396:
42:
2119:
213:
2131:
84:
1677:
488:
to the source. This restimulates the first neuron and also allows the path of transmission to continue to its output. A resulting repetitive pattern is the outcome that only stops if one or more of the synapses fail, or if an inhibitory feed from another source causes it to stop. This type of reverberating circuit is found in the respiratory center that sends signals to the
578:
patients) can yield insights into the underlying mechanisms for patterns of cognitive deficits observed in the particular patient group. Predictions from these models can be tested in patients or via pharmacological manipulations, and these studies can in turn be used to inform the models, making the
534:
techniques have been developed to investigate the activity of neural circuits and networks. The use of "brain scanners" or functional neuroimaging to investigate the structure or function of the brain is common, either as simply a way of better assessing brain injury with high-resolution pictures, or
487:
A reverberating circuit produces a repetitive output. In a signalling procedure from one neuron to another in a linear sequence, one of the neurons may send a signal back to initiating neuron. Each time that the first neuron fires, the other neuron further down the sequence fire again sending it back
216:
Proposed organization of motor-semantic neural circuits for action language comprehension. Gray dots represent areas of language comprehension, creating a network for comprehending all language. The semantic circuit of the motor system, particularly the motor representation of the legs (yellow dots),
499:
In a parallel after-discharge circuit, a neuron inputs to several chains of neurons. Each chain is made up of a different number of neurons but their signals converge onto one output neuron. Each synapse in the circuit acts to delay the signal by about 0.5 msec, so that the more synapses there are,
468:
In a diverging circuit, one neuron synapses with a number of postsynaptic cells. Each of these may synapse with many more making it possible for one neuron to stimulate up to thousands of cells. This is exemplified in the way that thousands of muscle fibers can be stimulated from the initial input
337:
and the postsynaptic action potential. LTP is induced by a series of action potentials which cause a variety of biochemical responses. Eventually, the reactions cause the expression of new receptors on the cellular membranes of the postsynaptic neurons or increase the efficacy of the existing
574:, where parts of the nodes are deliberately destroyed to see how the network performs, can also yield important insights in the working of several cell assemblies. Similarly, simulations of dysfunctional neurotransmitters in neurological conditions (e.g., dopamine in the basal ganglia of
551:
uses specific brain imaging technologies to take scans from the brain, usually when a person is doing a particular task, in an attempt to understand how the activation of particular brain areas is related to the task. In functional neuroimaging, especially fMRI, which measures
500:
the longer is the delay to the output neuron. After the input has stopped, the output will go on firing for some time. This type of circuit does not have a feedback loop as does the reverberating circuit. Continued firing after the stimulus has stopped is called
464:
There are four principal types of neural circuits that are responsible for a broad scope of neural functions. These circuits are a diverging circuit, a converging circuit, a reverberating circuit, and a parallel after-discharge circuit.
598:' and sparse coding phenomena develop and modify these ideas. The single cell experiments used intracranial electrodes in the medial temporal lobe (the hippocampus and surrounding cortex). Modern development of
1259:- C. elegans, a nematode with 302 neurons, is the only organism for whom the entire neural network has been uncovered. Use this site to browse through the network and to search for paths between any 2 neurons.
1233:
590:: "our perceptions are caused by the activity of a rather small number of neurons selected from a very large population of predominantly silent cells." This approach was stimulated by the idea of
144:. Thus, Hebbian pairing of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection and therefore either facilitate or inhibit
313:
Connections display temporal and spatial characteristics. Temporal characteristics refers to the continuously modified activity-dependent efficacy of synaptic transmission, called
357:
from causing a change in the intracellular sodium ion (Na) concentration, and preventing the generation of an action potential back towards the cell body. In some cells, however,
476:
In a converging circuit, inputs from many sources are converged into one output, affecting just one neuron or a neuron pool. This type of circuit is exemplified in the
570:
models serve as a test platform for different hypotheses of representation, information processing, and signal transmission. Lesioning studies in such models, e.g.
