1872:
1134:
1936:
1069:. Nothing escaped the concept of ownership. Thus, not only objects, houses and people could be property, but also fishing places for salmon, as generally places, rituals and ceremonies, songs and stories, which by all means not everyone was allowed to know. War was therefore above all a means of acquiring wealth, for example in the form of enslaved people, who created and maintained the means of living for the upper class. Nevertheless, they lived under the same roof with their owners. In addition, they were able to acquire spiritual power.
967:, could be exported to climatically unsuitable areas. The advantage of this way of life was that there were hardly any crop failures, and even if the crops failed in unfavorable years, one could switch to the sea. However, in order to secure access to such areas, the principle of family lineage came into play, which means that certain areas or devices, such as pots, could only be used along a line of family relationships. Consequently, the number of Coastal Salish was extremely large, although it cannot be precisely estimated. The explorers
1844:
1113:(a female member marries the corresponding widower) was common to secure relations between groups related by marriage. Kinship relationships were always bipartite, and marrying blood relatives was subject to prohibitions. These extensive kinships were extremely important. Local relationships also existed in the family, the household, the local group, and the winter village. The extended family remains an important emotional and economic base to this day. Family solidarity is still the basis of political life.
346:
63:
867:
1369:). Moreover, quite against the custom of local groups, "tribes" were formed that had not existed before. As Governor Stevens put it, "When gathered into large bands it is always in the power of the government to secure the influence of the chiefs, and through them to handle (manage) the people." Incidentally, like his contemporaries, he believed that Indians should be settled on reservations, left to fish, and made farmers by resident whites.
168:
22:
587:
110:
338:
270:
603:, was able to gain a say in the management of archaeological sites. Despite research that was initially hardly funded, the results of the last few decades are remarkable. The situation is similar in Washington. In 2003, an archaeological report stated that there were 14,000 archaeological sites ranging from entire villages to trees that have been modified for cultural reasons (
662:, which had been favored for a long time, now produced sufficiently large trees, and woodworking had advanced enough to work the giant trees. From 1000 AD at the latest, care was often taken not to kill the giant trees if possible. The processing of stone sculptures can also be proven for the first time from this time; fifty of these cultural belongings alone are now in the
878:
1405:. Protective measures by some missionaries and physicians, as in 1853 and 1862, helped only sporadically. Thus, numerous Salish survived around Victoria and in Puget Sound, but this time the North was helplessly exposed to the disaster. Nevertheless, the mission stations also benefited from these disasters, for the loss of cultural knowledge through the death of
1990:, inter-tribal dance gatherings have also gained in popularity. Still, not all songs can be sung and played, as they are tied to seasons or specific ceremonies, often to specific clans. These celebrations culminate annually in a large cross-border gathering of all Coast Salish, whose participants are welcomed by the tribes in turn.
1688:. In 1992, the provincial government recognized both land rights and the right to self-government (self-government). In 1993, the provincial Supreme Court even recognized legal rights, albeit limited, to non-reserve lands. Since then, treaty negotiations have been ongoing for each of the negotiating groups. Of the Salish, only the
2147:, or 15%. Of this, 8,000 ha are secured as parks and protected areas. Over 84% is thus privately owned, of which nearly 200,000 ha alone is in the hands of a few timber companies. But this is what the often poor communities fear most, that their members will gradually sell out in the event of privatization.
863:). They were reserved for the "nobility". Similar rules applied to building houses and hunting, but also to collecting numerous plants, such as berries, grasses, etc. It could happen that family clans migrated to certain areas that "belonged" to them, depending on the best time to harvest the plants – Year for year.
1620:, recognized pre-European rights as continuing until the contrary was established. The government postponed the issue from 1925, allowing plenty of time before a parliamentary inquiry, which was to take place in 1927. At that time, Parliament passed the aforementioned ban on hiring lawyers. Barely a year later, the
674:
phase. Strings of beads and rings made during this period with copper from Alaska have been found. Such finds point to a far-reaching system of trade contacts, whose goods may have served to satisfy special representational needs, which are probably connected with the emergence of a class of nobility.
2203:
has increased from 11 to almost 30% since the 1960s. The number of people employed by the Stó:lō nation increased tenfold between 1990 and 1997, from about 20 to about 200. Meanwhile, people also receive money for useful work they have long done without pay, such as caregiving, teaching, maintenance,
1643:
In 1947, as a kind of by-product of a worldwide development in favor of voting rights for minorities, the
Indians were given the right to vote at the provincial level. In 1951, they succeeded in getting cultural practices, such as potlatch, exempted from all prohibitions. Children were now allowed to
1261:
also often from the specially kept dogs. Dogs were probably kept like flocks of sheep and provided white and dark fibers for blankets, mats, baskets, and clothing that were widely traded. With the severance of numerous trade contacts, blankets became an important commodity soon traded by the Hudson's
1179:
also often from the specially kept dogs. Dogs were probably kept like flocks of sheep and provided white and dark fibers for blankets, mats, baskets, and clothing that were widely traded. With the severance of numerous trade contacts, blankets became an important commodity soon traded by the Hudson's
1081:
traced themselves back to a common ancestor, who in turn appears in the ritual objects. Society was thus organized according to this particular type of family, not primarily by tribe. Thus, kinship relations determined the family-bound dialect, but also who worked together, who shared resources. This
890:
It has long been known that the Salish were not only hunter-gatherers, but also farmers tied to a specific area, who undertook migrations according to the cycles of nature. For example, they planted camas, a bulbous tuber from the asparagus family with blue flowers. Their onions taste like very sweet
2002:
Part of the repertoire of pre-European education was the recitation of oral tradition, which included family histories, history and genealogy, legends and myths. This task was the responsibility of elders, but also took place through instruction of young women by elders in menstrual huts, and in the
1716:
Indians increasingly hired themselves out as loggers, sawmill assistants, and for a time even as miners in the coal mines and as sailors. Others worked in the fishing industry, the men mostly as fishermen, the women gutting and packing. But
Chinese displaced them first in railroad construction, then
1224:
is estimated to have cost the lives of at least one-third of the
Pacific Coast Indians; among the Salish in what is now the United States, the losses were probably much higher, so high that they could hardly defend themselves against raids by the initially less affected peoples from the north. Again
796:
that was then on the coast, but which has now been shifted further west by Fraser deposits. The village, situated on a shell mound, was several hectares in size, the mound 3 to 4 m high. A peak of complexity was reached on the South Coast. Permanent winter settlements can be proven, from around 1 AD
2215:
This historical legacy ensures that it is not easy to determine what constitutes a tribe, even though the government has established a seven-criteria catalog. Since only the tribes as a whole are allowed to operate casinos, and these in turn have proven to be enormously important providers of jobs,
2182:
Tribes should be considered. The report outlined the traditional and current uses of the affected lands, considered the importance to the aforementioned tribes. Lessons learned from this led to the protection of various areas in the newly formed city and resulted in Native
American participation in
2078:
In 1993, British
Columbia responded by establishing the BC Treaty Commission. Its initial purpose was to clarify and, if possible, resolve overlapping land claims. At the end of the six-step process, a treaty was to be reached. But the treaty process has divided opinion. The number of holdouts, who
1972:
ban was lifted, there was a corresponding movement, but when the ban was lifted in 1951, they were allowed to go public again. Ten years later, there were still only about 100 dancers, but by the 1990s, 500 or more dancers often gathered. A song and spirit helper introduces the necessary knowledge,
1834:
Since the 1960s, numerous positions have been created in self-government through state funding. These positions were often held by women. In the meantime, many tribes are trying to become economically independent again by using their territory for tourism after a large part of the natural resources
1294:
of 1858, the population further north also skyrocketed. Thousands of mostly armed gold prospectors - mostly from
California - combed the region, displacing or killing an unknown number of Indians. In the process, the "old settlers" quickly became a minority. This in turn forced the British colonial
557:
and escalated to the point of the forced removal of
Indigenous children to residential schools for which the Canadian government apologized in 2008. During this phase the population collapsed, most languages were lost and migration to the cities increased so much that the vast majority of the Coast
525:
and explorers coming from Europe also used the trade routes and well-known waterways. However, they also brought in unknown diseases that wiped out numerous tribes, for the Salish were decimated by smallpox as early as 1775 onwards. In addition, there was a particularly warlike phase, characterized
1337:
was initially of little importance. However, the first settlers from about 1850 onward came into conflict with the indigenous peoples through their land claims and ruthless dealings. The latter had previously dealt mainly with traders, some of whom had even married into their families. This system
594:
The early history of the
Coastal Salish and their predecessor cultures can only be grasped archaeologically and later by oral tradition. Approximately 400 construction permits are issued annually for around 23,000 archaeological sites in British Columbia. This often leads to conflicts, because the
1144:
Trade played a role not consistently comparable to
European trade. The voyages served for the exchange of goods, but also for the establishment and consolidation of kinship relations, which one could fall back on, even after a longer period of dormancy. Thus, the coastal Salish had places to stay
1708:
The Coast Salish on the lower Fraser River (and Puget Sound) were the first to be affected. In addition, the emerging farms made gathering and digging impossible for Indian women. Then, increasingly industrial fishing, which the
Canadian government assisted with restrictions against the Indians,
1926:
on southern Puget Sound, which by 1850 consisted of only 50 survivors of severe epidemics, slowly rebounded at first. Gaining land rights, sovereignty, and economic self-sufficiency not only attracted new residents to the reservation and its environs, but more and more people acknowledged their
928:
Seasonal migrations shaped the course of the year. They hibernated along the rivers, and larger groups then got together. The most important ceremonies and celebrations took place from October/November to February/March. In spring we went fishing to replenish the depleted supplies. The fish was
673:
from circa 500 AD, but then disappeared. In contrast, the northern coastal areas still have piercings as part of their traditions today. A type of ear coil from about 500 BC also survived. Soapstone objects of unclear use (sometimes called "whatzits") can possibly also be classified within this
565:
of some tribes, but above all the growing awareness of the common cultural values, there was a partial revival of the community of the Salish groups. Many groups are still fighting for tribal recognition as a prerequisite to even entering into negotiations for their sovereignty and land. Tribal
1120:
of the tribes were mostly men, but women were often the heads of their households. Leadership depended on the ability to acquire and properly exercise spiritual power and on personal ability. There was no formal, super-personal authority. Related to this is the concept of the redistribution of
2195:
First Nations. The 13-Monde system again plays an important role in this. In the year 2000 the Beecher Bay invited to a celebration, to which all involved people appeared. According to the rituals, the younger ones served as servants, namely the ancestors, to whose honor food was also burned.
