123:
160:
896:
84:
1784:
1805:
885:
1794:
191:. Their frequencies more closely couple with the ice shelf natural frequencies and they produce a larger amplitude ice shelf movement than the normal ocean swell of gravity waves. Further, they are not damped by sea ice as normal ocean swell is. As a result, they flex floating ice shelves such as the Ross Ice Shelf; this flexure contributes significantly to the breakup on the ice shelf.
144:
methods, the now well-known result. Namely, the mean sea level oscillates with a wavelength that is equal to the length of the group, with a low level where the wind waves are highest and a high level where these waves are lowest. This oscillation of the sea surface is proportional to the square of the short wave amplitude and becomes very large when the
143:
induced by these groupy waves transports more water where the waves are highest. The waves also push the water around in a way that can be interpreted as a force: the divergence of the radiation stresses. Combining mass and momentum conservation, Longuet-Higgins and
Stewart give, with three different
148:
approaches the speed of shallow water waves. The details of this process are modified when the bottom is sloping, which is generally the case near the shore, but the theory captures the important effect, observed in most conditions, that the high water of this 'surf beat' arrives with the waves of
152:
Another process was proposed later by Graham
Symonds and his collaborators. To explain some cases in which this phase of long and short waves were not opposed, they proposed that the position of the breaker line in the surf, moving towards deep water when waves are higher, could act like a wave
130:
Two main processes can explain the transfer of energy from the short wind waves to the long infragravity waves, and both are important in shallow water and for steep wind waves. The most common process is the
57:
generated by ocean waves of shorter periods. The amplitude of infragravity waves is most relevant in shallow water, in particular along coastlines hit by high amplitude and long period wind waves and
65:
are shorter, with typical dominant periods of 1 to 25 s. In contrast, the dominant period of infragravity waves is typically 80 to 300 s, which is close to the typical periods of
422:
Lugo-Fernández, A.; H. H. Roberts; W. J. Wiseman Jr.; B. L. Carter (December 1998). "Water level and currents of tidal and infragravity periods at Tague Reef, St. Croix (USVI)".
99:
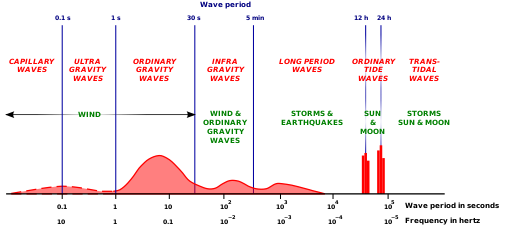
Technically infragravity waves are simply a subcategory of gravity waves and refer to all gravity waves with periods greater than 30 s. This could include phenomena such as
135:
interaction of trains of wind waves which was first observed by Munk and Tucker and explained by
Longuet-Higgins and Stewart. Because wind waves are not
1524:
207:
1514:
573:
210:; Arshad Rawat; Jerome Aucan (2014), "A numerical model for free infragravity waves: Definition and validation at regional and global scales",
80:
Whatever the details of their generation mechanism, discussed below, infragravity waves are these subharmonics of the impinging gravity waves.
126:
Surf can be seen breaking as it crosses the sand bar offshore. Sandbars aid in generating infragravity waves and in turn are shaped by them.
348:
Longuet-Higgins, Michael; R.W. Stewart (1962), "Radiation stress and mass transport in gravity waves, with application to 'surf beats",
378:
Symonds, Graham; D. A. Huntley; A. J. Bowent (1982), "Two-dimensional surf beat: Long wavegeneration by a time-varying breakpoint",
176:, unusually large and long-duration waves that cause water to surge far onshore and that have killed a number of people in the US
1430:
1797:
845:
613:
1077:
183:
Infragravity waves generated along the
Pacific coast of North America have been observed to propagate transoceanically to
566:
294:
967:
1672:
1099:
987:
1519:
790:
977:
937:
1707:
693:
526:
1787:
1380:
559:
835:
107:, but the common scientific usage is limited to gravity waves that are generated by groups of wind waves.
