692:
more than 300 m (1,000 ft) in depth. The depth of the actual valley walls at the seashore range from 300 m (1,000 ft) at the Waipiʻo Valley
Lookout at the southeastern corner of Kohala mountain, to a high of over 500 m (1,600 ft) in Honopue, then diminishing to less than 150 m (490 ft) at Pololu Lookout at the northern end of the valleys. In the back, deeper in the mountain, all of the valleys have sheer walls well in excess of 1,000 m (3,300 ft). Numerous spectacular waterfalls cascade or fall over these cliffs. Some, such as Hi'ilawe Falls in Waipi'o valley, have single drops exceeding 300 m (1,000 ft).
148:
470:
double set of samples, collected from the western part in 1996, was measured to be 80,000 years in age. The samples have been treated with skepticism by the scientific community, and their ages have been directly challenged. The rocks collected from the west site have not been tested by subsequent experiments. The lava samples collected from the eastern site were allegedly found under a Mauna Loa lava flow, which had been previously dated to 187,000 years. The Kohala lava flows could be as young as 120,000 years although they may be even younger.
155:
1059:
688:
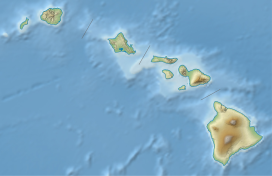
capture; Waipiʻo, the largest, at some point drained
Waimanu Valley as well, and the former headwaters of Waimanu are now one of its branches. Waimanu valley, cut off from its headwaters to the summit and left with Wai'ilikahi as its main tributary, still had managed to form a substantial floodplain, although less than half the size of Waipiʻo. Honokane Nui, the third largest valley, has its drainage almost exclusively from the north side of the summit, and as a result is a deep, long, narrow bottomed valley with little habitable floodplain.
2479:
388:
748:
1038:. The optimal rainfall level for the sweet potato lies between 30 and 50 inches (76–127 cm) per year. A combination of factors makes the rainfall at Kohala variable both from location to location and from year to year. In addition, Kohala is buffeted by strong winds, which are directly correlated to soil erosion; ancient farmers utilized a series of earthen embarkments and stone walls to protect their crops. This technique has been shown to reduce wind by at least 20–30 percent.
1102:, community-based organization for research and education. It was established as a response to requests by island residents to create an educational and employment opportunity related to Hawaii's natural and cultural significance. The center's mission is "to respectfully engage the Island of Hawaiʻi as an extraordinary and vibrant research and learning laboratory for humanity." The land around Kohala is administered as two districts, North Kohala and South Kohala, of the
978:
621:
1164:
485:, 61 m (200 ft) above the current sea level. The team dated the fossils and nearby volcanic rock at about 120,000 years old. Based on the rate of Kohala's subsidence over the past 475,000 years, it was estimated that the fossils were deposited at a height of about 500 m (1,600 ft), well out of reach of storms and far above the normal sea level at the time. The timing corresponds with the last great landslide of nearby
1178:
826:
29:
727:
Iki - as well as the many smaller gulches which are not yet valleys, are deprived of groundwater by the orientation of the rift zone and its dikes. Without the large amount of water that is received by the bigger valleys, these valleys grow far more slowly. Due to its topography as essentially a flat crater floor surrounded by cones and fault scarps, the main caldera is affected relatively little by erosion from water.
719:. The dikes act as impermeable vertical walls through which groundwater cannot flow. Deep layers of ash compact into impermeable layers between lava flows, preventing percolation of the rainwater. Rainwater that would ordinarily seep right through the ground gets trapped in the dike "reservoirs," located well above sea level. The groundwater is confined to a flow along the dike until it finds a means to escape.
489:. Researchers hypothesize that the underwater landslide from the nearby volcano triggered a gigantic tsunami, which swept up coral and other small marine organisms, depositing them on the western face of Kohala. Mauna Loa, an active volcano, has since repaired its flank. Marine geologist Tappin believes that a "future collapse on this volcano, with the potential for mega-tsunami generation, is almost certain."
734:, which causes the valley walls to frequently collapse, accelerating valley development. This abundance of surface water inspired the first of Kohala's three massive irrigation diversion "ditches", the Upper Hamakua Ditch, although the water was initially used for transporting ("fluming") sugarcane to the mills rather than irrigation. Surface water supplies, however, were not stable enough for the large scale
446:
794:
portion of the precipitation is let down to the ground slowly by this three-story cover of trees, bushes, and floor plants and in this manner the rain, falling on a well-forested area, is held back and instead of rushing down to the sea rapidly in the form of destructive floods, is fed gradually to the springs and to the underground artesian basins where it is held for use over a much longer interval...
664:
612:, arranged parallel to the northern coast. The faults were originally regarded to be a direct result of the collapse; however scientists note the fault lines do not go all the way to the coast but are arranged tightly clustered around the caldera. This indicates that the fault lines may have been caused indirectly, possibly due to the sudden release of stress during the event.
426:. However, based on a sharp increase of incline on the submarine slope of the volcano at a depth of 1,000 m (3,300 ft), scientists estimate that in its prime the portion of Kohala that was above the water was more than 50 km (31 mi) wide. Geologists estimate that the volcano was once about twice its current size.
461:. Debris from the slide was found on the ocean floor up to 130 km (81 mi) away from the volcano. Twenty kilometers wide at the shoreline, the landslide cut back to the summit of the volcano, and is partially, if not largely, responsible for the volcano losing 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in height since then. The famous
2162:
715:. Rainwater easily seeps into the lava, creating a large lens of fresh water below the island surface. In most places, the top of the water table is just a few feet from sea level, as the fresh water lens is floating on salt water. Unlike porous lava flows, however, dikes cool underground into dense rock with few cracks and
660:). Northeast of the Kohala summit, where the most rainfall occurs, the faulted structure prevents summit rainwater from naturally flowing northeast down the mountain slope. Instead, the rainwater flows down laterally and empties into the back of what have thus become the largest valleys (Waipiʻo and Honokane Nui).
