591:
570:. The specific timing and manner that the ectodermal organs form is dependent on the invagination of the epithelial cells. FGF-9 is an important factor during the initiation of tooth germ development. The rate of epithelial invagination in significantly increased by action of FGF-9, which is only expressed in the epithelium, and not in the mesenchyme. FGF-10 helps to stimulate epithelial cell proliferation, in order make larger tooth germs. Mammalian teeth develop from ectoderm derived from the mesenchyme: oral ectoderm and neural crest. The epithelial components of the stem cells for continuously growing teeth form from tissue layers called the stellate reticulum and the suprabasal layer of the surface ectoderm.
542:
606:, the inability to produce sufficient amounts of sweat, which is attributed to missing or dysfunctional sweat glands. This aspect represents a major handicap particularly in the summer, limits the patient's ability to participate in sports as well as his working capacity, and can be especially dangerous in warm climates where affected individuals are at risk of life-threatening
52:
586:
is a rare but severe condition where the tissue groups (specifically teeth, skin, hair, nails and sweat glands) derived from the ectoderm undergo abnormal development. This is a diffuse term, as there are over 170 subtypes of ectodermal dysplasia. It has been accepted that the disease is caused by a
347:
is governed by "selective affinity", meaning that the inner surface of the ectoderm has a strong (positive) affinity for the mesoderm, and a weak (negative) affinity for the endoderm layer. This selective affinity changes during different stages of development. The strength of the attraction between
503:
occurs in two parts, primary and secondary neurulation. Both processes position neural crest cells between a superficial epidermal layer and the deep neural tube. During primary neurulation, the notochord cells of the mesoderm signal the adjacent, superficial ectoderm cells to reposition themselves
594:
Dental abnormalities in a five-year-old girl from northern Sweden who suffered from various symptoms of autosomal dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) a) Intraoral view. Note that the upper incisors have been restored with composite material to disguise their original conical shape. b)
528:
regarding their wedge like shape, however, the DLHP cells result in the ectoderm converging. This convergence is led by ectodermal cells above the DLHP cells known as the neural crest. The neural crest cells eventually pull the adjacent ectodermal cells together, which leaves neural crest cells
404:. During convergent extension, cells that approach the lip intercalate mediolaterally, in such a way that cells are pulled over the lip and inside the embryo. These two processes allow for the prospective mesoderm cells to be placed between the ectoderm and the endoderm. Once
40:
516:(MHPs). As the ectoderm continues to elongate, the ectodermal cells of the neural plate fold inward. The inward folding of the ectoderm by virtue of mainly cell division continues until another group of cells forms within the neural plate. These cells are termed
278:. Baer took Pander's concept of the germ layers and through extensive research of many different types of species, he was able to extend this principle to all vertebrates. Baer also received credit for the discovery of the
549:
All of the organs that rise from the ectoderm such as the nervous system, teeth, hair and many exocrine glands, originate from two adjacent tissue layers: the epithelium and the mesenchyme. Several signals mediate the
590:
587:
mutation or a combination of mutations in certain genes. Research of the disease is ongoing, as only a fraction of the mutations involved with an ectodermal dysplasia subtype have been identified.
392:. The once superficial cells of the animal pole are destined to become the cells of the middle germ layer called the mesoderm. Through the process of radial extension, cells of the
521:
517:
602:(HED) is the most common subtype of the disease. Clinical cases of patients with this condition display a range of symptoms. The most relevant abnormality of HED is
525:
103:
614:
are also related to HED, such as pointed or absent teeth, wrinkled skin around the eyes, a misshaped nose along with scarce and thin hair. Skin problems like
671:
416:, where the ectoderm cells divide in a way to form one layer. This creates a uniform embryo composed of the three germ layers in their respective positions.
513:
1091:"The Anhidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Gene (EDA) Undergoes Alternative Splicing and Encodes Ectodysplasin-A with Deletion Mutations in Collagenous Repeats"
771:
Baer KE von (1986) In: Oppenheimer J (ed.) and
Schneider H (transl.), Autobiography of Dr. Karl Ernst von Baer. Canton, MA: Science History Publications.