2067:
ruled that prior to 1867, aboriginal rights had never been extinguished, and therefore had continued since the founding of Canada. In addition, several court rulings held that Indians had the right to teach their particular culture to their children, with the territory being an integral part.
1667:
rejected this. In 1969, the Chief Justice of British Columbia, Davey, nevertheless rejected the Nisga'a land rights, and in 1973 the Supreme Court declared that the Nisga'a had held the rights. While several provinces and the federal government now recognized the land rights in principle, the
1048:, nevertheless reported: "I could not believe that any uncultivated land was ever discovered that such a gave a rich picture." The fact that the population was quite thin, because smallpox had claimed so many lives shortly before, probably contributed to this impression. Around 1913/1916 the
1472:
The competition between the denominations led to new internal borders among the Salish. The respective community leaders not only watched over the lifestyles of their youngsters - for which they reinterpreted the watchman system of the Indians and turned it into an instrument of control and
552:
While the Salish were initially able to play an important economic role in British Columbia before they were pushed out of most industries by legislation, in the USA they were often relegated to comparatively inhospitable regions. The two states also pursued different strategies of forced
2211:
and hotels have become important sources of income. At the same time, tribal territories are much less sharply defined on the one hand, and much more heavily populated by non-tribal members on the other. In addition, the tribes are often considerably larger. They strive predominantly for
1879:
Seasonal employment was available in the state's agriculture, especially during the harvest season. For example, the important cultivation of hops for beer production provided numerous summer employment opportunities. In many cases, families moved from one harvest operation to the next.
499:, the general population, and enslaved people, who were mostly prisoners of war and their descendants. In addition, there were enslaved people as objects of trade and the exchange in the form of ritual gifts within the leading groups. Similar to membership in the nobility, the rank of
569:
While attempts were made in the USA for several decades to break up tribal lands into parcels and privatize them, the majority of Canadian reserves remained tribal property. British Columbia has been trying to implement this privatization in exchange for enlarged reserves since 1993
932:
During the summer, wood was still collected, but now wood was also cut, from which not only house poles and planks, canoes, totem poles, weapons and tools were made, but also headgear and clothing. In addition, a white-haired dog breed provided the material for blankets, which
1818:
But most Indians worked in the fishing industry. While 1,500 to 2,000 worked as fishermen and rowers around 1900, by 1929 there were 3,632. Again, they participated in the first fishermen's strike as early as 1893. Likewise, they were involved in union formations, such as the
2141:. Coal mining, forestry and other industries have left little of the original landscape. As a result, virgin forest now exists on only 0.5% of the tribe's territory. Most reservations are smaller than 40 ha. In the traditional tribal area, only 48,000 ha are still
2219:
Despite such opposition, the Coast Salish see themselves as a transboundary, cohesive group that has been developing a program to restore and protect the natural environment since 2007. To that end, representatives of both Canadian and U.S. Salish tribes gathered on the
1704:
put prestige, weapons, and political power into fewer hands than before. Initially, those tribes that were the first to profit from the fur trade had an advantage. But this also brought whites into their territory, and the danger of being hit by epidemics grew rapidly.
731:
provide numerous clues to the society behind them. They consist not only of shells, but also of ashes, rocks shattered by the heat of a fire, animal bones and refuse. From about 1500 AD a more food-storing society seems to have developed, depending primarily on salmon.
952:. It formed the time frame in which economic activities such as catching, searching, and harvesting were combined with ceremonial and educational aspects. With this, places of residence, ceremonies, the right moments for teaching were assigned to each lunar month.
1895:). These gambling establishments have since evolved into profitable entertainment venues, which have shifted their original focus in favor of comprehensive tourism and entertainment offerings. Several Coast Salish tribes also maintain such casinos, such as the
2068:
Therefore, any decision affecting this land would have to involve consultation with the affected tribe. In 1997, the Supreme Court ruled that the rights refer to rights to land, resources, and the right to cultural traditions, as well as political autonomy.
2228:
reservation in Washington from January 24–26, 2007, and February 27–29, 2008, respectively. These meetings have been held since 2005. Their participants consider themselves responsible for the entire coast claimed by Salish tribes, and consequently call it
1295:
government to provide a counterbalance. Thus, it urgently encouraged immigration from Great Britain, pushing the Stó:lō or Tait (also spelled Tiyt, Upper Stó:lō) in particular even closer together, and deporting others to tiny, out-of-the-way reservations.
2408:
1527:
succeeded him until 1898. The federal government repeatedly clashed with provincial policy, and in 1908 the commission began to disband. In 1911, the case was to go to the Supreme Court, but the province refused to cooperate. On September 24, 1912, the
634:
Traditionally, the Coast Salish have asserted that they have always lived where they live today. Creation stories are widespread, often of animals in human form, of creators or ancestors of today's tribes or Nations. In addition, there is the idea of a
1835:
have been used up or destroyed. Since 1993, they have also been allowed to engage in limited salmon fishing on the Fraser for commercial purposes. However, salmon stocks are in massive decline, partly due to fish farms, partly due to climatic changes.
1277:, which were intensified by the first fur traders and the steady influx of arms, may have done considerable damage to the trade in some years. What economic changes the looted people led to among the northern tribes seems to have been little explored.
1195:, which were intensified by the first fur traders and the steady influx of arms, may have done considerable damage to the trade in some years. What economic changes the looted people led to among the northern tribes seems to have been little explored.
1145:
practically everywhere in the vast residential area, which in turn facilitated trade. However, this knowledge was "private" and belonged to only one family at a time. The lower class was much more restricted regionally and possessed no such knowledge.
1976:
Potlatches are meanwhile celebrated when someone is to receive the name of an ancestor, a funeral is pending, in memory of a deceased. Guests are invited from all over the Salish area to attend. Sometimes everything in the house is given away.
2758:
495:. At the latest from 1600 BC A rural way of life developed with a corresponding transformation of the landscape. There were also large villages that were sometimes inhabited in winter for centuries. Societies differentiated into a dominant
618:
should be gone for good. This probably explains, at least in part, why there are hardly any artifacts from before about 8000 BC, except in places that have never been flooded. Artifacts dating back to the 9th millennium BC were found on
1683:
was formed, chaired by Bill Wilson. Beginning in 1989, he held non-binding talks with resource companies, to which the government soon agreed. Unrest in other provinces also led to blockades in British Columbia, especially among the
1064:
of the coast Salish was clearly more pronounced than in the hinterland. In doing so, it in turn became more rigid from south to north. In addition to the leadership group, which had the resources, there were the simple tribesmen and
791:
Because of the paramount importance of salmon fishing, an immigration from the lower Fraser Valley or the Plateaus was long assumed, but Marpole culture appears to be regionally based. This culture is named for a site in present-day
463:
the Indigenous Peoples, with the US relying far more heavily on interbreeding, land privatization, and economic pressure. What they had in common was the attempt to wipe out the Indigenous cultures through bans and a corresponding
488:, which provide valuable insights into their ancestral practices and methods of processing resources. These trees bear traces of human modification, signifying their cultural significance within the Coast Salish communities.
1611:
of 1927, which denied all land claims. In addition, the Indians were explicitly prohibited from hiring lawyers to assert their rights. This was due, in turn, to the fact that the supreme court of jurisdiction in London, the
914:
The sparsely treed zones, which were equally necessary for the cultivation of camas and for the potatoes already adopted around 1800, were created through the targeted use of fire. Of particular importance was the Garry Oak
1072:
Sometimes large settlements existed with more than a thousand inhabitants. The houses were usually inhabited by several families, which had a common, but divided household. These houses were decorated with symbols, such as
553:
assimilation. These began in both states with proselytizing - against which their own spiritual forms developed as a reaction - led to bans on the most important cultural expressions, excluded all native inhabitants from
1237:
alone, at least 335 skeletons were found at Tse-whit-zen in 2005. Overland trade soon played as large a role in the spread as it did in transmission by the crews of fur trader ships. Thus, among the inland Salish of the
1662:
In 1960, the Indians were given the right to vote at the federal level, but in 1965 the Court of Justice in Victoria tried to enforce that in undiscovered British Columbia the law of 1763 had no validity. However, the
788:. It was already characterized by the same social differentiation, plank houses housing multiple families, salmon fishing and conservation, rich carvings of often monumental proportions, and complex ceremonies.
2216:
one tribe or another tries to prevent (as yet) unrecognized tribes from being accepted by the state in order to keep out the competition. Thus, it is not only the state that delays and complicates procedures.