376:
neurons are required to produce firing. This picture is further complicated by variation in time constant between neurons, as some cells can experience their
492:, causing inhalation. When the circuit is interrupted by an inhibitory signal the muscles relax causing exhalation. This type of circuit may play a part in
248:
The establishment of synapses enables the connection of neurons into millions of overlapping, and interlinking neural circuits. Presynaptic proteins called
302:). These are often divided into short-term plasticity and long-term plasticity. Long-term synaptic plasticity is often contended to be the most likely
1246:
2039:
766:
427:
279:
to the terminal endings to transmit a signal to other neurons. Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission is realized mostly by
163:
published the first works on the processing of neural networks. They showed theoretically that networks of artificial neurons could
1306:
1228:
387:
synaptic depression has been particularly widely observed it has been speculated that it changes to facilitation in adult brains.
317:. It has been observed in several studies that the synaptic efficacy of this transmission can undergo short-term increase (called
1275:
1511:
345:
Backpropagating action potentials cannot occur because after an action potential travels down a given segment of the axon, the
536:
557:
449:
are responsible for controlling motor instructions involved in rhythmic behaviours. Rhythmic behaviours include walking,
644:
540:
284:
280:
2019:
983:
723:
377:
334:
314:
354:
346:
801:
J. Y. Lettvin; H. R. Maturana; W. S. McCulloch; W. H. Pitts (1959), "What the frog's eye tells the frog's brain.",
325:) according to the activity of the presynaptic neuron. The induction of long-term changes in synaptic efficacy, by
867:"Conditional Routing of Information to the Cortex: A Model of the Basal Ganglia's Role in Cognitive Coordination"
64:
to carry out a specific function when activated. Multiple neural circuits interconnect with one another to form
1469:
384:
322:
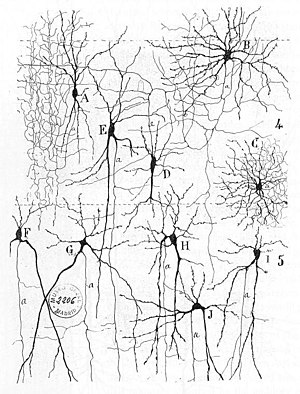
606:
give mathematical background to unexpected effectiveness of small neural ensembles in high-dimensional brain.
484:, which responds to a number of inputs from different sources by giving out an appropriate breathing pattern.
2135:
1860:
739:
136:'s Project for a Scientific Psychology (composed 1895). The first rule of neuronal learning was described by
17:
916:"Central pattern generator for locomotion: anatomical, physiological, and pathophysiological considerations"
2014:
1835:
1299:
350:
294:
level, there are various phenomena which alter the response characteristics of individual synapses (called
2054:
256:
191:
1720:
1243:
1581:
1504:
1464:
603:
594:
put forward two years earlier. Barlow formulated "five dogmas" of neuron doctrine. Recent studies of '
65:
2157:
2049:
2024:
1893:
1414:
571:
544:
525:
446:
230:
72:
31:
88:
1988:
1963:
1888:
1795:
1700:
1596:
1456:
599:
372:
to stimulate contraction of the postsynaptic muscle cell. In the spinal cord, however, at least 75
156:
1825:
1536:
1531:
1292:
1049:
548:
179:
777:
1820:
1810:
1601:
1556:
1474:
1423:
1323:
669:
615:
575:
561:
489:
369:
358:
326:
260:
535:
by examining the relative activations of different brain areas. Such technologies may include
2123:
1883:
1878:
1685:
1576:
1497:
1216:
2104:
1855:
1695:
1666:
1561:
1262:
1238:
1208:
1118:
1061:
674:
553:
330:
299:
217:
is incorporated when leg-related words are comprehended. Adapted from
Shebani et al. (2013)
8:
1998:
1898:
1775:
1745:
1730:
773:
407:
318:
295:
1122:
1065:
434:, thalamus, and back to the cortex. The largest structure within the basal ganglia, the
2162:
2074:
1968:
1908:
1631:
1611:
1182:
1155:
1108:
1030:
942:
915:
891:
866:
842:
817:
664:
659:
477:
458:
242:
187:
137:
100:
1272:
582:
The modern balance between the connectionist approach and the single-cell approach in
1993:
1928:
1903:
1755:
1715:
1351:
1253:- A free Matlab toolbox for simulating networks of several different types of neurons
1187:
1136:
1077:
1022:
979:
947:
896:
847:
800:
719:
627:
493:
291:
222:
221:
The connections between neurons in the brain are much more complex than those of the
145:
46:
1097:"The unreasonable effectiveness of small neural ensembles in high-dimensional brain"
1034:
2034:
1918:
1845:
1760:
1641:
1591:
1177:
1167:
1126:
1069:
1012:
937:
927:
886:
878:
837:
829:
614:
Sometimes neural circuitries can become pathological and cause problems such as in
595:
591:
264:
238:
198:). Later models also provided for excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission.