726:
from seeping downslope to the northeast, where it naturally wants to go. Rather, the Kohala dike complex guides it northwest or southeast, down the axis of the rift zones, just like the surface water. On the other hand, the three smaller valleys between the large ones - Honopue, Honokea, and
Honokane
1074:
designed to capture water at the higher elevations and distribute it to the then-extensive sugarcane industry. In 1905, after 18 months and the loss of 17 lives, the Kohala Ditch, a vast network of flumes and ditches, measuring 22 mi (35 km) in length, was completed. It has since come into
755:
The natural habitats in the Kohala district range across a wide rainfall gradient in a very short distance—from less than 5 in (130 mm) a year on the coast near
Kawaihae, to more than 150 in (3,800 mm) a year near the summit of Kohala Mountain, a distance of just 11 mi
469:
Kohala is thought to have last erupted 120,000 years ago. However, several samples of a more recent date have been obtained. Two samples collected about 120 m (390 ft) apart, obtained from Waipiʻo Valley on the volcano's east flank in 1977, were dated reliably to 60,000 years. Another
1602:
Areas of super-enhanced flow may exist where there are combined accelerations from large-scale and small-scale terrain influences or between two large-scale features. Such areas of super-enhanced flow, caused by these types of combined accelerations, have been verified in Hawaii. For example,
529:
Geologists have classified the volcano's lava flows into two units. The Hawi
Volcanic layers were deposited in the postshield stage of the volcano's life, and the younger Pololu Volcanics were deposited in the volcano's shield-building stage. The rock in the younger Hawi section, which overlies the
821:
from other species, as it was separated from the nearest major landmass by over 2,000 mi (3,200 km) of open water. The early colonizers of Kohala came by wind, storm or floating on the ocean. Successful colonizations occur on the magnitude of once every 35,000 years. The 2,000 successful
691:
The remaining valleys derive all their water from the lower northeastern slopes of the volcano, and as a result are smaller. In addition, there are innumerable gulches of various depths which have not yet reached sea level and began to form flood plains, becoming valleys. Still, some of these are
793:
The happy combination of small trees, bushes, ferns, vines, and other forms of ground cover keep the soil porous and allow the water to percolate more easily into underground channels. The foliage of the trees breaks the force of rain and prevents the impact of soil by raindrops. A considerable
648:, forced their way out of the magma reservoir and intruded into the rift zone, which was weakened by the collapse. As the dikes forced their way up, they formed fractures and faults parallel to the rift zone. The exertion caused by the dikes produced a series of faults along its length, forming
643:
in a southwest–northeast alignment, cutting into the flanks of the volcano. North of Kohala's summit the volcano's northwest–southeast trending rift zone separates rainfall into two streams, going southeast, into Waipiʻo Valley, or northwest, into
Honokane Nui Valley. When the volcano was still
687:
bring most of the rainfall to the northeastern slope of the volcano. The seven windward valleys of Kohala are, from southeast to northwest, Waipiʻo, Waimanu, Honopue, Honokea, Honokane Iki, Honokane Nui, and Pololu. The size of the valleys reflects the amount of drainage they have been able to
1041:
In addition to walls, there are a series of stone paths that divided the farmed area into plots of variable size. These structures are unique because although many people used such systems at the time, Kohala has some of the few to survive. The leeward slopes of Kohala were used for sugarcane
738:
developing in
Hamakua and North Kohala, so later ditches tapped the spring fed base flows of the valleys and larger gulches. Only Waimanu Valley escaped with none of its tributaries tapped, along with the 16 smaller streams between Waikoloa Stream and the Wailoa river in Waipi'o Valley.
441:
in the Pololu section are of normal polarity, indicating that they were deposited within the last 780,000 years. Radiometric dating ranged mostly from 450,000 to 320,000 years ago, although several pieces strayed lower; this indicated a period of eruptive history at the time.
571:
The United States
Geological Survey has assessed the extinct Kohala as a low-risk area. The volcano is in zone 9 (bottom risk), while the border of the volcano with Mauna Kea is zone 8 (second lowest), as Mauna Kea has not produced lava flows for 4,500 years.
596:
Kohala, like other shield volcanoes, has a shallow surface slope due to the low viscosity of the lava flows that formed it; however, the northwest shoreline boasts some of the highest seacliffs on Earth. Events during and after its eruptions give the volcano several unique
822:
ancestors that arrived at Kohala evolved into about 8,500 to 12,500 unique species, resulting in a very high ratio of the species present being found nowhere else on Earth. Only about 2.5% of the world's rainforest is cloud rainforest, making it a unique habitat as well.
465:
of the windward Kohala shoreline stand as evidence of the massive geologic disaster, and mark the topmost part of the debris from this ancient landslide. There are also several other unique features found on the volcano, all marks made by the decimating collapse.
413:
away and subside into the ocean. The oldest lava flows that are still exposed at the surface are just under 780,000 years old. It is difficult to determine the original size and shape of the volcano, as the southeast flank has been buried by volcanic
1079:, centered just southwest of the mountain. The Hawaii County Department of Water Supply relies on streams from Kohala to supply water to the population of the island. With increasing demand, the original surface channels have been supplemented by deep
813:
E. M. Griffith wrote "Forest protection means not only increasing the rainfall, but more important still, conserving the water supply. The future welfare and agricultural prosperity of the
Hawaiian Islands depends upon the preservation of the forest."
521:, as indicated by the relationship between collected lava samples. In addition, the two features align to one another more closely than does the ridge to Mauna Kea, of which it was once thought to constitute a part. The bulk of the ridge is built of
954:
Kohala's native
Hawaiian rain forest has a thick layer of ferns and mosses carpeting the floor, which act as sponges, absorbing water from rain and passing much of it through to the groundwater in aquifers below; when feral animals like
1054:
by 1937. At the peak of its production, the company had 600 employees, 13,000 acres (20 sq mi) of land, and a capacity of 45,000 t (99,000,000 lb) of raw sugar per year. In 1975 the company finally closed down.
392:
1603:
on island of Hawaii , low-level flow that is diverted to the north around Mauna Kea (4200 m) undergoes an additional acceleration as it flows over the Kohala ridge, causing an area of super-enhanced flow along the Kohala ridge.
808:
and abundant rainfall. Thus the rain forests carpeting Kohala are vital to the supply of groundwater on the island. The role of Kohala's ecosystem in supporting water flow has long been recognized. As early as 1902,
695:
The volcano stayed active well into the formation of these mountainside valleys, as illustrated by later Pololu lava flows, which covered the north and northwestern end of Kohala volcano and often flowed into
525:
with reverse magnetic polarity, evidence that the volcano is at least 780,000 years old. Older lava dated from the toe of the ridge was estimated to be roughly between 1.1 and 1.2 million years old.
1440:, This is the author's personal version of a paper that was published on 2006-05-16 as "Geochemistry, and Earthquake History of Lōʻihi Seamount, Hawaiʻi's youngest volcano", in - Geochemistry (66) 2:81-108,
670:
satellite composite of Kohala, showing its foot-like shape. Two of the deep gorges visible in this photo are Waipiʻo and Waimanu Valleys. All of the gorges visible lie on the east side, the result of trade
700:. Recent seafloor mapping seems to show that the valley extends a short way beyond the seashore, then terminates at what may be the headwall of the great landslide found off the northeast coast of Kohala.
601:
features, some possibly resulting from the ancient collapse and landslide. The volcano is shaped like a foot; the northeast coast is prominently indented across 20 km (12 mi) of shoreline.