2020:, were closed in the 1970s and 1980s. Both the churches and the state have since apologized for the conditions that prevailed there and have set up a program to make amends. Tribes, such as the Stó:lō Band on
1038:, blueberries, black currants, etc., with the boundaries between farming methods, gardening and simply keeping the area free for certain plants, e.g. by fire, or protection of a suitable area by stone walls.
844:
As was the case throughout the Pacific coast, the Salish tribes subsisted extensively on marine animals. The salmon, which swam up the rivers every year to spawn, played a prominent role. Other fish such as
2784:
in 2007, casinos throughout the United States employed 670,000 people. Revenues totaled $ 25 billion, with $ 7.7 of that in California alone. According to a December 17, 2007 article on SignOnSunDiego.com,
831:. At that time, a rank or prestige society probably still prevailed. It was not until around 1000 that an elite monopolized not only inherited and ascribed prestige, but also means of power and resources.
1993:
Engaging in culture and history has also made some familiar. Sonny McHalsie, a Stó:lō, has researched and documented numerous Halkomelem place names. He is employed by his tribe as a cultural specialist.
1289:
was flooded with gold seekers. This was joined by early settlers in Washington and Oregon. In 1850, a census recorded 1,049 white residents in what is now Washington; by 1860, there were 11,594. With the
1851:
reservation indicating their sovereign rights: "You are entering the legal territory of the Upper Skagit Indian Tribe - By doing so, you are subject to the laws and ordinances of the Upper Skagit Tribe
2751:
2607:
Brian Thom: Coast Salish Transformation Stories: Kinship, Place and Aborigingal Rights and Title in Canada, Discussion Paper for the Annual Meeting of the Canadian Anthropology Society, Toronto 1998
2071:
This decision relates, for example, to the fishing industry, which is Canada's fourth-largest industry. One third of the value is generated in British Columbia alone. It was not until 1990 that the
2024:
offer language courses and taught their children themselves. Language courses have been increasing sharply since the 1990s, and admissions to high schools and universities are also on the rise. The
1725:
By then, Indians, even dominantly until 1862, supplied the growing city of Victoria with building materials, labor, and food. In 1859, over 2,800 Indians camped near the city, including perhaps 600
1599:, but arrests occurred, including of chiefs beginning in 1920. In 1923, two of their leaders, Peter Kelly and Andrew Paull, presented demands to the government, first for compensation (2.5 million
808:, a winter village in the Fraser Valley. There are various depressions of houses that are large but not yet precisely measured. The children's graves are remarkably richly furnished, e.g. T. with
945:
similar, who guarded villages and camps. In July and August, when the salmon were migrating upstream, fishing was again the priority. In the late summer they finally went back to the mountains.
2497:
1554:
The Salish were the first to attempt to move more extensively in the initially unfamiliar political arena, within the three-tiered system of government. In 1906, a delegation traveled to King
853:, but also birds and game were on the menu. However, not everyone was allowed to hunt everywhere, because certain families had their reef nets and certain gathering areas, such as that of the
561:
The situation only changed with the changed legal situation, which the tribal representatives were able to enforce before the highest courts. Thanks to more open borders and the increasing
1346:
per capita. During the five years it was in effect, some 8,000 claims totaling 3 million acres went to white settlers through this act. The Indians were dispossessed without circumstance.
402:, as well as hunting and gathering activities. Recent research shows that some groups lived as early as the 2nd millennium BC. to a rural way of life with seasonally inhabited villages.
1462:
1257:), but also timber for the plank houses and for the forts of the fur trading companies. In addition, there were blankets, some of which were made from the hair of goats, around the
1175:), but also timber for the plank houses and for the forts of the fur trading companies. In addition, there were blankets, some of which were made from the hair of goats, around the
1489:. This is partly due to the immigration of gold miners from California, who, with their complete lack of sense of injustice, drove even friendly tribes into rebellion, as in the
959:
for a temporarily nomadic life. In bad years long-distance trade, using the coasts as routes for large trading canoes, could save lives. In the opposite direction, camas, later
1717:
Japanese and Europeans in fishing. Legislation prevented commercial fishing among the Indians. They increasingly relied on day labor, unskilled work, and seasonal employment.
998:. The wapatos, according to Clark on November 22, 1805, taste like Irish potatoes and they are a viable substitute for bread. The Kwagewlth maintained stone walled gardens of
639:
who created the landscapes, the animal and plant inhabitants, the foundations of the social order. Often they contain memories of the immigration period and of a great flood.
514:, which could reach over 50 m high, but also for the houses (early plank houses), but also for food, clothing and blankets. Metal, on the other hand, was extremely rare.
819:
Around 400 BC A society developed that favored the individual acquisition of prestige. Between about 500 and 1000 AD many South Salish groups are identified by cairn graves
1049:
955:
Hence, to limit disputes, the tribes claimed a traditional territory that ensured their survival on their annual circular migrations. So these areas are dozens of smaller
804:
replaced the various types of articulated harpoons. The number of ornamental works clearly increased, such as stone figures. An important site for the Marpole culture is
1250:
living in the backcountry, a "great disease" occurred in 1807 to 1808, but it is not until the epidemic of 1853 that it can be said with certainty that it was smallpox.
2150:
In 1994, in accordance with the change in the law, there was an opportunity for the first time in the expansion of Victoria, the capital of British Columbia, under the
1984:
has achieved national fame. In addition, there is canoe building. Canoe trips now attract many tourists, but there are also competitions between the tribes and clans.
1709:
destroyed the Salish fish trade. Structures, such as the railroad bridge over the Fraser, destroyed even the fish ladders necessary for fish, ending some of the mass
2086:
The hallmark of Salish politics has long been a certain smallness, broken first by cross-border ties but then by representatives in the highest bodies. For example,
1883:
In 1934, the U.S. abandoned its policy of weakening tribal associations and breaking them up into individuals. A significant breakthrough was the 1987 California v.
978:
Other fruits were also grown and transformed the landscape, but until very recently this was not recognized as a product of the peasant way of life. This is how the
1082:
kinship extended far beyond the local house group and village into other communities. The village, on the other hand, played a role in certain types of ceremonies.
911:-like character. At the same time, the harvest was a good opportunity to make social contacts in the camps on the fields and to strengthen society through rituals.
610:
In the early phase of human settlement, the landscape was still undergoing major changes. Glaciers, meltwater, swaying coastlines, a significantly lower sea level,
2438:
Recapturing the History and Rights of First Nations Peoples of British Columbia: A Political Analysis of Past and Present Relationships with the Dominion of Canada
549:
resulted in extreme dispersal of settlements, while in the United States, several tribes were often grouped together, creating new associations known as "tribes".
541:
along the 49th parallel, severing traditional territories, kinship and trade ties. The onset of settlement led to battles, especially in Washington, such as the
2273:
The ten Salish tribes that have applied for recognition but are not recognized in the United States include (as of 15. February 2007) in Washington include the
2079:
believe too many rights and titles are being relinquished, is growing, yet the first treaties are all but finalized. The Sechelt, on the other hand, signed the
1757:. They had integrated the newcomers into their extensive trading system. They were so successful in this that even the protracted wars were largely absent. The
1125:. Therefore, the governmental prohibitions valid until 1934 (USA) and 1951 (Canada) were an attack on one of the supporting pillars of the Indigenous cultures.
1799:
if it had any value on the black mountain burning. He himself had already shipped coal from there to Victoria. In 1852, Joseph MacKay, senior officer at Fort
956:
929:
air-dried, smoked, eaten fresh, but never salted. Dried fish was also an important commodity. Equally important food sources were roots, shoots and berries.
614:
shaped this phase, and there were also uplifts and lowerings of the coastlines, which were triggered by the melting of the huge ice masses. With that, many
185:
35:
1871:
1856:
The Coast Salish in the United States took a different economic trajectory. Here, strong impetus for self-organization initially came from the California
1477:. This further weakened the kinship-based communication system of the Coast Salish, as the denominations, and thus the tribes, kept more to themselves.
1607:
in reservation size, plus certain hunting and fishing rights. In addition, there were education and health benefits. The government countered with the
1208:
The first contacts with Europeans occurred among the southernmost Salish tribes. Here, two Spanish ships appeared in 1775, at least one of which, the
484:
and subsequent claims in the late 18th century. In addition to these sources, the Coast Salish history is enriched by oral traditions and research on
2494:
1692:
have so far accepted a treaty, and another has yet to be ratified, but the only one that has gone through the entire process is that of the Nisga'a.
1474:
760:
the most important localities are St. Mungo, Glenrose, and Crescent Beach. Mussels were clearly important here, and fish (especially salmon and the
440:. In return, the Indians received metal goods and weapons, which greatly changed the local hierarchies and the balance of power between the tribes.
2858:
1575:
1973:
rituals such as bathing in the wilderness, restriction to certain food, are meant to strengthen the novice in his isolation from the environment.
1052:
still clung to the prejudice that only uncultivated land could be Indian land, and in many places refused to add garden land to the reservations.