396:
that were once several layers thick divide to form a thin layer. At the same time, when this thin layer of dividing cells reaches the dorsal lip of the
388:. The cells continue to extend inward and migrate along the inner wall of the blastula to form a fluid-filled cavity called the
1475:
756:
1148:
942:"FGF-9 accelerates epithelial invagination for ectodermal organogenesis in real time bioengineered organ manipulation"
147:(the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the
852:
599:
356:
is crucial to maintaining separation of precursor neural cells from precursor epithelial cells. Likewise, while the
311:. At the start of this process, the developing embryo has divided into many cells, forming a hollow ball called the
412:, which will become endoderm cells, is completely engulfed by the prospective ectoderm, as these top cells undergo
559:
255:
in 1817. He began his studies in embryology using chicken eggs, which allowed for his discovery of the ectoderm,
786:"A new hypothesis for foregut and heart tube formation based on differential growth and actomyosin contraction"
595:
Orthopantomogram showing absence of ten primary and eleven permanent teeth in the jaws of the same individual.
98:
626:, while in females the second, usually unaffected X chromosome may be sufficient to prevent most symptoms.
713:
Gilbert, Scott F. Developmental
Biology. 9th ed. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, 2010: 333-370. Print.
1433:
1378:
1157:
1126:
567:
17:
381:
212:. The surface ectoderm gives rise to most epithelial tissues, and the neural plate gives rise to most
409:
393:
324:
320:
316:
882:
335:
Like the other two germ layers – i.e., the mesoderm and endoderm – the ectoderm forms shortly after
252:
1438:
1350:
1235:
1141:
726:
555:
425:
86:
1089:
Bayes, M.; Hartung, A. J.; Ezer, S.; Pispa, J.; Thesleff, I.; Srivastava, A. K.; Kere, J. (1998).
282:. Baer published his findings, including his germ layer theory, in a textbook which translates to
1202:
1423:
1322:
636:
449:
228:
110:
1485:
1428:
1418:
1262:
563:
512:
change their shape, forming a wedge in the ectodermal region. These special cells are called
136:
1470:
583:
405:
401:
618:
are also observed in a number of cases. Most patients carry variants of the X-chromosomal
8:
1480:
1172:
1134:
611:
444:. Each of these three components will give rise to a particular complement of cells. The
275:
58:
1066:
1041:
1017:
992:
968:
941:
870:
812:
785:
263:. Due to his findings, Pander is sometimes referred to as the "founder of embryology".
914:
897:
1465:
1401:
1187:
1177:
1112:
1071:
1022:
973:
919:
858:
848:
817:
752:
162:
622:
gene. This disease typically affects males more severely because they have only one
1340:
1303:
1284:
1102:
1061:
1053:
1012:
1004:
963:
953:
909:
840:
807:
797:
530:
469:
441:
361:
357:
197:
182:
1217:
481:
216:. For this reason, the neural plate and neural crest are also referred to as the
91:
1396:
1294:
477:
232:
213:
166:
148:
844:
343:
begins. The position of the ectoderm relative to the other germ layers of the
1459:
1345:
1289:
551:
365:
340:
336:
244:
217:
1107:
1090:
958:
508:. As the cells continue to elongate, a group of cells immediately above the
1360:
1315:
1310:
1026:
977:
923:
821:
666:
656:
623:
607:
603:
505:
453:
437:
308:
209:
201:
186:
1116:
1075:
1057:
862:
835:
O'Rahilly, R; Müller, F (1994). "Neurulation in the Normal Human Embryo".
541:
185:, linings of the mouth, anus, nostrils, sweat glands, hair and nails, and
1355:
1280:
1222:
1008:
520:(DLHPs), and, once formed, the inward folding of the ectoderm stops. The
500:
457:
445:
433:
429:
389:
205:
170:
1156:
352:
molecules present on the cells' surface. For example, the expression of
348:
two surfaces of two germ layers is determined by the amount and type of
1411:
1298:
1272:
1212:
1207:
1192:
802:
751:. United States of America: Pearson. pp. 146, 482–483, 1102–1106.
646:
619:
397:
385:
300:
240:
193:
132:
116:
1244:
509:
485:
465:
461:
369:
236:
1388:
1370:
1249:
940:
Tai, Y. Y.; Chen, R. S.; Lin, Y.; Ling, T. Y.; Chen, M. H. (2012).
661:
651:
349:
327:. It is the animal hemisphere will eventually become the ectoderm.
312:
279:
260:
256:
144:
140:
413:
271:
267:
248:
1042:"Clinical Aspects of X-linked Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia"
196:
embryos, the ectoderm can be divided into two parts: the dorsal
1406:
1197:
1182:
839:. Novartis Foundation Symposia. Vol. 181. pp. 70–82.
641:
615:
344:
1040:
Clarke, A.; Phillips, D. I.; Brown, R.; Harper, P. S. (1987).
993:"Ectodermal Dysplasias: A New Clinical-Genetic Classification"
456:
cells give rise to the peripheral and enteric nervous system,
384:
invaginate on the dorsal surface of the blastula to form the
178:
174:
784:
Hosseini, Hadi S.; Garcia, Kara E.; Taber, Larry A. (2017).
