305:. The tissue when dried is dull, firm, and immobile, with varying amounts of stippling. The width of the attached gum varies according to its location. The width of the attached gum on the facial aspect differs in different areas of the mouth. It is generally greatest in the incisor region (3.5 to 4.5 mm in the maxilla and 3.3 to 3.9 mm in the mandible) and less in the posterior segments, with the least width in the first premolar area (1.9 mm in the maxilla and 1.8 mm in the mandible). However, certain levels of attached gum may be necessary for the stability of the underlying root of the tooth.
373:
47:
216:
279:(CEJ) of the teeth. The marginal gingiva has a more translucent appearance than the attached gingiva, yet has a similar clinical appearance, including pinkness, dullness, and firmness. In contrast, the marginal gingiva lacks the presence of stippling, and the tissue is mobile or free from the underlying tooth surface, as can be demonstrated with a periodontal probe. The marginal gingiva is stabilized by the
689:
517:
360:
340:
covering the col consists of the marginal gum of the adjacent teeth, except that it is nonkeratinized. It is mainly present in the broad interdental gingiva of the posterior teeth, and generally is not present with those interproximal tissue associated with anterior teeth because the latter tissue is
196:
lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier
271:
The marginal gum is the edge of the gums surrounding the teeth in collar-like fashion. In about half of individuals, it is demarcated from the adjacent, attached gums by a shallow linear depression, the free gingival groove. This slight depression on the outer surface of the gum does not correspond
341:
narrower. In the absence of contact between adjacent teeth, the attached gum extends uninterrupted from the facial to the lingual aspect. The col may be important in the formation of periodontal disease but is visible clinically only when teeth are extracted.
212:, leading to a poorer prognosis for long-term retention of the teeth. Both the type of periodontal therapy and homecare instructions given to patients by dental professionals and restorative care are based on the clinical conditions of the tissue.
272:
to the depth of the gingival sulcus but instead to the apical border of the junctional epithelium. This outer groove varies in depth according to the area of the oral cavity. The groove is very prominent on mandibular anteriors and premolars.
208:. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in health and disease. When gum tissue is not healthy, it can provide a gateway for periodontal disease to advance into the deeper tissue of the
292:
The attached gums are continuous with the marginal gum. It is firm, resilient, and tightly bound to the underlying periosteum of alveolar bone. The facial aspect of the attached gum extends to the relatively loose and movable
283:
that have no bony support. The gingival margin, or free gingival crest, at the most superficial part of the marginal gingiva, is also easily seen clinically, and its location should be recorded on a patient's chart.
500:
away from the tooth by mechanical (such as brushing), chemical, or surgical means. Gingival retraction, in turn, may expose the dental neck and leave it vulnerable to the action of external stimuli, and may cause
411:
Healthy gums have a smooth curved or scalloped appearance around each tooth. Healthy gums fill and fit each space between the teeth, unlike the swollen gum papilla seen in gingivitis or the empty interdental
395:
Since the colour of the gums can vary, uniformity of colour is more important than the underlying color itself. Excess deposits of melanin can cause dark spots or patches on the gums (melanin gingival
275:
The marginal gum varies in width from 0.5 to 2.0 mm from the free gingival crest to the attached gingiva. The marginal gingiva follows the scalloped pattern established by the contour of the
197:
to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation.
388:"). Although described as the colour coral pink, variation in colour is possible. This can be the result of factors such as: thickness and degree of keratinization of the
128:
846:
562:
464:, fueled by food residues and saliva, can support the growth of many microorganisms, of which some can be injurious to health. Improper or insufficient
1046:
1011:
484:
is when there is an apical movement of the gum margin away from the biting (occlusal) surface. It may indicate an underlying inflammation such as
432:. Unhealthy gums, on the other hand, are often swollen and less firm. Healthy gums have an orange-peel like texture to it due to the stippling.