232:
1581:
After realizing the failure, most of the tribes pursued a policy of connecting with each other. Thus, in 1909, the backcountry tribes formed the
1105:
and Salish, two-line kinship prevailed through father and mother alike. Heredity did not prevail among the coastal Salish. Among all Salish, the
204:
2824:
1534:
was established. From 1913 to 1916, the commission visited the reservations. In the end, it recommended 54 reserve reductions totaling 47,000
1160:. Even before white settlers arrived, Indigenous Peoples grew tomatoes and potatoes, which they probably obtained from the first forts of the
1807:
unearthed, half were from them. Also, many of them became members in the unions. In 1890, Thomas Salmon, a resident of Nanaimo, was sent to
127:
211:
704:
was only smoked on the south coast, whereas in the north it was chewed. Northern cultures also grew tobacco in gardens. At the same time,
991:
627:. The region was settled between 8000 and 3000 BC. It was inhabited by semi-sedentary and sedentary groups who processed coarse-grained
432:
more than 50 years later. Thus, the canoe as a means of transport and the trade routes laid out by the coastal inhabitants, such as the
2581:, in: The American Journal of Human Genetics 82/3 (March 3, 2008) 583-592 and Renée Hetherington, Andrew J. Weaver, Álvaro Montenegro:
2670:
2648:
2630:
2313:
460:
405:
Already the first contacts with Europeans around 1775 decimated numerous groups to a great extent by imported diseases, above all by
218:
84:
41:
2133:
Tribe. They are concerned with 59,000 ha of land sold to settlers in the 1860s, 268,000 ha granted in 1884 to build the
455:
by military force. While in British Columbia each group that was considered a "tribe" received its own, albeit mostly very small,
1615:
686:
468:. In the meantime, many Indigenous communities have succeeded in reviving their cultural heritage and enforcing self-government.
1644:
attend public schools, legal counsel could be obtained, and the punishability of alcohol consumption and possession was lifted.
1453:
But the southern Salish tribes in Washington were also decimated by epidemics, and some tribes disappeared forever, such as the
200:
2799:
1357:, for example, rose up against them. But mass troop deployment suppressed the uprisings (1855-1858), which in the case of the
1298:
Douglas had already swung toward reservation policy some time ago; even the first treaties with the tribes around Victoria or
2618:
Archaeological Impact Assessment. Sonora Enterprises and Woodbrook Aggregates' Proposed Gravel Pit Expansion Near Deroche, BC
2430:
2435:
1133:
372:
show great uniformity early on, with a discernible continuity that in some places stretches back more than seven millennia.
2775:
Rolf Knight, Indians at Work: An Informal History of Native Labor in British Columbia. Vancouver: New Star Books 1996, 186.
1815:. During the coal strike in Nanaimo from 1912 to 1914, Indians refused to work as strikebreakers, ending up on blacklists.
1669:
1659:
began a new offensive with regard to land claims. Other groups, such as the Nuu-chah-nulth, also began to organize (1958).
2191:
instructional program since then has included not only biological content, but also cultural aspects, in this case of the
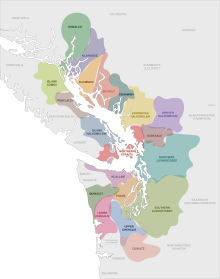
2047:
demanded, "Recognize our sovereignty, recognize our rights, so that we can fully recognize your rights." Indeed, in 1982,
1465:
were missionizing as early as 1840 and 1850, respectively, but initially with little success. It was not until after the "
288:
280:
2579:
Mitochondrial Population Genomics Supports a Single Pre-Clovis Origin with a Coastal Route for the People of the Americas
1423:
772:
found on almost all coasts of the North Pacific. was likely more important than game or marine mammals However, game and
2596:
Design of Stone Tool Technology during the Early Period (ca. 10,000–5,000 BP) at Namu, Central Coast of British Columbia
1515:
The reservations thus created were to be held in trust and reduced or enlarged according to population trends. In 1877,
1152:, which were 4–8 cm in diameter and could weigh over 100 g, there was an intensive trade, especially with the
566:
associations are pooling their efforts, borders are being marked and sovereignty rights are being successively granted.
2397:
2307:
2207:
The situation south of the U.S. border is strongly influenced by attempts to participate in tourism and entertainment.
2021:
1672:
now made a new argument, namely that nothing had been paid for the cession of these rights when joining Confederation.
1325:
Such a mild Indian policy had existed in the United States at best until 1846 or 1855, that is, at the moment when the
406:
358:
2482:
2887:
2454:
1949:, combining Christian and indigenous spiritual concepts, is based on the personal death and rebirth experiences of a
1591:
1524:
324:
306:
251:
149:
49:
2892:
1390:
1382:
1221:
620:
1137:
Canoeists on Lake Union near Seattle, ca. 1885. This traditional type of boat was later supplanted by that of the
2326:
1512:
which in turn was assigned as a whole a territory, usually not a closed one but a collection of specific points.
1415:
and healers, plus the belief that their own powers were too weak, caused many Salish to convert to Christianity.
451:
in 1846. These displaced the Indigenous Peoples to a much greater extent through settlement and forced them into
225:
708:
and other objects related to blanket-making appear. These blankets were probably made from the hair of dogs and
595:
majority of the sources on Salish history are - often not easily recognizable - underground or in shell mounds (
1595:
in 1916 as a counter organization to the McKenna-McBride Commission. Ostentatiously, they again celebrated the
1329:, which profited from Indian trade, had to vacate the field in 1846, new interests entered the power game. The
189:
574:), but only a few contracts have been concluded so far. Since 2007 it has been unclear whether this so-called
2336:
2134:
1253:
Other important trade goods were otter and beaver pelts, fish oil and fat (especially the buttery fat of the
1171:
Other important trade goods were otter and beaver pelts, fish oil and fat (especially the buttery fat of the
663:
599:), some of which are several meters high. It was not until 1995 that a First Nation in British Columbia, the
80:
1026:, Rubus parviflorus (Thimbleberry), Wild Onions, Strawberries, Cow Parsnip (Heracleum maximum, too known as
526:
by plundering raids by the northern coastal peoples, which were intensified by European weapons technology.
2012:
465:
2331:
2267:
2003:
case of shamans, by some sort of mentor. Grandparents were very important in this. Even as children, the
922:
824:
2865:
2786:
1493:- after all, it ended almost bloodlessly on the part of the Indians. If Ottawa had still considered 160
459:, the USA set up larger "reservations" in which several tribes lived. Both states attempted to forcibly
1701:
1530:
1431:
522:
131:
120:
2739:
The Lands We Lost: A History of Cut-Off Lands and Land Losses from Indian Reserves in British Columbia
1393:. In addition, there were diseases unknown to the Indians, and therefore all the more deadly, such as
739:
from about 1300 and 600 BC. In Gitaus and at the Paul Mason Site there were summer fishing camps. The
735:
At the lower Skeena River, in the Kitselas Canyon, several phases can be distinguished, including the
727:(1250–1800 AD) is characterized by small projectile tips of certain types of fortifications. The huge
2405:
Changing Views of Nuu-Chah-Nulth Culture History: Evidence of Population Replacement in Barkley sound
2099:
1887:
court case, which strengthened Indian sovereignty and prohibited state interference in the important
1781:
was eventually purchased by Chief James Claplanhoo, and three more schooners were added, finally the
1713:
In addition, there were dams. Lakes, like Lake Sumas, were simply drained in the 1920s for farmland.
1652:
1262:
Bay Company. They were also offered as barter for abandoned land when reservations were established.
1180:
Bay Company. They were also offered as barter for abandoned land when reservations were established.
921:), a species of oak. It is distributed between British Columbia and California but grows best around
604:
75:
2832:
975:
stated in 1805 that the number of inhabitants was not less than "in any part of the United States".
2711:
2192:
1230:
485:
1500:
Land per family considered appropriate, the provincial government would grant only 25. In 1875 an
743:(1600–1200 BC), which can only be verified in Gitaus, shows molded, single-edged and lance-shaped
2506:
2064:
1796:
1750:
1664:
1504:
was appointed to settle the land question. The principle was to make a deal with each individual
1366:
1326:
1291:
1247:
1161:
934:
444:
178:
907:) . Cultivation and care of the soil transformed the landscape over the centuries and gave it a
2800:"Themes, thoughts, and theories on strategic planning for Hul'qumi'num language revitalization"
2052:
1516:
1447:
1078:
624:
615:
369:
2527:- Multimedialer Ansatz der University of British Columbia in Victoria für den Sprachunterricht
2366:
The Power of Place, The Problem of Time: A Study of History and Aboriginal Collective Identity
2212:
self-governance and maintain their own political bodies, courts, executive organs, and so on.
2158:
a cohesive project was developed to address the demands of the six affected tribes, i.e., the
1485:
British Columbia's Indian policy has always been more ruthless than that of the government in
797:
there were also plank houses or long houses. The burial sites show strong status differences.
2126:
1458:
1411:
1265:
The raiding and pillaging campaigns of the tribes living north of the Salish, especially the
1183:
The raiding and pillaging campaigns of the tribes living north of the Salish, especially the
2897:
2239:
2171:
2159:
1945:
1334:
903:
659:
600:
507:
481:
2652:
2634:
1968:
was rediscovered since the 1950s and reached its first peak in the 1990s. Even before the
1935:
1225:
and again the disease flared up, as in 1790, when the visit of a ship led by the Spaniard
8:
1258:
1176:
1014:
regularly burned down terrain to make berries grow better. Other tilled soil for growing
2512:
1077:
and painted house walls. Equally famous are the masks of the coastal peoples. Often the
2723:
2461:
Aboriginal People and Politics: The Indian Land Question in British Columbia, 1849-1990
2355:
1156:, because the majority of the coveted fruit grew in the less humid and warmer south of
705:
452:
388:
2631:"Steatite Human Figure Bowl, Lower Fraser Valley at the Museum of Anthropology at UBC"
1803:, expressed satisfaction with the work of the Indians in the mines. Of the first 1400
1651:
in London, from 1949 only Canadian courts were eligible. However, in the early 1950s,
891:
baked tomatoes, some like pears. The Salish used two species, namely the Common Camas(
881:
The highly poisonous (hence the name Deathcamas), best on the Blossom distinguishable
2695:
2530:
2525:
Language Revitalization in Vancouver Island Salish Communities: A Multimedia Approach
2450:
2426:
1916:
1490:
1023:
571:
554:
2825:"Hul'qumi'num Treaty Group - Six First Nations working as one - The Great Land Grab"
1843:
2807:
2138:
1900:
1754:
1600:
1398:
1358:
1342:
of 1850, a law that allowed virtually any settler to appropriate land of up to 320
1330:
1270:
1243:
1188:
1157:
1041:
968:
925:. Around 1800, this system covered around 15 km² in the area of today's city.