579:
1191:
2292:
703:
In addition to being a primary factor in the development of the largest valleys, the dike complex plays another important role —that of creating and maintaining the
730:
Most of Kohala's summit groundwater ends up in either Waipi'o or Honokane Nui; the enormous amount of water routed through these valleys results in a large amount of
74:
409:
wore the volcano down faster than Kohala rebuilt itself through volcanic activity. Decreasing eruptions combined with increasing erosion caused Kohala to slowly
1051:
578:
538:. The separation between the two layers is not clear; the lowest layers may actually be in the Pololu section, based on their depositional patterns and low
393:
1778:
316:
destroyed the northeast flank of the volcano, reducing its height by over 1,000 m (3,300 ft) and traveling 130 km (81 mi) across the
959:
trample the covering, the forest loses its ability to hold in water effectively, and instead of recharging the aquifer, it results in a severe loss of
405:
more than 500,000 years ago. Beginning 300,000 years ago, the rate of eruption slowly decreased over a long period of time to a point where
391:
1441:
549:
between 240,000 and 120,000 years ago. Kohala completed its shield-building stage 245,000 years ago and has been in decline ever since.
2841:
1739:
877:, and their predators. Estimates on the water capacity of the forest range from 320 to 1,600 US gal/acre (3,000 to 15,000 L/ha).
401:
Studies of the volcano's lava accumulation rate have put the volcano's age at somewhere near one million years. It is believed to have breached
2866:
1922:
Ralph H. Riley; Peter M. Vitousek (1995). "Nutrient Dynamics and Nitrogen Trace Gas Flux During Ecosystem Development in Montane Rain Forest".
350:, have been cultivated on the Leeward side of the volcano for centuries. The northern part of the island is named after the mountain, with two
636:
brings most of the rainfall to the northeastern slope of Kohala. The windward side of Kohala mountain is dissected by multiple, deeply eroded
1435:
2279:
1407:
1383:
518:
1971:
343:, resulting in a unique ecosystem. There are several initiatives to preserve this ecosystem against invasive species. Crops, especially
2831:
1827:
394:
1563:
473:
In 2004, unidentified marine fossils were found at the base of the volcano 6 km (3.7 mi) inshore. A research team led by
558:
542:
content. The time intervals separating the two periods of volcanic evolution were extremely brief, something first noted in 1988.
510:
562:
309:
285:
more than 500,000 years ago and to have last erupted 120,000 years ago. Kohala is 606 km (234 sq mi) in
1126:
506:
943:
never made it onto the island, so the ecosystem never developed defenses against them, leaving Hawaii vulnerable to damage by
278:
2851:
2846:
2230:
2205:
1597:
2748:
2554:
1626:
1619:
761:
1841:
676:
2743:
2136:
1979:
147:
2652:
2272:
2216:
2191:
888:
in the soil prevents proper water drainage, resulting in an accumulation of water that impedes the root systems of
437:
interchange) that happened 780,000 years ago. Fifty flow units in the top 140 m (460 ft) of exposed
2733:
1240:
1075:
use by ranches, farms, and homes. A portion of the ditch became a tourist attraction until it was damaged by the
565:
248:
199:
1497:
308:. Unlike the typical symmetry of other Hawaiian volcanoes, Kohala is shaped like a foot. Toward the end of its
1833:
1541:
810:
277:. Kohala is an estimated one million years old—so old that it experienced, and recorded, the reversal of
2064:
2034:
2489:
765:
757:
1087:
was formed, a voluntary group of private land owners and state managers, designed to help manage the Kohala
2856:
2836:
2758:
585:
67:
2763:
2316:
1694:
2871:
2778:
2265:
1043:
769:
255:
1896:
2672:
2662:
2657:
2222:
2197:
1473:
1076:
2738:
1771:
1434:
Garcia, Michael O.; Caplan-Auerbanch, Jackie; De Carlo, Eric H.; Kurz, M.D.; Becker, N. (2005-09-20),
2463:
2311:
1746:
1517:
884:, which exist as breaks in the cloud forests. It is believed that bogs form in low-lying areas where
804:
The forest lies perpendicular to the prevailing trade winds, a characteristic that leads to frequent
478:
434:
2682:
1993:
433:(a change in the orientation of Earth's magnetic field so that the positions of the North and South
2861:
2667:
2245:
1450:
1897:"Working together to protect and sustain the forest, the water, and the people of Kohala Mountain"
1664:
1445:
829:
A native oha wai, or Clermontia species, a common flowering shrub of Kohala Mountain's wet forest.
545:
The forest-covered summit of the volcano consists of many cones which generated lava from its two
2803:
2250:
1801:
1046:
in the late 19th century. The trip from the fields to the mills and then boats was mechanized by
1343:
861:
further add to the variety. In fact, up to a quarter of the plants in the forest are mosses and
2544:
2534:
2006:
1988:
1869:
1106:. The beaches, parks, golf courses, and resorts in South Kohala are called "the Kohala Coast."
550:
351:
340:
222:
57:
2712:
2343:
1311:
2499:
1146:
1103:
324:
have been found on the flank of the volcano, far too high to have been deposited by standard
320:. This huge landslide may be partially responsible for the volcano's foot-like shape. Marine
1309:
913:
The same isolation that produced Kohala's unique ecosystem also makes it very vulnerable to
2431:
2426:
1529:
1485:
995:
on the leeward slopes of Kohala. From 1400 to 1800, the principal crop grown at Kohala was
992:
818:
817:
Before humans arrived, the wildlife population at Kohala and on the rest of the island was
657:
474:
430:
270:
8:
2677:
2411:
2187:
1617:
1571:
212:
1533:
1489:
2448:
1949:
1745:. Kohala Watershed Partnership. December 2007. pp. 9, 18–19, 25–28. Archived from
1701:
735:
313:
2692:
2002:
632:
to divert around it, increasing wind to super-enhanced flow over the Kohala ridge and
2753:
2687:
2504:
2226:
2201:
1941:
1924:
1837:
1545:
1130:
1118:
716:
640:
363:
128:
114:
2589:
1058:
2634:
2614:
2584:
2579:
2569:
2519:
2301:
2257:
1998:
1933:
1537:
1493:
1169:
1150:
1047:
929:
914:
679:
northwestern slope of Kohala has few stream valleys cut into it, the result of the
530:
older Pololu flows, is mostly 260,000 to 140,000 years old, and composed mainly of
502:
187:
2458:
1972:"Archeological Evidence for agricultural development in Kohala, Island of Hawaiʻi"
553:
indicates that the volcano last erupted about 120,000 years ago in the late
2798:
2599:
2574:
2564:
2326:
1969:
1003:
935:
displace native species. Prior to human settlement, many major organisms such as
854:
805:
649:
633:
605:
274:
231:
194:
1865:
1261:
747:
2793:
2707:
2629:
2624:
2609:
2594:
2288:
2240:
1592:
Elliott, DL; Aspliden, CI; Gower, GL; Holladay, CG; Schwartz, MN (April 1987).
