735:
378:
approach, termed endokeratoplasty, is most appropriate for disease processes that exclusively or predominantly involve the corneal endothelium. Penetrating keratoplasty is preferred when the disease process involves irreversible damage not just to the corneal endothelium, but to other layers of the cornea as well. Compared to full-thickness keratoplasty, endokeratoplasty techniques are associated with shorter recovery times, improved visual results, and greater resistance to wound rupture. Although instrumentation and surgical techniques for endokeratoplasty are still in evolution, one commonly performed form of endokeratoplasty at present is
Descemet's Stripping (Automated) Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK ). In this form of endokeratoplasty, the diseased host endothelium and associated
291:
corneal endothelium is described by the "pump-leak hypothesis." Since the cornea is avascular, which renders it optimally transparent, the nutrition of the corneal epithelium, stromal keratocytes, and corneal endothelium must occur via diffusion of glucose and other solutes from the aqueous humor, across the corneal endothelium. The corneal endothelium then transports water from the stromal-facing surface to the aqueous-facing surface by an interrelated series of active and passive ion exchangers. Critical to this energy-driven process is the role of
734:
258:. The postnatal total endothelial cellularity of the cornea (approximately 300,000 cells per cornea) is achieved as early as the second trimester of gestation. Thereafter the endothelial cell density (but not the absolute number of cells) rapidly declines, as the fetal cornea grows in surface area, achieving a final adult density of approximately 2400 - 3200 cells/mm. The number of endothelial cells in the fully developed cornea decreases with age up until early adulthood, stabilizing around 50 years of age.
138:
32:
370:
symptoms can sometimes be obtained through the instillation of topical hypertonic saline drops, use of bandage soft contact lenses, and/or application of anterior stromal micropuncture. In cases in which irreversible corneal endothelial failure develops, severe corneal edema ensues, and the only effective remedy is replacement of the diseased corneal endothelium through the surgical approach of
312:. This threshold of endothelial cell density varies considerably amongst individuals, but is typically in the range of 500 - 1000 cells/mm. Typically, loss of endothelial cell density is accompanied by increases in cell size variability (polymegathism) and cell shape variation (polymorphism). Corneal
321:
fibrils, creating light scatter. In addition, excessive corneal hydration can result in edema of the corneal epithelial layer, which creates irregularity at the optically critical tear film-air interface. Both stromal light scatter and surface epithelial irregularity contribute to degraded optical
307:
Corneal endothelial cells are post-mitotic and divide rarely, if at all, in the post-natal human cornea. Wounding of the corneal endothelium, as from trauma or other insults, prompts healing of the endothelial monolayer by sliding and enlargement of adjacent endothelial cells, rather than mitosis.
386:
Investigational methods of corneal endothelial surgical replacement include
Descemet's Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK), in which the donor tissue consists only of Descemet's membrane and endothelium, and corneal endothelial cell replacement therapy, in which in vitro cultivated endothelial
290:
The principal physiological function of the corneal endothelium is to allow leakage of solutes and nutrients from the aqueous humor to the more superficial layers of the cornea while at the same time pumping water in the opposite direction, from the stroma to the aqueous. This dual function of the
377:
Historically, penetrating keratoplasty, or full thickness corneal transplantation, was the treatment of choice for irreversible endothelial failure. More recently, new corneal transplant techniques have been developed to enable more selective replacement of the diseased corneal endothelium. This
770:
1:posterior segment 2:ora serrata 3:ciliary muscle 4:ciliary zonules 5:Schlemm's canal 6:pupil 7:anterior chamber 8:cornea 9:iris 10:lens cortex 11:lens nucleus 12:ciliary process 13:conjunctiva 14:inferior oblique muscule 15:inferior rectus muscule 16:medial rectus muscle 17:retinal arteries and
369:
There is no medical treatment that can promote wound healing or regeneration of the corneal endothelium. In early stages of corneal edema, symptoms of blurred vision and episodic ocular pain predominate, due to edema and blistering (bullae) of the corneal epithelium. Partial palliation of these
382:
are removed from the central cornea, and in their place a specially harvested layer of healthy donor tissue is grafted. This layer consists of posterior stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium that has been dissected from cadaveric donor corneal tissue, typically using a mechanized (or
387:
cells are transplanted. These techniques, although still in an early developmental stage, aim to improve the selectivity of the transplantation approach by eliminating the presence of posterior stromal tissue from the grafted tissue.