917:
893:
859:
429:
384:
365:
2059:) and put the relationship with the levels of government on a new footing. In the
2501:
2247:
2243:
2221:
2179:
2114:
1927:
Native American heritage. Today, the tribe again boasts more than 3,800 members.
1923:
1820:
1742:
1685:
1563:
1559:
1354:
1239:
1217:
1213:
979:
761:
542:
443:
While the northern portion of the Salish-inhabited territory fell to the British
2797:
2387:
Indians in the Making: Ethnic Relations and Indian Identities around Puget Sound
1980:
Also revived were the arts of carving, painting and weaving. Susan Point of the
1168:
were also occasionally planted, but they were apparently not a trade commodity.
623:, at Far West Point. One of the oldest sites in British Columbia was found near
2208:
2083:
in 1986. Whether they are more than a municipal government remains to be seen.
1908:
1762:
1738:
1419:
1362:
1274:
1226:
1192:
1153:
1138:
1086:
1007:
995:
655:
538:
534:
456:
425:
413:
376:
2380:
Canada's Other Newcomers: Aboriginal Interactions with People from the Pacific
2143:
1922:
At the same time, some tribes are showing tremendous growth. For example, the
1508:
But this meant that each individual, regardless of kinship, was assigned to a
1442:, whose numbers, however, had collapsed from about 5,000 to 200. In 1859, the
1385:
that raged among the Salish. Perhaps in 1801, but certainly in 1824 and 1848,
436:, gained great importance for the initially most important trade in otter and
364:
on the Pacific coast of North America bound by a common culture, kinship, and
2881:
2666:
2122:
1939:
Klallam men in Sunday clothes on the beach, a Shaker church in the background
1888:
1774:
1315:
972:
709:
697:
530:
448:
2649:"Steatite Spindle Whorl, Milliken Site at the Museum of Anthropology at UBC"
2368:, Dissertation, Department of History, University of British Columbia, 2003.
2250:
as well as other Salish tribes, a section of the Squamish, particularly the
2075:
recognized Indian fishing rights, with priority over other economic claims.
1647:
Since the Canadian government curtailed the possibility of appealing to the
1285:
But still the number of settlers in the region was extremely small, even if
345:
1912:
1848:
1730:
1402:
1266:
1184:
1117:
1090:
1019:
987:
757:
713:
596:
500:
433:
361:
2311:. In Oregon, the Tchinouk Indians are not recognized (rejected 1986). The
1961:. From there, the doctrine, launched in 1882, spread to British Columbia.
1044:, who had seen extensive camas fields on southern Vancouver Island and at
62:
2524:
2091:
1958:
1954:
1896:
1466:
1435:
1098:
1045:
1015:
866:
648:
477:
410:
2270:, on the other hand, support the Olympics and derive profits from them.
2105:
One of the tribal councils representing a larger group of Salish is the
1838:
1349:
In 1855, several treaties were made, but the terms were so bad that the
424:
did not begin on the Pacific coast accessible by ship, but first on the
2846:
2518:
2259:
2231:
2184:
2167:
1689:
1656:
1555:
1306:
to take measures to establish reservation boundaries. The expansion of
1286:
1254:
1172:
1109:(a male member of the deceased man's family marries his widow) and the
1074:
983:
682:
562:
511:
437:
2425:, University of British Columbia Press, 1. Aufl. 2006, 2. Aufl. 2007.
1338:
was quickly destroyed. The basis of the settlers' land claims was the
2130:
2110:
1997:
1828:
1734:
1454:
1443:
1394:
1314:
themselves. This comparatively mild Indian policy ended in 1864 with
1094:
1061:
883:
839:
828:
793:
628:
167:
2679:
2263:
2163:
2087:
1981:
1969:
1892:
1791:
When extensive coal deposits were discovered, it was thanks to the
1746:
1726:
1596:
1538:; after protests, it reduced to 35 affected reservations or 36,000
1378:
1149:
1122:
1110:
1106:
1102:
801:
773:
769:
750:
670:
496:
521:
permitted warfare along the coasts, but also extensive trade. The
2225:
2175:
2042:
1904:
1800:
1439:
1406:
1386:
1299:
1234:
850:
846:
745:
701:
611:
586:
503:
was mostly hereditary in certain families, but could be revoked.
476:
The early history of the Coast Salish people primarily relies on
2423:
The First Nations of British Columbia. An Anthropological Survey
1222:
catastrophic smallpox epidemic in the 1770s on the western coast
658:
became characteristic of the west coast culture. Presumably the
2118:
1987:
1808:
1785:
in Victoria. In 1886, Chief Peter Brown purchased the schooner
1571:
1486:
1350:
1066:
1011:
1003:
964:
960:
942:
813:
728:
546:
492:
399:
392:
380:
2477:, in: Southwestern Journal of Anthropology 7/3 (1951) 272–288.
2409:
Canadian Journal of Archaeology/Journal Canadien d'Archéologie
651:
also assert that they have always lived where they are today.
420:
agreed in 1790 not to have trading posts, the construction of
2585:, Geological Society of America Special Papers 2007, 113-132.
1758:
1495:
948:
The basis of this hike was a kind of spiritual calendar, the
877:
717:
518:
417:
2798:
Suzanne Urbanczyk; Joanne Charlie; Brian Thom; Edna Thomas.
2583:
Climate and the migration of early peoples into the Americas
1574:, but no action could be taken from there because the lower
685:. Sites from this period include Esilao, Katz, Pipeline and
395:, traces of human presence go back over ten thousand years.
2055:
recognized in principle the claims of the original people (
1868:
many of whose representatives relied on existing treaties.
1720:
1675:
In the mid-1980s, 75% of the participants in a vote of the
1523:
but he was overthrown in 1880 for conceding too much land.
1438:
even succeeded in virtually imposing a God-state among the
1165:
908:
681:(350 BC to 250 AD) is notable for the disappearance of the
421:
337:
2553:
Aboriginal slavery on the Northwest Coast of North America
2400:, Bd. 7: Northwest Coast, Hrsg. Wayne Suttles, S. 159–168.
2358:
Native Americans of the Pacific Northwest: An Introduction
631:
into tools. Recent studies suggest the use of watercraft.
2254:, opposes the expropriation of the territory they claim (
2109:, formed in 1993. It represents the 6,200 members of the
1558:
in Britain to lobby for their land claims. Chiefs of the
2710:
Unearthing Tse-whit-zen, Seattle Times May 22–25, 2005:
2475:
The Early Diffusion of the Potato among the Coast Salish
642:
2463:, University of British Columbia Press, Vancouver 1990.
2199:
Among the Coast Salish, the number of women working as
1827:
in 1912. They also participated in the dock strikes in
1480:
937:
met in 1808. At the same time there were the so-called
491:
The semi-nomadic Salish on the coast lived mainly from
2468:
Native Seattle: Histories from the Crossing-Over Place
2258:). The leaders of the so-called four host tribes, the
1578:
based in Canada would have had to deal with it first.
2564:
M. Leland Stilson, Dan Meatte and Robert G. Whitlam:
2447:
A Guide to the Indian Tribes of the Pacific Northwest
1875:
Family tent harvesting hops in Washington, circa 1900
1864:
In the Northwest, tribes banded together to form the
1839:
Gambling and Entertainment, Tourism and Culture (USA)
1566:
in 1912, but he lost the next election. In 1913, the
816:, which was extremely rare and valuable at the time.
779:
130:. Please help to ensure that disputed statements are
2532:
American Indians of the Pacific Northwest Collection
1549:
784:
The Coast Salish of today can be traced back to the
2521:- Virtuelle Ausstellung der Simon Fraser University
2481:This article is translated from the German article
2183:the development of marine protected areas, such as
1679:recognized the rights of the Indians. In 1988, the
1121:property which was conducted primarily through the
994:. There were also large fields of wapato along the
398:The livelihood was provided by fishing, especially
192:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
2534:, Digital Collections der University of Washington
1998:Aftermath: Mission, Residential Schools, Education
1862:Southern California Tribal Chairmen's Association.
840:Traditional livelihoods, hunter-gatherers, farmers
480:evidence, as written sources emerge only with the
2812:University of Victoria, Hul'qumi'num Treaty Group
2555:, Berkeley: University of California Press, 1997.
2154:to find workable ways. Under the auspices of the
2007:of families and tribes were selected and taught.
1473:punishment - but also disliked the occurrence of
1203:
379:, for example in the broad coastal border of the
341:Current distribution area of the Salish languages
2879:
2741:, Vancouver: Union of BC Indian Chiefs 1974, 4f.
2616:This and the following according to Ryan Spady:
2598:, Diss. Simon Fraser University, Vancouver 2006.
1860:(1919-1965), which was succeeded in 1972 by the
1813:Miners and Mine Labourers Protective Association
1361:went to near extinction. The reservation of the
2726:Central Columbia River Plateau Epidemic History
2449:, University of Oklahoma Press, 2. Aufl. 1992.
1302:made this clear. Thus, in 1861, he ordered the
510:, which not only provided the material for the
349:Distribution area of the Coast Salish languages
2394:History of Coastal British Columbia Since 1849
1434:was established on the Fraser in 1861. Bishop
2698:The hair of the dog: was it a sheep or a dog?
