651:
422:
29:
367:
specifier is necessary and/or sufficient for the expression of all other specifiers, demonstrating the existence of extensive cross-regulation. Moreover, this model organism was instrumental in the elucidation of the role of the
Hedgehog signaling pathway in the specification of the neural crest, with the transcription factor Gli2 playing a key role.
250:
embryo respectively. However, this method suffers from drawbacks of stability, since every time the labeled cell divides the signal is diluted. Modern cell labeling techniques such as rhodamine-lysinated dextran and the vital dye diI have also been developed to transiently mark neural crest lineages.
335:
has been suggested as a source of neural crest inductive signal. Researchers have demonstrated that the expression of dominate-negative Fgf receptor in ectoderm explants blocks neural crest induction when recombined with paraxial mesoderm. The understanding of the role of BMP, Wnt, and Fgf pathways
1080:. Despite these, and other advances much remains to be discovered about how ethanol affects neural crest development. For example, it appears that ethanol differentially affects certain neural crest cells over others; that is, while craniofacial abnormalities are common in PAE, neural crest-derived
814:
result from the abnormal specification, migration, differentiation or death of neural crest cells throughout embryonic development. This group of diseases comprises a wide spectrum of congenital malformations affecting many newborns. Additionally, they arise because of genetic defects affecting the
1307:
Several structures that distinguish the vertebrates from other chordates are formed from the derivatives of neural crest cells. In their "New head" theory, Gans and
Northcut argue that the presence of neural crest was the basis for vertebrate specific features, such as sensory ganglia and cranial
245:
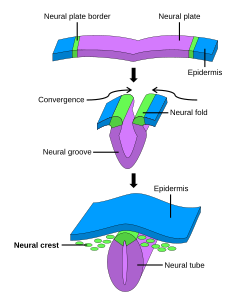
in 1868 as "the cord in between" (Zwischenstrang) because of its origin between the neural plate and non-neural ectoderm. He named the tissue ganglionic crest since its final destination was each lateral side of the neural tube where it differentiated into spinal ganglia. During the first half of
405:
Putative neural crest gene-regulatory network functioning at the neural plate border in vertebrates. Red arrows represent proven direct regulatory interactions. Black arrows show genetic interactions based on loss-of-function and gain-of-functions studies. Gray lines denote repression. Adapted
344:
Signaling events that establish the neural plate border lead to the expression of a set of transcription factors delineated here as neural plate border specifiers. These molecules include Zic factors, Pax3/7, Dlx5, Msx1/2 which may mediate the influence of Wnts, BMPs, and Fgfs. These genes are
249:
Cell labeling techniques advanced the field of neural crest because they allowed researchers to visualize the migration of the tissue throughout the developing embryos. In the 1960s, Weston and Chibon utilized radioisotopic labeling of the nucleus with tritiated thymidine in chick and amphibian
402:
366:
Following the expression of neural plate border specifiers is a collection of genes including Slug/Snail, FoxD3, Sox10, Sox9, AP-2 and c-Myc. This suite of genes, designated here as neural crest specifiers, are activated in emergent neural crest cells. At least in
Xenopus, every neural crest
327:
The current role of BMP in neural crest formation is associated with the induction of the neural plate. BMP antagonists diffusing from the ectoderm generates a gradient of BMP activity. In this manner, the neural crest lineage forms from intermediate levels of BMP signaling required for the
1761:
Le
Douarin, N.M. (1969). "Particularités du noyau interphasique chez la Caille japonaise (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Utilisation de ces particularités comme "marquage biologique" dans les recherches sur les interactions tissulaires et les migrations cellulaires au cours de l'ontogenèse"".
730:
Semaphorin-neuropilin repulsive signaling works synergistically with EphB signaling to guide neural crest cells down the rostral half of somites in mice. In chick embryos, semaphorin acts in the cephalic region to guide neural crest cells through the
1226:
Cranial neural crest migrates dorsolaterally to form the craniofacial mesenchyme that differentiates into various cranial ganglia and craniofacial cartilages and bones. These cells enter the pharyngeal pouches and arches where they contribute to the
1212:-posterior axis develop into various tissues. These regions of neural crest can be divided into four main functional domains, which include the cranial neural crest, trunk neural crest, vagal and sacral neural crest, and cardiac neural crest.
257:, generated through transplantation, enabled researchers to distinguish neural crest cells of one species from the surrounding tissue of another species. With this technique, generations of scientists were able to reliably mark and study the
209:
genes that confer cell characteristics such as multipotency and migratory capabilities. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of neural crest formation is important for our knowledge of human disease because of its contributions to multiple
1294:
develops into melanocytes, cartilage, connective tissue and neurons of some pharyngeal arches. Also, this domain gives rise to regions of the heart such as the musculo-connective tissue of the large arteries, and part of the
398:, function in delamination by regulating cell morphology and adhesive properties. Sox9 and Sox10 regulate neural crest differentiation by activating many cell-type-specific effectors including Mitf, P0, Cx32, Trp and cKit.
702:
with one another. While Ephrin and Eph proteins have the capacity to undergo bi-directional signaling, neural crest cell repulsion employs predominantly forward signaling to initiate a response within the
2942:
Takamura, Kazushi; Okishima, Takahiro; Ohdo, Shozo; Hayakawa, Kunio (1990). "Association of cephalic neural crest cells with cardiovascular development, particularly that of the semilunar valves".
1957:
Dottori, M.; Gross, M.K.; Labosky, P.; Goulding, M. (2001). "The winged-helix transcription factor Foxd3 suppresses interneuron differentiation and promotes neural crest cell fate".
312:
Wnt signaling has been demonstrated in neural crest induction in several species through gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments. In coherence with this observation, the
751:
of the extracellular matrix as they travel. Additionally, crest cells have intrinsic contact inhibition with one another while freely invading tissues of different origin such as
861:. Type III gives rise to upper limb abnormalities. Lastly, type IV is also known as Waardenburg-Shah syndrome, and afflicted individuals display both Waardenburg's syndrome and
386:
Finally, neural crest specifiers turn on the expression of effector genes, which confer certain properties such as migration and multipotency. Two neural crest effectors,
2636:
Rogers, J. M. (2016). "Search for the missing lncs: gene regulatory networks in neural crest development and long non-coding RNA biomarkers of
Hirschsprung's disease".
1333:
a lineage of cells (melanocytes) has been identified, which are similar to neural crest cells in vertebrates. This implies that a rudimentary neural crest existed in a
468:
into different populations, in this case neural crest cells separating from the surrounding tissue. Conversely, EMT is a series of events coordinating a change from an
1053:
and decreased distances travelled by migrating neural crest cells. The mechanisms behind these changes are not well understood, but evidence suggests PAE can increase
425:
Delamination of neural crest cells during development. Downregulation of CAMs and tight junction proteins is followed by secretion of MMPs and subsequent delamination.
1317:. Instead, new structures often arise through modification of existing developmental regulatory programs. For example, regulatory programs may be changed by the
3746:
246:
the 20th century, the majority of research on neural crest was done using amphibian embryos which was reviewed by Hörstadius (1950) in a well known monograph.
85:
1299:, which divides the pulmonary circulation from the aorta. The semilunar valves of the heart are associated with neural crest cells according to new research.
1253:
migrates dorsolaterally into the ectoderm towards the ventral midline. A second group of cells migrates ventrolaterally through the anterior portion of each
727:
rearrangements within the crest cells inducing them to repel. This phenomenon allows neural crest cells to funnel through the rostral portion of each somite.
1491:
1321:
of new upstream regulators or by the employment of new downstream gene targets, thus placing existing networks in a novel context. This idea is supported by
1329:, which suggest that part of the neural crest precursor network was present in a common ancestor to the chordates. In some non-vertebrate chordates such as
3390:
1373:
1365:
654:
Migration of neural crest cells during development. Grey arrows indicate the direction of the paths crest cells migrate. (R=Rostral, C=Caudal)
253:
The quail-chick marking system, devised by Nicole Le
Douarin in 1969, was another instrumental technique used to track neural crest cells.
3739:
3071:
Sauka-Spengler, T.; Bronner-Fraser, M. (2006). "Development and evolution of the migratory neural crest: a gene regulatory perspective".