473:
353:
304:
189:. Other types of epithelium are derived from the endoderm.
39:
1039:
489:
51:
504:
into a columnar pattern to form cells of the ectodermal
161:
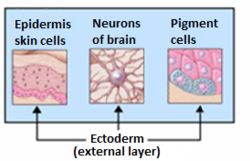
Generally speaking, the ectoderm differentiates to form
408:
and radial intercalation are underway, the rest of the
139:. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the
779:
777:
1088:
672:
List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
266:
Pander's work of the early embryo was continued by a
837:
Ciba
Foundation Symposium 181 - Neural Tube Defects
834:
783:
774:
239:, has been credited for the discovery of the three
432:, wherein the ectoderm differentiates to form the
424:Once the three germ layers have been established,
691:Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010.
1457:
895:
990:
939:
709:
707:
705:
703:
701:
699:
697:
1142:
200:also known as the external ectoderm, and the
935:
933:
746:
694:
428:can occur. The first major process here is
368:is induced along the neural pathway by the
1149:
1135:
372:, which is typically positioned above it.
50:
38:
1106:
1065:
1016:
967:
957:
930:
913:
811:
801:
27:Outer germ layer of embryonic development
991:Priolo, M.; Laganà, C (September 2001).
898:"Mechanisms of ectodermal organogenesis"
747:Marieb, Elaine N.; Hoehn, Katja (2019).
589:
573:
540:
727:"Derivation of Tissues | SEER Training"
578:
14:
1458:
896:Pispa, J; Thesleff, I (Oct 15, 2003).
721:
719:
299:The ectoderm can first be observed in
1130:
294:
742:
740:
419:
380:During the process of gastrulation,
330:
319:, and its two halves are called the
716:
247:. Pander received his doctorate in
24:
289:
56:Section through embryonic disk of
25:
1497:
737:
600:Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
524:function in a similar fashion as
1046:Archives of Disease in Childhood
946:Cell Communication and Signaling
536:
400:, another process occurs termed
204:, which invaginates to form the
1082:
1033:
984:
375:
889:
828:
765:
749:Human Anatomy & Physiology
685:
495:
13:
1:
915:10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00325-7
678:
468:region will give rise to the
284:On the Development of Animals
131:is one of the three primary
44:Organs derived from ectoderm.
1476:Animal developmental biology
7:
1434:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
1379:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
1158:Human embryonic development
997:Journal of Medical Genetics
629:
307:during the later stages of
286:which he released in 1828.
10:
1502:
566:, and regulators from the
223:
1387:
1369:
1331:
1271:
1258:
1231:
1165:
845:10.1002/9780470514559.ch5
554:of the ectoderm such as:
533:and hollow, neural tube.
488:and oral epithelium, and
109:
97:
85:
80:
72:
67:
49:
37:
32:
1439:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
1351:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
1160:in the first three weeks
1095:Human Molecular Genetics
731:training.seer.cancer.gov
545:Ectodermal specification
529:between the prospective
518:dorsolateral hinge cells
426:cellular differentiation
959:10.1186/1478-811X-10-34
448:cells give rise to the
154:meaning "outside", and
143:(the middle layer) and
1323:Regional specification
637:Ectoderm specification
596:
546:
450:central nervous system
253:University of Würzburg
229:Heinz Christian Pander
111:Anatomical terminology
1429:Intraembryonic coelom
1108:10.1093/hmg/7.11.1661
1058:10.1136/adc.62.10.989
902:Developmental Biology
593:
574:Clinical significance
544:
181:). This includes the
137:embryonic development
1009:10.1136/jmg.38.9.579
584:Ectodermal dysplasia
579:Ectodermal dysplasia
406:convergent extension
402:convergent extension
339:, after which rapid
276:Karl Ernst von Baer
59:Vespertilio murinus
803:10.1242/dev.145193
597:
547:
514:medial hinge cells
325:vegetal hemisphere
315:. The blastula is
295:Initial appearance
1453:
1452:
1449:
1448:
1178:Oocyte activation
1101:(11): 1661–1669.
796:(13): 2381–2391.
758:978-0-13-458099-9
420:Later development
331:Early development
321:animal hemisphere
243:that form during
125:
124:
120:
16:(Redirected from
1493:
1341:Surface ectoderm
1304:Primitive groove
1285:Primitive streak
1269:
1268:
1151:
1144:
1137:
1128:
1127:
1121:
1120:
1110:
1086:
1080:
1079:
1069:
1037:
1031:
1030:
1020:
988:
982:
981:
971:
961:
937:
928:
927:
917:
893:
887:
886:
880:
876:
874:
866:
832:
826:
825:
815:
805:
781:
772:
769:
763:
762:
744:
735:
734:
723:
714:
711:
692:
689:
482:sebaceous glands
358:surface ectoderm
274:biologist named
198:surface ectoderm
158:meaning "skin".