2566:A Field Guide to Washington State Archaeology
2551:On the meaning of slavery see Leland Donald:
2016:, whose primary goal was assimilation to the
1613:
2373:The Sto:lo in Canada's Pacific Coast History
1668:province still refused. However, the ruling
1635:In addition, there was participation in the
1603:), then for increases in entitlement to 160
1377:Worse, however, from the beginning were the
1055:
669:On the south coast there is evidence of lip
2752:"Report of Governor Isaac I. Stevens, 1854"
2382:, Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, 2006.
2361:, University of Washington Libraries, o. J.
1469:" that missionary successes were achieved.
700:appeared, probably around 500 AD. However,
50:Learn how and when to remove these messages
1930:
1761:in northwest Washington, belonging to the
1641:Confederation of British Columbia Indians.
1198:
545:. The establishment of Indian reserves in
2314:Mitchell Bay Band of the San Juan Islands
325:Learn how and when to remove this message
307:Learn how and when to remove this message
252:Learn how and when to remove this message
150:Learn how and when to remove this message
2859:"List of Petitioners by State - page 39"
2224:reservation in British Columbia and the
1934:
1870:
1842:
1825:International Longshoremen's Association
1721:Industrialization by and with the Salish
1372:
1132:
876:
865:
834:
585:
471:
344:
336:
126:Relevant discussion may be found on the
2665:
2470:, University of Washington Press, 2007.
2352:, Eugene: Oregon University Press 1955.
2081:Sechelt Indian Band Self-Government Act
1629:Native Brotherhood of British Columbia,
1616:Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
2880:
1546:were divided into over 1,700 parcels.
1389:followed, and again in 1837 and 1853,
1216:, probably introduced smallpox to the
812:, i.e. shells, and above all with the
368:, dates back several millennia. Their
2495:First Nations Digital Document Source
2416:The Prehistory of The Northwest Coast
2389:, University of Oklahoma Press, 1998.
1589:These organizations gave rise to the
1320:Chief Commissioner of Lands and Works
1304:Chief Commissioner of Lands and Works
753:. Flint was of paramount importance.
712:. The former were mainly kept on the
643:From the Milliken phase (ca. 7500 BC)
201:"History of the Coast Salish peoples"
2375:, Chilliwack, British Columbia 1997.
2350:The Coast Salish of British Columbia
1481:Reserve policy and the Trutch system
1422:, a Catholic missionary who reached
1310:, however, was to be set out by the
823:. There are hundreds of them around
590:Distribution of the Salish languages
506:The extremely rainy region produced
428:and further inland and only reached
263:
190:adding citations to reliable sources
161:
103:
56:
15:
2764:from the original on 25 April 2014.
2303:Chinook Indian Tribe/Chinook Nation
2032:contributed significantly to this.
1695:
1280:
1233:transmitted the disease; among the
447:, the southern portion fell to the
13:
2864:. 15 February 2007. Archived from
2398:Handbook of North American Indians
2308:Snoqualmoo Tribe of Whidbey Island
2152:Bamberton Town Development Project
1631:which published the monthly paper
1585:and those of the coast formed the
780:Marpole culture (400 BC to 400 AD)
776:were also important food sources.
279:tone or style may not reflect the
14:
2909:
2804:Brian Thom page at istar internet
2488:
2418:, Academic Press, San Diego 1995.
2035:
1592:Allied Tribes of British Columbia
1550:Resistance under the Constitution
654:In addition, from about 500 B.C.
31:This article has multiple issues.
2242:planned on the territory of the
2156:Environmental Assessment Office,
1866:Northwest Federation of Indians,
581:
289:guide to writing better articles
268:
166:
108:
61:
20:
2851:
2839:
2817:
2791:
2778:
2769:
2744:
2731:
2716:
2704:
2688:
2483:de:Geschichte der Küsten-Salish
2445:Robert H. Ruby, John A. Brown:
2295:Snoqualmie Tribal Organization,
2026:First Nations House of Learning
1885:Cabazon Band of Mission Indians
1769:in 1880 and chartered the ship
1627:In 1931, the tribes formed the
177:needs additional citations for
39:or discuss these issues on the
2659:
2641:
2623:
2610:
2601:
2588:
2571:
2558:
2545:
2519:A Journey into Time Immemorial
2030:University of British Columbia
1637:Indian Homemakers' Association
1204:First contacts and mass deaths
1:
2509:in: The Canadian Encyclopedia
2342:
2337:History of Washington (state)
2204:landscape conservation, etc.
2135:Esquimalt and Nanaimo Railway
664:Royal British Columbia Museum
578:can and should be continued.
2327:Geschichte der First Nations
2301:(denied in 2002), the resp.
1767:Neah Bay Fur Sealing Company
1521:Indian Reserve Commissioner,
1475:mixed-denomination marriages
950:system of the thirteen moons
7:
2696:31237445_ITM Barbara Huck:
2332:History of British Columbia
2320:
2317:is similarly unrecognized.
355:History of the Coast Salish
74:to comply with Knowledge's
10:
2914:
2414:RG Matson, Gary Coupland:
2279:Snohomish Tribe of Indians
2256:No Olympics on Stolen Land
2094:narrowly lost election as
1587:Indian Rights Association.
1531:McKenna-McBride Commission
1050:McKenna-McBride-Commission
1002:(Potentilla pacifica) and
2287:Cowlitz Tribe of Indians,
2189:Lester B. Pearson College
2107:Hul'qumi'num Treaty Group
2100:Assembly of First Nations
1858:Mission Indian Federation
1737:, plus 223 Stikine River
1681:BC First Nations Congress
1614:
1502:Indian Reserve Commission
1418:The first missionary was
1056:Societies and hierarchies
749:, a type of double-edged
605:Culturally Modified Trees
486:culturally modified trees
2888:History of North America
2669:; Pauly, Daniel (eds.).
2539:
2515:in: Multicultural Canada
2283:Samish Tribe of Indians,
2065:Supreme Court of Justice
1847:Sign on the road to the
1823:in the formation of the
1562:met with Prime Minister
1340:Oregon Donation Land Act
1231:Beecher Bay First Nation
1128:
857:, a species of mollusk (
87:may contain suggestions.
72:may need to be rewritten
2893:Native American history
1931:Revival of spirituality
1367:Treaty of Point Elliott
1292:Gold Rush on the Fraser
1199:Europeans and Americans
1060:Around 1800 the social
901:) and the Large Camas (
558:Salish now live there.
375:In the area of today's
2694:Fraser 119 et al. Cf.
2281:(denied in 2004), the
1940:
1915:, and as of 2009, the
1876:
1853:
1542:The remaining 733,891
1517:Gilbert Malcolm Sproat
1141:
1034:), carrots, so-called
887:
874:
873:whose bulbs are edible
591:
350:
342:
2673:Platichthys stellatus
2655:on 18 September 2008.
2637:on 18 September 2008.
2371:Keith Carlson (Hg.):
2305:(rejected 2003), the
2252:Native Youth Movement
2127:Lyackson First Nation
2053:Canadian Constitution
1938:
1874:
1846:
1583:Interior Tribes of BC
1373:Epidemics and mission
1365:was simply sold (see
1136:
880:
869:
835:Societies around 1800
766:Platichthys stellatus
589:
508:temperate rainforests
472:Introductory Overview
387:and the US states of
348:
340:
2240:Olympic Winter Games
2045:-Carrier Declaration
2018:Canadian way of life
1946:Indian Shaker Church
1797:Hudson's Bay Company
1383:pox epidemic of 1775
1335:Washington Territory
1327:Hudson's Bay Company
1162:Hudson's Bay Company
1006:at the mouth of the
904:Camassia leichtlinii
756:In the delta of the
482:European exploration
445:Hudson's Bay Company
186:improve this article
119:factual accuracy is
2871:on 31 October 2007.
2835:on 2 December 2008.
2829:Hul'qumi'num People
2513:Aboriginals: Salish
2061:Delgamuukw Decision
2013:Residential Schools
1670:Social Credit Party
1391:1862 again smallpox
1333:or, from 1853, the
1259:Juan de Fuca Strait
1235:Lower Elwha Klallam
1177:Juan de Fuca Strait
957:settlement chambers
2810:on 28 April 2007.
2594:Farid Rahemtulla:
2500:2016-01-01 at the
2421:Robert J. Muckle:
2403:Alan D. McMillan:
2385:Alexander Harmon:
2348:Homer G. Barnett:
2291:Jamestown Clallam,
1941:
1877:
1854:
1831:of 1923 and 1935.
1649:Judicial Committee
1409:and medicine men,
1142:
1000:Pacific Silverweed
888:
875:
592:
351:
343:
2431:978-0-7748-1349-5
2356:David M. Buerge:
2275:Steilacoom Tribe,
2178:Bands]], and the
1811:to represent the
1793:Nanaimo Coal Tyee
1491:Fraser Canyon War
1097:are described as
1024:Rubus spectabilis
576:BC Treaty Process
572:BC Treaty Process
555:the right to vote
537:divided the vast
335:
334:
327:
317:
316:
309:
283:used on Knowledge
281:encyclopedic tone
262:
261:
254:
236:
160:
159:
152:
102:
101:
76:quality standards
54:
2905:
2873:
2872:
2870:
2863:
2855:
2849:
2843:
2837:
2836:
2831:. Archived from
2821:
2815:
2814:
2806:. Archived from
2795:
2789:
2782:
2776:
2773:
2767:
2765:
2763:
2756:
2748:
2742:
2735:
2729:
2720:
2714:
2708:
2702:
2692:
2686:
2684:
2663:
2657:
2656:
2651:. Archived from
2645:
2639:
2638:
2633:. Archived from
2627:
2621:
2620:, February 2007.