233:
Therefore, defining the mechanisms of neural crest development may reveal key insights into vertebrate evolution and neurocristopathies.
1468:
1308:
skeleton. Furthermore, the appearance of these features was pivotal in vertebrate evolution because it enabled a predatory lifestyle.
2697:
2680:
324:
involved in the activation of Wnt-dependent target genes, suggestive of a direct role of Wnt signaling in neural crest specification.
3381:
2501:
Cerrizuela, Santiago; Vega‐Lopez, Guillermo A.; Aybar, Manuel J. (2020-01-11). "The role of teratogens in neural crest development".
269:
A molecular cascade of events is involved in establishing the migratory and multipotent characteristics of neural crest cells. This
857:
and physiological features. Types I and II are distinguished based on whether or not family members of the affected individual have
186:
and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in
2310:
Taneyhill, L.A. (2008). "To adhere or not to adhere: the role of
Cadherins in neural crest development". Cell Adh Migr. 2, 223–30.
2466:
Bolande, Robert P. (1974-07-01). "The neurocristopathies: A unifying concept of disease arising in neural crest maldevelopment".
509:. Although all neural crest cells undergo EMT, the timing of delamination occurs at different stages in different organisms: in
370:
Outside of the tightly regulated network of neural crest specifiers are two other transcription factors Twist and Id. Twist, a
3732:
642:, during migration. Once the basal lamina becomes permeable the neural crest cells can begin migrating throughout the embryo.
4021:
2557:
Mallory, S.B.; Wiener, E; Nordlund, J.J. (1986). "Waardenburg's
Syndrome with Hirschprung's Disease: A Neural Crest Defect".
2292:
579:
461:
1076:
stores. It has also been proposed that the decreased viability of ethanol-exposed neural crest cells is caused by increased
3417:
2679:
Sampson, P. D.; Streissguth, A. P.; Bookstein, F. L.; Little, R. E.; Clarren, S. K.; Dehaene, P.; Graham, J. M. Jr (1997).
73:
1826:"Cloning and characterization of the three Xenopus slug promoters reveal direct regulation by Lef/beta-catenin signaling"
460:. For migration to begin, neural crest cells must undergo a process called delamination that involves a full or partial
378:
structures. Id is a direct target of c-Myc and is known to be important for the maintenance of neural crest stem cells.
2161:
1992:
Cerrizuela, Santiago; Vega-López, Guillermo A.; Palacio, María Belén; Tríbulo, Celeste; Aybar, Manuel J. (2018-12-01).
667:
179:
3211:
Kalcheim, C. and Le
Douarin, N. M. (1998). The Neural Crest (2nd ed.). Cambridge, U. K.: Cambridge University Press.
429:
The migration of neural crest cells involves a highly coordinated cascade of events that begins with closure of the
358:
for the expression of Slug, Snail, and FoxD3. Furthermore, Pax3 is essential for FoxD3 expression in mouse embryos.
33:
The formation of neural crest during the process of neurulation. Neural crest is first induced in the region of the
1165:
during the early embryonic stage, which ultimately leads to mid and lower face abnormalities. TCS is caused by the
1521:
Huang, X.; Saint-Jeannet, J.P. (2004). "Induction of the neural crest and the opportunities of life on the edge".
345:
expressed broadly at the neural plate border region and precede the expression of bona fide neural crest markers.
3372:
1005:
591:
2867:
2236:"Neural crest delamination and migration: From epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition to collective cell migration"
4036:
792:
348:
Experimental evidence places these transcription factors upstream of neural crest specifiers. For example, in
3362:
1119:
595:
543:
223:
80:
622:
of the neural tube to allow neural crest cells to escape. Additionally, neural crest cells begin expressing
3849:
2681:"The incidence of fetal alcohol syndrome and prevalence of the alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder"
768:
663:
659:
555:
430:
2102:"Xenopus Id3 is required downstream of Myc for the formation of multipotent neural crest progenitor cells"
1706:"The avian embryo as a model to study the development of the neural crest: a long and still ongoing story"
3702:
3647:
3426:
1115:
882:
674:. For this reason the crest cell migration process is termed "free migration". Instead of scaffolding on
1789:
Le
Douarin, N.M. (1973). "A biological cell labeling technique and its use in experimental embryology".
3395:
1291:
1013:
874:
760:
575:
559:
487:
294:
870:
833:
that results from defective neural crest cell migration. The condition's main characteristics include
4031:
3908:
1158:
902:
862:
764:
530:
Prior to delamination, presumptive neural crest cells are initially anchored to neighboring cells by
416:
136:
68:
3223:"Epidermal progenitors give rise to Merkel cells during embryonic development and adult homeostasis"
3707:
3619:
3504:
3410:
1127:
962:
878:
788:
708:
615:
355:
298:
56:
2364:
Sakuka-Spengler, Tatjana (2008). "A gene regulatory network orchestrates neural crest formation".
3471:
2407:
Vega-Lopez, Guillermo A.; Cerrizuela, Santiago; Tribulo, Celeste; Aybar, Manuel J. (2018-12-01).
838:
800:
704:
270:
198:
3960:
3692:
3591:
3385:
1455:
1274:
1065:
937:. Genes playing a role in the healthy migration of these neural crest cells to the gut include
930:
776:
539:
92:
41:
closure, neural crest delaminates from the region between the dorsal neural tube and overlying
3697:
3687:
3531:
2985:
Gans, C.; Northcutt, R. G. (1983). "Neural crest and the origin of vertebrates: A new head".
1369:
1322:
1249:
Trunk neural crest gives rise two populations of cells. One group of cells fated to become
1139:
993:
981:
are then implicated in the same signaling network. When this signaling is disrupted in mice,
720:
719:. When these two domains interact it causes receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, activation of
712:
491:
473:
388:
290:
219:
202:
190:
evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate
3856:
3844:
3168:
2994:
1441:
1286:
1258:
1221:
1000:. Depending on the extent of the exposure and the severity of the resulting abnormalities,
826:
695:
627:
498:
321:
183:
1311:
However, considering the neural crest a vertebrate innovation does not mean that it arose
8:
3441:
3403:
1480:
1429:
1096:
755:. Neural crest cells that migrate through the rostral half of somites differentiate into
510:
494:
313:
3172:
2998:
889:
are equally affected. There is no current cure or treatment for Waardenburg's syndrome.