620:
648:
380:
Healthy gums usually have a color that has been described as "coral pink". Other colours like red, white, and blue can signify inflammation (
104:
100:
96:
667:
609:
721:
1858:
1444:
866:
416:
seen in periodontal disease. Healthy gums hold tight to each tooth in that the gum surface narrows to "knife-edge" thin at the
1255:
885:
693:
1215:
1210:
200:
Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an
699:
2144:
1159:
856:
1800:
1026:
996:
244:
861:
559:
123:
2263:
714:
588:
Illustrated Dental
Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 123
1851:
1437:
2075:
2049:
2044:
1886:
1485:
428:
Healthy gums have a firm texture that is resistant to movement, and the surface texture often exhibits
645:
2070:
1988:
1962:
1957:
1757:
1411:
1185:
1092:
606:
756:
1983:
1240:
1220:
1175:
1149:
1016:
971:
906:
841:
836:
79:
336:
The col varies in depth and width, depending on the expanse of the contacting tooth surfaces. The
2258:
2096:
1680:
1406:
1154:
1117:
1082:
1062:
899:
707:
664:
17:
1310:
472:
or periodontitis, which are major causes for tooth failure. Recent studies have also shown that
2192:
2182:
2091:
2009:
1844:
1767:
1700:
1430:
1401:
276:
135:
111:
91:
403:(aka gum bleaching) is a procedure used in cosmetic dentistry to remove these discolorations.
2004:
1881:
1815:
1795:
1673:
1599:
1589:
1584:
1480:
1235:
1230:
913:
831:
806:
791:
786:
535:
429:
302:
298:
1737:
1732:
1727:
1365:
1340:
1250:
1144:
991:
941:
920:
876:
796:
766:
477:
417:
256:
248:
31:
8:
2215:
1762:
1656:
1594:
1564:
1380:
1263:
1245:
1195:
1077:
1031:
927:
801:
445:
318:
1810:
1752:
1661:
1278:
1001:
892:
729:
481:
413:
400:
314:
392:, blood flow to the gums, natural pigmentation of the skin, disease, and medications.
2137:
2054:
1624:
1350:
1335:
1300:
1273:
1200:
1190:
966:
949:
823:
497:
441:
396:
2253:
1967:
1668:
1546:
1470:
1370:
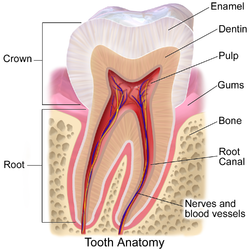
1315:
1268:
986:
473:
2228:
1931:
1904:
1825:
1820:
1742:
1579:
1574:
1569:
1320:
1021:
781:
776:
671:
652:
624:
613:
566:
522:
294:
280:
263:
The gums are divided anatomically into marginal, attached and interdental areas.
252:
84:
1360:
440:
Healthy gums usually have no reaction to normal disturbance such as brushing or
2202:
2167:
2132:
2115:
1867:
1772:
1636:
1541:
1513:
1475:
1225:
731:
461:
372:
240:
46:
2247:
2124:
1924:
1644:
1385:
1345:
1067:
1041:
1036:
851:
751:
540:
485:
236:
220:
205:
116:
384:) or pathology. Smoking or drug use can cause discoloring as well (such as "
2187:
2157:
2101:
2014:
1914:
1649:
1604:
1375:
1330:
1205:
1107:
1102:
1087:
746:
570:
465:
228:
209:
201:
317:, which is the interproximal space beneath the area of tooth contact. The
1896:
1690:
1536:
1531:
1454:
1355:
1305:
934:
193:
181:
2162:
1790:
1495:
1422:
1325:
1180:
1072:
1006:
976:
469:
420:. On the other hand, inflamed gums have a "puffy" or "rolled" margin.
389:
385:
381:
376:
Hyperpigmentation of the gum in a 22 year old non smoker female patient
337:
259:(PDL). J, horizontal fibers of the PDL. K, oblique fibers of the PDL.
141:
1722:
1112:
1097:
530:
493:
313:
The interdental gum lies between the teeth. They occupy the gingival
2028:
1919:
1614:
1609:
1490:
981:
761:
489:
232:
173:
1941:
1909:
1836:
1619:
771:
330:
326:
177:
169:
184:. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
2197:
1711:
1523:
688:
468:
can thus lead to many gum and periodontal disorders, including
215:
359:
1805:
1505:
224:
67:
1462:
449:
322:
597:
Mosby's
Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009, Elsevier.