2614:
2608:
2605:
2599:
2592:
2586:
2575:
2569:
2562:
2556:
2549:
2507:Salish, Interior
2378:Darren Friesen:
2238:In light of the
2139:Vancouver Island
2073:Sparrow decision
1696:Economic changes
1619:
1618:
1609:Great Settlement
1519:became the sole
1399:venereal disease
1331:Oregon Territory
1281:Mass immigration
1158:Vancouver Island
1042:George Vancouver
969:Meriwether Lewis
918:Quercus garryana
894:Camassia quamash
871:Camassia quamash
860:Tresus nuttallii
768:), a species of
687:Silverhope Creek
543:Puget Sound Wars
430:Vancouver Island
385:British Columbia
330:
323:
312:
305:
301:
298:
292:
291:for suggestions.
287:See Knowledge's
272:
271:
264:
257:
250:
246:
243:
237:
235:
194:
170:
162:
155:
148:
144:
141:
135:
132:reliably sourced
112:
111:
104:
97:
94:
88:
65:
57:
46:
24:
23:
16:
2913:
2912:
2908:
2907:
2906:
2904:
2903:
2902:
2878:
2877:
2876:
2868:
2861:
2857:
2856:
2852:
2844:
2840:
2823:
2822:
2818:
2796:
2792:
2783:
2779:
2774:
2770:
2761:
2754:
2750:
2749:
2745:
2736:
2732:
2721:
2717:
2709:
2705:
2693:
2689:
2664:
2660:
2647:
2646:
2642:
2629:
2628:
2624:
2615:
2611:
2606:
2602:
2593:
2589:
2576:
2572:
2563:
2559:
2550:
2546:
2542:
2502:Wayback Machine
2491:
2473:Wayne Suttles:
2440:, wohl von 2004
2411:22 (1998) 5–18.
2364:Keith Carlson:
2345:
2323:
2266:, Squamish and
2187:, in 1998. The
2038:
2000:
1933:
1889:casino business
1841:
1723:
1698:
1624:disintegrated.
1568:Nishga Petition
1564:Wilfrid Laurier
1552:
1483:
1375:
1308:Indian Reserves
1283:
1214:Bruno de Hezeta
1206:
1201:
1131:
1085:However, while
1067:enslaved people
1058:
842:
837:
786:Marpole culture
782:
762:starry flounder
645:
584:
474:
411:colonial powers
359:Native American
331:
320:
319:
318:
313:
302:
296:
293:
286:
277:This article's
273:
269:
258:
247:
241:
238:
195:
193:
183:
171:
156:
145:
139:
136:
125:
117:This article's
113:
109:
98:
92:
89:
79:
66:
25:
21:
12:
11:
5:
2911:
2901:
2900:
2895:
2890:
2875:
2874:
2850:
2838:
2816:
2790:
2777:
2768:
2743:
2730:
2715:
2703:
2687:
2667:Froese, Rainer
2658:
2640:
2622:
2609:
2600:
2587:
2570:
2568:, 2003, p. 14.
2557:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2537:
2536:
2528:
2522:
2516:
2510:
2504:
2490:
2489:External links
2487:
2479:
2478:
2471:
2464:
2459:Paul Tennant:
2457:
2443:
2436:Anita Pascoe,
2433:
2419:
2412:
2401:
2390:
2383:
2376:
2369:
2362:
2353:
2344:
2341:
2340:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2322:
2319:
2299:Duwamish Tribe
2268:Tsleil-Waututh
2125:First Nation,
2121:First Nation,
2113:First Nation,
2037:
2036:Recent history
2034:
2022:Seabird Island
1999:
1996:
1951:coastal Salish
1932:
1929:
1909:Shoalwater Bay
1840:
1837:
1795:who asked the
1763:Nuu-chah-nulth
1722:
1719:
1697:
1694:
1551:
1548:
1525:Peter O'Reilly
1482:
1479:
1432:Oblate Mission
1426:in 1841. With
1420:Modeste Demers
1381:, such as the
1374:
1371:
1282:
1279:
1227:Manuel Quimper
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1154:Nuu-chah-nulth
1139:Nuu-chah-nulth
1130:
1127:
1057:
1054:
1008:Nimpkish River
996:Columbia River
897:, also called
841:
838:
836:
833:
781:
778:
696:(250-1250 AD)
644:
641:
583:
580:
539:Oregon Country
517:The seaworthy
478:archaeological
473:
470:
457:Indian reserve
377:Coastal Salish
333:
332:
315:
314:
276:
274:
267:
260:
259:
174:
172:
165:
158:
157:
116:
114:
107:
100:
99:
69:
67:
60:
55:
29:
28:
26:
19:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2910:
2899:
2896:
2894:
2891:
2889:
2886:
2885:
2883:
2867:
2860:
2854:
2848:
2842:
2834:
2830:
2826:
2820:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2801:
2794:
2787:
2781:
2772:
2766:(PDF, 2.2 MB)
2760:
2753:
2747:
2740:
2737:Reuben Ware:
2734:
2728:
2727:
2719:
2712:
2707:
2700:
2699:
2691:
2682:
2681:
2676:
2674:
2668:
2662:
2654:
2650:
2644:
2636:
2632:
2626:
2619:
2613:
2604:
2597:
2591:
2584:
2580:
2574:
2567:
2561:
2554:
2548:
2544:
2535:
2533:
2529:
2526:
2523:
2520:
2517:
2514:
2511:
2508:
2505:
2503:
2499:
2496:
2493:
2492:
2486:
2484:
2476:
2472:
2469:
2466:Coll Thrush:
2465:
2462:
2458:
2456:
2455:0-8061-2479-2
2452:
2448:
2444:
2441:
2439:
2434:
2432:
2428:
2424:
2420:
2417:
2413:
2410:
2406:
2402:
2399:
2395:
2392:Michael Kew:
2391:
2388:
2384:
2381:
2377:
2374:
2370:
2367:
2363:
2360:
2359:
2354:
2351:
2347:
2346:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2324:
2318:
2316:
2315:
2310:
2309:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2292:
2288:
2284:
2280:
2276:
2271:
2269:
2265:
2261:
2257:
2253:
2249:
2245:
2241:
2236:
2234:
2233:
2227:
2223:
2217:
2213:
2210:
2205:
2202:
2197:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2181:
2177:
2173:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2153:
2148:
2146:
2145:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2123:Lake Cowichan
2120:
2116:
2112:
2108:
2103:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2084:
2082:
2076:
2074:
2069:
2066:
2062:
2058:
2054:
2050:
2049:section 35(1)
2046:
2044:
2040:In 1977, the
2033:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2014:
2008:
2006:
1995:
1991:
1989:
1985:
1983:
1978:
1974:
1971:
1967:
1962:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1948:
1947:
1937:
1928:
1925:
1920:
1918:
1914:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1881:
1873:
1869:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1850:
1845:
1836:
1832:
1830:
1826:
1822:
1816:
1814:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1789:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1776:
1775:Port Townsend
1772:
1768:
1765:, formed the
1764:
1760:
1756:
1755:Kwakwaka'wakw
1752:
1748:
1744:
1741:, 111 Duncan
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1718:
1714:
1712:
1706:
1703:
1693:
1691:
1687:
1682:
1678:
1677:Vancouver Sun
1673:
1671:
1666:
1665:Supreme Court
1660:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1645:
1642:
1638:
1634:
1633:Native Voice.
1630:
1625:
1623:
1622:Allied Tribes
1617:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1593:
1588:
1584:
1579:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1547:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1532:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1513:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1499:
1497:
1492:
1488:
1478:
1476:
1470:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1451:
1450:joined them.