3826:
3779:
3337:
3312:
3247:
3222:
3189:
3156:
3132:
3107:
3018:
2967:
2836:
2811:
2746:
2721:
2661:
2582:
2570:
2534:
2389:
2206:
2181:
2077:
2052:
1244:
1069:
1017:
958:
938:
898:
846:
811:
699:
650:
254:
206:
3366:
3288:
3271:
2479:
1749:
The Neural Crest: Its Properties and Derivatives in the Light of Experimental Research
1744:
1185:
of the TCOF1 gene are among the best characterized in their role in TCS, mutations in
4026:
3874:
3670:
3456:
3446:
3342:
3293:
3252:
3194:
3137:
3088:
3053:
3010:
2959:
2924:
2916:
2841:
2792:
2751:
2702:
2653:
2609:
2574:
2538:
2526:
2518:
2483:
2448:
2440:
2381:
2343:
2288:
2260:
2211:
2157:
2123:
2082:
2033:
2025:
1974:
1939:
1908:"Regulation of Msx genes by Bmp gradient is essential for neural crest specification"
1888:
1847:
1806:
1802:
1771:
1727:
1683:
1639:
1573:
1538:
1397:
1166:
1162:
1092:
1028:
929:, or even slowed growth. In healthy development, neural crest cells migrate into the
671:
332:
227:
178:. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an
3724:
3022:
2971:
2665:
2586:
2393:
1142:. Patients with 22q11 deletions have also been reported to have higher incidence of
3965:
3893:
3888:
3609:
3572:
3553:
3332:
3324:
3283:
3242:
3234:
3184:
3176:
3127:
3119:
3080:
3045:
3002:
2951:
2906:
2896:
2831:
2823:
2782:
2741:
2733:
2692:
2645:
2566:
2510:
2475:
2430:
2420:
2373:
2333:
2250:
2235:
2201:
2193:
2113:
2072:
2064:
2015:
2005:
1966:
1929:
1919:
1878:
1837:
1798:
1717:
1673:
1629:
1565:
1530:
1433:
1147:
1077:
934:
830:
465:
306:
215:
421:
3937:
3923:
3898:
3486:
3006:
1994:"Gli2 is required for the induction and migration of Xenopus laevis neural crest"
1678:
1661:
1634:
1617:
1411:
1262:
1035:
918:
732:
683:
675:
599:
375:
242:
144:
61:
2425:
2408:
2255:
2068:
1534:
3756:
3665:
3563:
1557:
1425:
1385:
1361:
1357:
1111:
1100:
1050:
1009:
853:. There are four different types of Waardenburg's syndrome, each with distinct
756:
735:. On top of repulsive repulsive signaling, neural crest cells express β1and α4
531:
457:
140:
3084:
2010:
1993:
1722:
1705:
4015:
3950:
3814:
3799:
3614:
3558:
3328:
3313:"Enteric nervous system development: migration, differentiation, and disease"
3038:
Journal of Experimental Zoology Part B: Molecular and Developmental Evolution
2920:
2522:
2487:
2444:
2409:"Neurocristopathies: New insights 150 years after the neural crest discovery"
2053:"An absence of Twist1 results in aberrant cardiac neural crest morphogenesis"
2029:
1388:(membranous bones), dorsal fins and the turtle plastron (lower vertebrates),
1326:
1178:
1143:
1131:
1107:
1073:
982:
914:
128:
2787:
2770:
1970:
1569:
1122:
system, which receives contribution from rostral migratory crest cells. The
602:
residues to decrease adhesiveness. Neural crest cells also begin expressing
3998:
3988:
3970:
3821:
3804:
3764:
3584:
3579:
3346:
3297:
3256:
3198:
3157:"Identification of a rudimentary neural crest in a non-vertebrate chordate"
3141:
3092:
3057:
3014:
2928:
2845:
2827:
2796:
2755:
2657:
2530:
2452:
2385:
2347:
2264:
2215:
2127:
2086:
2037:
1978:
1943:
1883:
1866:
1851:
1842:
1825:
1731:
1687:
1643:
1577:
1542:
1445:
1353:
1261:, whereas those that continue more ventrally form the sympathetic ganglia,
1232:
1197:
1135:
1032:
997:
858:
724:
619:
516:
453:
317:
211:
159:
155:
124:
34:
3238:
2963:
2901:
2884:
2706:
2613:
2578:
1892:
1810:
1775:
1659:
1400:
of head and neck glands (pituitary, salivary, lachrymal, thymus, thyroid)
1325:
data that shows the conservation of the neural plate border specifiers in
1313:
3955:
3945:
3866:
3809:
3784:
3624:
3549:
3491:
2883:
Vega-Lopez, Guillermo A.; Cerrizuela, Santiago; Aybar, Manuel J. (2017).
2698:
10.1002/(SICI)1096-9926(199711)56:5<317::AID-TERA5>3.0.CO;2-U
1662:"Ancient evolutionary origin of the neural crest gene regulatory network"
1660:
Sauka-Spengler, T.; Meulemans, D.; Jones, M.; Bronner-Fraser, M. (2007).
1437:
1415:
1250:
910:
877:
pattern of inheritance. Overall, Waardenburg's syndrome is rare, with an
748:
707:
bearing neural crest cell. Burgeoning neural crest cells express EphB, a
635:
563:
524:
449:
445:
433:
175:
171:
167:
120:
38:
3425:
3180:
3049:
2600:
Arias, S (1971). "Genetic heterogeneity in the Waardenburg's syndrome".
2435:
2020:
1618:"Gene-regulatory interactions in neural crest evolution and development"
1273:
The vagal and sacral neural crest cells develop into the ganglia of the
897:
Also implicated in defects related to neural crest cell development and
374:
transcription factor, is required for mesenchyme differentiation of the
273:
can be subdivided into the following four sub-networks described below.
98:
3918:
3903:
3883:
3680:
3567:
3541:
3481:
3476:
3461:
3376:
3123:
2955:
2911:
2737:
2338:
2321:
1934:
1462:
1334:
1318:
1254:
1161:(TCS) results from the compromised development of the first and second
1081:
905:(HD or HSCR), characterized by a lack of innervation in regions of the
850:
842:
834:
780:
691:
469:
187:
116:
3221:
Van Keymeulen, A; Mascre, G; Youseff, KK; et al. (October 2009).
2649:
2514:
2118:
2101:
1924:
1907:
1031:, the mechanisms by which these abnormalities arise is still unclear.
3913:
3879:
3794:
3513:
3317:
American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology
1597:
Brooker, R.J. 2014, Biology, 3rd edn, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1084
1330:
1182:
1174:
1054:
1043:
922:
906:
816:
772:
476:
394:
282:
281:
First, extracellular signaling molecules, secreted from the adjacent
16:
Pluripotent embyronic cell group giving rise to diverse cell lineages
2377:
2197:
328:
development of the neural plate (low BMP) and epidermis (high BMP).
3993:
3657:
3639:
3601:
3518:
1389:
1209:
1123:
1021:
1001:
866:
854:
796:
752:
740:
736:
631:
623:
607:
603:
583:
535:
302:
286:
258:
163:
113:
112:
cells are a temporary group of cells that arise from the embryonic
42:
1991:
1208:
Neural crest cells originating from different positions along the
3789:
2678:
1393:
1377:
1061:
1058:
1046:
1039:
1025:
744:
678:, neural crest migration is the result of repulsive guidance via
639:
520:
480:
350:
3155:
Abitua, P. B.; Wagner, E.; Navarrete, I. A.; Levine, M. (2012).
2406:
2287:. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. pp. 1197–1199.
970:
946:
791:
and specification into their final cell type is biased by their
3675:
3466:
3451:
2720:
Smith, S. M.; Garic, A.; Flentke, G. R.; Berres, M. E. (2014).
1401:
1381:
1296:
1228:
1190:
1186:
926:
784:
716:
687:
611:
483:
132:
28:
3270:
Szeder, V; Grim, M; Halata, Z; Sieber-Blum, M (January 2003).
3036:
Northcutt, Glenn (2005). "The new head hypothesis revisited".
2626:"Waardenburg syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. October 2012.
1004:
are diagnosed within a continuum of disorders broadly labeled
1485:
1193:
1170:
1104:
978:
954:
679:
571:
567:
515:
embryos there is a massive delamination that occurs when the
506:
502:
191:
3070:
2941:
845:
areas are caused by a total absence of neural crest-derived
401:
119:, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including
3269:
3154:
2885:"Trunk neural crest cells: formation, migration and beyond"
2182:"Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition"
1956:
974:
966:
950:
942:
587:
547:
371:
148:
3220:
2882:
2500:
886:
336:
on neural crest specifier expression remains incomplete.
316:
region of slug (a neural crest specific gene) contains a
562:
initiate delamination by inducing the expression of the
241:
Neural crest was first described in the chick embryo by
158:, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the
2719:
1615:
815:
formation of neural crest and because of the action of
779:. Cells migrating through this path differentiate into
1404:
and adipose tissue of calvaria, ventral neck and face
795:
subjection to morphogenic cues such as BMP, Wnt, FGF,
3754:
2556:
1864:
1492:
List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
739:
which allows for binding and guided interaction with
170:, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the
2726:
Birth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews
2722:"Neural crest development in fetal alcohol syndrome"
2415:. The Neural Crest: 150 years after His' discovery.
1432:, cephalic ganglia (VII and in part, V, IX, and X),
3105:
1392:and smooth muscle of branchial arteries and veins,
578:. These factors play a direct role in inducing the
519:is not entirely fused, whereas delamination in the
2889:The International Journal of Developmental Biology
2812:"Review of the Genetic Basis of Jaw Malformations"
1867:"Role of FGF and noggin in neural crest induction"
1520:
1257:. The cells that stay in the sclerotome form the
988:
767:. The other main route neural crest cells take is
214:. Abnormalities in neural crest development cause
1173:gene, which causes neural crest cells to undergo
1110:. This deletion may disrupt rostral neural crest
339:
4013:
3106:Donoghue, P.C.; Graham, A.; Kelsh, R.N. (2008).