2094:
2089:
2084:
2079:
1973:
1913:
1850:
1765:
1725:
1710:
1661:
1651:
1606:
1279:
1250:
649:
521:
395:
339:
307:
112:
104:
92:
1131:
1096:
818:"Synaptic Neurexin Complexes: A Molecular Code for the Logic of Neural Circuits"
41:
2059:
1958:
1933:
1923:
1770:
1750:
1740:
1626:
1546:
1441:
1315:
833:
689:
586:
has been achieved through a lengthy discussion. In 1972, Barlow announced the
373:
268:
164:
152:
141:
35:
2151:
1983:
1978:
1943:
1840:
1830:
1790:
1636:
1571:
1566:
1431:
1402:
1172:
932:
654:
623:
619:
567:
431:
415:
226:
133:
122:
310:" refers to changes in the brain that are caused by activity or experience.
2069:
2064:
1948:
1780:
1705:
1656:
1646:
1621:
1616:
1586:
1520:
1446:
1378:
1212:
1191:
1140:
1081:
951:
900:
851:
694:
679:
583:
531:
470:
419:
272:
160:
1048:
Quian
Quiroga, R; Reddy, L; Kreiman, G; Koch, C; Fried, I (Jun 23, 2005).
1026:
1001:"Single units and sensation: a neuron doctrine for perceptual psychology?"
275:
goes above threshold an action potential will occur that travels down the
1938:
1785:
1436:
1388:
1336:
1229:
Comparison of Neural
Networks in the Brain and Artificial Neural Networks
684:
454:
442:
423:
411:
183:
1073:
34:. For projections from one region of the nervous system to another, see
2099:
1800:
1361:
1257:
WormWeb.org: Interactive
Visualization of the C. elegans Neural Network
1095:
Gorban, Alexander N.; Makarov, Valeri A.; Tyukin, Ivan Y. (July 2019).
740:"Neural Circuits | Centre of Excellence for Integrative Brain Function"
505:
400:
365:
and may have important effects on synaptic plasticity and computation.
171:
128:
117:
91:. The figure illustrates the diversity of neuronal morphologies in the
1050:"Invariant visual representation by single neurons in the human brain"
2044:
1735:
1373:
1346:
882:
481:
450:
212:
195:
1256:
1017:
1000:
457:. The central pattern generators are made up of different groups of
194:(i.e., potentials at the post-synaptic membrane will summate in the
1953:
1395:
1368:
1331:
1113:
764:
639:
435:
362:
333:(LTD), depends strongly on the relative timing of the onset of the
249:
87:
From "Texture of the
Nervous System of Man and the Vertebrates" by
83:
1284:
1156:"A Review of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus in Parkinson's Disease"
234:
207:
61:
1489:
1383:
509:
303:
175:
57:
865:
Stocco, Andrea; Lebiere, Christian; Anderson, John R. (2010).
1341:
1047:
602:
theory (stochastic separation theorems) with applications to
167:
1356:
276:
1676:
718:(5th ed.). Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer. p. 507.
560:) which is closely linked to neural activity, PET, and
430:. These circuits carry information between the cortex,
864:
438:, is seen as having its own internal microcircuitry.