265:
tiling scheme yields the greatest efficiency, in terms of total perimeter, of packing the posterior corneal surface with cells of a given area. The corneal endothelium is attached to the rest of the cornea through
771:
veins 18:optic disc 19:dura mater 20:central retinal artery 21:central retinal vein 22:optic nerve 23:vorticose vein 24:bulbar sheath 25:macula 26:fovea 27:sclera 28:choroid 29:superior rectus muscle 30:retina
246:. The corneal endothelium governs fluid and solute transport across the posterior surface of the cornea and maintains the cornea in the slightly dehydrated state that is required for optical transparency.
316:
can also occur as the result of compromised endothelial function due to intraocular inflammation or other causes. Excess hydration of the corneal stroma disrupts the normally uniform periodic spacing of
279:
754:
199:
283:
751:
1014:
338:. Surgical causes of endothelial failure include both acute intraoperative trauma as well as chronic postoperative trauma, such as from a malpositioned
752:
757:
766:
309:
753:
758:
308:
Endothelial cell loss, if sufficiently severe, can cause endothelial cell density to fall below the threshold level needed to maintain corneal
738:
299:. Bicarbonate ions formed by the action of carbonic anhydrase are translocated across the cell membrane, allowing water to passively follow.
187:
744:
749:
96:
68:
742:
358:
761:
760:
614:
583:
741:
75:
49:
740:
1260:
748:
261:
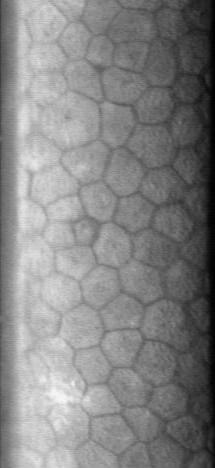
The normal corneal endothelium is a single layer of uniformly sized cells with a predominantly hexagonal shape. This
115:
82:
759:
750:
747:
756:
755:
739:
64:
762:
330:
Leading causes of endothelial failure include inadvertent endothelial trauma from intraocular surgery (such as
53:
194:
763:
142:
Vertical section of human cornea from near the margin. (Corneal endothelium is #5, labeled at bottom right.)
1321:
1205:
1173:
1010:
1158:
1127:
1119:
799:
1311:
954:
944:
765:
746:
406:"Prenatal and postnatal cellularity of the human corneal endothelium. A quantitative histologic study"
607:
486:"Human corneal endothelial cell transplantation using nanocomposite gel sheet in bullous keratopathy"
764:
767:
636:
170:
745:
949:
905:
371:
89:
42:
1326:
1316:
1089:
982:
713:
571:
379:
342:
or retained nuclear fragment in the anterior chamber. Other risk factors include narrow-angle
267:
206:
182:
743:
1265:
1070:
994:
932:
920:
875:
1255:
600:
8:
1280:
986:
937:
925:
915:
870:
804:
665:
335:
592:
137:
1250:
1030:
1026:
1022:
970:
809:
693:
660:
502:
485:
461:
436:
296:
20:
1290:
1006:
910:
827:
698:
624:
579:
548:
507:
466:
417:
1275:
1213:
1050:
703:
655:
538:
497:
456:
448:
339:
331:
239:
1188:
1147:
1143:
1065:
175:
1193:
1183:
1168:
1163:
860:
852:
832:
708:
683:
235:
278:
1305:
1218:
1153:
990:
1178:
1002:
837:
819:
552:
527:"Injection of Cultured Cells with a ROCK Inhibitor for Bullous Keratopathy"
511:
255:
543:
526:
470:
421:
1270:
1139:
1096:
1034:
998:
452:
212:
1084:
842:
405:
234:
The corneal endothelium are specialized, flattened, mitochondria-rich
1060:
1055:
974:
628:
292:
262:
243:
31:
978:
403:
343:
227:
is a single layer of endothelial cells on the inner surface of the
1230:
1131:
1075:
791:
231:. It faces the chamber formed between the cornea and the iris.