1138:
1134:
1114:
1099:
1088:
972:
902:, and oha wai, native members of the bellflower family. Other habitats include
645:
458:
367:
359:
297:
227:
180:
2697:
2335:
1630:
2825:
2808:
2768:
2619:
2468:
2339:
1945:
1549:
1412:
1183:
1035:
922:
731:
697:
522:
243:
89:
76:
1593:
1520:(December 1969). "Potassium-argon ages on lavas of Kohala volcano, Hawaii".
1232:
776:
is rare, and contains a disproportionate percentage of the world's rare and
2788:
2529:
2421:
2140:
1695:"Hofstra University Geology 280F - Field Trip Guidebook: Geology of Hawaii"
1618:
Thomas W. Giambelluca; Michael A. Nullet; Thomas A. Schroeder (June 1986).
1310:
David R. Sherrod; John M. Sinton; Sarah E. Watkins; Kelly M. Brunt (2007).
1110:
996:
981:
870:
866:
371:
355:
344:
239:
2728:
2406:
624:
Waipiʻo Valley, the most prominent valley cutting into the volcano's flank
501:, a characteristic common to Hawaiian volcanoes. The double ridge, shaped
2773:
2453:
1375:
1122:
1067:
903:
889:
723:
704:
680:
554:
2783:
2358:
2321:
1437:
Geology, geochemistry and earthquake history of Lōʻihi Seamount, Hawaiʻi
1070:. In the early part of the 20th century, this was exploited by building
1050:
in 1883. Several plantations on the mountain were consolidated into the
977:
2604:
2509:
2068:
2038:
1953:
1080:
1071:
838:
834:
684:
629:
598:
539:
429:
The volcano is so old that it experienced, and recorded, a reversal of
410:
325:
2331:
620:
328:. Analysis indicated that the fossils had been deposited by a massive
2702:
2524:
2374:
2363:
2353:
2347:
1665:"Origin of the Big Island's Great Valleys Revealed in Hawaiian chant"
1024:
948:
921:
are among the greatest threats to the local ecology. Plants like the
907:
874:
546:
514:
498:
486:
462:
454:
423:
419:
415:
402:
336:
317:
282:
34:
2388:
1937:
1899:. Hawaii Association of Watershed Partnerships. 2008. Archived from
397:
The location of Kohala relative to the other volcanoes of the island
1970:
Thegn N. Ladefoged; Michael W. Gravesb; Mark D. McCoy (July 2003).
1163:
1142:
944:
898:
842:
781:
777:
768:
that obtains much of its moisture from "cloud drip" in addition to
751:
The multi-storied canopy of a native wet forest on Kohala Mountain.
712:
708:
588:
Radar imaging of Kohala's flank demonstrating its deeply dissected
535:
531:
1692:
1433:
1091:
and to protect it from threats, most especially invasive species.
825:
28:
2416:
960:
936:
865:. These work to capture the water from clouds, in turn providing
667:
663:
609:
482:
438:
406:
329:
305:
2090:
963:, much of which ends up being dumped by streams into the ocean.
2514:
2437:
2114:
1921:
1017:
940:
858:
653:
644:
active, vertical sheets of magma, arranged in what is known as
637:
589:
445:
321:
301:
290:
167:
47:
1083:
designed to channel groundwater for domestic use. In 2003 the
293:, and thus constitutes just under 6% of the island of Hawaii.
2539:
2395:
2381:
1900:
1031:
918:
893:
850:
846:
773:
1591:
1094:
Another project to raise awareness of Kohala's ecosystem is
2443:
2401:
1672:
1567:
1498:
10.1130/0016-7606(1992)104<1471:VGAEOT>2.3.CO;2
1351:
1322:
1010:
885:
862:
785:
286:
1542:
10.1130/0016-7606(1969)80[2597:PAOLOK]2.0.CO;2
1192:
List of volcanoes in the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain
1062:
The northern Kohala district, centered on the town of Hawi
833:
The mountain supports approximately 155 native species of
335:
Because it is so far from the nearest major landmass, the
956:
881:
2218:
Volcanoes of North America: The United States and Canada
513:
stages. The southeast rift zone passes under the nearby
2186:
481:
found that the fossils had been deposited by a massive
2190:; Abbott, Agatin Townsend; Peterson, Frank L. (1983).
1965:
1963:
1808:. Virtually Hawaii group, Hawaii Center of Volcanology
1659:
1657:
1655:
1653:
1651:
1474:"Volcano growth and evolution of the island of Hawaii"
772:. These large cloud forests dominate its slopes. This
722:
In Kohala, the numerous dikes near the summit inhibit
2028:
2026:
1734:
1732:
1730:
1728:
1726:
1724:
1722:
1720:
1718:
1556:
799:
C S Judd, Superintendent of Forestry in Hawaiʻi, 1924
2287:
1891:
1889:
1887:
1885:
1471:
1159:
2137:"Kohala Coast vacation on the Big Island of Hawaii"
1960:
1648:
1369:
1367:
281:780,000 years ago. It is believed to have breached
2023:
1715:
1472:Moore, James G.; David A. Clague (November 1992).
2214:
1882:
1740:"Kohala Mountain Watershed Management Plan DRAFT"
1564:"Lava Flow Hazand Zone Maps:Mauna Kea and Kohala"
1408:"Hawaiian tsunami left a gift at foot of volcano"
1125:, the northern tip of Kohala. The site is within
557:. Kohala is currently in transition between the
304:, which are the product of thousands of years of
2823:
1779:Hawai'i Department of Land and Natural Resources
1772:"Puu O Umi Natural Area Reserve Management Plan"
1442:School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology
1364:
449:Cliffs as seen from the beach at Waipiʻo Valley
390:
2139:. www.kohalacoastweb.com. 2009. Archived from
1829:Sugar water : Hawaii's plantation ditches
1613:
1611:
1336:
289:and 14,000 km (3,400 cu mi) in
2273:
2062:
2032:
1693:Charles Merguerian; Steven Okulewicz (2007).
1227:
1825:
1305:
1303:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1207:
2193:Volcanoes in the Sea: The Geology of Hawaii
2058:
2056:
1608:
1301:
1299:
1297:
1295:
1293:
1291:
1289:
1287:
1285:
1283:
1133:stands in front of the community center in
756:(18 km). At the coast are remnants of
2280:
2266:
1427:
1344:"Kohala Volcano, Hawaii-Photo Information"
1137:, and replicas of the statue are found at
1992:
1799:
1793:
1516:
1254:
1204:
568:in the life cycle of Hawaiian volcanoes.
2215:Wood, Charles A.; Jürgen Kienle (1992).