233:. The basic kinds of connections between neurons are
1273:
Delaying Pulse
Networks (Wave Interference Networks)
368:
A neuron in the brain requires a single signal to a
1094:
744:
Centre of
Excellence for Integrative Brain Function
353:close, thus blocking any transient opening of the
2149:
1041:
1153:
201:
1505:
1300:
1263:Introduction to Neurons and Neuronal Networks
2040:Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring
75:, though there are significant differences.
71:Neural circuits have inspired the design of
765:Michael S. C. Thomas; James L. McClelland.
428:cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop
426:. There are several neural circuits in the
1512:
1498:
1307:
1293:
978:(3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 364.
1181:
1171:
1130:
1112:
1016:
992:
969:
967:
965:
963:
961:
941:
931:
890:
841:
380:over a wider period of time than others.
609:
394:
211:
82:
40:
973:
913:
255:One principle by which neurons work is
14:
2150:
1147:
998:
958:
907:
815:
713:
406:An example of a neural circuit is the
30:For larger structures of neurons, see
1493:
1288:
858:
809:
537:functional magnetic resonance imaging
267:will sum up in the cell body. If the
2130:
707:
504:. This circuit type is found in the
190:. These simple models accounted for
1234:Lecture notes at MIT OpenCourseWare
767:"Connectionist models of cognition"
24:
1314:
1269:(electronic neuroscience textbook)
1211:Robert H. Cudmore, Niraj S. Desai
1202:
1154:French, IT; Muthusamy, KA (2018).
732:
645:List of regions in the human brain
626:can also give rise to a number of
541:brain positron emission tomography
285:inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
281:excitatory postsynaptic potentials
25:
2174:
2020:Development of the nervous system
1244:Biological Neural Network Toolbox
1222:
805:, no. 47, pp. 1940–1951
399:Model of a neural circuit in the
335:excitatory postsynaptic potential
315:spike-timing-dependent plasticity
2129:
2118:
2117:
1675:
1519:
515:
182:were set up, now usually called
1160:Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience
1088:
999:Barlow, HB (December 1, 1972).
816:Südhof, TC (2 November 2017).
794:
758:
622:are involved. Problems in the
306:substrate. Usually, the term "
78:
13:
1:
1861:Social cognitive neuroscience
1217:doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.1363
700:
351:voltage-gated sodium channels
252:are central to this process.
27:Network or circuit of neurons
1836:Molecular cellular cognition
390:
180:models of biological neurons
7:
2055:Neurodevelopmental disorder
2030:Neural network (biological)
2025:Neural network (artificial)
1132:10.1016/j.plrev.2018.09.005
633:
628:neurodegenerative disorders
229:neural computing models of
202:Connections between neurons
99:Early treatments of neural
10:
2179:
1582:Computational neuroscience
834:10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.024
604:artificial neural networks
572:artificial neural networks
519:
447:central pattern generators
298:) and individual neurons (
231:artificial neural networks
205:
73:artificial neural networks
66:large scale brain networks
29:
2113:
2050:Neurodegenerative disease
2007:
1894:Evolutionary neuroscience
1869:
1809:
1684:
1673:
1545:
1527:
1455:
1422:
1415:Peripheral nervous system
1413:
1322:
545:computed axial tomography
526:Cognitive neuropsychology
383:While in synapses in the
32:biological neural network
2015:Brain–computer interface
1964:Neuromorphic engineering
1889:Educational neuroscience
1796:Nutritional neuroscience
1701:Clinical neurophysiology
1597:Integrative neuroscience
1239:Computation in the Brain
1173:10.3389/fnagi.2018.00099
933:10.3389/fneur.2012.00183
600:concentration of measure
588:single neuron revolution
157:Warren Sturgis McCulloch
109:Principles of Psychology
1826:Behavioral neuroscience
1101:Physics of Life Reviews
803:Proc. Inst. Radio Engr.
630:including Parkinson's.
549:Functional neuroimaging
441:Neural circuits in the
361:does occur through the
1821:Affective neuroscience
1602:Molecular neuroscience
1557:Behavioral epigenetics
1324:Central nervous system
920:Frontiers in Neurology
670:Pulse-coupled networks
562:electroencephalography
403:
370:neuromuscular junction
359:neural backpropagation
327:long-term potentiation
218:
178:functions. Simplified
111:, 3rd edition (1872),
96:
89:Santiago Ramón y Cajal
49:
1884:Cultural neuroscience
1879:Consumer neuroscience
1721:Neurogastroenterology
1577:Cellular neuroscience
714:Purves, Dale (2011).