135:formed in early
117:edit on Wikidata
114:
54:
42:
30:
29:
21:
1501:
1500:
1496:
1495:
1494:
1492:
1491:
1490:
1456:
1455:
1454:
1445:
1383:
1365:
1327:
1260:
1254:
1233:
1227:
1218:Inner cell mass
1161:
1155:
1125:
1124:
1087:
1083:
1038:
1034:
989:
985:
938:
931:
894:
890:
878:
877:
868:
867:
855:
833:
829:
782:
775:
770:
766:
759:
745:
738:
725:
724:
717:
712:
695:
690:
686:
681:
676:
632:
581:
576:
568:hedgehog family
539:
498:
422:
378:
333:
297:
292:
290:Differentiation
226:
121:
63:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1499:
1489:
1488:
1483:
1478:
1473:
1468:
1451:
1450:
1447:
1446:
1444:
1443:
1442:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1421:
1416:
1415:
1414:
1409:
1399:
1397:Axial mesoderm
1393:
1391:
1385:
1384:
1382:
1381:
1375:
1373:
1367:
1366:
1364:
1363:
1358:
1353:
1348:
1343:
1337:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1320:
1319:
1318:
1308:
1307:
1306:
1301:
1295:Primitive node
1292:
1277:
1275:
1266:
1256:
1255:
1253:
1252:
1247:
1241:
1239:
1229:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1215:
1210:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1169:
1167:
1163:
1162:
1154:
1153:
1146:
1139:
1131:
1123:
1122:
1081:
1052:(10): 989–96.
1032:
1003:(9): 579–585.
983:
929:
908:(2): 195–205.
888:
879:|journal=
853:
827:
773:
764:
757:
736:
715:
693:
683:
682:
680:
677:
675:
674:
669:
664:
659:
654:
649:
644:
639:
633:
631:
628:
580:
577:
575:
572:
538:
535:
497:
494:
440:cells and the
421:
418:
377:
374:
332:
329:
296:
293:
291:
288:
225:
222:
214:neural tissues
167:neural tissues
123:
122:
113:
107:
106:
101:
95:
94:
89:
83:
82:
78:
77:
74:
70:
69:
65:
64:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1498:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1463:
1461:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1426:
1425:
1424:Lateral plate
1422:
1420:
1417:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1405:
1404:
1403:
1400:
1398:
1395:
1394:
1392:
1390:
1386:
1380:
1377:
1376:
1374:
1372:
1368:
1362:
1359:
1357:
1354:
1352:
1349:
1347:
1346:Neuroectoderm
1344:
1342:
1339:
1338:
1336:
1334:
1330:
1324:
1321:
1317:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1309:
1305:
1302:
1300:
1296:
1293:
1291:
1290:Primitive pit
1288:
1287:
1286:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1274:
1270:
1267:
1264:
1257:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1230:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1173:Fertilization
1171:
1170:
1168:
1164:
1159:
1152:
1147:
1145:
1140:
1138:
1133:
1132:
1129:
1118:
1114:
1109:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1085:
1077:
1073:
1068:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1036:
1028:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
998:
994:
987:
979:
975:
970:
965:
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
936:
934:
925:
921:
916:
911:
907:
903:
899:
892:
884:
872:
864:
860:
856:
854:9780470514559
850:
846:
842:
838:
831:
823:
819:
814:
809:
804:
799:
795:
791:
787:
780:
778:
768:
760:
754:
750:
743:
741:
732:
728:
722:
720:
710:
708:
706:
704:
702:
700:
698:
688:
684:
673:
670:
668:
665:
663:
660:
658:
655:
653:
650:
648:
645:
643:
640:
638:
635:
634:
627:
625:
621:
617:
613:
612:malformations
609:
605:
601:
592:
588:
585:
571:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
552:organogenesis
543:
537:Organogenesis
534:
532:
527:
523:
519:
515:
511:
507:
502:
493:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
460:, and facial
459:
455:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
417:
415:
411:
407:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
373:
371:
367:
366:neuroectoderm
363:
359:
355:
351:
346:
342:
341:cell division