2160:
2154:
2107:
2053:
1280:
1057:
976:
824:
746:
662:
619:
444:
386:
1686:
1312:"Geological Map of the State of Hawaii"
517:and reappears further southeast in the
457:between 250,000 and 300,000 years
2842:Extinct volcanoes of the United States
2824:
1465:
1127:Kohala Historical Sites State Monument
127:
2867:Shield volcanoes of the United States
2261:
1598:Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
1002:, although there is also evidence of
892:. Kohala's bogs are characterized by
880:The mountain is also home to several
477:Gary McMurtry and Dave Tappin of the
312:250,000 to 300,000 years ago, a
1625:. Water Resources Research Center -
1402:
1400:
1863:
1233:"Kohala - Hawai'i's Oldest Volcano"
453:Kohala was devastated by a massive
354:named North and South Kohala. King
13:
2477:
2180:
1145:, and in Emancipation Hall at the
14:
2883:
2832:Volcanoes of the Island of Hawaii
1980:Journal of Archaeological Science
1866:"Hawaiian High Islands Ecoregion"
1397:
1373:
332:approximately 120,000 years ago.
2653:1955 Hawaiian submarine eruption
2063:S. Schweitzer, Veronica (2006).
2033:S. Schweitzer, Veronica (2006).
1176:
1162:
966:
577:
153:
146:
27:
2749:Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain
2744:Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park
2734:Evolution of Hawaiian volcanoes
2163:"Island of Hawaii Golf Courses"
2129:
2083:
1915:
1857:
1819:
1764:
1585:
1241:United States Geological Survey
1066:Kohala supports a very complex
780:species. The soil at Kohala is
249:Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain
2067:. Coffee Times. Archived from
2037:. Coffee Times. Archived from
1627:University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa
1510:
1266:Peakbagger: Kaunu o Kaleioohie
154:
1:
2003:10.1016/s0305-4403(02)00271-6
1826:Carol Wilcox (January 1998).
1376:"Kohala Volcano - John Seach"
1197:
1072:surface irrigational channels
760:, and near the summit lies a
707:. Hawaiian lava is extremely
2852:Pleistocene shield volcanoes
2847:Polygenetic shield volcanoes
2759:Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
1319:USGS Hawaii geology pamphlet
1237:Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
1085:Kohala Watershed Partnership
987:of the type grown on Kohala.
615:
608:on and near the main summit
492:
52:5,480 ft (1,670 m)
33:Kohala volcano as seen from
7:
2035:"Sugar and Steam in Kohala"
1834:University of Hawai'i Press
1620:"Rainfall Atlas of Hawaiʻi"
1155:
604:There is a small string of
10:
2888:
2673:2022 eruption of Mauna Loa
2663:1984 eruption of Mauna Loa
2658:1975 eruption of Mauna Loa
2223:Cambridge University Press
2198:University of Hawaii Press
1077:2006 Kiholo Bay earthquake
970:
849:. A diverse complexion of
742:
382:
377:
339:of Kohala has experienced
62:2,600 ft (790 m)
2721:
2643:
2553:
2488:
2475:
2464:North Arch volcanic field
2312:South Arch volcanic field
2300:
2161:Sperling, Kandra (2009).
2117:. The Kohala Center. 2008
505:, was active in both the
479:British Geological Survey
254:
237:
221:
211:
206:
193:
179:
140:
135:
120:
110:
105:
66:
56:
46:
41:
26:
21:
2668:2018 lower Puna eruption
2246:Global Volcanism Program
1380:Volcanism reference base
1119:unified Hawaiian Islands
926:(Hedychium gardnerianum)
683:effect, as the dominant
566:Hawaiian volcanic stages
2804:Puna Geothermal Venture
2739:Haleakalā National Park
2251:Smithsonian Institution
1028:(Saccharum officinarum)
260:About 120,000 years ago
125:Hawaiian pronunciation:
2545:Pearl and Hermes Atoll
2482:
1870:The Nature Conservancy
1416:(2464): 14. 2004-09-11
1063:
993:pre-modern agriculture
988:
896:, mosses of the genus
830:
796:
752:
672:
625:
551:Potassium-argon dating
497:Kohala had two active
475:University of Hawaii's
450:
398:
279:Earth's magnetic field
90:20.08611°N 155.71722°W
2500:French Frigate Shoals
2481:
1802:"Airphotos of Kohala"
1800:Mouginis-Mark, Pete.
1147:United States Capitol
1061:
1014:(Colocasia esculenta)
991:There is evidence of
980:
828:
791:
750:
666:
628:Mauna Kea causes the
623:
448:
396:
310:shield-building stage
300:cut by multiple deep
2432:East Molokai Volcano
2427:West Molokai Volcano
2225:. pp. 337–339.
2188:Macdonald, Gordon A.
1752:on 28 September 2010
1052:Kohala Sugar Company
933:(Psidium cattleinum)
341:geographic isolation
95:20.08611; -155.71722
2857:Pleistocene Oceania
2837:Mountains of Hawaii
2779:Mauna Loa eruptions
2678:Keanakakoi eruption
2115:"The Kohala Center"
2041:on 15 December 2010
1669:USGS weekly feature
1594:"DE-AC06-76RL01830"
1534:1969GSAB...80.2597M
1490:1992GSAB..104.1471M
917:. Alien plants and
217:>1,000,000 years
86: /
2872:Calderas of Hawaii
2483:
2289:Hawaiian volcanism
2091:"Flumin' da Ditch"
1702:Hofstra University
1149:Visitor Center in
1098:, an independent,
1068:hydrological cycle
1064:
989:
831:
753:
736:plantation economy
673:
626:
451:
399:
42:Highest point
2817:
2816:
2764:Kīlauea eruptions
2754:Hawaiian eruption
2683:ʻAilāʻau eruption
2644:Notable eruptions
2505:Gardner Pinnacles
2232:978-0-521-43811-7
2207:978-0-8248-0832-7
2071:on 3 January 2010
1528:(12): 2597–2600.
1484:(11): 1471–1484.
1131:Kamehameha Statue
1104:County of Hawaiʻi
1096:The Kohala Center
1000:(Ipomoea batatas)
985:(Ipomoea batatas)
431:magnetic polarity
364:Kingdom of Hawaii
348:(Ipomoea batatas)
273:that make up the
269:is the oldest of
264:
263:
129:[koˈhɐlə]
16:Volcano in Hawaii
2879:
2520:Lisianski Island
2480:
2317:Kamaʻehuakanaloa
2282:
2275:
2268:
2259:
2258:
2254:
2236:
2211:
2174:
2173:
2171:
2170:
2165:. MerchantCircle
2158:
2152:
2151:
2149:
2148:
2133:
2127:
2126:
2124:
2122:
2111:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2101:
2087:
2081:
2080:
2078:
2076:
2060:
2051:
2050:
2048:
2046:
2030:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2017:
2011:
2005:. Archived from
1996:
1976:
1967:
1958:
1957:
1919:
1913:
1912:
1910:
1908:
1893:
1880:
1879:
1877:
1876:
1861:
1855:
1854:
1852:
1850:
1823:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1813:
1806:Photos of Kohala
1797:
1791:
1790:
1788:
1786:
1776:
1768:
1762:
1761:
1759:
1757:
1751:
1744:
1736:
1713:
1712:
1710:
1708:
1699:
1690:
1684:
1683:
1681:
1680:
1661:
1646:
1645:
1643:
1641:
1635:
1629:. Archived from
1624:
1615:
1606:
1605:
1589:
1583:
1582:
1580:
1579:
1570:. Archived from
1560:
1554:
1553:
1514:
1508:
1507:
1505:
1504:
1469:
1463:
1462:
1461:
1460:
1454:
1444:, archived from
1431:
1425:
1424:
1422:
1421:
1404:
1395:
1394:
1392:
1391:
1371:
1362:
1361:
1359:
1358:
1340:
1334:
1332:
1330:
1329:
1316:
1307:
1278:
1277:
1275:
1273:
1268:. peakbagger.com
1262:"Kohala, Hawaii"
1258:
1252:
1251:
1249:
1248:
1229:
1186:
1181:
1180:
1179:
1172:
1170:Volcanoes portal
1167:
1166:
1151:Washington, D.C.