156:
In the case of coral reefs, the infragravity periods are established by resonances with the reef itself.
895:
1032:
502:
153:
maker. It appears that this is probably a good explanation for infragravity wave generation on a reef.
77:, which are created by wind acting on the surface of the sea, and are slower than the generating wind.
458:
1567:
972:
932:
400:
1697:
1072:
1062:
1002:
638:
608:
1830:
1734:
1717:
1554:
1047:
912:
850:
840:
733:
1729:
1667:
1094:
780:
395:
1562:
1544:
1052:
947:
582:
527:"Breaking waves: The coup de grace that shatters ice shelves is administered by ocean waves"
1835:
1749:
1582:
1285:
1142:
1007:
718:
473:
387:
245:
23:
8:
1744:
1629:
1624:
1350:
1022:
982:
698:
477:
421:
391:
249:
1687:
1400:
1390:
1355:
1255:
1240:
1137:
439:
361:
263:
1769:
1759:
1702:
1682:
1365:
1330:
1265:
1245:
1235:
1117:
805:
365:
330:
308:
177:
443:
267:
122:
1724:
1692:
1662:
1471:
1456:
1325:
1260:
1152:
1067:
997:
922:
703:
673:
603:
598:
481:
431:
405:
353:
298:
253:
92:
1529:
1425:
1375:
1340:
1300:
1192:
1162:
1012:
962:
872:
830:
763:
688:
648:
159:
288:
1639:
1634:
1539:
1534:
1370:
1310:
1305:
1037:
927:
748:
683:
658:
188:
70:
884:
357:
136:
1824:
1809:
1657:
1577:
1466:
1385:
1360:
1295:
1225:
1132:
1027:
904:
825:
785:
758:
668:
618:
456:
312:
231:
62:
58:
43:
39:
409:
233:
1764:
1712:
1652:
1603:
1481:
1476:
1451:
1435:
1410:
1127:
1017:
957:
743:
653:
628:
459:"Forcing of resonant modes on a fringing reef during tropical storm Man-Yi"
173:
140:
74:
69:, with which they share similar propagation properties including very fast
54:
435:
334:
1754:
1486:
1415:
1280:
1220:
1187:
1177:
1172:
1057:
992:
952:
942:
917:
800:
773:
753:
713:
678:
486:
284:
258:
145:
132:
111:
104:
73:
in deep water. This distinguishes infragravity waves from normal oceanic
551:
1572:
1420:
1395:
1290:
1270:
1197:
1182:
1167:
1157:
1122:
1042:
862:
857:
820:
815:
810:
708:
184:
1804:
303:
83:
1644:
1506:
1491:
1405:
1250:
1089:
1084:
867:
795:
723:
643:
633:
590:
31:
27:
232:
Bromirski, Peter D.; Olga V. Sergienko; Douglas R. MacAyeal (2010).
1739:
1461:
1320:
1212:
1202:
1147:
623:
457:
Péquignet, A. C.; J. M. Becker; M. A. Merrifield; J. Aucan (2009).
215:
172:
Infragravity waves are thought to be a generating mechanism behind
88:
35:
1608:
1598:
768:
738:
327:
Wind Waves: Their
Generation and Propagation on the Ocean Surface
234:"Transoceanic infragravity waves impacting Antarctic ice shelves"
66:
377:
16:
Surface gravity waves with frequencies lower than the wind waves
1315:
728:
290:
206:
352:, vol. 13, Cambridge University Press, pp. 481–504,
1677:
1496:
1275:
1230:
47:
110:
The term "infragravity wave" appears to have been coined by
1109:
347:
100:
329:. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. pp. 22–23.