610:Clinical significance
558:BOLD-contrast imaging
398:
271:of the neuron at the
265:postsynaptic membrane
215:
86:
44:
1856:Sensory neuroscience
1696:Behavioral neurology
1667:Systems neuroscience
1209:Intrinsic plasticity
914:Guertin, PA (2012).
871:Psychological Review
675:Systems neuroscience
554:hemodynamic activity
300:intrinsic plasticity
292:electrophysiological
1999:Social neuroscience
1899:Global neurosurgery
1776:Neurorehabilitation
1746:Neuro-ophthalmology
1731:Neurointensive care
1562:Behavioral genetics
1267:Neuroscience Online
1123:2019PhLRv..29...55G
1074:10.1038/nature03687
1066:2005Natur.435.1102Q
1060:(7045): 1102–1107.
974:Saladin, K (2011).
774:Stanford University
616:Parkinson's disease
579:process iterative.
490:respiratory muscles
459:spinal interneurons
408:trisynaptic circuit
363:dendritic branching
296:synaptic plasticity
243:electrical synapses
146:signal transmission
56:is a population of
2075:Neuroimmune system
1969:Neurophenomenology
1909:Neural engineering
1632:Neuroendocrinology
1612:Neural engineering
1278:2016-03-30 at the
1249:2016-07-14 at the
665:Neural oscillation
660:Neural engineering
494:epileptic seizures
478:respiratory center
404:
338:receptors through
223:artificial neurons
219:
188:artificial neurons
97:
60:interconnected by
50:
2145:
2144:
1994:Paleoneurobiology
1929:Neuroepistemology
1904:Neuroanthropology
1870:Interdisciplinary
1756:Neuropharmacology
1716:Neuroepidemiology
1487:
1486:
1483:
1482:
543:(brain PET), and
414:. Another is the
47:multipolar neuron
16:(Redirected from
2170:
2158:Neural circuitry
2133:
2132:
2121:
2120:
2035:Detection theory
1919:Neurocriminology
1846:Neurolinguistics
1761:Neuroprosthetics
1679:
1642:Neuroinformatics
1592:Imaging genetics
1514:
1507:
1500:
1491:
1490:
1420:
1419:
1309:
1302:
1295:
1286:
1285:
1196:
1195:
1185:
1175:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1134:
1116:
1092:
1086:
1085:
1045:
1039:
1038:
1020:
996:
990:
989:
971:
956:
955:
945:
935:
911:
905:
904:
894:
883:10.1037/a0019077
862:
856:
855:
845:
813:
807:
806:
798:
792:
791:
789:
788:
782:
776:. Archived from
771:
762:
756:
755:
753:
751:
736:
730:
729:
711:
596:grandmother cell
592:grandmother cell
385:developing brain
257:neural summation
192:neural summation
140:in 1949, in the
103:can be found in
21:
2178:
2177:
2173:
2172:
2171:
2169:
2168:
2167:
2148:
2147:
2146:
2141:
2109:
2095:Neurotechnology
2090:Neuroplasticity
2085:Neuromodulation
2080:Neuromanagement
2003:
1974:Neurophilosophy
1871:
1865:
1851:Neuropsychology
1812:
1805:
1766:Neuropsychiatry
1726:Neuroimmunology
1711:Neurocardiology
1687:
1680:
1671:
1662:Neurophysiology
1652:Neuromorphology
1607:Neural decoding
1548:
1541:
1523:
1518:
1488:
1479:
1470:Parasympathetic
1451:
1409:
1318:
1313:
1280:Wayback Machine
1251:Wayback Machine
1225:
1205:
1203:Further reading
1200:
1199:
1152:
1148:
1093:
1089:
1046:
1042:
1018:10.1068/p010371
997:
993:
986:
972:
959:
912:
908:
863:
859:
814:
810:
799:
795:
786:
784:
780:
769:
763:
759:
749:
747:
738:
737:
733:
726:
712:
708:
703:
650:Network science
636:
612:
564:(EEG) is used.