1121:, was born near
1048:steam locomotive
930:strawberry guava
915:invasive species
800:
581:
389:
275:island of Hawaii
188:Hawaiian Islands
183:
157:
156:
150:
131:
126:
111:Language of name
101:
100:
98:
97:
96:
91:
87:
84:
83:
82:
79:
31:
19:
18:
2887:
2886:
2882:
2881:
2880:
2878:
2877:
2876:
2862:Cenozoic Hawaii
2822:
2821:
2818:
2813:
2784:Pāhoehoe (lava)
2717:
2693:Kīlauea Caldera
2645:
2639:
2556:
2549:
2491:
2484:
2478:
2473:
2303:
2296:
2286:
2239:
2233:
2208:
2183:
2181:Further reading
2178:
2177:
2168:
2166:
2159:
2155:
2146:
2144:
2135:
2134:
2130:
2120:
2118:
2113:
2112:
2108:
2099:
2097:
2089:
2088:
2084:
2074:
2072:
2061:
2054:
2044:
2042:
2031:
2024:
2015:
2013:
2009:
1994:10.1.1.535.2842
1974:
1968:
1961:
1938:10.2307/1940650
1920:
1916:
1906:
1904:
1903:on 10 July 2009
1895:
1894:
1883:
1874:
1872:
1862:
1858:
1848:
1846:
1844:
1824:
1820:
1811:
1809:
1798:
1794:
1784:
1782:
1781:. November 1989
1774:
1770:
1769:
1765:
1755:
1753:
1749:
1742:
1738:
1737:
1716:
1706:
1704:
1697:
1691:
1687:
1678:
1676:
1663:
1662:
1649:
1639:
1637:
1636:on 3 March 2012
1633:
1622:
1616:
1609:
1590:
1586:
1577:
1575:
1562:
1561:
1557:
1515:
1511:
1502:
1500:
1470:
1466:
1458:
1456:
1448:
1432:
1428:
1419:
1417:
1406:
1405:
1398:
1389:
1387:
1386:, volcanologist
1372:
1365:
1356:
1354:
1342:
1341:
1337:
1333:pp. 41–43
1327:
1325:
1314:
1308:
1281:
1271:
1269:
1260:
1259:
1255:
1246:
1244:
1231:
1230:
1205:
1200:
1182:
1177:
1175:
1168:
1161:
1158:
1139:Aliʻiōlani Hale
1129:. The original
1007:(Dioscorea sp.)
975:
969:
947:, rodents, and
910:(wet) forests.
806:cloud formation
802:
798:
784:, facilitating
745:
634:orographic lift
618:
594:
593:
592:
587:
582:
495:
395:
387:
385:
380:
232:Hotspot volcano
181:
175:
174:
173:
172:
171:
165:
164:
163:
162:
158:
124:
94:
92:
88:
85:
80:
77:
75:
73:
72:
37:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2885:
2875:
2874:
2869:
2864:
2859:
2854:
2849:
2844:
2839:
2834:
2815:
2814:
2812:
2811:
2806:
2801:
2796:
2791:
2786:
2781:
2776:
2771:
2766:
2761:
2756:
2751:
2746:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2725:
2723:
2719:
2718:
2716:
2715:
2710:
2708:Powers Caldera
2705:
2700:
2695:
2690:
2685:
2680:
2675:
2670:
2665:
2660:
2655:
2649:
2647:
2641:
2640:
2638:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2617:
2612:
2607:
2602:
2597:
2592:
2587:
2582:
2577:
2572:
2567:
2561:
2559:
2551:
2550:
2548:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2527:
2522:
2517:
2512:
2507:
2502:
2496:
2494:
2486:
2485:
2476:
2474:
2472:
2471:
2466:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2446:
2441:
2434:
2429:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2409:
2404:
2399:
2392:
2385:
2378:
2371:
2366:
2361:
2356:
2351:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2308:
2306:
2298:
2297:
2285:
2284:
2277:
2270:
2262:
2256:
2255:
2237:
2231:
2212:
2206:
2182:
2179:
2176:
2175:
2153:
2128:
2106:
2082:
2065:"Kohala Ditch"
2052:
2022:
1987:(7): 923–940.
1959:
1932:(1): 292–304.
1914:
1881:
1864:Gon III, S.M.
1856:
1843:978-0824820442
1842:
1818:
1792:
1763:
1714:
1685:
1647:
1607:
1600:. p. 28.