1525:North West Shelf Operational Oceanographic System
415:
46:lower than the frequencies directly generated by
1822:
1515:Deep-ocean Assessment and Reporting of Tsunamis
227:
225:
567:
450:
222:
574:
560:
371:
287:(1950), "Origin and generation of waves",
200:
42:– thus corresponding with the part of the
581:
485:
399:
302:
257:
158:
121:
82:
324:
1823:
846:one-dimensional Saint-Venant equations
500:
341:
279:
277:
555:
53:Infragravity waves are ocean surface
1793:
503:"Why Sneaker Waves Are So Insidious"
283:
274:
13:
1673:National Oceanographic Data Center
1100:World Ocean Circulation Experiment
988:Global Ocean Data Analysis Project
14:
1847:
1520:Global Sea Level Observing System
547:
91:of ocean waves according to wave
1803:
1792:
1783:
1782:
978:Geochemical Ocean Sections Study
894:
883:
1708:Ocean thermal energy conversion
1431:Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis
519:
380:Journal of Geophysical Research
494:
318:
1:
194:
117:
968:El Niño–Southern Oscillation
938:Craik–Leibovich vortex force
694:Luke's variational principle
238:Geophysical Research Letters
187:and there to impinge on the
7:
501:Golden, Kate (2022-11-17).
10:
1852:
1033:Ocean dynamical thermostat
881:
350:Journal of Fluid Mechanics
293:, Long Beach, California:
1778:
1617:
1591:
1568:Ocean acoustic tomography
1553:
1505:
1444:
1381:Mohorovičić discontinuity
1339:
1211:
1108:
973:General circulation model
903:
609:Benjamin–Feir instability
589:
358:10.1017/S0022112062000877
167:
1698:Ocean surface topography
1073:Thermohaline circulation
1063:Subsurface ocean current
1003:Hydrothermal circulation
836:Wave–current interaction
614:Boussinesq approximation
1735:Sea surface temperature
1718:Outline of oceanography
913:Atmospheric circulation
851:shallow water equations
841:Waves and shallow water
734:Significant wave height
410:10.1029/JC087iC01p00492
325:Kinsman, Blair (1965).
1730:Sea surface microlayer
1095:Wind generated current
164:
139:they form groups. The
127:
96:
87:Classification of the
1563:Deep scattering layer
1545:World Geodetic System
1053:Princeton Ocean Model
933:Coriolis–Stokes force
583:Physical oceanography
436:10.1007/s003380050137
162:
125:
86:
34:– consisting of both
24:surface gravity waves
1583:Underwater acoustics
1143:Perigean spring tide
1008:Langmuir circulation
719:Rossby-gravity waves
487:10.1029/2008GL036259
259:10.1029/2009GL041488
163:Ice shelf processes.
105:oceanic Rossby waves
1745:Science On a Sphere
1351:Convergent boundary
1023:Modular Ocean Model
983:Geostrophic current
699:Mild-slope equation
533:. February 18, 2010
478:2009GeoRL..36.3607P
392:1982JGR....87..492S
250:2010GeoRL..37.2502B
1401:Seafloor spreading
1391:Outer trench swell
1356:Divergent boundary
1256:Continental margin
1241:Carbonate platform
1138:Lunitidal interval
466:Geophys. Res. Lett
165:
149:lowest amplitude.
128:
97:
50:through the wind.