1467:, and even associated with some tumors (such as
1268:
881:of ~ 2/100,000 people in the United States. All
197:Underlying the development of neural crest is a
3272:"Neural crest origin of mammalian Merkel cells"
2363:
985:, or the lack of these enteric ganglia occurs.
464:. Delamination is defined as the separation of
3310:
3108:"The origin and evolution of the neural crest"
1865:Mayor, R.; Guerrero, N.; Martinez, C. (1997).
1555:
1049:exposed to ethanol show a decreased number of
381:
3740:
3411:
2984:
1376:, quadrate, articular, hyoid and columella),
497:that induces the expression of EMT promoting
201:, described as a set of interacting signals,
174:, converge at the dorsal midline to form the
1153:
1024:. However, due to the promiscuous nature of
1008:(FASD). Severe FASD can impair neural crest
2809:
1340:
1020:, an elongated upper lip, and a smoothened
841:. In the case of piebaldism, the colorless
3747:
3733:
3418:
3404:
3148:
2861:
2859:
2857:
2855:
1788:
1760:
1703:
1616:Meulemans, D.; Bronner-Fraser, M. (2004).
1469:melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
1231:, bones of the middle ear and jaw and the
1118:. Some defects observed are linked to the
361:
74:crest_by_E5.0.2.1.0.0.2 E5.0.2.1.0.0.2
27:
3336:
3287:
3246:
3188:
3131:
3035:
2910:
2900:
2835:
2786:
2745:
2696:
2434:
2424:
2337:
2254:
2233:
2205:
2179:
2154:Development of the Nervous System, 3rd ed
2117:
2076:
2019:
2009:
1933:
1923:
1882:
1841:
1751:. Oxford University Press, London, 111 p.
1721:
1699:
1697:
1677:
1633:
996:(PAE) is among the most common causes of
892:
821:
666:direction without the need of a neuronal
305:(epidermis) from the neural plate during
3311:Lake, JI; Heuckeroth, RO (1 July 2013).
2768:
2156:. Oxford: ELSEVIER INC. pp. 70–72.
2050:
1488:—may control neural crest cell migration
1265:, and the nerves surrounding the aorta.
806:
711:, which binds the EphrinB transmembrane
658:Neural crest cell migration occurs in a
649:
420:
400:
2865:
2852:
2465:
1905:
1549:
1280:
1215:
462:epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
45:and migrates out towards the periphery.
4014:
2635:
2282:
1823:
1694:
1655:
1653:
1611:
1609:
1607:
1605:
1603:
1556:Shakhova, Olga; Sommer, Lukas (2008).
1516:
1514:
1512:
1510:
1508:
1506:
1444:of all autonomic and sensory ganglia,
3728:
3399:
2599:
2552:
2550:
2548:
2366:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
2359:
2357:
2319:
2306:
2304:
2278:
2276:
2274:
2229:
2227:
2225:
2186:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
2175:
2173:
2151:
2147:
2145:
2143:
2141:
2139:
2137:
2099:
1238:
715:expressed in the caudal half of each
2810:Ahmed, M.; Ye, X.; Taub, P. (2016).
2051:Vincentz, J.W.; et al. (2008).
1087:
873:fashion, while II and IV exhibit an
276:
180:epithelial to mesenchymal transition
1650:
1600:
1503:
1396:of ocular and masticatory muscles,
523:embryo occurs during fusion of the
218:, which include conditions such as
13:
2571:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1986.tb00501.x
2545:
2354:
2301:
2271:
2222:
2170:
2134:
452:, cells originally located in the
14:
4048:
3356:
1906:Tribulo, C.; et al. (2003).
1558:"Neural crest-derived stem cells"
1277:and the parasympathetic ganglia.
1084:appear to be minimally affected.
1038:of neural crest cells as well as
1012:, as evidenced by characteristic
694:signaling, interactions with the
580:epithelial-mesenchymal transition
1824:Vallin, J.; et al. (2001).
1448:cells of all peripheral nerves.
1203:
616:matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
3304:
3263:
3214:
3205:
3099:
3064:
3029:
2978:
2935:
2876:
2803:
2762:
2713:
2672:
2629:
2620:
2593:
2494:
2459:
2400:
2313:
2100:Light, W.; et al. (2005).
2093:
2044:
1985:
1950:
1899:
1858:
1817:
1564:. Harvard Stem Cell Institute.
1465:, iris muscle and pigment cells
1006:Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
989:Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
917:abnormalities like an enlarged
479:. For example, delamination in
439:
2771:"The 22q11 deletion syndromes"
1782:
1754:
1738:
1591:
1337:of vertebrates and tunicates.
645:
566:protein transcription factors
340:Neural plate border specifiers
1:
3289:10.1016/s0012-1606(02)00015-5
2816:Journal of Pediatric Genetics
2480:10.1016/S0046-8177(74)80021-3
1497:
1269:Vagal and sacral neural crest
1196:have also been linked to the
1126:of DiGeorge syndrome include
4022:Embryology of nervous system
3850:Cardiac neural crest complex
3007:10.1126/science.220.4594.268
2285:Principles of Neural Science
1803:10.1016/0012-1606(73)90061-4
1679:10.1016/j.devcel.2007.08.005
1635:10.1016/j.devcel.2004.08.007
1302:
965:(RTK), forms a complex with
787:. Further neural crest cell
410:
264:
7:
3703:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
3648:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
3427:Human embryonic development
2769:Scambler, Peter J. (2000).
2426:10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.05.013
2256:10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.041
2069:10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.04.037
1535:10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.07.033
1474:
618:that degrade the overlying
456:border become neural crest
382:Neural crest effector genes
10:
4053:
2866:Gilbert, Scott F. (2000).
1284:
1242:
1219:
1103:of a small segment in the
1014:craniofacial abnormalities
582:by reducing expression of
414:
236:
3981:
3936:
3865:
3835:
3772:
3763:
3656:
3638:
3600:
3540:
3527:
3500:
3434:
3085:10.1016/j.gde.2006.06.006
2011:10.1016/j.mod.2018.07.010
1998:Mechanisms of Development
1723:10.1016/j.mod.2004.06.003
1704:Le Douarin, N.M. (2004).
1422:Peripheral nervous system
1159:Treacher Collins Syndrome
1154:Treacher Collins Syndrome
994:Prenatal alcohol exposure
765:peripheral nervous system
590:in addition to promoting
417:Collective cell migration
224:Waardenburg–Shah syndrome
91:
79:
67:
55:
50:
26:
21:
3708:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
3620:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
3429:in the first three weeks
3329:10.1152/ajpgi.00452.2012
2775:Human Molecular Genetics
2638:Neurogastroenterol Motil
2234:Theveneau, Eric (2012).
2180:Lamouille, Samy (2014).
1414:of the adrenal medulla,
1341:Neural crest derivatives
1235:of the tooth primordia.
1128:congenital heart defects
963:receptor tyrosine kinase
709:receptor tyrosine kinase
406:from Bronner-Fraser 2004
356:necessary and sufficient
301:separate the non-neural
182:, delaminating from the
2320:Mayor, Roberto (2013).
1971:10.1242/dev.128.21.4127
1570:10.3824/stembook.1.51.1
540:cell adhesion molecules
362:Neural crest specifiers
271:gene regulatory network
261:of neural crest cells.
199:gene regulatory network
3592:Regional specification
3386:University of Michigan
2944:Anatomy and Embryology
2828:10.1055/s-0036-1593505
2503:Birth Defects Research
1884:10.1006/dbio.1997.8634
1843:10.1074/jbc.M103167200
1456:Enterochromaffin cells
1275:enteric nervous system
925:), obstruction of the
903:Hirschsprung's disease
893:Hirschsprung's Disease
865:. Types I and III are
863:Hirschsprung's disease
827:Waardenburg's syndrome
822:Waardenburg's syndrome
655:
426:
407:
93:Anatomical terminology
4037:Animal nervous system
3698:Intraembryonic coelom
3391:Hox domains in chicks
3239:10.1083/jcb.200907080
2902:10.1387/ijdb.160408gv
2872:. Sinauer Associates.
2788:10.1093/hmg/9.16.2421
2559:Pediatric Dermatology
2413:Developmental Biology
2283:Kandel, Eric (2013).