528:
522:Neuropsychology
518:
502:after-discharge
393:
340:phosphorylation
321:) or decrease (
308:neuroplasticity
210:
204:
153:neuroscientists
113:Theodor Meynert
105:Herbert Spencer
93:auditory cortex
81:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2176:
2166:
2165:
2160:
2143:
2142:
2140:
2139:
2127:
2114:
2111:
2110:
2108:
2107:
2105:Self-awareness
2102:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2067:
2062:
2060:Neurodiversity
2057:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2037:
2032:
2027:
2022:
2017:
2011:
2009:
2005:
2004:
2002:
2001:
1996:
1991:
1986:
1981:
1976:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1959:Neuromarketing
1956:
1951:
1946:
1941:
1936:
1934:Neuroesthetics
1931:
1926:
1924:Neuroeconomics
1921:
1916:
1911:
1906:
1901:
1896:
1891:
1886:
1881:
1875:
1873:
1867:
1866:
1864:
1863:
1858:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1823:
1817:
1815:
1807:
1806:
1804:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1788:
1783:
1778:
1773:
1771:Neuroradiology
1768:
1763:
1758:
1753:
1751:Neuropathology
1748:
1743:
1741:Neuro-oncology
1738:
1733:
1728:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1708:
1703:
1698:
1692:
1690:
1682:
1681:
1674:
1672:
1670:
1669:
1664:
1659:
1654:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1627:Neurochemistry
1624:
1619:
1614:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1594:
1589:
1584:
1579:
1574:
1569:
1564:
1559:
1553:
1551:
1543:
1542:
1540:
1539:
1534:
1528:
1525:
1524:
1517:
1516:
1509:
1502:
1494:
1485:
1484:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1461:
1459:
1453:
1452:
1450:
1449:
1444:
1442:Cranial nerves
1439:
1434:
1428:
1426:
1417:
1411:
1410:
1408:
1407:
1406:
1405:
1400:
1399:
1398:
1393:
1392:
1391:
1386:
1371:
1366:
1365:
1364:
1359:
1354:
1339:
1334:
1328:
1326:
1320:
1319:
1316:Nervous system
1312:
1311:
1304:
1297:
1289:
1283:
1282:
1270:
1260:
1254:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1224:
1223:External links
1221:
1220:
1219:
1204:
1201:
1198:
1197:
1146:
1087:
1040:
1011:(4): 371–394.
991:
984:
957:
906:
857:
828:(4): 745–769.
808:
793:
757:
746:. 13 June 2016
731:
724:
705:
704:
702:
699:
698:
697:
692:
690:Neural pathway
687:
682:
677:
672:
667:
662:
657:
652:
647:
642:
635:
632:
611:
608:
517:
514:
469:from a single
392:
389:
269:depolarization
203:
200:
142:Hebbian theory
127:Principles of
80:
77:
54:neural circuit
36:neural pathway
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2175:
2164:
2161:
2159:
2156:
2155:
2153:
2138:
2137:
2128:
2126:
2125:
2116:
2115:
2112:
2106:
2103:
2101:
2098:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2041:
2038:
2036:
2033:
2031:
2028:
2026:
2023:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2013:
2012:
2010:
2006:
2000:
1997:
1995:
1992:
1990:
1989:Neurotheology
1987:
1985:
1984:Neurorobotics
1982:
1980:
1979:Neuropolitics
1977:
1975:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1960:
1957:
1955:
1952:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1944:Neuroethology
1942:
1940:
1937:
1935:
1932:
1930:
1927:
1925:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1895:
1892:
1890:
1887:
1885:
1882:
1880:
1877:
1876:
1874:
1868:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1841:Motor control
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1831:Chronobiology
1829:
1827:
1824:
1822:
1819:
1818:
1816:
1814:
1808:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1792:
1791:Neurovirology
1789:
1787:
1784:
1782:
1779:
1777:
1774:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1764:
1762:
1759:
1757:
1754:
1752:
1749:
1747:
1744:
1742:
1739:
1737:
1734:
1732:
1729:
1727:
1724:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1709:
1707:
1704:
1702:
1699:
1697:
1694:
1693:
1691:
1689:
1683:
1678:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1637:Neurogenetics
1635:
1633:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1623:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1613:
1610:
1608:
1605:
1603:
1600:
1598:
1595:
1593:
1590:
1588:
1585:
1583:
1580:
1578:
1575:
1573:
1572:Brain-reading
1570:
1568:
1567:Brain mapping
1565:
1563:
1560:
1558:
1555:
1554:
1552:
1550:
1544:
1538:
1535:
1533:
1530:
1529:
1526:
1522:
1515:
1510:
1508:
1503:
1501:
1496:
1495:
1492:
1476:
1473:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1462:
1460:
1458:
1454:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1432:Sensory nerve
1430:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1412:
1404:
1403:Limbic system
1401:
1397:
1394:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1381:
1380:
1377:
1376:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1363:
1360:
1358:
1355:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1345:
1344:
1343:
1340:
1338:
1335:
1333:
1330:
1329:
1327:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1310:
1305:
1303:
1298:
1296:
1291:
1290:
1287:
1281:
1277:
1274:
1271:
1268:
1264:
1261:
1258:
1255:
1252:
1248:
1245:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1227:
1226:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1207:
1206:
1193:
1189:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1150:
1142:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1091:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1044:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
995:
987:
985:9780071222075
981:
977:
976:Human anatomy
970:
968:
966:
964:
962:
953:
949:
944:
939:
934:
929:
925:
921:
917:
910:
902:
898:
893:
888:
884:
880:
877:(2): 541–74.
876:
872:
868:
861:
853:
849:
844:
839:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
812:
804:
797:
783:on 2015-09-06
779:
775:
768:
761:
745:
741:
735:
727:
725:9780878936953
721:
717:
710:
706:
696:
693:
691:
688:
686:
683:
681:
678:
676:
673:
671:
668:
666:
663:
661:
658:
656:
655:Neural coding
653:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
637:
631:
629:
625:
624:Papez circuit
621:
620:basal ganglia
617:
607:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
580:
577:
573:
569:
568:Connectionist
565:
563:
559:
555:
550:
547:(CAT) scans.
546:
542:
538:
533:
527:
523:
516:Study methods
513:
511:
507:
503:
497:
495:
491:
485:
483:
479:
474:
472:
466:
462:
460:
456:
452:
448:
444:
439:
437:
433:
432:basal ganglia
429:
425:
421:
417:
416:Papez circuit
413:
409:
402:
397:
388:
386:
381:
379:
375:
371:
366:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
343:
341:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
311:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
288:
286:
283:(EPSPs), and
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
253:
251:
246:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
227:connectionist
224:
214:
209:
199:
197:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
166:
162:
158:
154:
151:In 1959, the
149:
147:
143:
139:
135:
134:Sigmund Freud
131:
130:
124:
123:William James
120:
119:
114:
110:
106:
102:
94:
90:
85:
76:
74:
69:
67:
63:
59:
55:
48:
45:Anatomy of a
43:
37:
33:
19:
18:Brain circuit
2134:
2122:
2070:Neuroimaging
2065:Neurogenesis
2029:
1949:Neurohistory
1914:Neurobiotics
1813:neuroscience
1781:Neurosurgery
1706:Epileptology
1688:neuroscience
1657:Neurophysics
1647:Neurometrics
1622:Neurobiology
1617:Neuroanatomy
1587:Connectomics
1521:Neuroscience
1447:Spinal nerve
1379:Diencephalon
1266:
1213:Scholarpedia
1163:
1159:
1149:
1104:
1100:
1090:
1057:
1053:
1043:
1008:
1004:
994:
975:
923:
919:
909:
874:
870:
860:
825:
821:
811:
802:
796:
785:. Retrieved
778:the original
760:
748:. Retrieved
743:
734:
716:Neuroscience
715:
709:
695:Nerve plexus
680:Connectomics
613:
587:
584:neurobiology
581:
566:
532:neuroimaging
529:
501:
498:
486:
475:
471:motor neuron
467:
463:
440:
420:hypothalamus
418:linking the
405:
382:
367:
344:
319:facilitation
312:
289:
273:axon hillock
254:
247:
225:used in the
220:
161:Walter Pitts
150:
132:(1890), and
126:
116:
108:
98:
70:
53:
51:
1939:Neuroethics
1786:Neurotology
1465:Sympathetic
1437:Motor nerve
1389:Optic nerve
1337:Spinal cord
1215:3(2):1363.