1584:
1555:
1518:McDougall, Ian
1509:
1464:
1426:
1396:
1363:
1335:
1279:
1253:
1202:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1188:
1187:
1173:
1157:
1154:
1100:not-for-profit
1034:of the family
1021:(Musa hybrids)
973:Kohala, Hawaii
968:
965:
945:hoofed animals
790:
744:
741:
617:
614:
584:
583:
576:
575:
574:
494:
491:
459:before present
384:
381:
379:
376:
366:, was born in
298:shield volcano
271:five volcanoes
262:
261:
258:
252:
251:
246:
235:
234:
228:Shield volcano
225:
219:
218:
215:
209:
208:
204:
203:
197:
191:
190:
185:
177:
176:
166:
160:
159:
152:
151:
145:
144:
143:
142:
141:
138:
137:
133:
132:
122:
118:
117:
112:
108:
107:
103:
102:
70:
64:
63:
60:
54:
53:
50:
44:
43:
39:
38:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2884:
2873:
2870:
2868:
2865:
2863:
2860:
2858:
2855:
2853:
2850:
2848:
2845:
2843:
2840:
2838:
2835:
2833:
2830:
2829:
2827:
2820:
2810:
2809:Volcano House
2807:
2805:
2802:
2800:
2797:
2795:
2792:
2790:
2787:
2785:
2782:
2780:
2777:
2775:
2772:
2770:
2769:Lava fountain
2767:
2765:
2762:
2760:
2757:
2755:
2752:
2750:
2747:
2745:
2742:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2730:
2727:
2726:
2724:
2720:
2714:
2711:
2709:
2706:
2704:
2701:
2699:
2696:
2694:
2691:
2689:
2686:
2684:
2681:
2679:
2676:
2674:
2671:
2669:
2666:
2664:
2661:
2659:
2656:
2654:
2651:
2650:
2648:
2642:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2611:
2608:
2606:
2603:
2601:
2598:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2588:
2586:
2583:
2581:
2578:
2576:
2573:
2571:
2568:
2566:
2563:
2562:
2560:
2558:
2552:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2535:Necker Island
2533:
2531:
2528:
2526:
2523:
2521:
2518:
2516:
2513:
2511:
2508:
2506:
2503:
2501:
2498:
2497:
2495:
2493:
2487:
2470:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2439:
2435:
2433:
2430:
2428:
2425:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2408:
2405:
2403:
2400:
2398:
2397:
2393:
2391:
2390:
2386:
2384:
2383:
2379:
2377:
2376:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2349:
2345:
2341:
2340:Pauahi Crater
2337:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2309:
2307:
2305:
2299:
2294:
2290:
2283:
2278:
2276:
2271:
2269:
2264:
2263:
2260:
2252:
2248:
2247:
2242:
2238:
2234:
2228:
2224:
2220:
2219:
2213:
2209:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2194:
2189:
2185:
2184:
2164:
2157:
2143:on 2009-10-19
2142:
2138:
2132:
2116:
2110:
2096:
2092:
2086:
2070:
2066:
2059:
2057:
2040:
2036:
2029:
2027:
2012:on 2011-06-06
2008:
2004:
2000:
1995:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1981:
1973:
1966:
1964:
1955:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1931:
1927:
1926:
1918:
1902:
1898:
1892:
1890:
1888:
1886:
1871:
1867:
1860:
1845:
1839:
1835:
1831:
1830:
1822:
1807:
1803:
1796:
1780:
1773:
1767:
1748:
1741:
1735:
1733:
1731:
1729:
1727:
1725:
1723:
1721:
1719:
1703:
1696:
1689:
1674:
1670:
1666:
1660:
1658:
1656:
1654:
1652:
1632:
1628:
1621:
1614:
1612:
1604:
1599:
1595:
1588:
1574:on 2009-01-29
1573:
1569:
1565:
1559:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1523:
1519:
1513:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1468:
1455:on 2011-07-18
1452:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1438:
1430:
1415:
1414:
1413:New Scientist
1409:
1403:
1401:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1374:Seach, John.
1370:
1368:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1339:
1324:
1320:
1313:
1306:
1304:
1302:
1300:
1298:
1296:
1294:
1292:
1290:
1288:
1286:
1284:
1267:
1263:
1257:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1228:
1226:
1224:
1222:
1220:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1210:
1208:
1203:
1193:
1190:
1189:
1185:
1184:Hawaii portal
1174:
1171:
1165:
1160:
1153:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1092:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1073:
1069:
1060:
1056:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1039:
1037:
1036:Cucurbitaceae
1033:
1029:
1026:
1022:
1019:
1015:
1012:
1008:
1005:
1001:
998:
994:
986:
983:
979:
974:
967:Human history
964:
962:
958:
952:
950:
946:
942:
938:
934:
931:
927:
924:
923:kahili ginger
920:
919:feral animals
916:
911:
909:
905:
901:
900:
895:
891:
887:
883:
878:
876:
872:
871:invertebrates
868:
867:microhabitats
864:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
827:
823:
820:
815:
812:
807:
801:
795:
789:
787:
783:
782:nitrogen-rich
779:
775:
771:
770:precipitation
767:
763:
759:
749:
740:
737:
733:
732:water erosion
728:
725:
720:
718:
714:
710:
706:
701:
699:
698:Pololu Valley
693:
689:
686:
682:
678:
669:
665:
661:
659:
655:
651:
647:
642:
639:
635:
631:
622:
613:
611:
607:
602:
600:
591:
586:
580:
573:
569:
567:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
543:
541:
537:
533:
527:
524:
523:volcanic rock
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
500:
490:
488:
484:
480:
476:
471:
467:
464:
460:
456:
447:
443:
440:
436:
432:
427:
425:
421:
417:
412:
408:
404:
375:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
346:
342:
338:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
294:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
259:
257:
256:Last eruption
253:
250:
247:
245:
241:
236:
233:
229:
226:
224:
223:Mountain type
220:
216:
214:
210:
205:
201:
198:
196:
192:
189:
186:
184:
178:
169:
149:
139:
134:
130:
123:
121:Pronunciation
119:
116:
113:
109:
104:
99:
71:
69:
65:
61:
59:
55:
51:
49:
45:
40:
36:
30:
25:
20:
2819:
2799:Pele's tears
2789:Pele (deity)
2688:Halemaʻumaʻu
2530:Midway Atoll
2436:
2422:Penguin Bank
2394:
2387:
2380:
2373:
2368:
2244:
2217:
2192:
2167:. Retrieved
2156:
2145:. Retrieved
2141:the original
2131:
2119:. Retrieved