2243:Developmental Biology
1442:Satellite glial cells
1323:in situ hybridization
1140:learning disabilities
998:developmental defects
807:Clinical significance
653:
606:capable of degrading
499:transcription factors
424:
415:Further information:
404:
322:transcription factors
220:frontonasal dysplasia
203:transcription factors
3857:Truncal neural crest
3845:Cranial neural crest
1292:Cardiac neural crest
1287:cardiac neural crest
1281:Cardiac neural crest
1222:cranial neural crest
1216:Cranial neural crest
913:can lead to further
696:extracellular matrix
630:proteins, including
628:extracellular matrix
626:that associate with
444:After fusion of the
127:cartilage and bone,
3755:Development of the
3181:10.1038/nature11589
3173:2012Natur.492..104A
3073:Curr Opin Genet Dev
3050:10.1002/jez.b.21063
2999:1983Sci...220..268G
2152:Sanes, Dan (2012).
1481:First arch syndrome
1430:dorsal root ganglia
1259:dorsal root ganglia
1095:is associated with
875:autosomal recessive
839:congenital deafness
162:and the non-neural
3827:Adult neurogenesis
3780:Neural development
3363:Embryology at UNSW
3124:10.1002/bies.20767
2956:10.1007/BF00185519
2738:10.1002/bdrc.21078
2339:10.1242/dev.091751
2322:"The Neural Crest"
1370:Meckel's cartilage
1245:trunk neural crest
1239:Trunk neural crest
1070:release of calcium
1018:palpebral fissures
871:autosomal dominant
859:dystopia canthorum
812:Neurocristopathies
700:contact inhibition
656:
486:is triggered by a
427:
408:
216:neurocristopathies
4009:
4008:
3932:
3931:
3875:Rostral neuropore
3722:
3721:
3718:
3717:
3447:Oocyte activation
3167:(7427): 104–107.
2993:(4594): 268–274.
2781:(16): 2421–2426.
2650:10.1111/nmo.12776
2515:10.1002/bdr2.1644
2332:(11): 2247–2251.
2294:978-0-07-139011-8
2119:10.1242/dev.01734
1965:(21): 4127–4138.
1925:10.1242/dev.00878
1764:Bull Biol Fr Belg
1440:in the whisker,
1434:Rohon-Beard cells
1398:connective tissue
1167:missense mutation
1163:pharyngeal arches
1093:DiGeorge syndrome
1088:DiGeorge syndrome
1064:levels caused by
1057:due to increased
733:pharyngeal arches
672:radial glial cell
534:proteins such as
333:paraxial mesoderm
277:Inductive signals
228:DiGeorge syndrome
205:, and downstream
107:
106:
102:
4044:
4032:Chordate anatomy
3966:Surface ectoderm
3894:Cervical flexure
3889:Cephalic flexure
3770:
3769:
3749:
3742:
3735:
3726:
3725:
3610:Surface ectoderm
3573:Primitive groove
3554:Primitive streak
3538:
3537:
3420:
3413:
3406:
3397:
3396:
3351:
3350:
3340:
3308:
3302:
3301:
3291:
3267:
3261:
3260:
3250:
3218:
3212:
3209:
3203:
3202:
3192:
3152:
3146:
3145:
3135:
3103:
3097:
3096:
3068:
3062:
3061:
3033:
3027:
3026:
2982:
2976:
2975:
2939:
2933:
2932:
2914:
2904:
2880:
2874:
2873:
2869:The Neural Crest
2863:
2850:
2849:
2839:
2807:
2801:
2800:
2790:
2766:
2760:
2759:
2749:
2717:
2711:
2710:
2700:
2676:
2670:
2669:
2633:
2627:
2624:
2618:
2617:
2597:
2591:
2590:
2554:
2543:
2542:
2498:
2492:
2491:
2463:
2457:
2456:
2438:
2428:
2404:
2398:
2397:
2361:
2352:
2351:
2341:
2317:
2311:
2308:
2299:
2298:
2280:
2269:
2268:
2258:
2240:
2231:
2220:
2219:
2209:
2177:
2168:
2167:
2149:
2132:
2131:
2121:
2097:
2091:
2090:
2080:
2048:
2042:
2041:
2023:
2013:
1989:
1983:
1982:
1954:
1948:
1947:
1937:
1927:
1903:
1897:
1896:
1886:
1862:
1856:
1855:
1845:
1821:
1815:
1814:
1786:
1780:
1779:
1758:
1752:
1742:
1736:
1735:
1725:
1701:
1692:
1691:
1681:
1657:
1648:
1647:
1637:
1613:
1598:
1595:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1584:
1553:
1547:
1546:
1518:
1428:and glia of the
1412:chromaffin cells
1374:scleral ossicles
1148:bipolar disorder
1120:pharyngeal pouch
1078:oxidative stress
1016:including short
831:neurocristopathy
676:progenitor cells
670:such as along a
307:neural induction
99:edit on Wikidata
96:
31:
19:
18:
4052:
4051:
4047:
4046:
4045:
4043:
4042:
4041:
4012:
4011:
4010:
4005:
3977:
3928:
3924:Germinal matrix
3899:Pontine flexure
3861:
3831:
3759:
3753:
3723:
3714:
3652:
3634:
3596:
3529:
3523:
3502:
3496:
3487:Inner cell mass
3430:
3424:
3359:
3354:
3309:
3305:
3268:
3264:
3219:
3215:
3210:
3206:
3153:
3149:
3104:
3100:
3069:
3065:
3034:
3030:
2983:
2979:
2940:
2936:
2881:
2877:
2864:
2853:
2808:
2804:
2767:
2763:
2718:
2714:
2677:
2673:
2634:
2630:
2625:
2621:
2602:Birth Defects B
2598:
2594:
2555:
2546:
2499:
2495:
2468:Human Pathology
2464:
2460:
2405:
2401:
2378:10.1038/nrm2428
2362:
2355:
2318:
2314:
2309:
2302:
2295:
2281:
2272:
2238:
2232:
2223:
2198:10.1038/nrm3758
2178:
2171:
2164:
2150:
2135:
2098:
2094:
2049:
2045:
1990:
1986:
1955:
1951:
1918:(26): 6441–52.
1904:
1900:
1863:
1859:
1836:(32): 30350–8.
1822:
1818:
1787:
1783:
1759:
1755:
1743:
1739:
1716:(9): 1089–102.
1702:
1695:
1658:
1651:
1614:
1601:
1596:
1592:
1582:
1580:
1554:
1550:
1519:
1504:
1500:
1477:
1426:Sensory neurons
1408:Endocrine cells
1384:cartilage, the
1358:dental papillae
1348:(also known as
1343:
1335:common ancestor
1305:
1289:
1283:
1271:
1263:adrenal medulla
1247:
1241:
1224:
1218:
1206:
1156:
1090:
1051:migratory cells
991:
935:enteric ganglia
909:. This lack of
895:
824:
809:
789:differentiation
763:neurons of the
723:, and eventual
648:
600:polysialic acid
442:
419:
413:
384:
376:pharyngeal arch
364:
342:
285:and underlying
279:
267:
243:Wilhelm His Sr.
239:
184:neuroepithelium
145:adrenal medulla
141:enteric neurons
103:
46:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4050:
4040:
4039:
4034:
4029:
4024:
4007:
4006:
4004:
4003:
4002:
4001:
3996:
3985:
3983:
3979:
3978:
3976:
3975:
3974:
3973:
3963:
3958:
3953:
3948:
3942:
3940:
3934:
3933:
3930:
3929:
3927:
3926:
3921:
3916:
3911:
3906:
3901:
3896:
3891:
3886:
3877:
3871:
3869:
3863:
3862:
3860:
3859:
3854:
3853:
3852:
3841:
3839:
3833:
3832:
3830:
3829:
3824:
3819:
3818:
3817:
3812:
3802:
3797:
3792:
3787:
3782:
3776:
3774:
3767:
3761:
3760:
3757:nervous system
3752:
3751:
3744:
3737:
3729:
3720:
3719:
3716:
3715:
3713:
3712:
3711:
3710:
3705:
3700:
3690:
3685:
3684:
3683:
3678:
3668:
3666:Axial mesoderm
3662:
3660:
3654:
3653:
3651:
3650:
3644:
3642:
3636:
3635:
3633:
3632:
3627:
3622:
3617:
3612:
3606:
3604:
3598:
3597:
3595:
3594:
3589:
3588:
3587:
3577:
3576:
3575:
3570:
3564:Primitive node
3561:
3546:
3544:
3535:
3525:
3524:
3522:
3521:
3516:
3510:
3508:
3498:
3497:
3495:
3494:
3489:
3484:
3479:
3474:
3469:
3464:
3459:
3454:
3449:
3444:
3438:
3436:
3432:
3431:
3423:
3422:
3415:
3408:
3400:
3394:
3393:
3388:
3379:
3370:
3358:
3357:External links
3355:
3353:
3352:
3303:
3262:
3213:
3204:
3147:
3098:
3063:
3044:(4): 274–297.