1225:
1135:
889:
675:
647:
437:"Effect of age on the endothelial cell count in the normal eye"
351:
318:
228:
270:, which is an acellular layer composed mostly of collagen IV.
16:
Single layer of endothelial cells on the surface of the cornea
865:
578:(24th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2426–42.
347:
313:
158:
322:
performance of the cornea and can compromise visual acuity.
254:
The corneal endothelium is embryologically derived from the
779:
404:
Murphy, C; Alvarado, J; Juster, R; Maglio, M (March 1984).
238:
that line the posterior surface of the cornea and face the
622:
434:
282:
Hexagonal cells of corneal endothelium visualized by
364:
56:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1303:
410:Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science
325:
737:
574:. In Goldman, Lee; Schafer, Andrew I. (eds.).
302:
608:
569:
615:
601:
136:
542:
524:
501:
483:
460:
249:
116:Learn how and when to remove this message
570:Yanoff, Myron; Cameron, Douglas (2012).
277:
1304:
359:X-linked endothelial corneal dystrophy
596:
435:Wilson, R S; Roper-Hall, M J (1982).
54:adding citations to reliable sources
25:
13:
733:
563:
14:
1338:
365:Treatment for endothelial disease
441:British Journal of Ophthalmology
30:
572:"Diseases of the Visual System"
41:needs additional citations for
518:
477:
428:
397:
1:
390:
326:Causes of endothelial disease
273:
1261:Optical coherence tomography
1015:Photosensitive ganglion cell
164:epithelium posterius corneae
19:Not to be confused with the
7:
1011:Giant retina ganglion cells
800:Capillary lamina of choroid
303:Mechanisms of corneal edema
10:
1343:
955:Retinal pigment epithelium
945:External limiting membrane
18:
1243:
1204:
1118:
1109:
1043:
963:
898:
888:
851:
818:
790:
778:
731:
674:
646:
635:
383:"automated") instrument.
205:
193:
181:
169:
157:
152:
147:
135:
130:
576:Goldman's Cecil Medicine
950:Layer of rods and cones
906:Inner limiting membrane
372:corneal transplantation
361:was described in 2006.
772:
357:A rare disease called
287:
250:Embryology and anatomy
207:Anatomical terminology
1266:Eye care professional
1071:Foveal avascular zone
933:Outer plexiform layer
921:Inner plexiform layer
876:Iris sphincter muscle
769:
544:10.1056/NEJMoa1712770
525:Kinoshita, S (2018).
484:Parikumar, P (2018).
281:
65:"Corneal endothelium"
1286:Physiological Optics
1256:Ocular immune system
995:Retina ganglion cell
453:10.1136/bjo.66.8.513
50:improve this article
1322:Human head and neck
1110:Anatomical regions
971:Photoreceptor cells
938:Outer nuclear layer
926:Inner nuclear layer
916:Ganglion cell layer
871:Iris dilator muscle
666:Trabecular meshwork
380:Descemet's membrane
284:specular microscopy
268:Descemet's membrane
225:corneal endothelium
131:Corneal endothelium
773:
297:carbonic anhydrase
288:
21:corneal epithelium
1312:Human eye anatomy
1299:
1298:
1291:Visual perception
1239:
1238:
1206:Posterior segment
1174:Posterior chamber
1105:
1104:
1007:Bistratified cell
911:Nerve fiber layer
884:
883:
828:Ciliary processes
729:
728:
585:978-1-4377-1604-7
221:
220:
216:
126:
125:
118:
100:
1334:
1276:Refractive error
1214:Vitreous chamber
1159:Anterior chamber
1120:Anterior segment
1116:
1115:
896:
895:
805:Bruch's membrane
788:
787:
780:Uvea / vascular
736:
656:Episcleral layer
644:
643:
617:
610:
603:
594:
593:
589:
557:
556:
546:
537:(11): 995–1003.