641:
639:
637:
635:
633:
399:), especially at the base of the interdental papillae.
665:
Mondofacto medical dictionary > gingival retraction
617:
325:" shape. Attached gums are resistant to the forces of
560:
Gum disease opens up the body to a host of infections
231:(A). Dentin (B). The root of the tooth is covered by
847:
Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease
730:
Dentistry involving supporting structures of teeth (
630:
512:
365:Natural "coral pink" gums without any pigmentation
344:
2245:
27:Soft tissue surrounding the roots of the teeth
1852:
1438:
715:
646:mexicodentaldirectory.com: dental sensitivity
204:that is possibly due to the accumulation of
1859:
1845:
1445:
1431:
722:
708:
435:
51:Cross-section of a tooth with gums labeled
45:
658:
607:Gingival Recession - Causes and treatment
480:requiring a gingivectomy for many cases.
444:. Unhealthy gums, conversely, will show
1452:
455:
371:
214:
867:Combined periodontic-endodontic lesions
627:. Oct 2007. American Dental Association
14:
2246:
1840:
1426:
1256:Subepithelial connective tissue graft
703:
297:, from which it is demarcated by the
2123:
842:Generalized aggressive periodontitis
584:
582:
580:
578:
255:. I, alveolar crest fibers of the
219:A diagram of the periodontium. The
161:
24:
1866:
837:Localized aggressive periodontitis
308:
25:
2275:
1160:Full mouth ultrasonic debridement
681:
575:
476:are also closely associated with
301:. Attached gum may present with
857:Necrotizing periodontal diseases
687:
515:
358:
266:
1801:Plica semilunaris of the fauces
345:Characteristics of healthy gums
287:
241:subepithelial connective tissue
600:
591:
553:
13:
1:
862:Abscesses of the periodontium
546:
30:For other uses of "Gum", see
321:can be pyramidal or have a "
187:
7:
508:
251:. G, gingival sulcus. H,
10:
2280:
1887:Universal Numbering System
1486:Labial commissure of mouth
1216:Guided tissue regeneration
423:
406:
172:tissue that lies over the
29:
2224:
2211:
2178:
2153:
2114:
2084:
2063:
2037:
2027:
1997:
1976:
1950:
1940:
1895:
1874:
1783:
1710:
1689:
1635:
1555:
1522:
1504:
1461:
1394:
1293:
1186:Coronally positioned flap
1168:
1137:
1130:
1055:
959:
875:
822:
815:
739:
253:principal gingival fibers
192:The gums are part of the
134:
122:
110:
90:
78:
66:
61:
56:
44:
39:
1241:Pocket reduction surgery
1221:Enamel matrix derivative
1211:Guided bone regeneration
1176:Apically positioned flap
1150:Scaling and root planing
1056:Treatment and prevention
1017:Linear gingival erythema
972:Clinical attachment loss
886:A. actinomycetemcomitans
655:Retrieved on August 2010
349:
1681:Tubarial salivary gland
1294:Important personalities
1155:Full mouth disinfection
1118:Host modulatory therapy
1083:Chlorhexidine gluconate
1063:Periodontal examination
496:or displacement of the
436:Reaction to disturbance
2193:Dental-enamel junction
2183:Cementoenamel junction
2145:Zuckerkandl's tubercle
1768:Glossoepiglottic folds
1012:Horizontal bony defect
492:, a pocket formation,
377:
277:cementoenamel junction
260:
136:Anatomical terminology
1882:Glossary of dentistry
1816:Palatopharyngeal arch
1590:Mucogingival junction
1585:Junctional epithelium
1481:Frenulum of lower lip
1236:Open flap debridement
1231:Lateral pedicle graft
832:Chronic periodontitis
792:Mucogingival junction
787:Junctional epithelium
536:Head and neck anatomy
456:Clinical significance
375:
299:mucogingival junction
218:
1625:Periodontal ligament
1366:Paul Roscoe Stillman
1341:Willoughby D. Miller
1311:Per-Ingvar Brånemark
1138:Conventional therapy
1047:Vertical bony defect
992:Gingival enlargement
942:Entamoeba gingivalis
797:Periodontal ligament
767:Free gingival margin
696:at Wikimedia Commons
478:gingival enlargement
460:The gingival cavity
418:free gingival margin
257:periodontal ligament
249:free gingival margin
32:Gum (disambiguation)
2264:Human mouth anatomy
1763:Sublingual caruncle
1657:Submandibular gland
1595:Sulcular epithelium
1565:Interdental papilla
1381:James Leon Williams
1246:Socket preservation
1196:Free gingival graft
1078:Bleeding on probing
1032:Periodontal disease
802:Sulcular epithelium
618:http://jada.ada.org
446:bleeding on probing
442:periodontal probing
319:interdental papilla
1811:Palatoglossal arch
1027:Periodontal pocket
1002:Gingival recession
893:Capnocytophaga sp.