3028:
2977:
2934:
2875:
2851:
2822:(4): 209–219.
2802:
2761:
2732:(3): 210–220.
2712:
2691:(5): 317–326.
2671:
2644:(2): 161–166.
2628:
2619:
2592:
2565:(2): 119–124.
2544:
2509:(8): 584–632.
2493:
2474:(4): 409–429.
2458:
2399:
2372:(7): 557–568.
2353:
2312:
2300:
2293:
2270:
2221:
2192:(3): 178–196.
2169:
2163:978-0123745392
2162:
2133:
2112:(8): 1831–41.
2092:
2043:
1984:
1949:
1898:
1857:
1816:
1781:
1753:
1737:
1693:
1649:
1599:
1590:
1548:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1495:
1494:
1489:
1483:
1476:
1473:
1386:dermatocranium
1362:chondrocranium
1346:Ectomesenchyme
1342:
1339:
1327:protochordates
1304:
1301:
1285:Main article:
1282:
1279:
1270:
1267:
1243:Main article:
1240:
1237:
1220:Main article:
1217:
1214:
1205:
1202:
1155:
1152:
1132:facial defects
1112:cell migration
1101:translocations
1089:
1086:
990:
987:
894:
891:
823:
820:
808:
805:
793:spatiotemporal
769:dorsolaterally
647:
644:
614:and secreting
532:tight junction
512:Xenopus laevis
448:to create the
441:
438:
412:
409:
383:
380:
363:
360:
341:
338:
278:
275:
266:
263:
238:
235:
105:
104:
95:
89:
88:
83:
77:
76:
71:
65:
64:
59:
53:
52:
48:
47:
37:border. After
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4049:
4038:
4035:
4033:
4030:
4028:
4025:
4023:
4020:
4019:
4017:
4000:
3997:
3995:
3992:
3991:
3990:
3987:
3986:
3984:
3980:
3972:
3969:
3968:
3967:
3964:
3962:
3959:
3957:
3954:
3952:
3951:Optic vesicle
3949:
3947:
3944:
3943:
3941:
3939:
3935:
3925:
3922:
3920:
3917:
3915:
3912:
3910:
3907:
3905:
3902:
3900:
3897:
3895:
3892:
3890:
3887:
3885:
3881:
3878:
3876:
3873:
3872:
3870:
3868:
3864:
3858:
3855:
3851:
3848:
3847:
3846:
3843:
3842:
3840:
3838:
3834:
3828:
3825:
3823:
3820:
3816:
3815:Neural groove
3813:
3811:
3808:
3807:
3806:
3803:
3801:
3800:Neuroectoderm
3798:
3796:
3793:
3791:
3788:
3786:
3783:
3781:
3778:
3777:
3775:
3771:
3768:
3766:
3762:
3758:
3750:
3745:
3743:
3738:
3736:
3731:
3730:
3727:
3709:
3706:
3704:
3701:
3699:
3696:
3695:
3694:
3693:Lateral plate
3691:
3689:
3686:
3682:
3679:
3677:
3674:
3673:
3672:
3669:
3667:
3664:
3663:
3661:
3659:
3655:
3649:
3646:
3645:
3643:
3641:
3637:
3631:
3628:
3626:
3623:
3621:
3618:
3616:
3615:Neuroectoderm
3613:
3611:
3608:
3607:
3605:
3603:
3599:
3593:
3590:
3586:
3583:
3582:
3581:
3578:
3574:
3571:
3569:
3565:
3562:
3560:
3559:Primitive pit
3557:
3556:
3555:
3551:
3548:
3547:
3545:
3543:
3539:
3536:
3533:
3526:
3520:
3517:
3515:
3512:
3511:
3509:
3506:
3499:
3493:
3490:
3488:
3485:
3483:
3480:
3478:
3475:
3473:
3470:
3468:
3465:
3463:
3460:
3458:
3455:
3453:
3450:
3448:
3445:
3443:
3442:Fertilization
3440:
3439:
3437:
3433:
3428:
3421:
3416:
3414:
3409:
3407:
3402:
3401:
3398:
3392:
3389:
3387:
3383:
3380:
3378:
3374:
3371:
3369:
3368:
3364:
3361:
3360:
3348:
3344:
3339:
3334:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3318:
3314:
3307:
3299:
3295:
3290:
3285:
3282:(2): 258–63.
3281:
3277:
3273:
3266:
3258:
3254:
3249:
3244:
3240:
3236:
3233:(1): 91–100.
3232:
3228:
3224:
3217:
3208:
3200:
3196:
3191:
3186:
3182:
3178:
3174:
3170:
3166:
3162:
3158:
3151:
3143:
3139:
3134:
3129:
3125:
3121:
3118:(6): 530–41.
3117:
3113:
3109:
3102:
3094:
3090:
3086:
3082:
3078:
3074:
3067:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3047:
3043:
3039:
3032:
3024:
3020:
3016:
3012:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2996:
2992:
2988:
2981:
2973:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2957:
2953:
2950:(3): 263–72.
2949:
2945:
2938:
2930:
2926:
2922:
2918:
2913:
2908:
2903:
2898:
2895:(1–2): 5–15.
2894:
2890:
2886:
2879:
2871:
2870:
2862:
2860:
2858:
2856:
2847:
2843:
2838:
2833:
2829:
2825:
2821:
2817:
2813:
2806:
2798:
2794:
2789:
2784:
2780:
2776:
2772:
2765:
2757:
2753:
2748:
2743:
2739:
2735:
2731:
2727:
2723:
2716:
2708:
2704:
2699:
2694:
2690:
2686:
2682:
2675:
2667:
2663:
2659:
2655:
2651:
2647:
2643:
2639:
2632:
2623:
2615:
2611:
2608:(4): 87–101.
2607:
2603:
2596:
2588:
2584:
2580:
2576:
2572:
2568:
2564:
2560:
2553:
2551:
2549:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2524:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2508:
2504:
2497:
2489:
2485:
2481:
2477:
2473:
2469:
2462:
2454:
2450:
2446:
2442:
2437:
2432:
2427:
2422:
2419:: S110–S143.
2418:
2414:
2410:
2403:
2395:
2391:
2387:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2371:
2367:
2360:
2358:
2349:
2345:
2340:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2316:
2307:
2305:
2296:
2290:
2286:
2279:
2277:
2275:
2266:
2262:
2257:
2252:
2248:
2244:
2237:
2230:
2228:
2226:
2217:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2176:
2174:
2165:
2159:
2155:
2148:
2146:
2144:
2142:
2140:
2138:
2129:
2125:
2120:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2103:
2096:
2088:
2084:
2079:
2074:
2070:
2066:
2062:
2058:
2054:
2047:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2022:
2017:
2012:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1988:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1953:
1945:
1941:
1936:
1931:
1926:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1902:
1894:
1890:
1885:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1861:
1853:
1849:
1844:
1839:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1820:
1812:
1808:
1804:
1800:
1797:(1): 217–22.
1796:
1792:
1785:
1777:
1773:
1770:(3): 435–52.
1769:
1765:
1757:
1750:
1747:, S. (1950).
1746:
1741:
1733:
1729:
1724:
1719:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1700:
1698:
1689:
1685:
1680:
1675:
1672:(3): 405–20.