522:
516:
515:
505:
481:
475:
474:
464:
432:
426:
425:
401:
340:intraocular lens
336:Fuchs' dystrophy
332:cataract surgery
240:anterior chamber
213:edit on Wikidata
210:
140:
128:
127:
121:
114:
110:
107:
101:
99:
58:
34:
26:
1342:
1341:
1337:
1336:
1335:
1333:
1332:
1331:
1302:
1301:
1300:
1295:
1235:
1200:
1189:Capsule of lens
1144:Lacrimal system
1111:
1101:
1061:Parafoveal area
1056:Perifoveal area
1039:
983:Horizontal cell
959:
880:
847:
814:
810:Sattler's layer
781:
774:
768:
725:
670:
661:Schlemm's canal
639:
631:
623:Anatomy of the
621:
586:
566:
564:Further reading
561:
560:
523:
519:
490:Am J Stem Cells
482:
478:
433:
429:
402:
398:
393:
367:
328:
319:Type I collagen
305:
276:
252:
217:
143:
122:
111:
105:
102:
59:
57:
47:
35:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1340:
1330:
1329:
1324:
1319:
1314:
1297:
1296:
1294:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1247:
1245:
1241:
1240:
1237:
1236:
1234:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1222:
1221:
1210:
1208:
1202:
1201:
1199:
1198:
1197:
1196:
1194:Zonule of Zinn
1191:
1181:
1176:
1171:
1166:
1164:Aqueous humour
1161:
1156:
1151:
1124:
1122:
1113:
1107:
1106:
1103:
1102:
1100:
1099:
1094:
1093:
1092:
1082:
1081:
1080:
1079:
1078:
1073:
1063:
1058:
1047:
1045:
1041:
1040:
1038:
1037:
967:
965:
961:
960:
958:
957:
952:
947:
941:
940:
935:
929:
928:
923:
918:
913:
908:
902:
900:
893:
886:
885:
882:
881:
879:
878:
873:
868:
863:
857:
855:
849:
848:
846:
845:
840:
835:
833:Ciliary muscle
830:
824:
822:
816:
815:
813:
812:
807:
802:
796:
794:
785:
776:
775:
732:
730:
727:
726:
724:
723:
722:
721:
716:
711:
706:
701:
696:
686:
680:
678:
672:
671:
669:
668:
663:
658:
652:
650:
641:
633:
632:
620:
619:
612:
605:
597:
591:
590:
584:
565:
562:
559:
558:
517:
476:
447:(8): 513–515.
427:
395:
394:
392:
389:
366:
363:
327:
324:
304:
301:
275:
272:
251:
248:
219:
218:
209:
203:
202:
197:
191:
190:
185:
179:
178:
173:
167:
166:
161:
155:
154:
150:
149:
145:
144:
141:
133:
132:
124:
123:
38:
36:
29:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1339:
1328:
1327:Ophthalmology
1325:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1317:Visual system
1315:
1313:
1310:
1309:
1307:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1281:Accommodation
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1248:
1246:
1242:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1220:
1219:Vitreous body
1217:
1216:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1203:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1154:Fibrous tunic
1152:
1149:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1126:
1125:
1123:
1121:
1117:
1114:
1108:
1098:
1095:
1091:
1088:
1087:
1086:
1083:
1077:
1074:
1072:
1069:
1068:
1067:
1064:
1062:
1059:
1057:
1054:
1053:
1052:
1049:
1048:
1046:
1042:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
991:Amacrine cell
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
969:
968:
966:
962:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
942:
939:
936:
934:
931:
930:
927:
924:
922:
919:
917:
914:
912:
909:
907:
904:
903:
901:
897:
894:
891:
887:
877:
874:
872:
869:
867:
864:
862:
859:
858:
856:
854:
850:
844:
841:
839:
836:
834:
831:
829:
826:
825:
823:
821:
817:
811:
808:
806:
803:
801:
798:
797:
795:
793:
789:
786:
783:
777:
720:
717:
715:
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
700:
697:
695:
692:
691:
690:
687:
685:
682:
681:
679:
677:
673:
667:
664:
662:
659:
657:
654:
653:
651:
649:
645:
642:
638:
637:Fibrous tunic
634:
630:
626:
618:
613:
611:
606:
604:
599:
598:
595:
587:
581:
577:
573:
568:
567:
554:
550:
545:
540:
536:
532:
528:
521:
513:
509:
504:
499:
495:
491:
487:
480:
472:
468:
463:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
431:
423:
419:
416:(3): 312–22.