20:Infragravity waves
1818:
1817:
1810:Oceans portal
1770:World Ocean Atlas
1760:Underwater glider
1703:Ocean temperature
1366:Hydrothermal vent
1331:Submarine volcano
1266:Continental shelf
1246:Coastal geography
1236:Bathymetric chart
1118:Amphidromic point
806:Wave nonlinearity
664:Infragravity wave
304:10.9753/icce.v1.1
178:Pacific Northwest
61:. Wind waves and
1843:
1808:
1807:
1796:
1795:
1786:
1785:
1725:Pelagic sediment
1663:Marine pollution
1457:Deep ocean water
1326:Submarine canyon
1261:Continental rise
1153:Rule of twelfths
1068:Sverdrup balance
998:Humboldt Current
923:Boundary current
898:
887:
704:Radiation stress
674:Iribarren number
649:Equatorial waves
604:Ballantine scale
599:Airy wave theory
576:
569:
562:
553:
552:
542:
541:
539:
538:
523:
517:
516:
514:
513:
498:
492:
491:
489:
463:
454:
448:
447:
419:
413:
412:
403:
375:
369:
368:
345:
339:
338:
322:
316:
315:
306:
297:, pp. 1–4,
281:
272:
271:
261:
229:
220:
219:
218:, pp. 20–32
214:, vol. 77,
208:Ardhuin, Fabrice
204:
1851:
1850:
1846:
1845:
1844:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1821:
1820:
1819:
1814:
1802:
1774:
1613:
1587:
1549:
1530:Sea-level curve
1501:
1440:
1426:Transform fault
1376:Mid-ocean ridge
1342:
1335:
1301:Oceanic plateau
1207:
1193:Tidal resonance
1163:Theory of tides
1104:
1013:Longshore drift
963:Ekman transport
899:
893:
892:
891:
890:
889:
888:
879:
831:Wave turbulence
764:Trochoidal wave
689:Longshore drift
585:
580:
550:
545:
536:
534:
525:
524:
520:
511:
509:
499:
495:
472:(L03607): n/a.
461:
455:
451:
420:
416:
401:10.1.1.474.7148
386:(C1): 492–498,
376:
372:
346:
342:
323:
319:
285:Munk, Walter H.
282:
275:
244:(L02502): n/a.
230:
223:
212:Ocean Modelling
205:
201:
197:
170:
120:
30:lower than the
17:
12:
11:
5:
1849:
1839:
1838:
1833:
1831:Fluid dynamics
1816:
1815:
1813:
1812:
1800:
1790:
1779:
1776:
1775:
1773:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1757:
1752:
1750:Stratification
1747:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1727:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1710:
1705:
1700:
1695:
1690:
1685:
1680:
1675:
1670:
1665:
1660:
1655:
1650:
1642:
1640:Color of water
1637:
1635:Benthic lander
1632:
1627:
1621:
1619:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1611:
1606:
1601:
1595:
1593:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1570:
1565:
1559:
1557:
1551:
1550:
1548:
1547:
1542:
1540:Sea level rise
1537:
1535:Sea level drop
1532:
1527:
1522:
1517:
1511:
1509:
1503:
1502:
1500:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1484:
1479:
1474:
1469:
1464:
1459:
1454:
1448:
1446:
1442:
1441:
1439:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1398:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1371:Marine geology
1368:
1363:
1358:
1353:
1347:
1345:
1337:
1336:
1334:
1333:
1328:
1323:
1318:
1313:
1311:Passive margin
1308:
1306:Oceanic trench
1303:
1298:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1217:
1215:
1209:
1208:
1206:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1170:
1165:
1160:
1155:
1150:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1130:
1125:
1120:
1114:
1112:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1102:
1097:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1081:
1080:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1050:
1045:
1040:
1038:Ocean dynamics
1035:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1010:
1005:
1000:
995:
990:
985:
980:
975:
970:
965:
960:
955:
950:
945:
940:
935:
930:
928:Coriolis force
925:
920:
915:
909:
907:
901:
900:
882:
880:
878:
877:
876:
875:
865:
860:
855:
854:
853:
848:
838:
833:
828:
823:
818:
813:
808:
803:
798:
793:
788:
783:
778:
777:
776:
766:
761:
756:
751:
749:Stokes problem
746:
741:
736:
731:
726:
721:
716:
711:
706:
701:
696:
691:
686:
684:Kinematic wave
681:
676:
671:
666:
661:
656:
651:
646:
641:
636:
631:
626:
621:
616:
611:
606:
601:
595:
593:
587:
586:
579:
578:
571:
564:
556:
549:
548:External links
546:
544:
543:
518:
493:
449:
430:(4): 343–349.