670:2018-12-09 at the
651:2016-03-09 at the
623:2013-01-25 at the
612:2010-09-17 at the
565:2018-01-23 at the
482:Gingival recession
401:Gum depigmentation
378:
261:
2241:
2240:
2237:
2236:
2138:Cusp of Carabelli
2110:
2109:
2023:
2022:
1834:
1833:
1420:
1419:
1395:Other specialties
1351:John Mankey Riggs
1336:Preston D. Miller
1301:Tomas Albrektsson
1289:
1288:
1226:Implant placement
1201:Gingival grafting
1191:Crown lengthening
1126:
1125:
1093:Hydrogen peroxide
950:Trichomonas tenax
692:Media related to
474:anabolic steroids
430:surface stippling
397:hyperpigmentation
303:surface stippling
168:) consist of the
150:
149:
145:
16:(Redirected from
2271:
2121:
2120:
2035:
2034:
1948:
1947:
1861:
1854:
1847:
1838:
1837:
1669:Sublingual gland
1547:Incisive papilla
1471:Vermilion border
1447:
1440:
1433:
1424:
1423:
1412:Prosthodontology
1371:Dennis P. Tarnow
1316:Robert Gottsegen
1135:
1134:
987:Furcation defect
820:
819:
724:
717:
710:
701:
700:
691:
675:
662:
656:
643:
628:
604:
598:
595:
589:
586:
573:
557:
525:
520:
519:
518:
503:root sensitivity
450:purulent exudate
362:
206:bacterial plaque
163:
142:edit on Wikidata
139:
49:
37:
36:
21:
2279:
2278:
2274:
2273:
2272:
2270:
2269:
2268:
2244:
2243:
2242:
2233:
2229:Dental alveolus
2220:
2207:
2174:
2149:
2106:
2080:
2076:Second premolar
2059:
2050:Lateral incisor
2045:Central incisor
2019:
1993:
1989:Second premolar
1972:
1963:Lateral incisor
1958:Central incisor
1936:
1891:
1870:
1865:
1835:
1830:
1826:Palatine tonsil
1821:Tonsillar fossa
1779:
1758:Fimbriated fold
1743:Lingual tonsils
1733:Terminal sulcus
1706:
1685:
1631:
1580:Gingival fibers
1575:Gingival margin
1570:Gingival sulcus
1551:
1518:
1500:
1457:
1453:Anatomy of the
1451:
1421:
1416:
1390:
1321:Gary Greenstein
1285:
1164:
1122:
1051:
1022:Occlusal trauma
997:Gingival pocket
955:
871:
811:
782:Gingival sulcus
777:Gingival fibers
735:
728:
684:
679:
678:
672:Wayback Machine
663:
659:
653:Wayback Machine
644:
631:
625:Wayback Machine
616:JADA, Vol 138.