415:
411:
407:
400:
396:
388:
384:
381:
375:
373:
362:
360:
355:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
323:
320:
315:
311:
310:deturgescence
300:
298:
294:
285:
280:
271:
269:
264:
259:
257:
247:
245:
241:
237:
232:
230:
226:
214:
208:
204:
201:
198:
196:
192:
189:
186:
184:
180:
177:
174:
172:
168:
165:
162:
160:
156:
151:
146:
139:
134:
129:
120:
117:
109:
98:
95:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67: –
66:
62:
61:Find sources:
55:
51:
45:
44:
39:This article
37:
33:
28:
27:
22:
1285:
1179:Ciliary body
1019:Diencephalon
1018:
1003:Parasol cell
987:Bipolar cell
838:Pars plicata
820:Ciliary body
718:
688:
575:
534:
531:N Engl J Med
530:
520:
496:(1): 18–24.
493:
489:
479:
444:
440:
430:
413:
409:
399:
385:
376:
368:
356:
329:
306:
289:
260:
256:neural crest
253:
233:
224:
222:
188:A15.2.02.022
163:
112:
106:January 2015
103:
93:
86:
79:
72:
60:
48:Please help
43:verification
40:
1271:Eye disease
1251:Keratocytes
1140:Conjunctiva
1097:Ora serrata
1035:Muller glia
999:Midget cell
719:Endothelium
709:Dua's layer
153:Identifiers
1306:Categories
1112:of the eye
1085:Optic disc
843:Pars plana
714:Descemet's
694:Epithelium
391:References
293:Na/KATPase
274:Physiology
76:newspapers
1090:Optic cup
975:Cone cell
629:human eye
263:honeycomb
979:Rod cell
784:(middle)
699:Bowman's
553:29539291
512:29531856
344:glaucoma
1231:Choroid
1132:Eyebrow
1076:Foveola
892:(inner)
792:Choroid
640:(outer)
627:of the
503:5840311
471:7104267
462:1039838
422:6698749
242:of the
176:D004728
148:Details
90:scholar
1226:Retina
1136:Eyelid
1128:Adnexa
1051:Macula
1031:K cell
1027:M cell
1023:P cell
899:Layers
890:Retina
861:Stroma
704:Stroma
689:layers
684:Limbus
676:Cornea
648:Sclera
582:
551:
510:
500:
469:
459:
420:
352:iritis
350:, and
334:) and
229:cornea
200:312267
92:
85:
78:
71:
63:
1244:Other
1148:Orbit
1066:Fovea
1044:Other
981:) → (
964:Cells
866:Pupil
782:tunic
625:globe
348:aging
314:edema
236:cells
211:[
159:Latin
97:JSTOR
83:books
1184:Lens
1169:Iris
1017:) →
993:) →
985:) →
853:Iris
580:ISBN
549:PMID
508:PMID
467:PMID
418:PMID
295:and
223:The
183:TA98
171:MeSH
69:news
989:→ (
539:doi
535:378
498:PMC
457:PMC
449:doi
244:eye
195:FMA
52:by
1308::
1146:,
1142:,
1138:,
1134:,
1033:,
1029:,
1025:,
1021::
1013:,
1009:,
1005:,
1001:,
977:,
547:.
533:.
529:.
506:.
492:.
488:.
465:.
455:.
445:66
443:.
439:.
414:25
412:.
408:.
374:.
354:.
346:,
1150:)
1130:(
997:(
973:(
616:e
609:t
602:v
588:.
555:.
541::
514:.
494:7
473:.
451::
424:.
286:.
215:]
119:)
113:(
108:)
104:(
94:·
87:·
80:·
73:·
46:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.