414:
370:
340:
317:
273:
221:
198:
196:
193:
189:Ross Ice Shelf
169:
166:
119:
116:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1848:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1828:
1826:
1811:
1806:
1801:
1799:
1791:
1789:
1781:
1780:
1777:
1771:
1768:
1766:
1763:
1761:
1758:
1756:
1753:
1751:
1748:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1719:
1716:
1715:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1699:
1696:
1694:
1691:
1689:
1686:
1684:
1681:
1679:
1676:
1674:
1671:
1669:
1666:
1664:
1661:
1659:
1658:Marine energy
1656:
1654:
1651:
1649:
1648:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1626:
1625:Acidification
1623:
1622:
1620:
1616:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1596:
1594:
1590:
1584:
1581:
1579:
1578:SOFAR channel
1576:
1574:
1571:
1569:
1566:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1558:
1556:
1552:
1546:
1543:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1533:
1531:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1512:
1510:
1508:
1504:
1498:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1483:
1480:
1478:
1475:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1458:
1455:
1453:
1450:
1449:
1447:
1443:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1422:
1419:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1397:
1394:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1386:Oceanic crust
1384:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1361:Fracture zone
1359:
1357:
1354:
1352:
1349:
1348:
1346:
1344:
1338:
1332:
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1314:
1312:
1309:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1296:Oceanic basin
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1226:Abyssal plain
1224:
1222:
1219:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1210:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1166:
1164:
1161:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1151:
1149:
1146:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1133:Internal tide
1131:
1129:
1126:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1115:
1113:
1111:
1107:
1101:
1098:
1096:
1093:
1091:
1088:
1086:
1083:
1079:
1076:
1075:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1064:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1049:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1028:Ocean current
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
1004:
1001:
999:
996:
994:
991:
989:
986:
984:
981:
979:
976:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
961:
959:
956:
954:
951:
949:
946:
944:
941:
939:
936:
934:
931:
929:
926:
924:
921:
919:
916:
914:
911:
910:
908:
906:
902:
897:
886:
874:
871:
870:
869:
866:
864:
861:
859:
856:
852:
849:
847:
844:
843:
842:
839:
837:
834:
832:
829:
827:
826:Wave shoaling
824:
822:
819:
817:
814:
812:
809:
807:
804:
802:
799:
797:
794:
792:
789:
787:
786:Ursell number
784:
782:
779:
775:
772:
771:
770:
767:
765:
762:
760:
757:
755:
752:
750:
747:
745:
742:
740:
737:
735:
732:
730:
727:
725:
722:
720:
717:
715:
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
700:
697:
695:
692:
690:
687:
685:
682:
680:
677:
675:
672:
670:
669:Internal wave
667:
665:
662:
660:
657:
655:
652:
650:
647:
645:
642:
640:
637:
635:
632:
630:
627:
625:
622:
620:
619:Breaking wave
617:
615:
612:
610:
607:
605:
602:
600:
597:
596:
594:
592:
588:
584:
577:
572:
570:
565:
563:
558:
557:
554:
532:
531:The Economist
528:
522:
508:
504:
497:
488:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
460:
453:
445:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
418:
411:
407:
402:
397:
393:
389:
385:
381:
374:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
344:
336:
332:
328:
321:
314:
310:
305:
300:
296:
292:
291:
286:
280:
278:
269:
265:
260:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
228:
226:
217:
213:
209:
203:
199:
192:
190:
186:
181:
179:
175:
174:sneaker waves
161:
157:
154:
150:
147:
142:
138:
137:monochromatic
134:
124:
115:
113:
108:
106:
102:
94:
90:
85:
81:
78:
76:
75:gravity waves
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
55:gravity waves
51:
49:
45:
44:wave spectrum
41:
37:
33:
29:
25:
21:
1765:Water column
1713:Oceanography
1688:Observations
1683:Explorations
1653:Marginal sea
1646:
1604:OSTM/Jason-2
1436:Volcanic arc
1411:Slab suction
1128:Head of tide
1018:Loop Current
958:Ekman spiral
744:Stokes drift
663:
654:Gravity wave
629:Cnoidal wave
535:. Retrieved
530:
521:
510:. Retrieved
506:
496:
469:
465:
452:
427:
423:
417:
383:
379:
373:
349:
343:
326:
320:
289:
241:
237:
211:
202:
182:
171:
155:
151:
141:Stokes drift
129:
109:
98:
79:
63:ocean swells
59:ocean swells
52:
19:
18:
1836:Water waves
1755:Thermocline
1472:Mesopelagic
1445:Ocean zones
1416:Slab window
1281:Hydrography
1221:Abyssal fan
1188:Tidal range
1178:Tidal power
1173:Tidal force
1058:Rip current
993:Gulf Stream
953:Ekman layer
943:Downwelling
918:Baroclinity
905:Circulation
801:Wave height
791:Wave action
774:megatsunami
754:Stokes wave
714:Rossby wave
679:Kelvin wave
659:Green's law
424:Coral Reefs
146:group speed
133:subharmonic
112:Walter Munk
28:frequencies
1825:Categories
1693:Reanalysis
1592:Satellites
1573:Sofar bomb
1421:Subduction
1396:Ridge push
1291:Ocean bank
1271:Contourite
1198:Tide gauge
1183:Tidal race
1168:Tidal bore
1158:Slack tide
1123:Earth tide
1043:Ocean gyre
863:Wind setup
858:Wind fetch
821:Wave setup
816:Wave radar
811:Wave power
709:Rogue wave
639:Dispersion
537:2010-11-25
512:2022-11-22
507:Bay Nature
195:References
185:Antarctica
118:Generation
71:celerities
32:wind waves
1555:Acoustics
1507:Sea level
1406:Slab pull
1343:tectonics
1251:Cold seep
1213:Landforms
1090:Whirlpool
1085:Upwelling
868:Wind wave
796:Wave base
724:Sea state
644:Edge wave
634:Cross sea
396:CiteSeerX
366:117932573
313:2156-1028
114:in 1950.
1788:Category
1740:Seawater
1467:Littoral
1462:Deep sea
1321:Seamount
1203:Tideline
1148:Rip tide
1078:shutdown
1048:Overflow
781:Undertow
624:Clapotis
444:24665450
268:38071443
216:Elsevier
89:spectrum
67:tsunamis
36:wind sea
1798:Commons
1668:Mooring
1618:Related
1609:Jason-3
1599:Jason-1
1482:Pelagic
1477:Oceanic
1452:Benthic
769:Tsunami
739:Soliton
474:Bibcode
388:Bibcode
246:Bibcode
48:forcing
1487:Photic
1316:Seabed
729:Seiche
442:
398:
364:
335:489729
333:
311:
266:
168:Impact
93:period
1678:Ocean
1647:Alvin
1497:Swash
1341:Plate
1286:Knoll
1276:Guyot
1231:Atoll
1110:Tides
873:model
759:Swell
591:Waves
462:(PDF)
440:S2CID
362:S2CID
264:S2CID
101:tides
40:swell
26:with
1645:DSV
1630:Argo
1492:Surf
948:Eddy
331:OCLC
309:ISSN
295:ASCE
103:and
38:and
22:are
482:doi
432:doi
406:doi
354:doi
299:doi
254:doi
1827::
529:.
505:.
480:.
470:36
468:.
464:.
438:.
428:17
426:.
404:,
394:,
384:87
382:,
360:,
307:,
276:^
262:.
252:.
242:37
240:.
236:.
224:^
180:.
575:e
568:t
561:v
540:.
515:.
490:.
484::
476::
446:.
434::
408::
390::
356::
337:.
301::
270:.
256::
248::
95:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.