614:Wayback Machine
605:
601:
596:
592:
587:
576:
567:Wayback Machine
558:
554:
549:
523:Medicine portal
521:
516:
514:
511:
458:
438:
426:
409:
370:
369:
368:
367:
366:
363:
352:
347:
329:and covered in
311:
309:Interdental gum
295:alveolar mucosa
290:
281:gingival fibers
269:
245:oral epithelium
190:
146:
103:
99:
52:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2277:
2267:
2266:
2261:
2259:Periodontology
2256:
2239:
2238:
2235:
2234:
2232:
2231:
2225:
2222:
2221:
2219:
2218:
2212:
2209:
2208:
2206:
2205:
2203:Dental papilla
2200:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2179:
2176:
2175:
2173:
2172:
2171:
2170:
2168:Apical foramen
2160:
2154:
2151:
2150:
2148:
2147:
2142:
2141:
2140:
2129:
2127:
2118:
2112:
2111:
2108:
2107:
2105:
2104:
2099:
2094:
2088:
2086:
2082:
2081:
2079:
2078:
2073:
2071:First premolar
2067:
2065:
2061:
2060:
2058:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2041:
2039:
2032:
2025:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2017:
2012:
2007:
2001:
1999:
1995:
1994:
1992:
1991:
1986:
1984:First premolar
1980:
1978:
1974:
1973:
1971:
1970:
1965:
1960:
1954:
1952:
1945:
1938:
1937:
1935:
1934:
1929:
1928:
1927:
1922:
1917:
1912:
1901:
1899:
1893:
1892:
1890:
1889:
1884:
1878:
1876:
1872:
1871:
1868:Dental anatomy
1864:
1863:
1856:
1849:
1841:
1832:
1831:
1829:
1828:
1823:
1818:
1813:
1808:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1780:
1778:
1777:
1776:
1775:
1773:Lingual septum
1770:
1765:
1760:
1755:
1747:
1746:
1745:
1740:
1735:
1730:
1725:
1716:
1714:
1708:
1707:
1705:
1704:
1695:
1693:
1687:
1686:
1684:
1683:
1678:
1677:
1676:
1666:
1665:
1664:
1654:
1653:
1652:
1641:
1639:
1633:
1632:
1630:
1629:
1628:
1627:
1622:
1617:
1612:
1602:
1597:
1592:
1587:
1582:
1577:
1572:
1567:
1561:
1559:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1549:
1544:
1542:Palatine raphe
1539:
1534:
1528:
1526:
1520:
1519:
1517:
1516:
1514:Buccal fat pad
1510:
1508:
1502:
1501:
1499:
1498:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1478:
1473:
1467:
1465:
1459:
1458:
1450:
1449:
1442:
1435:
1427:
1418:
1417:
1415:
1414:
1409:
1407:Orthodontology
1404:
1398:
1396:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1358:
1353:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1333:
1328:
1323:
1318:
1313:
1308:
1303:
1297:
1295:
1291:
1290:
1287:
1286:
1284:
1283:
1282:
1281:
1276:
1271:
1266:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1198:
1193:
1188:
1183:
1178:
1172:
1170:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1162:
1157:
1152:
1147:
1141:
1139:
1132:
1128:
1127:
1124:
1123:
1121:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1105:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1080:
1075:
1070:
1065:
1059:
1057:
1053:
1052:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1004:
999:
994:
989:
984:
979:
974:
969:
963:
961:
957:
956:
954:
953:
946:
938:
931:
924:
917:
910:
903:
896:
889:
881:
879:
873:
872:
870:
869:
864:
859:
854:
849:
844:
839:
834:
828:
826:
817:
813:
812:
810:
809:
804:
799:
794:
789:
784:
779:
774:
769:
764:
759:
757:Biologic width
754:
749:
743:
741:
737:
736:
732:Periodontology
727:
726:
719:
712:
704:
698:
697:
683:
682:External links
680:
677:
676:
657:
629:
599:
590:
574:
569:April 6, 2016
551:
550:
548:
545:
544:
543:
538:
533:
527:
526:
510:
507:
462:microecosystem
457:
454:
437:
434:
425:
422:
408:
405:
364:
357:
356:
355:
354:
353:
351:
348:
346:
343:
310:
307:
289:
286:
268:
265:
227:is covered by
189:
186:
148:
147:
138:
132:
131:
126:
120:
119:
114:
108:
107:
94:
88:
87:
82:
76:
75:
70:
64:
63:
59:
58:
54:
53:
50:
42:
41:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2276:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2251:
2249:
2230:
2227:
2226:
2223:
2217:
2214:
2213:
2210:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2196:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2180:
2177:
2169:
2166:
2165:
2164:
2161:
2159:
2156:
2155:
2152:
2146:
2143:
2139:
2136:
2135:
2134:
2131:
2130:
2128:
2126:
2122:
2119:
2117:
2113:
2103:
2100:
2098:
2095:
2093:
2090:
2089:
2087:
2083:
2077:
2074:
2072:
2069:
2068:
2066:
2062:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2042:
2040:
2036:
2033:
2030:
2026:
2016:
2013:
2011:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2002:
2000:
1996:
1990:
1987:
1985:
1982:
1981:
1979:
1975:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1955:
1953:
1949:
1946:
1943:
1939:
1933:
1930:
1926:
1923:
1921:
1918:
1916:
1913:
1911:
1908:
1907:
1906:
1903:
1902:
1900:
1898:
1894:
1888:
1885:
1883:
1880:
1879:
1877:
1873:
1869:
1862:
1857:
1855:
1850:
1848:
1843:
1842:
1839:
1827:
1824:
1822:
1819:
1817:
1814:
1812:
1809:
1807:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1792:
1789:
1788:
1786:
1784:Back of mouth
1782:
1774:
1771:
1769:
1766:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1756:
1754:
1751:
1750:
1748:
1744:
1741:
1739:
1738:Foramen cecum
1736:
1734:
1731:
1729:
1728:Median sulcus
1726:
1724:
1721:
1720:
1718:
1717:
1715:
1713:
1709:
1703:
1702:
1701:tooth anatomy
1697:
1696:
1694:
1692:
1688:
1682:
1679:
1675:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1667:
1663:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1655:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1646:
1645:Parotid gland
1643:
1642:
1640:
1638:
1634:
1626:
1623:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1607:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1588:
1586:
1583:
1581:
1578:
1576:
1573:
1571:
1568:
1566:
1563:
1562:
1560:
1558:
1554:
1548:
1545:
1543:
1540:
1538:
1535:
1533:
1530:
1529:
1527:
1525:
1521:
1515:
1512:
1511:
1509:
1507:
1503:
1497:
1494:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1448:
1443:
1441:
1436:
1434:
1429:
1428:
1425:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1405:
1403:
1402:Endodontology
1400:
1399:
1397:
1393:
1387:
1386:W. J. Younger
1384:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1357:
1354:
1352:
1349:
1347:
1346:Carl E. Misch
1344:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1314:
1312:
1309:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1299:
1298:
1296:
1292:
1280:
1277:
1275:
1272:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1261:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1192:
1189:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1173:
1171:
1167:
1161:
1158:
1156:
1153:
1151:
1148:
1146:
1143:
1142:
1140:
1136:
1133:
1129:
1119:
1116:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1064:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1037:Periodontitis
1035:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
998:
995:
993:
990:
988:
985:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
968:
965:
964:
962:
958:
952:
951:
947:
944:
943:
939:
937:
936:
932:
930:
929:
925:
923:
922:
918:
916:
915:
914:P. intermedia
911:
909:
908:
907:P. gingivalis
904:
902:
901:
897:
895:
894:
890:
888:
887:
883:
882:
880:
878:
874:
868:
865:
863:
860:
858:
855:
853:
852:Periodontosis
850:
848:
845:
843:
840:
838:
835:
833:
830:
829:
827:
825:
821:
818:
814:
808:
805:
803:
800:
798:
795:
793:
790:
788:
785:
783:
780:
778:
775:
773:
770:
768:
765:
763:
760:
758:
755:
753:
752:Alveolar bone
750:
748:
745:
744:
742:
738:
733:
725:
720:
718:
713:
711:
706:
705:
702:
695:
690:
686:
685:
673:
669:
666:
661:
654:
650:
647:
642:
640:
638:
636:
634:
626:
622:
619:
615:
611:
608:
603:
594:
585:
583:
581:
579:
572:
568:
564:
561:
556:
552:
542:
541:Periodontitis
539:
537:
534:
532:
529:
528:
524:
513:
506:
504:
499:
498:marginal gums
495:
491:
487:
486:periodontitis
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
453:
451:
448:(BOP) and/or
447:
443:
433:
431:
421:
419:
415:
404:
402:
398:
393:
391:
387:
383:
374:
361:
342:
339:
334:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
306:
304:
300:
296:
285:
282:
278:
273:
267:Marginal gums
264:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
237:alveolar bone
234:
230:
226:
222:
217:
213:
211:
207:
203:
198:
195:
185:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
159:
155:
143:
137:
133:
130:
127:
125:
121:
118:
115:
113:
109:
106:
102:
98:
95:
93:
89:
86:
83:
81:
77:
74:
71:
69:
65:
60:
55:
48:
43:
38:
33:
19:
2097:Second molar
2010:Second molar
1875:Nomenclature
1698:
1605:Periodontium
1556:
1376:Hom-Lay Wang
1361:Jørgen Slots
1331:Brian Mealey
1206:Gingivectomy
1108:Tetracycline
1103:Oral hygiene
948:
940:
933:
928:T. denticola
926:
921:T. forsythia
919:
912:
905:
900:F. nucleatum
898:
891:
884:
747:Periodontium
660:
602:
593:
571:Science News
555:
502:
466:oral hygiene
459:
439:
427:
410:
394:
379:
335:
312:
291:
288:Attached gum
274:
270:
262:
210:periodontium
202:inflammation
199:
191:
165:
157:
153:
151:
105:A03.1.03.004
101:A03.1.03.003
97:A05.1.01.108
72:
2102:Third molar
2092:First molar
2015:Third molar
2005:First molar
1537:Soft palate
1532:Hard palate
1476:Cupid's bow
1356:Jay Seibert
1306:Frank Beube
1145:Debridement
935:Red complex
674:05 Mar 2000
194:soft tissue
180:inside the
62:Identifiers
2248:Categories
2163:Root canal
2029:Mandibular
1791:Oropharynx
1749:Underside
1496:White roll
1326:Jan Lindhe
1251:Sinus lift
1181:Bone graft
1068:Ante's law
1007:Gingivitis
977:Edentulism
547:References
470:gingivitis
390:epithelium
386:meth mouth
382:gingivitis
338:epithelium
1942:Maxillary
1932:Deciduous
1905:Permanent
1723:Taste bud
1600:Stippling
1131:Treatment
1113:Triclosan
1098:Mouthwash
945:(amoebic)
877:Infection
824:Diagnoses
807:Stippling
531:Gum graft
494:dry mouth
414:embrasure
315:embrasure
188:Structure
2064:Premolar
1977:Premolar
1920:premolar
1753:Frenulum
1615:Philtrum
1610:Cementum
1491:Philtrum
1269:Membrane
1088:Flossing
1073:Brushing
982:Fremitus
967:Calculus
762:Cementum
668:Archived
649:Archived
621:Archived
610:Archived
563:Archived
509:See also
490:pyorrhea
233:cementum
174:mandible
166:gingivae
2254:Gingiva
2216:Mamelon
2038:Incisor
1951:Incisor
1910:incisor
1620:Gingiva
1264:Curette
1169:Surgery
816:Disease
772:Gingiva
740:Anatomy
424:Texture
407:Contour
331:keratin
327:chewing
235:. C,
223:of the
178:maxilla
170:mucosal
158:gingiva
85:D005881
73:gingiva
57:Details
18:Gingiva
2198:Dentin
2188:Enamel
2055:Canine
1968:Canine
1915:canine
1796:fauces
1712:Tongue
1637:Glands
1524:Palate
1279:Scaler
1260:Tools
1042:Plaque
247:. F,
243:. E,
239:. D,
229:enamel
2125:Crown
2116:Parts
2085:Molar
2031:teeth
1998:Molar
1944:teeth
1925:molar
1897:Teeth
1806:Uvula
1691:Teeth
1506:Cheek
1455:mouth
1274:Probe
960:Other
350:Color
225:tooth
221:crown
182:mouth
140:[
129:59762
68:Latin
2158:Pulp
2133:Cusp
1719:Top
1699:see
1674:duct
1662:duct
1650:duct
1557:Gums
694:Gums
176:and
154:gums
152:The
117:2790
92:TA98
80:MeSH
40:Gums
1463:Lip
488:or
323:col
162:pl.
156:or
124:FMA
112:TA2
2250::
632:^
577:^
505:.
452:.
333:.
164::
1860:e
1853:t
1846:v
1446:e
1439:t
1432:v
734:)
723:e
716:t
709:v
160:(
144:]
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.