1671:
1667:
1663:
1656:
1654:
1645:
1641:
1636:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1612:
1610:
1608:
1606:
1604:
1594:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1552:
1544:
1540:
1536:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1517:
1515:
1513:
1511:
1509:
1507:
1502:
1493:
1490:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1472:
1470:
1466:
1464:
1459:
1457:
1453:
1452:Enteric cells
1449:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1405:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1366:nasal capsule
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1338:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1315:
1309:
1300:
1298:
1293:
1288:
1278:
1276:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1246:
1236:
1234:
1230:
1223:
1213:
1211:
1204:Cell lineages
1201:
1199:
1195:
1192:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1179:embryogenesis
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1151:
1149:
1145:
1144:schizophrenia
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1108:chromosome 22
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1085:
1083:
1082:pigment cells
1079:
1075:
1074:intracellular
1071:
1067:
1063:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1034:
1030:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1003:
999:
995:
986:
984:
983:aganglionosis
980:
976:
972:
968:
964:
960:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
936:
933:and form the
932:
928:
924:
920:
916:
915:physiological
912:
908:
904:
900:
890:
888:
884:
880:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
828:
819:
818:
813:
804:
802:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
781:pigment cells
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
750:
746:
742:
738:
734:
728:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
652:
643:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
581:
577:
573:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
551:
545:
541:
537:
533:
528:
526:
522:
518:
514:
513:
508:
504:
500:
496:
493:
489:
485:
482:
478:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
451:
447:
437:
435:
432:
423:
418:
403:
399:
397:
396:
391:
390:
379:
377:
373:
368:
359:
357:
353:
352:
346:
337:
334:
331:Fgf from the
329:
325:
323:
319:
315:
310:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
274:
272:
262:
260:
256:
251:
247:
244:
234:
231:
229:
225:
221:
217:
213:
212:cell lineages
208:
204:
200:
195:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
152:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
129:smooth muscle
126:
122:
118:
115:
111:
100:
94:
90:
87:
84:
82:
78:
75:
72:
70:
66:
63:
60:
58:
54:
49:
44:
40:
36:
30:
25:
20:
3999:Otic vesicle
3989:Otic placode
3971:Lens placode
3837:Neural crest
3836:
3822:Neuropoiesis
3805:Neural plate
3765:Neurogenesis
3688:Intermediate
3630:Neural crest
3629:
3585:Gastrulation
3367:Notes/ncrest
3365:
3323:(1): G1–24.
3320:
3316:
3306:
3279:
3275:
3265:
3230:
3227:J. Cell Biol
3226:
3216:
3207:
3164:
3160:
3150:
3115:
3111:
3101:
3079:(4): 360–6.
3076:
3072:
3066:
3041:
3037:
3031:
2990:
2986:
2980:
2947:
2943:
2937:
2892:
2888:
2878:
2868:
2819:
2815:
2805:
2778:
2774:
2764:
2729:
2725:
2715:
2688:
2684:
2674:
2641:
2637:
2631:
2622:
2605:
2601:
2595:
2562:
2558:
2506:
2502:
2496:
2471:
2467:
2461:
2436:11336/101713
2416:
2412:
2402:
2369:
2365:
2329:
2325:
2315:
2284:
2249:(1): 34–54.
2246:
2242:
2189:
2185:
2153:
2109:
2105:
2095:
2063:(1): 131–9.
2060:
2056:
2046:
2021:11336/101714
2001:
1997:
1987:
1962:
1958:
1952:
1915:
1911:
1901:
1874:
1870:
1860:
1833:
1829:
1819:
1794:
1790:
1784:
1767:
1763:
1756:
1748:
1740:
1713:
1709:
1669:
1665:
1628:(3): 291–9.
1625:
1621:
1593:
1581:. Retrieved
1561:
1551:
1526:
1522:
1461:
1460:
1451:
1450:
1438:Merkel cells
1421:
1420:
1416:glomus cells
1407:
1406:
1354:odontoblasts
1349:
1345:
1344:
1312:
1310:
1306:
1290:
1272:
1248:
1233:odontoblasts
1225:
1207:
1198:pathogenesis
1157:
1136:neurological
1091:
1033:Cell culture
992:
896:
825:
810:
777:dermamyotome
771:between the
729:
725:cytoskeletal
657:
620:basal lamina
592:modification
549:
529:
517:neural plate
511:
454:neural plate
443:
440:Delamination
428:
393:
387:
385:
369:
365:
349:
347:
343:
330:
326:
318:binding site
311:
280:
268:
252:
248:
240:
232:
196:
172:neural folds
160:neural plate
156:gastrulation
153:
125:craniofacial
110:Neural crest
109:
108:
35:neural plate
22:Neural crest
3956:Optic stalk
3946:Neural tube
3909:Basal plate
3867:Neural tube
3810:Neural fold
3785:Neurulation
3625:Neurulation
3550:Archenteron
3542:Germ layers
3492:Trophoblast
2912:11336/53692
2326:Development
2106:Development
2004:: 219–239.
1959:Development
1935:11336/95313
1912:Development
1877:(1): 1–12.
1830:J Biol Chem
1583:27 December
1529:(1): 1–11.
1463:Melanocytes
1418:type I/II.
1350:mesectoderm
1251:melanocytes
1181:. Although
1134:, and some
1116:development
1042:developing
911:innervation
851:melanocytes
849:-producing
761:sympathetic
749:fibronectin
636:fibronectin
564:zinc finger
525:neural fold
474:mesenchymal
450:neural tube
446:neural fold
434:neural tube
389:Rho GTPases
176:neural tube
168:neurulation
121:melanocytes
51:Identifiers
39:neural tube
4016:Categories
3919:Neuroblast
3904:Alar plate
3884:Rhombomere
3681:Somitomere
3568:Blastopore
3532:Trilaminar
3482:Blastocyst
3477:Blastocoel
3472:Cavitation
3462:Blastomere
3377:NeuroNames
2685:Teratology
1745:Hörstadius
1498:References
1255:sclerotome
1068:-mediated
835:piebaldism
817:Teratogens
721:rhoGTPases
692:neuropilin
688:semaphorin
588:N-Cadherin
558:expressed
470:epithelial
188:vertebrate
166:. During
137:peripheral
117:germ layer
3961:Optic cup
3914:Glioblast
3880:Neuromere
3795:Notochord
3514:Hypoblast
3505:Bilaminar
3373:ancil-445
3276:Dev. Biol
3112:BioEssays
2921:0214-6282
2539:210151171
2523:2472-1727
2488:0046-8177
2445:0012-1606
2030:0925-4773
1710:Mech. Dev
1523:Dev. Biol
1390:pericytes
1382:laryngeal
1331:tunicates
1319:co-option
1303:Evolution
1183:mutations
1175:apoptosis
1097:deletions
1059:cytosolic
1055:apoptosis
1044:zebrafish
1010:migration
923:megacolon
907:intestine
899:migration
879:incidence
867:inherited
773:epidermis
737:integrins
646:Migration
624:integrins
608:cadherins
604:proteases
477:phenotype
411:Migration
395:cadherins
283:epidermis
265:Induction
4027:Ectoderm
3994:Otic pit
3671:Paraxial
3658:Mesoderm
3640:Endoderm
3602:Ectoderm
3580:Gastrula
3519:Epiblast
3457:Cleavage
3347:23639815
3298:12645929
3257:19786578
3199:23135395
3142:18478530
3093:16793256
3058:16003768
3023:39290007
3015:17732898
2972:32986727
2929:28287247
2846:27895973
2797:11005797
2756:25219761
2666:12394126
2658:26806097
2587:23858201
2531:31926062
2453:29802835
2394:10746234
2386:18523435
2348:23674598
2265:22261150
2216:24556840
2128:15772131
2087:18539270
2057:Dev Biol
2038:30086335
1979:11684651
1944:14627721
1871:Dev Biol
1852:11402039
1791:Dev Biol
1732:15296974
1688:17765683
1666:Dev Cell
1644:15363405
1622:Dev Cell
1578:20614636
1562:StemBook
1543:15464568
1475:See also
1378:tracheal
1210:anterior
1200:of TCS.