2109:
2098:. Retrieved
2094:
2085:
2073:. Retrieved
2069:the original
2043:. Retrieved
2039:the original
2014:. Retrieved
2007:the original
1984:
1978:
1929:
1923:
1917:
1905:. Retrieved
1901:the original
1873:. Retrieved
1859:
1847:. Retrieved
1832:. Honolulu:
1828:
1821:
1810:. Retrieved
1805:
1795:
1783:. Retrieved
1766:
1754:. Retrieved
1747:the original
1705:. Retrieved
1688:
1677:. Retrieved
1675:. 2006-02-16
1668:
1638:. Retrieved
1631:the original
1601:
1587:
1576:. Retrieved
1572:the original
1558:
1525:
1522:GSA Bulletin
1521:
1512:
1501:. Retrieved
1481:
1478:GSA Bulletin
1477:
1467:
1457:, retrieved
1446:the original
1436:
1429:
1418:. Retrieved
1411:
1388:. Retrieved
1379:
1355:. Retrieved
1347:
1338:
1326:. Retrieved
1318:
1270:. Retrieved
1265:
1256:
1245:. Retrieved
1243:. 1998-03-20
1236:
1113:, the first
1111:Kamehameha I
1108:
1095:
1093:
1084:
1065:
1040:
1027:
1020:
1013:
1006:
999:
997:sweet potato
990:
984:
982:Sweet potato
953:
932:
925:
912:
897:
890:woody plants
879:
832:
816:
803:
797:
792:
764:, a type of
762:cloud forest
754:
729:
721:
702:
694:
690:
674:
658:fault blocks
627:
603:
595:
570:
544:
528:
496:
472:
468:
452:
428:
418:from nearby
400:
368:North Kohala
358:, the first
356:Kamehameha I
347:
345:sweet potato
334:
296:Kohala is a
295:
266:
265:
182:Parent range
2794:Pele's hair
2774:Limu o Pele
2729:ʻAʻā (lava)
2698:Kīlauea Iki
2336:Kīlauea Iki
2121:16 December
2075:25 December
2045:25 December
1907:15 December
1756:16 December
1272:17 February
1123:Upolu Point
1044:plantations
904:rain forest
839:crustaceans
835:vertebrates
811:US Forester
786:root growth
758:dry forests
724:groundwater
705:water table
685:trade winds
681:rain shadow
630:trade winds
555:Pleistocene
326:ocean waves
213:Age of rock
93: /
81:155°43′02″W
68:Coordinates
2826:Categories
2510:Kure Atoll
2375:Kahoʻolawe
2169:2009-11-07
2147:2009-11-07
2100:2009-12-25
2016:2009-12-18
1875:2009-05-13
1812:2009-03-30
1679:2009-04-12
1578:2009-03-30
1503:2008-12-18
1459:2009-03-20
1420:2008-12-18
1390:2009-03-30
1384:John Seach
1357:2009-03-30
1348:USGS Image
1328:2009-04-12
1247:2008-08-22
1198:References
971:See also:
908:mesophytic
875:amphibians
766:rainforest
599:geomorphic
559:postshield
547:rift zones
540:phosphorus
519:Hilo Ridge
511:postshield
499:rift zones
463:sea cliffs
416:lava flows
78:20°05′10″N
58:Prominence
2713:Puʻu ʻŌʻō
2703:Mauna Ulu
2646:and vents
2575:Daikakuji
2557:Seamounts
2525:Maro Reef
2412:West Maui
2407:Haleakalā
2364:Mauna Kea
2354:Mauna Loa
2348:Mauna Ulu
2344:Puʻu ʻŌʻō
1989:CiteSeerX
1946:0012-9658
1785:27 August
1707:27 August
1640:27 August
1550:0016-7606
1089:watershed
1025:sugarcane
949:predation
855:liverwort
709:permeable
616:Hydrology
563:erosional
515:Mauna Kea
493:Structure
487:Mauna Loa
455:landslide
424:Mauna Loa
420:Mauna Kea
403:sea level
352:districts
337:ecosystem
318:sea floor
314:landslide
283:sea level
238:Volcanic
136:Geography
48:Elevation
35:Mauna Kea
2469:Waiʻanae
2449:Honolulu
2417:Molokaʻi
2359:Hualālai
2322:Māhukona
2302:Windward
2291:topics (
2241:"Kohala"
2095:web site
1849:22 March
1156:See also
1143:Honolulu
937:conifers
928:and the
899:Sphagnum
843:mollusks
819:isolated
717:vesicles
536:trachyte
532:hawaiite
195:Topo map
115:Hawaiian
2635:Yuryaku
2615:Nintoku
2585:Hancock
2580:Detroit
2570:Colahan
2555:Emperor
2490:Leeward
2459:Koʻolau
2438:Niʻihau
2332:Kīlauea
2327:Hawaiʻi
1954:1940650
1925:Ecology
1530:Bibcode
1486:Bibcode
1135:Kapaʻau
1117:of the
1018:bananas
961:topsoil
941:rodents
778:endemic
743:Ecology
677:leeward
668:Landsat
654:grabens
641:valleys
610:caldera
590:valleys
503:axially
483:tsunami
411:weather
407:erosion
383:History
378:Geology
370:, near
362:of the
330:tsunami
322:fossils
306:erosion
207:Geology
202:Kamuela
2722:Topics
2600:Kimmei
2565:Abbott
2515:Laysan
2454:Kaʻena
2396:Lānaʻi
2389:Kaʻula
2382:Kauaʻi
2369:Kohala
2229:
2204:
1991:
1952:
1944:
1840:
1548:
1032:gourds
1030:, and
894:sedges
859:mosses
857:, and
847:plants
845:, and
713:porous
671:winds.
650:horsts
638:stream
606:faults
507:shield
439:strata
302:gorges
291:volume
267:Kohala
170:, U.S.
168:Hawaii
161:Kohala
106:Naming
22:Kohala
2630:Yomei
2625:Suiko
2610:Meiji
2595:Kammu
2590:Jingū
2540:Nihoa
2492:Isles
2444:Oʻahu
2304:Isles
2010:(PDF)
1975:(PDF)
1950:JSTOR
1775:(PDF)
1750:(PDF)
1743:(PDF)
1698:(PDF)
1634:(PDF)
1623:(PDF)
1315:(PDF)
1109:King
1081:wells
863:ferns
851:fungi
774:biome
646:dikes
435:poles
2620:Ojin
2605:Koko
2402:Maui
2293:list
2227:ISBN
2202:ISBN
2123:2009
2077:2009
2047:2009
1942:ISSN
1909:2009
1851:2014
1838:ISBN
1787:2012
1758:2009
1709:2012
1673:USGS
1642:2012
1568:USGS
1546:ISSN
1352:USGS
1323:USGS
1274:2015
1115:King
1011:taro
1004:yams
957:pigs
939:and
906:and
886:clay
882:bogs
873:and
869:for
711:and
675:The
652:and
561:and
534:and
509:and
422:and
372:Hawi
360:King
287:area
244:belt
200:USGS
1999:doi
1934:doi
1538:doi
1494:doi
1482:104
1451:PDF
1141:in
240:arc
2828::
2346:,
2342:,
2338:,
2249:.
2243:.
2221:.
2200:.
2196:.
2093:.
2055:^
2025:^
1997:.
1985:30
1983:.
1977:.
1962:^
1948:.
1940:.
1930:76
1928:.
1884:^
1868:.
1836:.
1804:.
1777:.
1717:^
1700:.
1671:.
1667:.
1650:^
1610:^
1596:.
1566:.
1544:.
1536:.
1526:80
1524:.
1492:.
1480:.
1476:.
1410:.
1399:^
1382:.
1378:.
1366:^
1350:.
1346:.
1321:.
1317:.
1282:^
1264:.
1239:.
1235:.
1206:^
1023:,
1016:,
1009:,
951:.
853:,
841:,
837:,
788:.
374:.
230:,
2350:)
2334:(
2295:)
2281:e
2274:t
2267:v
2253:.
2235:.
2210:.
2172:.
2150:.
2125:.
2103:.
2079:.
2049:.
2019:.
2001::
1956:.
1936::
1911:.
1878:.
1853:.
1815:.
1789:.
1760:.
1711:.
1682:.
1644:.
1581:.
1552:.
1540::
1532::
1506:.
1496::
1488::
1453:)
1449:(
1423:.
1393:.
1360:.
1331:.
1276:.
1250:.
656:(
242:/
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.