338:
337:fertilization
328:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
306:
302:
287:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
264:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
245:embryogenesis
242:
238:
234:
233:Baltic German
230:
221:
219:
218:neuroectoderm
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
190:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
164:
159:
157:
153:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
118:
112:
108:
105:
102:
100:
96:
93:
90:
88:
84:
79:
75:
71:
66:
61:
60:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1486:Gastrulation
1419:Intermediate
1361:Neural crest
1332:
1316:Gastrulation
1098:
1094:
1084:
1049:
1045:
1035:
1000:
996:
986:
949:
945:
905:
901:
891:
836:
830:
793:
789:
767:
748:
730:
687:
667:Neural plate
657:Gastrulation
624:X chromosome
608:hyperthermia
604:hypohidrosis
598:
582:
548:
506:neural plate
499:
454:neural crest
438:neural crest
423:
410:vegetal pole
382:bottle cells
379:
376:Gastrulation
360:becomes the
334:
309:gastrulation
298:
283:
265:
227:
210:neural crest
202:neural plate
191:
187:tooth enamel
160:
155:
151:
128:
126:
57:
1471:Germ layers
1356:Neurulation
1281:Archenteron
1273:Germ layers
1223:Trophoblast
790:Development
501:Neurulation
496:Neurulation
458:melanocytes
446:neural tube
434:neural tube
430:neurulation
394:animal pole
241:germ layers
206:neural tube
171:spinal cord
133:germ layers
81:Identifiers
1481:Embryology
1460:Categories
1412:Somitomere
1299:Blastopore
1263:Trilaminar
1213:Blastocyst
1208:Blastocoel
1203:Cavitation
1193:Blastomere
679:References
647:Embryology
522:DLHP cells
464:, and the
398:blastopore
390:blastocoel
386:blastopore
354:N-cadherin
301:amphibians
194:vertebrate
163:epithelial
18:Ectodermal
1245:Hypoblast
1236:Bilaminar
952:(1): 34.
881:ignored (
871:cite book
610:. Facial
531:epidermis
526:MHP cells
510:notochord
486:olfactory
470:epidermis
466:epidermal
462:cartilage
442:epidermis
370:notochord
362:epidermis
251:from the
237:biologist
235:–Russian
1466:Ectoderm
1402:Paraxial
1389:Mesoderm
1371:Endoderm
1333:Ectoderm
1311:Gastrula
1250:Epiblast
1188:Cleavage
1027:11546825
978:23176204
924:14550785
822:28526751
662:Mesoderm
652:Endoderm
630:See also
350:cadherin
313:blastula
280:blastula
272:Estonian
268:Prussian
261:endoderm
257:mesoderm
145:endoderm
141:mesoderm
129:ectoderm
33:Ectoderm
1259:Week 3
1232:Week 2
1117:9736768
1076:2445301
1067:1778691
1018:1734928
969:3515343
863:8005032
813:5536863
414:epiboly
249:zoology
224:History
92:D004475
68:Details
1407:Somite
1198:Morula
1183:Zygote
1166:Week 1
1115:
1074:
1064:
1025:
1015:
976:
966:
922:
861:
851:
820:
810:
755:
642:Coelom
616:eczema
364:, the
345:embryo
175:nerves
478:nails
317:polar
179:brain
156:derma
152:ektos
149:Greek
115:[
104:69070
1113:PMID
1072:PMID
1023:PMID
974:PMID
920:PMID
883:help
859:PMID
849:ISBN
818:PMID
753:ISBN
560:TGFβ
490:eyes
474:hair
323:and
305:fish
303:and
259:and
231:, a
208:and
183:skin
177:and
165:and
127:The
87:MeSH
73:Days
1103:doi
1062:PMC
1054:doi
1013:PMC
1005:doi
964:PMC
954:doi
910:doi
906:262
841:doi
808:PMC
798:doi
794:144
620:EDA
564:Wnt
556:FGF
192:In
99:FMA
1462::
1111:.
1097:.
1093:.
1070:.
1060:.
1050:62
1048:.
1044:.
1021:.
1011:.
1001:38
999:.
995:.
972:.
962:.
950:10
948:.
944:.
932:^
918:.
904:.
900:.
875::
873:}}
869:{{
857:.
847:.
816:.
806:.
792:.
788:.
776:^
739:^
729:.
718:^
696:^
562:,
558:,
492:.
484:,
480:,
476:,
472:,
452:,
436:,
220:.
173:,
76:16
1297:/
1283:/
1265:)
1261:(
1238:)
1234:(
1150:e
1143:t
1136:v
1119:.
1105::
1099:7
1078:.
1056::
1029:.
1007::
980:.
956::
926:.
912::
885:)
865:.
843::
824:.
800::
761:.
733:.
270:–
169:(
119:]
62:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.