1124:symptoms
1036:explants
1022:philtrum
1002:patients
775:and the
753:mesoderm
741:collagen
705:receptor
668:scaffold
632:collagen
610:such as
584:occludin
556:Dorsally
552:Cadherin
542:such as
536:occludin
501:such as
354:Msx1 is
314:promoter
303:ectoderm
289:such as
287:mesoderm
259:ontogeny
255:Chimeras
207:effector
164:ectoderm
114:ectoderm
43:ectoderm
3790:Neurula
3773:General
3528:Week 3
3501:Week 2
3382:Diagram
3338:3725693
3248:2762088
3190:4257486
3169:Bibcode
3133:2692079
2995:Bibcode
2987:Science
2964:2268069
2837:5123890
2747:4827602
2707:9451756
2614:5006208
2579:3952027
2207:4240281
2078:2572997
1893:9281332
1811:4121410
1776:4191116
1446:Schwann
1436:, some
1394:tendons
1314:de novo
1177:during
1169:of the
1062:calcium
1047:embryos
1040:in vivo
1029:binding
1026:ethanol
855:genetic
847:pigment
783:of the
757:sensory
745:laminin
684:EphrinB
660:rostral
640:laminin
495:cascade
484:embryos
351:Xenopus
237:History
62:D009432
3676:Somite
3467:Morula
3452:Zygote
3435:Week 1
3345:
3335:
3296:
3255:
3245:
3197:
3187:
3161:Nature
3140:
3130:
3091:
3056:
3021:
3013:
2970:
2962:
2927:
2919:
2844:
2834:
2795:
2754:
2744:
2705:
2664:
2656:
2612:
2585:
2577:
2537:
2529:
2521:
2486:
2451:
2443:
2392:
2384:
2346:
2291:
2263:
2214:
2204:
2160:
2126:
2085:
2075:
2036:
2028:
1977:
1942:
1891:
1850:
1809:
1774:
1730:
1686:
1642:
1576:
1541:
1402:dermis
1360:, the
1297:septum
1229:thymus
1191:POLR1D
1187:POLR1C
953:, and
927:bowels
869:in an
799:, and
785:dermis
747:, and
717:somite
713:ligand
698:, and
664:caudal
638:, and
612:ADAM10
574:, and
466:tissue
431:dorsal
226:, and
154:After
133:dentin
3019:S2CID
2968:S2CID
2662:S2CID
2583:S2CID
2535:S2CID
2390:S2CID
2239:(PDF)
1486:DGCR2
1194:genes
1171:TCOF1
1105:human
1072:from
979:EDNRB
955:EDNRB
919:colon
887:sexes
883:races
829:is a
801:Notch
598:with
596:NCAMs
576:twist
568:snail
521:chick
507:FoxD3
503:SNAI2
481:chick
458:cells
192:clade
97:[
86:86666
3343:PMID
3294:PMID
3253:PMID
3195:PMID
3138:PMID
3089:PMID
3054:PMID
3042:304B
3011:PMID
2960:PMID
2925:PMID
2917:ISSN
2842:PMID
2793:PMID
2752:PMID
2703:PMID
2654:PMID
2610:PMID
2575:PMID
2527:PMID
2519:ISSN
2484:ISSN
2449:PMID
2441:ISSN
2382:PMID
2344:PMID
2289:ISBN
2261:PMID
2212:PMID
2158:ISBN
2124:PMID
2083:PMID
2034:PMID
2026:ISSN
1975:PMID
1940:PMID
1889:PMID
1848:PMID
1807:PMID
1772:PMID
1728:PMID
1684:PMID
1640:PMID
1585:2019
1574:PMID
1539:PMID
1380:and
1189:and
1146:and
1138:and
977:and
975:EDN3
971:GFRα
969:and
967:GDNF
961:, a
951:EDN3
947:GFRα
943:GDNF
885:and
843:skin
837:and
759:and
686:and
680:EphB
586:and
572:slug
560:BMPs
546:and
544:NCAM
538:and
505:and
392:and
372:bHLH
320:for
299:Fgfs
297:and
295:BMPs
291:Wnts
149:glia
147:and
139:and
57:MeSH
3982:Ear
3938:Eye
3384:at
3375:at
3333:PMC
3325:doi
3321:305
3284:doi
3280:253
3243:PMC
3235:doi
3231:187
3185:PMC
3177:doi
3165:492
3128:PMC
3120:doi
3081:doi
3046:doi
3003:doi
2991:220
2952:doi
2948:182
2907:hdl
2897:doi
2832:PMC
2824:doi
2783:doi
2742:PMC
2734:doi
2730:102
2693:doi
2646:doi
2567:doi
2511:doi
2507:112
2476:doi
2431:hdl
2421:doi
2417:444
2374:doi
2334:doi
2330:140
2251:doi
2247:366
2202:PMC
2194:doi
2114:doi
2110:132
2073:PMC
2065:doi
2061:320
2016:hdl
2006:doi
2002:154
1967:doi
1963:128
1930:hdl
1920:doi
1916:130
1879:doi
1875:189
1838:doi
1834:276
1799:doi
1768:103
1718:doi
1714:121
1674:doi
1630:doi
1566:doi
1531:doi
1527:275
1471:).
1352:):
1114:or
1099:or
1066:IP3
959:RET
939:RET
931:gut
901:is
797:Hox
662:to
594:of
492:Wnt
488:BMP
472:to
194:.
81:FMA
4018::
3882:/
3341:.
3331:.
3319:.
3315:.
3292:.
3278:.
3274:.
3251:.
3241:.
3229:.
3225:.
3193:.
3183:.
3175:.
3163:.
3159:.
3136:.
3126:.
3116:30
3114:.
3110:.
3087:.
3077:13
3075:.
3052:.
3040:.
3017:.
3009:.
3001:.
2989:.
2966:.
2958:.
2946:.
2923:.
2915:.
2905:.
2893:61
2891:.
2887:.
2854:^
2840:.
2830:.
2820:05
2818:.
2814:.
2791:.
2777:.
2773:.
2750:.
2740:.
2728:.
2724:.
2701:.
2689:56
2687:.
2683:.
2660:.
2652:.
2642:28
2640:.
2606:07
2604:.
2581:.
2573:.
2561:.
2547:^
2533:.
2525:.
2517:.
2505:.
2482:.
2470:.
2447:.
2439:.
2429:.
2411:.
2388:.
2380:.
2368:.
2356:^
2342:.
2328:.
2324:.
2303:^
2273:^
2259:.
2245:.
2241:.
2224:^
2210:.
2200:.
2190:15
2188:.
2184:.
2172:^
2136:^
2122:.
2108:.
2104:.
2081:.
2071:.
2059:.
2055:.
2032:.
2024:.
2014:.
2000:.
1996:.
1973:.
1961:.
1938:.
1928:.
1914:.
1910:.
1887:.
1873:.
1869:.
1846:.
1832:.
1828:.
1805:.
1795:30
1793:.
1766:.
1726:.
1712:.
1708:.
1696:^
1682:.
1670:13
1668:.
1664:.
1652:^
1638:.
1624:.
1620:.
1602:^
1572:.
1560:.
1537:.
1525:.
1505:^
1458:.
1454::
1424::
1410::
1372:,
1368:,
1356:,
1150:.
1130:,
973:.
957:.
949:,
945:,
941:,
803:.
743:,
634:,
570:,
554:.
527:.
436:.
309:.
293:,
230:.
222:,
151:.
143:,
135:,
131:,
123:,
69:TE
3748:e
3741:t
3734:v
3566:/
3552:/
3534:)
3530:(
3507:)
3503:(
3419:e
3412:t
3405:v
3349:.
3327::
3300:.
3286::
3259:.
3237::
3201:.
3179::
3171::
3144:.
3122::
3095:.
3083::
3060:.
3048::
3025:.
3005::
2997::
2974:.
2954::
2931:.
2909::
2899::
2848:.
2826::
2799:.
2785::
2779:9
2758:.
2736::
2709:.
2695::
2668:.
2648::
2616:.
2589:.
2569::
2563:3
2541:.
2513::
2490:.
2478::
2472:5
2455:.
2433::
2423::
2396:.
2376::
2370:9
2350:.
2336::
2297:.
2267:.
2253::
2218:.
2196::
2166:.
2130:.
2116::
2089:.
2067::
2040:.
2018::
2008::
1981:.
1969::
1946:.
1932::
1922::
1895:.
1881::
1854:.
1840::
1813:.
1801::
1778:.
1734:.
1720::
1690:.
1676::
1646:.
1632::
1626:7
1587:.
1568::
1545:.
1533::
1364:(
921:(
690:/
682:/
550:-
548:N
490:/
101:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.