
2851:.
2847:.
2824:.
2814:.
2806:.
2794:.
2790:.
2766:.
2758:.
2746:.
2742:.
2719:.
2709:.
2701:.
2687:.
2683:.
2660:.
2650:.
2642:.
2630:.
2626:.
2603:.
2595:.
2585:.
2575:70
2573:.
2549:.
2539:.
2525:.
2521:.
2498:.
2486:66
2484:.
2480:.
2457:.
2447:.
2435:.
2431:.
2405:.
2393:65
2391:.
2387:.
2361:.
2349:44
2347:.
2343:.
2317:.
2291:.
2287:.
2265:.
2253:.
2230:.
2220:.
2210:40
2208:.
2204:.
2181:.
2167:.
2163:.
2142:}}
2138:{{
2126:.
2116:.
2085:.
2075:.
2028:^
1982:^
1968:.
1954:.
1950:.
1933:94
1931:.
1906:.
1782:NH
1602:.
1584:Ca
1434:,
1340:.
1122:.
1078:,
681:,
657:,
622:.
431:.
323:.
258:.
187:,
157:,
149:,
145:,
141:,
103:.
61:.
6777:S
6769:P
6761:N
6753:O
6745:H
6737:C
6632:e
6625:t
6618:v
6386:/
6364::
6319::
6284:/
6265::
6214:e
6207:t
6200:v
6153:)
6147:(
6142:)
6138:(
6134:.
6116:.
6085:.
6063:.
6041:.
6021::
6004:.
5984::
5967:.
5947::
5930:.
5918::
5901:.
5881::
5847:.
5817::
5795:.
5773::
5746:.
5742::
5736:8
5719:)
5684:.
5662::
5608:.
5596::
5572:.
5550::
5523:.
5511::
5488:.
5466::
5439:.
5415::
5407::
5380:.
5368::
5345:.
5323::
5296:.
5274::
5247:.
5228:)
5193:.
5189::
5166:.
5162::
5139:.
5135::
5081:.
5059::
5032:.
5018::
4991:.
4977::
4939:5
4922:.
4910::
4902::
4876:.
4870::
4836:.
4824::
4816::
4810:6
4793:.
4771::
4744:.
4720::
4712::
4675:.
4649:.
4615:.
4595::
4572:.
4560::
4537:.
4517::
4494:.
4482::
4459:)
4421:)
4383:.
4363::
4337:.
4317::
4309::
4285:.
4265::
4238:.
4216::
4189:.
4167::
4140:.
4118::
4091:.
4071::
4013:.
3993::
3970:)
3924:.
3889:.
3865::
3857::
3830:.
3816::
3788:.
3774::
3768:8
3747:.
3720:.
3706::
3687:.
3665::
3638:.
3634::
3611:.
3597::
3583:"
3566:.
3552::
3525:.
3503::
3476:.
3456::
3430:.
3420:6
3400:.
3378::
3370::
3343:.
3321::
3291:.
3287::
3263:.
3238:.
3218::
3195:.
3191::
3168:.
3146::
3119:.
3101:.
3083:.
3058:.
3033:.
2979:.
2946:.
2918::
2891:.
2859::
2832:.
2802::
2774:.
2754::
2727:.
2695::
2668:.
2638::
2632:4
2611:.
2589::
2581::
2557:.
2533::
2527:8
2506:.
2492::
2465:.
2443::
2413:.
2399::
2369:.
2355::
2328:.
2303:.
2273:.
2261::
2238:.
2216::
2189:.
2175::
2148:)
2134:.
2112::
2093:.
2071::
2051:.
2022:.
1976:.
1962::
1916:.
1902::
1784:4
1394:a
1391:K
1388:(
1306:m
1303:T
1267:a
1264:K
1262:p
1057:2
1053:1
1041:2
1037:1
1025:2
1021:1
1009:2
1005:1
993:4
989:1
977:4
973:1
970:(
955:2
951:1
939:2
935:1
923:2
919:1
901:2
897:1
885:2
881:1
869:2
865:1
856:4
852:1
849:(
840:4
836:1
833:(
818:4
814:1
805:2
801:1
792:4
788:1
785:(
776:2
772:1
760:4
756:1
744:4
740:1
26:–
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.