685:Nerve tract
576:Parkinson's
508:of certain
506:reflex arcs
455:ejaculation
443:spinal cord
424:limbic lobe
412:hippocampus
184:perceptrons
79:Early study
2152:Categories
2100:Neurotoxin
1801:Psychiatry
1362:Cerebellum
1114:1809.07656
1005:Perception
787:2015-08-31
701:References
530:Different
520:See also:
401:cerebellum
331:depression
323:depression
261:potentials
206:See also:
172:arithmetic
129:Psychology
118:Psychiatry
2163:Cognition
2045:Neurochip
1811:Cognitive
1736:Neurology
1457:Autonomic
1374:Forebrain
1347:Hindbrain
1107:: 55–88.
618:when the
482:brainstem
451:urination
391:Circuitry
329:(LTP) or
287:(IPSPs).
250:neurexins
196:cell body
165:implement
2124:Category
2008:Concepts
1954:Neurolaw
1686:Clinical
1396:Cerebrum
1369:Midbrain
1332:Meninges
1276:Archived
1247:Archived
1192:29755338
1141:30366739
1082:15973409
1035:17487970
952:23403923
901:20438237
852:29100073
640:Feedback
634:See also
539:(fMRI),
510:reflexes
436:striatum
374:afferent
239:chemical
235:synapses
176:symbolic
121:(1884),
101:networks
62:synapses
2136:Commons
1549:science
1537:History
1532:Outline
1475:Enteric
1424:Somatic
1352:Medulla
1183:5933166
1119:Bibcode
1062:Bibcode
1027:4377168
943:3567435
926:: 183.
892:3064519
843:5694349
556:(using
480:of the
445:called
422:to the
410:in the
347:m gates
290:On the
263:at the
237:: both
208:Synapse
168:logical
58:neurons
1872:fields
1384:Retina
1190:
1180:
1166:: 99.
1139:
1080:
1054:Nature
1033:
1025:
982:
950:
940:
899:
889:
850:
840:
750:4 June
722:
453:, and
355:h gate
304:memory
174:, and
1547:Basic
1342:Brain
1109:arXiv
1031:S2CID
781:(PDF)
770:(PDF)
378:EPSPs
1357:Pons
1188:PMID
1137:PMID
1078:PMID
1023:PMID
980:ISBN
948:PMID
897:PMID
848:PMID
822:Cell
752:2018
720:ISBN
524:and
277:axon
241:and
159:and
138:Hebb
1178:PMC
1168:doi
1127:doi
1070:doi
1058:435
1013:doi
938:PMC
928:doi
887:PMC
879:doi
875:117
838:PMC
830:doi
826:171
349:on
186:or
115:'s
107:'s
2154::
1265:,
1186:.
1176:.
1164:10
1162:.
1158:.
1135:.
1125:.
1117:.
1105:29
1103:.
1099:.
1076:.
1068:.
1056:.
1052:.
1029:.
1021:.
1007:.
1003:.
960:^
946:.
936:.
922:.
918:.
895:.
885:.
873:.
869:.
846:.
836:.
824:.
820:.
772:.
742:.
512:.
496:.
473:.
461:.
342:.
259:–
245:.
170:,
155:,
148:.
125:'
68:.
52:A
1513:e
1506:t
1499:v
1308:e
1301:t
1294:v
1194:.
1170::
1143:.
1129::
1121::
1111::
1084:.
1072::
1064::
1037:.
1015::
1009:1
988:.
954:.
930::
924:3
903:.
881::
854:.
832::
790:.
754:.
728:.
95:.
38:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.