1449:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1416:
1414:
1413:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1370:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1347:
1345:
1341:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1323:
1321:
1317:
1316:Joseph Trutch
1313:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1296:
1293:
1288:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1271:Kwakwaka'wakw
1268:
1263:
1260:
1256:
1251:
1249:
1248:Coeur d'Alene
1245:
1241:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1196:
1194:
1190:
1189:Kwakwaka'wakw
1186:
1181:
1178:
1174:
1169:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1140:
1135:
1126:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1083:
1080:
1076:
1070:
1068:
1063:
1053:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1028:Indian Celery
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
986:roots to the
985:
981:
976:
974:
973:William Clark
970:
966:
962:
958:
953:
951:
946:
944:
940:
936:
930:
926:
924:
920:
919:
912:
910:
906:
905:
900:
896:
895:
886:
885:
879:
872:
868:
864:
862:
861:
856:
852:
848:
832:
830:
826:
822:
817:
815:
811:
807:
803:
798:
795:
789:
787:
777:
775:
771:
767:
763:
759:
754:
752:
748:
747:
742:
738:
733:
730:
726:
721:
719:
715:
711:
710:mountain goat
707:
706:hand spindles
703:
699:
695:
690:
688:
684:
680:
679:Skarnel Phase
675:
672:
667:
665:
661:
657:
652:
650:
640:
638:
637:(transformer)
632:
630:
629:effusion rock
626:
622:
621:Dundas Island
617:
613:
608:
606:
602:
598:
597:shell middens
588:
582:Early history
579:
577:
573:
567:
564:
559:
556:
550:
548:
544:
540:
536:
535:Great Britain
532:
529:In 1846, the
527:
524:
523:fur merchants
520:
515:
513:
509:
504:
502:
498:
494:
489:
487:
483:
479:
469:
467:
466:school system
462:
458:
454:
450:
446:
441:
439:
435:
434:Grease trails
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
414:Great Britain
412:
408:
403:
401:
396:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
373:
371:
367:
363:
360:
357:, a group of
356:
347:
339:
329:
326:
311:
308:
300:
290:
284:
282:
275:
266:
265:
256:
253:
245:
234:
231:
227:
224:
220:
217:
213:
210:
206:
203: –
202:
198:
197:Find sources:
191:
187:
181:
180:
175:This article
173:
169:
164:
163:
154:
151:
143:
133:
129:
123:
122:
115:
106:
105:
96:
86:
82:
77:
73:
70:This article
68:
64:
59:
58:
53:
51:
44:
43:
38:
37:
32:
27:
18:
17:
2866:the original
2853:
2841:
2833:the original
2828:
2819:
2811:
2808:the original
2803:
2793:
2780:
2771:
2746:
2738:
2733:
2725:
2718:
2706:
2697:
2690:
2678:
2672:
2661:
2653:the original
2643:
2635:the original
2625:
2617:
2612:
2603:
2595:
2590:
2582:
2578:
2573:
2565:
2560:
2552:
2547:
2531:
2480:
2474:
2467:
2460:
2446:
2437:
2422:
2415:
2404:
2393:
2386:
2379:
2372:
2365:
2357:
2349:
2312:
2306:
2302:
2298:
2294:
2290:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2274:
2272:
2255:
2251:
2237:
2230:
2218:
2214:
2206:
2200:
2198:
2188:
2155:
2151:
2149:
2142:
2106:
2104:
2095:
2085:
2080:
2077:
2072:
2070:
2060:
2056:
2048:
2041:
2039:
2029:
2025:
2017:
2011:
2009:
2004:
2001:
1992:
1986:
1979:
1975:
1966:Spirit Dance
1965:
1963:
1950:
1944:
1942:
1921:
1913:Upper Skagit
1884:
1882:
1878:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1855:
1849:Upper Skagit
1833:
1824:
1817:
1812:
1804:
1792:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1770:
1766:
1724:
1715:
1710:
1707:
1699:
1680:
1676:
1674:
1661:
1653:Frank Calder
1648:
1646:
1640:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1626:
1621:
1608:
1604:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1580:
1570:followed in
1567:
1553:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1529:
1520:
1514:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1494:
1484:
1471:
1452:
1427:
1424:Fort Langley
1417:
1410:
1403:tuberculosis
1376:
1348:
1343:
1339:
1324:
1319:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1297:
1284:
1264:
1252:
1209:
1207:
1182:
1170:
1147:
1143:
1115:
1101:, among the
1084:
1071:
1059:
1040:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1020:Gooseberries
1004:cloverfields
999:
988:Gulf Islands
977:
954:
949:
947:
938:
935:Simon Fraser
931:
927:
916:
913:
902:
899:Indian Camas
898:
892:
889:
882:
870:
858:
854:
843:
820:
818:
809:
805:
799:
790:
785:
783:
765:
758:Fraser River
755:
744:
741:Skeena Phase
740:
737:Gitaus Phase
736:
734:
729:mussel heaps
725:Esilao Phase
724:
722:
714:Gulf Islands
693:
691:
678:
676:
668:
653:
646:
636:
633:
609:
593:
575:
568:
560:
551:
528:
516:
505:
490:
475:
453:reservations
442:
438:beaver pelts
409:. Since the
404:
397:
383:province of
374:
354:
352:
321:
303:
297:October 2022
294:
278:
248:
242:October 2022
239:
229:
222:
215:
208:
196:
184:Please help
179:verification
176:
146:
140:October 2022
137:
118:
93:October 2022
90:
81:You can help
71:
47:
40:
34:
33:Please help
30:
2898:Puget Sound
2442:PDF, 1,2 MB
2201:councillors
2193:Beecher Bay
2096:Grand Chief
2092:Wendy Grant
2057:aboriginals
1959:John Slocum
1955:Puget Sound
1911:tribe, the
1897:Muckleshoot
1467:Indian Wars
1436:Paul Durieu
1150:camas bulbs
1099:matrilineal
1075:totem poles
1046:Puget Sound
1036:crab apples
1016:Cranberries
806:Beach Grove
720:in Europe.
694:Emery Phase
656:post houses
512:totem poles
362:ethnicities
2882:Categories
2847:Salish Sea
2343:References
2232:Salish Sea
2185:Race Rocks
2168:Pauquachin
2144:Crown Land
2129:, and the
2090:candidate
2005:historians
1917:Snoqualmie
1751:Pacheedaht
1711:fish runs.
1700:The early
1690:Tsawwassen
1556:Edward VII
1463:Methodists
1444:Methodists
1428:St. Mary's
1287:California
1255:candlefish
1173:candlefish
855:horse clam
683:microliths
660:rainforest
563:prosperity
461:assimilate
389:Washington
212:newspapers
36:improve it
2248:St'at'imc
2131:Penelakut
2111:Chemainus
1901:Skokomish
1829:Vancouver
1787:Champion.
1783:Discovery
1753:, and 44
1735:Tsimshian
1702:fur trade
1686:St'at'imc
1576:instances
1459:Catholics
1455:Snokomish
1379:epidemics
1095:Tsimshian
1062:hierarchy
992:Arrowwort
939:camp dogs
884:Zigadenus
829:Metchosin
794:Vancouver
671:piercings
616:artifacts
370:artifacts
366:languages
128:talk page
85:talk page
42:talk page
2759:Archived
2680:FishBase
2498:Archived
2321:See also
2264:Musqueam
2246:and the
2244:Squamish
2222:Cowichan
2180:Cowichan
2164:Tsartlip
2117:Tribes,
2115:Cowichan
2088:Musqueam
1982:Musqueam
1970:potlatch
1924:Puyallup
1893:Cahuilla
1821:Squamish
1747:Heiltsuk
1743:Cowichan
1727:Songhees
1639:and the
1597:potlatch
1560:Lillooet
1440:Sechelts
1407:shamanss
1355:Puyallup
1353:and the
1240:Flathead
1218:Quinault
1210:Santiago
1123:potlatch
1111:sororate
1107:levirate
1103:Wakashan
1079:lineages
982:brought
980:Cowichan
923:Victoria
825:Victoria
821:(cairns)
810:Dentalia
802:harpoons
770:flatfish
751:hand axe
612:tsunamis
497:nobility
426:Columbia
407:smallpox
381:Canadian
121:disputed
2260:Lil'wat
2226:Tulalip
2209:casinos
2176:Tsawout
2172:Tseycum
2160:Malahat
2098:of the
2051:of the
2043:Gitksan
2028:at the
1988:Powwows
1964:Winter
1905:Tulalip
1899:or the
1805:barrels
1801:Nanaimo
1739:Tlingit
1657:Nisga'a
1655:of the
1506:nation.
1387:measles
1363:Cowlitz
1359:Chinook
1312:natives
1300:Nanaimo
1275:Tlingit
1244:Spokane
1229:to the
1220:. This
1212:led by
1193:Tlingit
1087:Tlingit
990:, i.e.
965:potaton
961:tomaton
943:Coyoten
851:Halibut
847:Herring
800:Barbed
746:bifaces
702:tobacco
692:In the
601:Nanoose
226:scholar
2724:Table
2453:
2429:
2407:, in:
2396:, in:
2119:Halalt
2063:, the
1957:named
1907:, the
1903:, the
1809:Ottawa
1779:Lottie
1777:. The
1771:Lottie
1745:, 126
1733:, 574
1729:, 405
1572:London
1540:acres.
1510:tribe,
1487:Ottawa
1412:elders
1401:, and
1351:Yakima
1273:, and
1246:, and
1191:, and
1118:chiefs
1093:, and
1032:Pushki
1012:Sto:lo
1010:. The
984:Wapato
814:copper
649:Stó:lō
547:Canada
519:canoes
493:salmon
400:salmon
393:Oregon
228:
221:
214:
207:
199:
83:. The
2869:(PDF)
2862:(PDF)
2762:(PDF)
2755:(PDF)
2540:Notes
1953:from
1891:(see
1759:Makah
1749:, 62
1731:Haida
1605:acres
1544:acres
1536:acres
1496:acres
1430:, an
1344:acres
1267:Haida
1185:Haida
1166:Beans
1148:With
1129:Trade
1091:Haida
941:who,
774:seals
718:sheep
716:like
698:pipes
501:chief
422:forts
418:Spain
233:JSTOR
219:books
2845:Cf.
2577:Cf.
2451:ISBN
2427:ISBN
2297:the
2293:the
2289:the
2285:the
2277:the
2174:and
2010:The
1943:The
1852:..."
1461:and
1448:Hope
1116:The
971:and
909:park
849:and
827:and
723:The
677:The
647:The
625:Namu
533:and
416:and
391:and
353:The
205:news
2722:S.
2137:on
1773:in
1601:CAD
1446:in
1395:flu
1318:as
1030:or
963:or
607:).
531:USA
449:USA
188:by
2884::
2827:.
2802:.
2757:.
2677:.
2485:.
2262:,
2235:.
2170:,
2166:,
2162:,
2102:.
1919:.
1457:.
1397:,
1322:.
1269:,
1242:,
1187:,
1164:.
1089:,
1022:,
1018:,
689:.
666:.
45:.
2788:,
2713:.
2701:.
2685:)
2683:.
2675:"
2671:"
1498:'
915:(
764:(
570:(
328:)
322:(
310:)
304:(
299:)
295:(
285:.
255:)
249:(
244:)
240:(
230:·
223:·
216:·
209:·
182:.
153:)
147:(
142:)
138:(
134:.
124:.
95:)
91:(
78:.
52:)
48:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.